Breadcrumb
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Articles .
A brief outline of the European defence system, integrated into the European External Action Service and its importance to the Union
The European Union will launch the Conference on the Future of Europe on May 9th, marking the beginning of the event that will feature debates between institutions, politicians and civil society on several topics that concern the community, including security and defense. It is clear that the majority of the European Union favors a common defense effort, and the Union has taken steps to ensure a solid structure to lay the framework for a possible integration of forces. Following the efforts to unify foreign policy objectives, a unified defence is the next logical step for European integration.
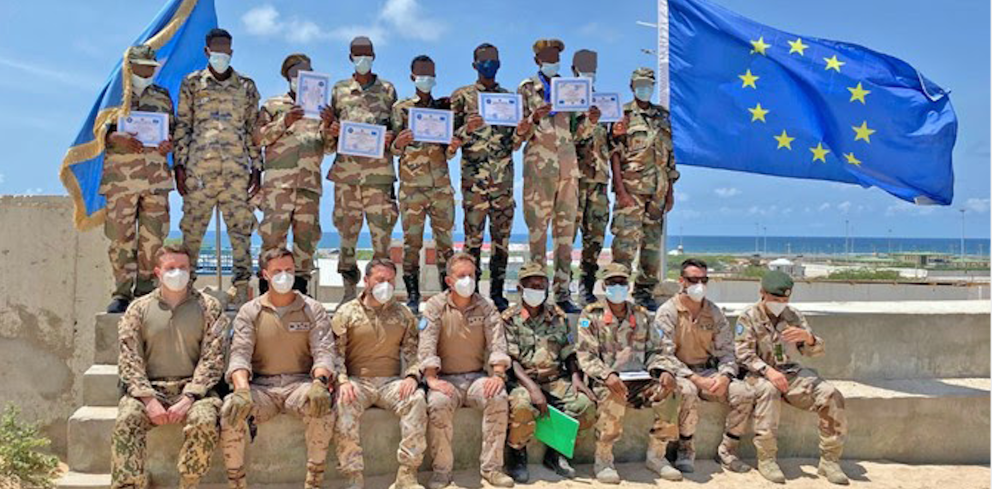

Course for the Somali National Armed Forces, led by a Spanish Colonel with instructors from Italy, Sweden, Finland and Spain [EUTM-Somalia].
ARTICLE / José Antonio Latorre
According to the last standard Eurobarometer, around 77% of Europeans support a common defense and security policy among European Union member states. The support for this cause is irregular, with the backing spanning from 58% (Sweden) to 93% (Luxembourg). Therefore, it is expected that security and defense will definitely take a prominent role in the future of the Union.
In 2017, the European Commission launched the "White Paper on the Future of Europe," a document that outlines the challenges and consequently the possible scenarios on how the Union could evolve by 2025. In the field of security, the document considers three different scenarios: Security and Defense Cooperation, Shared Security and Defense, and Common Defense and Security. In the first scenario, the member states would cooperate on a voluntary basis, similarly to an ad-hoc system. The second scenario details one where the tendency would be to project a stronger security, sharing military and economic capabilities to enhance efficiency. The final scenario would be one where members expand mutual assistance and take part in the integration of defence forces; this includes a united defence spending and distribution of military assets to reduce costs and boost capabilities.
Although these are three different predictions, what is clear is that the enhancement of European security is of greatest importance. As former European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker said in the 2016 State of the Union address: "Europe can no longer afford to piggyback on the military might of others. We have to take responsibility for protecting our interests and the European way of life. It is only by working together that Europe will be able to defend itself at home and abroad". He was referring to the paramountcy of a strategic autonomy that will permit the union to become stronger and have more weight in international relations, while depending less on the United States.
The existing framework on security
The European Union does not have to start from scratch to achieve these goals, since it currently has a Military Planning and Conduct Capability (MPCC) branch. The bureau is situated within the EU Military Staff, part of the European External Action Service in Brussels. This operational headquarters was established on June 8th, 2017, with the aim of boosting defence capabilities for the European Union outside its borders. It was created in order to strengthen civil/military cooperation through the Joint Support Coordination Cell and the Civil Planning and Conduct Capability, avoiding unnecessary overlap with NATO. Its main responsibilities include operational planning and conduct of the current non-executive missions; namely the European Union Training Missions (EUTM) in Mali, Somalia and Central African Republic.
A non-executive mission is an operation conducted to support a host nation with an advisory role only. For example, EUTM Somalia was established in 2010 to strengthen the Somali federal defence institutions through its three-pillar approach: training, mentoring and advising. The mission is supporting the development of the Somali Army General Staff and the Ministry of Defense through advice and tactical training. The mission has no combat mandate, but it works closely with the EU Naval Force - Operation ATALANTA (prevention and deterrence of privacy and protection of shipping), EUCAP Somalia (regional civilian mission), and AMISOM (African Union peacekeeping mission in Somalia), in close cooperation with the European Union. The mission, which is located in Mogadishu, has a strength of over 200 personnel, with seven troop contributing states, primarily from Italy and Spain. Non-executive missions have a clear mandate of advising, but they can be considered as a prototype of European defence cooperation for the future.
The Common Security and Defense Policy (CSDP) is the framework for cooperation between EU member states in order to conduct missions to maintain security and establish ties with third countries through the use of military and civilian assets. It was launched in 1999 and it has become a bedrock for EU foreign policy. It gives the Union the possibility to intervene outside its borders and cooperate with other organisations, such as NATO and the African Union, in peacekeeping and conflict prevention. The CSDP is the umbrella for many branches that are involved with security and defence, but there is still a need for an enhancement and concentration of forces that will expand its potential.
Steppingstones for a larger, unified project
Like all the European Union, the CSDP is still a project that needs construction, and a European Union military should be a priority. In recent years, there have been efforts to implement measures to advance towards this goal. Firstly, Permanent Structured Cooperation (PESCO) was launched in 2017 to reinforce defence capabilities and increase military coordination at an interoperable level. Participation is voluntary, but once decided, the country must abide by legally binding commitments. So far, 25 member states have joined the integrated structure, which depends on the European External Action Service, EU Military Staff and the European Defence Agency. Presently, there are 46 projects being developed, including a Joint EU Intelligence School, the upgrade of Maritime Surveillance, a European Medical Command and a Cyber and Information Domain Coordination Center, among the many others. Although critics have suggested that the structure will overlap with NATO competences, Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg said that he believed "that PESCO can strengthen European defence, which is good for Europe but also good for NATO". It is important to add that its alliance with NATO was strengthened through common participation in the cybersecurity sector, joint exercises, and counterterrorism. Secondly, the launch of the European Defense Fund in 2017 permits co-funded defense cooperation, and it will be part of the 2021-2027 long-term EU budget. Finally, the mentioned Military Planning and Conduct Capability branch was established in 2017 to improve crisis management and operational surveillance.
Therefore, it is a clear intention of the majority of the European Union to increase capabilities and unify efforts to have a common defense. Another aspect is that a common military will make spending more efficient, which will permit the Union to compete against powers like China or the United States. Again, the United States is mentioned because although it is an essential ally, Europeans cannot continue to depend on their transatlantic partner for security and defense.
A European Union military?
With a common army, the European Union will be a significant player in the international field. The integration of forces, technology and equipment reduces spending and boosts efficiency, which would be a historical achievement for the Union. European integration is a project based on peace, democracy, human dignity, equality, freedom and the protection and promotion of human rights. If the Union wants to continue to be the bearer of these values and protect those that are most vulnerable against the injustices of this century, then efforts must be concentrated to reach this objective.
The Union is facing tough challenges, from nationalisms and internal divides to economic and sanitary obstacles. However, it is not the first time that unity has been put at risk. Brexit has shown that the European project is not invulnerable, that it is still not fully constructed. The European way of life is a model for freedom and security, but this must be fought for and protected; it can never be taken for granted.
Europe has lived an unprecedented period of peace and prosperity due to past endeavours at its foundation. It is evident that there will always be challenges and critics, but the only way to continue to be a leader is through unification; and it starts with a European Army. There are already mechanisms in place to ensure cooperation, such as those explored with non-executive missions. These are the stepping-stones for defence coordination and partnerships in the future. Although it is a complex task, it seems more necessary than ever before. For the protection of Western values and culture, for the promotion of human rights and dignity, and for the defense of freedom and democracy, European integration at the defense level is the next step in the future of the European Union.
The former ECB president takes the helm of Italy with a diary of reforms and a return to Atlanticism.
After years of political instability, in mid-February Italy inaugurated an in principle stronger government headed by Mario Draghi, former president of the European Central Bank. His technical profile , his prestige after eight years in European governance and the formation of a government with a certain national unity character are an opportunity for Italy to overcome the current health and economic crisis and undertake the reforms the country needs.

Mario Draghi, accepting the task of forming a government in February 2021 [Presidency of the Republic].
article / Matilde Romito, Jokin de Carlos Sola
For more than a year, the government of Italian Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte had been strongly contested from within, especially by the disagreements of Italia Viva, the party led by Matteo Renzi, at subject economic. The straw that broke the camel's back was Renzi's civil service examination over Conte's proposed plan for the use of aid from the Recovery Fund set up by the European Union to deal with the crisis caused by the Covid-19 pandemic. Conte lost his majority on 13 January following the resignation of three ministers belonging to Italia Viva and on 26 January presented his Withdrawal. On 3 February the President of the Republic, Sergio Mattarella, entrusted the new government to Mario Draghi, former president of the European Central Bank (ECB), with the task of leading the new government training .
At the start of his mandate, Mario Draghi set out his objectives. He stressed the importance of the country maintaining a certain unity at such a difficult historical moment and indicated that his priority would be to provide more opportunities and to fight against the status quo that prevents the implementation of reforms.
On 17 February, Mario Draghi won the confidence of Parliament, one of the largest majorities since the Second World War. purpose management Draghi then formed a government made up of different political forces, with the aim of tackling the consequences of the pandemic in a framework of national unity: in addition to various technical ministers (8), the 5 Star Movement (4), the Democratic Party (3), the Lega (3), Forza Italia (3), Liberi e Uguali (1) and Italia Viva (1) are represented in the Cabinet. This internal diversity, which on some issues manifests itself in opposing positions, could lead to some governmental instability.
Domestic politics: recovery and reforms
The Draghi government has made the vaccination campaign and economic recovery a priority, as well as reforms to the tax system and to public administration and the judiciary. The former ECB president has shown a certain capacity for both innovation in organisational Structures and the delegation of tasks, all of which will be tackled swiftly, according to his maxim that "we'll do it soon, we'll do it very soon".
Accelerating vaccination
As for the vaccination campaign, Draghi is applying maximisation and firmness. First of all, he reformed the administrative summits in charge of the vaccination plan and appointed General Francesco Paolo Figliuolo, a military logistician, as the new extraordinary commissioner for the Covid-19 emergency. By then, the daily doses provided reached 170,000, but Figliuolo, together with the director of the Civil Protection, Fabrizio Curcio, and the Minister of Health, Roberto Speranza, have set as goal to triple this number issue. To this end, new vaccination sites have been set up, such as businesses, gyms and empty car parks, and a mobilisation of staff has been promoted for vaccination work.
The Draghi government has also become more assertive at the international level, such as the decision to block the export of 250,000 doses of the AstraZeneca vaccine to Australia. Although supported by the EU, the measure took many countries by surprise and made Italy the first EU member to apply such a legal mechanism. On 12 March the government announced the possibility of future production in Italy of some of the already internationally approved vaccines.
Economicsstructural reforms
The new government's economic diary will be characterised by structural reforms to promote productivity, as well as by the implementation of economic aid targeted at those most affected by the crisis, with the goal aim of relaunching the country and combating new social inequalities. The government is finalising the Recovery Plan to be submitted to Brussels in order to obtain the EU funds.
During his term as ECB President Draghi promoted structural reforms in several European countries; therefore, his leadership will be core topic in promoting reforms aimed at increasing productivity, reducing bureaucracy and improving the quality of Education. The government promises more expense on Education and the promotion of a more sustainable and digitised Economics , as called for by the EU Green Deal.
Through the "Sostegni" legislative decree, the government is implementing an aid plan. Some of them are aimed at defraying the modification of the framework redundancies implemented by Conte, but this requires a more consensual negotiation.
Streamlining of public administration and Justice
The reform of public administration has been entrusted to framework D'Alberti, lawyer and professor of Administrative Law at La Sapienza in Rome. The reform will follow two paths: greater connectivity and an update of the competences of civil servants.
In relation to Justice, the purpose is to implement several of the recommendations forwarded by the EU in 2019 and 2020. Among other measures, the EU calls for greater efficiency of the Italian civil justice system, through a faster work of courts, better burden-sharing work, the adoption of simpler procedural rules and an active crackdown on corruption.
Foreign policy: Atlanticism and less enthusiasm for China
One of the first consequences of Draghi's election as prime minister has been the new image of stability and willingness to cooperate that Italy has come to project not only in Brussels but also in Washington, both politically and economically. Nevertheless, many aspects of Conte's foreign policy will be maintained, given the continuity of Luigi di Maio as foreign minister.
Beyond Europe, Draghi's priorities will be mainly two: a new rapprochement with Washington - at framework of a convinced Atlanticism, within multilateralism - and the reinforcement of Italy's Mediterranean policy. Draghi's arrival also has the potential to break with Conte's rapprochement with China, such as the inclusion of Italian ports in the New Silk Road. While this may secure Italy as a key US ally, any decision will have to take into account the Chinese investment that may be committed.
Contribution to European governance
Italy is the third largest Economics in the EU and the eighth largest in the world, so its economic performance has some international repercussions. Draghi has assured his commitment to recovery and his contacts with European elites may help ease tensions in discussions with other EU members on the distribution of funds, especially the so-called Next Generation EU. During the Euro Crisis Draghi was one of the main advocates of structural reforms and now these are again vital to avoid a rise in expense that could cause debt to grow too high or cuts to budget that would damage growth.
Draghi has declared that "without Italy there is no Europe, but without Europe there is less Italy" and intends to make Italy a more active and engaged player in Europe, while trying to balance the interests of France, Germany and the Netherlands. Merkel's departure at the end of 2021 opens the possibility of a power vacuum in the European committee ; with France and Italy being the second and third Economics her partnership could bring stability and ensure the persistence of the Recovery Fund. This in turn may end up causing governance problems with Germany and the Netherlands should there be disagreements over the use of the funds. However, Draghi has been reticent about France's geopolitical proposals to establish Europe as an actor independent of the US. This could end up poisoning the potential new special relationship between Rome and Paris.
The advertisement willingness to engage in dialogue and concord with both Turkey and Russia may end up causing problems in Brussels with other countries. In Turkey's case, it could jeopardise relations with Greece in the Mediterranean. However, the strong criticism of Erdogan, whom he called a dictator, for having diplomatically humiliated Ursula von der Leyen in his visit to Ankara, seems to rule out counterproductive approaches. On the other hand, his desire for dialogue also with Moscow may end up sitting badly in the Baltic capitals, as well as in Washington.
The Mediterranean: immigration, Libya and Turkey
Draghi also referred to strategic areas outside the EU that are close to Italy: the Maghreb, the Middle East and the Mediterranean. Regarding the latter, Italy's priorities do not seem likely to change: the goal is to control immigration. To this end, Draghi hopes to establish cooperation with Spain, Greece and Cyprus.
In this area the stability of Libya is important, and Italian support for the Government of National agreement Government (GNA) established in Tripoli, one of whose main advocates in the EU has been Luigi Di Maio, who remains at the helm of Foreign Affairs, will continue. Libyan Prime Minister Abdul Hamid Dbeibah has declared his readiness to collaborate on immigration issues with Draghi, but Draghi seems sceptical towards bilateral deals and would prefer this to be done at a European framework .
This runs counter to the policy of Greece and France, which support the Libyan National Army, based in Tubruk, because of the GNA's Islamist connections and Turkey's support for them. These differences over Libya have already caused problems and hindered the possibility of sanctions against Ankara.
Seizing the opportunity
The new Draghi government is an opportunity for Italy to achieve some political stability after a few years of ups and downs. The integration in the same government of people from different ideological backgrounds can contribute to the national unity required by the present status. The emergency and exceptional nature of the Covid-19 crisis gives Italy an opportunity to implement not only anti-pandemic measures but also radical structural changes to transform Economics and public administration, something that would otherwise be too much of a hindrance.
On the other hand, although within a certain continuity, Draghi's government represents a change in the international strategic chessboard, not only for Brussels, Berlin and Paris but also for Washington and Beijing, as more Atlanticist tendencies will distance him from both Russia and China.
Italian governments are not known for their longevity, nor does this one offer any guarantee of permanence, bearing in mind that the unity effort made is due to the temporary nature of the crisis. Nevertheless, Draghi's own profile projects an image of seriousness and responsibility.
Spain, although affected, is not as badly affected as other European partners.
The UK's exit from the European Union finally materialised on the last day of 2020. The compromise on fisheries was the last point of the arduous negotiations and the differences were only overcome some conference before the unpostponable deadline. The fisheries agreement reached provides that for five and a half years EU vessels will continue to have access to fish in British waters. Although affected, Spain is not as badly affected as other European partners.

Fishing fleet in the Galician town of Ribeira [Luis Miguel Bugallo].
article / Ane Gil
The Brexit-culminating withdrawalagreement ran aground in its final stretch on the issue of fisheries, despite the fact that the UK's fishing activity in its waters contributes only 0.12% of British GDP.
That discussion, which nearly derailed the negotiations, centred on the delimitation of the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), the area beyond territorial waters - at a maximum distance from the coast of 200 nautical miles (about 370 kilometres) - in which a coastal country has sovereign rights to explore and exploit, conserve and manage natural resources, whether living or non-living. The UK EEZ is home to fish-rich fishing grounds, which account, with a average of 1.285 million tonnes of fish per year, according to a 2019 study by the European Parliament's Fisheries Committee, for 15% of the EU's total fish catch. Of these catches, only 43% was taken by British fishermen, while the remaining 57% was taken by other EU countries. The European countries that had access to fishing in British waters were Spain, Germany, Belgium, Denmark, France, the Netherlands, Ireland and Sweden.
Therefore, the entrance in force of Brexit would mark the UK's withdrawal from the Common Fisheries Policy, which defines the access of European vessels to the Exclusive Economic Zone.
Initial perspectives
During its membership of the EU, the UK was part of the Common Fisheries Policy, whereby all EU member states' fishing fleets have equal access to European waters. In the EU, fishing rights are negotiated annually by the ministers of each member state and national quotas (the amount of fish of each species that each country's fleet can catch) are set using data historical data such as reference letter.
The Spanish fishing fleet followed the negotiations closely, as it had a lot to lose from a bad agreement. On the one hand, a Brexit without agreement could mean a reduction in income of 27 million euros related to fishing in British waters; it would also entail a drastic reduction in hake, megrim and mackerel catches for Spanish fishing boats specialising in these species. On the other hand, the employment would also be affected if the agreement established a drastic reduction in catches. Eighty Spanish vessels have licence to fish in British waters, which means almost 10,000 jobs for work related to this activity.
The negotiations
Until Brexit, British waters and their exploitation were negotiated jointly with the rest of the European Union's maritime areas. Brussels tried to maintain this relationship even if the UK left the EU, so the position of European negotiators focused on preserving the system of fishing quotas that had been in place, for a period of fifteen years deadline . However, British Prime Minister Boris Johnson always ruled out any trade agreement that would grant European vessels access to British waters in exchange for better conditions for British financial services in the single market as offered by Brussels. London wanted to implement a regime similar to the Norwegian one, which negotiates year by year the catches of EU fleets in its waters, with the difference that in the Norwegian case the pact refers to average dozen species, compared to almost a hundred in British waters.
We should bear in mind that the service sector accounts for 80% of the UK's GDP, while fishing activities account for only 0.12%. It is therefore quite clear that London's positions on the fisheries section were more political than economic. Although fishing activities have little impact on the British Economics , the fishing sector does have political importance for the Eurosceptic cause, as regaining control of the waters was one of the promises made in the Brexit referendum. Thus, this issue became a symbol of national sovereignty.
The starting point for the negotiations was the UK government's demand to repatriate up to 80% of the catches in its waters of control, while the EU offered refund to the UK between 15% and 18%. Johnson wanted to keep management from exploiting its waters and to negotiate with the EU as partner preferential. He expressed his initial intention to establish, from January 2021, more frequent negotiations on how to fish in his EEZ. This resulted in a finalagreement which implies that European vessels will continue to be able to fish in British waters for five and a half years, in exchange for refund 25% of the quotas EU vessels fish there, estimated to be worth around 161 million euros. In return, fish products will continue to enter the European market at zero tariff. After this transitional phase, the EU and the UK will have to renegotiate year after year. If the agreement is violated, there are mechanisms in place to ensure compensation, such as tariffs.
Consequences for Spain and its European neighbours
The agreement provoked discontent in the UK fishing industry, which accused Johnson of caving in on this agreement. The National Federation of Fishermen's Organisations expressed disappointment that only marginal changes had been made to quotas and that EU fleets would continue to have access to UK waters up to the six-mile limit. The prime minister responded that the UK could now catch "prodigious amounts of extra fish".
For the time being, the UK has already encountered some problems. The new customs agreement has been causing delays and lorries have to be checked at the borders. With a sudden overproduction, there will not be enough veterinarians to make the necessary export health certificates. Therefore, the new bureaucratic requirements has led to several cases of seafood rotting on the docks before it can be exported to the EU. It is estimated that the fishing industry is losing 1 million pounds per day due to these new requirements, which has caused many fishermen to reduce their daily catches.
But EU fishermen will also be affected, as until now they have been catching fish in British waters with a total annual value of 650 million euros, according to the European Parliament, especially at position from Danish, Dutch and French vessels. In addition, Belgium is one of the countries most affected, as 43% of its catches are taken in British waters; it will now have to reduce its catches by 25% over the next 5 years. Moreover, Belgian fishermen used to land their fish in British ports and then truck it to Belgium. However, this will no longer be possible. Alongside Belgium, other countries that will suffer most from the loss of fishing rights due to Brexit are Ireland, Denmark and the Netherlands.
As for Spain, the fishing sector has acknowledged its unease about the annual negotiation that will take place after the initial five-year period, as well as the consequences for the future distribution of the rest of the fishing quotas, for the Common Fisheries Policy itself, for the exchange of quotas between countries and for the sustainable management of marine stocks. However, in the short term deadline the Spanish fleet does not seem to be so affected in comparison with other European countries.
In fact, the Minister of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, Luis Planas, gave a positive assessment of this agreement, considering it a "good agreement, which provides stability and legal certainty". Planas argued that the 25% reduction in the average value of catches by the eight European countries fishing in British waters has limited effects on Spanish fishing activity and, by way of example, he stated that hake catches will only be reduced by 1%. In other words, the current quota of 29.5% would fall to 28.5% in 2026. In addition, other species of greater interest to Spain (such as mackerel, horse mackerel and blue whiting) have not been included in the agreement and there are no reductions in deep-water species in high demand (such as black scabbardfish or grenadiers). In conclusion, Planas said that Spain has only conceded on 17 of the 32 fishery resources allocated to the country. However, it is up to Brussels to go into the details and decide on fishing quotas during the transition period that opened on 1 January, in which the eight countries fishing in British waters will have lower quotas.
In conclusion, Britain now has the ability to dictate its own rules at subject on fishing. By 2026, the UK can decide to completely withdraw access for EU vessels to British waters. But the EU could then respond by suspending access to its waters or imposing tariffs on UK fish exports.
An update on the Iranian nuclear accord between 2018 and the resumed talks in April 2021
The signatories of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), reached in 2015 to limit Iran's nuclear program, met again on April 6 in Vienna to explore the possibility of reviving the accord. The US withdrawal after Donald Trump becoming president put the agreement on hold and lead Tehran to miss its commitments. Here we offer an update on the issue until the international talks resumed.

Trump's announcement of the US withdrawal from the JCPOA on May 8, 2018 [White House].
ARTICLE / Ana Salas Cuevas
The Islamic Republic of Iran is a key player in the stability of its regional environment, which means that it is a central country worth international attention. It is a regional power not only because of its strategic location, but also because of its large hydrocarbon reserves, which make Iran the fourth country in oil reserves and the second one in gas reserves.
In 2003, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) brought to the light and warned the international community about the existence of nuclear facilities, and of a covert program in Iran which could serve a military purpose. This prompted the United Nations and the five permanent members of the UN Security Council (the P5: France, China, Russia, the United States and the United Kingdom) to take measures against Iran in 2006. Multilateral and unilateral economic sanctions (the UN and the US) were implemented, which deteriorated Iran's economy, but which did not stop its nuclear proliferation program. There were also sanctions linked to the development of ballistic missiles and to the support of terrorist groups. These sanctions, added to the ones the United States imposed on Tehran in the wake of the 1979 revolution, and together with the instability that cripples the country, caused a deep deterioration of Iran's economy.
In November 2013, the P5 plus Germany (P5+1) and Iran came to terms with an initial agreement on Iran's nuclear program (a Joint Plan of Action) which, after several negotiations, translated into a final pact, the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), signed in 2015. The European Union adhered to the JCPOA.
The focus of Iran's motives for succumbing and accepting restrictions on its nuclear program lies in the Iranian regime's concern that the deteriorating living conditions of the Iranian population due to the economic sanctions could result in growing social unrest.
The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action
The goal of these negotiations was to reach a long-term comprehensive solution agreed by both parties to ensure that Iran's nuclear program would be completely peaceful. Iran reiterated that it would not seek or develop any nuclear weapons under any circumstances. The real aim of the nuclear deal, though, was to extend the time needed for Iran to produce enough fissile material for bombs from three months to one year. To this end, a number of restrictions were reached.
This comprehensive solution involved a mutually defined enrichment plan with practical restrictions and transparent measures to ensure the peaceful nature of the program. In addition, the resolution incorporated a step-by-step process of reciprocity that included the lifting of all UN Security Council, multilateral and national sanctions related to Iran's nuclear program. In total, these obligations were key to freeze Iran's nuclear program and reduced the factors most sensitive to proliferation. In return, Iran received limited sanctions relief.
More specifically, the key points in the JCPOA were the following: Firstly, for 15 years, Iran would limit its uranium enrichment to 3.67%, eliminate 98% of its enriched uranium stocks in order to reduce them to 300 kg, and restrict its uranium enrichment activities to its facilities at Natanz. Secondly, for 10 years, it would not be able to operate more than 5,060 old and inefficient IR-1 centrifuges to enrich uranium. Finally, inspectors from the IAEA would be responsible for the next 15 years for ensuring that Iran complied with the terms of the agreement and did not develop a covert nuclear programme.
In exchange, the sanctions imposed by the United States, the European Union and the United Nations on its nuclear program would be lifted, although this would not apply to other types of sanctions. Thus, as far as the EU is concerned, restrictive measures against individuals and entities responsible for human rights violations, and the embargo on arms and ballistic missiles to Iran would be maintained. In turn, the United States undertook to lift the secondary sanctions, so that the primary sanctions, which have been in place since the Iranian revolution, remained unchanged.
To oversee the implementation of the agreement, a joint committee composed of Iran and the other signatories to the JCPOA would be established to meet every three months in Vienna, Geneva or New York.
United States withdrawal
In 2018, President Trump withdrew the US from the 2015 Iran deal and moved to resume the sanctions lifted after the agreement was signed. The withdrawal was accompanied by measures that could pit the parties against each other in terms of sanctions, encourage further proliferation measures by Iran and undermine regional stability. The US exit from the agreement put the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action on hold.
The United States argued that the agreement allowed Iran to approach the nuclear threshold in a short period of time. With the withdrawal, however, the US risked bringing this point closer in time by not waiting to see what could happen after the 10 and 15 years, assuming that the pact would not last after that time. This may make Iran's proliferation a closer possibility.
Shortly after Trump announced the first anniversary of its withdrawal from the nuclear deal and the assassination of powerful military commander Qasem Soleimani by US drones, Iran announced a new nuclear enrichment program as a signal to nationalists, designed to demonstrate the power of the mullah regime. This leaves the entire international community to question whether diplomatic efforts are seen in Tehran as a sign of weakness, which could be met with aggression.
On the one hand, some opinions consider that, by remaining within the JCPOA, renouncing proliferation options and respecting its commitments, Iran gains credibility as an international actor while the US loses it, since the agreements on proliferation that are negotiated have no guarantee of being ratified by the US Congress, making their implementation dependent on presidential discretion.
On the other hand, the nuclear agreement adopted in 2015 raised relevant issues from the perspective of international law. The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action timeline is 10 to 15 years. This would terminate restrictions on Iranian activities and most of the verification and control provisions would expire. Iran would then be able to expand its nuclear facilities and would find it easier to develop nuclear weapons activities again. In addition, the legal nature of the Plan and the binding or non-binding nature of the commitments made under it have been the subject of intense discussion and analysis in the United States. The JCPOA does not constitute an international treaty. So, if the JCPOA was considered to be a non-binding agreement, from the perspective of international law there would be no obstacle for the US administration to withdraw from it and reinstate the sanctions previously adopted by the United States.
The JCPOA after 2018
As mentioned, the agreement has been held in abeyance since 2018 because the IAEA inspectors in Vienna will no longer have access to Iranian facilities.
Nowadays, one of the factors that have raised questions about Iran's nuclear documents is the IAEA's growing attention to Tehran's nuclear contempt. In March 2020, the IAEA "identified a number of questions related to possible undeclared nuclear material and nuclear-related activities at three locations in Iran". The agency's Director General Rafael Grossi stated: "The fact that we found traces (of uranium) is very important. That means there is the possibility of nuclear activities and material that are not under international supervision and about which we know not the origin or the intent".
The IAEA also revealed that the Iranian regime was violating all the restrictions of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action. The Iranian leader argued that the US first violated the terms of the JCPOA when it unilaterally withdrew the terms of the JCPOA in 2018 to prove its reason for violating the nuclear agreement.
In the face of the economic crisis, the country has been hit again by the recent sanctions imposed by the United States. Tehran ignores the international community and tries to get through the signatory countries of the agreement, especially the United States, claiming that if they return to compliance with their obligations, Iran will also quickly return to compliance with the treaty. This approach has put strong pressure on the new US government from the beginning. Joe Biden's advisors suggested that the agreement could be considered again. But if Washington is faced with Tehran's full violation of the treaty, it will be difficult to defend such a return to the JCPOA.
In order to maintain world security, the international community must not succumb to Iran's warnings. Tehran has long issued empty threats to force the world to accept its demands. For example, in January 2020, when the UK, France and Germany triggered the JCPOA's dispute settlement mechanism, the Iranian Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a direct warning, saying: "If Europeans, instead of keeping to their commitments and making Iran benefit from the lifting of sanctions, misuse the dispute resolution mechanism, they'll need to be prepared for the consequences that they have been informed about earlier".
Conclusions
The purpose of the agreement is to prevent Iran from becoming a nuclear power that would exert pressure on neighbouring countries and further destabilize the region. For example, Tehran's military influence is already keeping the war going in Syria and hampering international peace efforts. A nuclear Iran is a frightening sight in the West.
The rising in tensions between Iran and the United States since the latter unilaterally abandoned the JCPOA has increased the deep mistrust already separating both countries. Under such conditions, a return to the JCPOA as it was before 2018 seems hardly imaginable. A renovated agreement, however, is baldly needed to limit the possibilities of proliferation in an already too instable region. Will that be possible?
Following referendums in 2018 and 2019, the Guatemalan government submitted its report to The Hague in 2020 and the Belizean government has one year to reply.
Guatemala presented its position before the International Court of Justice in The Hague last December, with a half-year delay attributed to the Covid-19 emergency status ; Belize will now have a year to respond. Although the ICJ will then take its time to draft a judgement, it can be said that the territorial dispute between the two neighbours has entered its final stretch, bearing in mind that the dispute over this Central American enclave dates back to the 18th century.

Coats of arms of Guatemala (left) and Belize (right) on their respective flags.
article / Álvaro de Lecea
The territorial conflict between Guatemala and Belize has its roots in the struggle between the Spanish Empire in the Americas and British activity in the Caribbean during the colonial era. The Spanish Crown's inaction in the late 18th century in the face of British encroachment on what is now Belize, then Spanish territory, allowed the British to establish a foothold in Central America and begin exploiting mainland lands for precious woods such as dyewood and mahogany. However, Guatemala's reservations over part of the Belizean land - it claims over 11,000 square kilometres, almost half of the neighbouring country; it also claims the corresponding maritime extension and some cays - generated a status of tension and conflict that has continued to the present day.
In 2008, both countries decided to hold referendums on the possibility of taking the dispute to the International Court of Justice (ICJ), which would rule on the division of sovereignty. The Belizeans approved taking that step in 2018 and the Guatemalans the following year. The issue was formalised before the ICJ in The Hague on 12 June 2019.
Historical context
The territory of present-day Belize was colonised by Spain in the mid-16th century as part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain and dependent on the captaincy of Guatemala. However, as there were no mineral resources there and hardly any population, the metropolis paid little attention to the area. This scant Spanish presence favoured pirate attacks, and to prevent them, the Spanish Crown allowed increasing English exploitation in exchange for defence. England carried out a similar penetration on the Caribbean coast of Nicaragua, but while the Spanish managed to expel the English from there, they consolidated their settlement at area Belize and finally obtained the territory by the Treaty of Paris in 1783, whereby Spain disengaged itself from this corner of Central America. That concession and another three years later covered just 6,685 square kilometres, a space close to the coast that was later enlarged inland and southward by England, since Spain was not active in the area. From then on the enclave became known as "British Honduras".
The cession did not take into account the claims of the Guatemalans, who considered the space between the Sarstún and Sibún rivers to be their own. Both rivers run west-east, the former forming the border with Guatemala in the south of what is now Belize; the other, further north, runs through the centre of Belize, flowing into the capital, splitting the country in two. However, given the urgency for international recognition when it declared independence in 1821, Guatemala signed several agreements with England, the great power of the day, to ensure the viability of the new state. One of these was the Aycinena-Wyke Treaty (1859), whereby Guatemala accepted Belize's borders in exchange for the construction of a road to improve access from its capital to the Caribbean. However, both sides blamed the other for not complying with the treaty (the road was not built, for example) and Guatemala declared it null and void in 1939.
In the constitution enacted in 1946, Guatemala included the claim in the drafting, and has insisted on this position since the neighbouring country, under the name Belize, gained its independence from the United Kingdom in 1981. As early as 1978, the UN passed a resolution guaranteeing the rights to self-determination and territorial protection of the Belizean people, which also called for a peaceful resolution of the neighbouring conflict. Guatemala did not recognise the existence of the new sovereign state until 1991, and even today still places some limits on Belize's progressive integration into the Central American Integration System. Because of its English background, Belize has historically maintained a closer relationship with the English-speaking Caribbean islands.
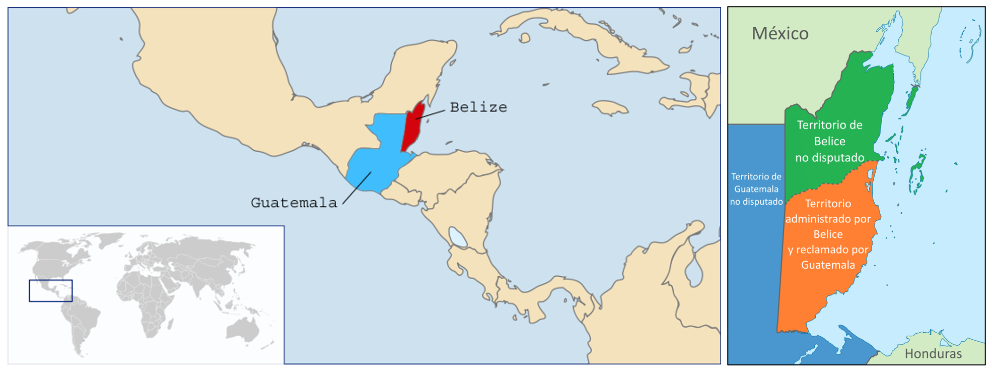
Map of Central America and, in detail, the territorial dispute between Guatemala and Belize [Rei-artur / Janitoalevic Bettyreategui].
Adjacency Line and the role of the OAS
Since 2000, the Organisation of American States (OAS), of which both nations are members, has been mediating between the two countries. In the same year, the OAS facilitated a agreement with the goal aim of building confidence and negotiations between the two neighbours. In order to achieve these objectives, the OAS, through its Peace Fund, actively supported the search for a solution by providing technical and political support. Indeed, as a result of this rapprochement, talks on the dispute were resumed and the creation of the "Adjacency Line" was agreed.
This is an imaginary line that basically follows the line that "de facto" separated the two countries from north to south and is where most of the tensions are taking place. Over the years, both sides have increased their military presence there, in response to incidents attributed to the other side. Due to these frequent disputes, in 2015 Belize had to request financial aid military presence from the British navy. It is precisely in the Adjacency Zone that an OAS office is located, whose purpose purpose is to promote contacts between the communities and to verify certain transgressions of the agreements already signed.
One of the most promising developments that took place under the umbrella of the OAS was the signature in 2008 of what was called the "specialagreement between Guatemala and Belize to submit Guatemala's territorial, insular and maritime claim to the International Court of Justice". Under this agreement both countries undertook to submit the acceptance of the Court's mediation to simultaneous popular consultations. However, in 2015, through the protocol of the agreement Special between Belize and Guatemala, these popular consultations were not allowed to take place at the same time. Both parties committed to accept the Court's decision as "decisive and binding" and to comply with and implement it "fully and in good faith".
The Hague and the impact of the future resolution
The referendums were held in 2018 in the case of Guatemala and in 2019 in the case of Belize. Although the percentages of both popular consultations were somewhat mixed, the results were positive. In Belize, the Yes vote won 55.37% of the votes and the No vote 44.63%. In Guatemala, on the other hand, the results were much more favourable for the Yes vote, with 95.88% of the votes, compared to 4.12% for the No vote.
These results show how the Belizeans are wary of resorting to the Hague's decision because, although by fixing final the border they will forever close any claim, they risk losing part of their territory. On the other hand, the prospect of gain is greater in the Guatemalan case, since if its proposal is accepted - or at least part of it - it would strategically expand its access to the Caribbean, now somewhat limited, and in the event of losing, it would simply remain as it has been until now, which is not a serious problem for the country.
The definition of a clear and respected border is necessary at this stage. The adjacent line, observed by the OAS peace and security mission statement , has been successful in limiting tensions between the two countries, but the reality is that certain incidents continue to take place in this unprotected area. These incidents, such as the assassination of citizens of both countries or mistreatment attributed to the Guatemalan military, cause the conflict to drag on and tensions to rise. On the other hand, the lack of a clear definition of borders facilitates drug trafficking and smuggling.
This conflict has also affected Belize's economic and trade relations with its regional neighbours, especially Mexico and Honduras. This is not only due to the lack of land boundaries, but also to the lack of maritime boundaries. This area is very rich in natural resources and has the second largest coral reef reservation in the world, after Australia. This has, unsurprisingly, affected bilateral relations between the two countries. Whilst regional organisations are calling for greater regional integration, the tensions between Belize and Guatemala are preventing any improvement in this regard.
The Guatemalan president has stated that, regardless of the Court's result , he intends to strengthen bilateral relations, especially in areas such as trade and tourism, with neighbouring Belize. For their part, the Caricom heads of state expressed their support for Belize in October 2020, their enthusiasm for the ICJ's intervention and their congratulations to the OAS for its mediation work.
Qatar's economic strengthening and expanding relations with Russia, China and Turkey have made the blockade imposed by its Gulf neighbours less effective.
It is a reality: Qatar has won its battle against the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia after more than three years of diplomatic rupture in which both countries, along with other Arab neighbours, isolated the Qatari peninsula commercially and territorially. Economic and geopolitical reasons explain why the imposed blockade has finally faded without Qatar giving in to its autonomous diplomatic line.

Qatar's Emir Tamim Al Thani at lecture Munich Security 2018 [Kuhlmann/MSC].
article / Sebastián Bruzzone
In June 2017, Egypt, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, Libya, Yemen and the Maldives accused the Al Thani family of supporting Islamic terrorism and the Muslim Brotherhood and initiated a total blockade on trade to and from Qatar until Doha met thirteen conditions. On 5 January 2021, however, Saudi Arabia's Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman welcomed Qatar's Emir Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani with an unexpected embrace in the Saudi city of Al-Ula, sealing the end of yet another dark chapter in the modern history of the Persian Gulf. But how many of the thirteen demands has Qatar met to reconcile with its neighbours? None.
As if nothing had happened. Tamim Al Thani arrived in Saudi Arabia to participate in the 41st Summit of the committee Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) where member states pledged to make efforts to promote solidarity, stability and multilateralism in the face of the challenges in the region, which is confronted by Iran's nuclear and ballistic missile programme, as well as its plans for sabotage and destruction. In addition, the GCC as a whole welcomed the mediating role of Kuwait, then US President Donald J. Trump and his son-in-law, Jared Kushner.
The Gulf Arab leaders' meeting has been a thaw in the political desert after a storm of mutual accusations and instability in what was called the "Qatar diplomatic crisis"; this rapprochement, as an immediate effect, clears the way for the normal preparation of the football World Cup scheduled to take place in Qatar next year. The return of regional and diplomatic understanding is always positive in emergency situations such as an economic crisis, a global pandemic or a common Shia enemy arming missiles on the other side of the sea. In any case, the Al Thani's Qatar may be crowned as the winner of the economic pulse against the Emirati Al Nahyan and the Saudi Al Saud unable to suffocate the tiny peninsula.
The factors
The relevant question brings us back to the initial degree scroll before these lines: how has Qatar managed to withstand the pressure without buckling at all in the face of the thirteen conditions demanded in 2017? Several factors contribute to explaining this.
First, the capital injection by the QIA (Qatar Investment Authority). At the beginning of the blockade, the banking system suffered a capital flight of more than 30 billion dollars and foreign investment fell sharply. The Qatari sovereign wealth fund responded by pumping in $38.5 billion to provide liquidity to banks and revive Economics. The sudden trade blockade by the UAE and Saudi Arabia led to a financial panic that prompted foreign investors, and even Qatari residents, to transfer their assets out of the country and liquidate their positions in fear of a market collapse.
Second, rapprochement with Turkey. In 2018, Qatar came to Turkey's rescue by pledging to invest $15 billion in Turkish assets across subject and, in 2020, to execute a currency swap agreement to raise the value of the Turkish lira. In reciprocity, Turkey increased commodity exports to Qatar by 29 per cent and increased its military presence in the Qatari peninsula against a possible invasion or attack by its neighbours, building a second Turkish military base near Doha. In addition, as an internal reinforcement measure, the Qatari government has invested more than $30 billion in military equipment, artillery, submarines and aircraft from American companies.
Third, rapprochement with Iran. Qatar shares with the Persian country the South Pars North Dome gas field, considered the largest in the world, and positioned itself as a mediator between the Trump administration and the Ayatollah government. Since 2017, Iran has supplied 100,000 tonnes of food daily to Doha in the face of a potential food crisis caused by the blockade of the only land border with Saudi Arabia through which 40 per cent of the food enters.
Fourth, rapprochement with Russia and China. The Qatari sovereign wealth fund acquired a 19% stake in Rosneft, opening the door to partnership between the Russian oil company and Qatar Petroleum and to more joint ventures between the two nations. In the same vein, Qatar Airways increased its stake in China Southern Airlines to 5%.
Fifth, its reinforcement as the world's leading exporter of LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas). It is important to know that Qatar's main economic engine is gas, not oil. That is why, in 2020, the Qatari government launched its expansion plan by approving a $50 billion investment to expand its liquefaction and LNG carrier capacity, and a $29 billion investment to build more offshore offshore platforms at North Dome. The Qatari government has forecast that its LNG production will grow by 40% by 2027, from 77 million tonnes to 110 million tonnes per year.
We should bear in mind that LNG transport is much safer, cleaner, greener and cheaper than oil transport. Moreover, Royal Dutch Shell predicted in its report "Annual LNG Outlook Report 2019" that global LNG demand would double by 2040. If this forecast is confirmed, Qatar would be on the threshold of impressive economic growth in the coming decades. It is therefore in its best interest to keep its public coffers solvent and maintain a stable political climate in the Middle East region at status . As if that were not enough, last November 2020, Tamim Al Thani announced that future state budgets will be configured on the basis of a fictitious price of $40 per barrel, a much smaller value than the WTI Oil Barrel or Brent Oil Barrel, which is around $60-70. In other words, the Qatari government will index its public expense to the volatility of hydrocarbon prices. In other words, Qatar is seeking to anticipate a possible collapse in the price of crude oil by promoting an efficient public expense policy.
And sixth, the maintenance of the Qatar Investment Authority's investment portfolio , valued at $300 billion. The assets of the Qatari sovereign wealth fund constitute a life insurance policy for the country, which can order its liquidation in situations of extreme need.
Qatar has a very important role to play in the future of the Persian Gulf. The Al Thani dynasty has demonstrated its capacity for political and economic management and, above all, its great foresight for the future vis-à-vis the other countries of the Gulf Cooperation committee . The small peninsular "pearl" has struck a blow against Saudi Arabia's Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman and Abu Dhabi's Crown Prince Mohammed bin Zayed, who did not even show up in Al-Ula. This geopolitical move, plus the Biden administration's decision to maintain a hardline policy towards Iran, seems to guarantee the international isolation of the Ayatollah regime from the Persian country.
Several countries in the Americas are celebrating in 2021 their two hundredth anniversary of a break with Spain that did not always mean independence.ca celebrate in 2021 their two centuries of a break with Spain that did not always mean independence. final
This year, several American nations are commemorating two centuries of their separation from Spain, recalling a process that took place in all the Spanish possessions in continental America within a few years of each other. In some cases, it was a process of successive independence, as was the case with Guatemala, which later belonged to the Mexican Empire and then to a Central American republic, and Panama, which was part of Colombia until the 20th century. But even later, both countries experienced direct interference by the United States, in episodes that were very decisive for the region as a whole.

Ceremony of submission of the Panama Canal to the Panamanian authorities, 31 December 1999
article / Angie Grijalva
During 2021 several American countries celebrate their independence from Spain, the largest and most festively celebrated being Mexico. In other nations, the date of 1821 is qualified by later historical developments: Panama also commemorates every year the day in 1903 when it broke with Bogotá, while in the case of Guatemala that independence did not immediately imply a republic of its own, since together with its neighbouring nations in 1822 it was nominally dependent on Mexico and between 1823 and 1839 it formed part of the United Provinces of Central America and the Federal Republic of Central America. Moreover, US regional hegemony called into question the full sovereignty of these countries in subsequent decades: Guatemala suffered the first coup d'état openly promoted by Washington in the Western Hemisphere in 1954, and Panama did not have full control over its entire territory until the Americans handed over the canal in 1999.
Panama and its canal
The project of the Panama Canal was important for the United States because it made it possible to easily link its two coasts by sea and consolidated the global rise sought by Theodore Roosevelt's presidency, guided by the maxim that only the nation that controlled both oceans would be a truly international power. Given the refusal of Colombia, to which the province of Panama then belonged, to accept the conditions set by the United States to build the canal, resuming the work on the paralysed French project , Washington was faced with two options: invade the isthmus or promote Panama's independence from Colombia[1]. The Republic of Panama declared its independence on 3 November 1903 and with it Roosevelt negotiated a very favourable agreement which gave the United States perpetual sovereignty over the canal and a wide strip of land on either side of it. Washington thus gained control of Panama and extended its regional dominance.
After a decade of difficult work and a high issue death toll among the workforce, who came from all over the Caribbean and also from Asia, not least due to dengue fever, malaria and yellow fever, in 1913 the Atlantic and Pacific oceans were finally connected and the canal was opened to ship traffic.
Over time, US sovereignty over a portion of the country and the instructions military installations there fuelled a rejection movement in Panama that became particularly virulent in the 1960s. The Carter Administration agreed to negotiate the cession of the canal in a 1977 agreement that incorporated the Panamanians into the management of inter-oceanic traffic and set the submission of all installations for 1999. When this finally happened, the country experienced the occasion as a new independence celebration, saying goodbye to US troops that only ten years earlier had been very active, invading Panama City and other areas to arrest President Manuel Noriega for drug trafficking.
Critical moment in Guatemala
The Panama Canal gave the United States an undoubted projection of power over its hemisphere. However, during the Cold War, Washington also found it necessary to use operations, in some cases direct, to overthrow governments it considered close to communism. This happened with the overthrow of Jacobo Árbenz in Guatemala in 1954.
The arrival of Árbenz to the presidency in 1951 was a threat to the United Fruit Company (UFCO) because of the agrarian reform he was promoting[2]. Although the advance of communist parties in Latin America was beginning to grow, the real threat in certain countries was the expropriation of land from US monopolies. It is estimated that by 1950, the UFCO owned at least 225,000 hectares of land in Guatemala, of which the agrarian reform was to expropriate 162,000 hectares in 1952. With political support from Washington, UFCO claimed that the compensation it was being offered did not correspond to the true value of the land and branded the Árbenz government as communist, even though this was not true.
In 1953, the newly inaugurated Eisenhower Administration established a plan to destabilise the government and stage a coup against Árbenz. On the one hand, Secretary of State John F. Dulles sought the support of the Organisation of American States, prompting condemnation of Guatemala for receiving a shipment of arms from the Soviet Union, which had been acquired because of the US refusal to sell arms to the Central American country. On the other hand, the CIA launched the mission statement PBSUCCESS to guarantee the quartermastering of a faction of the Guatemalan army ready to rebel against Árbenz. The movement was led by Colonel Castillo Armas, who was in exile in Honduras and from there launched the invasion on 18 June 1954. When the capital was bombed, the bulk of the army refused to respond, leaving Árbenz alone, who resigned within days.
Once in power, Castillo Armas returned the expropriated land to UFCO and brought new US investors into the country. Dulles called this victory "the greatest triumph against communism in the last five years". The overthrow of Árbenz was seen by the US as a model for further operations in Latin America. development The award Nobel Literature Prize winner Mario Vargas Llosa has pointed out that this action against Árbenz could be seen as "the moment when Latin America was screwed", as for many it was evidence that a normal democracy was not possible, and this pushed certain sectors to defend revolution as the only way to make their societies prosper.
[1] McCullough, D. (2001). The Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870-1914. Simon & Schuster.
[2] G. Rabe, S. (2017). Intervention in Guatemala, 1953-1954. In S. G. Rabe, Eisenhower and Latin America: The Foreign Policy of Anticommunism. The University of North Carolina Press.
The nascent English kingdom consolidated its power across the English Channel at civil service examination , giving rise to a particularism that is particularly vivid today.
With no turning back now that Brexit has been consummated, Britain is seeking to establish a new relationship with its European neighbours. Its departure has not been supported by any other country, which means that London has to come to terms with a European Union that remains a bloc. Despite the drama with which many Europeans have greeted Britain's farewell, this is yet another chapter in the complex relationship that a large island has with the continent to which it is close. Island and continent remain where geography has placed them - at a distance of particular value - and are likely to reproduce vicissitudes already seen throughout their mutual history.

Fragment of the Bayeux tapestry, illustrating the Battle of Hastings in 1066.
article / María José Beltramo
The result of the 2016 referendum on Brexit may have come as a surprise, as the abrupt manner in which the UK finally and effectively left the European Union on 31 December 2020 has undoubtedly come as a surprise. However, what we have seen is not so alien to the history of the British relationship with the rest of Europe. If we go back centuries, we can see a geopolitical patron saint that has been repeated on other occasions, and also today, without having to speak of determinism.
Although it is worth mentioning some previous moments in the relationship of insular Britain with the continent next to it, such as the period of Romanisation, the gestation of the patron saint which at the same time combines linkage and distancing, or even rejection, can perhaps be placed at the beginning of the second millennium, when the Norman invasions across the English Channel consolidated the nascent kingdom of England precisely against the power of the other side of the Channel.
England in Norman times
Normandy became a political entity in northern France when in 911, following Viking invasions, the Norman chief Rolon reached an agreement with the Frankish king, agreement , guaranteeing him the territory in exchange for its defence[1]. 1] Normandy became a duchy and gradually adopted the Frankish feudal system, facilitating the gradual integration of the two peoples. This intense relationship would eventually lead to the full incorporation of Normandy into the kingdom of France in 1204.
Before the gradual Norman dissolution, however, the Scandinavian people settled in that part of northern France carried their particular character and organisational capacity, which ensured their independence for several centuries, across the English Channel.
The Norman-English relationship began in 1066 with the Battle of Hastings, in an invasion that led to the Duke of Normandy, William the Conqueror, being crowned King of England in London. The arrival of the Normans had a number of consequences. Politically, they brought the islands into the European relations of the time and brought English feudalism into line with Norman feudalism, a mixture that would lay the foundations for future English parliamentarianism instructions . In terms of Economics, the Normans demonstrated their Scandinavian organisational skills in the reorganisation of productive activities. In their different conquests, the Normans knew how to take the best of each system and adapt it to their culture and needs, and this was the case in England, where they developed a particular idiosyncrasy.
With this takeover of contact with the continent, England began to consolidate as a monarchy, while retaining its links with the Duchy of Normandy. However, with its strengthening after the fall of the Plantagenets in France, England gained the momentum it lacked to finally become an independent kingdom, completely separate from the continent, detached from a Normandy whose lineage was weak and in a critical state. Indeed, the Kingdom of France's absorption of the Norman duchy facilitated the development and consolidation of the English monarchy as an independent and strong entity[2].
The separation from the European continent brings us back to Ortega y Gasset's analysis of European decadence and the moral crisis it is going through[3]. The continental powers, being in a status of geographical continuity, and therefore in greater contact, are more likely to spread their status among themselves and to be dominated by another major power. England, having broken the bridge of feudal ties that connected it with the rest of Europe, finds no difficulty in distancing itself when it sees fit, always in its own interests, something we see repeated several times throughout its history. This is particularly evident in the vicissitudes that punctuate the UK's relationship with the continent throughout the final decades of the second millennium.
The English status since 1945
The Second World War greatly weakened the UK, not only economically but also as an empire. In the process of decolonisation that followed, London lost possessions in Asia and Africa, and the Suez Canal conflict confirmed its decline as a major player to its successor as the world's leading power, the United States. The post-war confrontation with the Soviet Union and the US presence in Europe meant that the transatlantic relationship was no longer based on Washington's preferential link with Britain, so the role of the British also declined[4].
In 1957 France, Germany, Italy, Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg created the European Economic Community (EEC). The Conservative Harold MacMillan, British Prime Minister from 1957 to 1963, refused to include the United Kingdom in the initiative, but aware of the need to revitalise the British Economics and "the difficulty of maintaining a policy that was alien to European interests", he promoted the creation of the EFTA (European Free Trade Association) in 1959, together with Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Switzerland, Austria and Portugal.
The Common Market proved to be a success and in 1963 the UK considered joining, but was blocked by de Gaulle's France. In 1966 the British again submitted a proposal application, but it was again rejected by de Gaulle. The French general's conception of Europe did not include the Atlantic bloc; he still envisaged building Europe on a Franco-German axis.
The 1970s saw a directional shift in European politics. The British Conservatives won the 1970 elections and in 1973 Britain joined the EEC. The international economic crisis, which was particularly difficult in the UK, led Labour, back in power, to propose a review of the terms of membership and Premier Harold Wilson called a referendum in 1975: 17 million Britons wanted to remain (67% of voters) compared with only 8 million who called for a first Brexit.
However, when the European Monetary System (EMS) was launched in 1979 to equalise currencies and achieve "economic convergence", the UK decided not to join this voluntary agreement . Europe was experiencing a gradual economic boom, but the UK's Economics was not keeping pace, which partly led to the early elections of 1979. These were won by the Conservatives with Margaret Thatcher, who remained in Downing Street until 1990. The Thatcher revolution "marked the way out of the crisis of the 1970s". In 1984, London reduced its contribution to EU funds and Thatcher, very reluctant to accept EU budgets and other procedures that reduced national sovereignty, again called for a review of the agreements.
In 1985 the Schengen Agreements were signed (the opening of borders between certain countries creating a kind of much wider second border), which came into force ten years later. Again, the UK stayed out of it. As was also the case in relation to the euro, when the single currency came into effect in 2002, maintaining the pound sterling to this day.
Immigration from Central and Eastern European countries following the 2004 EU enlargement, accepted by Labour's Tony Blair, and the acceleration of financial harmonisation mechanisms in the wake of the 2008-2011 crisis, met with displeasure by the Conservative David Cameron, provided arguments for the anti-EU speech in the United Kingdom. This led to the rise of the anti-European UKIP and the subsequent adoption of its positions by broad Tory sectors, eventually amalgamated by the controversial personality of Boris Johnson.
In an interview with the BBC in 2016, Johnson referred to many of the arguments used in favour of Brexit, such as the UK's dialectical vision of its relationship with the continent or the fear of losing sovereignty and the dissolution of its own profile into the European magma. The premier returned to these ideas in his message to the British people as the country prepared to begin its final year in the EU. His words were in some ways an echo of a centuries-old tug-of-war.
Repeating patterns
As we have seen, England has always maintained its own rhythm. Its geographical separation from the continent - far enough away to be able to preserve a particular dynamic, but also close enough to fear a threat, which was sometimes effective - determined the distinctly insular identity of the British and their attitude towards the rest of Europe.
We are dealing with a power that throughout history has always sought to maintain its national sovereignty at all costs and whose geopolitical imperative has been to prevent the continent from being dominated by a rival great power (the perception, during the 2008 crisis management , that Germany was once again exercising a certain hegemony in Europe could have fuelled the Brexit).
Perhaps in the medieval period, we cannot link this to a thought-out political strategy, but we do see how unintentionally and circumstantially, from the outset, certain conditions are in place that favour the distancing of the island from the mainland, although without radically losing contact . In more recent history we observe this same distant attitude, this time premeditated, in pursuit of interests focused on the search for economic prosperity and the maintenance of both its global influence and its national sovereignty.
[1] Charles Haskins, The Normans in European History (Boston and New York: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1915).
[2] Yves Lacoste, Géopolitique : La longue histoire d'aujourd'hui (Paris: Larousse, 2006).
[3] José Ortega y Gasset, La rebelión de las masas (Madrid: Alianza publishing house, 1983).
[4] José Ramón Díez Espinosa et al., Historia del mundo actual (desde 1945 hasta nuestros días), (Valladolid: Universidad de Valladolid, 1996).
Attempt by both to reposition France at the geostrategic centre of Europe, with civil service examination from Germany.
Napoleon Bonaparte's nephew and the current president of the French Republic are not entirely parallel lives, but there are some suggestive similarities between the two. It is often said that French presidents revive some of the longed-for packaging of the decapitated monarchy; in Macron's case there is probably a lot of that, but also the assumption of geopolitical imperatives already evident in the Second Empire.

Napoleon III in uniform in an 1850 portrait, and Macron in his New Year's Eve 2019 televised message.
article / José Manuel Fábregas
Emmanuel Macron's decision to hold the G7 summit in the French Basque town of Biarritz in August 2019 brought about a symbolic rapprochement with the figure of Napoleon III. The emperor, and nephew of Napoleon Bonaparte, transformed the former fishing village into a cosmopolitan holiday resort where European aristocrats and members of the international political elite gathered. Macron, for his part, has put Biarritz back on the stage of the world's major political discussions.
Thus two personalities come together who, with the attraction of having been the youngest heads of state in the country, share two fundamental aspects in their understanding of French politics. First, the influence that their childhood has had on both of them in developing a personalist way of understanding the head of state. And second, how both have tried to reposition France at the geostrategic centre of Europe and have been blocked by Germany.
What is the role of the head of state?
Born fifth in the order of Napoleon I's succession, the young Louis Napoleon Bonaparte never foresaw that he would become heir to the imperial house in 1832. According to his biographer Paul Guériot, his mother, Hortense de Beauharnais, instilled in him from an early age the idea that he was destined to rebuild the now-defunct Napoleonic Empire. His mother's insistence that he had a perfect intellectual and military training transformed Louis Napoleon - who received Education from the Jacobin, and follower of Robespierre, Philippe Le Bas - into a solitary, shy and megalomaniacal person obsessed with restoring Napoleonic France[1].
The revolution of February 1848, according to Jacob Talmon, was inevitable "although it was, nevertheless, an accident"[2]. The Israeli historian explains that the uprisings in various parts of Europe were a direct reaction to the territorial reordering of the Vienna congress (1815). In this context of discontent or disillusionment with the Restoration system, the figure of Louis Napoleon Bonaparte may have benefited from the image of a romantic revolutionary assigned to him by the newspapers and opinion writings of the time. After failed coup attempts in Strasbourg (1836) and Bologna (1840), the future emperor spent a brief period in prison. This was a determining factor in the construction of the romantic hero character that aroused such admiration in a society that loved the novels of Alexandre Dumas[3]. The exploitation of this personality by means of a huge propaganda apparatus enabled him to win the elections of December 1848 by a landslide. Thus, it could also be said that the establishment of the Second Empire - ratified by a popular plebiscite in November 1852 - was the next step in his main political project : the revival of Napoleonic France.
For his part, the current president of the French Republic also experienced an overprotective childhood that forged, like the last emperor of France, a solitary personality and an individualistic way of understanding politics. Anne Fulda stresses in her biography of Emmanuel Macron that, being born a year after the death of his older sister and after a complicated birth, his birth was considered a miracle. This may have fostered, along with a competitive Education in which he excelled as a 'child prodigy', his self-conviction that he was destined to rule the country[4]. However, his election as head of state was not the fruit of a long-term strategy deadline, but rather, like Louis Napoleon's, a tactical move. Macron's image of renewal was cleverly exploited in an election in which he faced rivals with certain communicative weaknesses, such as those with a low profile like François Fillon (Republican) and Benoît Hamon (Socialist), or others with more extremist tones like Marine Le Pen (National Front) and Jean-Luc Mélenchon (Unsubmissive France).
In 2015, while still minister of Economics, Emmanuel Macron made an interesting reflection for the weekly Le 1 on the role of the president in France. He understood that French citizens felt a lack after the fall of the monarchy, which they had tried to fill by strengthening the figure of the president. This excessive weight of personalism in Macron's understanding of politics has also been demonstrated recently in the replacement of Édouard Philippe as prime minister. Because the latter's popularity had grown over the last year as he had shown himself to be more charismatic and calm in contrast to the president's overacting and abusive protagonism, Macron chose Jean Castex as his replacement, with a more technocratic profile that does not overshadow the president in the face of his re-election.
What role France should play in Europe
This firm commitment by both leaders to give greater importance and visibility to the position head of state transcends the borders of France. Napoleon III and Emmanuel Macron also share the desire to place France at the centre of the European balance.
Having won the elections with a speech against the order inherited from the congress of Vienna, Napoleon III had his own European project based on the free integration or separation of the different national identities of the old continent. A clear example of this was the Crimean War (1854-1856). Fearing that the declining Ottoman Empire would end up as a vassal of Russia, the emperor defended, together with the United Kingdom and the Kingdom of Sardinia, its independence from the Ottomans in a conflict that would temporarily separate Russia from the other Western powers[5]. 5] The Treaty of Paris (1856) would not only end the war, but also motivate Napoleon III to initiate an interventionist policy in Europe.
Napoleon III's imperial dream forced him to develop an active foreign policy focused on expanding France's borders and reordering the continent with two main values in mind: nationalism and liberalism. However, Henry Kissinger rightly remarks that his diplomatic work was so confused that "France got nothing"[6]. By supporting the unification of Italy at the cost of the Austrian Empire's loss of territory, Napoleon unwittingly favoured the creation of Germany. These events severely weakened France's geostrategic influence in the new European order to which he aspired. In contrast, it was Bismarck's clever diplomatic tactics that would really put an end to the Vienna system, hastening the fall of the Second French Empire at the Battle of Sedan (1870).
Alongside this, Emmanuel Macron is presenting himself as the saviour of the European Union in a context marked by the rise of populist and Eurosceptic movements. However, his ambitious reform projects have met with Angela Merkel's reluctance.
In a recent interview for The Economist, Emmanuel Macron said that NATO was "brain-dead" and that Europe was "on the edge of a precipice" because of its dependence on the United States and lack of independence in terms of defence. Macron opted for greater EU integration in the strategic field, going so far as to propose a single pan-European army. In response, German Chancellor Angela Merkel objec ted that Europe does not currently have the capacity to defend itself and is therefore dependent on the Atlantic Alliance. In addition, Macron has also challenged the apparent agreement among EU member states over membership and the relationship with Russia. The French president's veto of Albania and North Macedonia's possible membership, on the grounds that they did not comply with EU corruption clauses, has even been described as a 'historic mistake', leaving the future of the Balkan countries at the mercy of Russia and China. This position is not shared by Russia, with which he is willing to ease diplomatic relations and even suggests further integration of the country into Europe.
On final, Emmanuel Macron and Napoleon III share an excessively egocentric vision. The overexposure of certain personal characteristics in matters of state and the excessive claim to leadership in Europe are two aspects common to these two young leaders. While historiography has already judged the mistakes that precipitated Louis Napoleon into exile, it remains to be seen whether or not Macron is doomed to repeat the history of his predecessor.
[1] Guériot, P. (1944). Napoleon III. Madrid: Ediciones Técnicas.
[2] Talmón, J.L. (1960). Political messianism. La etapa romántica. Mexico City: Ed. Aguilar.
[3] Guériot, P. (1944). Napoleon III. Madrid: Ediciones Técnicas.
[4] Fulda, A. (2017). Emmanuel Macron, the president who has surprised Europe. Madrid: Ediciones Península.
[5] Milza, P. (2004). Napoleon III. Paris: Éditions Perrin.
[6] Kissinger, Henry (1994). Diplomacy (First Edition). Barcelona: Ediciones B.
Prepare to project "credible combat power" in the new era of "strategic competition".
If the Arctic was an important stage in the Cold War, in the new geopolitical tension its progressive thawing even accentuates its strategic characteristics. In 2019, the US Defence department adapted its Arctic strategy to the new rivalry with Russia and China, and then it was up to the forces most involved in the region to implement it: in 2020 the Air Force presented its own document and in 2021 the Navy did so, also involving the Marine Corps and the Coast Guard. The guidelines seek to ensure the projection of "credible combat power".

The crew of the submarine USS Connecticut at the ICEX 2020 exercises [US Navy].
article / Pablo Sanz
The Arctic is important because of the untapped natural wealth contained in its subsoil (22% of the world's hydrocarbon deposits, or 90 billion barrels of oil) and because of its strategic position on the globe: the two great continental masses of Eurasia and America converge here. The opening of new maritime routes thanks to the progressive melting of the ice is not only a commercial advantage, but also makes it possible to act militarily more quickly in this and other scenarios.
Many countries are interested in promote cooperation and multilateralism in the region, and this is done from the committee Arctic; however, the complex security environment of the Arctic Circle has led the major powers to set strategies to defend their respective interests. In the case of the United States, the Defence department updated in June 2019 the Arctic strategy it had developed three years earlier, in order to bring it into line with the new approach that emerged with the 2017 National Security Strategy (NSS) and carried over into the 2018 National Defence Strategy (NDS), documents that leave behind the era of combating international terrorism and elevate the relationship with China and Russia to 'rivalry', in a new geopolitical status of 'strategic competition'.
The Pentagon's strategy for the Arctic was then fleshed out by the air force in its own report , presented in July 2020, and then by the navy in January 2021. Along the same general lines, these approaches framework are aimed at three objectives:
1) As an "Arctic nation", because of its sovereignty over Alaska, the United States must ensure security in its territory and prevent polar positions from threatening other parts of the country.
2) The United States seeks to establish and lead alliances and agreements in the Arctic in accordance with international law in order to maintain a stable status in the area.
3) The United States commits to preserving free navigation and overflight in the Arctic Circle, while limiting Russian and Chinese interference contrary to this general freedom of access and transit.
To achieve these objectives, the Pentagon has defined three mechanisms for action:
i) Raising awareness of the importance of the area: the ability of the Defence department to detect threats in the Arctic is a prerequisite for deterring or responding to activities of strategic competitors in the region.
ii) Enhance and promote operations in the Arctic: department Defence will improve the ability of its forces to operate in the Arctic through regular exercises and deployments to the region, both independently and with allies. Some exercises will be conducted within the NATO context while others will be bilateral or multilateral.
iii) Strengthen the rules-based order in the Arctic: department Defence will continue to work with US allies to maintain and strengthen the freedom of navigation and overflight regime. This will help deter aggressive acts in the area.
From the new NDS the Defence department states that the US military must be able to solve the main problem identified - the erosion of the competitive edge against China and Russia - by being able to "deter and, if necessary, defeat great power aggression". To do so, it must develop a force that is "more lethal, resilient, agile and ready", which in the Arctic region must achieve "credible deterrent power".
US military doctrine warns that the Arctic's character as a 'strategic buffer' is 'eroding', becoming 'a pathway of threat to national territory due to the advances of competing great powers'. It also 'hosts critical launching points for global power projection and increasingly accessible natural resources'. However, it warns that "the immediate possibility of conflict is leave".
Thus, in the context of implementing the national defence strategy, the Pentagon states that it will continue to prepare its units to ensure that the Arctic is a secure and stable region in which US national interests, regional security and the work joint efforts of the nations involved to address common problems are safeguarded.
The US Air Force and Navy documents outline supporting measures to ensure the ability to deter hostile actions in the Arctic by other regional competitors in the area, while prioritising a cooperative and continuous approach that preserves the rules by which the Arctic is governed.
Air and sea
Because the Gulf of Mexico current heads towards the European side of the Arctic, the North American side of the Arctic suffers even harsher environmental conditions, with less maritime infrastructure and land routes. As a result, the Air Force's role in the defence of this area is clearly greater, accounting for 80% of the resources the Pentagon devotes to the region.
Its operations are based at a number of locations. Six of these are in Alaska: the large airborne instructions at Elmendorf-Richardson and Eielson; the early missile notice facility at Clear and the missile defence radar at Eareckson; and other coordination, training and survival school sites. Two others are in Greenland: the Raven training range for LC-130 aircraft and the Thule early missile notice site. In Canada, it has a system of some fifty radars shared by NORAD (North American Air Defence Command).
The air force intends to improve these capabilities, as well as command, control, communications, intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (C3ISR) capabilities. It has also set goal to enhance refuelling conditions. Once the F-35 deployment at Eielson is complete, Alaska will host more advanced fighters than any other location in the world.
For its part, the US Navy is positioning itself around the concept of the "Blue Arctic", thus graphically expressing the progressive homologation with the rest of the world's oceans of what has historically been an impassable white cap. The navy envisages increasing its presence, both with manned ships and new unmanned vessels. In its strategy document, it warns that the research in new capabilities "may not be fully realised and integrated into the naval force for at least a decade".
The increased naval presence in the region will also be realised through increased operations already routinely conducted in the Arctic by the Second and Sixth Fleets and through synchronisation with the Marine Corps and Coast Guard based in Alaska. To ensure this operational augmentation, the Navy will undertake an upgrade of docking facilities and attendance for its ships.
The Navy document, which does not specify specific preparations, also does not include the Coast Guard's announced plans for a new fleet of icebreakers. There are currently only two in service and the plan is to build three medium and three heavy icebreakers by 2029.
In doing so, Washington is trying to counter the accelerated efforts of its closest competitors. In July 2020, department warned of growing interest in the Arctic from Russia and China, accusing them of engaging in "increasingly aggressive" competition and lamenting that those countries that want "peace, freedom and democracy", including the United States, have been "naïve".
Russia and China
Russia has the largest land mass and population within the Arctic Circle, a region from which Russia derives 25 per cent of its GDP. No other country has such a permanent military presence above the 66th parallel; no other nation has so many icebreaking ships, a fleet Moscow wants to increase with fourteen new vessels, one of them nuclear-powered.
Russia formed its joint strategic command of the Northern Fleet in December 2014. "Since then, Russia has gradually strengthened its presence by creating new Arctic units, refurbishing old infrastructure and airfields, and establishing new military instructions along the coast. There is also a concerted effort to establish a network of air and coastal defence missile systems, early notice radars, rescue centres and a variety of sensors," according to the US defence report strategic Arctic department . The US also warns that Russia is attempting to regulate maritime traffic in the Northern Route in ways that may exceed its authority under international law.
China, on the other hand, without being an Arctic nation (Mohe, its northernmost city is at the same latitude as Philadelphia or Dublin) wants to be a major player in the region. It is an observer country of the committee Arctic and claims a "near-Arctic nation" status that Washington does not recognise. In 2018 it produced the first white paper on its Arctic policy and has integrated this area into its New Silk Road initiative.
China's diplomatic, economic and scientific activities in the Arctic have grown exponentially in recent years. At the moment its operational presence is limited: it has one Ukrainian-built polar-capable icebreaker (the Xuelong; it has recently built the Xuelong 2), which has sailed in Arctic waters on operations that China describes as research expeditions.
 The opening of Arctic sea lanes is in China's interest, as it could shorten trade shipment times to Europe and reduce its dependence on flows through the particularly vulnerable Strait of Malacca.
The opening of Arctic sea lanes is in China's interest, as it could shorten trade shipment times to Europe and reduce its dependence on flows through the particularly vulnerable Strait of Malacca.
Lately, China has been engaging in increased diplomatic activities with the Nordic countries and has research stations in Iceland and Norway, as well as mining resources in Greenland. This highlights Beijing's growing interest in consolidating its presence in the Arctic despite its remoteness from the region.
Russia's great financial capacity also means that it is counting on China to develop energy and infrastructure projects in the region, such as a liquefied natural gas facility in Yamal. According to Frédéric Laserre, an expert on Arctic geopolitics at Laval University, Russia has no choice but to accept Chinese capital to build and develop the infrastructure needed to exploit the resources due to Western economic sanctions.
