Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Articles .
India's trade with the region has increased twenty-fold since 2000, but is only 15% of the trade flow with China.
China's rapid trade, credit and investment spillover into Latin America in the first decade of this century suggested that India, if it intended to follow in the footsteps of its continental rival, could perhaps stage a similar landing in the second decade. This has not happened. India has certainly increased its economic relationship with the region, but it is a far cry from that developed by China. Even Latin American countries' trade flows are greater with Japan and South Korea, although it is foreseeable that in a few years they will be surpassed by those with India given its potential. In an international context of confrontation between the US and China, India emerges as a non-confrontational option, specialising in IT services that are so necessary in a world that has discovered the difficulty of mobility for Covid-19.

article / Gabriela Pajuelo
India has historically paid little attention to Latin America and the Caribbean; the same had been true of China, apart from episodes of migration from both countries. development But China's emergence as a major power and its landing in the region prompted the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) to ask in a 2009 report whether, after the Chinese push, India was going to be "the next big thing" for Latin America. Even if India's figures were to lag behind China's, could India become an actor core topic in the region?
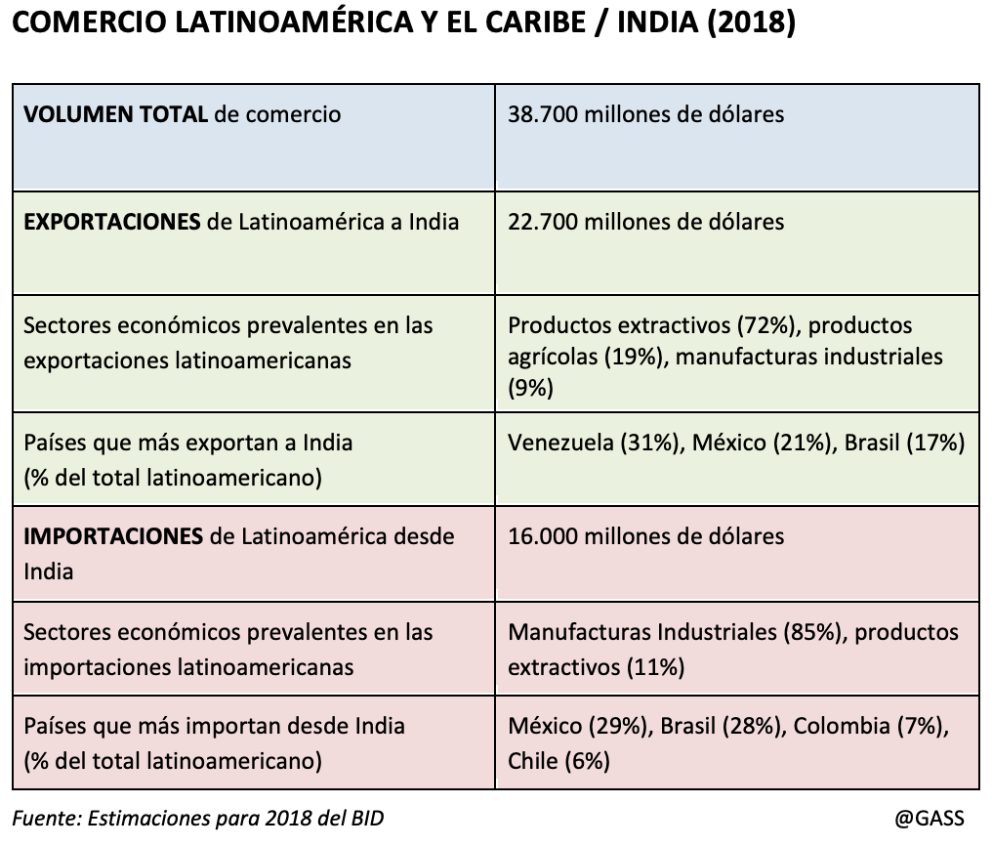
Latin American countries' relationship with New Delhi has certainly grown. Even Brazil has developed a special link with India thanks to the BRICS club, as evidenced by Brazilian president Jair Bolsonaro's visit in January 2020 to his counterpart Narendra Modi. In the last two decades, India's trade with the region has increased twenty-fold, from $2 billion in 2000 to almost $40 billion in 2018, as a new IDB report found last year.
This volume, however, falls far short of the trade flow with China, of which it constitutes only 15 per cent, because if Indian interests in Latin America have increased, Chinese interests have continued to do so to a greater extent. Investment from both countries in the region is even more disproportionate: between 2008 and 2018, India's investment was $704 million, compared to China's $160 billion.
Even India's trade growth is less regionally intertwined than global figures might suggest. Of the total $38.7 billion of transactions in 2018, $22.7 billion were Latin American exports and $16 billion were imports of Indian products. Indian purchases have already surpassed imports from Latin America by Japan ($21 billion) and South Korea ($17 billion), but this is largely due to the purchase of oil from Venezuela. Adding the two directions of flow, the region's trade with Japan and Korea is still larger (around $50 billion in both cases), but the potential for growth in the trade relationship with India is clearly greater.
There is interest not only from American countries, but also from India. "Latin America has a young and skilled workforce, work , and is rich in natural and agricultural resource reserves," said David Rasquinha, director general manager of the Export-Import Bank of India.
Last decade
The two IDB reports cited above are a good reflection of the leap in relations between the two markets in the last decade. In the 2009 report, under degree scroll 'India: Opportunities and Challenges for Latin America', the Inter-American institution presented the opportunities offered by contacts with India. Although it was committed to increasing them, the IDB was uncertain about the evolution of a power that for a long time had opted for autarky, as Mexico and Brazil had done in the past; however, it seemed clear that the Indian government had finally taken a more conciliatory attitude towards the opening up of its Economics.
Ten years later, the report graduate "The Bridge between Latin America and India: Policies for Deepening Economic Cooperation" delved into the opportunities for cooperation between the two actors and noted the importance of strengthening ties to favour the growing internationalization of the Latin American region, through the diversification of trade partners and access to global production chains. In the context of the Asian Century, the flow of exchange trade and direct investment had increased exponentially from previous levels, result largely due to the demand for Latin American raw materials, something that is often criticised as not fostering the region's industry.
The new relationship with India presents an opportunity to correct some of the trends in interaction with China, which has focused on investment by state-owned companies and loans from Chinese state-owned banks. In the relationship with India, there is greater participation of Asian private initiative and a commitment to new economic sectors, as well as the hiring of indigenous staff , including at the management and management levels.
agreement According to General Manager of the IDB's Integration and Trade Sector, Fabrizio Opertti, "the development of an effective institutional framework and business networks" is crucial. The IDB suggests possible governmental measures such as increasing the coverage of trade and investment agreements, the development of proactive and targeted trade promotion activities, boosting investments in infrastructure, promoting reforms in the logistics sector, among others.
Post-Covid context
The questioning of global production chains and, ultimately written request, of globalisation itself because of the Covid-19 pandemic, is not conducive to international trade. Moreover, the economic crisis of 2020 may have a long-lasting effect on Latin America. But it is precisely in this global framework that the relationship with India could be particularly interesting for the region.
Within Asia, in a context of polarisation over the geopolitical interests of China and the United States, India emerges as a partner core topic , one might even say neutral; something that New Delhi could use strategically in its approach to different areas of the world and in particular to Latin America.
Although "India does not have pockets as deep as the Chinese", as Deepak Bhojwani, founder of the consultancy firm Latindia[1], says in relation to the enormous public funding that Beijing manages, India could be the origin of interesting technological projects, given the variety of IT and telecommunications companies and experts it has. Thus, Latin America could be the target of the "technology foreign policy" of a country that, according to agreement with its Ministry of Electronics and IT, has the ambition of growing its digital Economics to "one trillion dollars by 2025". New Delhi will focus its efforts on influencing this economic sector through NEST (New, Emerging and Strategic Technologies), promoting a unified Indian message on emerging technologies, such as governance of data and artificial intelligence, among others. The pandemic has highlighted Latin America's need for more and better connectivity.
There are two prospects for the expansion of India's influence on the continent. One is the obvious path of strengthening its existing alliance with Brazil, within the BRICS, whose pro tempore presidency India holds this year. That should lead to more diversified ties with Brazil, the region's largest market, especially in science and technology cooperation, in the fields of IT, pharmaceuticals and agribusiness. "Both governments committed to expand bilateral trade to 15 billion dollars by 2022. Despite the difficulties brought by the pandemic, we are pursuing this ambitious goal", says André Aranha Corrêa do Lago, Brazil's current ambassador to India.
On the other hand, a greater effort could be made in bilateral diplomacy, insisting on pre-existing ties with Mexico, Peru and Chile. The latter country and India are negotiating a preferential trade agreement and the Bilateral Investment Protection Treaty signature . A rapprochement with Central America, which still lacks Indian diplomatic missions, may also be of interest. These are necessary steps if, closely following in China's footsteps, India wants to be the "next big thing" for Latin America.
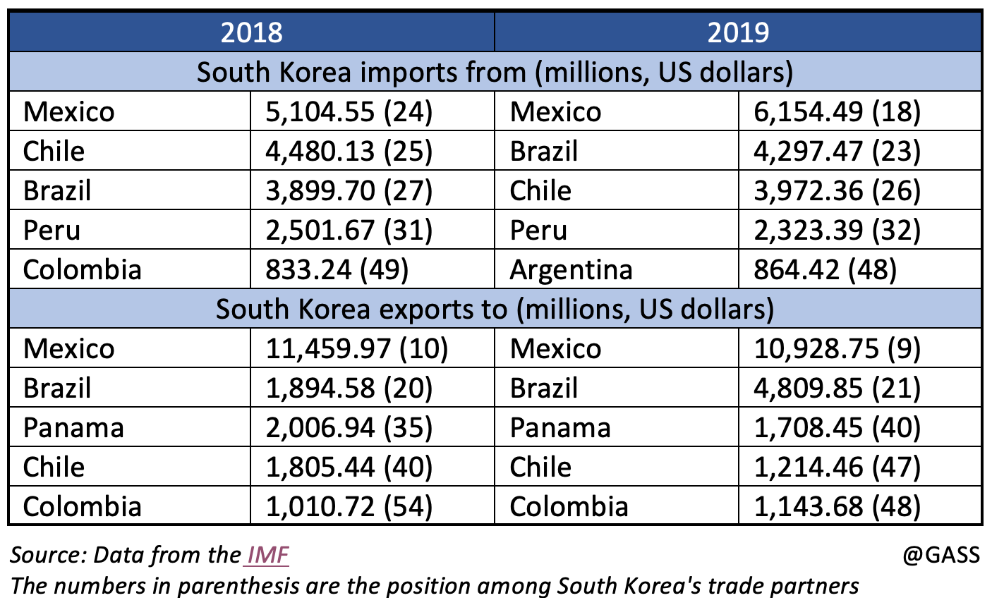
The increase in South Korean trade with Latin American countries has allowed the Republic of Korea to reach Japan's exchange figures with the region.
Throughout 2018, South Korea's trade with Latin America exceeded USD 50 billion, putting itself at the same level of trade maintained by Japan and even for a few months becoming the second Asian partner in the region after China, which had flows worth USD 300 billion (half of the US trade with its continental neighbours). South Korea and Japan are ahead of India's trade with Latin America (USD 40 billion).

ARTICLE / Jimena Villacorta
Latin America is a region highly attractive to foreign markets because of its immense natural resources which include minerals, oil, natural gas, and renewable energy not to mention its agricultural and forest resources. It is well known that for a long time China has had its eye in the region, yet South Korea has also been for a while interested in establishing economic relations with Latin American countries despite the spread of new protectionism. Besides, Asia's fourth largest economy has been driving the expansion of its free trade network to alleviate its heavy dependence on China and the United States, which together account for approximately 40% of its exports.
The Republic of Korea has already strong ties with Mexico, but Hong Nam-ki, the South Korean Economy and Finance Minister, has announced that his country seeks to increase bilateral trade between the regions as it is highly beneficial for both. "I am confident that South Korea's economic cooperation with Latin America will continue to persist, though external conditions are getting worse due to the spread of new protectionism", he said. While Korea's main trade with the region consists of agricultural products and manufacturing goods, other services such as ecommerce, health care or artificial intelligence would be favourable for Latin American economies. South Korean investment has significantly grown during the past decades, from USD 620 million in 2003, to USD 8.14 billion in 2018. Also, their trade volume grew from USD 13.4 billion to 51.5 billion between the same years.
Apart from having strong ties with Mexico, South Korea signed a Free Trade Agreement with the Central American countries and negotiates another FTA with the Mercosur block. South Korea would like to join efforts with other Latin American countries in order to breathe life into the Trans-Pacific Partnership, bringing the US again into the negotiations after a change of administration in Washington.
Mexico
Mexico and South Korea's exports and imports have increased in recent years. Also, between 1999 and 2015, the Asian country's investments in Mexico reached USD 3 billion. The growth is the result of tied partnerships between both nations. Both have signed an Agreement for the Promotion and Reciprocal Protection of Investments, an Agreement to Avoid Income Tax Evasion and Double Taxation and other sectoral accords on economic cooperation. Both economies are competitive, yet complementary. They are both members of the G20, the OECD and other organisations. Moreover, both countries have high levels of industrialization and strong foreign trade, key of their economic activity. In terms of direct investment from South Korea in Mexico, between 1999 and June 2019, Mexico received USD 6.5 billion from Korea. There are more than 2,000 companies in Mexico with South Korean investment in their capital stock, among which Samsung, LG, KORES, KEPCO, KOGAS, Posco, Hyundai and KIA stand out. South Korea is the 12th source of investment for Mexico worldwide and the second in Asia, after Japan. Also, two Mexican multinationals operate in South Korea, group Promax and KidZania. Mexico's main exports to South Korea are petrol-based products, minerals, seafood and alcohol, while South Korea's main exports to Mexico are electronic equipment like cellphones and car parts.
Mercosur
Mercosur is South America's largest trading economic bloc, integrated by Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. With a GDP exceeding USD 2 trillion, it is one of the major suppliers of raw materials and agricultural and livestock products. South Korea and Mercosur launched trade negotiations on May 2018, in Seoul. Actually, the Southern Common Market and the Republic of Korea have been willing to establish a free trade agreement (FTA) since 2005. These negotiations have taken a long time due to Mercosur's protectionism, so the Asian country has agreed on a phased manner agreement to reach a long-term economic cooperation with the bloc. The first round of negotiations finally took place in Montevideo, the Uruguayan capital, in September 2018. Early this year, they met again in Seoul to review the status of the negotiations for signing the Mercosur-Korea trade agreement. This agreement covers on the exchange of products and services and investments, providing South Korean firms faster access to the Latin American market. The Asian tiger main exports to South America are industrial goods like auto parts, mobile devices and chips, while its imports consist of mineral resources, agricultural products, and raw materials like iron ore.
Among Mercosur countries, South Korea has already strong ties with Brazil. Trade between both reached USD 1.70 billion in 2019. Also, South Korean direct investments totaled USD 3.69 billion that same year. With the conclusion of the trade agreement with the South American block, Korean products exported to Brazil would benefit from tariff eliminations, as would Korean position trucks, and other products going to Argentina. It would also be the first Asian country to have established a trade agreement with Mercosur.
Central America
South Korea is the first Asian-Pacific country to have signed a FTA with Central American countries (Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and Panama). According to Kim Yong-beom, South Korean Deputy Minister of Economy and Finance, bilateral cooperation will benefit both regions as state regulatory powers won't create unnecessary barriers to commercial exchange between both. "The FTA will help South Korean companies have a competitive edge in the Central American region and we can establish a bridgehead to go over to the North and South American countries through their FTA networks", said Kim Hak-do, Deputy Trade Minister, when the agreement was reached in November 2016. Also, both economic structures will be complimented by each other by encouraging the exchange between firms from both regions. They signed the FTA on February 21st, 2018, after eighth rounds of negotiations from June 2015 to November 2016 that took place in Seoul, San Salvador, Tegucigalpa and Managua. Costa Rica also signed a memorandum of understanding with South Korea to boost trade cooperation and investment. This partnership will create new opportunities for both regions. South Korean consumers will have access to high-quality Central American products like grown coffee, agricultural products, fruits like bananas, and watermelons, at better prices and free of tariffs and duties. Additionally, Central American countries will have access to goods like vehicle parts, medicines and high-tech with the same advantages. Besides unnecessary barriers to trade, the FTA will promote fair marketing, ease the exchange of goods and services, to encourage the exchange businesses to invest in Central America and vice versa. Moreover, having recently joined the Central American Bank for Economic Integration (CABEI) as an extra-regional member, has reinforced the development of partner-economic projects around the region.
Opportunity
The Republic of Korea faces challenges related to the scarcity of natural resources, there are others, such as slower growth in recent decades, heavy dependence on exports, competitors like China, an aging population, large productivity disparities between the manufacturing and service sectors, and a widening income gap. Inasmuch, trade between Latin America and the Caribbean and the Republic of Korea, though still modest, has been growing stronger in recent years. Also, The Republic of Korea has become an important source of foreign direct investment for the region. The presence of Korean companies in a broad range of industries in the region offers innumerable opportunities to transfer knowledge and technology and to create links with local suppliers. FTAs definitely improve the conditions of access to the Korean market for the region's exports, especially in the most protected sectors, such as agriculture and agro-industry. The main challenge for the region in terms of its trade with North Korea remains export diversification. The region must simultaneously advance on several other fronts that are negatively affecting its global competitiveness. It is imperative to close the gaps in infrastructure, education and labor training.
The Sahara conflict becomes more complicated for Spain with the migration crisis in the Canaries
The reactivation of the war in the former colony leaves Madrid with little room for manoeuvre in the face of the wave of migrants arriving in the Canary Islands.
The reactivation of the war in the former colony leaves Madrid with little room for manoeuvre due to the wave of migrants arriving in the Canary Islands.
Spain has never had an easy role in the Western Sahara conflict. Its exit from the North African territory took place in a context of decolonisation haste on the part of a UN that then preferred to take its time in the process. Spain has been caught between defending the rights of the Saharawis and the desirability of not damaging the complicated neighbourhood with Morocco. Now that the Polisario Front has reopened the war, with the aim of getting something moving internationally on the conflict, Spain is hamstrung by crises over the arrival of migrants in the Canary Islands, an archipelago located across the dividing line between Morocco and Western Sahara. Here is summary of the latest developments in the Saharawi question.

article / Irene Rodríguez Caudet
The Polisario Front has declared war on Morocco after 29 years of peace. This organisation, created primarily to defend the independence of Western Sahara from Spain, represents an important part of the Sahrawi population seeking self-determination for its people.
The Alawite kingdom, for its part, claims sovereignty over the territories. It undertook measures that triggered the recent conflict at the Guerguerat border crossing, where demonstrators blocked the road linking Western Sahara to Morocco. The Moroccan military fired on the rally on 13 November and the Polisario Front declared a state of war.
Western Sahara is a territory in a state of decolonisation since 1960 under the auspices of the UN as part of the processes carried out during the second half of the 20th century to put an end to the European colonial empires. This process continued until 1975, the year of the Green March, when an army of 350,000 Moroccan civilians marched into the former colony to claim it as their own, alongside Mauritania. At that point, the Popular Front for the Liberation of Saguia el Hamra and Rio de Oro (Polisario Front) began a guerrilla war that would not find a ceasefire until 1991.
Despite Morocco's efforts to possess the former Spanish colony, the Saharawis have had their own proclaimed republic since 1976, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (also known by the acronym SADR), recognised by several states - 84 in total, although more than half of them have cancelled, frozen or suspended recognition due to violations of their international obligations - and presided over by Brahim Gali.
Since Spain left the territory, the UN has issued several resolutions calling for a referendum on self-determination that would mark the future of Western Sahara as an independent country or propose other alternatives.
In this conflict, the different parties involved are pursuing different strategies. Morocco, for its part, intends to prolong the conflict in order to consolidate its power in Sahrawi territory. It does not envisage independence for the former Spanish colony, but promotes plans for limited autonomy in a project of agreement framework known as the "third way" for what it considers to be its southern provinces. Moreover, it occupies these provinces militarily, through border crossings, six military instructions and with more than half of the Saharawi territory under its control.
Frustrated by the UN's immobile position, the Polisario Front has always counted on the threat of a return to armed conflict. SADR consists of only a few territories that are fully supervised by it - roughly a quarter of Western Sahara - and has gained less global recognition than the Polisario Front as an organisation, which the UN admits as the representative of the Saharawi people.
The lack of new and more imaginative proposals from the UN, coupled with the attitude of the parties involved, particularly the Moroccan side, have made progress towards a satisfactory solution to the conflict impossible. The lack of progress, however, is not only due to these reasons. The Sahrawi refugees in Tindouf, Algeria, must also be taken into account. This is the longest humanitarian crisis in history, dragging on for 45 years and affecting 173,600 refugees, many of whom have known no other life.
The violent strategy, which prevailed for more than fifteen years, was abandoned in 1991 in favour of a ceasefire and negotiation tactics that are not proving very fruitful. Despite attempts at peaceful settlements, in mid-November this year, the Polisario Front declared a state of war, ending a peace that had lasted almost 20 years.
Morocco claims the Saharawi territories as its own and goes so far as to include them unabashedly as part of Morocco on the Kingdom's most recent official maps, similar to those of the early 20th century, when the Maghreb country had control over the Sahara. For this reason, after Spanish colonisation and subsequent decolonisation, Morocco claims the former colony. According to its authorities, the so-called "Sahrawi provinces" have always been under Moroccan sovereignty.
The conflict not only pits Rabat against El Aaiún, but also involves parties that support one leader or the other. On the one hand, there are the Arab countries - Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait - that support Morocco, and on the other hand, a nation that, despite having a very express desire to exercise its own sovereignty and claim SADR's legitimacy, has little or no international support.
In 2021, MINURSO, the mission statement deployed by the UN to guarantee peace and the holding of the referendum on self-determination, will be 30 years old since it began its deployment; to date it has 240 observers, but has not seen its goal. The Saharawis argue that the UN's work has not been effective in any respect and that it has only allowed the Moroccan plundering of the Sahara's natural resources. Nor has there been any progress on the referendum on self-determination, and the lack of action has led to the lifting of the ceasefire by the Saharawi government. The Polisario Front has now chosen to take these measures as the lack of progress by the UN's mission statement becomes increasingly evident.
The country of Mohammed VI has sent troops to quell the demonstrations in the main Saharawi towns and on the roads connecting Morocco to Western Sahara. Meanwhile, its counterpart claims to have caused material and human losses in the Moroccan military instructions located in Saharawi territory. Morocco does not recognise any of these allegations, but defends itself with fire in the face of the Polisario Front's threat.
Meanwhile, Dakhla, the second most populated city in Western Sahara, is serving as a corridor for small boats and dinghies, which in recent days have been arriving in large numbers at the port of Arguineguín, in Gran Canaria. This fact is causing Morocco and Spain to be even more concerned about status in the Sahara and to have to face this problem jointly, something complicated due to the historical confrontations between the two countries over the Saharawi conflict. However, while some are passing through, others are returning to their homeland: the Polisario Front has appealed to all Saharawis living in the country and abroad to join the struggle.
The status of Western Sahara is pending further developments in the conflict and the decisions taken by Morocco. While there are international positions that continue to call for a referendum on self-determination, the status quo will end up influencing the UN to accept the Moroccan autonomy proposal proposal . The Spanish government has avoided pronouncing itself in favour of the plebiscite, although there is division between the PSOE and Podemos, training which urges the holding of the enquiry. Although the migration crisis in the Canaries is due to more complex dynamics, the suspicion that Morocco has allowed the arrival of more refugees at a decisive moment in the reopened Sahara conflict obliges Spain to adopt a cautious attitude.
One third of countries have developed a national cybersecurity strategy, but mobilized capabilities are minimal
A dozen Latin American countries have already developed a national cybersecurity strategy, but overall the capacities mobilized in the region to deal with cybercrime and cyberattacks are so far limited. In a continent with a high use of social networks, but at the same time with some problems of network electricity and internet access that make it difficult to react to cyber-attacks, the risk of widespread organized crime groups increasingly resorting to cybernetics is high.

article / Paula Suárez
In recent years, globalization has made its way in all parts of the world, and with it have emerged several threats in the field of cyberspace, which requires special treatment by the governments of all states. Globally, and not only in Latin America, the main areas under threat in terms of cybersecurity are, essentially, computer crime, network intrusions and politically motivated operations.
The latest reports on cybersecurity in Latin America and the Caribbean, carried out jointly by the Inter-American Bank development (IDB) and the Organization of American States (OAS), indicate that one third of the countries in the region have begun to take some steps to address the growing cybersecurity risks. However, they also note that efforts are still limited, given the general lack of preparedness for the threat of cybercrime; they also point to the need for a reform of protection policies in the coming years, especially with the problems that have come to light with the Covid-19 crisis.
The IDB and the OAS (OAS) have collaborated on different occasions to publicize status and raise awareness of cybersecurity issues, which have been increasing as globalization has become part of everyday life and social networks and the internet become more deeply integrated into our day-to-day lives. To address this new reality, both institutions have created a Cybersecurity Observatory for the region, which has published several programs of study.
If until the 2016report cybersecurity was a topic little discussed in the region, currently with the increase of technology in Latin America and the Caribbean it has become a topic of interest for which states tend to be increasingly concerned, and therefore, to implement relevant measures, as highlighted in the 2020report .
Transportation, educational activities, financial transactions, many services such as food, water or energy supply and many other activities require cybersecurity policies to protect civil rights in the digital realm such as the right to privacy, often violated by the use of these systems as a weapon.
Not only socially, but also economically, investment in cybersecurity is essential to prevent the damage caused by online crime. For the Gross Domestic Product of many countries in the region, attacks on infrastructure can account for from 1% to 6% of GDP in the case of attacks on critical infrastructure, which translates into incompetence on the part of these countries to identify cyber dangers and to take the necessary measures to combat them.
According to the aforementioned study, 22 of the 32 countries analyzed are considered to have limited capabilities to investigate crimes, only 7 have a plan to protect their critical infrastructure, and 18 of them have established a so-called CERT or CSIRT (Computer Security Incident or Emergency Response Team). These systems are not currently developed uniformly in the region, and they lack the capacity and maturity to provide an adequate response to threats at network, but their implementation is necessary and, increasingly, they are supported by institutions such as the OAS for their improvement.
In this area, the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST) has a work core topic , because of the great need in this region, for attend to governments so that they can benefit from the identification of cyber threats and the strategic security mechanisms of the association, mainly to protect the economies of these countries.
As already mentioned, awareness of the need for such measures has been increasing as cyber attacks have also increased, and countries such as Colombia, Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago and Panama have established a proper strategy to combat this damage. In contrast, many other countries in Latin America and the Caribbean such as Dominica, Peru, Paraguay and Suriname have lagged behind in this development, and although they are on the way, they need institutional support to continue in this process.
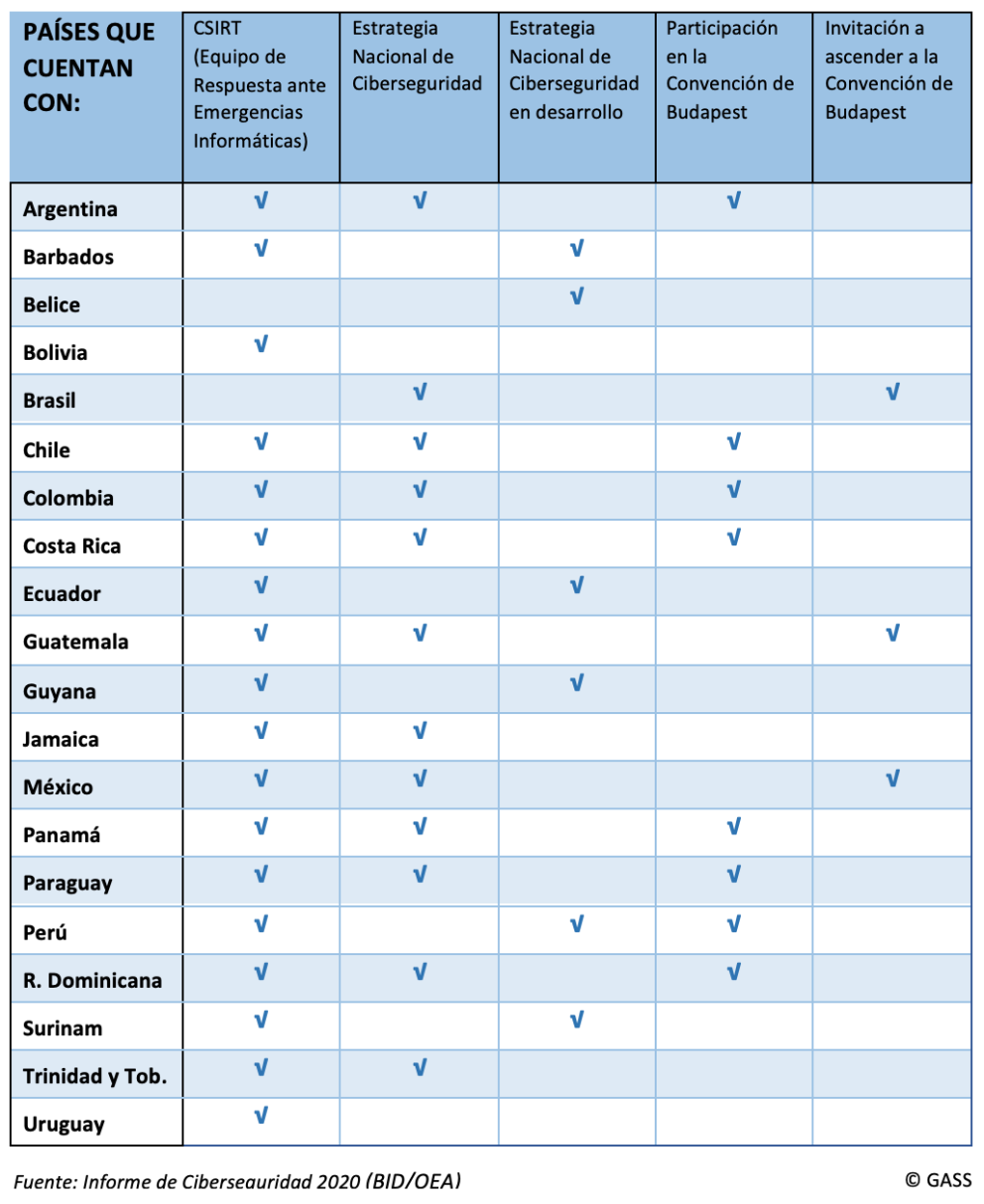
The problem in combating such problems is generally rooted in the states' own laws. Only 8 of the 32 countries in the region are part of the Budapestagreement , which advocates international cooperation against cybercrime, and one third of these countries do not have appropriate legislation in their legal framework for cybercrime.
For the states party to agreement, these guidelines can serve as a great financial aid to develop domestic and procedural laws with respect to cybercrime, so it is promoting the adherence or at least the observation of them from organizations such as the OAS, with the recommendations of specialized units such as group of work on Cybercrime of the REMJA, which advises on the reform of criminal law with respect to cybercrime and electronic evidence.
On the other hand, it was not until the beginning of this year that, with the incorporation of Brazil, 12 countries in Latin America and the Caribbean have established a national cybersecurity strategy, due to the lack of qualified human talent. Although it is worth mentioning the two countries in the region with the largest development in the field of cybersecurity, which are Jamaica and Trinidad and Tobago.
Of the problems mentioned, we can say that the lack of national strategy in terms of cybersecurity exposes these countries to various attacks, but to this must be added that the companies that sell cybersecurity services and provide technical and financial support in the region are mostly from Israel or the United States, and are linked to a rather militarized security and defense perspective, which will be a challenge in the coming years because of the skill that China is showing on this side of the hemisphere, especially linked to 5G technology.
Cyber malpractices are a threat not only to the Economics of Latin America and the Caribbean, but also to the functioning of democracy in these states, an attack on the rights and freedoms of citizens and the values of society. For this reason, the need for investment in civilian infrastructure and military capacity is becoming apparent. To achieve this, the states of the region are willing to cooperate, firstly, in the unification of their legal frameworks based on the models of the Budapest agreement and the instructions of the European Union, whose perspective to face the new challenges in cyberspace is having a great impact and influence in the region.
In addition, with the upcoming Covid-19 crisis, the states of the region are generally willing to collaborate by developing their own national strategies, consistent with the values of the organizations they are part of, to protect both their current means and their emerging technologies (artificial intelligence, quantum, computing from high performing and others). Cyber threats are intended to be addressed from channels open to partnership and dialogue, since the Internet has no borders, and the harmonization of legal frameworks is the first step to strengthen not only regional but also international cooperation.
The Trump Administration concludes its management in an assertive manner in the region and passes the baton to the Biden Administration, which seems to be committed to multilateralism and cooperation.
With the world at a standstill due to Covid-19, the Asian giant has taken the opportunity to resume a whole series of operations with the aim of expanding its control over the territories around its coastline, goal . Such activities have not left the United States indifferent, and despite its internal status complex, it has taken matters into its own hands. With Mike Pompeo's visits throughout the Asia-Pacific, the US has stepped up the process of containing Beijing, which has taken the form of a quadruple alliance between the United States, Japan, India and Australia. The new executive that the White House will inaugurate in January may involve a renewal of US action that, without breaking with the Trump Administration, recovers the spirit of the Obama Administration, that is, guided by greater cooperation with the countries of the Asia-Pacific and a commitment to dialogue.
![Airstrip installed by China on Thitu or Pagasa Island, the second largest of the Spratlys, whose administration has been internationally recognised for the Philippines [Eugenio Bito-ononon Jr]. Airstrip installed by China on Thitu or Pagasa Island, the second largest of the Spratlys, whose administration has been internationally recognised for the Philippines [Eugenio Bito-ononon Jr].](/documents/16800098/0/mar-china-blog.jpg/221fc42a-0d93-e77e-fb3e-4aac0a9ecef0?t=1621874942557&imagePreview=1)
Airstrip installed by China on Thitu or Pagasa Island, the second largest of the Spratlys, whose administration has been internationally recognised for the Philippines [Eugenio Bito-ononon Jr].
article / Ramón Barba
During the pandemic, Beijing has taken the opportunity to resume its actions in Asia Pacific waters. In mid-April, China proceeded to designate land in the Spratly Islands, the Paracel Archipelago and Macclesfield Bank as new districts of the city of Sansha, a town on China's Hainan Island. This designation management assistant caused subsequent protests from the Philippines and Vietnam, who claim sovereignty over these areas. Beijing's attitude has been accompanied by incursions and sabotage of ships in the area. See the sinking of a Vietnamese fishing boat, which China denies, arguing that it had suffered an accident and was carrying out illegal activities.
China's actions since the summer have been increasing instability in the region through military exercises near Taiwan or confrontations with India due to its border problems; on the other hand, in addition to the Philippine and Vietnamese civil service examination towards Chinese movements, there is growing tension with Australia after the latter requested an investigation into the origin of the COVID-19, and the increase in maritime tensions with Japan. All this has led to a response from the United States, which claims to be a defender of free navigation in the Asia-Pacific, justifying its military presence by emphasising that the People's Republic of China is not in favour of free transit, democracy or the rule of law.
US makes a move
Tensions between China and the US over the current dispute have been on the rise throughout the summer, with both increasing their military presence in the region (Washington has also sanctioned 24 Chinese companies that have helped militarise area). All of this has recently been reflected in Secretary of State Mike Pompeo's visits to the Asia-Pacific in October. Prior to this round of visits, he had made statements in September at the ASEAN Virtual Summit urging countries in the region to limit their relations with China.
The dispute over these waters affects Vietnam, the Philippines, Taiwan, Brunei and Malaysia, countries which, along with India and Japan, were visited by Pompeo (among others) in order to ensure greater control over Beijing's actions. During his tour, the US Secretary of State met with the foreign ministers of India, Australia and Japan to join forces against the Asian giant. Washington then signed in New Delhi a military agreement of exchange of data satellites to better track Chinese movements in the area, and made a state visit to Indonesia visit . It should be recalled that Jakarta had so far been characterised by a growing friendship with Beijing and a worsening relationship with the US over a decrease in Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) aid. However, during Pompeo's visit , the two countries agreed to improve their relations through greater cooperation in regional, military procurement, intelligence, joint training and maritime security.
This move by Washington has therefore implied:
-
The consolidation of a quadruple alliance between India, Japan, Australia and the United States, which materialised in joint military exercises in the Bay of Bengal in early November. It is worth recalling that this is in addition to Washington's traditional allies in the region (the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand). In addition, the possibility of closer ties with Vietnam remains open.
-
The expansion of its military presence in the area, increasing the flow of materiel sold to Taiwan, also highlighting the visits of high-level Washington officials throughout July and the following months.
-
Return of the destroyer USS Barry to the waters of the South China Sea with the goal to serve as a symbol of civil service examination to Chinese action, and as a defender of freedom of navigation, peace and stability.
-
Indonesia will move its Naval Combat Force (permanently based in Jakarta) to Natuna, islands bordering the resource-rich South China Sea that are disputed between the two countries.
-
ASEAN takes a stand for peace and stability and in favour of UNCLOS 1982 (which sets out the governing legal framework for the law of the sea framework ) at the summit held in Vietnam on 12-15 November.
 The ratio decidendi behind the Chinese performance
The ratio decidendi behind the Chinese performance
As a first approach to the ratio decidendi behind China's actions, it is worth recalling that since 2012, taking advantage of regional instability, the Asian giant has been citing its historical right over the South Sea territories to justify its actions, arguments that were rejected in 2016 by the Permanent Court of Arbitration in The Hague. Based on the argument that Chinese fishermen once frequented the area, it claimed to justify the appropriation of more than 80 per cent of the territory, which has since pitted Beijing against Manila.
On the other hand, Luis Lalinde, in his article China and the importance of dominating the Surrounding Sea (2017) gives a more complete view of the matter, alluding not only to historical reasons, but also to economic and geopolitical reasons. First, more than half of China's hydrocarbon supply transits the Asia-Pacific region, which is also the world's main economic hub. In addition, Beijing has been deeply affected by the "century of humiliations", characterised by a lack of Chinese control over its territory due to maritime invasions. Finally, the dominion of the seas, together with the already achieved continental weight, are vital for China's hegemonic projection in a area of ever-increasing economic weight at the global level. This is why the so-called "string of pearls" has been established for the defence of strategic, security and energy supply interests from the Persian Gulf to the South Sea.
Lalinde's arguments justify China's actions in recent years; however, Bishop (2020), in the Council on Foreign Relations, states that the reason behind China's recent attitude is due to issues of internal instability, while a small sector of the Chinese intelligentsia is critical and distrustful of Xi's leadership, sample . They argue that the pandemic has weakened the Economics and the Chinese government so that through foreign policy actions it must appear strong and vigorous. Finally, the importance of control of the seas in relation to the Silk Road project should be borne in mind. On the maritime side, China is investing heavily in Indian and Pacific ports, which it does not rule out using for military purposes (see ports in Sri Lanka, Myanmar and Pakistan). Among the main opponents of this alliance are the United States, Japan and India, also opposed to China's belligerent attitude, as we have seen.
Biden era: opportunities in a complicated scenario
Joe Biden's presidency will be marked by major challenges, both internal and external. We are facing a United States marked by a health crisis, with an increasingly polarised society and with a Economics whose recovery, despite the measures adopted, raises doubts as to whether it will be a "V" or a "W". Moreover, relations with Latin America and Europe have been deteriorating as a result of the measures taken by President Trump.
The relationship between China and the US has fluctuated in recent years. The Obama Administration, aware of the growing importance of the Asia-Pacific region, coupled with the opportunity that the Silk Road presents for Beijing to expand its economic and military dominance, introduced its Pivot to Asia policy in its second term, beginning to fund and provide aid to countries in the region. During the years of the Trump Administration, the relationship with Beijing has deteriorated considerably, putting Biden in a scenario in which he will have to face a trade war, the technological degree program battle for 5G, as well as regional security and human rights issues.
The countries of the region are demanding an effective response from the US giant to contain China in which Washington's promise of a free and open shipping zone is realised. However, the US has to be cautious, as with the exception of Vietnam, the Philippines, and to some extent Indonesia and Singapore, the other countries in the region do not feel an urgent need for US intervention. However, with the exception of Cambodia, the rest of the countries do not approve of the possibility of Chinese hegemony either.
In general, experts suggest that in the midst of this storm, the new US president will adopt a cautious but continuist attitude. Probably, in line with the Obama Administration, he will tend towards a commitment to multilateralism, economic alliances subject and regional integration without exercising an authoritarian attitude, reducing the aggressiveness of the Trump Administration, but being firm in his stance. This implies looking for different areas in which to cooperate, such as climate change, the reduction of Freedom of Navigation Missions, or the increase of Capacity Building.
A look into the near future
We will have to keep a close eye on the Trump administration's latest developments in relation to this conflict, as well as the measures that Biden adopts during his first months in office. However, everything suggests that, in this increasingly tense status , Washington will adopt a cautious stance. As we have seen, Pompeo's trips have served the US to reaffirm its presence in the region, assuming a leadership role and providing the response that some countries, such as the Philippines, desire. However, although, as has been said, we will have to keep an eye on the coming months, with instructions already established, it is most likely that Biden will continue the Trump Administration's line, but with a focus on regional integration, multilateralism, diplomacy and economic cooperation in order to win new support, strengthen its alliances and contain Beijing, thus justifying its presence in the region as the only power capable of bringing together regional forces to prevent a feared Chinese hegemony.
The EPP, the Paraguayan guerrilla group that grew out of political carelessness
The Paraguayan People's Army, which emerged in 2008, has created a conflict that has already claimed around 100 lives.
The Paraguayan People's Army, which emerged in 2008, has created a conflict that has already claimed around 100 lives.
Marxist guerrillas in Latin America are a thing of the past. This conviction led to an underestimation of the emergence in 2008 of the Paraguayan People's Army (EPP), which since then has carried out a hundred violent actions, especially in rural areas of the northeast of the country. The conflict has claimed a hundred dead and wounded; there have also been kidnappings of public figures, which have given the EPP special media coverage. The creation of a controversial special military-police corps has failed to achieve the goal goal of putting an end to the group, leading to criticism of the government's management of the problem.
article / Eduardo Villa Corta
The Paraguayan People's Army (EPP) was considered from the outset to be a small group of radicals who would have little to do. However, in barely ten years it has become an organisation capable of confronting the Paraguayan state: it has carried out a hundred terrorist actions, including a dozen kidnappings, causing some sixty deaths and a hundred wounded.
![EPP zones of influence (light red) and places where there has been instructions of group (dark red) [Mikelelgediento] [Mikelelgediento].](/documents/portlet_file_entry/16800098/epp-paraguay-mapa.png/604d99a8-454a-4a1c-3e01-b6bd6a1a799c?imagePreview=1)
EPP zones of influence (light red) and places where there has been instructions of group (dark red) [Mikelelgediento] [Mikelelgediento].
With a issue of activists ranging from thirty in its hard core to two hundred if its support networks are taken into account, the EPP has been a problem for the government for several years, which has been unable to dismantle it: 30 militants have died in confrontations with the forces of law and order and a hundred have been arrested, but the image offered by the authorities is one of ineffectiveness. The Paraguayan government's negative credit also includes the fact that it did not take seriously the threat posed by the creation of group and its first actions.
The EPP was officially formed on 1 March 2008. Although its founders and main leaders had already planned the creation of group prior to this date, its roots go back to 1992 and the Free Fatherland Party, as documented by researcher Jeremy McDermott. The EPP presents itself as an armed group against the "bourgeois liberal" parliamentary system, but above all it is a Marxist movement that promotes the uprising of Paraguay's peasantry, hence its attempts to take root in the rural north-east of the country.
The 2008 presidential victory of Fernando Lugo at the head of a left-wing alliance, ending six decades of political dominance by the Colorado Party, may have encouraged the formation of the EPP, which then felt justified in its actions with Lugo's removal in 2012 through a controversial impeachment trial in parliament that was labelled by Lugo's supporters as a coup d'état.
The first EPP attack, on 16 March 2008, consisted of the burning of agricultural machinery at department de Concepción. The next was in December of the same year, with an attack on a barracks in Tacuatí, in the department of San Pedro. Since then, their movements have focused especially between the south of the first of these Departments and the north of the second.
Despite being a more or less delimited area, dismantling the EPP is not easy because the EPP's modus operandi makes its movements unpredictable. This is because, as McDermott explains, group does not act like other insurgent organisations, such as the FARC. The core of the EPP is made up of around thirty fighters full-time, most of whom have family ties. They are led by the ringleaders Alcides Oviedo and his wife Carmen Villalba, who are in prison; one of the leaders on the ground is Oswaldo Villalba. In addition, there are some fifty activists part-time, a logistical network that could number up to two hundred people and local sympathisers who, without being very involved in the cause, provide information on search operations by the security forces. The group suffered in 2014 the split of one of its columns, which was renamed association Campesina Armada (ACA) and in 2018, from agreement with the authorities, the EPP split into two groups to face pressure from the security forces.
The aforementioned figures speak of a small group , far from the 8,000 members that the FARC had in 2016 at the time of its demobilisation, or the 4,000 members that the ELN currently has in Colombia, or the 3,000 that were attributed to the Chilean Frente Patriótico Manuel Rodríguez. group Although the EPP bears more resemblance to the latter, its operational cessation in 1999 left the FARC as the main training ground for those who would later create the EPP, as evidenced by the documentation found in the computer of FARC leader Raúl Reyes and the kidnapping of businesswoman Cecilia Cubas, daughter of a former Paraguayan president, at the end of 2004.
This action marked what has been a line of action of the EPP. Since 2008, in addition to extortion and assaults in order to finance itself, the group has carried out kidnappings in order to achieve greater media impact. order These have been carried out against relatives of former presidents of the country or high-level political figures profile , for whose release ransoms in excess of five million dollars have been paid, although lower figures have been agreed in negotiations. It is usually agreed that submit part of the money will be in cash and part in foodstuffs for the villages around the EPP's area of operations.
The group has also carried out extortions and assaults in those areas where it operates, demanding "revolutionary taxes" from landowners and cattle ranchers, from whom they also steal cattle and food to meet the organisation's daily sustenance needs.
Other notable actions carried out by the EPP are bomb attacks. For example, there was an attack against the Supreme Court of Justice in Asunción at the beginning of the operations of group. A more recent attack was perpetrated on 27 August 2016 against a military vehicle in the eastern area of Concepción: the explosives went off as the convoy passed by and then the terrorists liquidated the survivors with firearms; eight soldiers were killed in the attack. According to the authorities, this event marked a leap in the EPP's operations, from a group seeking economic resources to an organisation with greater operational and military capacity.
To confront the EPP, President Horacio Cartes created the Joint Task Force (FTC) in 2013 in response to evidence that police action was not effective, in part because of possible internal corruption. The JTF is composed of members of the Armed Forces, the National Police and the National Anti-Drugs administrative office , under the command of a military officer and reporting directly to the president. The more expeditious nature of this unit has generated some controversy in the social and political discussion .
The EPP's most recent operation was the kidnapping of former Paraguayan vice-president Óscar Denis on 9 September 2020. For the release of Denis, leader of the Authentic Radical Liberal Party and active participant in Lugo's impeachment, the terrorists demand the release of their leaders, Alcides Oviedo and Carmen Villalba, as well as the submission of food for the rural areas where they operate. The organisation's deadline expired a few days later without the government heeding their request. There have been citizen mobilisations demanding Denis' release and the status is being followed in the country with concern, putting President Mario Abdo Benítez in a tight spot.
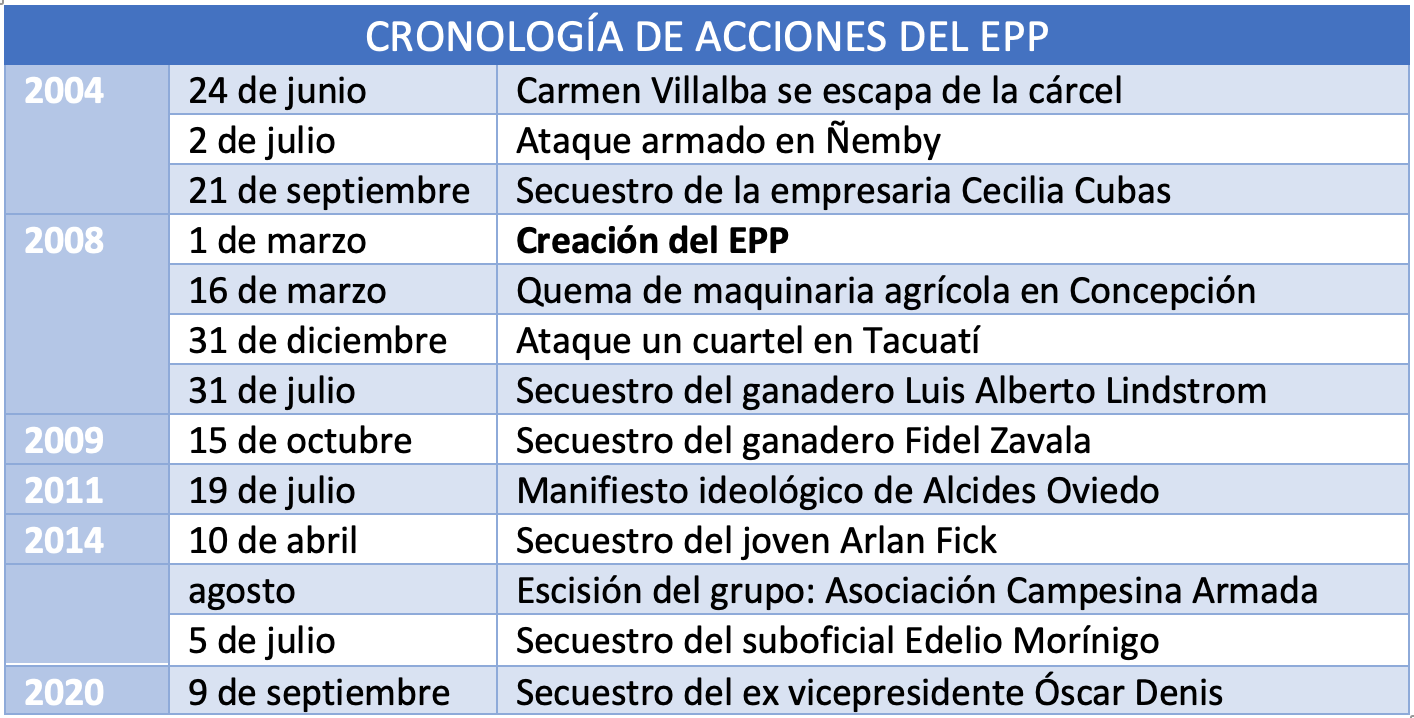
The current president made only one visit, also at the framework of the G-20, compared to the six that Bush and Obama made in their first four years.
International travel does not tell the whole story about a president's foreign policy, but it does give some clues. As president, Donald Trump has only travelled once to Latin America, and then only because the G20 summit he was attending was being held in Argentina. It is not that Trump has not dealt with the region - of course, Venezuela policy has been very present in his management- but the fact that he has not made the effort to travel to other countries on the continent reflects the more unilateral character of his policy, which is not very focused on gaining sympathy among his peers.
![signature in Mexico in 2018 of the free trade agreement between the three North American countries [department of State, USA]. signature in Mexico in 2018 of the free trade agreement between the three North American countries [department of State, USA].](/documents/16800098/0/viajes-trump-blog.jpg/157ee6c8-c573-2e22-6911-3ae54fe8a0a8?t=1621883760733&imagePreview=1)
▲ signature in Mexico in 2018 of the free trade agreement between the three North American countries [department of State, USA].
article / Miguel García-Miguel
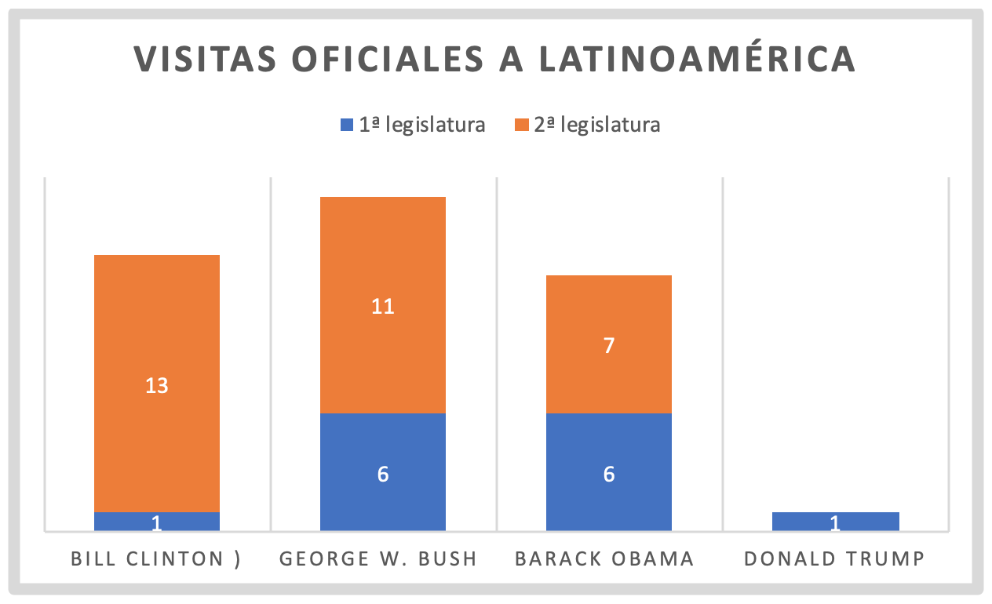
With only one visit visit to the region, the US president is the one who has made the fewest official visits since Clinton's first term in office, who also visited the region only once. In contrast, Bush and Obama paid more attention to the neighbouring territory, both with six visits in their first term. Trump focused his diplomatic campaign on Asia and Europe and reserved Latin American affairs for visits by the region's presidents to the White House or his Mar-a-Lago resort.
In reality, the Trump administration spent time on Latin American issues, taking positions more quickly than the Obama administration, as the worsening problem in Venezuela required defining actions. At the same time, Trump has discussed regional issues with Latin American presidents during their visits to the US. There has not, however, been an effort at multilateralism or empathy, going to his meeting in their home countries to deal with their problems there.
Clinton: Haiti
The Democratic president made only one visit to the region during his first term in office: visit . refund After the Uphold Democracy operation to bring Jean-Bertrand Aristide to power, on 31 March 1995 Bill Clinton travelled to Haiti for the transition ceremony organised by the United Nations. The operation had consisted of a military intervention by the United States, Poland and Argentina, with UN approval, to overthrow the military board that had forcibly deposed the democratically elected Aristide. During his second term, Clinton paid more attention to regional affairs, with thirteen visits.
Bush: free trade agreements
Bush made his first presidential trip to neighbouring Mexico, where he met with then President Fox to discuss a range of issues. Mexico paid attention to the US government's attention attention to Mexican immigrants, but the two presidents also discussed the functioning of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which came into force in 1994, and joint efforts in the fight against drug trafficking. The US president had the opportunity to visit Mexico three more times during his first term in office for the purpose of attend multilateral meetings. Specifically, in March 2002, he attended the lecture International Meeting on Financing for the development, organised by the United Nations and which resulted in the Monterrey Consensus; Bush also took the opportunity to meet again with the Mexican president. In October of the same year he attended the APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation) summit, which that year was held in the Mexican enclave of Los Cabos. Finally, he set foot on Mexican soil once again to attend the Special Summit of the Americas held in Monterrey in 2004.
During his first term in office, Bush pushed for the negotiation of new free trade agreements with several American countries, which was the hallmark of his administration's policy towards the Western Hemisphere. framework As part of this policy, he travelled to Peru and El Salvador on 23 and 24 March 2002. agreement In Peru, he met with the President of Peru and the Presidents of Colombia, Bolivia and Ecuador, in order to reach an agreement to renew the ATPA (Andean Trade Promotion Act), by which the US granted tariff freedom on a wide range of exports from these countries. The matter was finally resolved with the enactment in October of the same year of the ATPDEA (Andean Trade Promotion and Drug Eradication Act), which maintained tariff freedoms in compensation for the fight against drug trafficking, in an attempt to develop the region economically in order to create alternatives to cocaine production. Finally, in the case of El Salvador, he met with the Central American presidents to discuss the possibility of a Free Trade Agreement with the region (known in English as CAFTA) in exchange for a strengthening of security in the areas of the fight against drug trafficking and terrorism. The treaty was ratified three years later by the US congress . Bush revisited Latin America up to eleven times during his second term.
Graph 1. Own elaboration with data of Office of the Historian
Obama: two Summits of the Americas
Obama began his tour of diplomatic visits to Latin America with attendance to the Fifth Summit of the Americas, held in Port-au-Prince (Trinidad and Tobago). The Summit brought together all the leaders of the sovereign countries of the Americas, with the exception of Cuba, and was aimed at coordinating efforts to recover from the recent crisis of 2008, with mentions of the importance of environmental and energy sustainability. Obama returned to attend in 2012 to the VI Summit of the Americas held this time in Cartagena de Indias (Colombia). No representatives from Ecuador or Nicaragua attended this summit in protest at the exclusion of Cuba to date. Neither the President of Haiti nor Venezuelan President Hugo Chávez attended, citing medical reasons. At the summit, the issues of Economics and security were once again discussed, with the war on drugs and organised crime being of particular relevance, as well as the development of environmental policies. He also took advantage of this visit to announce, together with Juan Manuel Santos, the effective entrance of the Free Trade Agreement between Colombia and the US, negotiated by the Bush Administration and ratified after some delay by the US congress . The Democratic president also had the opportunity to visit the region on the occasion of the G-20 meeting in Mexico, meeting , but this time the main focus of topic was on solutions to curb the European debt crisis.
In terms of bilateral meetings, Obama undertook a diplomatic tour of Brazil, Chile and El Salvador between 19 and 23 March 2010, meeting with their respective presidents. He used the occasion to resume relations with the Brazilian left that had governed the country since 2002, to reiterate his economic and political alliance with Chile, and to announce a $200 million fund to strengthen security in Central America. During his second term in office, he made up to seven visits, including the resumption of diplomatic relations with Cuba, which had been paused since the triumph of the Revolution.
Trump: T-MEC
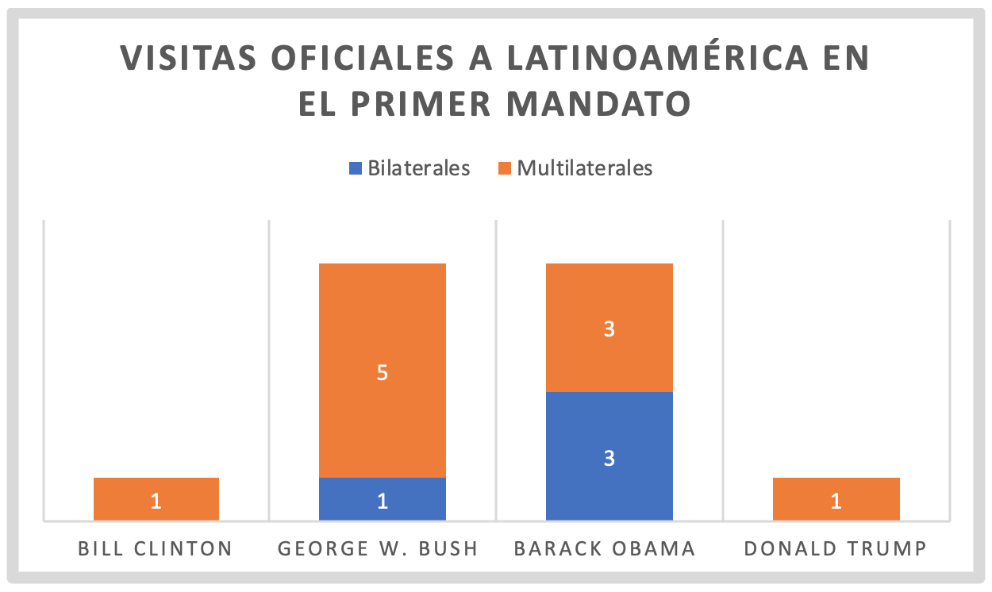
Donald Trump only visited Latin America on one occasion to attend meeting the G-20, a meeting that was not even regional, held in Buenos Aires in December 2018. Among the various agreements reached were the reform of the World Trade Organisation and the commitment of the attendees to implement the measures adopted at the Paris agreement , with the exception of the US, since the president had already reiterated his determination to withdraw from the agreement. Taking advantage of the visit, he signed the T-MEC (Treaty between Mexico, the United States and Canada, the new name for the renewed NAFTA, the renegotiation of which Trump had demanded) and met with the Chinese president in the context of the trade war. Trump, on the other hand, did not attend the VIII Summit of the Americas held in Peru in April 2018; the trip, which was also supposed to take him to Colombia, was cancelled at the last minute because the US president preferred to remain in Washington in the face of a possible escalation of the Syrian crisis.
The reason for the few visits to the region has been that Trump has directed his diplomatic campaign towards Europe, Asia and to a lesser extent the Middle East, in the context of the trade war with China and the loss of power on the US international stage.
Graph 2. Own elaboration with data of Office of the Historian
Only one trip, but monitoring of the region
Despite having hardly travelled to the rest of the continent, the Republican candidate has paid attention to the region's affairs, but without leaving Washington, as up to seven Latin American presidents have visited the White House. The main focus of the meetings has been the economic development and the reinforcement of security, as usual. Depending on the reality of each country, the meetings revolved more around the possibility of future trade agreements, the fight against drugs and organised crime, preventing the flow of illegal immigration to the United States, and the search to strengthen political alliances. Although the US government website does not list it as an official visit , Donald Trump also met at the White House in February 2020 with Juan Guaidó, recognised as president in charge of Venezuela.
Precisely, if there has been a common topic to all these meetings, it has been the status economic and political crisis in Venezuela. Trump has sought allies in the region to encircle and put pressure on Maduro's government, which is not only an example of continuous human rights violations, but also destabilises the region. The ironclad civil service examination to the regime served Donald Trump as propaganda to gain popularity and try to save the Latino vote in the November 3 elections, and that had its award at least in the state of Florida.
Graph 3. Own elaboration with data of Office of the Historian
The deterioration of the small Mediterranean country's status benefits Hezbollah and its patron saint, Iran.
With four different prime ministers so far this year, it is difficult to escape the vicious circle in which Lebanon finds itself, so that the continuity of the current political system and the severe financial crisis seem inevitable. From this perpetuation emerge some possibilities, almost all of them bleak, for Lebanon's future. Here are some of these scenarios.
![State of the port of Beirut after the explosion of 4 August 2020 [Mehr News Agency/Wikipedia]. State of the port of Beirut after the explosion of 4 August 2020 [Mehr News Agency/Wikipedia].](/documents/16800098/0/libano-futuro-blog.jpg/ed561a7d-5d73-93fa-3cbe-2afacd099fac?t=1621884521341&imagePreview=1)
State of the port of Beirut after the explosion on 4 August 2020 [Mehr News Agency/Wikipedia].
article / Salvador Sánchez Tapia
To say that the Lebanese political system is dysfunctional is nothing new. development Based on a sectarian balance of power established in 1989 after a long civil war, it perpetuates the existence of clientelistic networks, encourages corruption, hampers the country's economic development and hinders the creation of a transversal Lebanese national identity that transcends religious confessions.
For some time now, Lebanon has been immersed in an economic and social crisis of such magnitude that many analysts are wondering whether we are facing a new case of state failure. In October 2019, the country was rocked by a wave of demonstrations that the government itself considered unprecedented, triggered by the executive's advertisement attempt to tackle the serious economic crisis with several unpopular measures, including a tax on the use of the popular Whatsapp application. The protests, initially focused on this issue, soon incorporated complaints against rampant corruption, the uncontrolled increase in the cost of living, and the lack of employment and opportunities in the country.
Popular pressure forced the resignation of the unity government led by Saad Hariri later that month. The government was replaced in January 2020 by a more technical profile government led by former Education minister Hassan Diab. The new government had little room for reform before the coronavirus pandemic was declared, and soon found itself beset by the same street pressure that had toppled the previous government, with demonstrations continuing despite the restrictions imposed by the pandemic.
The devastating explosion in early August 2020 in the port of Beirut only further plunged the country into the downward spiral in which it was already mired. Despite voices that tried to see the hand of Israel or Hezbollah behind the catastrophe that took the lives of 163 people, the Lebanese population soon realised that this was merely the logical consequence of years of corruption, bureaucratic sloppiness and withdrawal of the national infrastructure. Again there was a crescendo of popular outrage; again the government was forced to resign at plenary session of the Executive Council.
With echoes of the explosion still lingering, at the end of August Mustafa Adib, Lebanon's former ambassador to Germany, was tasked by President Aoun to form a government. Unable to complete the arduous task, not least because of Hezbollah's insistence on controlling the Finance Ministry, Adib resigned on 26 September, leaving the country on the brink of the precipice it still finds itself on.
It is difficult to predict Lebanon's future, beyond predicting that it looks bleak, as a complex dynamic of internal and external forces grips the country. Despite the pressure, at least from urbanised and cosmopolitan Beirut, to end it, it is enormously complex to untangle the tangled web of clientelistic networks that have controlled the country since independence, not only because of the benefits it has generated for a small privileged group , but also because many fear the alternatives to a model that, for all its faults, has avoided a repeat of the savage civil war that took place between 1975 and 1990.
Its geographic status makes it difficult for Lebanon to escape the general climate of instability in the Middle East and the influence exerted on the country by regional and international actors such as Israel, Iran, Syria and France, especially considering that the problems of the Levant are so deep and its national leadership so weak that it does not seem to be able to overcome them on its own.
Lebanon's plight is that its own sectarian division makes it difficult for nations to emerge that are willing to donate on a cross-cutting basis to help bridge the divide that divides the country internally, and that the financial aid it may receive from actors such as Iran or Saudi Arabia only reinforces it. The efforts of French President Emmanuel Macron, self-appointed as the driving force behind Lebanese reconstruction, do not seem, for the moment, to be gaining momentum. At the donors' lecture he convened on 9 July with fifteen heads of state, he secured contributions worth $250 million to revitalise Lebanon's moribund Economics . Meanwhile, Beirut's mayor estimates the reconstruction costs of the August explosion in the capital's port at between $3 billion and $5 billion.
As a mirror image of this difficulty, Lebanese communities, comfortably ensconced in the status quo, reject an undoubtedly necessary financial aid if they feel it might be detrimental to their respective power instructions . Hezbollah, for example, does not accept IMF programmes, complicating the achievement of the necessary national consensus that would facilitate IMF support. It is difficult to escape this vicious circle, so that the continuation of the current political system, and with it the continuation of Lebanon's severe financial crisis, seems inevitable. From this perpetuation come some possibilities, almost all of them bleak, for the Lebanese future. The first is that Lebanon will continue to slide down the inclined plane that is turning it into a failed state, and that this condition will eventually lead to a civil war precipitated by events similar to those that occurred during the Arab Spring in other states in the region. Such an eventuality would resurrect the ghosts of the past, produce regional instability that is difficult to measure but which would undoubtedly provoke intervention by regional and international actors, and could ultimately dismember the country, result which would only sow the seeds of further instability throughout the region.
Without going to that extreme, the internal turmoil could break the precarious balance of power on which Lebanese political life is based, to the benefit of one of its sectarian groups. Hezbollah, the undisputed leader of the country's Shia faction, appears here as the most organised and strongest group within the country and, therefore, as the one that stands to gain the most from this breakdown. It should be borne in mind that, in addition to the support of internship all 27 percent of Lebanese Shiites, the militia organisation is viewed favourably by many members of the divided Christian community - some 45 percent of the country's population - who put their desire for an internal Security Service in the country before other considerations. Aware of this, Hezbollah's leader Hasan Nasrallah is sample moderate in his proposals, seeing the Sunni community, supported by Saudi Arabia, as his real rival, and seeking to broaden his power base.
Iran would undoubtedly be the real winner in this scenario, as it seems unrealistic to think of a Hezbollah that, once it has come of age, would have a life of its own outside the ayatollahs' regime. With this new piece, Tehran would complete the Shia arc that connects Iran with Iraq and, through Syria, with the Eastern Mediterranean. The destabilising effects of such a move status, however, cannot be underestimated if one considers that the mere possibility of the Islamic Republic of Iran taking full control of Lebanon constitutes a casus belli for Israel.
In a positive grade , the serious crisis the country is going through and the strong popular pressure, at least in urban areas, may, paradoxically, be a spur to overcome the sectarian system that has contributed so much to generate this status. However, such a transition only stands a chance of progress - however tenuous - with strong external wholesale support.
In this scenario, the role of the international community should not be limited to providing economic resources to prevent the country's collapse. Its involvement must favour the development and sustain civic-political movements with an intersecting base that are capable of replacing those who perpetuate the current system. To this end, in turn, it is imperative that contributing nations lend their financial aid vision, renouncing any attempt to shape a Lebanon to suit their respective national interests, and forcing the elites who control the factions to abdicate the status quo in favour of a true Lebanese identity. The obvious question is: is there any real chance of this happening? The reality, unfortunately, does not allow for much hope.
Armenia and Azerbaijan clash in a conflict that has also involved Turkey and Russia.
![Monument to the Armenian capture of the city of Shusha in the war over Nagorno-Karabakh in the 1990s [Wikipedia]. Monument to the Armenian capture of the city of Shusha in the war over Nagorno-Karabakh in the 1990s [Wikipedia].](/documents/16800098/0/nagorno-karabaj-blog.jpg/222b236d-6a6a-e4af-fd54-efef333f0717?t=1621884636053&imagePreview=1)
Monument to the Armenian capture of the city of Shusha in the war over Nagorno-Karabakh in the 1990s [Wikipedia].
ANALYSIS / Irene Apesteguía
The region of Nagorno-Karabakh, traditionally inhabited by Christian Armenians and Muslim Turks, is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. However, its population is Armenian-majority and pro-independence. In Soviet times it became an autonomous region within the Republic of Azerbaijan and it was in the war of the 1990s that, in addition to leaving some 30,000 dead and around a million people displaced, separatist forces captured additional Azeri territory. Since the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, ethnic discrepancies between Azerbaijan and Armenia have deepened. Even a 2015 census of Nagorno-Karabakh reported that no Azeris lived there, whereas in Soviet times Azeris made up more than a fifth of the population. Since the truce between the two former Soviet republics in 1994, there has been a status stalemate, with the failure of several negotiations to reach a permanent peace agreement . The dispute has remained frozen ever since.
On 27 September, the conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan once again led to a military confrontation. Recent developments go far beyond the usual clashes, with reports of helicopter shoot-downs, use of combat drones and missile attacks. In 2016 there was a violent escalation of the conflict, but Stepanakert, the capital of Nagorno-Karabakh, was not occupied and no martial law was declared. If one thing is clear, it is that the current escalation is a direct consequence of the freezing of the negotiation process. Moreover, this is the first time that armed outbreaks have occurred at such short intervals, the last escalation of the conflict having taken place last July.
Azerbaijan's Defence Minister Zakir Hasanov on 27 September threatened a "big attack" on Stepanakert if the separatists did not stop shelling its settlements. Nagorno-Karabakh declared that it would respond in a "very painful" way. Armenia, for its part, warned that the confrontation could unleash a "full-scale war in the region".
The leaders of both countries hold each other responsible for this new escalation of violence. According to Azerbaijan, the Armenian Armed Forces constantly provoked the country, firing on the army and on crowds of civilians. Moreover, on multiple local Azerbaijani television channels, President Ilham Aliyev has declared that Armenia is preparing for a new war, concentrating all its forces in Karabakh. Even the Azeri authorities have restricted internet use in the country, mainly limiting access to social media.
In its counter-offensive operation, Azerbaijan mobilised staff and tank units with the support of artillery and missile troops, front-line aviation and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), the ministry's press release statement said. Moreover, according to agreement with the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, a number of Syrians from jihadist groups, from Turkish-backed factions, are fighters in Nagorno-Karabakh. This has been corroborated by Russian and French sources. In any case, it would not be surprising when Turkey sits alongside Azerbaijan.
For its part, Armenia blames Azerbaijan for starting the fighting. Armenian officials announced that the Azerbaijani army had attacked with rocket-propelled grenade launchers and missiles. Armenia has not stopped preparing, as in the weeks leading up to the start of the fighting, multiple shipments of Russian weapons had been detected in the country via heavy transport flights. On the other hand, Armenia's defence minister has accused Turkey of exercising command and control over Azerbaijan's air operations via Boeing 737 Airborne Early Warning & Control aircraft , as Turkey has four of these planes.
Triggers
Both powers were on alert because of the July fighting. Since then, they have not abandoned military preparedness at the hands of their external allies. The current events cannot therefore be described as coming out of the blue. After the July outbreak, there has been a lingering sense that the armed confrontation had simply been left at Fail.
Hours after the outbreak of fighting, Armenia declared martial law and general mobilisation. Azerbaijan, on the contrary, declared that such action was not necessary, but eventually the parliament decided to impose martial law in some regions of the country. Not only was martial law decreed, but also the Azerbaijani Ministry of Defence declared the liberation of seven villages, the establishment of a curfew in several cities and the recapture of many important heights. It is clear that all occupied territories have crucial strategic value: Azerbaijan has secured visual control of the Vardenis-Aghdara road, which connects to Armenian-occupied Karabakh. The road was completed by Armenia three years ago in order to facilitate rapid military cargo transfers, an indication that this is a strategic position for Armenia.
Drone warfare has also been present in the conflict with Turkish and Israeli drones used by Azerbaijan. Armenia's anti-drone measures are bringing Iran into the picture.
An important factor that may have led to the conflict has been changes in the diplomatic leadership in Baku. Elmar Mammadyarov, Azerbaijan's foreign minister, left his position during the July clashes. He has been replaced by former Education minister Jeyhun Bayramov, who does not have much diplomatic experience. Meanwhile, Hikmet Hajiyev, the Azerbaijani president's foreign policy advisor has seen his role in these areas increase.
But the problem is not so much about new appointments. For the past few years, Mammadyarov was the biggest optimist about the concessions Armenia might be willing to make under Nikol Pashinyan's new government. Indeed, since Armenia's Velvet Revolution, which brought Pashinyan to the post of prime minister in 2018, Azerbaijan had been hopeful that the conflict could be resolved. This hope was shared by many diplomats and experts in the West. Moreover, even within Armenia, Pashinyan's opponents labelled him a traitor because, they claimed, he was selling out Armenia's interests in exchange for Western money. All this hope for Armenia disappeared, as the new Armenian prime minister's position on Nagorno-Karabakh was harsher than ever. He even declared on several occasions that "Karabakh is Armenia". All this led to a strengthening of Azerbaijan's position, which hardened after the July clashes. Baku has never ruled out the use of force to try to solve the problem of its territorial integrity.
In the 2016 conflict there were many efforts to minimise these armed disturbances, mainly by Russian diplomacy. These have been supported by the West, which saw Moscow's mediation as positive. However, negotiations between Armenia and Azerbaijan have not resumed, and the excuse of the coronavirus pandemic has not been very convincing, according to domestic media.
More points have led to the current escalation, such as increased Turkish involvement. After the July clashes, Turkey and Azerbaijan conducted joint military exercises. Ankara's representatives began to talk about the ineffectiveness of the peace process, and Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan, speaking last month at the UN General Assembly, described Armenia as the biggest obstacle to long-term peace deadline in the South Caucasus. This is not to say that Turkey provoked the new escalation, but it certainly helped push Azerbaijan into a more emboldened attitude. The Turkish president stated on Twitter that 'Turkey, as always, stands with all its brothers and sisters in Azerbaijan'. Moreover, last August, Azerbaijan's defence minister said that, with the Turkish army's financial aid , Azerbaijan would fulfil 'its sacred duty', which can be interpreted as the recovery of lost territories.
International importance
In a brief overview of the allies, it is worth mentioning that the Azeris are a majority ethnic Turkic population, with whom Turkey has close ties, although unlike the Turks, most Azeris are Shia Muslims. As for Armenia, Turkey has no relations with Armenia, as the former is a largely Orthodox Christian country that has historically always relied on Russia.
As soon as the hostilities began, several states and international organisations called for a ceasefire. For example, Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov, in a telephone conversation with his Armenian counterpart Zohrab Mnatsakanyan, called for an end to the fighting and declared that Moscow would continue its mediation efforts. Meanwhile, as it did after the July clashes, Turkey again expressed through various channels its plenary session of the Executive Council support for Azerbaijan. Turkey's Foreign Ministry assured that Ankara is ready to help Baku in any way it can. The Armenian president, hours before the start of the fire, mentioned that a new conflict could "affect the security and stability not only of the South Caucasus, but also of Europe". US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo expressed serious concerns and called on both sides to stop the fighting.
On the other hand, there is Iran, which is mainly Shia and also has a large ethnic Azeri community in the northwest of the country. However, it has good relations with Russia. Moreover, having borders with both countries, Iran has offered to mediate peace talks. This is the focus of Iran's current problem with the new conflict. Azeri activists called for protests in Iranian Azerbaijan, which is the national territory of Azeris under Iranian sovereignty, against Tehran's support for Armenia. The arrests carried out by the Iranian government have not prevented further protests by this social sector. This response on the streets is an important indicator of the current temperature in northwest Iran.
As for Western countries, France, which has a large Armenian community, called for a ceasefire and the start of dialogue. The US said it had contacted both sides to urge them to "cease hostilities immediately and avoid words and actions of little consequence financial aid".
Russia may have serious concerns about the resumption of full-scale hostilities. It has made it clear on multiple occasions that the important thing is to prevent the conflict from escalating. One reason for this insistence may be that the Kremlin already has open fronts in Ukraine, Syria and Libya, in addition to the current status in Belarus, and the poisoning of Alexei Navalni. Moreover, despite the current attempt by the presidents of Russia and Turkey to show that relations between their countries are going well, the discrepancies between them, such as their views on Syria and Libya, are growing and becoming more diverse. And now Vladimir Putin could not leave Armenia in the hands of Azerbaijan and Turkey.
The Minskgroup of the Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) has as its main mission statement mediation of peace negotiations between Armenia and Azerbaijan, and is co-chaired by Russia, France and the United States. In response to the current conflict, it called for a "return to a ceasefire and resumption of substantive negotiations". Earlier this year, Armenia rejected the Madrid Principles, the main conflict resolution mechanism proposed by group in Minsk. Moreover, this initiative has been made increasingly impossible by the Armenian Defence Ministry's concept of a "new war for new territories", as well as Nikol Pashinyan's idea of Armenia-Karabakh unification. All this has infuriated the Azeri government and citizens, who have increasingly criticised the Minsk group . Azerbaijan has also criticised the group 's passivity in the face of what it sees as Armenia's inflammatory actions, such as the relocation of Karabakh's capital to Susa, a city of great cultural importance for Azerbaijanis, or the illegal settlement of Lebanese and Armenians in occupied Azerbaijani territories.
If any conclusion is to be drawn from this it is that, for many in both Azerbaijan and Armenia, the peace process has been discredited by the past three decades of failed negotiations, prompting increasing warnings that the status quo would lead to a further escalation of the conflict.
There is growing concern among some experts that Western countries do not understand the current status and the consequences that could result from the worst flare-up in the region in years. The director of the South Caucasus Office at the Heinrich Boell Foundation, Stefan Meister, has argued that the fighting between these two regions could go far. In his opinion, "the conflict is underestimated by the EU and the West".
The EU has also taken a stand. It has already order to Armenia and Azerbaijan to de-escalate cross-border tensions, urging them to stop the armed confrontation and to refrain from actions that provoke further tension, and to take steps to prevent further escalation.
The conflict in the Caucasus is of great international importance. There are regular clashes and resurgences of tensions in the area. The relevance is that any escalation of violence could destabilise the global Economics , given that the South Caucasus is a corridor for gas pipelines from the Caspian Sea to world markets, and more specifically to Europe. If Armenia decides that Azerbaijan has escalated too far, it could attack Azerbaijan's South Caucasus Pipeline, which sends gas to Turkey's TANAP, and ends with TAP, which supplies Europe. Another strategic aspect is the control of the city of Ghana'a, as controlling it could connect Russia to Karabakh. In addition, control of the site could cut off gas pipeline connectivity between Azerbaijan, Georgia and Turkey. Conflicts already took place at area last July, which is why Azerbaijan is prepared to close the region's airspace as a result of the new conflict.
![In bright green, territory of Nagorno-Karabakh agreed in 1994; in soft green, territory controlled by Armenia until this summer [Furfur/Wikipedia]. In bright green, territory of Nagorno-Karabakh agreed in 1994; in soft green, territory controlled by Armenia until this summer [Furfur/Wikipedia].](/documents/16800098/0/nagorno-karabaj-mapa.jpg/112d46eb-041d-b714-85b0-10a262216ce3?t=1621884663387&imagePreview=1)
In bright green, territory of Nagorno-Karabakh agreed in 1994; in soft green, territory controlled by Armenia until this summer [Furfur/Wikipedia].
A new war?
There are several possible outcomes for the current status . The most likely is a battle over small and not particularly important areas, allowing for the symbolic declaration of a "victory". The problem centres on the fact that each opponent may have a very different view of things, so that a new strand of confrontation is inevitable, raising the stakes of the conflict, and leading to less chance of understanding between the parties.
Although unlikely, many analysts do not rule out the possibility that the current escalation is part of the preparations for negotiations and is necessary to shore up diplomatic positions and increase pressure on the opponent before talks resume.
Whatever the reasoning behind the armed clashes, one thing is clear: the importance of military force in the Nagorno-Karabakh peace process is growing by the day. The absence of talks is becoming critical. If the Karabakh pendulum does not swing from generals to diplomats soon, it may become irreparable. And it will be then that the prospects of another regional war breaking out once again will cease to be a mere scenario described by experts.
While Russia continues to insist that there is no other option but a peaceful way forward, the contact line between the two sides in Nagorno-Karabakh has become the most militarised area in Europe. Many experts have repeatedly suggested as a possible scenario that Azerbaijan might decide to launch a military operation to regain its lost territory. source The country, whose main source of income is its Caspian Sea oil wealth, has spent billions of dollars on new weaponry. Moreover, it is Azerbaijan that has replaced Russia as the largest carrier of natural gas to Turkey.
A major consequence of the conflict centres on potential losses for Russia and Iran. A further casualty of the conflict may be Russia's position as Eurasia's leader. Another argument is based on the Turkish committee , which has demanded Armenia's withdrawal from Azerbaijani lands. The problem is that the members of committee, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan, are also members of the Collective Security Treaty Organisation (CSTO), led by Russia together with Armenia. On the other hand, Iran sample also panics over Turkey's total solidarity with Azerbaijan, as more Azeris live in Iranian Azerbaijan than in the Republic of Azerbaijan.
This is one of the many conflicts that exemplify the new and current "style" of warfare, where major powers place themselves at the back of small conflicts. However, the territory of Nagorno-Karabakh may be small in size, but not in importance, as in addition to contributing to the continued destabilisation of the Caucasus area , it may affect neighbouring powers and even Europe. The West should give it the importance it deserves, because if it continues along the same lines, the door is open to a more violent, extensive and prolonged armed conflict.
France and Germany move closer to Poland as the third hard core country, rather than adding Italy or Spain.
Leaving aside criticism of Polish judicial reforms in recent years, Paris and Berlin are seeking a special cooperation Degree with Poland so that it does not act as the European gateway to Washington's influence that the UK used to be. For the French and Germans, Poland seems a more reliable partner than Italy and Spain, whose political instability complicates the elaboration of medium- and long-term security and defence strategies deadline.
![Macron with the Polish President and Prime Minister during his visit visit to Warsaw in February 2020 [Elysée Palace]. Macron with the Polish President and Prime Minister during his visit visit to Warsaw in February 2020 [Elysée Palace].](/documents/10174/16849987/triangulo-weimar-blog.jpg)
Macron with the Polish President and Prime Minister during his visit in Warsaw in February 2020 [Elysée Palace].
article / Jokin de Carlos Sola
The European committee is perhaps the most important body in the EU. It is in charge of setting objectives, it sets the diary to the Parliament and the Commission. It is in this body that the states are represented as such and where issues such as the weight of each country's population and Economics take on particular importance.
France and Germany thus achieve their high profile on the European committee , where their ideological influence over other European governments also translates into unofficial leadership of the Union. Both countries have sought to establish a special cooperation Degree with Poland in order to gain influence over one of the countries with the next largest population and thereby reduce the presence of the United States in Europe. This three-way partnership is embodied in the Weimar Triangle.
On the other hand, Brexit has opened an unofficial degree program to find out who will be the third most influential country in the European Union. All this at a time when politicians such as Emmanuel Macron and Ursula von der Leyen are calling for the strengthening of a common foreign policy. The Netherlands, under Mark Rutte, has sought such a position through alliances with ideologically like-minded countries in the so-called New Hanseatic League. However, Poland also seems to have supporters for the post. Two of the larger countries, Italy and Spain, seem to have fallen out of the degree program .
Recovering a forgotten idea
The Weimar Triangle was born in 1991, with the aim of helping Poland to emerge from communism. goal . In that year a meeting was held between the foreign ministers of the three countries: Roland Dumas, Hans-Dietrich Genscher and Krzysztof Skubiszewski. With this meeting, Poland managed to get France and Germany to give it special consideration among the European countries that had been on the other side of the Iron Curtain and were soon to join NATO and later the EU (Poland joined the Atlantic Alliance in 1999 and the EU in 2004).
Since then, representatives of the three governments have met relatively frequently. By 2016 there had been eight summits of heads of state, as well as 23 meetings of foreign ministers and two meetings of defence ministers. In 2013 the three countries decided to form a battalion under EU command (one of 18), under the name group Combat Weimar or Weimar Battalion, composed of officers and soldiers from the three countries.
Since 2015, however, relations began to cool as Poland's more Atlanticist and less tolerant Law and Justice party came to power. In 2016 Polish Foreign Minister Witold Waszczykowski went so far as to declare that the Weimar Triangle was of no great importance to his country. In the same year there was an attempt to revive tripartite cooperation with a meeting of the three foreign ministers to address issues such as Brexit or the refugee crisis, but without much success.
Over the next three years, cooperation declined and there was French and German criticism of the Polish government. The replacement of Waszczykowski moderated the demonstrations in Warsaw, but relations were not as smooth as they had been at the beginning. Poland's unease towards Berlin was mainly due to the construction of Nord Stream 2 (the doubling of the gas pipeline directly linking Germany and Russia); the distrust of Paris was due to its apparent sympathy with Moscow. For its part, especially after Macron's arrival at the Elysée, France began to distrust Poland because of its close relationship with Washington.
From 2019 onwards, however, a new rapprochement began to emerge. France came to believe that it was better to keep Poland close and thus keep the US at arm's length, while Poland felt that it could actually make its proximity to France and Germany compatible with US military support to defend itself against Russia. In February 2020 Macron visited Warsaw and met with President Duda and Prime Minister Morawiecki to improve relations between the two countries and revive the Triangle idea.
Marginalisation of Spain and Italy
It may come as a surprise that Germany and France look to Poland rather than wanting to rely more on Italy or Spain, countries not only with larger populations but also larger economies. But the reasons are clear. Despite the divergences in foreign policy between France and Poland, it is undeniable that the Slavic country is able to offer something that neither Spain nor Italy can provide: stability. Since 2016, the two Mediterranean countries have been experiencing one domestic political crisis after another, forcing their governments to keep foreign policy issues on the back burner.
In Spain, no government has had an absolute majority in Parliament since 2015, and that is not likely to change. Between 2015 and 2019 there have been four general elections and two prime ministers. This status makes it difficult to pass laws, including the fundamental budget, without which no foreign policy compromise can be expected.
In Italy the beginning of the tornado began with the fall of Matteo Renzi at the end of 2016. Since then the country has seen two prime ministers and three governments. This may not be surprising in the Italian case, but certainly the perceived instability is now greater. Moreover, there is distrust from other European partners over Italy's dealings with China over the New Silk Road, something that is generally more worrying than Poland's flirtations with the US. In geopolitical terms, the possibility of a political crisis making Salvini, who has not been subtle in his admiration for Putin's Russia, prime minister is also a cause for concern.
In contrast, despite a change of prime minister and cabinet in 2018, Poland has shown a clear foreign policy line since Law and Justice came to power, as well as steady economic growth. After the victory in the 2019 elections, everything seems to indicate that Mateusz Morawiecki will remain prime minister until at least 2023. Such policy durability makes Poland a more attractive ally, despite tensions over Poland's controversial judicial reforms.
Moreover, coordination with Poland offers Paris and Berlin a way to further integrate the former Soviet bloc countries into EU decision-making.
Three visions
However, the desire to create a cooperative body within the Weimar Triangle is a real challenge challenge, as each country represents, in one way or another, one of three of the foreign policy agendas that divide Europe.
At one end of the spectrum is French Gaullism, which advocates an independent Europe and is wary of a US presence in Europe, remembering that France already has a strong military. Paris abandoned this perspective for an Atlanticist one in 2007 under Sarkozy, but it has been regained by Macron. This means that Macron's rhetoric could lead to clashes with the Americans, while he also seeks to mark profile himself against Moscow and Beijing.
In the middle is German pragmatism: Germany does not want to increase conflict and prefers to focus on its Economics. On the one hand it is negotiating with the Russians to receive gas for its industrial activity, and on the other it wants US troops to remain on its territory, as their departure would force it to increase its security expense . In Europe's plans for recovery from the Covid-19 pandemic, Germany has clearly been more absent, with Macron taking the lead.
Finally, we find Polish Atlanticism. Poland is perhaps the most Atlanticist country in the EU. Even under the Trump Administration there has been a high level of pro-Americanism among the population and the political class . The government has pushed for the hosting of a US base and Defence Minister Mariusz Błaszczak has enthusiastically praised the role of the US as a defender of the free world. This is nothing new, as the 2003 invasion of Iraq was supported by Poland in the face of French and German rejection. Poland continues to see Russia as its greatest threat and the US and NATO as guarantors of protection.
The Triangle returns
Its geographical status explains Poland's position and it will not stop wanting NATO's instructions on its territory. However, it understands that it needs close allies with greater internal stability - hence its rapprochement with Germany and France - than that offered by the Trump Administration, whose international image is badly damaged, or a United Kingdom more occupied with managing Brexit than security issues.
On the other hand, Macron wants to avoid Poland replacing the UK as the representative of US policy in Europe, so he has changed his strategy to avoid alienating it by criticising its judicial reforms. Macron did not mention them in his visit to Warsaw in February this year and only encouraged 'respect for European values'. Somehow Macron understands that after Brexit he will need Poland to advance his European foreign policy plans, and that is why it is important to bring it to the conference room helm. Macron went so far as to say in Warsaw that Poland, Germany and France should lead the Union post-Brexit. He also announced the dispatch of 600 more men to Poland, which will bring the number of French soldiers in the country to 5,100.
At meeting, both leaders agreed to meet with German Chancellor Angela Merkel, although the limitations imposed by the coronavirus pandemic have slowed down some contacts, while also waiting for Economics to begin to recover. The newly inaugurated German presidency of committee , moreover, discourages Berlin from appearing overly aligned with a certain European vector. The Weimar Triangle may therefore hibernate temporarily; in any case, although this is a risky formula, if coordinated with the Parliament and the Commission, its consolidation could represent a step forward in European cohesion and governance.
