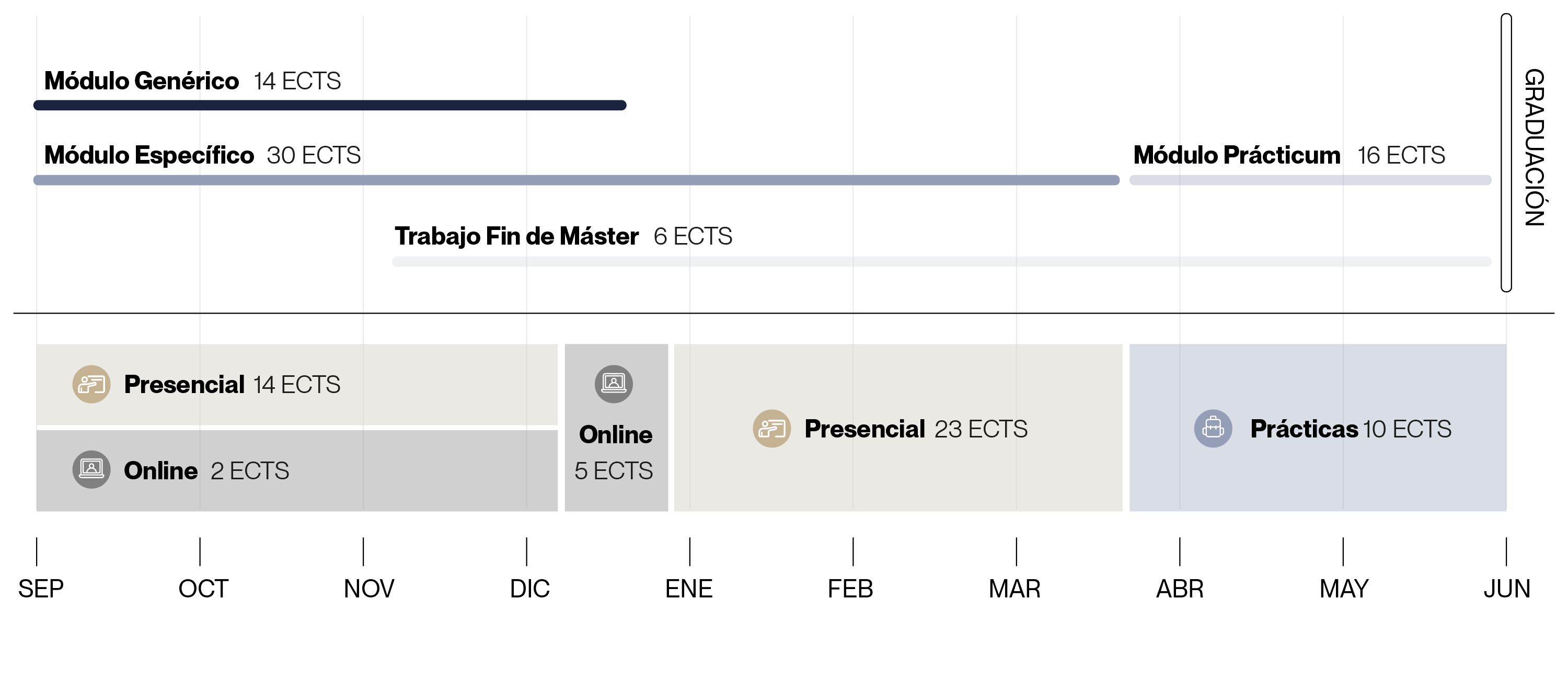
Structure
We combine complementary methodologies and learning strategies to achieve the best results through:
-
We combine complementary methodologies and learning strategies to achieve the best results through:
-
Theoretical face-to-face sessions: dynamic expository sessions based on interaction and prior preparation by the students according to the Materials distributed for each session.
-
Practical face-to-face classes: case studies, seminars, role-plays.
-
Special sessions with invited professionals in lecture format-colloquium.
-
Short specialised workshops, at position by professionals, on specific thematic aspects of Study program or on the use of certain techniques or strategies.
-
Non-attendance work (programmes, diagnostic reports, curricular adaptations, etc.) either individually or in small groups.
-
Practicum: practical placements (approximately two months) in schools and colleges, tutored by a teacher from the school (10 ECTS credit).
-
Completion by the student of a project or Master's thesis, including the oral and public defence of the work (6 ECTS credit).
-
Each student will have a advisor at the University (in addition to the tutor practicum) who will accompany them throughout the master's degree to guide their learning and focus their future professional insertion.
The Seminars of innovation in education have as goal to deepen in innovative teaching proposals in different areas (good practices), making known to student innovative actions, identifying challenges related to the process of teaching-learning.
These seminars have been designed with an eminently practical focus, with the aim of enabling participants to acquire, update or generate the strategies or principles they need in their professional development .
Seminar speakers are qualified professionals from public and private organisations and institutions.
Specialities
module II, Human and Social Sciences, focuses on the teaching specialties of Geography and History and Philosophy. In both cases, the aim is to analyze the educational value of these disciplines, while at the same time introducing the resources and techniques for their learning and teaching, the use of information resources and technologies and acquiring the necessary skills to carry out a didactic program. The student is introduced to the identification of problems related to teaching and, as a complement to what has already been seen in module I, it is intended to deepen in the "Content and Language Integrated Learning" (CLIL).
Module III, Languages and Literatures, focuses on the teaching specialities of language Spanish and Literature and Latin and Greek. In both cases, the aim is to analyse the educational value of these disciplines, while at the same time introducing the resources and techniques for their learning and teaching, the use of information resources and technologies, and acquiring the necessary skills to carry out a didactic programme. Lastly, basic competences related to research and the professional development are worked on .
Module IV, Experimental and Natural Sciences, focuses on the didactic aspects of three of the secondary school teaching specialities (Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry, and Biology and Geology). In addition to analysing the educational value of the disciplines, the aim of this module is to study in depth the resources and techniques for learning and teaching them, especially the experience of working on laboratory, on the knowledge of the curricula, on the use of information resources and technologies, and to acquire the necessary skills to carry out a didactic programme. In addition, student is introduced to the identification of problems related to teaching-learning and basic competences related to research and professional development are worked on. The subject "Content and Language Integrated Learning" (CLIL), which may subsequently constitute the context professor of their future teaching in education.
The module V. teaching of Languages, taught at Spanish and English, provides the student with knowledge in applied linguistics necessary for language teachers, in the history and developments of the teaching of languages, within the guidelines of the common European framework of reference letter, with special attention to the analysis of the internship professor and of the research at the classroom.
This module pays special attention to the training for teaching in Education compulsory secondary education, to the design of didactic activities, to the analysis of the internship professor and to the principles of assessment on the area of languages.
After providing basic training in the process of language acquisition and learning in general, and in the relevance of English as a language of international communication language , this Module focuses on teaching in the school context, considering development of the four fundamental skills (oral and written comprehension, oral and written expression), and of grammar and vocabulary. At the same time, it enables student to design teaching activities, programme content and assess language learning in its different facets.
It introduces the subject "Content and Language Integrated Learning" (CLIL), which can then form the context professor for future teaching in education.
Module VI. Educational Guidance, aimed primarily at pedagogues, psychologists and graduates in education studies (early childhood and primary education), aims to learn about the processes and resources for the prevention of learning problems, coexistence, evaluation problems and academic and professional guidance. It introduces student to communication techniques in guidance processes.
MUP Modules
Module I is common and compulsory for all students. It aims to introduce students to issues of psychology and development of personality in adolescence, to educational processes and contexts and to the context partner-family educational.
In addition, it studies the evolution of model educational up to the present day, introduces issues related to school guidance, emphasises the importance of the role of the family and society in the field educational and reflects on the codes of ethics and their formative potential for professor.
|
Module I: Generic General Educational Aspects |
ECTS CREDIT |
|
|
subject |
subject |
14 |
|
Personality learning and development |
2 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
Educational processes and contexts |
2 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
Society, family and education |
2 |
|
|
2 |
||
It focuses on the teaching specialties of Geography and History and Philosophy.
In both cases, the aim is to analyse the educational value of these disciplines, while at the same time introducing the resources and techniques for their learning and teaching, the use of information resources and technologies and acquiring the necessary skills to carry out a didactic programme.
|
Module II: Humanities and social sciences fields |
ECTS CREDIT |
|
|
subject |
subject |
30 |
|
Complements for disciplinary training |
3 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
Learning and teaching the subjects of the specialization program |
4 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
Innovation professor and initiation in educational research |
2 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
Module III focuses on the teaching specialities of language Spanish and Literature and Latin and Greek. As in the previous case, the aim is to deepen its formative nature and train in the use of teaching methodologies, in the use of ICT and in acquiring the skills to carry out a didactic programme.
|
Module III: Fields of languages and literatures |
ECTS CREDIT |
|
|
subject |
subject |
30 |
|
Complements for disciplinary training |
3 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
Learning and teaching the subjects of the specialization program |
4 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
Innovation professor and initiation in educational research |
2 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
Module IV, like the previous modules, focuses on the didactic aspects of three of the secondary school teaching specialities (Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry, Biology and Geology).
In this module, in addition to analysing the educational value of the disciplines, the aim is to study in depth the resources and techniques for their learning and teaching, especially the experience of working in laboratory, in the knowledge of the curricula, in the management of resources and information technologies and the necessary skills to carry out didactic programming are acquired. In addition, student is introduced to the identification of problems related to teaching-learning.
|
Module IV: Fields of Experimental and Natural Sciences |
ECTS CREDIT |
|
|
subject |
subject |
30 |
|
Complements for disciplinary training |
3 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
Learning and teaching the subjects of the specialization program |
4 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
Innovation professor and initiation in educational research |
2 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
Taught in Spanish and English, it provides the student with knowledge in applied linguistics necessary for language teachers, in the history and developments of language teaching, within the guidelines of the Common European Framework of Reference framework , with special attention to the analysis of practice professor and research at classroom.
|
Module V: Language teaching |
ECTS CREDIT |
|
|
subject |
subject |
30 |
|
Complements for disciplinary training |
3 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
Learning and teaching the subjects of the specialization program |
4 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
Innovation professor and initiation in educational research |
2 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
Module VI, aimed primarily at pedagogues, psychologists and graduates in education studies (early childhood and primary education), aims to learn about the processes and resources for the prevention of learning problems, coexistence, assessment problems and academic and professional guidance. It introduces student to communication techniques in guidance processes.
|
Module I: Generic General Educational Aspects |
ECTS CREDIT |
|
|
subject |
subject |
15 |
|
Personality learning and development |
2 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
Educational processes and contexts |
Educational Guidance: Intervention programs for the prevention and development |
2 |
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
Society, family and education |
2 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
Module VI: Educational Guidance |
ECTS CREDIT |
|
|
subject |
subject |
30 |
|
The fields of educational guidance and counselling |
1 |
|
|
2,5 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
Educational guidance processes and psycho-pedagogical counselling |
1 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
Inclusive education and attention to diversity |
3 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
1,5 |
||
|
Educational research and innovation and the management of change |
2 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
Innovation for Teaching and Learning (Module IB or Communication Strategies/CALEC) |
2 |
|
|
Module VII. Practicum |
ECTS CREDIT |
|
|
subject |
subject |
16 |
|
Practicum |
10 |
|
|
6 |
||
Module VII, which is common and compulsory for all students, is of particular importance as not only student can reflect the competences acquired, but it also puts the Master's students on contact with the reality of education and provides direct experience of various aspects of secondary education, vital for their subsequent professional development .
The internships account for a total of 10 credits ECTS credit.
For its implementation, signature has already signed an agreement with the Government of Navarre's department de Educación, and is open to signature of agreements with educational administrations in other autonomous communities.
|
Module VII. Practicum |
ECTS CREDIT |
|
|
subject |
subject |
16 |
|
Practicum |
10 |
|
|
6 |
||
The internship is part of module VII PRACTICUM, common and mandatory for all students. The internship has a total of 10 credits ECTS credit.
It is particularly important because not only can student reflect the skills acquired in a job, but it also puts the Master's students on contact with the reality of education and provides direct experience of various aspects of secondary education, vital for their subsequent professional development .
For its implementation, signature has already signed an agreement with the Government of Navarre's department de Educación, and is open to signature of agreements with educational administrations in other autonomous communities.
The Master's thesis consists of 6 ECTS credit and consists of a research project, reflecting some of the competences acquired in the Master's degree. The student must show their learning and reflection on their acquisition.
Specifically, the Master's thesis must reflect the following competences:
- Gain experience in the planning, teaching and evaluation of subjects corresponding to the specialisation.
- Demonstrate a good command of oral and written expression in practice professor.
- Master the social skills and abilities necessary to foster a climate that facilitates learning and coexistence.
- Participate in proposals for improvement in the different areas of action based on reflection based on practice.
- With regard to guidance, practice in psycho-pedagogical assessment, counselling other education professionals, students and families.
At the beginning of the work, the objectives and the evaluation criteria as well as the weight that the different activities will have in the final grade will be clearly and transparently communicated.
Each student will have a tutor to guide them in the elaboration of their work.
The Master's thesis must be distinct from the report and the reports or evaluations of the Practicum of the Master's degree. If a student is interested in doing a Master's thesis related to Practicum, it should be organised with Tutor in such a way that these two different areas of the Master's programme fulfil their respective objectives.
The Master's Thesis will be assessed by means of a public defence by student.
YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN
REGULATIONS
- Rules and regulations of permanence in the programs of study of Degree
- Rules and regulations of permanence in the programs of study of Master's Degree
- Rules and regulations of credit recognition for Degree
- Rules and regulations of credit recognition for Master's Degree
- Rules and regulations of Credit Recognition for Technician of training Profesional
- Rules and regulations University Basics
- Rules and regulations general about assessment