Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Security and defence .
One third of countries have developed a national cybersecurity strategy, but mobilized capabilities are minimal
A dozen Latin American countries have already developed a national cybersecurity strategy, but overall the capacities mobilized in the region to deal with cybercrime and cyberattacks are so far limited. In a continent with a high use of social networks, but at the same time with some problems of network electricity and internet access that make it difficult to react to cyber-attacks, the risk of widespread organized crime groups increasingly resorting to cybernetics is high.

article / Paula Suárez
In recent years, globalization has made its way in all parts of the world, and with it have emerged several threats in the field of cyberspace, which requires special treatment by the governments of all states. Globally, and not only in Latin America, the main areas under threat in terms of cybersecurity are, essentially, computer crime, network intrusions and politically motivated operations.
The latest reports on cybersecurity in Latin America and the Caribbean, carried out jointly by the Inter-American Bank development (IDB) and the Organization of American States (OAS), indicate that one third of the countries in the region have begun to take some steps to address the growing cybersecurity risks. However, they also note that efforts are still limited, given the general lack of preparedness for the threat of cybercrime; they also point to the need for a reform of protection policies in the coming years, especially with the problems that have come to light with the Covid-19 crisis.
The IDB and the OAS (OAS) have collaborated on different occasions to publicize status and raise awareness of cybersecurity issues, which have been increasing as globalization has become part of everyday life and social networks and the internet become more deeply integrated into our day-to-day lives. To address this new reality, both institutions have created a Cybersecurity Observatory for the region, which has published several programs of study.
If until the 2016report cybersecurity was a topic little discussed in the region, currently with the increase of technology in Latin America and the Caribbean it has become a topic of interest for which states tend to be increasingly concerned, and therefore, to implement relevant measures, as highlighted in the 2020report .
Transportation, educational activities, financial transactions, many services such as food, water or energy supply and many other activities require cybersecurity policies to protect civil rights in the digital realm such as the right to privacy, often violated by the use of these systems as a weapon.
Not only socially, but also economically, investment in cybersecurity is essential to prevent the damage caused by online crime. For the Gross Domestic Product of many countries in the region, attacks on infrastructure can account for from 1% to 6% of GDP in the case of attacks on critical infrastructure, which translates into incompetence on the part of these countries to identify cyber dangers and to take the necessary measures to combat them.
According to the aforementioned study, 22 of the 32 countries analyzed are considered to have limited capabilities to investigate crimes, only 7 have a plan to protect their critical infrastructure, and 18 of them have established a so-called CERT or CSIRT (Computer Security Incident or Emergency Response Team). These systems are not currently developed uniformly in the region, and they lack the capacity and maturity to provide an adequate response to threats at network, but their implementation is necessary and, increasingly, they are supported by institutions such as the OAS for their improvement.
In this area, the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST) has a work core topic , because of the great need in this region, for attend to governments so that they can benefit from the identification of cyber threats and the strategic security mechanisms of the association, mainly to protect the economies of these countries.
As already mentioned, awareness of the need for such measures has been increasing as cyber attacks have also increased, and countries such as Colombia, Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago and Panama have established a proper strategy to combat this damage. In contrast, many other countries in Latin America and the Caribbean such as Dominica, Peru, Paraguay and Suriname have lagged behind in this development, and although they are on the way, they need institutional support to continue in this process.
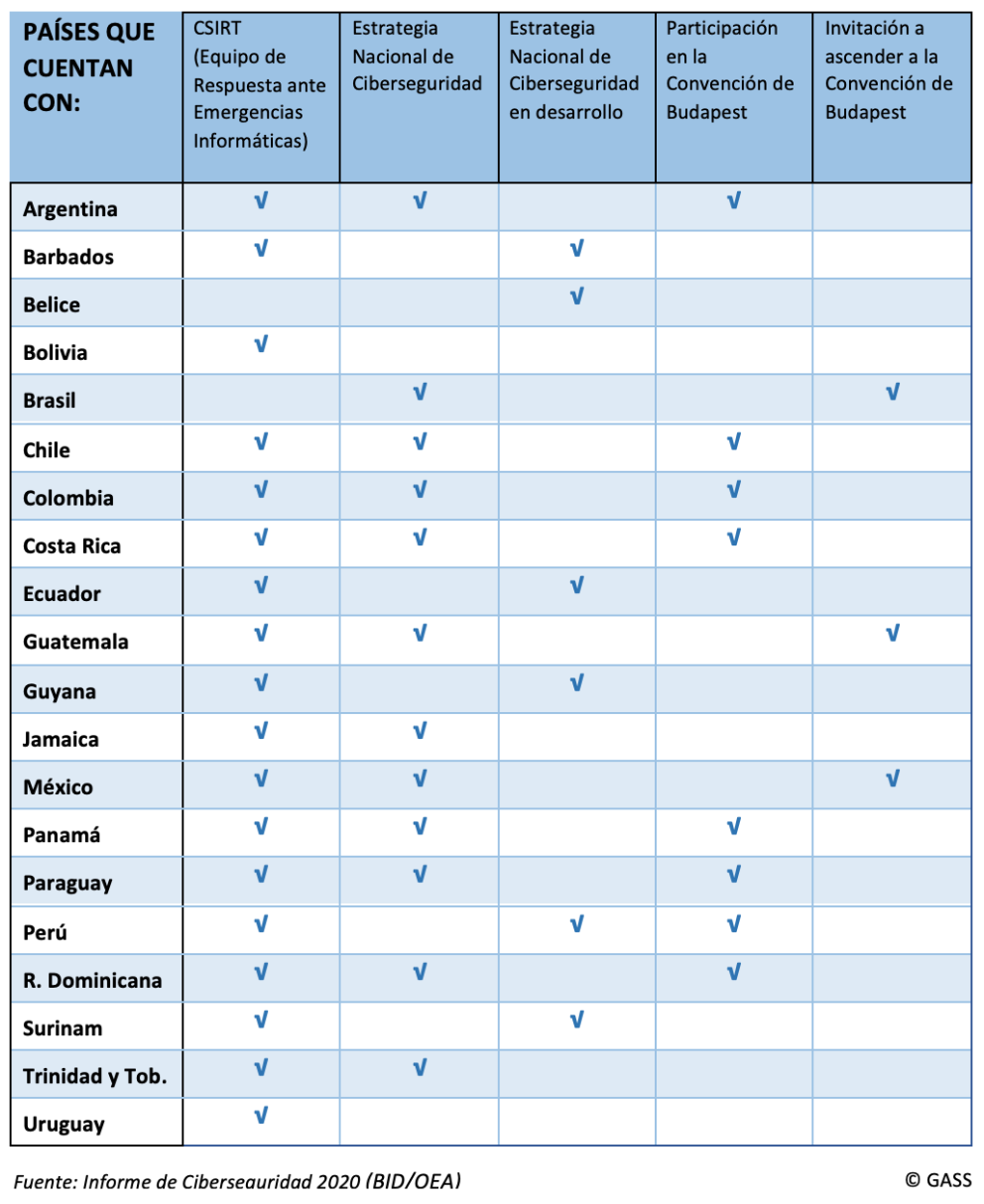
The problem in combating such problems is generally rooted in the states' own laws. Only 8 of the 32 countries in the region are part of the Budapestagreement , which advocates international cooperation against cybercrime, and one third of these countries do not have appropriate legislation in their legal framework for cybercrime.
For the states party to agreement, these guidelines can serve as a great financial aid to develop domestic and procedural laws with respect to cybercrime, so it is promoting the adherence or at least the observation of them from organizations such as the OAS, with the recommendations of specialized units such as group of work on Cybercrime of the REMJA, which advises on the reform of criminal law with respect to cybercrime and electronic evidence.
On the other hand, it was not until the beginning of this year that, with the incorporation of Brazil, 12 countries in Latin America and the Caribbean have established a national cybersecurity strategy, due to the lack of qualified human talent. Although it is worth mentioning the two countries in the region with the largest development in the field of cybersecurity, which are Jamaica and Trinidad and Tobago.
Of the problems mentioned, we can say that the lack of national strategy in terms of cybersecurity exposes these countries to various attacks, but to this must be added that the companies that sell cybersecurity services and provide technical and financial support in the region are mostly from Israel or the United States, and are linked to a rather militarized security and defense perspective, which will be a challenge in the coming years because of the skill that China is showing on this side of the hemisphere, especially linked to 5G technology.
Cyber malpractices are a threat not only to the Economics of Latin America and the Caribbean, but also to the functioning of democracy in these states, an attack on the rights and freedoms of citizens and the values of society. For this reason, the need for investment in civilian infrastructure and military capacity is becoming apparent. To achieve this, the states of the region are willing to cooperate, firstly, in the unification of their legal frameworks based on the models of the Budapest agreement and the instructions of the European Union, whose perspective to face the new challenges in cyberspace is having a great impact and influence in the region.
In addition, with the upcoming Covid-19 crisis, the states of the region are generally willing to collaborate by developing their own national strategies, consistent with the values of the organizations they are part of, to protect both their current means and their emerging technologies (artificial intelligence, quantum, computing from high performing and others). Cyber threats are intended to be addressed from channels open to partnership and dialogue, since the Internet has no borders, and the harmonization of legal frameworks is the first step to strengthen not only regional but also international cooperation.
![Bahraini and UAE foreign ministers sign Abraham Accords with Israeli premier in September 2020 [White House]. Bahraini and UAE foreign ministers sign Abraham Accords with Israeli premier in September 2020 [White House].](/documents/16800098/0/acuerdos-blog.jpg/ad268976-c84e-2b4c-d2a5-ca36909e72e2?t=1621877040390&imagePreview=1)
Bahraini and UAE foreign ministers sign Abraham Accords with Israeli premier in September 2020 [White House].
essay / Lucas Martín Serrano
It is interesting to incorporate into any geopolitical analysis subject a touch of history. History is a fundamental financial aid for understanding the present. And most conflicts, problems, frictions or obstacles, whether between nations or public or private entities, always have an underlying historical background. Moreover, taken to the field of negotiation, regardless of the level of negotiation, demonstrating a certain historical knowledge of the adversary is useful because, on the one hand, it is not only a sample of interest and respect for him, which will always place us in an advantageous position, but, on the other hand, any stumbling block or difficulty that appears has ample possibilities of having its historical counterpart, and precisely there the path to a solution can be found. The party that has a greater depth of knowledge will significantly increase the chances of a solution that is more favourable to its interests.
In ancient times, the territory now occupied by the United Arab Emirates was inhabited by Arab tribes, nomadic farmers, craftsmen and traders. Plundering the merchant ships of European powers that sailed along its coasts, coming closer than was advisable, was commonplace. And, in a way, a way of life for some of its inhabitants. It was in the 7th century that Islam took root in the local culture. Of the two currents that emerged after the disputes that followed the death of the Prophet, it was the Sunni current that became dominant from the 11th century onwards.
In order to put an end to piracy and secure the maritime trade routes, the United Kingdom signed a peace treaty with the sheikhs in the area in 1820, signature . In 1853, a further step was taken and another agreement was signed, placing the entire territory under the military protectorate of the United Kingdom.
signature The area attracted the attention of powers such as Russia, France and Germany, and in 1892, to protect their interests, the agreement was set up, guaranteeing the British a monopoly on trade and exports.
The area encompassing today's seven United Arab Emirates plus Qatar and Bahrain became known as the "Trucial States".
During World War I, the Gulf's airfields and ports played an important role in the conflict in favour of the UK, development . At the end of World War II in 1945, the League of Arab States (Arab League) was created, made up of those with some colonial independence. The organisation attracted the attention of the Truce states.
In 1960, the Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) was created, with Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait and Venezuela as founding members and headquartered in Vienna, Austria. The seven emirates, which would later form the United Arab Emirates, joined the organisation in 1967.
Since 1968, nine emirates on the eastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula had begun negotiations to form a federal state. Following the withdrawal of British troops final and after Bahrain and Qatar dissociated themselves from the process and gained independence separately, in 1971, six emirates became independent from the British Empire: Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm al Qaywayn and Fujairah, forming the federation of the United Arab Emirates, with a legal system based on the 1971 constitution. Once consolidated, they joined the Arab League on 12 June. The seventh emirate, Ras Al-Khaimah, joined the following year, with the strongest components being the emirates of Dubai and Abu Dhabi, the capital.
It was the beginning of the exploitation of the huge oil wells discovered years earlier that turned the tide at status. After the 1973 oil crisis, the Emirates began to accumulate enormous wealth, as OPEC members decided not to export any more oil to the countries that supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War.
Oil and tourism based on urban growth and technological development are the main sources of prosperity in the country today, and a very important fact from all points of view is that 80-85% of the UAE's population is currently immigrant.
status current
It has been especially during the last decade, and partly as a consequence of events in the region since what became known as the Arab Spring, that the US has emerged as a regional power with the capacity to influence the region.
The main characteristic that can be attributed to this emergence on the international scene is the transformation of a conservative foreign policy, very much geared towards "self-preservation", towards a more open-minded one with a clear vocation not only to play a relevant role in the region, but also to influence it in order to protect its interests.
What can be seen as Abu Dhabi's main ambition is to become a major player capable of influencing the definition and establishment of governance Structures throughout the region according to its own model, securing and expanding trade routes, bringing in its neighbours to create a sufficiently powerful economic node with the capacity to forge closer ties with the entire East African region and Southeast Asia, in what seems another clear example of how the global geopolitical centre is already shifting definitively towards the Asia-Pacific axis.
The Emirati model has been able to evolve to integrate increasing economic openness with a conservative and strong-government model political whose main speech is built on the foundation of a well-entrenched and secure state. And all of this is coupled with a strong capacity as a service provider provider. Interestingly, the social model is relatively secular and liberal based by regional standards.
But a fundamental fact that cannot be forgotten is the outright rejection of any political or religious ideology that poses the slightest threat to the hegemony and supremacy of the state and its leaders.
It is Abu Dhabi, as the largest and most prosperous of the seven emirates, that exerts the most influence in setting the broad lines of both domestic and foreign policy. Indeed, the evolution of the UAE's established model is firmly associated with Abu Dhabi's crown prince and de facto leader of the emirate, Mohamed bin Zayed (MbZ).
What cannot be lost sight of is that, although MbZ and his inner circle of trust share the same vision of the world and politics, their actions and decisions do not necessarily follow a pre-established plan. There is no basic doctrine with set tactical and strategic objectives and the lines of work to follow in order to achieve them.
Their way of carrying out country strategy, if it can be called that, is based on a small group belonging to that inner circle, which puts on the table a number of usually tactical and reactive options to any problems or issues that arise to carry out. Based on these, the top leadership follows an ad hoc decision-making process that can lead to an excessive need for subsequent corrections and adjustments that in turn lead to missed opportunities.
Threats - status security
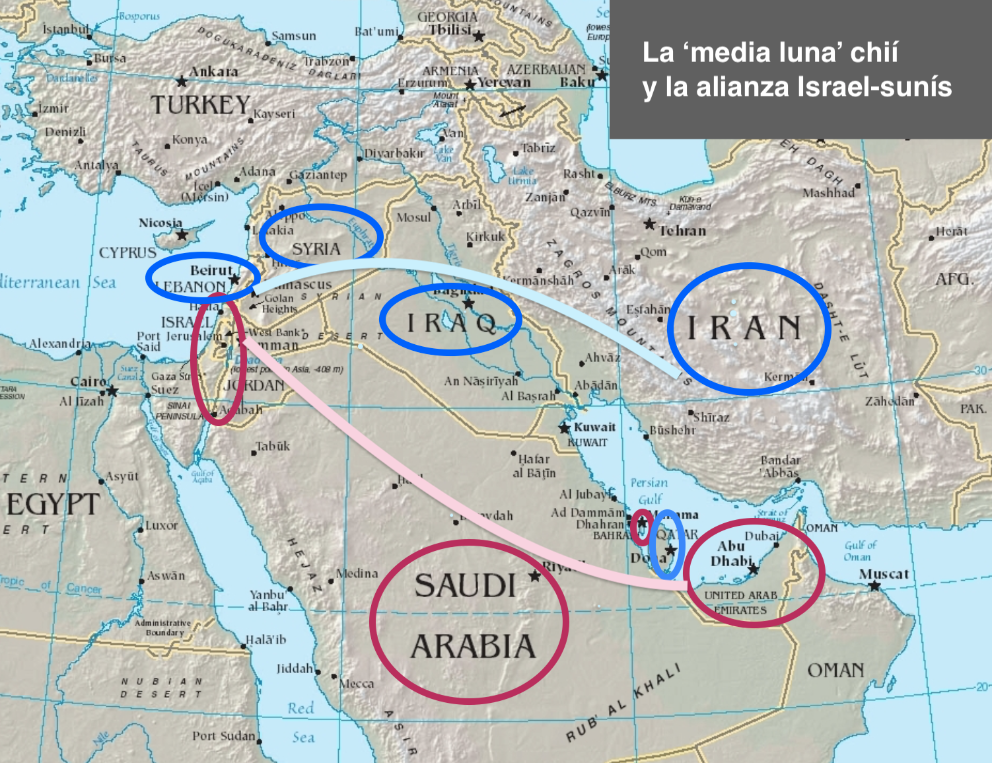
Emirati authorities have a clear perception of the main geostrategic threats to their development: on the one hand, the Iranian-promoted transnational spread of Islamist political ideology and, on the other, the influence sought by the Muslim Brotherhood and its promoters and supporters, including Qatar and Turkey, is perceived as an existential threat to their vision of a more secular form of government, as well as to the stability of the current regional status quo, given that it can act as a catalyst for radicalism in the area.
However, Abu Dhabi has been much more belligerent in its speech against the Muslim Brotherhood and its supporters, while remaining cautious in its stance against Iran.
The recent agreement with the State of Israel has served to undermine the credibility of many long-held clichés and has also highlighted the emergence of a Sunni-Jewish bloc as civil service examination to the belligerent and growing Shiite current led by Iran and its proxies, active in virtually every country in the region and in all regional conflicts.
This new status should serve to confirm to Western powers that in the Middle East region the view of their own problems has changed and Iran and its particular way of conducting foreign policy and defending its interests are now seen as a far more destabilising factor than the long-running Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The threat posed by Iran has acted as a catalyst in bringing together views, while Israel is nonetheless seen as providing stability both militarily and economically.
The UAE-Israel Treaty
On 15 September, Israel, the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain formalised the normalisation of their relations. This agreement means that four Arab states have now accepted Israel's right to exist, and this is undoubtedly a real diplomatic success.
The fact that it was precisely the UAE and Bahrain is no coincidence. Neither state has engaged in a direct war against Israel. And, if this characteristic is common to both states, Bahrain's relationship with Israel has been much smoother than that of the UAE. This reality is underpinned by the Jewish community based in Al-Qatif and its integration, which has translated into full and active participation in Bahrain's political life. This has helped to ensure that relations between Manama and Jerusalem have been far from conflictual.
Despite being seen as a novelty in the eyes of the general public, the truth is that the recent agreement is the third 'peace treaty' that signature has reached between the Hebrew country and an Arab nation. However, it is the first that seems to have been born with sufficiently solid foundations to augur a new, much more stable and lasting status , in clear contrast to the relations resulting from the previous agreements with Egypt and Jordan, which were very limited to personal relations and in the field of security and conventional diplomacy.
The new agreement with Israel sets out a new path for partnership affecting the Middle East as a whole, including substantially counterbalancing Iran's influence, fostering trade relations, tourism, partnership in subject military intelligence sharing, cooperation in health area and thereby helping to position the UAE to lead Arab diplomacy in the region by offering a solid civil service examination to Islamist groups such as the Muslim Brotherhood and its Palestinian arm in Gaza, Hamas, and thereby opening the door for other countries in the region to move in the same direction.
Israel's decision to fail the announced annexation under its sovereignty of certain areas of the West Bank is test that these moves in the region are much deeper and much more prepared and agreed in advance than might be imagined.
And this is precisely one of the major differences with previous agreements. The great expectation that has been created and the clear indications that other countries, including Saudi Arabia, will follow the UAE's lead.
In fact, one significant step in this direction was taken, and it was as simple as an Israeli "EI-Al" plane flying over Saudi airspace carrying a large issue group of businessmen, staff officials and investors on its way to the Emirates as a gesture of goodwill. And contrary to what might have been expected at other times, this had no repercussions in the Arab world, nor did it provoke any protests or demonstrations against it, subject .
Places such as Amman, Beirut, Tunis and Rabat, where demonstrations against the Israeli "occupation" and similar accusations are traditionally large in terms of participation, remained largely calm on this occasion.
But if this has gone unnoticed by the general population, it has not gone unnoticed by the leaders of the Middle Eastern powers and the violent organisations they use as proxies.
For those aspiring to follow in the UAE's footsteps and establish relations with Israel, this has served as a spur to reaffirm their decision, as the sense of unease or even danger emanating from the streets in the Arab world regarding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict that such a move might provoke has diminished.
For Iran and its proxies , on the other hand, it has been a hard lesson. Not only has the Palestinian cause, which has been raised and put on the table for so long, been significantly diminished in importance, but it has coincided in time with potestas in both Iraq and Lebanon in the opposite direction, i.e. against Iran's interference in the internal affairs of both countries.
In conclusion, it should be noted that, while this absence of protest at the agreement between Israel and the UAE may seem surprising, it is a clear sign of a long process of political maturation and evolution within the Arab world at large.
The people of the Middle East in general no longer aspire to pan-Arabist, pan-Islamic unity, to the establishment of the Great Caliphate or, in the case of Iran or Turkey, to imperialist dreams that are a thing of the past. What the mass of the people and society really want is to improve their well-being, to have more and more attractive economic opportunities, to have a good system educational, to improve the standards of development in all areas, to have the rule of law, and for the rule of law to be equal for all in their respective countries.
The treaty that is the subject of this point fits perfectly within these aspirations and this mental outline . The masses that once took to the streets no longer believe that the Palestinian cause is worthy of more effort and attention than their own struggle for a better future for their nations.
And, importantly, despite the opacity of the ayatollahs' regime, Iran's population is becoming less and less submissive to policies that are leading the country into a series of permanent conflicts with no end in sight, wasting the country's resources to sustain them.
Just two days after advertisement of agreement , the United Arab Emirates lifted the ban on telephone communication with Israel, with Hebrew Foreign Minister Gabi Ashkenazi and his Emirati counterpart Abdullah binZayed symbolising the opening of this new line of communication.
Almost immediately afterwards, a team from the Israeli Foreign Ministry travelled to Abu Dhabi to begin looking for possible sites for the future Israeli embassy.
A significant flow of investment from the UAE is being channelled to Israeli companies seeking new ways to treat COVID19 and to develop new tests to detect the disease. The increase in business deals between Israeli and Emirati companies has been almost immediate, and the "El-Al" company is already working to open a direct corridor between Tel Aviv and Abu Dhabi.
In view of the new status and the new approaches, Morocco, Oman and other Arab countries are now moving to follow in the UAE's footsteps. Israel's attractiveness is only growing, in a significant evolution from being the most hated country in the region to the most desired partner .
One factor to consider, however, is the impact in the US and Europe. In the West, the Palestinian cause is generally gaining support mainly due to the Boycott, Divestment and Sanctions (BDS) movement. As such, changes in relations with Israel are likely not only to fail to undermine that support, but also to spur increased efforts to prevent normalisation through disinformation campaigns spreading hatred towards Israel.
Finally, the civil service examination by Turkey, Qatar and Iran was predictable, but also clarifying. The Iranian president has called agreement a "grave mistake", while his Turkish counterpart has threatened to close the UAE embassy in Turkey. status In both cases, the ultimate reason for this reaction is the same: the use of the Palestinian cause for their own interests and, coincidentally, both are on this occasion coincidental: to distract public opinion from the difficult economic situation that, for different reasons, the two countries are going through.
Regional policy
The most important and enduring element of the UAE's foreign and security policy is its strategic alliances with the US and Saudi Arabia. Although the UAE has pursued a more independent course over the past decade, developments and this new direction would not have been possible without the support of the US, on whose protection the small but wealthy yet sparsely populated state relies, and who can be counted on to export its energy resources in the event of a conflict.
Even during the Obama administration, when relations were strained by US policy towards the events of the 'Arab Spring' and Iran, the strategic alliance between the two nations was maintained.
The clearly defined anti-Iranian policy of Donald Trump's administration, equivalent to that of the UAE, facilitated a rapid improvement in relations once again, and the new US administration saw the UAE as a fundamental pillar on which to base its Middle East policy. Thus, together with Israel and Saudi Arabia, the UAE is now the main US ally in the region.
In contrast to the US, Saudi Arabia became a strategic partner of the UAE's new regional policy under Obama. Indeed, the two nations have maintained close ties since the birth of the Emirates in 1971, but the new, young state unsurprisingly remained in the shadow of the other, more established nation, following the policies of its 'big brother'.
This status changed with the rise to power of Mohammed Bin Zayed who, since 2011, has been committed to spearheading a political line of joint actions in the region that have ultimately been decisive. MbZ found his perfect counterpart in Saudi Prince Mohammed Bin Salman, who gradually, since 2015, took the reins as the visible head of Saudi Arabia's policy. To such an extent that in certain cases, such as Yemen and Qatar, the UAE's leadership and drive seems to have been the unifying force behind joint regional policies.
Alliances
United States
The US role as an ally of the UAE dates back to the early 1980s, just after the 1979 Iranian revolution, which resulted in the loss of its most important ally in the region and the beginning of the Iran-Iraq war.
However, it was the 1990-1991 Gulf War that, with Iraq's invasion of Kuwait on 2 August 1990, showed the UAE how vulnerable the small Gulf states were to military aggression by any of their powerful neighbours.
In order to ensure its protection, and in common with other countries in the region, the UAE favoured an increased US presence on its territory in the years following the war. This concluded with a bilateral security agreement, agreement , signed in July 1994. This gave the US access to the UAE's air and seaports instructions and, in return, it undertook to protect the country from external aggression. Interestingly, and as a measure of how status has evolved, the agreement remained secret at Abu Dhabi's request because of the UAE's fear of criticism and protest both domestically and from Iran.
Initially, the UAE was no more than a US ally in the Persian Gulf. However, its importance as partner grew between 1990 and 2000, in part due to the port of Jebel Ali, which became the US Navy's most used base outside the country, and the Al Dhafra air base, a facility core topic for US activities in the region.
Moreover, since the late 1990s, the UAE has begun a process of presenting itself to its new ally as a reliable and more relevant partner , increasing the quantity and level of its cooperation. framework In line with this, UAE military forces have participated in all major US operations in the Middle East, from the Gulf War in 1991 to Somalia in 1992, Kosovo in 1999, Afghanistan since 2002, Libya since 2011, and Syria (in the fight against Da'esh) between 2014 and 2015. Only the UAE's participation in the invasion of Iraq in 2003 was vehemently avoided. From this involvement, the UAE Armed Forces have gained a great deal of experience on the ground, which has been beneficial to their effectiveness and professionalism.
This involvement in the often controversial US military actions in Arab countries has undoubtedly been a key element for the United States. Not only because of the image and narrative implications of having at least one Muslim country supporting them, but also because Abu Dhabi's contribution has not been limited to the military aspect. Humanitarian organisations have acted in parallel in order to win the support of the population wherever they have intervened by investing huge amounts of money. The most obvious example is Afghanistan, where the UAE has spent millions of dollars on humanitarian projects and development to help stabilise the country, while providing a small contingent of special operations forces in the particularly dangerous southern part of the country since 2003. In addition, between 2012 and 2014 they expanded their deployment with six F16 aircraft to support air operations against the Taliban. Even when the US began its phased withdrawal after 2014, Emirati troops remained in Afghanistan.
Getting the UAE on board in the fight against jihadists was not difficult at all, as its leaders are particularly averse to any form of religious extremism that affects the political system within Islam. This is the main reason for its air force's involvement in the US-led coalition against Daesh in Syria between 2014 and 2015. To such an extent that, after the US aircraft, it was the UAE aircraft that flew the most sorties against jihadist targets.
But partnership was not limited to the US. Both Australia and France had the emirates' air instructions at their disposal to carry out their operations.
Only the open breakdown of hostilities and the UAE's involvement in the 2015 Yemen War reduced its involvement in the fight against Daesh.
But it has not all been easy. The 2003 invasion of Iraq caused deep misgivings in the UAE, which saw it as a grave mistake. Their fear was that such an intervention would end up increasing Iran's influence over Iraq, or lead to civil war, which would destabilise the entire region.
Fears were realised when in 2005 a Shiite coalition close to Iran won the Iraqi elections and war broke out, leaving the UAE with its hands tied to try to influence status. Their main concern at the time was that a premature withdrawal of all US forces would further complicate status.
The renewed relationship with the Trump administration has led to the signature of a new security and cooperation agreement signed in 2017. reference letter In contrast to what happened in 1994, the contents of the agreement have been made public, and mainly relate to the presence of US troops on Emirati soil on a permanent basis. The agreement also covers the training of Emirati armed forces and regular joint exercises.
Thanks to this agreement, the US presence in the UAE is larger than ever. There are currently some 5,000 men deployed between the Al Dhafra airbase, the port of Jebel Ali and a few other small instructions or naval stations. At Al Dhafra air base alone, 3,500 men operate from F-15, F-22 and F-35 fighter jets, reconnaissance aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
For its part, the UAE has continued to develop its own military capabilities by acquiring US-made material, mainly anti-aircraft systems ("Patriot" and THAAD) and combat aircraft (110 F-16s). In addition, for a couple of years now, the UAE has shown great interest in acquiring the new F-35, although negotiations, not without some reluctance, are still ongoing.
In 2018, problems arose in supplying precision-guided munitions to both the UAE and Saudi Arabia, as both countries were using them in the Yemen War. The murder of Saudi journalist Jamal Kashoggi exacerbated resistance from the US congress , forcing President Trump to use his veto power in order to maintain the supply. This gives a measure of how decisive the current administration's attitude towards both countries is.
Despite all the difficulties mentioned above, the current US administration has redoubled its efforts to support the UAE in its regional policies, as they coincide with US objectives.
The first goal has been to build an anti-Iran alliance among Middle Eastern states that includes the UAE as partner core topic along with Saudi Arabia and Egypt. This plan is entirely in line with Abu Dhabi's aspiration to gain some leadership in the region, and is likely to succeed, as the UAE is likely to support the US in a solution to the Palestinian conflict that is quite in line with the Israeli proposal .
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is currently the UAE's most important ally in the region. Both states are financed by oil exports and both are equally wary of the expansionist ambitions of their powerful neighbours, especially Iran.
However, despite this alliance, the UAE has long feared that Saudi Arabia, using its unequal size in terms of population, military strength and oil production capacity, would seek to maintain a hegemonic position in the Persian Gulf.
In 1981, the Persian Gulf countries seized the opportunity to create an alliance that excluded the then major regional powers. Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the UAE created the committee Cooperation for the Arab States of the Gulf (GCC). This committee had a joint military force that never grew to any significant size. The biggest test of the GCC's weakness and ineffectiveness was Iraq's invasion of Kuwait without civil service examination by the supranational body.
As result of the above, the UAE relied on the US for its protection, the only country with both the will and the capacity to carry out the task of defending the small state against potential foreign aggression.
The consequence at the regional level is marked by the convergence of interests of Saudi Arabia and the UAE which, between 2011 and 2019, have pursued common regional political objectives, relying if necessary on their military capabilities.
For example, Bahrain's request for financial aid to the GCC in 2011 when its rulers felt threatened by Shia protest movements. However, its most significant intervention was its support for the coup d'état in Egypt against President Mohamed Morsi and the Muslim Brotherhood in 2013.
India
Socio-political and economic relations between the GCC members and India have always been very close, and have been based on the understanding that a secure and stable political and social environment in the Persian Gulf and Indian subcontinent are critical factors for the respective countries' development and their trans-regional ties.
From India's perspective, the improvement of its technological and economic development goes hand in hand with New Delhi's ability to strengthen its partnerships around the world. In this regard, the Persian Gulf countries, and especially the UAE, are seen as a bridge to knowledge, capabilities, resources and markets to enhance that development.
In 2016, the hitherto bilateral relations between the two countries were formalised in a strategic cooperation agreement called CSP(Comprehensive Strategic Partnership).
For the UAE, India is a modern country, a political phenomenon independent of the West that maintains strong religious and traditional roots without renouncing its diversity. In some ways, and with some reservations, it is a mirror for the UAE.
The agreement cooperation is cross-cutting and covers issues as diverse as counter-terrorism, exchange information and intelligence, anti-money laundering measures, cyber-security, as well as cooperation on subject defence, financial aid humanitarian, etc.
On the more economic side, the initiative includes concrete actions to facilitate trade and investment, with the UAE committing goal $75 billion to support the development of new generation infrastructure in India, especially railways, ports, roads, airports and industrial parks.
With regard to the energy sector, the agreement envisages the UAE's participation in the modernisation of the oil sector in all its branches, taking into account the development of a strategic reservation .
The part dealing with the development of technology for the peaceful use of nuclear energy, as well as cooperation in the aerospace sector including the development and joint launching of satellites, as well as the necessary ground control infrastructure and all necessary applications, is very significant.
Today, India has growing and multifaceted socio-economic ties with both Israel and the Persian Gulf countries, especially the UAE. The diaspora of Indian workers in the Gulf accounts for annual remittances of nearly $50 billion. Trade relations bring in more than $150 billion to India's coffers, and almost two-thirds of India's hydrocarbon needs come from the region. It is therefore evident that the new status is viewed with special interest from this part of the world, assessing opportunities and possible threats.
Clearly, any such agreement that at least a priori brings more stability and a normalisation of relations will always be beneficial, but its weaknesses and the possible evolution of status must also be taken into account.
Thus, from a geopolitical point of view, India has welcomed the re-establishment of relations between the UAE and Israel, as both are strategic partners.
The new landscape that is opening up between Israel and the GCC seems to bring a moderate and consistent solution to the Palestinian problem closer, making it much easier for Indian diplomacy to work .
But one must be cautious, and especially in this part of the world nothing is of one colour. This hopeful agreement could have a perverse effect, further polarising the jihadist sectors of the Arab world and pitting them even more against each other.
The possibility of the Persian Gulf region becoming the new battleground where Iranian and Israeli proxies clash cannot be completely ruled out, especially in Shia-controlled areas. However, this is not a likely option for the time being.
But for India it is even more important to manage the economic implications of the new treaty. With defence and security cooperation as key pillars, both sides are now beginning to contemplate the real economic potential of complementing their economies.
Reactions to the treaty: scenarios
Faced with an event as important as the one described above, it is to be expected that there will be reactions in various directions, and depending on these, the evolution of status may be different.
Actors likely to play a role in the different scenarios include the UAE and the new alliance, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Turkey, Palestine and the Muslim Brotherhood.
It should not be forgotten that the background to this treaty is economic. subject If its development is successful, it will bring stability to a region that has long been punished by all kinds of conflicts and clashes, and will lead to an exponential increase in trade operations, technology transfer and the opening of new routes and cooperation, mainly with Southeast Asia.
The role of the US will be decisive in any of the scenarios that may arise, but in any of them its position will be to minimise physical presence and support the signatories of the treaty with political, economic and defence actions through the supply of military materiel.
The treaty has a strong economic component fixed on the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. This is but one more sign of how the world's geopolitical centre of gravity is shifting to the Asia-Pacific region and this is one of the main reasons for the US's unconditional support.
Members of the UAE government have traditionally viewed more radical Islamist ideologies and policies as an existential threat to the country's core values. Both the Shiite sectarian regime in Iran and the Sunni Muslim Brotherhood, group , are seen as a constant threat to the stability of the region's powers.
For the UAE these transnational movements are a catalyst for radicalism across the region.
In view of the above, the following scenarios are plausible:
Scenario 1
For the moment, the Palestinians are the ones whose interests have been most harmed by the new status . Prominent figures in Palestinian society, as well as senior officials of the Palestinian Authority, have considered the new treaty a betrayal. As mentioned, the Palestinian issue is taking a back seat in the Arab world.
If, as is predicted, more countries join the new treaty in the coming months, the Palestinian Authority may try by all means to bring its demands and struggle back to the forefront. To this end, it would count on the support of Iran and its proxies and Turkey. This status would begin by delegitimising the governments of the countries that have aligned themselves with the UAE and Israel through a strong information campaign at all levels, with massive use of social networks in order to mobilise the most sensitive and pro-Palestinian population. The goal would be promote demonstrations and/or revolts that would create doubts among those who have not yet joined the pact. These doubts could lead to a change of decision or delay in new accessions, or these new treaty candidates could increase the Palestinian-related conditions for joining the treaty. This option is likely to be the most dangerous because of the possibility of internal dissension or disputes that could lead to an implosion of the pact.
It can be considered a likely scenario of intensity average/leave.
Scenario 2
The position that Saudi Arabia takes is core topic. And it will be decisive in gauging Iran's reaction. In the Middle East ecosystem, Iran is the power that has the most to lose from this new alliance. The struggle for hegemony within the Muslim world cannot be forgotten. And this struggle, which is also a religious one, pitting Shiites against Sunnis, has Iran and Saudi Arabia as its main protagonists.
Saudi Arabia is likely to join the treaty, but given the status, and in an attempt not to further strain relations with its main enemy, it may decide not to join the treaty, but to support it from the outside with specific or bilateral agreements. This would always be done with the rest of the Arab member countries, which would act as a bridge for its relations with Israel. It would be a way to wash its face and avoid express recognition of the state of Israel or direct relations with it. It should be borne in mind that there are pockets of Shiite majority in the country that could be spurred on by Iran.
However, in a worst-case scenario, Iran will react through its proxies, stepping up its activity in Yemen, trying to promote protests and revolts inside Saudi Arabia, reinforcing its support for Hamas in Palestine and Hezbollah in Lebanon and even its militias in Iraq.
Support for the protests that have already taken place in Sudan will also be part of this campaign. Sudan is a very unstable country, with a very weak Structures of power that is unlikely to be able to quell high-intensity revolts.
The goal would be to inflame the region under the cover of support for the Palestinian people in order to dissuade further accessions to the treaty, as well as undermine the treaty's effectiveness, giving the image of instability and insecurity in the region. This will discourage potential investors from approaching the UAE, attracted by the enormous economic possibilities it offers, while keeping Saudi Arabia occupied with its southern flank and its internal problems. Some action without a clear or acknowledged perpetrator against vessels transiting the Gulf, as has already happened, or the boarding of one by Iranian forces under any subject accusation or legal ruse, cannot be ruled out. Direct actions involving Iranian forces are unlikely.
Turkey may become involved by providing weapons, technology and even mercenary fighters to any of the factions acting as Iran's proxy.
This scenario can be considered as possible and of intensity average
Scenario 3
Iran needs either the governments or the populations of the various Middle Eastern countries to continue to see Israel as its main enemy and threat. Among other reasons because it is a narrative for domestic consumption that it uses recurrently to divert the attention of its own population from other subject problems. So far, the unifying element of this view of Israel has been the Palestinian conflict. It is therefore likely that actions will be taken that provoke a reaction from Israel. These actions may come from within the state of Israel itself, from Palestinian or Lebanese territory, always at position from Iran's proxies. A provocation that would result in an Israeli attack on Arab territory, most likely against Iran or Syria, cannot be ruled out: result . The final goal would not be the Hebrew state but undermining the instructions of the treaty, creating social unrest among the signatories, preventing Saudi Arabia's accession and being able to use the Palestinian conflict in its own interests.
This is a possible, high-intensity scenario.
Conclusions
The UAE's emergence as an emerging geopolitical power in the Middle East has been as surprising as it has been precipitous, as not so long ago international observers did not give much hope for the life of the new federation of small states that had just come into being.
By contrast, the UAE and Abu Dhabi, its largest and most prosperous emirate, in particular, has been increasing its position over the last decade, playing a decisive role in the region. To such an extent that, to this day, the UAE's actions are seen as having facilitated to some extent the changes we are witnessing.
Western policymakers are generally dazzled by the UAE's perceived liberalism and the ability of its elites to speak both literally and figuratively their own language. It is important that they familiarise themselves with the UAE's model in all its aspects and, importantly core topic, that they understand that Abu Dhabi expects to be treated by all as an equal. Dealing with the UAE in this way and considering it a robust and reliable partner also means sending them the message of a clear intention to support them.
One of the major consequences of this agreement may be to de-escalate the Palestinian conflict, if not end it, then permanently limit it. For generations, this conflict has been used by political and religious leaders across the Arab and Muslim world to distract their attention from other issues. It was an easy and readily available resource . But it is now recognised that it is a territorial dispute between two peoples, and future negotiations have no choice but to go down that road, with the focus on the outdated Palestinian leadership.
There is the not inconsiderable possibility that the agreement agreement could have a domino effect, leading other states in the region to follow in the UAE's footsteps, which in some cases would only mean publicising the de facto relations they already have with the state of Israel. In this sense, talks between Oman's foreign minister and his Israeli counterpart are known to have taken place just after the signature treaty with the UAE was signed.
The Israeli prime minister also held a meeting meeting with Sudanese leader Abdel Fattah Burhan, which could be a sign of upcoming moves on that flank as well.
Although the leak had consequences for a senior Sudanese official, the government did not deny the contacts. And it has all been confirmed when the US, advertisement of Sudan's forthcoming removal from the list of countries sponsoring terrorism, has followed the agreement between Israel and Sudan to normalise diplomatic relations.
For years, US policy has been to demilitarise its position in the Middle East; the cost of its presence has been very high compared to the benefits it brings, as well as generating some animosity. Both the US and other G8 members support the UAE as the region's economic leader. This support provides them with the ideal position to deploy their economic interests in the region(commodities, research and development & investment).
This position of US/UAE support (plus some G8 countries), strengthens the Arab country's role in the region at subject political and by default military, and in a way allows its new allies and supporters to have some influence in organisations such as OPEC, GCC, Arab League) and in neighbouring countries, but from a more Arab and less Western position.
On the issue of the UAE's purchase of the F-35, it is undeniable that this issue makes Israel uncomfortable despite the change in relations. The main reason for this is the fear of an equalisation in military capabilities that could be dangerous. However, this will not be an obstacle to progress on future peace agreements and on development of this one. Such a major operation would take years to materialise and by then, relations between Jerusalem and Abu Dhabi will have been consolidated. Indeed, it might even be welcomed by Israel, as it would strengthen its military capabilities vis-à-vis its main opponents in the region.
It is increasingly apparent in the Arab world that Israel is too small to harbour imperialist aspirations, in contrast to countries such as Turkey and Iran, both of which formed former empires, and which seem intent on trying to restore what they once achieved or were.
Instead, Israel is increasingly seen as a strong, prosperous and dynamic enough country that cooperation with Jerusalem is a smart move that can provide benefits to both sides.
The agreement between Israel and the UAE may have been driven in part by their fear of Iran's advances and the danger it poses. But the benefits to them go far beyond that issue.
These extend to economic investment possibilities, finance, tourism and especially the sharing of know-how. The UAE can benefit from Israel's technological and scientific edge just as Israel can profit from the UAE's position as an international service centre and a key gateway to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. entrance .
In relation to the entrance gateway to the Indian subcontinent, it should be noted that for India the most important part of agreement is to manage the economic side of the synergies caused by it.
The UAE and Bahrain can become intermediaries for Israeli exports of both commodities and services to various parts of the world.
Israel has a strong defence, security and surveillance equipment industry. It is a leader in dryland farming, solar energy, horticulture, high-tech jewellery and pharmaceuticals.
Moreover, Israel has the capacity to provide highly skilled and semi-skilled labour to GCC countries, especially if they come from Sephardic and Mizrahi ethnic groups, many of whom speak Arabic. Even Israeli Arabs can find opportunities to help further build ties and bridges across the cultural divide.
Israel's incursion into the Gulf has the potential to influence the political-economic architecture that India has been building for years, being, for example, one of the largest suppliers of labour, foodstuffs, pharmaceuticals etc.
The largest customers in Dubai's real estate market, as well as the largest issue of tourists visiting the country, come from India. But in this changing scenario there is scope for three-way synergies, making India a major player in this.
The final conclusion that can be drawn by way of evaluation for the future is that this new relationship will undoubtedly be a model for other Sunni states to follow, transforming a region mired in 19th century conflicts into one of the power centres of the 21st century.
* Lieutenant Colonel of Infantry. Geopolitical Analyst
REFERENCES
Acharya, Arabinda, 'COVID-19: A Testing Time for UAE-India Relations? A Perspective from Abu Dhabi", Strategic Analysis, September 2020.
Arab Center for Research and Policy studies, 'The Abraham Agreement: normalization of relations or announcement of an existing Emirati - Israeli alliance? Qatar, August 2020.
Karsh, Ephraim, ed., "The Israel-UAE Peace: A Preliminary Assessment", Ramat Gan: The Begin-Sadat Center for Strategic Studies, cafeteria-Ilan University, September 2020.
Salisbury, Peter, "Risk Perception and Appetite in UAE Foreign and National Security Policy", The Royal Institute of International Affairs, Chatham House Middle East and North Africa Programme, London: July 2020.
Steinber, Guido, "Regional Powers, United Arab Emirates", German Institute for International and Security Affairs, Berlin, July 2020.
The Trump Administration concludes its management in an assertive manner in the region and passes the baton to the Biden Administration, which seems to be committed to multilateralism and cooperation.
With the world at a standstill due to Covid-19, the Asian giant has taken the opportunity to resume a whole series of operations with the aim of expanding its control over the territories around its coastline, goal . Such activities have not left the United States indifferent, and despite its internal status complex, it has taken matters into its own hands. With Mike Pompeo's visits throughout the Asia-Pacific, the US has stepped up the process of containing Beijing, which has taken the form of a quadruple alliance between the United States, Japan, India and Australia. The new executive that the White House will inaugurate in January may involve a renewal of US action that, without breaking with the Trump Administration, recovers the spirit of the Obama Administration, that is, guided by greater cooperation with the countries of the Asia-Pacific and a commitment to dialogue.
![Airstrip installed by China on Thitu or Pagasa Island, the second largest of the Spratlys, whose administration has been internationally recognised for the Philippines [Eugenio Bito-ononon Jr]. Airstrip installed by China on Thitu or Pagasa Island, the second largest of the Spratlys, whose administration has been internationally recognised for the Philippines [Eugenio Bito-ononon Jr].](/documents/16800098/0/mar-china-blog.jpg/221fc42a-0d93-e77e-fb3e-4aac0a9ecef0?t=1621874942557&imagePreview=1)
Airstrip installed by China on Thitu or Pagasa Island, the second largest of the Spratlys, whose administration has been internationally recognised for the Philippines [Eugenio Bito-ononon Jr].
article / Ramón Barba
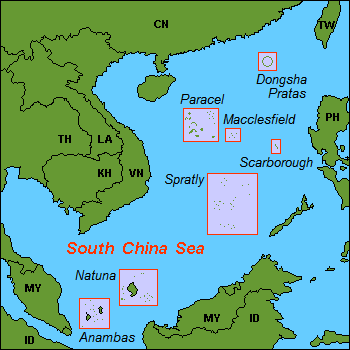
During the pandemic, Beijing has taken the opportunity to resume its actions in Asia Pacific waters. In mid-April, China proceeded to designate land in the Spratly Islands, the Paracel Archipelago and Macclesfield Bank as new districts of the city of Sansha, a town on China's Hainan Island. This designation management assistant caused subsequent protests from the Philippines and Vietnam, who claim sovereignty over these areas. Beijing's attitude has been accompanied by incursions and sabotage of ships in the area. See the sinking of a Vietnamese fishing boat, which China denies, arguing that it had suffered an accident and was carrying out illegal activities.
China's actions since the summer have been increasing instability in the region through military exercises near Taiwan or confrontations with India due to its border problems; on the other hand, in addition to the Philippine and Vietnamese civil service examination towards Chinese movements, there is growing tension with Australia after the latter requested an investigation into the origin of the COVID-19, and the increase in maritime tensions with Japan. All this has led to a response from the United States, which claims to be a defender of free navigation in the Asia-Pacific, justifying its military presence by emphasising that the People's Republic of China is not in favour of free transit, democracy or the rule of law.
US makes a move
Tensions between China and the US over the current dispute have been on the rise throughout the summer, with both increasing their military presence in the region (Washington has also sanctioned 24 Chinese companies that have helped militarise area). All of this has recently been reflected in Secretary of State Mike Pompeo's visits to the Asia-Pacific in October. Prior to this round of visits, he had made statements in September at the ASEAN Virtual Summit urging countries in the region to limit their relations with China.
The dispute over these waters affects Vietnam, the Philippines, Taiwan, Brunei and Malaysia, countries which, along with India and Japan, were visited by Pompeo (among others) in order to ensure greater control over Beijing's actions. During his tour, the US Secretary of State met with the foreign ministers of India, Australia and Japan to join forces against the Asian giant. Washington then signed in New Delhi a military agreement of exchange of data satellites to better track Chinese movements in the area, and made a state visit to Indonesia visit . It should be recalled that Jakarta had so far been characterised by a growing friendship with Beijing and a worsening relationship with the US over a decrease in Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) aid. However, during Pompeo's visit , the two countries agreed to improve their relations through greater cooperation in regional, military procurement, intelligence, joint training and maritime security.
This move by Washington has therefore implied:
-
The consolidation of a quadruple alliance between India, Japan, Australia and the United States, which materialised in joint military exercises in the Bay of Bengal in early November. It is worth recalling that this is in addition to Washington's traditional allies in the region (the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand). In addition, the possibility of closer ties with Vietnam remains open.
-
The expansion of its military presence in the area, increasing the flow of materiel sold to Taiwan, also highlighting the visits of high-level Washington officials throughout July and the following months.
-
Return of the destroyer USS Barry to the waters of the South China Sea with the goal to serve as a symbol of civil service examination to Chinese action, and as a defender of freedom of navigation, peace and stability.
-
Indonesia will move its Naval Combat Force (permanently based in Jakarta) to Natuna, islands bordering the resource-rich South China Sea that are disputed between the two countries.
-
ASEAN takes a stand for peace and stability and in favour of UNCLOS 1982 (which sets out the governing legal framework for the law of the sea framework ) at the summit held in Vietnam on 12-15 November.
 The ratio decidendi behind the Chinese performance
The ratio decidendi behind the Chinese performance
As a first approach to the ratio decidendi behind China's actions, it is worth recalling that since 2012, taking advantage of regional instability, the Asian giant has been citing its historical right over the South Sea territories to justify its actions, arguments that were rejected in 2016 by the Permanent Court of Arbitration in The Hague. Based on the argument that Chinese fishermen once frequented the area, it claimed to justify the appropriation of more than 80 per cent of the territory, which has since pitted Beijing against Manila.
On the other hand, Luis Lalinde, in his article China and the importance of dominating the Surrounding Sea (2017) gives a more complete view of the matter, alluding not only to historical reasons, but also to economic and geopolitical reasons. First, more than half of China's hydrocarbon supply transits the Asia-Pacific region, which is also the world's main economic hub. In addition, Beijing has been deeply affected by the "century of humiliations", characterised by a lack of Chinese control over its territory due to maritime invasions. Finally, the dominion of the seas, together with the already achieved continental weight, are vital for China's hegemonic projection in a area of ever-increasing economic weight at the global level. This is why the so-called "string of pearls" has been established for the defence of strategic, security and energy supply interests from the Persian Gulf to the South Sea.
Lalinde's arguments justify China's actions in recent years; however, Bishop (2020), in the Council on Foreign Relations, states that the reason behind China's recent attitude is due to issues of internal instability, while a small sector of the Chinese intelligentsia is critical and distrustful of Xi's leadership, sample . They argue that the pandemic has weakened the Economics and the Chinese government so that through foreign policy actions it must appear strong and vigorous. Finally, the importance of control of the seas in relation to the Silk Road project should be borne in mind. On the maritime side, China is investing heavily in Indian and Pacific ports, which it does not rule out using for military purposes (see ports in Sri Lanka, Myanmar and Pakistan). Among the main opponents of this alliance are the United States, Japan and India, also opposed to China's belligerent attitude, as we have seen.
Biden era: opportunities in a complicated scenario
Joe Biden's presidency will be marked by major challenges, both internal and external. We are facing a United States marked by a health crisis, with an increasingly polarised society and with a Economics whose recovery, despite the measures adopted, raises doubts as to whether it will be a "V" or a "W". Moreover, relations with Latin America and Europe have been deteriorating as a result of the measures taken by President Trump.
The relationship between China and the US has fluctuated in recent years. The Obama Administration, aware of the growing importance of the Asia-Pacific region, coupled with the opportunity that the Silk Road presents for Beijing to expand its economic and military dominance, introduced its Pivot to Asia policy in its second term, beginning to fund and provide aid to countries in the region. During the years of the Trump Administration, the relationship with Beijing has deteriorated considerably, putting Biden in a scenario in which he will have to face a trade war, the technological degree program battle for 5G, as well as regional security and human rights issues.
The countries of the region are demanding an effective response from the US giant to contain China in which Washington's promise of a free and open shipping zone is realised. However, the US has to be cautious, as with the exception of Vietnam, the Philippines, and to some extent Indonesia and Singapore, the other countries in the region do not feel an urgent need for US intervention. However, with the exception of Cambodia, the rest of the countries do not approve of the possibility of Chinese hegemony either.
In general, experts suggest that in the midst of this storm, the new US president will adopt a cautious but continuist attitude. Probably, in line with the Obama Administration, he will tend towards a commitment to multilateralism, economic alliances subject and regional integration without exercising an authoritarian attitude, reducing the aggressiveness of the Trump Administration, but being firm in his stance. This implies looking for different areas in which to cooperate, such as climate change, the reduction of Freedom of Navigation Missions, or the increase of Capacity Building.
A look into the near future
We will have to keep a close eye on the Trump administration's latest developments in relation to this conflict, as well as the measures that Biden adopts during his first months in office. However, everything suggests that, in this increasingly tense status , Washington will adopt a cautious stance. As we have seen, Pompeo's trips have served the US to reaffirm its presence in the region, assuming a leadership role and providing the response that some countries, such as the Philippines, desire. However, although, as has been said, we will have to keep an eye on the coming months, with instructions already established, it is most likely that Biden will continue the Trump Administration's line, but with a focus on regional integration, multilateralism, diplomacy and economic cooperation in order to win new support, strengthen its alliances and contain Beijing, thus justifying its presence in the region as the only power capable of bringing together regional forces to prevent a feared Chinese hegemony.
The EPP, the Paraguayan guerrilla group that grew out of political carelessness
The Paraguayan People's Army, which emerged in 2008, has created a conflict that has already claimed around 100 lives.
The Paraguayan People's Army, which emerged in 2008, has created a conflict that has already claimed around 100 lives.
Marxist guerrillas in Latin America are a thing of the past. This conviction led to an underestimation of the emergence in 2008 of the Paraguayan People's Army (EPP), which since then has carried out a hundred violent actions, especially in rural areas of the northeast of the country. The conflict has claimed a hundred dead and wounded; there have also been kidnappings of public figures, which have given the EPP special media coverage. The creation of a controversial special military-police corps has failed to achieve the goal goal of putting an end to the group, leading to criticism of the government's management of the problem.
article / Eduardo Villa Corta
The Paraguayan People's Army (EPP) was considered from the outset to be a small group of radicals who would have little to do. However, in barely ten years it has become an organisation capable of confronting the Paraguayan state: it has carried out a hundred terrorist actions, including a dozen kidnappings, causing some sixty deaths and a hundred wounded.
![EPP zones of influence (light red) and places where there has been instructions of group (dark red) [Mikelelgediento] [Mikelelgediento].](/documents/portlet_file_entry/16800098/epp-paraguay-mapa.png/604d99a8-454a-4a1c-3e01-b6bd6a1a799c?imagePreview=1)
EPP zones of influence (light red) and places where there has been instructions of group (dark red) [Mikelelgediento] [Mikelelgediento].
With a issue of activists ranging from thirty in its hard core to two hundred if its support networks are taken into account, the EPP has been a problem for the government for several years, which has been unable to dismantle it: 30 militants have died in confrontations with the forces of law and order and a hundred have been arrested, but the image offered by the authorities is one of ineffectiveness. The Paraguayan government's negative credit also includes the fact that it did not take seriously the threat posed by the creation of group and its first actions.
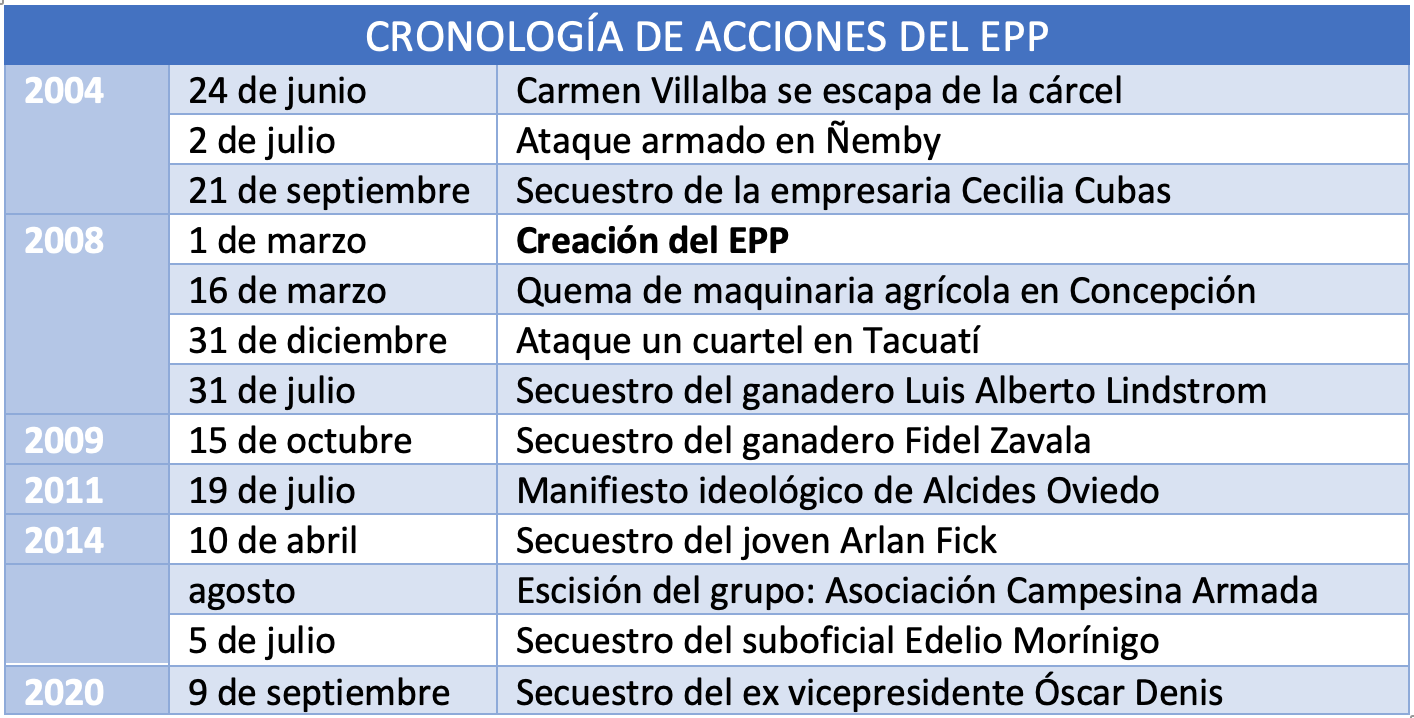
The EPP was officially formed on 1 March 2008. Although its founders and main leaders had already planned the creation of group prior to this date, its roots go back to 1992 and the Free Fatherland Party, as documented by researcher Jeremy McDermott. The EPP presents itself as an armed group against the "bourgeois liberal" parliamentary system, but above all it is a Marxist movement that promotes the uprising of Paraguay's peasantry, hence its attempts to take root in the rural north-east of the country.
The 2008 presidential victory of Fernando Lugo at the head of a left-wing alliance, ending six decades of political dominance by the Colorado Party, may have encouraged the formation of the EPP, which then felt justified in its actions with Lugo's removal in 2012 through a controversial impeachment trial in parliament that was labelled by Lugo's supporters as a coup d'état.
The first EPP attack, on 16 March 2008, consisted of the burning of agricultural machinery at department de Concepción. The next was in December of the same year, with an attack on a barracks in Tacuatí, in the department of San Pedro. Since then, their movements have focused especially between the south of the first of these Departments and the north of the second.
Despite being a more or less delimited area, dismantling the EPP is not easy because the EPP's modus operandi makes its movements unpredictable. This is because, as McDermott explains, group does not act like other insurgent organisations, such as the FARC. The core of the EPP is made up of around thirty fighters full-time, most of whom have family ties. They are led by the ringleaders Alcides Oviedo and his wife Carmen Villalba, who are in prison; one of the leaders on the ground is Oswaldo Villalba. In addition, there are some fifty activists part-time, a logistical network that could number up to two hundred people and local sympathisers who, without being very involved in the cause, provide information on search operations by the security forces. The group suffered in 2014 the split of one of its columns, which was renamed association Campesina Armada (ACA) and in 2018, from agreement with the authorities, the EPP split into two groups to face pressure from the security forces.
The aforementioned figures speak of a small group , far from the 8,000 members that the FARC had in 2016 at the time of its demobilisation, or the 4,000 members that the ELN currently has in Colombia, or the 3,000 that were attributed to the Chilean Frente Patriótico Manuel Rodríguez. group Although the EPP bears more resemblance to the latter, its operational cessation in 1999 left the FARC as the main training ground for those who would later create the EPP, as evidenced by the documentation found in the computer of FARC leader Raúl Reyes and the kidnapping of businesswoman Cecilia Cubas, daughter of a former Paraguayan president, at the end of 2004.
This action marked what has been a line of action of the EPP. Since 2008, in addition to extortion and assaults in order to finance itself, the group has carried out kidnappings in order to achieve greater media impact. order These have been carried out against relatives of former presidents of the country or high-level political figures profile , for whose release ransoms in excess of five million dollars have been paid, although lower figures have been agreed in negotiations. It is usually agreed that submit part of the money will be in cash and part in foodstuffs for the villages around the EPP's area of operations.
The group has also carried out extortions and assaults in those areas where it operates, demanding "revolutionary taxes" from landowners and cattle ranchers, from whom they also steal cattle and food to meet the organisation's daily sustenance needs.
Other notable actions carried out by the EPP are bomb attacks. For example, there was an attack against the Supreme Court of Justice in Asunción at the beginning of the operations of group. A more recent attack was perpetrated on 27 August 2016 against a military vehicle in the eastern area of Concepción: the explosives went off as the convoy passed by and then the terrorists liquidated the survivors with firearms; eight soldiers were killed in the attack. According to the authorities, this event marked a leap in the EPP's operations, from a group seeking economic resources to an organisation with greater operational and military capacity.
To confront the EPP, President Horacio Cartes created the Joint Task Force (FTC) in 2013 in response to evidence that police action was not effective, in part because of possible internal corruption. The JTF is composed of members of the Armed Forces, the National Police and the National Anti-Drugs administrative office , under the command of a military officer and reporting directly to the president. The more expeditious nature of this unit has generated some controversy in the social and political discussion .
The EPP's most recent operation was the kidnapping of former Paraguayan vice-president Óscar Denis on 9 September 2020. For the release of Denis, leader of the Authentic Radical Liberal Party and active participant in Lugo's impeachment, the terrorists demand the release of their leaders, Alcides Oviedo and Carmen Villalba, as well as the submission of food for the rural areas where they operate. The organisation's deadline expired a few days later without the government heeding their request. There have been citizen mobilisations demanding Denis' release and the status is being followed in the country with concern, putting President Mario Abdo Benítez in a tight spot.
[Francisco Cancio, Enmienda: una revisión de la causa y el actuar argentino en la Guerra de las Malvinas (Náutica Robinsón: Madrid, 2020), 406 pages].
review / Ignacio Cristóbal
 This is an excellent book that analyses some of the controversial issues of the Falklands War (1982). The author, Francisco Cancio, is an expert on the subject and has made a conscientious search for information over the years during his visits to Argentina and the UK.
This is an excellent book that analyses some of the controversial issues of the Falklands War (1982). The author, Francisco Cancio, is an expert on the subject and has made a conscientious search for information over the years during his visits to Argentina and the UK.
This is not a book on the history of the Falklands War; there are other manuals that explain it very well, but here the author has tried to do something else. Whoever opens the book should either have some knowledge of what happened in the South Atlantic, or else acquire it before delving into its pages.
In my case, it was not difficult to get "hooked" by reading the book. From the data the author gives, he had similar experiences to mine. I, too, watched the news in the spring of 1982 sitting next to my father, a military man; for our generation it was our first war. And like him, who on his trips to the UK, I imagine to practise his English language , used to dive into British bookshops in search of documentation, I too found out about the Falklands when I was there perfecting my English, going to museums and bookshops and the barracks in Colchester, the town where I spent two summers, to talk to veterans of the conflict. You will be forgiven, therefore, for this involvement staff, for letting my sympathy for the Argentine side go somewhat, while admiring the professionalism shown by the British troops.
The Falklands War was a full-scale war from a military point of view. There were air and naval engagements; submarine and satellite intervention; landing and ground operations by special operations units, as well as unit actions at battalion level. It is very welcome that the first chapter, graduate "Genesis", while introducing the conflict begins to "prick balloons" about the real reason for going to war.
And the chapters go on to deal with issues such as the "Super Etendart and the Exocet", where we imagine the Argentine naval pilots training in Brittany, France, and leaving the flag flying high, as it should have been. Interest is heightened when the author delves into the intelligence operations to "arm", without an "instruction book", the missiles that were already in Argentina. The French government played a complicated role in the conflict, but the diplomatic (it was a member of NATO) took precedence over the commercial. It was the French technicians who were sent to Argentina who did the "do de pecho" by siding with Argentina and juggling to avoid creating more problems in the international balance.
The chapter on land operations is excellent and makes a strong case for the Argentine forces who had to contend with the enemy and the lack of logistical support from the mainland. In those days there was a discussion in public opinion about the dichotomy of "conscript army" versus "professional army". The chapter makes clear the damage the Argentines inflicted on the reconquistadors, but also their adverse status : the lack of basic means for resistance, counterattack and, why not say it, hunger and cold.
The naval part is dealt with in two interesting chapters that tell the story of the submarine "San Luis", which was bothering the British fleet throughout the war. If there had been no war, this submarine would have stayed in port. This is the standard of those brave submariners. The other chapter is about the failed meeting, due to lack of wind, of the two fleets. It is possibly one of the most critical moments of the battle. Had there been wind, the Argentinean Navy's A-4 Skyhawks could have driven the British fleet back to their home ports.
A separate chapter is "La guerra en los cielos" (The war in the skies), which covers some of the most courageous operations of the Argentinean pilots in those days. The author puts us in the cockpits of the fighter planes whose images still make our hair stand on end. Without wanting to give anything away to the reader, the interview with the former head of the Argentine Air Force in those days is for me the best part of the book. It should not be forgotten that he was a member of the military board and the data he reveals about the "Russianfinancial aid " are very interesting and unknown.
And finally, the long-awaited chapter "The Attack on the Invincible", which deals with probably the most compromising wartime action of the entire war. The author scrupulously analyses the operation to attack one of the two British aircraft carriers, the Invincible, with a clarity that makes it clear that something happened.
"Amendment" is therefore a highly recommendable book for those who already have some knowledge of the Falklands War knowledge , but at the same time it can also arouse the curiosity of others who, without being initiated in this conflict, can help themselves in their reading by consulting basic information available on the internet. It was a unique contest, in which a country in the southern part of the world put the second NATO power in check, aided by the first and a neighbouring country. As Admiral Woodward, commander of the British fleet, said in his memoirs, "people don't know how close Britain came to losing the war". A fine final epitaph from a military professional who surely recognised the professionalism, courage and bravery of the enemy.
* Expert in military affairs
[Iván Garzón, Rebeldes, Románticos y Profetas. La responsabilidad de sacerdotes, políticos e intelectuales en el conflicto armado colombiano ( Bogotá: Ariel, 2020) 330 pp].
review / Paola Rosenberg
 The book "Rebeldes, románticos y profetas" written by Iván Garzón sample the role played by priests, politicians and intellectuals in the internal armed conflict in Colombia and the responsibility they had in it. A war that marked the country politically, economically, socially and ideologically. Revolutionary movements in Latin America were characterised by the use of violence and the employment use of arms to come to power; more or less strong depending on the country, guerrilla groups had a great influence on the course of events in the region during the second half of the 20th century. The essay by Garzón, professor of Political Theory at the Universidad de La Sabana, focuses especially on the role of the Catholic Church in the different movements and on the contradictory ideas and actions that sustained the conflict over time [this is how he sums up his purpose in this article video].
The book "Rebeldes, románticos y profetas" written by Iván Garzón sample the role played by priests, politicians and intellectuals in the internal armed conflict in Colombia and the responsibility they had in it. A war that marked the country politically, economically, socially and ideologically. Revolutionary movements in Latin America were characterised by the use of violence and the employment use of arms to come to power; more or less strong depending on the country, guerrilla groups had a great influence on the course of events in the region during the second half of the 20th century. The essay by Garzón, professor of Political Theory at the Universidad de La Sabana, focuses especially on the role of the Catholic Church in the different movements and on the contradictory ideas and actions that sustained the conflict over time [this is how he sums up his purpose in this article video].
"Rebels, Romantics and Prophets" questions and criticises the responsibility of these groups for the resource of violence and the use of arms to achieve social change in Colombia. Iván Garzón challenges the participants of the armed conflict in Colombia to reflect on their role in the conflict and to assume their responsibility to build a better society. In addition, the book aims to open a discussion on the past, present and future of the role and influence of the Catholic Church and intellectuals in society.
The revolutionary waves in Latin America in those years were strengthened by the Marxist ideas of the time. Those ideas defended that the economic development of the Third World countries was not possible without a break-up of the capitalist market; due to social inequality and class struggle. Therefore, the use of violence had to be advocated in order to come to power. After the triumph of the Cuban revolution in 1959, guerrilla ideas spread rapidly throughout Latin America. Cuba proved that revolution was possible: through armed struggle and Marxist ideas a social development could be achieved. This is how strong revolutionary movements began to emerge in these countries. Colombia was definitely no exception.
One of the young and main protagonists mentioned in the book is Camilo Torres, who was swept up in the revolutionary waves in Colombia. Also known as "the guerrilla priest" or the "Che Guevara of the Christians", Torres was a very influential leader in Colombia in the second half of the 20th century. A guerrilla priest, a hero to some, but a villain to others. Aged just 37, he died in a troop clash on 15 February 1966, a year after joining the National Liberation Army (ELN) guerrillas. Willing to sacrifice his life and take up arms for his country and social change, Torres asserted that revolution was inevitable and had to be contributed to. Different intellectuals assess his figure in the book: some criticise the priest for his "failure" and his incorrect decision to take up arms, others justify him by pointing out that he submitted to a "just war".
Camilo Torres represents the group of the rebels, whom the author describes as the "warriors of a failed revolution". They used arms out of an often religious commitment. They justified violence and saw it as a representation of honour, bravery and submission. The rebels decided to take up arms, go out into the bush and join the guerrilla in order to make the Christian faith effective and help the poor. Many of these rebels like Torres focused on Christianity's primary mandate to love one's neighbour. They felt an obligation to help bring about radical change in the political, economic and social Structures of the country. They wanted a more just society and sacrificed their lives to achieve it, no matter what the means. Many came to the conclusion that the only way to achieve this change was through violent struggle. Their actions sample how the dominant ideas of the time justified the use of violence, going against purely Christian ideas.
In the conflict there was also the group of the "romantics", those who approved of the cause, respected it, but did not get their hands dirty. They were priests, politicians and intellectuals who intervened in the moral and intellectual discussion to justify the reasons for the revolution. They were the passionate ones, the minds behind the acts that directly influenced the warriors who went into the bush to fight.
Finally, there were the "prophets": the priests, politicians and intellectuals who were completely opposed to armed struggle and the use of violence to bring about change in society. The prophets refused to make a pact with the devil and betray the moral values of the Church. They believed that there were other means to achieve social justice; peaceful and bloodless means. In the end, these were the ones who were right; it was a futile, costly and unwinnable struggle.
In conclusion, both the rebels and the Romantics found in their moral and political visions a full justification for the use of violence. The prophets never approved of this cause, but criticised it by emphasising its secularised and contradictory character. Iván Garzón aims to open a discussion on the legitimacy or illegitimacy of the use of violence as a political means to achieve justice.
Today, the word revolution is still linked to violence because of the many traumatic conflicts experienced by many Latin American nations. In Colombia, as in many other countries, the revolutionaries won ideologically, but not in practice. For this reason, it can be concluded that in general, violent internal conflicts only lead to the destabilisation of countries and the loss of innocent lives. The book attempts to make religious and intellectual participants in armed conflict reflect on their responsibility or guilt in the armed conflict. This discussion between criticism or justification of the armed struggle is still necessary today because of the constant threat to democratic institutions in Latin America.
The deterioration of the small Mediterranean country's status benefits Hezbollah and its patron saint, Iran.
With four different prime ministers so far this year, it is difficult to escape the vicious circle in which Lebanon finds itself, so that the continuity of the current political system and the severe financial crisis seem inevitable. From this perpetuation emerge some possibilities, almost all of them bleak, for Lebanon's future. Here are some of these scenarios.
![State of the port of Beirut after the explosion of 4 August 2020 [Mehr News Agency/Wikipedia]. State of the port of Beirut after the explosion of 4 August 2020 [Mehr News Agency/Wikipedia].](/documents/16800098/0/libano-futuro-blog.jpg/ed561a7d-5d73-93fa-3cbe-2afacd099fac?t=1621884521341&imagePreview=1)
State of the port of Beirut after the explosion on 4 August 2020 [Mehr News Agency/Wikipedia].
article / Salvador Sánchez Tapia
To say that the Lebanese political system is dysfunctional is nothing new. development Based on a sectarian balance of power established in 1989 after a long civil war, it perpetuates the existence of clientelistic networks, encourages corruption, hampers the country's economic development and hinders the creation of a transversal Lebanese national identity that transcends religious confessions.
For some time now, Lebanon has been immersed in an economic and social crisis of such magnitude that many analysts are wondering whether we are facing a new case of state failure. In October 2019, the country was rocked by a wave of demonstrations that the government itself considered unprecedented, triggered by the executive's advertisement attempt to tackle the serious economic crisis with several unpopular measures, including a tax on the use of the popular Whatsapp application. The protests, initially focused on this issue, soon incorporated complaints against rampant corruption, the uncontrolled increase in the cost of living, and the lack of employment and opportunities in the country.
Popular pressure forced the resignation of the unity government led by Saad Hariri later that month. The government was replaced in January 2020 by a more technical profile government led by former Education minister Hassan Diab. The new government had little room for reform before the coronavirus pandemic was declared, and soon found itself beset by the same street pressure that had toppled the previous government, with demonstrations continuing despite the restrictions imposed by the pandemic.
The devastating explosion in early August 2020 in the port of Beirut only further plunged the country into the downward spiral in which it was already mired. Despite voices that tried to see the hand of Israel or Hezbollah behind the catastrophe that took the lives of 163 people, the Lebanese population soon realised that this was merely the logical consequence of years of corruption, bureaucratic sloppiness and withdrawal of the national infrastructure. Again there was a crescendo of popular outrage; again the government was forced to resign at plenary session of the Executive Council.
With echoes of the explosion still lingering, at the end of August Mustafa Adib, Lebanon's former ambassador to Germany, was tasked by President Aoun to form a government. Unable to complete the arduous task, not least because of Hezbollah's insistence on controlling the Finance Ministry, Adib resigned on 26 September, leaving the country on the brink of the precipice it still finds itself on.
It is difficult to predict Lebanon's future, beyond predicting that it looks bleak, as a complex dynamic of internal and external forces grips the country. Despite the pressure, at least from urbanised and cosmopolitan Beirut, to end it, it is enormously complex to untangle the tangled web of clientelistic networks that have controlled the country since independence, not only because of the benefits it has generated for a small privileged group , but also because many fear the alternatives to a model that, for all its faults, has avoided a repeat of the savage civil war that took place between 1975 and 1990.
Its geographic status makes it difficult for Lebanon to escape the general climate of instability in the Middle East and the influence exerted on the country by regional and international actors such as Israel, Iran, Syria and France, especially considering that the problems of the Levant are so deep and its national leadership so weak that it does not seem to be able to overcome them on its own.
Lebanon's plight is that its own sectarian division makes it difficult for nations to emerge that are willing to donate on a cross-cutting basis to help bridge the divide that divides the country internally, and that the financial aid it may receive from actors such as Iran or Saudi Arabia only reinforces it. The efforts of French President Emmanuel Macron, self-appointed as the driving force behind Lebanese reconstruction, do not seem, for the moment, to be gaining momentum. At the donors' lecture he convened on 9 July with fifteen heads of state, he secured contributions worth $250 million to revitalise Lebanon's moribund Economics . Meanwhile, Beirut's mayor estimates the reconstruction costs of the August explosion in the capital's port at between $3 billion and $5 billion.
As a mirror image of this difficulty, Lebanese communities, comfortably ensconced in the status quo, reject an undoubtedly necessary financial aid if they feel it might be detrimental to their respective power instructions . Hezbollah, for example, does not accept IMF programmes, complicating the achievement of the necessary national consensus that would facilitate IMF support. It is difficult to escape this vicious circle, so that the continuation of the current political system, and with it the continuation of Lebanon's severe financial crisis, seems inevitable. From this perpetuation come some possibilities, almost all of them bleak, for the Lebanese future. The first is that Lebanon will continue to slide down the inclined plane that is turning it into a failed state, and that this condition will eventually lead to a civil war precipitated by events similar to those that occurred during the Arab Spring in other states in the region. Such an eventuality would resurrect the ghosts of the past, produce regional instability that is difficult to measure but which would undoubtedly provoke intervention by regional and international actors, and could ultimately dismember the country, result which would only sow the seeds of further instability throughout the region.
Without going to that extreme, the internal turmoil could break the precarious balance of power on which Lebanese political life is based, to the benefit of one of its sectarian groups. Hezbollah, the undisputed leader of the country's Shia faction, appears here as the most organised and strongest group within the country and, therefore, as the one that stands to gain the most from this breakdown. It should be borne in mind that, in addition to the support of internship all 27 percent of Lebanese Shiites, the militia organisation is viewed favourably by many members of the divided Christian community - some 45 percent of the country's population - who put their desire for an internal Security Service in the country before other considerations. Aware of this, Hezbollah's leader Hasan Nasrallah is sample moderate in his proposals, seeing the Sunni community, supported by Saudi Arabia, as his real rival, and seeking to broaden his power base.
Iran would undoubtedly be the real winner in this scenario, as it seems unrealistic to think of a Hezbollah that, once it has come of age, would have a life of its own outside the ayatollahs' regime. With this new piece, Tehran would complete the Shia arc that connects Iran with Iraq and, through Syria, with the Eastern Mediterranean. The destabilising effects of such a move status, however, cannot be underestimated if one considers that the mere possibility of the Islamic Republic of Iran taking full control of Lebanon constitutes a casus belli for Israel.
In a positive grade , the serious crisis the country is going through and the strong popular pressure, at least in urban areas, may, paradoxically, be a spur to overcome the sectarian system that has contributed so much to generate this status. However, such a transition only stands a chance of progress - however tenuous - with strong external wholesale support.
In this scenario, the role of the international community should not be limited to providing economic resources to prevent the country's collapse. Its involvement must favour the development and sustain civic-political movements with an intersecting base that are capable of replacing those who perpetuate the current system. To this end, in turn, it is imperative that contributing nations lend their financial aid vision, renouncing any attempt to shape a Lebanon to suit their respective national interests, and forcing the elites who control the factions to abdicate the status quo in favour of a true Lebanese identity. The obvious question is: is there any real chance of this happening? The reality, unfortunately, does not allow for much hope.
Ankara is implementing a strategic plan for the control of the three maritime zones surrounding the country.
![Parade of members of the Turkish Naval Force [Nérostrateur]. Parade of members of the Turkish Naval Force [Nérostrateur].](/documents/16800098/0/patria-azul-blog.jpg/5937153d-b304-227a-960f-0e5d972800a4?t=1621884766294&imagePreview=1)
▲ Parade of members of the Turkish Naval Force [Nérostrateur].
ANALYSIS / Lucas Martín*.
Several recent Turkish actions indicate the implementation of the so-called "Blue Homeland" doctrine.
Among the various facts to be taken into account we can take as an initial element the agreement signed with one of the two contenders for power in Libya, the GNA to be more precise.
Through it, the GNA de facto handed over control of Libyan territorial waters to Turkey while establishing a maritime corridor for Ankara in the eastern Mediterranean Sea.
The importance of having de facto control of these waters is not only the enormous volume of maritime traffic that passes through them, but also the fact that they contain strategic natural gas reserves and are also a transit area for several gas pipelines supplying Europe.
If we add this treaty to Turkey's movements in the Mediterranean, the Aegean, as well as its involvement in the conflicts in Syria and Libya, we see that they are but different but complementary parts of an ambitious plan that Ankara has been carefully plotting for several years to gain maritime control of the Eastern Mediterranean and adjacent areas. The ultimate goal of this plan is to give Turkey economic and energy independence that will ensure the country's growth in all areas.
"Mavi Vatam" - Blue Homeland
The so-called "Gerasimov Doctrine", which theorises the evolution of military conflicts and provides guidelines for action in today's framework , is well known. But it is much less well known that a country like Turkey developed its own doctrine almost two decades ago in an attempt to outline the geostrategic moves needed to achieve basic objectives for the Turkish nation's development and achieve its leading role in the international concert.
The father of this plan is Admiral Cem Gurdeniz, and it was first presented in 2006 under the name "Blue Homeland Doctrine".
The Admiral bases his theory on three pillars, which would take too long to discuss in detail. However, it is interesting to dwell at least briefly on the second pillar. Under this, Gurdeniz defines what he considers to be the areas of maritime jurisdiction that belong to Turkey and that he values as vital for its survival and development. These encompass areas of the Black Sea, the Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. By defining these he establishes territorial waters, the continental shelf and the exclusive economic zone (EEZ).
agreement The admiral himself acknowledges that the problem is far from being in the Black Sea, where an agreement was reached with the former Soviet Union to establish the limits of the continental shelf in 1978 and later, in 1987, the EEZ. Moreover, after the demise of the USSR, agreements were reached with Georgia, Bulgaria and Ukraine.
The issue is centred on the Mediterranean and the Aegean. Precisely the current epicentre of events.
The current established limits, EEZ agreements, etc., have been imposed on Turkey by the EU, according to our protagonist, who considers them particularly burdensome with regard to the Greek zone and Cyprus. Turkey places the onus on the EU to prevent Turkey's development to some extent, which is interesting when Turkey itself has tried to join the Union.
The pivot on which Turkey's recent actions have hinged is defiance. And this is found again in the admiral's own words, which state that the "Blue Homeland" is "challenging and notoriously challenging the current map".
But despite what it may seem, this is not the final goal of the "Mavi Vatam" doctrine. This challenge is the way to achieve its real goal, which is none other than to achieve control and consolidation of the three maritime areas surrounding the country in order to exert its influence at both the regional and international level and to gain the energy resources necessary to sustain Turkey's economic and demographic growth without having to rely on third countries.
But as is rule in these matters, history always plays a key role, and this time is no different.
The Turks continue to view as an affront the Treaty of Lausanne, signed in 1923, which confines the country to its current borders and boundaries. This invalidated the far more beneficial Treaty of Sèvres, signed by the Ottoman Empire after the First World War.
At Lausanne, the fragmentation of the empire was de facto dictated, defining not only Turkey's borders, but also those of Greece and Bulgaria, concluding Turkish sovereignty over the Dodecanese islands, Cyprus, Egypt, Sudan, Syria and Iraq. Kurdistan ceased to be a unit, split between several countries, and Armenia was divided between Turkey and the USSR. The conditions limited the Turks' ability to act, placing the country under the umbrella of Western powers, status which has been maintained for almost 100 years since signature.
In order to understand the current status , a number of factors and circumstances must be taken into account that form the basis of the current situation.
During the Cold War period and with the existence of the communist bloc and its military alliance, the Warsaw Pact, the West's protective umbrella over Turkey became more of a necessity forced by circumstances than an imposition. The Ottoman country's geostrategic status made it of vital importance to both blocs, and in the event of hostilities it would be one of the first territories to suffer the consequences. As a vivid example of this geostrategic core topic , it is worth recalling the role played by the American instructions equipped with nuclear ballistic missiles located on Turkish soil in the negotiations to de-escalate what later became known as the "Cuban missile crisis".
But from the distant 1960s to the present day, the world has changed completely. The balances of power have shifted, and events since the beginning of the 21st century, and especially during the last decade, have led today's leaders to believe that their time has come.
At the time, the fall of the communist bloc and Russia's period of weakness began to lay the groundwork instructions for an idea deeply rooted in Turkey today, the main thrust of which is that the protective umbrella of the West is no longer so necessary (it should not be forgotten that this umbrella was also seen in some ways as a corset).
The consolidation of this idea has coincided with a period of great economic and demographic growth in the Ottoman country, with forecasts of reaching 90 million inhabitants by 2030. Both parameters have major economic implications, as they imply an increase B in the country's energy needs. If these needs are not met, it will not be possible to sustain this population growth or to match it with an adequate industrial development .
The basis of the essential industrial development is energy independence. This is one of the factors core topic that can enable the various projects to go ahead. At present, energy needs are covered by supplies from third countries. The main exporters of energy resources to Turkey are Russia, Iran, Iraq and Libya. This external dependence is one of the reasons for the spectacular development of Turkey's military capabilities in recent years and its direct involvement in various unstable scenarios: maintaining an uninterrupted supply of energy. This is one of the main reasons for the interventions in northern Syria, northern Iraq and Libya.
However, this is not the only reason for such interventions; there are other political motivations, commitments that compel Turkey to take sides in one way or another. The Kurdish problem, worthy in itself of a monograph, is one of them.
But despite possible political motivations, the main focus of the "Blue Fatherland Doctrine" is the need to achieve energy independence. This requires taking control of the necessary energy resources and achieving freedom of action in this field.
There are two spheres that he defines to achieve this goal. The first would consist of the establishment of a security and immediate control of the seas surrounding the country: the Mediterranean, the Aegean and the Black Sea, area . The second, of a strategic nature, extends to the Red Sea, the Caspian Sea and the Arabian Sea, including the Persian Gulf.
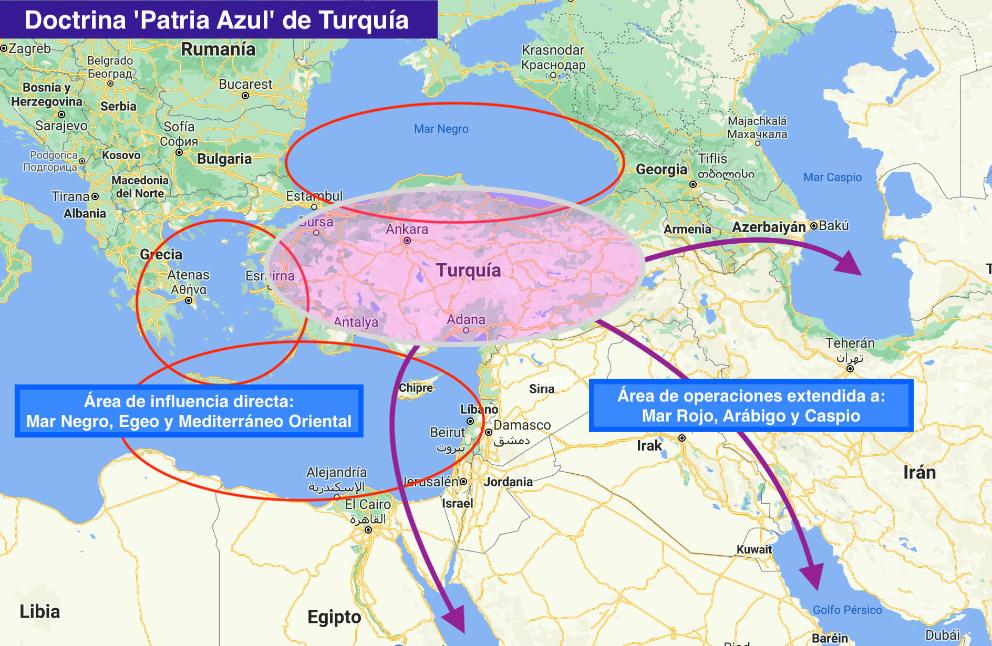
Turkey's dominance of the maritime space includes control over the oil and gas reserves in these waters. This position of maritime dominance is reinforced by establishing alliances with the countries in the area, providing them with support, setting up military instructions on their territory and providing military equipment and training to their armies, thus securing their support. This is a fact, and Turkey already has instructions in Somalia, Sudan, Libya and Qatar, to which it supplies its own weapons systems and with which it has various military agreements.
An aside is in order here. These moves are not welcomed by all countries in the region, some of which see their current position and their own aspirations to grow in power and influence in the region as threatened. The existence of a dominant regional power does not usually leave much room for manoeuvre. It is also important to quote here the words of the father of the "Blue Homeland" doctrine: "Turkey does not need an ally to protect the homeland. The homeland is the homeland. Our continental shelf is our homeland and we have to protect it.
However, he claims that in the future relations between Italy, Tunisia, Libya and Turkey will be the main axis of the Mediterranean. He deliberately leaves out countries such as France, Greece and Spain.
area Traditionally, the Turkish Naval Force's usual area of operations was the Mediterranean, the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea. Recently, however, it has expanded its area of operations to the Red Sea, the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf, and even operates closely with Pakistan. partnership .
This strategic vision, centred on the dominance of the sea, apart from the reasons given above regarding the control of energy resources, can be explained by Turkey's conviction that its special rugged terrain already offers a natural defence and deterrent against any land-based aggression.
Moreover, the "Blue Homeland" doctrine is based on the assumption that Turkey must be an eminently maritime power. It is therefore a realistic doctrine of self-defence of the maritime areas that are rightfully Turkey's, to protect them with an eye to future generations.
Thus, the maritime borders, which stretch across three different seas, are so far perceived as the nation's weak point. And this is precisely what is in the process of being transformed.
reference letter This view has its historical roots in the former Ottoman Empire, which Admiral Cem Gürdeniz refers to on numerous occasions in his writings. It was this view that led Erdogan, shortly after coming to power, to initiate a comprehensive programme of development and modernisation of his naval force known as "Milgem". In this project , heavy investments have been made all over subject, and no effort has been spared, because in order to achieve the development of an armed forces, especially in its maritime aspect, that will sustain the goal of establishing itself as a regional and international power, it is core topic an independent technological development of Turkish industry.
In recent years, the Turkish defence industry has undergone a dramatic evolution, demonstrating the effectiveness of its developments in the Libyan, Syrian and, more currently, Armenia-Azerbaijan conflict. Great emphasis has been placed on the development of warships, unmanned aerial systems (UAVs) and advanced weapons systems of high quality. The chapter on UAVs is particularly significant, and should be the subject of an in-depth study, including from a national point of view in Spain.
Once again, there are two clearly defined intentions here. On the one hand, to achieve a state-of-the-art technological level in its armed forces that will support the achievement of the objectives outlined above, and on the other, to position itself as reference letter in the field of arms exports, to earn revenue and to be able to influence the countries of its interest and their policies in the same way as the United States, China and Russia do.
More specifically, theMilgemprogramme framework has built four anti-submarine corvettes, an intelligence gathering vessel, four surface warfare frigates and four anti-aircraft frigates. The programme also includes four state-of-the-art corvettes for the Pakistan Navy as a way of exporting its advances, enhancing the already close partnership relationship between the two countries and, of course, providing economic benefits for the arms industry.
Similarly, 33 new landing craft capable of transporting both troops and armoured vehicles have been delivered to the Turkish Naval Force. Turkey's amphibious assault capabilities, development and further development, are a factor in a possible increase in tension with Greece, especially with regard to claims over the islands to the east of the country and its waters.
The development of naval warfare capabilities is completed with the production of six new submarines from invoice German-built under licence of HDW in Turkey itself, namely the model U-214. These new submersibles are equipped with an AIP system that allows them to remain for long periods without surfacing, and join the ten that the Ottoman country has operated so far.
This is one of the most significant in terms of its destabilising capacity. Until now it has been Greece that has maintained a certain technological superiority in this field. But the entry into service of the new Turkish units, entrance , significantly changes the balance of power. In addition to serving as perfect intelligence gathering platforms, especially in the SIGINT (Signals Intelligence) and COMINT (Communications Intelligence) disciplines, submarines are excellent deterrent weapons, capable of denying an entire fleet access to an extensive area.
The most significant element of Turkey's pretentious programme is an amphibious assault ship (LHD) called the "Anadolu". This ship, with very similar characteristics to the "Juan Carlos I" operated by the Spanish Navy, is a qualitative leap in terms of the capabilities it provides, as it can not only transport landing barges, but also operate different types of helicopters, UAVs and, where appropriate, vertical take-off fighter aircraft from its deck.
Currently, the only such aircraft compatible with the ship is the American F-35 B, which is the vertical take-off and landing (VSTOL) variant. Turkey was one of the nations that had decided to acquire this fighter aircraft, albeit in its A version, which is the standard version for the air force, the first units of which were already scheduled to be delivered to submission .
But the Ankara government's decision to acquire state-of-the-art Russian anti-aircraft equipment, such as the S-400 system, has led the US to veto its continuation of the F-35 B procurement programme. In fact, the first aircraft destined for the Ottoman country have been sold to the USAF. In any case, Turkey's intention was not to acquire the VSTOL version, which leaves Turkey's real intention as to which aircraft will equip the ship open to question.
The project will be completed with the construction of a second amphibious assault ship, the "Trakya". The possession of two units of this subject provides the Turkish naval force with capabilities far superior to those of its neighbours in the region, giving it the ability to project its amphibious force in strategic operations and in two theatres simultaneously.
The real value of these capabilities is not the operational capability itself, but the deterrent capability it represents.
Turkey's involvement in the conflicts in Syria and Libya has provided the Turkish Armed Forces, and within these its naval units, with enormous and valuable combat experience that has been very useful for update and improving its doctrine and operational capabilities. This, together with the high quality of the training quality of its units, the quality of its equipment and the technological and weapons development described above, are the three pillars necessary for the implementation of the "Blue Homeland" doctrine. The great unknown is how the other regional powers, which are directly affected by the advance of this strategic plan, will react.
In conclusion, it can be said that interests are multiple and often intersecting, affecting not only the countries bordering this area of the Mediterranean, but also powers such as Russia and France and international organisations such as NATO.
Incidents between supposedly allied nations have already occurred, even leading to France's withdrawal from NATO's Mediterranean operation due to a problem between a French and a Turkish frigate, and resulting in an attack on Turkish positions by "Rafale" aircraft from instructions in the United Arab Emirates, but whose nationality remains unclear.
status There is no doubt that Turkey's attitude, and the implementation of its plan, puts the Atlantic Alliance in a weak position, as one of the reasons behind the plan is Turkey's perception that it no longer needs the protection of the Western umbrella for the defence of its interests.
On the other hand, Turkey is playing with the trump card of holding the key to the door of entrance to the torrent of migrants from Syria, Libya, Somalia and Eritrea to the EU. And it will use it as a pressure measure in the face of any European reaction or stance against its interests.
The Eastern Mediterranean has regained the leading role in world geopolitics that it had in the 16th century, only this time we have new powers such as Russia that also claim their space and their need for a permanent and strong presence in the area. We cannot ignore the relationship between this Russian need and the Crimean conflict and the strategic need to be able to control to some extent both sides of the Bosporus and ensure the Black Sea fleet's access to the Mediterranean.
All these economic, energy and political interests are creating a very complicated status where the "internal" conflicts in Syria and Libya also come together, creating an over-presence of military units, combatants, private military companies, weapons systems, aircraft, UAVs, etc. that at any moment, and due to any unexpected error, could lead to an incident that, however slight, could have unforeseeable and irreparable consequences.
* The author is an infantry lieutenant colonel and geopolitical analyst.
REFERENCES
Kasapoglu, 'The Blue Homeland': Turkey's largest naval drill. Anadolu Agency 27 February.
SETA Security Sadar Turkey's geopolitical landscape in 2020
Kara Harp Okulu Bilim Dergisi, "An assesment of eastern mediterranean maritime boundary delimitation agreement between Turkey and Libya" Science Journal of Turkish Military Academy Haziran /June 2020
Eyal Pinko, "Turkey's Maritime Strategy Ambitions: The Blue Homeland Doctrine (Mavi Vatan)" Research Institute for European and American Studies(www.rieas.gr) April 2020
Armenia and Azerbaijan clash in a conflict that has also involved Turkey and Russia.
![Monument to the Armenian capture of the city of Shusha in the war over Nagorno-Karabakh in the 1990s [Wikipedia]. Monument to the Armenian capture of the city of Shusha in the war over Nagorno-Karabakh in the 1990s [Wikipedia].](/documents/16800098/0/nagorno-karabaj-blog.jpg/222b236d-6a6a-e4af-fd54-efef333f0717?t=1621884636053&imagePreview=1)
Monument to the Armenian capture of the city of Shusha in the war over Nagorno-Karabakh in the 1990s [Wikipedia].
ANALYSIS / Irene Apesteguía
The region of Nagorno-Karabakh, traditionally inhabited by Christian Armenians and Muslim Turks, is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. However, its population is Armenian-majority and pro-independence. In Soviet times it became an autonomous region within the Republic of Azerbaijan and it was in the war of the 1990s that, in addition to leaving some 30,000 dead and around a million people displaced, separatist forces captured additional Azeri territory. Since the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, ethnic discrepancies between Azerbaijan and Armenia have deepened. Even a 2015 census of Nagorno-Karabakh reported that no Azeris lived there, whereas in Soviet times Azeris made up more than a fifth of the population. Since the truce between the two former Soviet republics in 1994, there has been a status stalemate, with the failure of several negotiations to reach a permanent peace agreement . The dispute has remained frozen ever since.
On 27 September, the conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan once again led to a military confrontation. Recent developments go far beyond the usual clashes, with reports of helicopter shoot-downs, use of combat drones and missile attacks. In 2016 there was a violent escalation of the conflict, but Stepanakert, the capital of Nagorno-Karabakh, was not occupied and no martial law was declared. If one thing is clear, it is that the current escalation is a direct consequence of the freezing of the negotiation process. Moreover, this is the first time that armed outbreaks have occurred at such short intervals, the last escalation of the conflict having taken place last July.
Azerbaijan's Defence Minister Zakir Hasanov on 27 September threatened a "big attack" on Stepanakert if the separatists did not stop shelling its settlements. Nagorno-Karabakh declared that it would respond in a "very painful" way. Armenia, for its part, warned that the confrontation could unleash a "full-scale war in the region".
The leaders of both countries hold each other responsible for this new escalation of violence. According to Azerbaijan, the Armenian Armed Forces constantly provoked the country, firing on the army and on crowds of civilians. Moreover, on multiple local Azerbaijani television channels, President Ilham Aliyev has declared that Armenia is preparing for a new war, concentrating all its forces in Karabakh. Even the Azeri authorities have restricted internet use in the country, mainly limiting access to social media.
In its counter-offensive operation, Azerbaijan mobilised staff and tank units with the support of artillery and missile troops, front-line aviation and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), the ministry's press release statement said. Moreover, according to agreement with the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, a number of Syrians from jihadist groups, from Turkish-backed factions, are fighters in Nagorno-Karabakh. This has been corroborated by Russian and French sources. In any case, it would not be surprising when Turkey sits alongside Azerbaijan.
For its part, Armenia blames Azerbaijan for starting the fighting. Armenian officials announced that the Azerbaijani army had attacked with rocket-propelled grenade launchers and missiles. Armenia has not stopped preparing, as in the weeks leading up to the start of the fighting, multiple shipments of Russian weapons had been detected in the country via heavy transport flights. On the other hand, Armenia's defence minister has accused Turkey of exercising command and control over Azerbaijan's air operations via Boeing 737 Airborne Early Warning & Control aircraft , as Turkey has four of these planes.
Triggers
Both powers were on alert because of the July fighting. Since then, they have not abandoned military preparedness at the hands of their external allies. The current events cannot therefore be described as coming out of the blue. After the July outbreak, there has been a lingering sense that the armed confrontation had simply been left at Fail.
Hours after the outbreak of fighting, Armenia declared martial law and general mobilisation. Azerbaijan, on the contrary, declared that such action was not necessary, but eventually the parliament decided to impose martial law in some regions of the country. Not only was martial law decreed, but also the Azerbaijani Ministry of Defence declared the liberation of seven villages, the establishment of a curfew in several cities and the recapture of many important heights. It is clear that all occupied territories have crucial strategic value: Azerbaijan has secured visual control of the Vardenis-Aghdara road, which connects to Armenian-occupied Karabakh. The road was completed by Armenia three years ago in order to facilitate rapid military cargo transfers, an indication that this is a strategic position for Armenia.
Drone warfare has also been present in the conflict with Turkish and Israeli drones used by Azerbaijan. Armenia's anti-drone measures are bringing Iran into the picture.
An important factor that may have led to the conflict has been changes in the diplomatic leadership in Baku. Elmar Mammadyarov, Azerbaijan's foreign minister, left his position during the July clashes. He has been replaced by former Education minister Jeyhun Bayramov, who does not have much diplomatic experience. Meanwhile, Hikmet Hajiyev, the Azerbaijani president's foreign policy advisor has seen his role in these areas increase.
But the problem is not so much about new appointments. For the past few years, Mammadyarov was the biggest optimist about the concessions Armenia might be willing to make under Nikol Pashinyan's new government. Indeed, since Armenia's Velvet Revolution, which brought Pashinyan to the post of prime minister in 2018, Azerbaijan had been hopeful that the conflict could be resolved. This hope was shared by many diplomats and experts in the West. Moreover, even within Armenia, Pashinyan's opponents labelled him a traitor because, they claimed, he was selling out Armenia's interests in exchange for Western money. All this hope for Armenia disappeared, as the new Armenian prime minister's position on Nagorno-Karabakh was harsher than ever. He even declared on several occasions that "Karabakh is Armenia". All this led to a strengthening of Azerbaijan's position, which hardened after the July clashes. Baku has never ruled out the use of force to try to solve the problem of its territorial integrity.
In the 2016 conflict there were many efforts to minimise these armed disturbances, mainly by Russian diplomacy. These have been supported by the West, which saw Moscow's mediation as positive. However, negotiations between Armenia and Azerbaijan have not resumed, and the excuse of the coronavirus pandemic has not been very convincing, according to domestic media.
More points have led to the current escalation, such as increased Turkish involvement. After the July clashes, Turkey and Azerbaijan conducted joint military exercises. Ankara's representatives began to talk about the ineffectiveness of the peace process, and Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan, speaking last month at the UN General Assembly, described Armenia as the biggest obstacle to long-term peace deadline in the South Caucasus. This is not to say that Turkey provoked the new escalation, but it certainly helped push Azerbaijan into a more emboldened attitude. The Turkish president stated on Twitter that 'Turkey, as always, stands with all its brothers and sisters in Azerbaijan'. Moreover, last August, Azerbaijan's defence minister said that, with the Turkish army's financial aid , Azerbaijan would fulfil 'its sacred duty', which can be interpreted as the recovery of lost territories.
International importance
In a brief overview of the allies, it is worth mentioning that the Azeris are a majority ethnic Turkic population, with whom Turkey has close ties, although unlike the Turks, most Azeris are Shia Muslims. As for Armenia, Turkey has no relations with Armenia, as the former is a largely Orthodox Christian country that has historically always relied on Russia.
As soon as the hostilities began, several states and international organisations called for a ceasefire. For example, Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov, in a telephone conversation with his Armenian counterpart Zohrab Mnatsakanyan, called for an end to the fighting and declared that Moscow would continue its mediation efforts. Meanwhile, as it did after the July clashes, Turkey again expressed through various channels its plenary session of the Executive Council support for Azerbaijan. Turkey's Foreign Ministry assured that Ankara is ready to help Baku in any way it can. The Armenian president, hours before the start of the fire, mentioned that a new conflict could "affect the security and stability not only of the South Caucasus, but also of Europe". US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo expressed serious concerns and called on both sides to stop the fighting.
On the other hand, there is Iran, which is mainly Shia and also has a large ethnic Azeri community in the northwest of the country. However, it has good relations with Russia. Moreover, having borders with both countries, Iran has offered to mediate peace talks. This is the focus of Iran's current problem with the new conflict. Azeri activists called for protests in Iranian Azerbaijan, which is the national territory of Azeris under Iranian sovereignty, against Tehran's support for Armenia. The arrests carried out by the Iranian government have not prevented further protests by this social sector. This response on the streets is an important indicator of the current temperature in northwest Iran.
As for Western countries, France, which has a large Armenian community, called for a ceasefire and the start of dialogue. The US said it had contacted both sides to urge them to "cease hostilities immediately and avoid words and actions of little consequence financial aid".
Russia may have serious concerns about the resumption of full-scale hostilities. It has made it clear on multiple occasions that the important thing is to prevent the conflict from escalating. One reason for this insistence may be that the Kremlin already has open fronts in Ukraine, Syria and Libya, in addition to the current status in Belarus, and the poisoning of Alexei Navalni. Moreover, despite the current attempt by the presidents of Russia and Turkey to show that relations between their countries are going well, the discrepancies between them, such as their views on Syria and Libya, are growing and becoming more diverse. And now Vladimir Putin could not leave Armenia in the hands of Azerbaijan and Turkey.
The Minskgroup of the Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) has as its main mission statement mediation of peace negotiations between Armenia and Azerbaijan, and is co-chaired by Russia, France and the United States. In response to the current conflict, it called for a "return to a ceasefire and resumption of substantive negotiations". Earlier this year, Armenia rejected the Madrid Principles, the main conflict resolution mechanism proposed by group in Minsk. Moreover, this initiative has been made increasingly impossible by the Armenian Defence Ministry's concept of a "new war for new territories", as well as Nikol Pashinyan's idea of Armenia-Karabakh unification. All this has infuriated the Azeri government and citizens, who have increasingly criticised the Minsk group . Azerbaijan has also criticised the group 's passivity in the face of what it sees as Armenia's inflammatory actions, such as the relocation of Karabakh's capital to Susa, a city of great cultural importance for Azerbaijanis, or the illegal settlement of Lebanese and Armenians in occupied Azerbaijani territories.
If any conclusion is to be drawn from this it is that, for many in both Azerbaijan and Armenia, the peace process has been discredited by the past three decades of failed negotiations, prompting increasing warnings that the status quo would lead to a further escalation of the conflict.
There is growing concern among some experts that Western countries do not understand the current status and the consequences that could result from the worst flare-up in the region in years. The director of the South Caucasus Office at the Heinrich Boell Foundation, Stefan Meister, has argued that the fighting between these two regions could go far. In his opinion, "the conflict is underestimated by the EU and the West".
The EU has also taken a stand. It has already order to Armenia and Azerbaijan to de-escalate cross-border tensions, urging them to stop the armed confrontation and to refrain from actions that provoke further tension, and to take steps to prevent further escalation.
The conflict in the Caucasus is of great international importance. There are regular clashes and resurgences of tensions in the area. The relevance is that any escalation of violence could destabilise the global Economics , given that the South Caucasus is a corridor for gas pipelines from the Caspian Sea to world markets, and more specifically to Europe. If Armenia decides that Azerbaijan has escalated too far, it could attack Azerbaijan's South Caucasus Pipeline, which sends gas to Turkey's TANAP, and ends with TAP, which supplies Europe. Another strategic aspect is the control of the city of Ghana'a, as controlling it could connect Russia to Karabakh. In addition, control of the site could cut off gas pipeline connectivity between Azerbaijan, Georgia and Turkey. Conflicts already took place at area last July, which is why Azerbaijan is prepared to close the region's airspace as a result of the new conflict.
![In bright green, territory of Nagorno-Karabakh agreed in 1994; in soft green, territory controlled by Armenia until this summer [Furfur/Wikipedia]. In bright green, territory of Nagorno-Karabakh agreed in 1994; in soft green, territory controlled by Armenia until this summer [Furfur/Wikipedia].](/documents/16800098/0/nagorno-karabaj-mapa.jpg/112d46eb-041d-b714-85b0-10a262216ce3?t=1621884663387&imagePreview=1)
In bright green, territory of Nagorno-Karabakh agreed in 1994; in soft green, territory controlled by Armenia until this summer [Furfur/Wikipedia].
A new war?
There are several possible outcomes for the current status . The most likely is a battle over small and not particularly important areas, allowing for the symbolic declaration of a "victory". The problem centres on the fact that each opponent may have a very different view of things, so that a new strand of confrontation is inevitable, raising the stakes of the conflict, and leading to less chance of understanding between the parties.
Although unlikely, many analysts do not rule out the possibility that the current escalation is part of the preparations for negotiations and is necessary to shore up diplomatic positions and increase pressure on the opponent before talks resume.
Whatever the reasoning behind the armed clashes, one thing is clear: the importance of military force in the Nagorno-Karabakh peace process is growing by the day. The absence of talks is becoming critical. If the Karabakh pendulum does not swing from generals to diplomats soon, it may become irreparable. And it will be then that the prospects of another regional war breaking out once again will cease to be a mere scenario described by experts.
While Russia continues to insist that there is no other option but a peaceful way forward, the contact line between the two sides in Nagorno-Karabakh has become the most militarised area in Europe. Many experts have repeatedly suggested as a possible scenario that Azerbaijan might decide to launch a military operation to regain its lost territory. source The country, whose main source of income is its Caspian Sea oil wealth, has spent billions of dollars on new weaponry. Moreover, it is Azerbaijan that has replaced Russia as the largest carrier of natural gas to Turkey.
A major consequence of the conflict centres on potential losses for Russia and Iran. A further casualty of the conflict may be Russia's position as Eurasia's leader. Another argument is based on the Turkish committee , which has demanded Armenia's withdrawal from Azerbaijani lands. The problem is that the members of committee, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan, are also members of the Collective Security Treaty Organisation (CSTO), led by Russia together with Armenia. On the other hand, Iran sample also panics over Turkey's total solidarity with Azerbaijan, as more Azeris live in Iranian Azerbaijan than in the Republic of Azerbaijan.
This is one of the many conflicts that exemplify the new and current "style" of warfare, where major powers place themselves at the back of small conflicts. However, the territory of Nagorno-Karabakh may be small in size, but not in importance, as in addition to contributing to the continued destabilisation of the Caucasus area , it may affect neighbouring powers and even Europe. The West should give it the importance it deserves, because if it continues along the same lines, the door is open to a more violent, extensive and prolonged armed conflict.
COMMENTARY / Luis Ángel Díaz Robredo*.
It may seem sarcastic to some, and even cruel, to hear that these circumstances of a global pandemic by COVID-19 are interesting times for social and individual psychology. And it may be even stranger to take these difficult times into account when establishing relations with the security and defence of states.
First of all, we must point out the obvious: the current circumstances are exceptional, as we have never before known a threat to health that has transcended such diverse and decisive areas as the global Economics , international politics, geo-strategy, industry, demography... Individuals and institutions were not prepared a few months ago and, even today, we are dealing with them with a certain degree of improvisation. The fees mortality and contagion rates have skyrocketed and the resources mobilised by the public administration are unknown to date. Without going any further, the Balmis operation -mission statement of support against the pandemic, organised and executed by the Ministry of Defence - has deployed 20,000 interventions, during 98 days of state of alarm and with a total of 188,713 military personnel mobilised.
In addition to the health work of disinfection, logistics and health support, there have been other tasks more typical of social control, such as the presence of the military in the streets and at critical points or reinforcement at borders. This work, which some people may find disconcerting due to its unusual nature of authority over the population itself, is justified by atypical group behaviour that we have observed since the beginning of the pandemic. Suffice it to cite a few Spanish examples that reflect how at certain times there has been behaviour that is not very logical for social imitation, such as the accumulation of basic necessities (food) or not so basic necessities (toilet paper) that emptied supermarket shelves for a few hours.
There have also been moments of lack of solidarity and even some social tension due to the fear of contagion against vulnerable groups, such as elderly people with COVID-19 who were transferred from one town to another and were booed by the neighbourhood that received them and had to be escorted by the police. Also, infrequently but equally negative and unsupportive, there have been cases in which some health workers suffered fear and rejection by their neighbours. And lately, the sanctioning and arrest of people who did not respect the rules of social distance and individual protection has been another common action of the authorities and State Security Forces and Corps. These events, which fortunately have been limited and dealt with quickly by the authorities, have been far outweighed by many other positive social behaviours of solidarity, altruism and generosity among citizens.
However, since national security must consider not only ideal scenarios but also situations with shortcomings or potential risks, these social variables must be taken into account when establishing a strategy.
Secondly, the flow of information has been a veritable tsunami of forces and interests that have overwhelmed the information capacities of entire societies, business groups and even individuals. Official media, private media, social networks and even anonymous groups with destabilising interests have competed in this game for citizens' attention. If this status has shown anything, it is that too much information can be as disabling as too little information, and that even the use of false, incomplete or somehow manipulated information makes us more susceptible to influence by the public.
This poses clear dangers to social stability, the operation of health services, the facilitation of organised crime and even the mental health of the population.
Thirdly and finally, we cannot forget that society and our institutions - including those related to security and defence - have their greatest weakness and strength based on the people who make them up. If there is one thing that the pandemic is putting at test it is the psychological strength of individuals due to the circumstance of uncertainty about the present and future, management fear of illness and death, and an innate need for attachment to social relationships. Our ability to cope with this new VUCA (Vulnerability, Uncertainty, Complexity, Ambiguity) scenario that affects each and every social and professional
social and professional environments requires a strong leadership style, adapted to this demanding status , authentic and based on group values. There is no unilateral solution today, except through the efforts of many. It is not empty words to affirm that the resilience of a society, of an Armed Forces or of a human group , is based on working together, fighting together, suffering together, with a cohesion and a team work properly trained.
That said, we can understand that psychological variables - at the individual and grouplevels - are at play in this pandemic status and that we can and should use the knowledge provided by Psychology as a serious science, adapted to real needs and in a constructive spirit, to plan the tactics and strategy of the current and future scenarios arising from Covid-19.
Undoubtedly, these are interesting times for psychology.
* Luis Ángel Díaz Robredo is a professor at Schoolof Educationand Psychology at the University of Navarra.
