WHAT YOU ARE GOING TO STUDY
WHAT YOU ARE GOING TO STUDY 
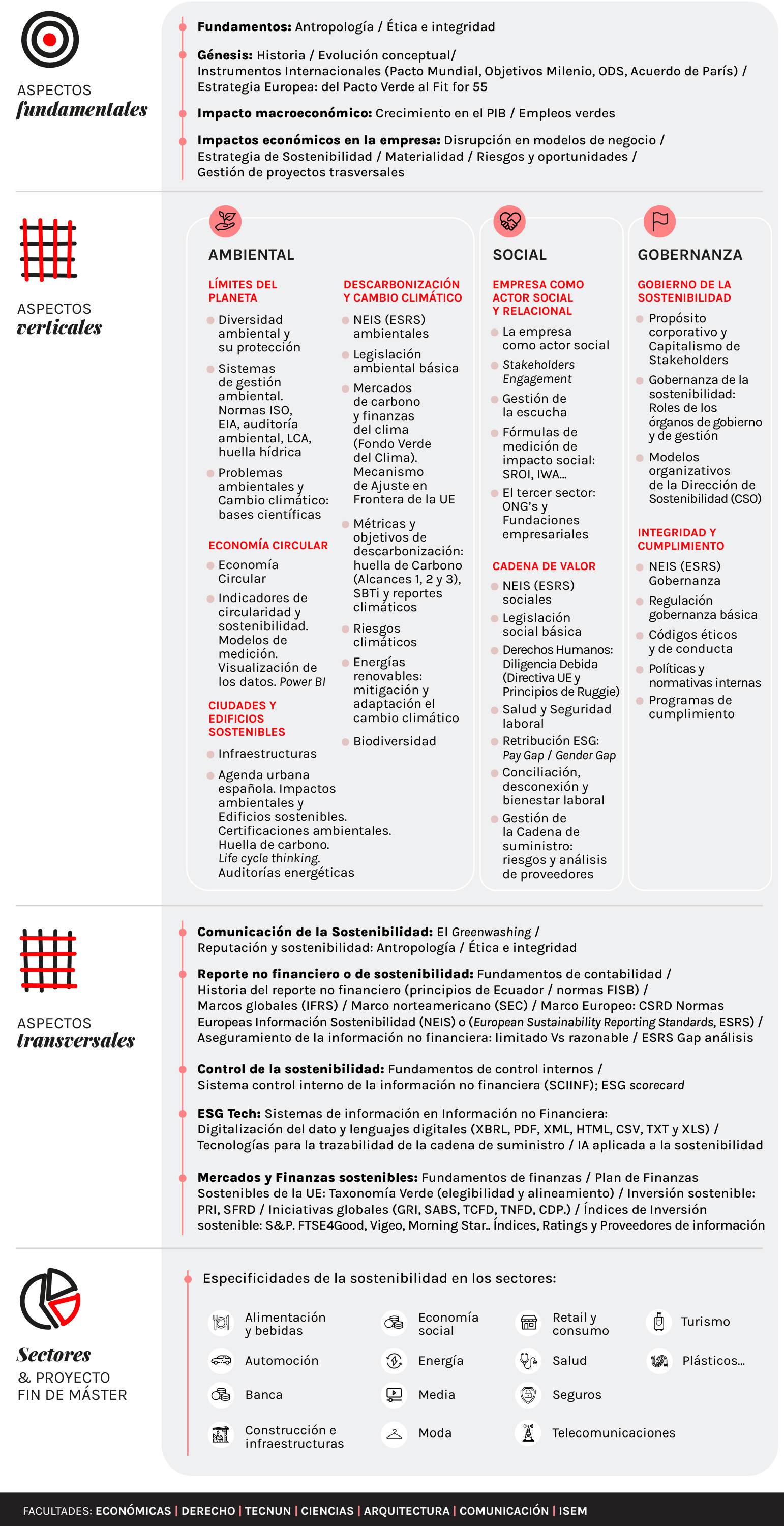
The design of the Study program is composed of 4 clearly differentiated modules: Fundamental; Cross-cutting; Vertical (ESG); and Sectorial + project End of Master's Degree. This design is largely based on the framework established by the European Union with the EuropeanSustainability Reporting Standards. From this point of view, students will be familiar from the outset with the models they will face in a professional environment.
BLOCK 1: FUNDAMENTAL ASPECTS (9 ECTS CREDIT)
development In this block we will study aspects related to the history and international instruments of sustainability (Global Compact, Millennium Development Goals, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), agreement of Paris...); global initiatives (GRI, SABS, TCFD, TNFD, CDP...); sustainable investment indices (S&P. FTSE4Good, Viegeo, Mornign Star...).
Other fundamental aspects of sustainability will also be studied, such as the basic pillars of sustainability of the European Union (from the European Green Pact to the European Sustainability Standards); methodologies of management of sustainability projects; and all aspects related to ethics and integrity (decision-making process, biases, technology...).
BLOCK 2: CROSS-CUTTING ISSUES (10 ECTS CREDIT)
In this block we will study the aspects that have an impact on the three dimensions of sustainability (environmental, social and governance).
Specifically, aspects such as sustainability reporting will be addressed [framework European: from NFRD to CSRD and ESRS: requirements of the CSRD for European companies; International IFRS / ISSB frameworks. framework US (SEC). Other international frameworks].
Sustainable Finance [European regulation and international initiatives. EU Sustainable Finance Plan 2018 (Taxonomy and SFRD). Sustainable investment. SRI. Investment strategies. Principles for Sustainable Investment (PRI).
Sustainability communication [Sustainability as a brand and reputation attribute; Active listening to the environment. Sustainability communication strategy: from conventional media to social networks; management Greenwashing].
And aspects of ESG Tech or technology applied to sustainability [Digitalization of data and digital languages (XBRL, PDF, XML, HTML, CSV, TXT and XLS). Information systems in non-financial information. Single European Access Point. Technologies for supply chain traceability. Data for Good. Artificial Intelligence and ESG].
BLOCK 3: VERTICAL ASPECTS
- ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS (10 ETCS)
In the general part, basic environmental concepts will be studied; new energy sources: Renewable energies; Biodiversity (TNFD); Environmental management systems; and Economics Circular.
In the specific part, environmental ESRS; carbon markets; EU Border Adjustment Mechanism; Carbon Footprint (Scope 1, 2 and 3 calculation formulas); decarbonization targets (science-based targets, STBi); climate scenarios; decarbonization and climate change strategy: mitigation and adaptation to climate change; climate risks: physical and transitional risks; climate risk management and mitigation (TCFD) will be studied.
- SOCIAL ASPECTS (8 ECTS credit)
In the general part, will study the methodologies of stakeholders engagement; the role of the third sector in sustainability (NGOs and corporate foundations).
In the specific part, will study the social ESRS [Own workforce (ESRS S1); Workers in the value chain (ESRS S2); Affected communities (ESRS S3); Consumers and Username end (ESRS S4)]; Due Diligence and Human Rights (Due Diligence Directive, CSDDD); management of the Supply Chain; Health, Safety at work and corporate welfare; Remuneration with ESG criteria; Pay Gap / Gender Gap; Measuring social impact: (SROI, IWA...)
- SOCIAL ASPECTS (8 ECTS credit)
In the general part, will study aspects such as the corporate purpose ; roles of the governing bodies and management in sustainability; the Corporate Sustainability Officer (CSO); and compliance programs.
In the specific part ESRS Governance [ Business Conduct (ESRS G1)]; Internal Control over Financial Reporting Systems (ICFR); Codes of Ethics; Internal Policies and Regulations: ESG Score Card (Sustainability Scorecard); Non-financial Risks: Identification, Prevention and Mitigation
BLOCK 4: SECTORS AND PROJECT END OF MASTER'S DEGREE (15 ECTS CREDIT)
Students may choose to specialize in one of these sectors and their project Final Master's Degree will focus on specific aspects of sustainability in the following sectors: Fashion; Banking / Insurance; Energy; Construction & Infrastructure; Automotive; Food; Tourism; Health; Transportation; Retail & Consumer; average. There will also be a dedicated space for understanding sustainability in cities and public spaces.
In this section, the following aspects will be addressed by reference letter companies in each of the sectors: impact of sustainability on the business model and its strategy; sectorial materiality; risks and opportunities; ecosystem of the most relevant stakeholders. The goal is to provide student body with a comprehensive view of the impact of sustainability in all branches of Economics.
 project end of Master's Degree
project end of Master's Degree
The project Final Master's Degree of the Master's Degree in Sustainability is one of the most relevant training modules of the program. It represents 20% of the load professor and through this subject articulates the real applied dimension of knowledge and allows the contact with different professional sectors and companies that are potential employers of graduates.
The project End of Master's Degree will be linked to projects and real needs of collaborating companies from different sectors: Fashion, Banking/Insurance, Automotive, Food, Energy, Construction and Infrastructure, Tourism, Health, Transportation, Retail, average, Cities and public spaces.
The goal is to provide the student with a real internship experience on the development of a project in the field of sustainability of a business.