U.S. LNG sales to its neighbors and exports from Latin American and Caribbean countries to Europe and Asia open new perspectives
Not depending on gas pipelines, but being able to buy or sell natural gas also to distant countries or countries without land connections, improves the energy prospects of many nations. The success of fracking has generated a surplus of gas that the U.S. has begun to sell to many parts of the world, including its hemispheric neighbors, which in turn have a wider choice of provider. In turn, being able to submit gas in tankers has expanded the customer portfolio of Peru and especially Trinidad and Tobago, which until last year were the only two American countries, apart from the US, with liquefaction plants. Argentina was added to them in 2019 and Mexico has driven investments in 2020 to join this revolution.
![A liquefied natural gas (LNG) freighter [Pline]. A liquefied natural gas (LNG) freighter [Pline].](/documents/16800098/0/gas-natural-blog.jpg/bc7b4699-c26c-a2d1-2971-f57cbb0345b8?t=1621873574093&imagePreview=1)
▲ A liquefied natural gas (LNG) freighter [Pline].
article / Ann Callahan
The United States is connected by pipeline only with Canada and Mexico, but is selling gas by ship to some thirty other countries (Spain, for example, has become a major buyer). In 2019, the US exported 47.5 billion cubic meters of liquefied natural gas (LNG), of which one-fifth went to American neighbors, agreement to the BP 2020report on the sector.
Eight countries in Latin America and the Caribbean already have regasification plants for gas arriving by cargo ship in liquid form: there are three plants in Mexico and Brazil; two in Argentina, Chile, Jamaica and Puerto Rico, and one each in Colombia, the Dominican Republic and Panama, according to the annual summary of the association of LNG importing countries. LNG arrives to these countries not only from the USA, but also from Norway, Russia, Angola, Nigeria and Indonesia. Two countries export LNG to various parts of the world: Trinidad and Tobago, which has three liquefaction plants, and Peru, which has one (another became operational in Argentina last year).
In an attempt to mitigate the risk of electricity shortages due to a drop in hydroelectric production due to drought or other difficulties in accessing energy sources, many countries in Latin America and the Caribbean are turning to LNG. As a cleaner energy source, it is also an attractive option for countries already struggling with climate change. In addition, financial aid gas financial aid overcome the discontinuity of alternative sources, such as wind and solar power.
In the case of small island countries, such as those in the Caribbean, which for the most part lack energy sources, cooperation programs for the development of LNG terminals can provide them with a certain independence from certain oil supplies, such as the influence exerted on them by Chavista Venezuela through Petrocaribe.
LNG is natural gas that has been liquefied (cooled to about -162°C) for storage and transportation. The Issue of natural gas in its liquid state is reduced by approximately 600 times compared to its gaseous state. The process makes it possible and efficient to transport it to places that cannot be reached by pipelines. It is also much more environmentally friendly, as the carbon intensity of natural gas is about 30% less than that of diesel or other heavy fuels.
The global natural gas market has evolved rapidly in recent years. Global LNG capacities are expected to continue to grow until 2035, led by Qatar, Australia and the US. According to BP's report on the sector, in 2019 the share of gas in primary energy reached an all-time high of 24.2%. Much of the growth in gas production in 2019, when it increased by 3.4%, was due to additional LNG exports. Thus, last year LNG exports grew by 12.7% to 485.1 billion cubic meters.
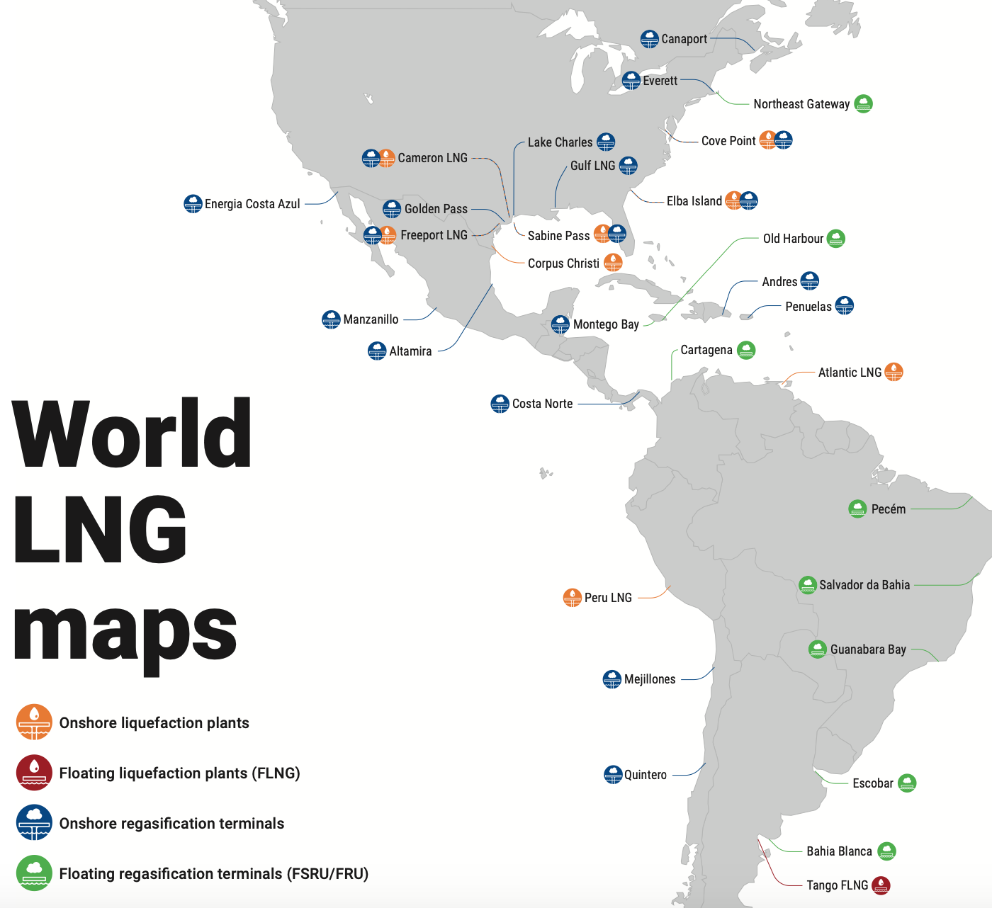
Liquefaction and regasification plants in the Americasreport GIIGNLreport ].
Boom
While the United States lagged behind in gas production at the beginning of the first decade of this century, the shale boom since 2009 has led the US to exponentially increase gas extraction and play a key role in the global trade of the liquefied product. With the relatively easy transportation of LNG, the US has been able to export and ship it to many parts of the world, with Latin America, due to its proximity, being one of the regions that are noticing this change the most. Of the 47.5 billion cubic meters of LNG exported by the US in 2019, 9.7 billion went to Latin America; the main destinations were Mexico (3.9 billion), Chile (2.3 billion), Brazil (1.5 billion) and Argentina (1 billion).
Although the region has promising export potential, given its proven natural gas reserves, its demand exceeds production and it must import. Venezuela is the country with the largest reserves in Latin America (although its gas power is smaller than its oil power), but its hydrocarbon sector is in decline and the largest production in 2019 corresponded to Argentina, an emerging shale country, followed by Trinidad and Tobago. Brazil matched Venezuela's production, followed by Bolivia, Peru and Colombia. In total, the region produced 207.6 billion cubic meters, while its consumption was 256.1 billion.
Some countries receive gas by pipeline, as is the case of Mexico and Argentina and Brazil: the former receives gas from the USA and the latter from Bolivia. But the booming option is to install regasification plants to receive liquefied gas; such projects require some investment, usually foreign. The largest exporter of LNG to the region in 2019 was the US, followed by Trinidad and Togado, which due to its low domestic consumption practically exports all its production: of its 17,000 million cubic meters of LNG, 6,100 went to Latin American countries. The third exporting country is Peru, which destined its 5.2 billion cubic meters to Asia and Europe (it did not sell on the continent itself). Argentina joined the exports in 2019 for the first time, although with a leave amount, 120 million cubic meters, almost all of them destined to Brazil.
The region imported a total of 19.7 billion cubic meters of LNG in 2019. The main buyers were Mexico (6.6 billion cubic meters), Chile (3.3 billion), Brazil (3.2 billion) and Argentina (1.7 billion).
Some of those that imported smaller quantities then re-exported part of the supplies, as did the Dominican Republic, Jamaica and Puerto Rico, generally with Panama as the main destination.
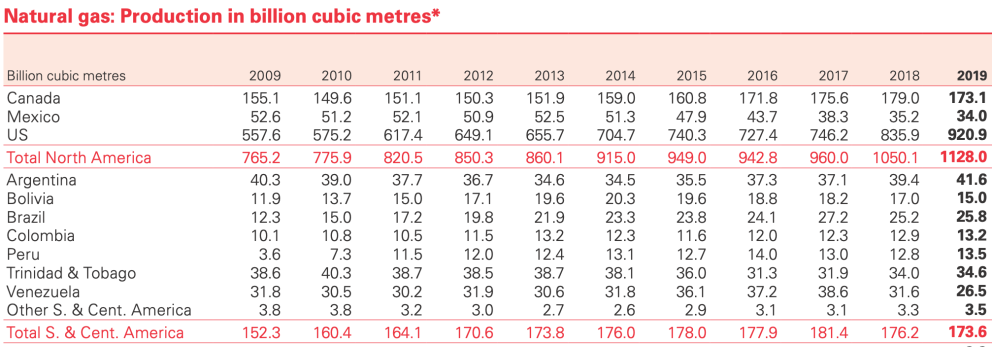
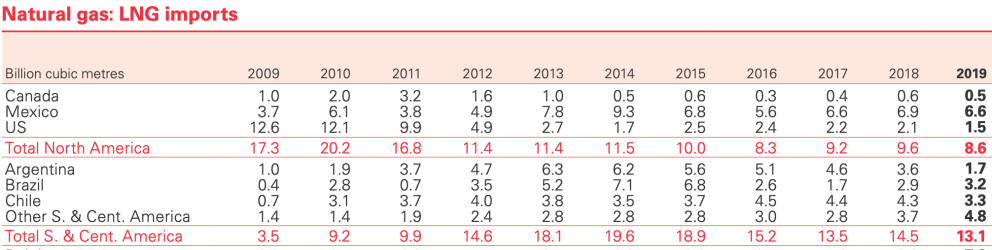
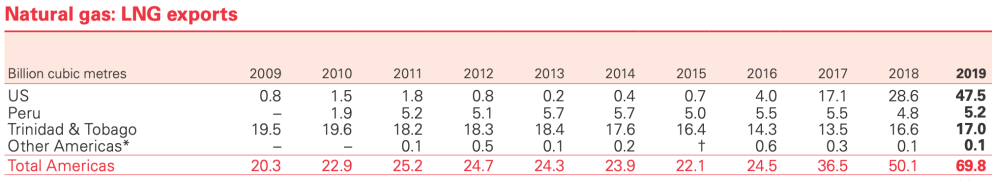
Tables extracted fromStatistical Review of World Energy 2020 report [BP].
By country
Mexico is the largest importer of LNG in Latin America; its supplies come mainly from the US. For a long time, Mexico has depended on gas shipments from its northern neighbor via pipeline. However, the development of LNG has opened up new prospects, as the country's location can help it boost both capacities: improved pipeline connections with the US can allow Mexico to have a gas surplus at Pacific terminals for re-exporting LNG to Asia, complementing the absence of liquefaction plants on the US West Coast for the time being.
The possibility of re-exporting from Mexico's Pacific coast to the large and growing Asian LNG market - without the need for tankers to pass through the Panama Canal - is a major attraction. The US department Energy granted in early 2019 two authorizations to Mexico's Energía Costa Azul project to re-export US-derived natural gas in the form of LNG to those countries that do not have a free trade agreement (FTA) with Washington, as stated in the 2020 report of the International group of Importers of Liquefied Natural Gas(GIIGNL).
During the last decade, Argentina has been importing LNG from the US; however, in recent years it has reduced its purchases by more than 20% as domestic gas production has increased thanks to the exploitation of Vaca Muerta. Those fields have also allowed it to reduce gas purchases from neighboring Bolivia and sell more gas, also by pipeline, to neighboring Chile and Brazil. In addition, in 2019 it started LNG exports from the Bahia Blanca plant.
With Argentina pumping gas to neighboring Chile, in 2019 Chilean LNG imports declined to their lowest Degree in three years, although it remains one of the important buyers from Latin America, which has switched Trinidad and Tobago to the US as a preferred provider . It should be noted, however, that Argentina's export capacity depends on the levels of domestic flows, especially during winter seasons, when widespread heating is a necessity for Argentines.
Over the past decade, Brazil' s LNG imports have varied significantly from year to year. However, it is projected to be more consistent in its reliance on LNG until at least the next decade, as renewable energy is developed. In Brazil, natural gas is largely used to back up Brazilian hydroelectric power.
In addition to Brazil, Colombia also considers LNG as an advantageous resource to back up its hydroelectric system in low periods. On its Pacific coast, Colombia is currently planning a second regasification terminal. Ecopetrol, the state-owned hydrocarbons business , will allocate US$500 million to unconventional gas projects in addition to oil. Along with the government's authorization to allow fracking, currently stagnant reserves are projected to increase.
Bolivia also has significant natural gas production potential and is the country in the region whose Economics is most dependent on this sector. It has the advantage of existing infrastructure and the size of neighboring gas markets; however, it faces the production skill of Argentina and Brazil. Also, being a landlocked country, it is limited in the commercialization of LNG.
Although Peru is the seventh largest producer of natural gas in the region, it has become the second largest exporter of LNG. Lower domestic consumption, compared to other neighboring markets, has led it to develop LNG exports, reinforcing its profile as a nation focused on Asia.
For its part, Trinidad and Tobago has adapted its gas production to its status as an island country, and therefore bases its hydrocarbon exports on tankers, which gives it access to distant markets. It is the leading exporter in the region and the only one with customers in all continents.