Ruta de navegación
Blogs
Entries with label india .
[Parag Khanna, The Future is Asian. Simon & Schuster. New York, 2019. 433 p.]
review / Emili J. Blasco
 Parag Khanna's book can be greeted with suspicion from entrance because of the apparent axiomatic character of his degree scroll. However, the blunt assertion on the cover is softened when one begins to read the pages inside. The thesis of the work is that the world is in a process of asianisationnot of chinisationMoreover, this process is presented as another coat of paint on the planet, not as a colour that will be clearly predominant or definitive.
Parag Khanna's book can be greeted with suspicion from entrance because of the apparent axiomatic character of his degree scroll. However, the blunt assertion on the cover is softened when one begins to read the pages inside. The thesis of the work is that the world is in a process of asianisationnot of chinisationMoreover, this process is presented as another coat of paint on the planet, not as a colour that will be clearly predominant or definitive.
It is possible that the discussion over whether the US is in decline and will be replaced by China as the pre-eminent superpower obscures other parallel developments. Those watching Beijing's rise in the world order, writes Khanna, "have often been paralysed by two views: either China will devour the world or it is on the verge of collapse. Neither is correct. "The future is Asian, even for China," he asserts.
Khanna believes that the world is moving towards a multipolar order, which is also the case in Asia, even if China's size often dazzles.
The author's Indian background and also his time living in the United States may have influenced this judgement, but he offers figures to support his words. Of the 5 billion people living in Asia, 3.5 billion are non-Chinese (70%): China thus has only a third of Asia's population; it also accounts for slightly less than half of Asia's GDP. Other data: half of outward investment from the continent is non-Chinese, and more than half of outward investment goes to Asian countries other than China. Asia is therefore "more than China plus".
It is not just a question of size, but of wills. "A China-led Asia is no more acceptable to most Asians than the notion of a US-led West is to Europeans," says Khanna. He rejects the idea that, because of China's power, Asia is heading towards a kind of tributary system like the one ruled in other centuries from Beijing. He points out that such a system did not extend beyond the Far East and was based primarily on trade.
The author reassures those who fear Chinese expansionism: "China has never been an indestructible superpower presiding over all of Asia like a colossus". He warns that while Europe's geographical characteristics have historically led many countries to fear the hegemony of a single power, Asia's geography makes it "inherently multipolar", as natural barriers absorb friction. Indeed, clashes between China and India, China and Vietnam or India and Pakistan have ended in stalemates. "Whereas in Europe wars have occurred when there is a convergence in power between rivals, in Asia wars have occurred when there is a perceived advantage over rivals. So the more powerful China's neighbours like Japan, India or Russia are, the less likely they are to conflict with each other.
For Khanna, Asia will always be a region of distinct and autonomous civilisations, especially now that we are witnessing a revival of old empires. Asia's geopolitical future will not be led by the US or China: "Japan, South Korea, India, Russia, Indonesia, Australia, Iran and Saudi Arabia will never come together under a hegemonic umbrella or unite into a single pole of power".
There will not be, then, a Chineseisation of the world, according to the author, and the Asianisation that is taking place - a shift of the world's weight towards the Indo-Pacific - need not be seen as a threat to those who live elsewhere. Just as there was a Europeanisation of the world in the 19th century, and an Americanisation in the 20th century, we are witnessing an Asianisation in the 21st century. Khanna sees this as "the most recent substratum of sedimentation in the geology of global civilisation", and as a "layer" it does not imply that the world Withdrawal to what came before. "Being more Asian does not necessarily mean being less American or European," he says.
The book analyses the weight and fit of different Asian countries on the continent. Of Russia, he argues that it is strategically closer to China today than at any time since its communist pact in the 1950s. Khanna believes that geography leads to this understanding, as it invites Canada to maintain good relations with the United States; he predicts that climate change will further open up the lands of Siberia, which will integrate them more with the rest of the Asian continent.
As for India and China's relationship, Khanna believes that both countries will have to accept each other as powers more normally. For example, despite India's reluctance towards China's Silk Road and India's own regional connectivity projects, in the end the two countries' preferred corridors will "overlap and even reinforce each other", ensuring that products from inland Asia reach the Indian Ocean. "Geopolitical rivalries will only accelerate the Asianisation of Asia," says Khanna.
In assessing the importance of Asia, the book includes Middle Eastern oil. Technically, the region is part of the continent, but it is such a separate chapter with its own dynamics that it is difficult to see it as Asian territory. The same is true when label is used to refer to Israel or Lebanon. It can give the impression that the author is lumping everything together in order to make the figures more impressive. He argues that the Middle East is becoming less and less dependent on Europe and the United States and is looking more to the East.
Khanna is in a position to reasonably defend himself against most of the objections to his text. Most controversial, however, is his near-defensive justification of technocracy as a system of government. Beyond the descriptive attitude of a model that in some countries has received an important economic and social development , Khanna even seems to endorse its moral superiority.
[Bruno Maçães, Belt and Road. A Chinese World Order. Penguin. Gurgaon, India, 2019. 227p.]
review / Emili J. Blasco
 |
Covered the moment of literature devoted to presenting the novelty of the project A Chinese leader of the New Silk Road, Bruno Maçães leaves aside many of the specific specifics of the Chinese initiative to deal with its more geopolitical aspects. That is why throughout the book Maçães uses the name Belt and Road all the time, instead of its acronyms – OBOR (One Belt, One Road) or the lately more used BRI ( Belt and Road Initiative) – because he is not referring so much to the layout of transport connections themselves as to the new world order that Beijing wants to model.
Through this economic integration, according to Maçães, China could project power over two-thirds of the world, including Central and Eastern Europe, in a process of geographical cohesion of Eurasia to which this politician and the European Union has already been able to achieve this goal. researcher He dedicated his earlier work.
Compared to other essays on the New Silk Road, this one directs a lot of attention to India (this is true in its general content, but also in this one). review A special edition has been used for that country, with a particular introduction).
Maçães grants India the role of core topic vault in the project integrator of Eurasia. If India decides not to participate at all and instead gamble on the alternative promoted by the United States, along with Japan and Australia, then the design China will not reach the dimension desired by Beijing. "If India decides that life in the Western order will be better than under alternative arrangements, the Belt and Road will struggle to achieve its original ambition," says the author.
However, Maçães believes that the West is not entirely that attractive to the subcontinent. In that Western order, India can only aspire to a secondary role, while the rise of China "offers it the exciting possibility of a genuinely multipolar, rather than merely multilateral, world in which India can legitimately hope to become an autonomous center of geopolitical power," at least on the same level as a declining Russia.
Despite these apparent advantages, India will not go completely to either side, Maçães predicts. "It will never join the Belt and Road because it could only consent to join China in a project that it was new. And it will never join a U.S. effort to rival the Belt and Road unless the U.S. makes it less confrontational." So, "India will leave everyone waiting, but it will never make a decision on the Belt and Road."
Without the involvement of Delhi, or even more so, with resistance from the Indian leadership, neither the US nor China's vision can be fully brought to fruition. internshipMaçães continues. Without India, Washington may be able to preserve its current model of alliances in Asia, but their ability to compete on the scale of the Belt and Road would collapse; For its part, Beijing is realizing that it alone cannot provide the financial resources needed for the ambitious project.
Maçães warns that China has "ignored and disdained" India's positions and interests, which may end up being "a big miscalculation." He believes that China's impatience to start building infrastructure, due to the need to demonstrate that its initiative is a success, "can become the worst enemy."
An adventure that the Chinese can correct the shot. "It is likely – perhaps even inevitable – that the Belt and Road will grow more and more decentralized, less Chinese-centric," he says, commenting that in the end this new Chinese order would not be so different from the structure of the existing world order led by Washington, where "the United States insists on being recognized as the state at the apex of the international power hierarchy" and leaves some autonomy to each regional power.
If Maçães puts India in a status Non-alignment plenary session of the Executive Council, does provide for an unequivocal partnership of that country with Japan. In his view, it is a "symbiotic" relationship, in which India sees Japan as its first source of technology, while Japan sees the Indian navy as "a partner indispensable in its efforts to contain Chinese expansion and safeguard freedom of navigation" in the region's seas.
As for Europe, Maçães sees it in the difficult position "of not being able to oppose a project economic integration, while it is equally incapable of joining as a mere participant" in the Chinese initiative, in addition to the seed of division that the project in the European Union.
Bangladesh to Pakistan and Djibouti
Despite the above-mentioned differences, Maçães believes that the relationship between China and India can develop positively, even if there is some element of latent conflict, encouraged by a certain mutual distrust. The commercial linkage of two such immense markets and production centers will generate economic ties "called dominating" the economy. Economics towards the middle of this century.
This movement of goods between the two countries will make Bangladesh and Myanmar the centre of a major trade corridor.
For its part, Pakistan, in addition to being a corridor for the exit to the Indian Ocean from western China, will be increasingly integrated into the Chinese production chain. Specifically, it can feed raw materials and basic manufactures to the textile industry that China is developing in Xinjiang, its export gateway to Europe for goods that can optimize rail transport. The capital of that province, Urumqi, will become the fashion capital of Central Asia in the next decade. agreement with the forecast of Maçães.
Another interesting observation is that the shrinking of Eurasia and the development of internal transport routes between the two ends of the supercontinent, may cause the container ports of the North Sea (Amsterdam, Rotterdam, Hamburg) to lose weight in trade between Europe and China at the expense of greater transit of those in the Mediterranean (Piraeus, especially).
The author also ventures that Chinese infrastructure works in Cameroon and Nigeria can help facilitate connections between these countries and Doralé, the port that China manages in Djibouti, which in this way, through these trans-African routes, could become "a serious rival" to the Suez Canal.
If China has its first, and so far only, military base outside its territory, it must be borne in mind that Beijing may give a possible military use to other ports whose territory is not the same. management has assumed. As Maçães recalls, in 2016 China approved a framework This is a legal law that obliges civilian companies to support military logistics operations requested by the Chinese Navy.
These are all aspects of a thought-provoking book that does not allow itself to be carried away by the determinism of China's rise, nor by an antagonistic vision that denies the possibility of a new world order. It is the work of a European who, although he served in the Portuguese Ministry of Foreign Affairs as a director for Europe, is realistic about the EU's weight in the design of the world.
This crucial shipping lane faces hard power pressures from both states as they yearn for naval control of contested waters
A thermometer to measure the future balance of power between China and India will be the Strait of Malacca, the key bottleneck that connects the northern Indian Ocean and the Asia-Pacific region. India is advancing positions towards the western mouth of the Strait in order to challenge the expansion of Chinese maritime interests, which pay greater attention to Malacca.
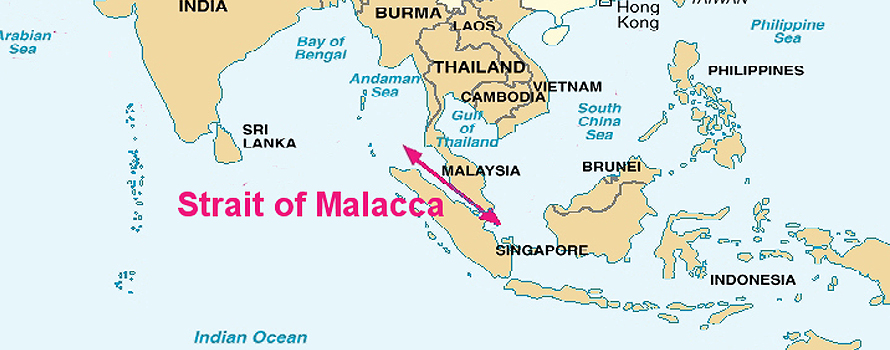
▲Map of the Indo-Pacific region [US DoD].
ARTICLE / Alejandro Puigrefagut [English version] [Spanish version].
Maritime routes are the basis of trade and communication between more than 80% of the countries of the world. This fact makes the natural geographic location of the States a great strategic feature. An especially important point for maritime traffic is the Strait of Malacca, key for trade in the region with the largest population on the planet.
The Strait of Malacca, which connects the South China Sea with the Burma Sea on its way to the Bay of Bengal, is the busiest commercial crossing in the world and, therefore, is a strategic place. Through this corridor that surrounds the western coast of the Malay peninsula and the Indonesian island of Sumatra, approximately 60% of the world's maritime trade transits, exceeding one hundred and fifty ships per day and is the main source of oil supply for two of the main Asian consumers; the People's Republic of China and Japan. This geographical point is key for the entire Indo Pacific region, thus ensuring the free movement of ships becomes strategic. That is why many States in the region, including China and the United States, see the need for protection of this passage in order to be able to supply themselves, export their merchandise and not be blocked by the control of a third country over this area.
In relation to China it is not easy to think that a blockade of its supply due to problems in the Strait of Malacca will happen. In order for this to happen, an armed conflict of great dimensions would have to be generated, propitiating this blockade by a subject that could control - and potentially interrupt - the passage towards the other countries of the region. This potential risk, which today can only be generated by the United States Navy, forces China to be alert and have to develop sufficient military capabilities to protect what it considers its territories in the South China Sea and, by extension, the supply of vital resources that must necessarily cross the Strait of Malacca.
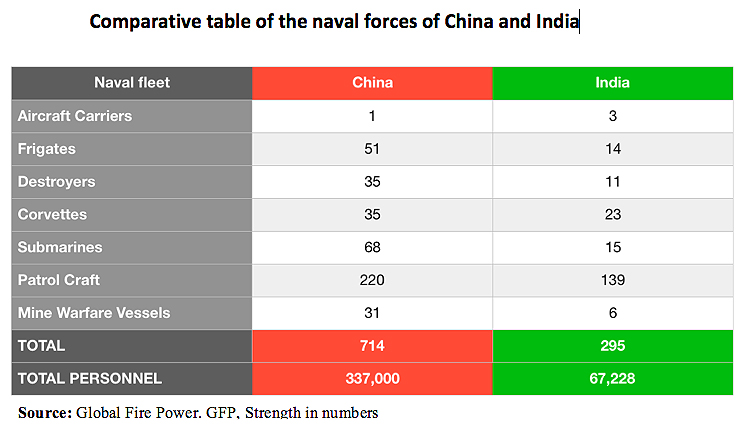 |
The positions and presence of the Asian giant in the South China Sea and in the areas adjacent to the Strait of Malacca have increased during the last years, in order to increase its influence on the States of the region. Moreover, to defend its oil and natural gas supplies (from the Persian Gulf), China has extended its presence to the Indian Ocean, although this is not enough. The reality is that in this area there is a great competition between two of the Asian powers with more influence in the region: China and India. Due to the increasing presence and influence of the People's Republic in the Indian Ocean, India has been forced to take proactive measures to improve peace and stability in the region, mobilizing and expanding its presence from its east coast towards the Strait, in order to rebalance the regional power. With this, India can dominate the western access to the Strait and, therefore, have a longer reaction time to maneuver in the Indian Ocean as in the Strait itself and, even, access to the waters of the South China Sea more agilely.
At the same time, this growing approximation of India to the South China Sea, is observed with concern in Beijing, and even, some analysts see India as a threat if an hypothetical case of a war between the two regional powers could occur and India were to block the Strait and, therefore, China's access to certain raw materials and other resources. For this reason, China has carried out various military maneuvers in the past three years together with third States in the Strait of Malacca, especially with Malaysia. During the first exercises in the area, the Ministry of Defence of the People's Republic of China concluded that bilateral relations with Malaysia were strengthened in terms of cooperation in security and defense and that "increase the capacity to jointly respond to real security threats and safeguard regional maritime security." In addition, for China, the protection of the Strait is a priority because of its great strategic value and because countries like the US or Japan also want to control it.
The well-trodden step, decisive in the strategies of both countries to counter each other
A thermometer to measure the future pulse of forces between China and India will be the Strait of Malacca, a passage through the Strait of Malay core topic for the connection between the northern Indian Ocean and the Asia-Pacific region. India is responding to the further expansion of Chinese maritime interests, which force Beijing to pay close attention to Malacca, by advancing positions towards the western mouth of the strait.

▲Map of the Indo-Pacific [US DoD]
article / Alejandro Puigrefagut [English version]
Sea routes are the basis of trade and communication between more than 80% of the world's countries. This fact makes the natural geographical location of States of great strategic importance. A particularly important point for maritime traffic is the Strait of Malacca. core topic for the trade of the most populous region on the planet.
The Strait of Malacca, which links the South China Sea with the Burma Sea on its way to the Bay of Bengal, is the world's busiest commercial passage and is therefore a strategic location. This corridor , which surrounds the western coast of the Malay Peninsula and the Indonesian island of Sumatra, is used by approximately 60% of the world's maritime trade, exceeding one hundred and fifty ships per day, and is the main oil supply route for two of Asia's main consumers: the People's Republic of China and Japan. This geographical point is core topic for the entire Indo-Pacific region, ensuring the free movement of ships is strategic. That is why many states in the region, including China and the United States, see the need to protect this passage in order to be able to supply themselves, export their goods and not be blocked by the control of a third country over this area.
In relation to China, it is not easy to think that a blockade of its supply due to problems in the Strait of Malacca will happen. For this to happen, an armed conflict of extraordinary dimensions would have to be generated, propitiating this blockade by a subject that could control – and potentially interrupt – the passage to the other countries of the region. This potential risk, which today can only be generated by the U.S. Navy, forces China to be vigilant and have to develop sufficient military capabilities to protect what it considers its territories in the South China Sea and, by extension, the supply of vital resources that must necessarily pass through the Strait of Malacca.
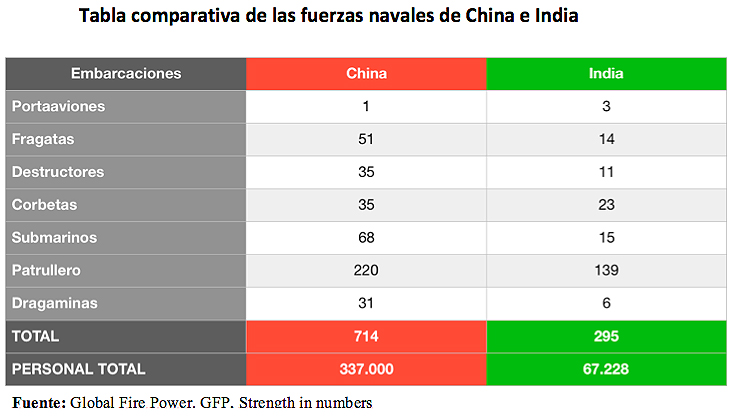 |
The Asian giant's positions and presence in the South China Sea and in the areas adjacent to the Strait of Malacca have increased in recent years, with the aim of increasing its influence over the states of the region. Moreover, in order to defend its supplies of oil and natural gas (from the Persian Gulf), China has extended its presence to the Indian Ocean, although this is not enough. The reality is that in this area there is a large skill between two of the most influential Asian powers in the region: China and India. Due to the growing presence and influence of the People's Republic in the Indian Ocean, India has been forced to take proactive measures to improve peace and stability in the region, mobilizing and expanding its presence from its east coast to the vicinity of the Strait, in order to rebalance the regional balance of power. In this way, India can dominate the western access to the Strait and, consequently, have a longer reaction time to manoeuvre in the Indian Ocean as well as in the Strait itself and even access the waters of the South China Sea more quickly.
At the same time, India's growing approach to the South China Sea is watched with concern in Beijing, and some analysts even see India as a threat in the hypothetical case of a war between the two regional powers and India blocks the Strait and, therefore, China's access to certain raw materials and other resources. For this reason, China has conducted a number of joint military exercises with third States in the Strait of Malacca over the past three years, especially with Malaysia. During the first exercises in the area, the Ministry of Defense of the People's Republic of China concluded that bilateral relations with Malaysia were strengthened in terms of security and defense cooperation and that the joint response capability to security threats was "increased." In addition, for China, the protection of the Strait is a priority because of its great strategic value and because countries such as the United States are a key factor in the protection of the Strait . The U.S. and Japan also want to control it.
