essay / Alejandro Palacios
The violent revolts in Nicaragua, the war in Syria or the status in Yemen are examples of some of the most bloody episodes that are being experienced around the world. Such episodes are, for the most part, aggravated by the disintegrative mentality that prevails in a large part of the world's societies. The promotion of an inclusive culture of peace is one of the challenges posed by the Norwegian sociologist and mathematician Johan Galtung.
Johan Galtung is considered, due to his long trajectory and wide academic experience, as one of the best experts in the topic of alternative conflict resolution. In addition, he has been the founder of two of the most renowned institutions in the field of conflict resolution, such as the high school International Peace research in Oslo (1959) and the Journal of research on Peace (1964). As a result, his books and essays have been widely echoed in the community of experts in this subject. Here we will focus especially on his work "After Violence, 3Rs: Reconstruction, Reconciliation and Resolution", published in 1999 and still very relevant today, as it sheds light on the causes of the conflict and its possible solutions.
His main thesis is that conflict is innate in society as there are limited resources and overlapping interests, but whether these lead to violence depends on the will of the individual. In his own words: "Violence is not like eating or sexual relations, which are found all over the world with slight variations". That is why the author rejects Hobbes' thesis in the famous sentence "Homo homini lupus", i.e. that man, in his state of nature, tends to his extinction. From this point Galtung provides a series of aspects that the peace worker must take into account for the correct resolution of a conflict.
Galtung emphasizes the need for a deep analysis of the conflict in order to understand its multidimensionality. Otherwise, the peace worker may misdiagnose the conflict. He puts it this way: "One of the problems is not understanding that conflict has a broader dimension. Therefore, sometimes it may not be given the right treatment (as if the doctor says that an ankle inflammation is an ankle disease and not a heart dysfunction // or hunger as insufficient food intake and not a social problem)".
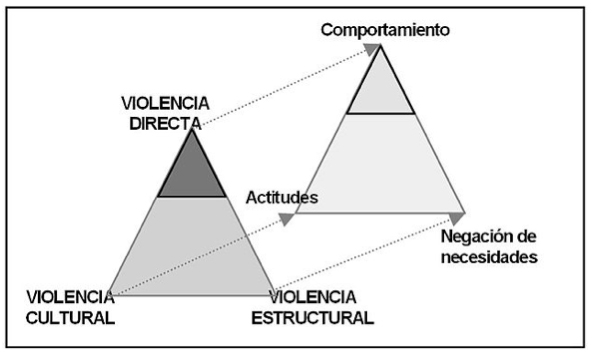
To make this task somewhat simpler, Galtung provides us with two triangles of violence, which are related to each other. The first is the ABC triangle: Attitudes adopted towards conflict or peace-making; behaviors adopted or peace-keeping; and contradiction underlying the (root) conflict or peace-building. The second triangle indicates that there are two types of violence: the visible and the invisible. The visible is direct violence and the invisible is cultural violence (which causes or feeds direct violence) and structural violence. This is why the author insists on the importance of promoting a culture of peace in which peaceful mechanisms to resolve a conflict without resorting to violence predominate, i.e. a culture based on non-violence, empathy and creativity (to go beyond the mental Structures of the parties to a conflict). Thus, the so-called golden rule "Don't do to others what you wouldn't want them to do to you," he says, is a good way to start forging such a culture. Although this, he says, has one problem: that tastes differ.
|
|
Politics, according to Galtung, can help create this culture, which he considers essential to avoid violence as much as possible. Galtung considers democracy to be the best system for creating what he calls a "culture of peace". However, he himself makes a number of criticisms of this political system. First of all, he claims that democracy is equivalent to the dictatorship of the 51% against the rest. This is something that, however, is mitigated thanks to human rights, as he himself acknowledges. Secondly, the author asserts that the sum of all democracies is not universal democracy. An action that affects other states does not have legitimacy just because it has been adopted democratically (something mitigated by international organizations, but which can lead to the status described in the first place). The conclusion to be drawn from all this is that democracy entails a certain Degree of structural violence, but less than with other systems of government.
Finally, Galtung makes a comparison between the Western and Eastern ways of resolving a dispute from the perspective of the temporal dimension of a conflict. While the Western one makes use of a diachronic approach of time, i.e. over time, the Eastern one makes use of a synchronic approach of time, i.e. at the same time. At summary, the Eastern perspective works in the three areas of resolution, reconciliation and reconstruction (the 3Rs) successively and not one after the other, as does the Western world.
Experts on subject of conflicts make a clear distinction between three types of conflicts. On the one hand we have direct violence staff (verbal or physical); indirect structural violence (political and economic exploitation); finally, there is cultural violence. In particular, the English economist Kenneth Boulding criticizes Galtung's analysis on the grounds that it analyzes conflicts from a purely structuralist perspective. In this way, he criticizes, on the one hand, that the method used is very taxonomic, since, according to Boulding, "taxonomy is a convenience of the human mind rather than a description of reality". On the other hand, Galtung's emphasis on equality, as opposed to hierarchies, for conflict mitigation is criticized, since, according to the Briton, Galtung does not take into account that such equality has negative consequences in terms of quality of life and freedom.