Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Asia .
[Tae-Hwan Kwak and Seung-Ho Joo (eds). One Korea: visions of Korean unification. Routledge. New York, 2017. 234 p.]
review / Eduardo Uranga
 Throughout the second half of the 20th century, tensions between superpowers in East Asia made this part of the world a hotspot of the International Office. Tensions remain today, such as the trade war that has pitted the United States against the People's Republic of China since 2018. However, over the past 70 years, one territory in particular has been affected by an ongoing conflict that has repeatedly claimed the world's attention. That region is undoubtedly the Korean peninsula.
Throughout the second half of the 20th century, tensions between superpowers in East Asia made this part of the world a hotspot of the International Office. Tensions remain today, such as the trade war that has pitted the United States against the People's Republic of China since 2018. However, over the past 70 years, one territory in particular has been affected by an ongoing conflict that has repeatedly claimed the world's attention. That region is undoubtedly the Korean peninsula.
This book, co-edited by Tae-Hwan Kwak and Seung-Ho Joo and bringing together various experts on inter-Korean relations, discusses the various possibilities for a future reunification of the two Koreas, as well as the various problems that need to be solved in order to achieve this goal. The perspectives of the various world powers on the conflict are also analysed.
The Korean issue dates back to World War II: after the country was occupied by Japan, its liberation ended up dividing the peninsula in two: North Korea (occupied by the Soviet Union) and South Korea (controlled by the United States). Between 1950 and 1953, the two halves fought a conflict, which eventually consolidated the partition, with a demilitarised zone in between known as the 38th Parallel or KDZ.
One of the formulas for Korean unification described in this book is unification through neutralisation, proposal by both Koreas. However, the constant long-range nuclear missile tests carried out by North Korea in recent years present a major obstacle to this formula. In this atmosphere of mistrust, Korean citizens play an important role in promoting cooperation and friendship on both sides of the border with the goal aim of achieving North Korea's denuclearisation.
Another aspect that plays an important role in forcing a change in North Korea's attitude is its strategic culture. This must be differentiated from the traditional Korean strategic culture. North Korea has adopted various unification strategies over the years, while maintaining the same principles and values. This strategic culture blends elements from the country's strategic position (geopolitically), history and national values. All of this is under the authority of the Juche ideology. This ideology contains some militaristic elements and promotes the unification of Korea through armed conflict and revolutionary actions.
Regarding the perspectives of the various world superpowers on future Korean reunification, China has stated that it favours a long-term approach to unification deadline; a short-term process deadline would collide with Chinese national interests, as Beijing would first have to settle its disputes with Taiwan, or end the trade war against the United States. China has stated that it will not accept Korean unification influenced by a military alliance between the US and South Korea.
On the other hand, the US has not yet opted for a specific Korean unification policy. Since the 1950s, the Korean peninsula has been but one part of the overall US strategic policy for the entire Asia-Pacific region.
The unification of the Korean peninsula will be truncated as long as the US, China and other powers in the region continue to recognise the status quo on the peninsula. It could be argued that armed conflict might be the only way to achieve unification. According to the authors of this book, this would be too costly in terms of resources used and human lives lost. On the other hand, such a war could trigger a conflict on a global scale.
[John West, Asian Century on A Knife Edge: A 360 Degree Analysis of Asia's Recent Economic Development. Palgrave Macmillan. Singapore, 2018. 329 p.]
REVIEW / Gabriela Pajuelo

The degree scroll of this book seems to contribute to the generalised chorus that the 21st century is Asia's century. In reality, the book's thesis is the opposite, or at least puts this claim "on a knife's edge": Asia is a continent of great economic complexity and competing geopolitical interests, posing a series of challenges whose resolution will determine the region's place in the world in the coming decades. For now, argues John West, a university professor in Tokyo, nothing is certain.
The book begins with a preamble on the recent history of Asia, from the Second World War to the present day. Already at the beginning of this period, economic liberalism was established as the standard doctrine in much of the world, including most Asian countries, in a process driven by the establishment of international institutions.
China joined this system, without renouncing its domestic doctrines, when it joined the World Trade Organisation in 2001. Since then, there have been some shocks such as the financial crisis of 2007-2008, which severely affected the US economy and had repercussions in the rest of the world, or the recent tariff tensions between Washington and Beijing, as well as the current global crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic.
The principles of protectionism and nationalism deployed by Donald Trump and an increased US resource to the hard power in the region, as well as a more assertive policy by Xi Jinping's China in its geographical surroundings, also resorting to positions of force, such as in the South China Sea, have damaged the multilateralism that had been built up in that part of the world.
The author provides some thought-provoking insights into the challenges that Asia will face, given that the factors core topic that favoured its development have now deteriorated (mainly due to the stability provided by international economic interdependence).
West examines seven challenges. The first is to gain a better position in global value chains, as since the 1980s the manufacture of components and the production of final products has taken place in different parts of the world. Asia is heavily involved in these supply chains, in fields such as technology or apparel production, but is subject to business decisions by multinationals whose practices are sometimes not socially responsible and allow abuse of labour rights, which are important for the middle classes development .
The second challenge is to maximise the potential of urbanisation, which has grown from 27% of the population in 1980 to 48% in 2015. The region is known for its densely populated mega-cities. This brings with it some challenges: people migrating to industrial centres generally move from leave productivity jobs to high productivity jobs, and health care capacity is put at test . But it is also an opportunity to improve environmental practices or encourage innovation through green technologies, even though much of Asia today still faces high levels of pollution.
Another challenge is to give all Asians equal opportunities in their respective societies, from LGBT people to women and indigenous communities, as well as ethnic and religious minorities. The region also faces a major demographic challenge , as many populations either age (such as China's, despite the correction of the "two-child policy") or continue to expand with presumed future supply problems (such as India's).
West also points to reference letter, the barriers to democratisation in the region, with China's notable immobility, and the spread of economic crime and corruption (counterfeiting, piracy, drug trafficking, human trafficking, cybercrime and money laundering).
Finally, the author speaks of challenge that Asian countries can live together in peace and harmony, while China consolidates its position as a regional leader: if there is a Chinese commitment to thesoft powerThrough the Belt and Road initiative, there is also a more confrontational attitude on the part of Beijing towards Taiwan, Hong Kong and the South China Sea, while actors such as India, Japan and North Korea want a greater role.
Overall, the book provides a comprehensive analysis of Asia's economic and social development and the challenges ahead. In addition, the author offers some thought-provoking insights, arguing that the proclaimed "Asian century" is unlikely due to the region's lagging economic development , as most countries have not caught up with their Western counterparts in terms of GDP per capita and technological sophistication. However, it leaves the future open: if the challenges are successfully met, the time may indeed come for an Asian century.
![Rice terraces in Vietnam [Pixabay]. Rice terraces in Vietnam [Pixabay].](/documents/10174/16849987/vietnam-blog.jpg)
▲ Rice field terraces in Vietnam [Pixabay].
COMMENT / Eduardo Arbizu
The combination of a market Economics and an authoritarian regime dominated by the Communist Party of Vietnam (VCP) has led Vietnam, a country of over 90 million people, to become a key player in the future of Southeast Asia.
Today's Vietnam is the consequence of a confusing and contradictory process of change that has transformed not only the country's Economics but has also had a profound impact on social life, urban configuration, environment, domestic and foreign policies and whose final effects will be seen in the long term deadline.
An impressive economic turnaround
The transformation of the economic model in Vietnam derives formally from the decision taken at the VCP's sixth congress in December 1986 to open the country to the market Economics , but its roots lie earlier, in the economic crisis that followed the war, in the collapse of agricultural production that the radical implementation of a communist model brought about in 1979. This debacle forced the private trading of any surplus production that exceeded the targets set by the state for public land or enterprises. This kind of state capitalism paved the way for the liberalisation that followed the death of Stalinist leader Le Duan in 1986. The approval of the do-moi or renovation policy meant the withdrawal of planning and the choice for the free market. It was not an ideological decision but an instrumental one. work If the CP wanted to maintain control of the country it needed to generate one million jobs a year, guarantee food for 90 million people and reduce poverty.
It has been an economic and social success: per capita income has increased dramatically and the population below the poverty line has been reduced from 60% to 20%. The US embargo ended in 1993 and in 1997 the two countries signed a new agreement trade agreement. In 2007 Vietnam was admitted to the WTO. In this context of openness, more than 150,000 new businesses were set up under the new enterprise law and major international companies such as Clarks, Canon, Samsung and Intel set up production facilities in Vietnam.
The achievements of the process, however, should not hide its weaknesses: a state-controlled Economics through joint ventures and state-owned enterprises, a fragile rule of law, massive corruption, a web of families loyal to the VCP accumulating wealth and owning most private businesses, growing inequality and deep ecological degradation.
Agriculture has evolved from the sudden drop in production that followed communist collectivisation to the current status where Vietnam is the second largest exporter of rice in the world, a crop that accounts for 20% of its exports. The industrialisation of Economics has meant that agriculture, which used to account for 40% of GDP, is now only 20%. Livelihoods still depend on rice cultivation, still the main source of income for rural households, where half of the population lives. source . Rice exports are managed by a combination of free market and corrupt officialdom, with the negative consequences experienced in the speculative crisis of 2008. There has been an intense migration from the countryside to the big cities where wages are five times higher. The pressure for wealth is converting agricultural land into residential or industrial plots. Every year 10,000 new hectares are re-zoned. The transformation of the rural world is pushing away the old Structures that provided security, meaning and purpose and it remains to be seen how it affects future stability.
Social and environmental change
The construction of proletarian towns after the war, under the communist housing programme, has not prevented overcrowding and the continuation of communal life. Migrants continue to arrive in search of work, money and protection. Tons of industrial waste remains untreated; the rivers around Ho Chi Min City are biologically dead and pollution in Hanoi is well above internationally accepted levels. Problems such as prostitution, with more than 1% of women working in the illicit sex trade, or abandoned children on the streets are a reality. However, while doubling or tripling its urban population, Vietnam has managed these problems better than neighbouring countries, largely avoiding the ghost cities and their problems of crime, extreme poverty and drug addiction so common in the rest of Asia.
Commercial and urban dynamism is reflected in thousands of illegal street food shops and small businesses, pioneers of small-scale capitalism, which are now a tourist symbol of Vietnam. In cities full of young people who identify freedom with a polluting motorbike, youth rebels against years of communist austerity but not against family traditions.
Vietnam is a country where a natural wonder like Ha Long Bay, one of the country's iconic images, is simultaneously a tourist attraction and an environmental disaster. It is also one of the areas most exposed to the effects of climate change, due to its low altitude and reliance on agricultural production in the Mekong Delta and tourism. Respect for wildlife and the environment are issues of high priority for the authorities leave .
The VCP remains in control
There are issues that have not changed with the same intensity. Vietnam still lives under a "natural system of control", the deep surveillance system put in place by the communist regime to control the values and behaviour of its people. A system in which one in six Vietnamese ended up working in the security forces and which resulted in the control of "cultivated families", those who behave in accordance with the values set by the party. agreement . Although it has proven its effectiveness in crises such as avian flu and now partly in the Covid-19 crisis, the system is now controversial due to the spread of the internet and social networks and radical social changes that call for more freedom. Despite this control, corruption is widespread and damaging to the country's future.
The VCP is still in power. Retaining its Leninist roots, it is now an elitist and intelligent organisation in search of its own survival. A new mandarinate that has evolved from a centralised power present in all aspects of public and social life to a fragile and partial control; from a "petty legal system", where decisions were taken directly by the VCP and their compliance with the law was irrelevant, to a "State based on Law", where rules are the tool to supervise entrepreneurs and investors, allowing them to create wealth and employment but simultaneously comply with the VCP's expectations. Similarly, the party controls the legislature, the courts and indirectly the press, media and news coverage, which prevents Vietnam from being considered a truly free country.
Life has been difficult and lonely for those few who tried to oppose the regime and promote real democracy. The name of the Catholic priest Father Ly and his followers, brutally repressed, tried and convicted in March 2007, once the country was admitted to the WTO, casts a shadow over the hope for a transition to effective political freedom.
Foreign policy and the future
Vietnam's foreign policy seeks to strike a balance in its relations with two main actors: the US and China, counterbalanced by a set of alliances with third countries. Overcoming war wounds and establishing trusting cooperation on subject security is the goal of the policy of rapprochement with the US, which is already a significant investor in the country. The special relationship with China, the largest importer of Vietnamese goods, an industrial giant and Asia's largest military, is the other axis of its policy despite long-standing territorial disputes.
The overexploited environment, inequality, elite entrenchment and, above all, uncertainty about the evolution of the Communist Party of Vietnam and the political system are aspects that are weighing on the outlook. However, a young and well-educated population, as well as the inflow of foreign investment, are reasons for optimism about further liberalisation of the country, including political liberalisation.
Looking beyond Kashmir: Past and present territorial disputes between Pakistan, India and Bangladesh
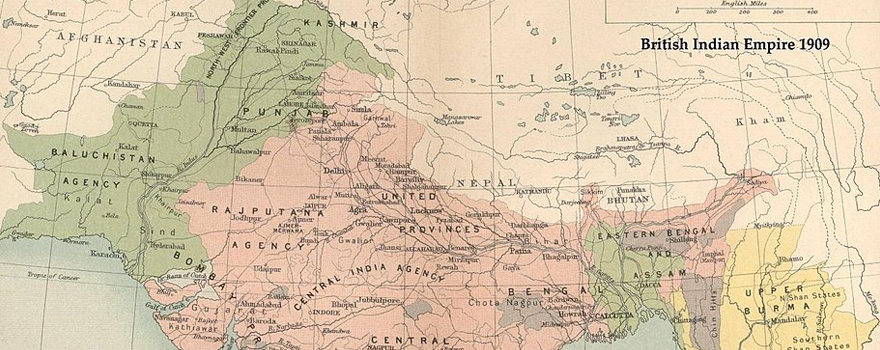
▲ The British Raj in 1909 showing Muslim majority areas in green
ESSAY / Victoria Paternina and Claudia Plasencia
Pakistan's partition from India in 1947 marked the beginning of a long road of various territorial disputes, causing different effects in the region. The geopolitics of Pakistan with India are often linked when considering their shared history; and in fact, it makes sense if we take the perspective of Kashmir as the prominent issue that Islamabad has to deal with. However, neither the history nor the present of Pakistan can be reduced to New Delhi and their common regional conflict over the Line of Control that divides Kashmir.
The turbulent and mistrustful relations between India and Pakistan go beyond Kashmir, with the region of Punjab divided in two sides and no common ground between New Delhi and Islamabad. In the same way, the bitter ties between Islamabad and a third country are not exclusively with India. Once part of Pakistan, Bangladesh has a deeply rooted hatred relationship with Islamabad since their split in 1971. Looking beyond Kashmir, Punjab and Bangladesh show a distinct aspect of the territorial disputes of the past and present-day Pakistan. Islamabad has a say in these issues that seem to go unnoticed due to the fact that they stand in the shadow of Kashmir.
This essay tries to shed light on other events that have a solid weight on Pakistan's geopolitics as well as to make clear that the country is worthy of attention not only from New Delhi's perspective but also from their own Pakistani view. In that way, this paper is divided in two different topics that we believe are important in order to understand Pakistan and its role in the region. Punjab and Bangladesh: the two shoved under the rug by Kashmir.
Punjab
The tale of territorial disputes is rooted deeply in Pakistan and Indian relations; the common mistake is to believe that New Delhi and Islamabad only fight over Kashmir. If the longstanding dispute over Kashmir has raised the independence claims of its citizens, Punjab is not far from that. On the edge of the partition, Punjab was another region in which territorial lines were difficult to apply. They finally decided to divide the territory in two sides; the western for Pakistan and the eastern for India. However, this issue automatically brought problems since the majority of Punjabis were neither Hindus nor Muslims but rather Sikhs. Currently, the division of Punjab is still in force. Despite the situation in Pakistan Punjab remains calm due to the lack of Sikhs as most of them left the territory or died in the partition. The context in India Punjab is completely different as riots and violence are common in the eastern side due to the wide majority of Sikhs that find no common ground with Hindus and believe that India has occupied its territory. Independence claims have been strengthened throughout the years on many occasions, supported by the Pakistani ISI in order to destabilize India. Furthermore, the rise of the nationalist Indian movement is worsening the situation for Punjabis who are realizing how their rights are getting marginalized in the eyes of Modi's government.
Nonetheless, the question of Punjabi independence is only a matter of the Indian side. The Pakistan-held Punjab is a crucial province of the country in which the wide majority are Muslims. The separation of Punjab from Islamabad would not be conceived since it would be devastating. For Pakistan, it would mean the loss of 72 million inhabitants; damaging the union and stability of the country. All of this taking into account that Punjab represents a strong pillar for the national economy since it is the place where the Indus river - one of the most important ones - flows. It can be said that there is no room for independence of the Pakistani side, nor for a rapprochement between both parts of the former Punjab region. They have lost their main community ties. Besides, the disagreements are between New Delhi and Eastern Punjab, so Islamabad has nothing to do here. According to that, the only likely long-term possibility would be the independence of the Indian side of the Punjab due to the growth of the hatred against New Delhi. Additionally, there are many Sikhs living abroad in UK or Canada who support the independence of Punjab into a new country "Khalistan" strengthening the movement into an international concern. Nevertheless, the achievement of this point would probably increase the violence in Punjab, and in case they would become independent it would be at the expense of many deaths.
There is a last point that must be taken into account when referring to India-Pakistan turbulent territorial relations. This is the case of the longstanding conflict over water resources in which both countries have been increasing tensions periodically. Considering that there is a scarcity of water resources and a high demand of that public good, it is easy to realize that two enemies that share those resources are going to fight for them. Furthermore, if they both are mainly agrarian countries, the interest of the water would be even harder as it is the case of Pakistan and India. However, for more than five decades both Islamabad and New Delhi have maintained the Indus Waters Treaty that regulates the consumption of the common waters. It divides the six rivers that flow over Pakistan and India in two sides. The three western ones for Pakistan, and the other three of the eastern part for India. Nevertheless, it does not mean that India could not make any use of the Pakistani ones or vice versa; they are allowed to use them in non-consumptive terms such as irrigation, but not for storage or building infrastructures[1]. This is where the problem is. India is seemed to have violated those terms by constructing a dam in the area of the Pakistani Indus river in order to use the water as a diplomatic weapon against Islamabad.
This term has been used as an Indian strategy to condemn the violence of Pakistan-based groups against India undermining in that way the economy of Pakistan which is highly dependent on water resources. Nevertheless, it is hard to think that New Delhi would violate one of the milestones treaties in its bilateral relations with Pakistan. Firstly, because it could escalate their already existent tensions with Pakistan that would transform into an increase of the violence against India. Islamabad's reaction would not be friendly, and although terrorist activities follow political causes, any excuse is valid to lead to an attack. Secondly, because it would bring a bad international image for PM Modi as the UN and other countries would condemn New Delhi of having breached a treaty as well as leaving thousands of people without access to water. Thirdly, they should consider that rivers are originated in the Tibet, China, and a bad movement would mean a reaction from Beijing diverting the water towards Pakistan[2]. Finally, India does not have enough infrastructure to use the additional water available. It is better for both New Delhi and Islamabad to maintain the issue over water resources under a formal treaty considering their mutual mistrust and common clashes. Nevertheless, it would be better for them to renew the Indus Waters Treaty in order to include new aspects that were not foreseen when it was drafted as well as to preserve the economic security of both countries.
Bangladesh
Punjab is a territory obligated to be divided in two between India and Pakistan, yet Bangladesh separated itself completely from Pakistan and finds itself in the middle of India. Bangladesh, once part of Pakistan, after a tumultuous war, separated into its own country. While India did not explicitly intervene with Bangladesh and Pakistan's split, it did promote the hatred between the two for its own diary and to increase in power. The scarring aspect of the split of Bangladesh from Pakistan is the bloody war and genocide that took place, something that the Bengali people still have not overcome to this day. The people of Bangladesh are seeking an apology from Pakistan, something that does not look like it is going to come anytime soon.
Pakistan and Bangladesh share a bitter past with one another as prior to 1971, they were one country which separated into two as a result of a bloody war and emerging political differences. Since 1971 up to today, India and the Awami league have worked to maintain this hatred between Bangladesh and Pakistan through propagandist programs and different techniques. For example, they set up a war museum, documentaries and films in order to boast more the self-proclamation of superiority on behalf of India against Bangladesh and Pakistan. India and the Awami League ignore the fact that they have committed atrocities against the Bengali people and that in large part they are responsible for the breakup between Pakistan and Bangladesh. The Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) worked to improve relations with Pakistan under the governments of Ziaur Rahman, Begum Khaldia Zia, and Hossain Mohammad Ershad in Bangladesh, who had maintained distance from India. Five Pakistani heads of government have visited Bangladesh since 1980, along with signing trade and cultural agreements to improve relations between the two nations. [3] While an alliance between Pakistan and Bangladesh against India is not a realistic scenario, what is important for Pakistan and Bangladesh for the next decade to come is attempt to put their past behind them in order to steer clear of India and develop mutually beneficial relations to help improve their economies. For example, a possible scenario for improving Pakistan and Bangladesh relations could be to join the CPEC to better take advantage of the trade opportunities offered within South Asia, West Asia, Central Asia, and China and Russia.[4]
Despite decades of improving trade and military links, especially as a defence against Indian supremacy in the region, the two countries continue to be divided by the question of genocide. Bangladesh wants Pakistan to recognize the genocide and its atrocities and teach them as a part of its history. However, Pakistan has refused to do so and has even referred to militant leader executed for war crimes as being killed for his loyalty to Pakistan.[5]
Even though India supported Bangladesh in its independence from Pakistan, Bangladesh thinks that India is self-serving and that they change ideas depending on their own convenience. [6] An alliance of Pakistan and Bangladesh, even though it is against a common enemy, India, is not realistic given the information recently provided. India is a country that yes, even though they helped Bangladesh against Pakistan, they are always going to look out for themselves, especially in search to be the central power in the region. India sees still a lot of potential for their power in the coming decades. Indian PM Narendra Modi is very keen on making strategic choices for the country to transform and increase its global leadership position.[7]
The hostile relations between Pakistan and India find their peak in its longstanding conflict over Kashmir, but Punjab and Bangladesh must not be put in the shadow. The further directions of both PM Imran Khan and PM Modi could have consequences that would alter the interests of Punjab and Bangladesh as different actors in the international order. In the case of Punjab their mutual feelings of mistrust could challenge the instability of a region far from being calm. It is true that independence claims is not an issue for Pakistan itself since both Islamabad and Pakistan-held Punjab would lose in that scenario, and they both know it. Nonetheless, Indian Punjabis' reality is different. They have crucial problems within New Delhi, again as a historical matter of identity and ethnicity that is still present nowadays. Sikhs have not found common ground with Hindus yet and it does not seem that it will happen in a near future. In fact, tensions are increasing, posing a threat for two nations with their views on Kashmir rather than on Punjab. In the case of Bangladesh, its relations with Pakistan did not have a great start. Bangladesh gained freedom with help from India and remained under its influence. Both Pakistan and Bangladesh took a long time to adjust to the shock of separation and their new reality, with India in between them.
In conclusion, Punjab and Bangladesh tend to be the less important territorial issues, and not a priority neither for Islamabad nor for New Delhi that are more engaged in Kashmir. However, considering the magnitude of both disputes, we should appreciate how the Sikhs in the Indian-held territory of Punjab as well as the Bengali people deserve the same rights as the Kashmiris to be heard and to have these territorial disputes settled once and for all.
REFERENCES
Ayres, Alyssa. "India: a 'Major Power' Still below Its Potential." Lowy Institute, July 24, 2018.
Iftikhar, Momin. "Pakistan-Bangladesh Relations." The Nation. The Nation, December 15, 2018.
"Indus Water Treaty: Everything You Need to Know". ClearIAS.
Muhammad Hanif, Col. "Keeping India out of Pakistan-Bangladesh Relations." Daily Times, March 6, 2018.
Sami, Shafi. "Pakistan Bangladesh Relations In the Changing International Environment." JSTOR. Pakistan Institute of International Affairs, 2017.
Shakoor, Farzana. "Pakistan Bangladesh Relations Survey. JSTOR. Pakistan Institute of International Affairs, 2017.
[1] "Indus Water Treaty: Everything You Need to Know". Clearias. Accessed March 24.
[2] ibid
[3] Muhammad Hanif, Col. "Keeping India out of Pakistan-Bangladesh Relations." Daily Times, March 6, 2018.
[4] Iftikhar, Momin. "Pakistan-Bangladesh Relations." The Nation. The Nation, December 15, 2018.
[5] Sami, Shafi. "Pakistan Bangladesh Relations In the Changing International Environment." JSTOR. Pakistan Institute of International Affairs, 2017.
[6] Shakoor, Farzana. "Pakistan Bangladesh Relations Survey." JSTOR. Pakistan Institute of International Affairs, 2017.
[7]Ayres, Alyssa. "India: a 'Major Power' Still below Its Potential." Lowy Institute, July 24, 2018.
[A. Patanru, M. Pangestu, M.C. Basri (eds), Indonesia in the New World: Globalisation, Nationalism and Sovereignty. ISEAS Yusof Ishak Institute. Singapore, 2018. 358 p.]
review / Irati Zozaya
 The book consists of fifteen articles, written by different experts, on how Indonesia has dealt with globalisation and what effect it has had on the country. The texts have been coordinated by Arianto A. Patunru, Mari Pangestu and M. Chatib Basri, Indonesian academics with experience also in public management having served as ministers in different governments. The articles combine general approaches with specific aspects, such as the consequences of the opening up to international trade and investment in the mining industry or the nationalisation of foodstuffs.
The book consists of fifteen articles, written by different experts, on how Indonesia has dealt with globalisation and what effect it has had on the country. The texts have been coordinated by Arianto A. Patunru, Mari Pangestu and M. Chatib Basri, Indonesian academics with experience also in public management having served as ministers in different governments. The articles combine general approaches with specific aspects, such as the consequences of the opening up to international trade and investment in the mining industry or the nationalisation of foodstuffs.
To explain Indonesia's present-day status , the book occasionally recapitulates periods of its history. In fact, one of the concepts that crops up frequently in the book is that of nationalism: it could be said, according to the authors, that this is what has most marked Indonesia's relationship with the world, beyond who has led this country of 260 million inhabitants at any given time.
The first part of the book reference letter looks more generally at Indonesia's experience with globalisation, nationalism and sovereignty. It begins by showing the colonial era and how, under Dutch and British pressure to open up to the world, a strong nationalist sentiment began to emerge. After the occupation by Japan during World War II, total autarchy was introduced, leading to a problem that is still very present in Indonesia today: internship smuggling. In 1945 the country achieved its long-awaited independence under President Sukarno, who closed Indonesia to the rest of the world in order to focus on reasserting national identity and developing its capabilities. This led to the deterioration of the Economics and subsequent hyperinflation, which ushered in a new era: the New Order.
In 1967, with Suharto's accession to the presidency, a cautious opening to foreign trade and investment flows began. However, Suharto repressed political activity and during his rule the military gained much influence and the government retained control over Economics. Moreover, the end of his presidency coincided with the Asian financial crisis (1997-1998), which led to a fall in the country's economic growth and a slowdown in poverty reduction, and consequently a growth in inequality. The financial crisis undermined confidence in the president and culminated in the collapse of the New Order.
The next period covered is the Reformasi, an era that marked the beginning of a more open and democratic political climate. The next two presidents, Abdurrahman Wahid (1999-2001) and Megawati Soekarnoputri (2001-2004), were more concerned with economic recovery and democratic consolidation, and a protectionist system endured in terms of Economics. The book does not focus much on the next president, Yudhoyono (2004-2014), noting only that he was an internationalist who maintained a more cautious and ambivalent stance on economic issues.
Finally, in the 2014 elections, Joko Widodo came to power and holds the position presidency today. Under him, Indonesia has returned to the path of economic growth and stabilised as a reasonably successful democracy. As the president, commonly known as Jokowi, has taken further steps to emphasise political sovereignty and promote economic autarky and national cultural renaissance, his term has been characterised as 'new nationalism'. In his political speech , Jokowi puts Indonesia as goal of foreign conspiracies and calls for vigilance against such threats. However, the country maintains an ambivalent stance towards international openness and cooperation since, although trade restrictions have increased again in recent decades, Jokowi emphasises global engagement and has revived regional negotiations.
All this has led to public dissatisfaction with globalisation, with up to 40% of citizens believing that globalisation threatens national unity. One of the most negative and important effects in Indonesia is that of workers who have been forced to migrate and work abroad under very poor conditions. However, the later parts of the book also show the positive consequences of globalisation in Indonesia, including higher productivity, increased wages and economic growth. The authors therefore emphasise the importance of constructing a narrative that can generate public and political support for the country's openness and counter the growing anti-globalisation sentiment.
As is the case with a book that is the sum of articles by different authors, its reading can be somewhat tiresome due to a certain reiteration of content. However, the variety of signatures also means a plurality of approaches, which undoubtedly provides the reader with a wealth of perspectives.
[Ming-Sho Ho, Challenging Beijing's Mandate of Heaven. Taiwan's Sunflower and Hong Kong's Umbrella Movement. Temple University Press. Philadelphia, 2019. 230 p.]
review / Claudia López
 Taiwan's Sunflower Movement and Hong Kong's Umbrella Movement achieved international notoriety during 2014, when they challenged the Chinese regime's 'Mandate of Heaven', to use the image that gives degree scroll to the book. The book analyses the origins, processes and also the outcomes of both protests, at a time of consolidation of the rise of the People's Republic of China. Challenging Beijing's Mandate of Heaven provides a detailed overview of where, why and how these movements came into being and achieved relevance.
Taiwan's Sunflower Movement and Hong Kong's Umbrella Movement achieved international notoriety during 2014, when they challenged the Chinese regime's 'Mandate of Heaven', to use the image that gives degree scroll to the book. The book analyses the origins, processes and also the outcomes of both protests, at a time of consolidation of the rise of the People's Republic of China. Challenging Beijing's Mandate of Heaven provides a detailed overview of where, why and how these movements came into being and achieved relevance.
Taiwan's Sunflower Movement developed in March and April 2014, when citizen demonstrations protested against the approval of a free trade agreement with China. Between September and December of the same year, the Umbrella Movement staged 79 days of protests in Hong Kong demanding universal suffrage to elect the highest authority in this enclave of special status within China. These protests attracted international attention for their peaceful and civilised organisation.
Ming-Sho Ho begins by describing the historical background of Taiwan and Hong Kong from their Chinese origins. He then analyses the status of the two territories so far this century, when Taiwan and Hong Kong have begun to face increased pressure from China. It also reviews the similar economic circumstances that produced the two waves of youth revolts. The second part of the book analyses the two movements: the voluntary contributions, the decision-making process and its improvisation, the internal power shift, the political influences and the challenges of the initiative. The book includes appendices with the list of Taiwanese and Hong Kong people interviewed and the methodology used for the analysis of the protests.
Ming-Sho Ho was born in 1973 in Taiwan and has been a close observer of the island's social movements; during his time as a student of doctorate in Hong Kong he also closely followed the political discussion in the former British colony. He is currently researching initiatives for promote renewable energy in East Asian nations.
Being from Taiwan gave him access to the Sunflower Movement and allowed him to build close relationships with several of its key activists. He was able to witness some of the students' internal meetings and conduct in-depth interviews with students, leaders, politicians, NGO activists, journalists and university professors. This provided him with a variety of sources for his research.
Although they are two territories with different characteristics - Hong Kong is under the sovereignty of the People's Republic of China, but enjoys autonomy management assistant; Taiwan remains independent, but its statehood is challenged - both represent a strategic challenge for Beijing in its consolidation as a superpower.
The author's sympathy for these two movements is obvious throughout the book, as is his admiration for the risk taken by these student groups, especially in Hong Kong, where many of them were convicted of 'public nuisance' and 'disturbing the peace' and, in many cases, sentenced to more than a year in prison.
The two movements had a similar beginning and a similar development beginning, but each ended in a very different way. In Taiwan, thanks to the initiative, the free trade agreement with China failed and was withdrawn, and the protesters were able to call hold a farewell rally to celebrate this victory. In Hong Kong, police repression succeeded in stifling the protest and a final massive raid brought a disappointing end for the protesters. However, it is possible that without the experience of those mobilisations, the new student reaction that throughout 2019 and early 2020 in Hong Kong has put the highest Chinese authorities on the ropes would not have been possible.
![Artistic image of a Pakistani Rupee [Pixabay]. Artistic image of a Pakistani Rupee [Pixabay].](/documents/10174/16849987/pakistan-country-risk-report-blog.jpg)
▲ Artistic image of a Pakistani Rupee [Pixabay].
COUNTRY RISK REPORT / M. J. Moya, I. Maspons, A. V. Acosta
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The government of Prime Minister (PM), Imran Khan, was slowly moving towards economic, social, and political improvements, but all these efforts might be hampered by the recent outbreak of the COVID-19 virus since the government must temporarily shift its focus and resources to keeping its population safe. Additionally, high logistical, legal, and security challenges still generate an uncompetitive operating environment and thus, an unattractive market for foreign investment in Pakistan.
Firstly, in relation to the country's economic outlook, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) was expected to gradually recover around 5% in the upcoming years. However, according to latest estimates, this growth will suffer a negative impact and fall to around 2%, straining the country's most recent recorded improvements. On the other hand, in the medium to long-term, Pakistan will benefit from the success of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), which is a strategic economic project aiming to improve infrastructure capacity in the country. Pakistan is also facing an energy crisis along with a growing demand from a booming population that hinder a proper economic progress.
Secondly, Pakistan's political future will be shaped by Khan's ability to transform his short-term policies into long-term strategies. However, in order to achieve this, the government must tackle the root causes of political instability in Pakistan, such as long-lasting corruption, the constant military influence in decision-making processes, the historical discussion among secularism and Islamism, and the new challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Still, PM Khan's progressive reforms could represent the beginning towards a "Naya Pakistan" ("New Pakistan").
Thirdly, Pakistan's social stability is contextualized within a high risk of terrorist attacks due to its internal security gaps. The ethnic dilemma among the provinces along with the government's violent oppression of insurgencies will continue to impede development and social cohesion within the country. This will further aggravate in light of a current shortage of resources and the impacts of climate change.
In addition, in terms of Pakistan's security outlook, the country is expected to tackle terrorist financing and money laundering networks in order to avoid being blacklisted by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF). Nonetheless, due to a porous border with Afghanistan, Pakistan faces drug trafficking challenges that further destabilize national security. Finally, the turbulent Indo-Pakistani relation is the most significant conflict for the South Asian country. The disputed region of Jammu and Kashmir, a possible nuclear confrontation, and the increase of nationalist movements along the Punjab region, hamper regional and international peace.
![Logo of Pakistan's Inter-Services Intelligence organization. It depicts Pakistan's national animal, Markhor, eating a snake [Wikipedia]. Logo of Pakistan's Inter-Services Intelligence organization. It depicts Pakistan's national animal, Markhor, eating a snake [Wikipedia].](/documents/10174/16849987/pakistan-isi-blog.jpg)
Logo of Pakistan's Inter-Services Intelligence organization. It depicts Pakistan's national animal, Markhor, eating a snake [Wikipedia].
ESSAY / Manuel Lamela
Jihadism continues to be one of the main threats Pakistan faces. Its impact on Pakistani society at the political, economic and social levels is evident, it continues to be the source of greatest uncertainty, which acts as a barrier to any company that is interested in investing in the Asian country. Although the situation concerning terrorist attacks on national soil has improved, jihadism is an endemic problem in the region and medium-term prospects are not positive. The atmosphere of extreme volatility and insistence that is breathed does not help in generating confidence. If we add to this the general idea that Pakistan's institutions are not very strong due to their close links with certain radical groups, the result is a not very optimistic scenario. In this essay, we will deal with the current situation of jihadism in Pakistan, offering a multidisciplinary approach that helps to situate itself in the complicated reality that the country is experiencing.
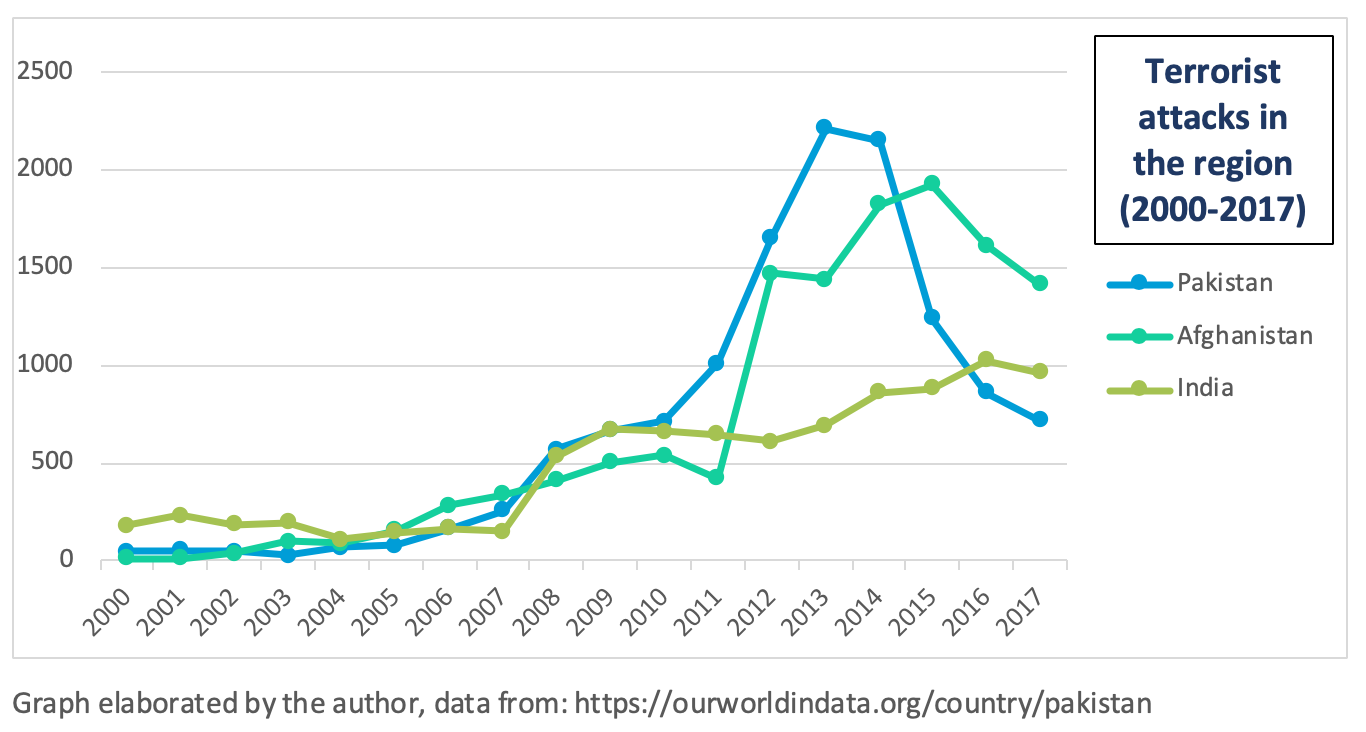
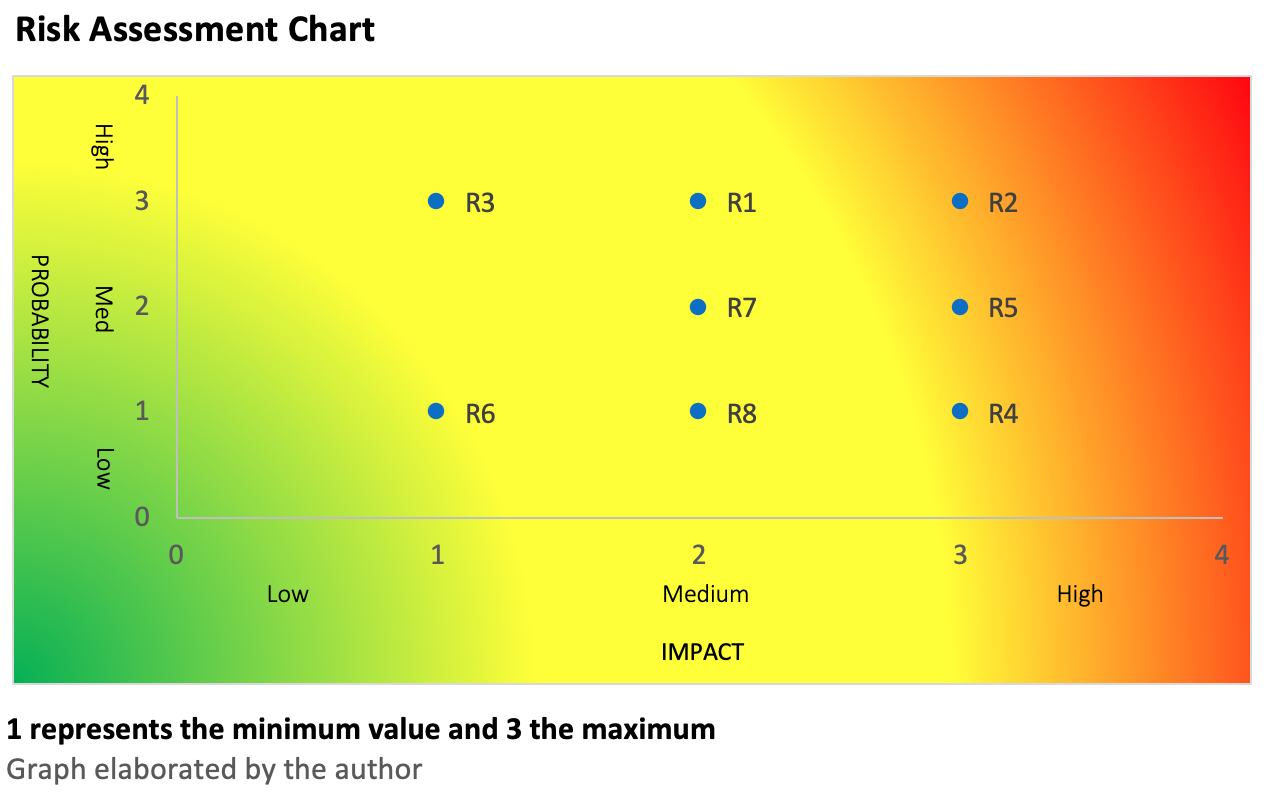
1. Jihadism in the region, a risk assessment
Through this graph, we will analyze the probability and impact of various risk factors concerning jihadist activity in the region. All factors refer to hypothetical situations that may develop in the short or medium term. The increase in jihadist activity in the region will depend on how many of these predictions are fulfilled.
Risk Factors:
A1: US-Taliban treaty fails, creating more instability in the region. If the United States is not able to make a proper exit from Afghanistan, we may find ourselves in a similar situation to that experienced during the 1990s. Such a scenario will once again plunge the region into a fierce civil war between government forces and Taliban groups. The proposed scenario becomes increasingly plausible if we look at the recent American actions regarding foreign policy.
A2: Pakistan two-head strategy facing terrorism collapse. Pakistan's strategy in dealing with jihadism is extremely risky, it's collapse would lead to a schism in the way the Asian state deals with its most immediate challenges. The chances of this strategy failing in the medium term are considerably high due to its structure, which makes it unsustainable over the time.
R3: Violations of the LoC by the two sides in the conflict. Given the frequency with which these events occur, their impact is residual, but it must be taken into account that it in an environment of high tension and other factors, continuous violations of the LoC may be the spark that leads to an increase in terrorist attacks in the region.
R4: Agreement between the afghan Taliban and the government. Despite the recent agreement between Ashraf Ghani and Abdullah Albduallah, it seems unlikely that he will be able to reach a lasting settlement with the Taliban, given the latter's pretensions. If it is true that if it happens, the agreement will have a great impact that will even transcend Afghan borders.
R5: Afghan Taliban make a coup d'état to the afghan government. In relation to the previous point, despite the pact between the government and the opposition, it seems likely that instability will continue to exist in the country, so a coup attempt by the Taliban seems more likely than a peaceful solution in the medium or long term
R6: U.S. Democrat party wins the 2020 elections. Broadly speaking, both Republican and Democratic parties are betting on focusing their efforts on containing the growth of their great rival, China.
R7: U.S. withdraw its troops from Afghanistan regarding the result of the peace process. This is closely related to the previous point as it responds to a basic geopolitical issue.
R8: New agreement between India and Pakistan regarding the LoC. If produced, this would bring both states closer together and help reduce jihadist attacks in the Kashmir region. However, if we look at recent events, such a possibility seems distant at present.
2. The ties between the ISI and the Taliban and other radical groups
Pakistan's Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) has been accused on many occasions of being closely linked to various radical groups; for example, they have recently been involved with the radicalization of the Rohingya refugees in Bangladesh[1]. Although Islamabad continues strongly denying such accusations, reality shows us that cooperation between the ISI and various terrorist organisations has been fundamental to their proliferation and settlement both on national territory and in the neighbouring states of India and Afghanistan. The West has not been able to fully understand the nature of this relationship and its link to terrorism. The various complaints to the ISI have been loaded with different arguments of different kinds, lacking in unity and coherence. Unlike popular opinion, this analysis will point to the confused and undefined Pakistani nationalism as the main cause of this close relationship.
The Directorate for Inter-Services Intelligence, together with the Intelligence Bureau and the Military Intelligence, constitute the intelligence services of the Pakistani State, the most important of which is the ISI. ISI can be described as the intellectual core and center of gravity of the army. Its broad functions are the protection of Pakistan's national security and the promotion and defense of Pakistan's interests abroad. Despite the image created around the ISI, in general terms its activities and functions are based on the same "values" as other intelligence agencies such as the MI6, the CIA, etc. They all operate under the common ideal of protecting national interests, the essential foundation of intelligence centers without which they are worthless. We must rationalize their actions on the ground, move away from inquisitive accusations and try to observe what are the ideals that move the group, their connection with the government of Islamabad and the Pakistani society in general.
2.1. The Afghan Taliban
To understand the idiosyncrasy of the ISI we must go back to the war in Afghanistan[2], it is from this moment that the center begins to build an image of itself, independent of the rest of the armed forces. From the ISI we can see the victory of the Mujahideen on Afghan territory as their own, a great achievement that shapes their thinking and vision. But this understanding does not emerge in isolation and independently, as most Pakistani society views the Afghan Taliban as legitimate warriors and defenders of an honourable cause[3]. The Mujahideen victory over the USSR was a real turning point in Pakistani history, the foundation of modern Pakistani nationalism begins from this point. The year 1989 gave rise to a social catharsis from which the ISI was not excluded.
Along with this ideological component, it is also important to highlight the strategic aspect; we are dealing with a question of nationalism, of defending patriotic interests. Since the emergence of the Taliban, Pakistan has not hesitated to support them for major strategic reasons, as there has always been a fear that an unstable Afghanistan would end up being controlled directly or indirectly by India, an encirclement strategy[4]. Faced with this dangerous scenario, the Taliban are Islamabad's only asset on the ground. It is for this reason, and not only for religious commitment, that this bond is produced, although over time it is strengthened and expanded. Therefore, at first, it is Pakistani nationalism and its foreign interests that are the cause of this situation, it seeks to influence neighbouring Afghanistan to make the situation as beneficial as possible for Pakistan. Later on, when we discuss the situation of the Taliban on the national territory, we will address the issue of Pakistani nationalism and how its weak construction causes great problems for the state itself. But on Afghan territory, from what has been explained above, we can conclude that this relationship will continue shortly, it does not seem likely that this will change unless there are great changes of impossible prediction. The ISI will continue to have a significant influence on these groups and will continue its covert operations to promote and defend the Taliban, although it should be noted that the peace treaty between the Taliban and the US[5] is an important factor to take into account, this issue will be developed once the situation of the Taliban at the internal level is explained.
2.2. The Pakistani Taliban (Al-Qaeda[6] and the TTP)
The Taliban groups operating in Pakistan are an extension of those operating in neighbouring Afghanistan. They belong to the same terrorist network and seek similar objectives, differentiated only by the place of action. Despite this obvious similarity, from Islamabad and increasingly from the whole of Pakistani society, the two groups are observed in a completely different way. On the one hand, as we said earlier, for most Pakistanis, the Afghan Taliban are fighting a legitimate and just war, that of liberating the region from foreign rule. However, groups operating in Pakistan are considered enemies of the state and the people. Although there was some support among the popular classes, especially in the Pashtun regions, this support has gradually been lost due to the multitude of atrocities against the civilian population that have recently been committed. The attack carried out by the Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP)[7] in the Army Public School in Peshawar in the year 2014 generated a great stir in society, turning it against these radical groups. This duality marks Pakistan's strategy in dealing with terrorism both globally and internationally. While acting as an accomplice and protector of these groups in Afghanistan, he pursues his counterparts on their territory. We have to say that the operations carried out by the armed forces have been effective, especially the Zarb-e-Azb operation carried out in 2014 in North Waziristan, where the ISI played a fundamental role in identifying and classifying the different objectives. The position of the TTP in the region has been decimated, leaving it quite weakened. As can be seen in this scenario, there is no support at the institutional level from the ISI[8], as they are involved in the fight against these radical organisations. However, on an individual level if these informal links appear. This informal network is favoured by the tribal character of Pakistani society, it can appear in different forms but often draw on ties of Kinship, friendship or social obligation[9]. Due to the nature of this type of relationship, it is impossible to know to what extent the ISI's activity is conditioned and how many of its members are linked to Taliban groups. However, we would like to point out that these unions are informal and individual and not institutional, which provides a certain degree of security and control, at least for the time being, the situation may vary greatly due to the lack of transparency.
2.3. ISI and the radical groups that operate in Kashmir
Another part of the board is made up of the radical groups that focus their terrorist attention on the conflict with India over control of Kashmir, the most important of which are: Lashkar-e-Taiba (Let) and Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM). Both groups have committed real atrocities over the past decades, the most notorious being the one committed by LeT in the Indian city of Mumbai in 2008. There are numerous testimonies, in particular, that of the American citizen David Haedy, which point to the cooperation of the ISI in carrying out the aforementioned attack.[10]
Recently, Hafiz Saeed, founder of Let and intellectual planner of the bloody attack, was arrested. The news generated some turmoil both locally and internationally and opened the discussion as to whether Pakistan had finally decided to act against the radical groups operating in Kashmir. We are once again faced with a complex situation, although the arrest shows a certain amount of willpower, it is no more than a way of making up for the situation and relaxing international pressure. The above coincides with the FATF's[11] assessment of Pakistan's status within the institution, which is of great importance for the short-term future of the country's economy. Beyond rhetoric, there is no convincing evidence that suggests that Pakistan has made a move against those groups. The link and support provided by the ISI in this situation are again closely linked to strategic and ideological issues. Since its foundation, Pakistani foreign policy has revolved around India[12], as we saw on the Afghan stage. Pakistani nationalism is based on the maxim that India and the Hindus are the greatest threat to the future of the state. Given the significance of the conflict for Pakistani society, there has been no hesitation in using radical groups to gain advantages on the ground. From Pakistan perspective, it is considered that this group of terrorists are an essential asset when it comes to putting pressure on India and avoiding the complete loss of the territory, they are used as a negotiating tool and a brake on Indian interests in the region.
As we can see, the core between the ISI and certain terrorist groups is based on deep-seated nationalism, which has led both members of the ISI and society, in general, to identify with the ideas of certain radical groups. They have benefited from the situation by bringing together a huge amount of power, becoming a threat to the state itself. The latter has compromised the government of Pakistan, sometimes leaving it with little room for maneuver. The immense infrastructure and capacity of influence that Let has thanks to its charitable arm Jamaat-ud-Dawa, formed with re-localized terrorists, is a clear example of the latter. A revolt led by this group could put Islamabad in a serious predicament, so the actions taken both in Kashmir and internally to try to avoid the situation should be measured very well. The existing cooperation between the ISI and these radical groups is compromised by the development of the conflict in Kashmir, which may increase or decrease depending on the situation. What is certain, because of the above, is that it will not go unnoticed and will continue to play a key role in the future. These relationships, this two-way game could drag Pakistan soon into an internal conflict, which could compromise its very existence as a nation.
[1] Ahmed, Zobaer. "Is Pakistani Intelligence Radicalizing Rohingya Refugees? | DW | 13.02.2020". DW.COM, 2020.
[2] Idrees, Muhammad. Instability In Afghanistan: Implications For Pakistan. PDF, 2019.
[3] Lieven, Anatol. Pakistan a Hard Country. 1st ed. London: Penguin, 2012.
[4] United States Institute for Peace. The India-Pakistan Rivalry In Afghanistan, 2020.
[5] Maizland, Lindsay. "U.S.-Taliban Peace Deal: What To Know". Council On Foreign Relations, 2020.
[6] Blanchard, Christopher M. Al Qaeda: Statements And Evolving Ideology. PDF, 2007.
[7] Mapping Militant Organisations. "Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan." Stanford University. Last modified July 2018.
[8] Gabbay, Shaul M. Networks, Social Capital, And Social Liability: The Fall Of Pakistan ISI, The Taliban And The War Against Terrorism.PDF, 2014. http://www.scirp.org/journal/sn.
[9] Lieven, Anatol. Pakistan a Hard Country. 1st ed. London: Penguin, 2012.
[10] Lieven, Anatol. Pakistan a Hard Country. 1st ed. London: Penguin, 2012.
[11]"Pakistan May Remain On FATF Grey List Beyond Feb 2020: Report". The Economic Times, 2019.
[12]"India And Pakistan: Forever Rivals?". Aljazeera.com, 2017.
![Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur, also called Kartarpur Sahib, is a Sikh holy place in Kartarpur, in the Pakistani Punjab [Wikimedia Commons]. Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur, also called Kartarpur Sahib, is a Sikh holy place in Kartarpur, in the Pakistani Punjab [Wikimedia Commons].](/documents/10174/16849987/pakistan-punjab-blog.jpg)
▲ Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur, also called Kartarpur Sahib, is a Sikh holy place in Kartarpur, in the Pakistani Punjab [Wikimedia Commons].
ESSAY / Pablo Viana
Punjab region has been part of India until the year 1947, when the Punjab province of British India was divided in two parts, East Punjab (India) and West Punjab (Pakistan) due to religious reasons. After the division a lot of internal violence occurred, and many people were displaced.
East and West Punjab
The partition of Punjab proved to be one of the most violent, brutal, savage debasements in the history of humankind. The undivided Punjab, of which West Punjab forms a major region today, was home to a large minority population of Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus unto 1947 apart from the Muslim majority[1]. This minority population of Punjabi Sikhs called for the creation of a new state in the 1970s, with the name of Khalistan, but it was detained by India, sending troops to stop the militants. Terrorist attacks against the Sikh majority emerged, by those who did not accept the creation of the state of Khalistan and wished to stay in India.
The Sikh population is the dominant religious ethnicity in East Punjab (58%) followed by the Hindu (39%). Sikhism and Islamism are both monotheistic religions, they do believe on the same concept of God, although it is different on each religion. Sikhism was developed during the 16th and 17th century in the context of conflict in between Hinduism and Islamism. It is important to mention Sikhism if we talk about Punjab, as its origins were in Punjab, but most important in recent times, is that the Guru Nanak Dev[2] was buried in Pakistani territory. Four kilometres from the international border the Sikh shrine was conceded to Pakistan at the time of British India's Partition in 1947. For followers of Sikhism this new border that cut through Punjab proved especially problematic. Sikhs overwhelmingly chose India over the newly formed Pakistan as the state that would best protect their interests (there are an estimated 50,000 Sikhs living in Pakistan today, compared to the 24 million in India). However, in making this choice, Sikhs became isolated from several holy sites, creating a religious disconnection that has proved a constant spiritual and emotional dilemma for the community[3].
In order to let the Sikhist population visit the Gurdwara Darbar Sahib[4], the Kartarpur Corridor was created in November 2019. However, there is an incessant suspicion in between India and Pakistan that question Pakistan motives. Although it seems like a generous move work of the Pakistani government, there is a clear perception that Pakistan is engaged in an act of deception[5]. Thus, although this scenario might seem at first beneficial for the rapprochement of East and West Punjab, it is not at all. Pakistan is involved in a rhetorical policy which could end up worsening its relations with India.
The division of Punjab in 1947 was like the division of Pakistan and India on that same year. Territorial disputes have been an issue that defines very well India-Pakistan relations since the independence. In the case of Punjab, there has not been a territorial discussion. The division was clear and has been respected ever since. Why would Pakistan and/or India be willing to unify Punjab? There is no reason. East and West Punjab represent two different nations and three religions. If we think about reunifying Pakistan and India, the conclusion is the same (although more dramatic); too many discrepancies and recent unrest to think about bringing back together the nations. However, if the Kartarpur Corridor could be placed out of bonds for the territorial disputes between Pakistan and India (e.g. Kashmir), Islamabad and New Delhi could use this situation as a model to find out which are the pressure points and trying to find a path for identifying common solutions. In order to achieve this, there should be a clear behaviour by both parties of cooperation. Sadly, in recent times both Pakistan and India have discrepancies regarding many topics and suspicious behaviours that clearly show that they won't be interested in complicating more the situation in Punjab searching for unification. The riots of 1947 left a terrific era on the region and now that both sides are established and no major disputes have emerged (except for Sikh nationalism), the situation should and will most likely remain as it is.
The Indus Water Treaty
The Indus Waters Treaty was signed in 1960 after nine years of negotiations between India and Pakistan with the help of the World Bank, which is also a signatory. Seen as one of the most successful international treaties, it has survived frequent tensions, including conflict, and has provided a framework for irrigation and hydropower development for more than half a century. The Treaty basically provides a mechanism for exchange of information and cooperation between Pakistan and India regarding the use of their rivers. This mechanism is well known as the Permanent Indus Commission. The Treaty also sets forth distinct procedures to handle issues which may arise: "questions" are handled by the Commission; "differences" are to be resolved by a Neutral Expert; and "disputes" are to be referred to a seven-member arbitral tribunal called the "Court of Arbitration." As a signatory to the Treaty, the World Bank's role is limited and procedural[6].
Since 1948, India has been confident on the fact that East Punjab and the acceding states have a prior and superior claim to the rivers flowing through their territory. This leaves West Punjab in disadvantage regarding water resources, as East Punjab can access the highest sections of the rivers. Even under a unified control designed to ensure equitable distribution of water, in years of low river flow cultivators on tail distributaries always tended to accuse those on the upper reaches of taking an undue amount of the water, and after partition any temporary shortage, whatever the cause, could easily be attributed to political motives. It was therefore wise of Pakistan-indeed it became imperative-to cut the new feeder from the Ravi for this area and thus become independent of distributaries in East Punjab[7]. The Treaty acknowledges the control of the eastern rivers to India, and to the western rivers to Pakistan.
The main issue of water distribution in between East and West Punjab is then a matter of geography. Even though West Punjab covers more territory than East Punjab, and the water flow of West Punjab is almost three times the water flow of East Punjab rivers, the Indus Water Treaty gives the following advantage to India: since Pakistan rivers receive much more water flow from India, the treaty allowed India to use western rivers water for limited irrigation use and unlimited use for power generation, domestic, industrial and non-consumptive uses such as navigation, floating of property, fish culture and this is where the disputes mainly came from, as Pakistan has objected all Indian hydro-electric projects on western rivers irrespective of size and layout.
It is worth mentioning that with the World Bank mediating the Treaty in between India and Pakistan, the water access will not be curtailed, and since the ratification of the Treaty, India and Pakistan have not engaged in any water wars. Although there have been many tensions the disputes have been via legal procedures, but they haven't caused any major cause for conflict. Today, both countries are strengthening their relationship, and the scenario is not likely to get worse, it is actually the opposite, and the Indus Water Treaty is one of the few livelihoods of the relationship. If the tensions do not cease, the World Bank should consider the possibility of amending the treaty, obviously if both Pakistan and India are willing to cooperate, although with the current environment, a renegotiation of the treaty would probably bring more complications. There is no shred of evidence that India has violated the Indus Water Treaty or that it is stealing Pakistan's water[8], although Pakistan does blame India for breaching the treaty, as shown before. This is pointed out by Hindu politicians as an attempt by Pakistan to divert the attention of its own public from the real issues of gross mismanagement of water resources[9].
Pakistan has a more hostile attitude regarding water distribution, trying to find a way to impeach India, meanwhile India focuses on the development of hydro-electric projects. India won't stop providing water to the West Punjab, as the treaty is still in force and is fulfilled by both parties. Pakistan should reconsider its role and its benefits received thanks to the treaty and meditate about the constant pressure towards India, as pushing over the limit could mean a more hostile activity carried out by India, which in the worst case scenario (although not likely to happen) could mean a breakdown of the treaty.
[1] The Punjab in 1920s - A Case study of Muslims, Zarina Salamat, Royal Book Company, Karachi, 1997. table 45, pp. 136.
[2] Guru Nanak Dev was the founder of Sikhism (1469-1540)
[3] Wyeth, G. (Dec 28, 2019). Opening the Gates: The Kartarpur Corridor. Australian Institute of International Affairs.
[4] Site where Guru Nanak Dev settled the Sikh community, and lived for 18 years after his death in 1539.
[5] Islamabad promoted the activity of Sikhs For Justice including the will to establish the state of Khalistan.
[6] World Bank (June 11, 2018). Fact Sheet: The Indus Waters Treaty 1960 and the Role of the World Bank.
[7] F.J. Fowler (Oct 1950) Some Problems of Water Distribution between East and West Punjab p. 583-599.
[8] S. Chandrasekharan (Dec 11, 2017) Indus Water Treaty: Review is not an Option South Asia Analysis Group.
[9] Mohan, G. (Feb 3, 2020). India rejects Pakistan average report on Indus water sharing India Today.
![Attack in Kashmir linked to groups of Pakistani origin [tweeted by @ANI]. Attack in Kashmir linked to groups of Pakistani origin [tweeted by @ANI].](/documents/10174/16849987/pakistan-yihadismo-blog.jpg)
▲ Attack in Kashmir linked to groups of Pakistani origin [twitted by @ANI].
ESSAY / Isabel Calderas [Ignacio Lucas as research assistant].
There is a myriad of security concerns regarding external factors when it comes to Pakistan: India, Afghanistan, the Saudi Arabia-Iran split and the United States, to name a few. However, there are also two main concerns that come from within: jihadism and organised crime. They are interconnected but differ in many ways. The latter is frequently overlooked to focus on the former, but both have the capacity of affecting the country, internally and externally, as the effectiveness of dealing with them impacts the perception the international community has of Pakistan. While internally disrupting, these problems also have international reach, as such groups often export their activities, adversely affecting at a global scale. Therefore, international actors put so much pressure on Pakistan to control them. Historically, there has been much scepticism over the government's ability, or even willingness to solve these risks. We will examine both problems separately, identifying the impact they have on the national and international arena, as well as the government's approach to dealing with either and the future risks they entail.
1. JIHADISM
Pakistan's education system has become a central part of the country's radicalization phenomenon[1], in the materialization of madrassas. These schools, which teach a more puritanical version of Islam than had traditionally been practiced in Pakistan, have been directly linked to the rise of jihadist groups[2]. Saudi Arabia, who has always had very close relations with Pakistan, played a key role in their development, by funding the Ahl-e-Hadith and Deobandi madrassas since the 1970s. The Iranian revolution bolstered the Saudi's imperative to control Sunnism in Pakistan, and the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan gave them the vehicle to do so[3]. In these schools, which teach a biased view of the world, students display low tolerance for minorities and are more likely to turn to jihadism.
Saudi and American funding of madrassas during the Soviet occupation helped the Pakistani army's intelligence agency, the Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), become more powerful, as they channelled millions of dollars to them, a lot of which went into the madrassas which sent mujahedeen fighters to fight for their cause[4]. The Taliban's origins can also be traced to these, as the militia was raised mainly from Afghan refugee camps in Pakistan and Saudi-funded madrassas[5].
Madrassas are especially popular in the poorer provinces of the country, where parents send their children to them for several non-religious reasons. First, because the Qur'an is written in Arabic and madrassas teach this language[6]. The dire situation of many families forces millions of Pakistanis to migrate to neighbouring, oil-rich Arabic-speaking countries, from where they send remittances home to help support their families. Secondly, the public-school system in Pakistan is weak, often failing to teach basic reading skills[7], something the madrassas do teach.
Partly in response to the international pressure[8] it has been under to fight terrorism within its territory; Pakistan has tried to reform the madrassas. The government has stated its intention to bring madrassas under the umbrella of the education ministry, financing these schools by allocating cash otherwise destined to fund anti-terrorism security operations[9]. It plans to add subjects like science to the curriculum, to lessen the focus on Islamic teachings. However, this faces several challenges, among which the resistance from the teachers and clerical authorities who run the madrassas outstands[10].
Before moving on to the prominent radical groups in Pakistan, we would like to make a brief summary on a different cause of radicalization: the unintended effect of the drone strategy adopted by the United States.
The United States has increasingly chosen to target its radical enemies in Pakistan through the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), which can be highly effective in neutralizing objectives, but also pose a series of risks, like the killing of innocent civilians that are in the neighbouring area. This American strategy, which Pakistan has publicly criticized, has fomented anti-American sentiment among the Pakistanis, at a ratio on average of every person killed resulting in the radicalization of several more people[11]. The growing unpopularity of drone strikes has further weakened relations between both governments, but shows no signs of changing in the future, if recent attacks carried by the U.S. are any indication. Pakistan's efforts to de-radicalize its population will continue to be undermined by the U.S. drone strikes[12].
Pakistan's anti-terrorism strategy is linked to its geostrategic and regional interests, especially dealing with its eastern and western neighbours[13]. There are many radical groups operating within their territory, and the government's strategy towards them shifts depending on their goal[14]. Groups like the Afghan Taliban, who target foreign invasions in their own country, and Al Qaeda, whose jihad against the West is on a global scale, have been allowed to use Pakistani territory to coordinate operations and take refuge. Their strategy is quite different for Pakistani Taliban group, Tehrik-e-Taliban (TTP) who, despite being allied with the Afghan Taliban, has a different goal: to oust the Pakistani government and impose Sharia law[15]. Most of the military's campaigns aimed at cracking down on radicals have been targeted at weakening groups affiliated with TTP. Lastly, there are those groups with whom some branches of the Pakistani government directly collaborate with.
Pakistan has been known to use jihadi organisations to advance its security objectives through proxy conflicts. Pakistan's policy of waging war through terrorist groups is planned, coordinated, and conducted by the Pakistani Army, specifically the ISI[16] who, as previously mentioned, plays a vital role in running the State.
Although this has been a longstanding cause of tension between the Pakistani and the American governments, the U.S. has made no progress in persuading or compelling the Pakistani military to sever ties with the radical groups[17], even though the Pakistani government has stated that it has, over the past year, 'fought and eradicated the menace of terrorism from its soil' by carrying out arrests, seizing property and freezing bank accounts of groups proscribed by the United States and the United Nations[18]. Their actions have been enough to keep them off the FATF's blacklist for financing terrorism and money laundering[19], which would prevent them from getting financing, but concerns remain about ISI's involvement with radical groups, the future of the relations between them, the overall activity of these groups from within Pakistani territory, and the risk of a future attack to its neighbours.
We will use two of Pakistan's main proxy groups, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba and Jaish-e-Muhammad, to analyse the feasibility of an attack in the near future.
1.1. Lashkar-e-Tayyiba (LeT)
Created to support the resistance against the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, LeT now focuses on the insurgencies in Afghanistan and Kashmir, the highest priorities for the Pakistani military's foreign policy. The Ahl-e-Hadith group is led by its founder, Hafiz Saeed. Its headquarters are in Punjab. Unlike its counterparts, it is a well-organized, unified, and hierarchical organization, which has become highly institutionalized in the last thirty years. As a result, it has not suffered any major losses or any fractures since its inception[20].
Since the Mumbai attacks in 2008 (which also involved ISI), for which LeT were responsible, its close relationship with the military has defined the group's operations, most noticeably by restraining their actions in India, which reflects both the Pakistani military's desire to avoid international pressure and conflict with their neighbour and the group's capability to contain its members. The group has calibrated its activities, although it possesses the capability to expand its violence. Its outlets for violence have been Afghanistan and Kashmir, which align with the Pakistani military's diary: to bring Afghanistan under Pakistan's sphere of influence while keeping India off-balance in Kashmir[21]. The recent U.S.-Taliban deal in Afghanistan and militarization of Kashmir by India may change this. LeT has benefited handsomely for its loyalty, receiving unparalleled protection, patronage, and privilege from the military. However, after twelve years of restraint, Lashkar undoubtedly faces pressures from within its ranks to strike against India again, especially now that Narendra Modi is prime minister.
1.2. Jaish-e-Muhammad (JeM)
The Deobandi organisation, led by its founder Masood Azhar, has had close bonds with Al-Qaeda and the Taliban since they came into light in 2000. With the commencement of the war on terror in Afghanistan, JeM reciprocated by launching an attack on the Indian Parliament on December 2001, in cooperation with LeT. However, it ignored the Pakistani military's will in 2019 when it launched the Pulwama attack, after which the government of Pakistan launched a countrywide crackdown on them, taking leaders and members into preventive custody[22].
1.3. Risk assessment
Although it has gone rogue before, Jaish-e-Muhammad has been weakened by the recent government's crackdown. What remains of the group, consolidated under Masood Azhar, has repaired ties with the military. Although JeM has demonstrated it still possesses formidable capability in Indian Kashmir, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba represents the main concern for an attack on India in the near future.
Lashkar has been both the most reliable and loyal of all the proxy groups and has also proven it does not take major action without prior approval from the ISI, which could become a problem. Pakistan has adopted a policy of maintaining plausible deniability for any attacks in order to avoid international pressure after 9/11, thus LeT's close ties with the military make it more likely that its actions will provoke a war between the two countries.
The United States has tried for several years to get Pakistan to stop using proxies. There are several scenarios in which Lashkar would break from the Pakistani state (or vice versa), but they are farfetched and beyond foreign influence: a) a change in Pakistan's security calculus, b) a resolution on Kashmir, c) a shift in Lashkar's responsiveness and d) a major Lashkar attack in the West[23].
a) A change in Pakistan's security calculus is the least likely, as the India-centric understanding of Pakistan's interests and circumstances is deeply embedded in the psyche of the security establishment[24].
b) A resolution on Kashmir would trouble Lashkar, who seeks full unification of all Kashmir with Pakistan, which would not be the outcome of a negotiated resolution. More so, Modi's recent decision regarding article 370 puts this possibility even further into the future.
c) A shift in Lashkar responsiveness would be caused by the internal pressures to perform another attack, after more than a decade of abiding by the security establishment's will. If perceived as too powerful of insufficiently responsive, ISI would most likely seek to dismantle the group, as they did with Jaish-e-Muhammad, by focusing on the rogue elements and leaving Lashkar smaller but more responsive. This presents a threat, as the group would not allow itself to be simply dismantled but would probably resist to the point of becoming hostile[25].
d) The last option, a major Lashkar attack in the West, is also unlikely, as the group has not undertaken any major attack without perceived greenlight from ISI.
This does not mean that an attack from LeT can be ruled out. ISI could allow the group to carry out an attack if, in the absence of a better reason, it feels that the pressure from within the group will start causing dissent and fractures, just like it happened in 2008. It is in ISI's best interest that Lashkar remains a strong, united ally. Knowing this, it is important to note that a large-scale attack in India by Lashkar is arguably the most likely trigger to a full-blown conflict between the two nations. Even a smaller-scale attack has the potential of provoking India, especially under Modi.
If such an attack where to happen, India would not be expected to display a weak-kneed gesture, as PM Modi's policy is that of a tough and powerful approach in defence vis-à-vis both Pakistan and China. This has already been made evident by its retaliation for the Fidayeen attack at Uri brigade headquarters by Jaish-e-Muhammad in 2016[26]. It has now become evident that if Pakistan continues to harbour terrorist groups against India as its strategic assets, there will be no military restraint by India as long as Modi is in power, who will respond with massive retaliation. In its fragile economic condition, Pakistan will not be able to sustain a long-drawn war effort[27].
On the other hand, Afghanistan, which has been the other focus of Pakistan's proxy groups, is now undergoing a process which could result in a major organisational shift. The Taliban insurgent movement has been able survive this long due to the sanctuary and support provided by Pakistan[28]. Furthermore, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba's participation in the Afghan insurgency furthered the Pakistani military's goal of having a friendly, anti-India partner on its western border[29]. The development and outcome of the intra-Afghan talks will determine the continued use of proxies in the country. However, we can realistically assume that, at least in the near future, radical groups will maintain some degree of activity in Afghanistan.
It is highly unlikely that the Pakistani intelligence establishment will stop engaging with radical groups, as it sees in them a very useful strategic tool for achieving its security goals. However, Pakistan's plausible deniability approach will come into question, as its close ties with Lashkar-e-Tayyiba make it increasingly hard for it to deny involvement in its acts with any credibility. Regarding India, any kind of offensive from this group could result in a large-scale conflict. This is precisely the most likely scenario to occur, as Modi's history with Lashkar-e-Tayyiba and their twelve-year-long "hiatus" from impactful attacks could propel the organisation to take action that will impact the whole region.
2. DRUG TRAFFICKING
Drug trafficking constitutes an important problem for Pakistan. It originates in Afghanistan, from where thousands of tonnes are smuggled out every year, using Pakistan as a passageway to provide the world with heroin and opioids[30]. The following concept map has been elaborated with information from diverse sources[31] to present the different aspects of the problem aimed to better comprehend the complex situation.
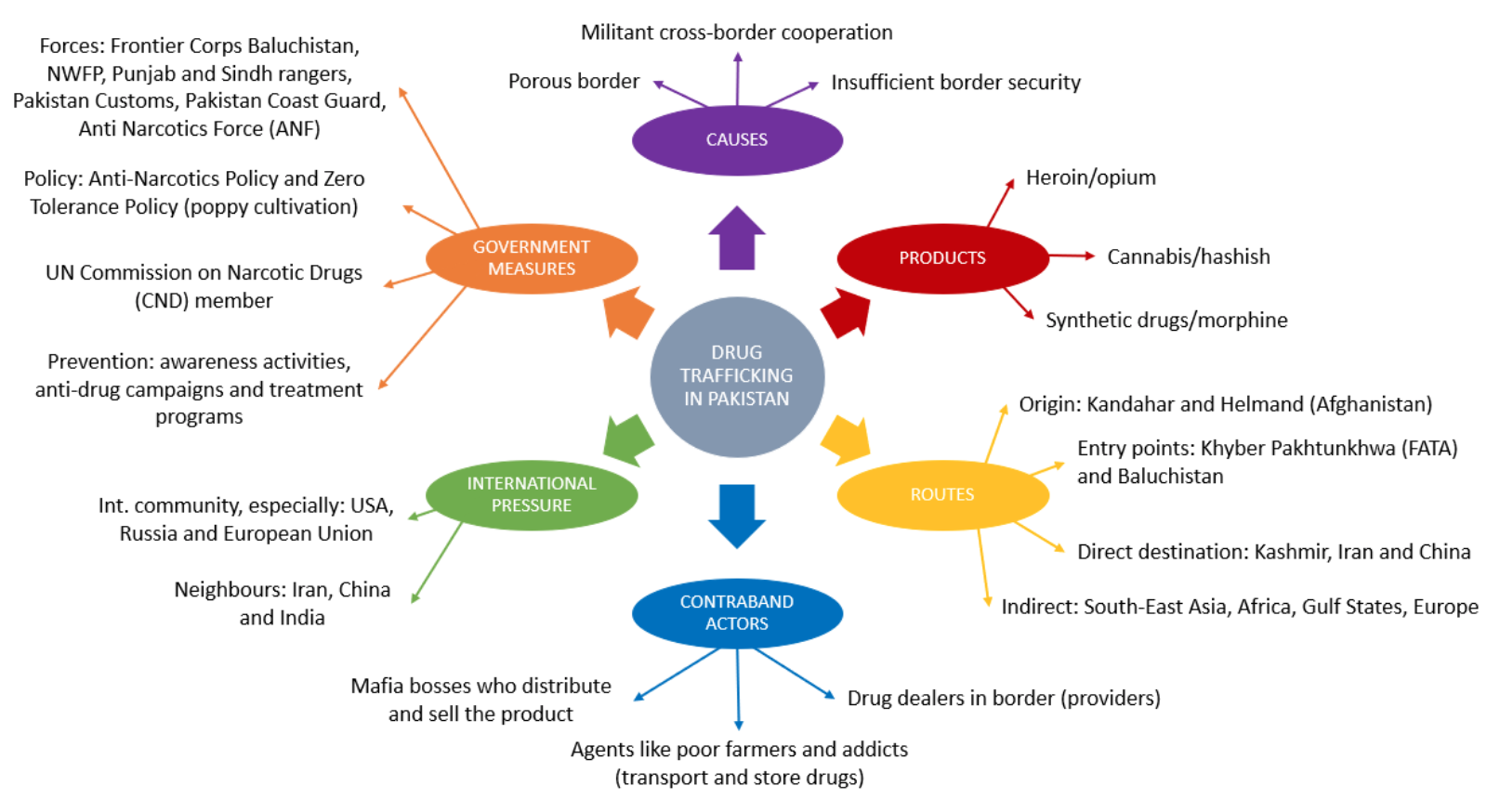
Afghanistan, one of the world's largest heroin producers, has supplied up to 60% and 80% of the U.S. and European markets, respectively. The landlocked country takes advantage of its blurred border line, and the remoteness and inaccessibility of the sparsely populated bordering regions with Pakistan, using it as a conduit to send its drugs globally. The Pakistani government is under a lot of pressure from the international community to fight and minimise drug trafficking from its territory.
Pakistan feels a special kind of pressure from the European Union, as its GSP+ status could be affected if it does not control this problem. The GSP+ is dependent on the implementation of 27 international conventions related to human rights, labour rights, protection of the environment and good governance, including the UN Convention on Fighting Illegal Drugs[32]. Pakistan was granted GSP+ status in 2014 and has shown commitment to maintaining ratifications and meeting reporting obligations to the UN Treaty bodies[33]. However, one of the aspects of the scheme is its "temporary withdrawal and safeguard" measure, which means the preferences can be immediately withdrawn if the country is unable to control drug trafficking effectively[34]. This has not been the case, and the EU has recognised Pakistan's efforts in the fight on drugs; the UN has also removed it from the list of cannabis resin production countries[35]. Anti-corruption frameworks have been strengthened, along with legislation review and awareness building, but they have been advised that better coordination between law enforcement agencies is needed[36].
The GSP+ status is very important to Pakistan, as the European Union is their first trade partner, absorbing over a third of their total exports in 2018, followed by the U.S., China and Afghanistan[37]. The Union can use this as leverage to obtain concessions from Pakistan. However, the approach they have taken so far has been of collaboration in many areas, including transnational organised crime, money laundering and counter-narcotics[38]. In this sense, the EU ambassador to Pakistan recently stated that the new Strategic Engagement Plan of 2019 would "further boost their relations in diverse fields"[39].
Even with combined efforts, eradicating the drug trafficking problem in Pakistan has proven to be very difficult. This is because production of the drug is not done in its territory, and even if border patrols are strengthened, it will be very hard to stop drugs from coming in from its neighbour if the Afghan government doesn't take appropriate measures themselves.
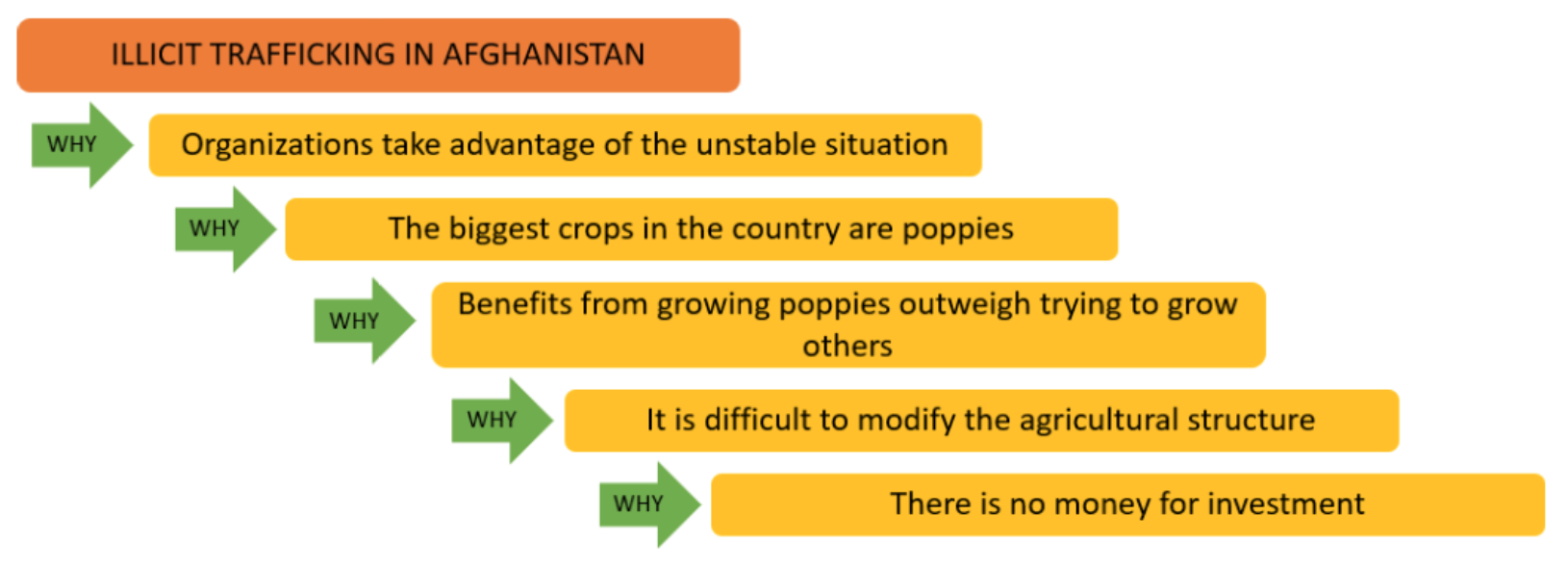
A "5 whys" exercise has led us to understand that the root cause of the problem is the fact that most farmers in Afghanistan are too poor to turn to different crops. A nearly two decade war has ravaged the country's land, leaving opium crops, which are cheaper and easier to maintain, as the only option for most farmers in this agrarian nation. A substantial investment in the country's agriculture to produce more economic options would be needed if any serious advance is expected to be made in stopping illegal drug trafficking. These investments will have to be a joint effort of the international community, and funding for the government will also be necessary, if stability is to be reached. Unless this is done, opium will likely remain entangled in the rural economy, the Taliban insurgency, and the government corruption whose sum is the Afghan conundrum.[40]. And as long as this does not happen, it is highly unlikely that Pakistan will be able to make any substantial progress in its effort to fight illicit drugs.
[1] Khurshid Khan and Afifa Kiran, "Emerging Tendencies of Radicalization in Pakistan," Strategic Studies, vol. 32, 2012.
[2] Hassan N. Gardezi, "Pakistan: The Power of Intelligence Agencies," South Asia Citizenz Web, 2011, http://www.sacw.net/article2191.html.
[3] Madiha Afzal, "Saudi Arabia's Hold on Pakistan," 2019, https://www.brookings.edu/research/saudi-arabias-hold-on-pakistan/.
[4] Gardezi, "Pakistan: The Power of Intelligence Agencies."
[5] Ibid.
[6] Myriam Renaud, "Pakistan's Plan to Reform Madrasas Ignores Why Parents Enrol Children in First Place," The Globe Post, May 20, 2019, https://theglobepost.com/2019/05/20/pakistan-madrasas-reform/.
[7] Ibid.
[8] Drazen Jorgic and Asif Shahzad, "Pakistan Begins Crackdown on Mlitant Groups amid Global Pressure," Reuters, March 5, 2019, https://www.reuters.com/article/us-india-kashmir-pakistan-un/pakistan-begins-crackdown-on-militant-groups-amid-global-pressure-idUSKCN1QM0XD.
[9] Saad Sayeed, "Pakistan Plans to Bring 20,000 Madrasas under Government Control," Reuters, April 29, 2019.
[10] Renaud, "Pakistan's Plan to Reform Madrasas Ignores Why Parents Enrol Children in First Place".
[11] International Human Rights and Conflict Resolution Clininc (Stanford Law Review) and Global Justice Clinic (NYE School of Law), "Living Under Drones: Death, Injury, and Trauma to Civilians From US Drone Practices in Pakistan," 2012, https://law.stanford.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/default/files/publication/313671/doc/slspublic/Stanford_NYU_LIVING_UNDER_DRONES.pdf.
[12] Saba Noor, "Radicalization to De-Radicalization: The Case of Pakistan," Counter Terrorist Trends and Analyses 5, no. 8 (2013): 16-19.
[13] Muhammad Iqbal Roy and Abdul Rehman, "Pakistan's Counter Terrorism Strategy (2001-2019): Evolution, Paradigms, Prospects and Challenges," Journal of Politics and International Studies 5, no. July-December (2019): 1-13.
[14] Madiha Afzal, "A Country of Radicals? Not Quite," in Pakistan Under Siege: Extremism, Society, and the State (Brookings Institution Press, 2018), 208, https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/chapter-one_-pakistan-under-siege.pdf.
[15] Ibid.
[16] John Crisafulli et al., "Recommendations for Success in Afghanistan," 2019, https://www.jstor.org/stable/resrep20107.7.
[17] Tricia Bacon, "The Evolution of Pakistan's Lashkar-e-Tayyiba," Orbis, no. Winter (2019): 27-43.
[18] Susannah George and Shaiq Hussain, "Pakistan Hopes Its Steps to Fight Terrorism Will Keep It off a Global Blacklist," The Washington Post, February 21, 2020.
[19] Husain Haqqani, "FAFT's Grey List Suits Pakistan's Jihadi Ambitions. It Only Worries Entering the Black List," Hudson Institute, February 28, 2020.
[20] Bacon, "The Evolution of Pakistan's Lashkar-e-Tayyiba."
[21] Ibid.
[22] Farhan Zahid, "Profile of Jaish-e-Muhammad and Leader Masood Azhar," Counter Terrorist Trends and Analyses 11, no. 4 (2019): 1-5, https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.2307/26631531.
[23] Tricia Bacon, "Preventing the Next Lashkar-e-Tayyiba Attack," The Washington Quarterly 42, no. 1 (2019): 53-70.
[24] Ibid.
[25] Ibid.
[26] Abhinav Pandya, "The Future of Indo-Pak Relations after the Pulwama Attack," Perspectives on Terrorism 13, no. 2 (2019): 65-68, https://www.jstor.org/stable/26626866.
[27] Ibid.
[28] Crisafulli et al., "Recommendations for Success in Afghanistan."
[29] Bacon, "The Evolution of Pakistan's Lashkar-e-Tayyiba."
[30] Alfred W McCoy, "How the Heroin Trade Explains the US-UK Failure in Afghanistan," The Guardian, January 9, 2018, https://www.theguardian.com/news/2018/jan/09/how-the-heroin-trade-explains-the-us-uk-failure-in-afghanistan.
[31] Dr. Bibhu Prasad Routray and Dr. Shanthie Mariet D Souza, "The Afghanistan-India Drug Trail - Analysis," Eurasia Review, August , https://www.eurasiareview.com/02082019-the-afghanistan-india-drug-trail-analysis/; Mehmood Hassan Khan, "Kashmir and Power Politics," Defence Journal 23, no. 2. 2 (2019); McCoy, "How the Heroin Trade Explains the US-UK Failure in Afghanistan"; Pakistan United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime Country Office, "Illicit Drug Trends in Pakistan," 2008, https://www.unodc.org/documents/regional/central-asia/Illicit Drug Trends Report_Pakistan_rev1.pdf; "Country Profile - Pakistan," United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), 2020, https://www.unodc.org/pakistan/en/country-profile.html.
[32] European Commission, "Generalised Scheme of Preferences (GSP)," 2020, https://ec.europa.eu/trade/policy/countries-and-regions/development/generalised-scheme-of-preferences/.
[33] High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, 'The EU Special Incentive Arrangement for Sustainable Development and Good Governance ('GSP+') Assessment of Pakistan Covering the Period 2018-2019' (Brussels, 2020).
[34] Dr. Zobi Fatima, "A Brief Overview of GSP+ for Pakistan," Pakistan Journal of European Studies 34, no. 2 (2018), https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333641020_A_BRIEF_OVERVIEW_OF_GSP_FOR_PAKISTAN.
[35] High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, "The EU Special Incentive Arrangement for Sustainable Development and Good Governance ('GSP+') Assessment of Pakistan Covering the Period 2018-2019".
[36] Fatima, "A Brief Overview of GSP+ for Pakistan."
[37] UN Comtrade Analytics, "Trade Dashboard," accessed March 27, 2020, https://comtrade.un.org/labs/data-explorer/.
[38] European External Action Services, 'EU-Pakistan Five Year Engagement Plan' (European Union, 2017), https://eeas.europa.eu/sites/eeas/files/eu-pakistan_five-year_engagement_plan.pdf; European Union External Services, 'EU-Pakistan Strategic Engagement Plan 2019' (European Union, 2019), https://eeas.europa.eu/sites/eeas/files/eu-pakistan_strategic_engagement_plan.pdf.
[39] "EU Ready to Help Pakistan in Expanding Its Reports: Androulla," Business Recorder, October 23, 2019.
[40] McCoy, "How the Heroin Trade Explains the US-UK Failure in Afghanistan".

 [
[