The high issue of murdered social leaders continues to dismay the country: 904 assassinations since the 2016 Peace agreement
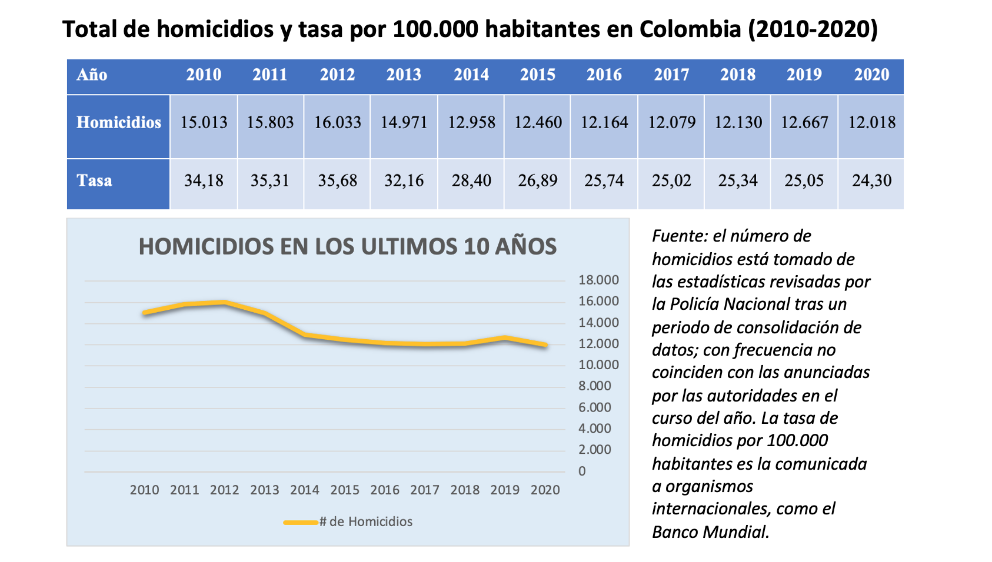
° In 2020 there were 24.3 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants in Colombia, the most leave since 1975, when there was a similar rate, and below that of other countries in the region.
° The issue homicide rate in 2020 was 12,018, following the progressive decline recorded since 2002, only openly broken in 2012, when 16,033 murders were committed.
° programs of study concludes that there is a link between the demobilisation of the FARC and the consistent decrease in the level of violence that the country is experiencing.

Religious ceremony in Dabeiba in February 2020, after recovering the remains of a man who disappeared in 2002 [JEP].
report SRA 2021 / Isabella Izquierdo [PDF version].
MAY 2021-Colombia is gradually reducing its levels of violence, at least in terms of the homicide rate, which in 2020 fell to 24.3 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants, the most leave since 1975. Although the drama of the murder of social leaders has overwhelmed Colombian society in the post-conflict management , the objectivity of the total figures speaks of a reduction in violent deaths. This decrease has been sponsored in the last years by the withdrawal of the armed struggle by the FARC and presumably has been favored in 2020 by the prolonged confinements established to face the spread of the Covid-19 pandemic.
The country closed 2020 with 12,018 homicides, the most leave in decades, less than half the number in the early 1990s, during the worst period of the armed conflict. At that time, issue homicides exceeded 28,000 per year, or around 80 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants. Since then, with slight upturns in 2002 and 2012, Colombia has been reducing its levels of violence and today its homicide rate is far from the records being set by other countries in the region: although in some cases the health emergency has also helped to lower the figures, in 2020 the highest fees were those of Jamaica (46.5 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants), Venezuela (45.6), Honduras (37.6), Trinidad and Tobago (28.2) and Mexico (27).
(In the case of Colombia, the authorities spoke at the end of 2020 of a rate of 23.79, although later homicide figures from the National Police and data population figures give as result the estimate of 24.3 that has been chosen here).
Conflict and post-conflict
While ELN guerrillas remain active and several FARC dissidents continue to engage in criminal activities, around 8,000 ex-combatants were incorporated into civilian life as a result of the agreement peace agreement between the Colombian government and the FARC, which began negotiations in 2012 and was signed in 2016.
The years prior to the beginning of the contacts saw an increase in violence, and then a steady decrease since then, not only in violence related to the political conflict, but also in violence related to crime in general. When investigating the homicide fees during the years of the peace talks with the FARC, the Directorate of research Criminal and Interpol in Colombia revealed a close relationship: when the armed confrontation increased or decreased, depending on the interests of the negotiators, so did the total number of homicides. The good progress of the negotiation marked a dynamic of de-escalation of the armed conflict, with a reduction of 8.57% in the homicide rate between 2012 and 2015.
In 2017, after the signing of the peace agreement agreement , violence in Colombia reached its lowest levels in 30 years, with 12,079 homicides and a rate of 25.02 homicides per 100,000 inhabitants. However, in 2018 the trend changed slightly (12,130 homicides), something that was pronounced in 2019 (12,667), which alerted to the need to rapidly implement the conditions for the reintegration of ex-combatants, improve security in demilitarised zones and increase state presence in the territory.
The high school of Medicina Legal concluded that the homicide figures for 2018 seemed to show a reactivation of the Colombian armed conflict. status For its part, the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights presented in 2019 a report evaluating the human rights situation in Colombia, with emphasis on the implementation of the contents of agreement de Paz: the highest homicide figures were in Antioquia, Cauca and Norte de Santander, where the clashes for the control of illicit economies were most violent.
Effect of Covid
Post-conflict measures and the arrival of the pandemic, with its restrictions on movement, again led to a drop in homicides in 2020. In the period from 20 March to 17 August 2020, when the strictest confinements were in place, daily homicides per municipality fell, on average, by 16% from their pre-social distancing trend. In the weeks of full quarantine, the daily homicide issue even fell by around 40% from the pre-quarantine trend. From June 2020 onwards, the homicide issue returned to pre-emergency trends. Crime dropped in the first months due to fear of contagion, but quickly returned to the usual figures, especially in terms of robbery and theft, as the economic status worsened and the need for food among the poor increased. However, because of what happened in the first semester of the year, Colombia closed 2020 with thehighest homicide rate leave in the last 46 years.
A clear negative of 2020, however, was the continuation of violence directed against social leaders and ex-combatants. Last year, 297 local leaders were killed, bringing the total number of social actors killed from 2016 to February 2021 to 904. In the same period, 276 former guerrillas were killed, most of them involved in appearances before the Special Jurisdiction for Peace.