Examination of the reformulation of Castro's economic model attempted by Fidel's successor
Next April, a year and a half after Fidel Castro's death, his brother Raul plans to leave the presidency of Cuba, where he has been for a decade. His bequest is the attempt to extend the Castro regime in time by means of the forced economic reorganization of the island. But the restrictions of the reforms themselves, the slowness of their implementation and the fact that they are not accompanied by greater political freedom, have limited the effect of the changes. In any case, they may be a good starting point for the next president, if he really wants to move towards a full opening.
article / Valeria Vásquez
Raúl Castro replaced his brother Fidel as president of Cuba's State committee in 2008. Since then, the island has undergone changes in its organization, although without abandoning its communist structure or the revolutionary principles set in motion in 1959. Upon his arrival to power, Castro made the decision to embark on a path of structural reforms to "update" the Cuban economic-social model and overcome the serious economic crisis.
As part of this program, Raúl Castro approved a series of social and economic reforms of a "transformative" nature, which tended to introduce market mechanisms, while maintaining adherence to socialist principles based on centralized planning (and without accompanying these changes with political liberalization). Revitalization was the main goal of the reforms in the economic sphere, turning around what had been a policy with a totally socialist approach and rejection of free market reforms.
Ten years after the changeover between the Castros brothers, the Cuban regime is preparing for the arrival in April of the first president from outside the family. Although it has not yet been confirmed who the new president will be, it is expected that the current vice-president, Miguel Díaz-Canel, will be the one appointed as part of a continuity.
The country is currently at a disadvantage, with the political uncertainty about the new stage that is opening, the serious economic difficulties that Venezuela (the main benefactor country of the island for more than a decade) is going through, and the truncated foreign expectations that the arrival of Donald Trump to the White House meant a year ago.
update of the economic model
Since 1959, the Cuban economic model has been based on revolutionary socialist principles. Since Raúl Castro came to power, however, a transformation process was undertaken, considered necessary to move forward an Economics that was stagnant and immersed in a serious crisis.
In reality, there was no substantial modification of the economic model , but rather an update it, maintaining the predominance of central state planning and state ownership over the laws of the free market. The goal of this process has been to guarantee the continuity and irreversibility of socialism, as stated by the Cuban authorities, as well as to promote the economic development of the country and improve the standard of living of the population.
The reform framework was approved at the VI congress of the Cuban Communist Party, held in 2011. Among other points, the approved agreements established the submission of a usufruct to peasants and cooperatives, and opened the door to the massive dismissal of hundreds of state employees. The reform guidelines, however, did not establish the specific role that the state and state-owned sector should play in the Economics.
The so-called update of the Cuban model has achieved the expansion of the market and of non-state properties, but in an Economics that continues to be conditioned by state planning, this measure continues to be inefficient, as it happened in China or Vietnam. Although state business continues to prevail (in a more decentralized form, through self-financing and without fiscal subsidies), the private sector has become more flexible, but the heavy taxes on this sector continue to hinder its development.
Land in usufruct
One of the main pillars of the Castro government's reforms was the submission in usufruct of idle state lands to peasants and cooperatives, with the purpose of reducing imports and increasing production. The usufructuaries have obtained the right to cultivate these lands and to keep what they harvest, but the State continues to maintain ownership and may terminate the contract for reasons of public interest.
The regulation was carried out through two laws: a first one, in 2008, subject to many restrictions and actually disadvantageous for farmers; and a second one, in 2012, more flexible, through which the government expanded the size of the plot (from 13 to 67 hectares), approved the planting of orchards and forests, and also allowed the construction of houses next to the land (previously prohibited).
In March 2011, the government reported that 128,000 usufructs, totaling 1.2 million hectares, had already been handed over. In any case, although the 2012 law was less restrictive than the previous one, as mentioned above, it still included certain obstacles that discouraged farmers' involvement: they recorded gains, but only after overcoming various obstacles.
Mass dismissal of civil servants and self-employment
At the beginning of 2011, the state payroll presented an "inflated" rate, with millions of state employees in precarious jobs and work conditions. For this reason, Raúl Castro promoted the dismissal of 500,000 surplus state workers between October 2010 and March 2011, which raised the unemployment rate to 12%. To counteract this measure, 250,000 self-employed jobs were created in a first stage and other private activities were also promoted.
This measure was necessary to raise labor productivity, reduce expenses and increase wages. The agreements of the 6th CCP congress allowed the approval of 178 self-employed activities: many of them were very specific and unskilled (such as forklift drivers or bath attendants), and a few were skilled (such as translators or insurance agents). This made private work more flexible.
Thus, in a country with a labor force of 5 million people, of the total of 11.2 million who reside on the island, a total of 4.2 million of those who work are state employees and the rest are located in the non-state sector, made up of agricultural cooperatives, private farmers and self-employed [1]. The latter now number 500,000 people. Despite this development of what is known in Cuba as "cuestapropismo", there are restrictions that prevent most professionals from working on their own in their profession, and this reduces the human capital available to boost the country's Economics .
Openness to foreign investment
The flow of investments from abroad has not accompanied the reforms promoted by Raúl Castro, which has been one of the major obstacles to the desired success. To attract these foreign investments, the Special development Zone Mariel (ZEDM) was inaugurated in 2013. The port of Mariel, located 45 kilometers west of Havana, was allocated a 465.4 square kilometer industrial zone and an advanced ship terminal. The purpose was to convert the ZEDM, through the existence of incentives to attract investment, into the main entrance for foreign trade and the largest industrial structure in Cuba [2]. However, four years after its inauguration, the results have not been as expected. In an administrative process that has followed an extraordinarily slow pace, today only 33 companies have C installed, which is far from the 2.5 billion dollars that the ZEDM planned to attract annually.
The restoration of diplomatic relations with Washington carried out at the end of the Obama Administration has not accelerated investments from the United States or other Western countries. In addition to the U.S. embargo remaining in place, the Trump Administration has reversed provisions passed by his predecessor that opened a timid door to greater economic engagement.
economic status
Raul Castro's reform plan has not been as successful as expected, mainly due to the Degree restriction that regulates them. The lack of the intended economic revitalization has manifested itself in the poor performance of Cuban Economics in recent years. In 2016, Cuba fell into recession, with an economic decrease of 0.9%. In 2017, it was able to recover slightly (figures not yet closed speak of a 1.6% increase in GDP) thanks to a boom in tourism and better agricultural results.
In the last decade, tourism has been precisely one of the assets of the Cuban Economics . agreement to an ECLACreport , tourism to the island grew by 11.9% in 2017, with 4.7 million visitors. This increase includes the largest issue of visits from the United States, made possible by the elimination of restrictions approved by Obama, but that Trump has reimposed.
On the other hand, Cuba maintains its chronic trade deficit. Although in 2016 it managed to reduce it to 9.6% of GDP, prospects are not good, given Venezuela's difficulties to continue supplying oil, practically on a sunk cost basis. In 2015, Venezuela was Cuba's main trading partner , with which it maintains 36% of its foreign trade, in an exchange valued at 4 billion dollars. It is followed by China, with 28%, a country that sells under soft credit conditions to the island.
|
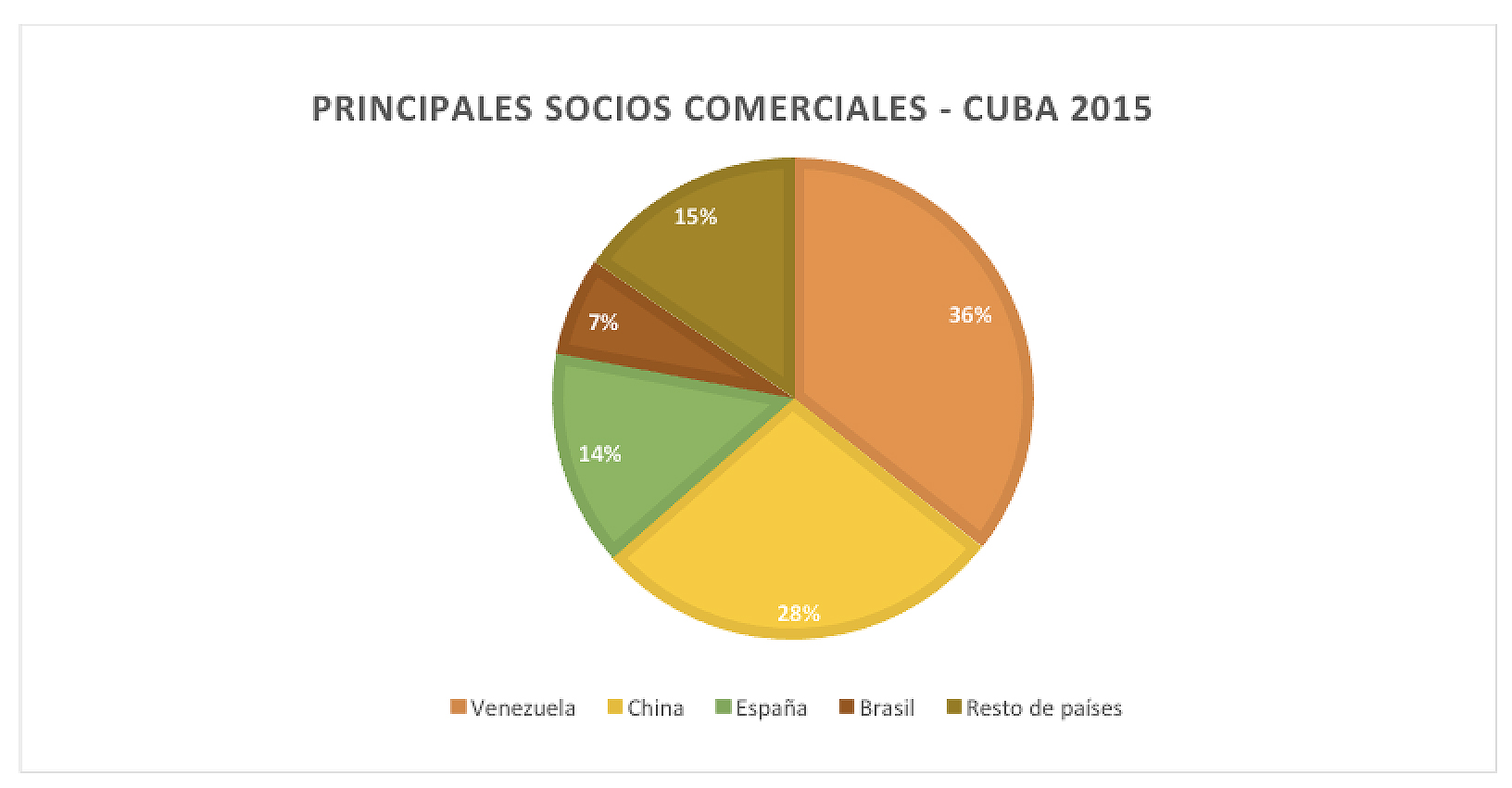
source: ONEI. 2015 Statisticalyearbook of Cuba, external sector.
|
|
bequest and new challenges
As Raúl Castro's presidency draws to a close, Cuba finds itself in an unfavorable status , with an Economics that is struggling to emerge from stagnation and a program of structural reforms that have been insufficient to solve the partner problems accumulated during more than 60 years of centralized state socialism. The timid nature and slow pace of economic reforms have not helped to revive Economics.
However, during his decade in power, Castro has led changes in the management of the model, something that should be taken into account even though in the political sphere he has perpetuated the lack of freedom and the persecution of opposition activity, without underestimating the moral guilt of the dictatorship. Among the changes that have taken place are the opening to foreign investment, new diplomatic relations, participation in Latin American forums and the immersion of Cubans in work .
Probably forced by circumstances, Raúl Castro was able to break some of the obstacles and ideological barriers that his brother Fidel had implemented on the island for more than 40 years in power. The bequest of the outgoing president marks a certain progress, but it will be the actions of the incoming president that will indicate whether Cuba is truly moving towards the economic -and political- opening longed for by Cubans.
[1] VIDAL, P. and PÉREZ Villanueva, Omar E. "Se extiende el cuentrapropismo en Cuba". Espacio Laical, vol. 6, n. 3 (2010), p. 53-58.
[2] HERSHBERG, E., & LEOGRANDE, W. M. (2016). A new chapter in US-Cuba relations: social, political, and economic implications. New York: Palgrave Macmillan.