Ruta de navegación
Blogs
Entries with label Northern Triangle .
US agreements with the Northern Triangle may have had a deterrent effect before entering into force
In the first month following the extension of the Asylum Cooperation Agreements (ACA) to the three Northern Triangle countries, apprehensions at the US border have fallen below the levels of recent years. The actual reduction in migrant inflows that this evidences has to do with Mexico's increased control over its border with Guatemala, but may also be due to the deterrent effect of advertisement of the agreements, whose implementation has not yet fully begun and therefore has yet to demonstrate whether they will be directly effective.
![Honduran migrants held by Guatemalan border guards, October 2018 [Wikimedia Commons]. Honduran migrants held by Guatemalan border guards, October 2018 [Wikimedia Commons].](/documents/10174/16849987/tercer-pais-blog.jpg)
▲ Honduran migrants held by Guatemalan border guards, October 2018 [Wikimedia Commons].
article / María del Pilar Cazali
Attempts to entrance attempt to enter the United States through its border with Mexico have not only returned to the levels of the beginning of the year, before the number of migrants soared and each month set a new record high, reaching 144,116 apprehensions and inadmissions in May( USBorder Guard figures that provide an indirect assessment of migration trends), but have continued to fall to below several previous years.
In October (the first month of the US fiscal year 2020), there were 45,250 apprehensions and inadmissions at the US southern border, down from October 2018, 2015 and 2016 (but not 2017). This suggests that the total number of apprehensions and inadmissions in the new fiscal year will be well below the record of 977,509 recorded in 2019. This boom had to do with the caravans of migrants that began at the end of 2018 in the Central American Northern Triangle (Honduras, El Salvador and Guatemala), following a migratory flow that, with different intensities, began in the 1980s due to political and economic instabilities in those countries.
This migration crisis led President Trump's US administration to implement tougher deportation policies, including changing conditions for expedited deportations. In addition, the White House pressured Mexico with the threat of tariffs on its products if it did not help reduce the flow of migrants crossing Mexican soil, prompting President López Obrador to deploy the newly created National Guard to the border with Guatemala. Trump combined these measures with the negotiation of Asylum Cooperation Agreements (ACAs) with the Northern Triangle countries, which were initially improperly referred to as "safe third countries", adding to the controversy they generated.
agreement with Guatemala
Due to US threats to impose tariffs on Guatemala if it failed to reduce the issue of migrants from or through Guatemala on their way to the US, the Guatemalan government accepted the terms of a attention announced by Trump on 26 July 2019. The agreement foresees that those who apply for asylum in the US but have previously passed through Guatemala will be brought back to the US so that they can remain there as asylum seekers if they qualify. The US sees this as a safe third country agreement .
A safe third countryagreement is an international mechanism that makes it possible to host in one country those seeking asylum in another. The agreement signed in July prevents asylum seekers from receiving US protection if they passed through Guatemala and did not first apply for asylum there. The US goal is intended to prevent migrants from Honduras and El Salvador from seeking asylum in the US. Responsibility for processing protection claims will fall to Washington in only three cases: unaccompanied minors, persons with a US-issued visa or document Admissions Office , or persons who are not required to obtain a visa. Those who do not comply with requirements will be sent to Guatemala to await the resolution of their case, which could take years. On the other hand, the agreement does not prevent Guatemalan and Mexican applicants from seeking asylum in the US.
Guatemalan President Jimmy Morales had previously announced that a similar agreement could become part of the migration negotiations with the US. In Guatemala, after advertisement of what had been agreed, multiple criticisms arose, because the security conditions in both countries are incomparable. This was compounded by rumours about the true content of the agreement that Morales had signed, as it was not immediately revealed to the public. Faced with this uncertainty, Interior Minister Enrique Degenhart declared that the agreement was only for Hondurans and Salvadorans, not for nationals of other Latin American countries, and that the text did not explicitly mention the term "safe third country".
In the week following the advertisement, three appeals for amparo against the agreement were lodged with Guatemala's Constitutional Court, arguing that the country is not in a position to provide the protection it supposedly offers and that the resulting expense would undermine the economic status of the population itself. However, Degenhart defended agreement by saying that the economic repercussions would have been worse if the pact with Washington had not been reached, because with the US tariffs, half of Guatemala's exports and the jobs that accompany these sectors would be at risk.
These criticisms came not only from Guatemalan citizens, but also from public figures such as Guatemala's Human Rights Ombudsman, Jordán Rodas, citing a lack of transparency on the part of the government. Rodas insisted that Guatemala is not fit to be a safe third country because of its low indicators of production, Education, public health and security. Similar ideas have also been expressed by organisations such as Amnesty International, for whom Guatemala is not safe and cannot be considered a safe haven.
In its pronouncement, Guatemala's Constitutional Court affirmed that the Guatemalan government needs to submit the agreement to congress for it to become effective. This has been rejected by the government, which considers that international policy is skill directly the responsibility of the country's president and will therefore begin to implement what has been decided with Washington without further delay.
![Apprehensions and inadmissibilities by US Border Guard, broken down by month over the last fiscal years (FY) [Taken from CBP]. Apprehensions and inadmissibilities by US Border Guard, broken down by month over the last fiscal years (FY) [Taken from CBP].](/documents/10174/16849987/tercer-pais-grafico.png)
Apprehensions and inadmissibilities by US Border Guard, broken down by month over the last fiscal years (FY) [Taken from CBP].
Also with El Salvador and Honduras
Despite all the controversy generated since July as a result of the pact with Guatemala, the US developed similar efforts with El Salvador and Honduras. On 20 September 2019, El Salvador's president, Nayib Bukele, signed a agreement similar to the safe third country figure, although it was not explicitly called that either. It commits El Salvador to receive asylum seekers who cannot yet enter the US, similar to the agreement with Guatemala. El Salvador's agreement has the same three assumptions in which the US will have to make position of migrant protection.
The Salvadoran government has received similar criticism, including a lack of transparency in the negotiation and denial of the reality that the country is unsafe. Bukele justified signature by saying it would mean the extension of Temporary Protected Status (TPS) for the more than 190,000 Salvadorans living in the US. In October 2019, the Salvadoran Foreign Ministry said that this agreement is not a safe third country because El Salvador is not in the serious migratory situations in which Guatemala and Honduras are in terms of the flow of people, so it is only a agreement of non-violation of rights to minimise the number of migrants.
On 21 September 2019 the Honduran government also made public the advertisement of a agreement very similar to the one accepted by its two neighbours. It states that the US will be able to deport to Honduras asylum seekers who have passed through Honduras. Like the other two countries, the Honduran government was criticised as not being a safe destination for migrants as it is one of the countries with fees highest homicide rates in the world.
Despite criticism of the three agreements, in late October 2019 the Trump administration announced that it was in final preparations to begin sending asylum seekers to Guatemala. However, by the end of November, no non-Guatemalan asylum seekers had yet been sent. The inauguration in early January of President-elect Alejandro Giammattei, who announced his desire to rescind certain terms of agreement, may introduce some variation, though perhaps his purpose will be to wring some more concessions from Trump, in addition to the agricultural visas that Morales negotiated for Guatemalan seasonal workers.
Washington warns of the increase in violent transnational gangs, estimates that MS-13 has as many as 10,000 members
The Trump administration has drawn attention to an increase in violent transnational gangs in the United States, particularly the Mara Salvatrucha or MS-13, which maintains links to gang members in Central America's Northern Triangle. Although Trump has invoked this issue in a demagogic way, criminalizing immigration and forgetting that the Central American gangs were born in Los Angeles, the FBI notes that these organizations are recruiting more young people than ever before and demanding greater violence from their members. U.S. authorities believe that these gangs are governed to some extent from El Salvador, but that hierarchy is less clear.

▲ Mara Salvatrucha graffiti [Wikimedia Commons]
Never before has the word "animal" caused so much controversy in the United States as when it was uttered by President Donald Trump in reference to the members of the Marasalvatrucha or MS 13, on May 16. It initially appeared to refer to all undocumented immigrants, prompting widespread pushback; He went on to say that the label he had wanted to apply it to gang members who come to the United States illegally to commit acts of violence. Trump placed his war on gangs in the framework of its zero-tolerance migration policy and the reinforcement of national agencies such as Immigration and Customs Enforcement, in order to reduce migratory flows from Latin America to the United States.
The description of the phenomenon of Latino youth gangs as a migration problem had already surfaced in the United States. speech of the State of the Union that Trump delivered on Jan. 28. In the face of the congress Trump told the story of two teenagers, Kayla Cuevas and Nisa Mickens, who had been brutally murdered by six MS-13 members on their way home. He said that criminals had taken advantage of loopholes in immigration legislation to live in the United States and reiterated that the congress It had to act to close them down and prevent gang members from using them to enter the country.
Despite Trump's demagogic simplification, the truth is that Latino gangs are a product of the United States. They are, as The Washington Post has put it, "as made in America as Google." They were born in Los Angeles, first to children of Mexican immigration and then fueled by the arrival of emigrants and refugees fleeing armed conflicts in Central America. Thus, El Salvador saw the emergence of a twelve-year civil war between the government and leftist guerrillas during the 1980s. The duration and brutality of the conflict, along with the political and economic instability that the country was experiencing, drove the exodus of Salvadorans to the United States. The influx of young people from El Salvador, as well as Honduras and Guatemala, led to the emergence of the Salvatrucha and Barrio 18 gangs, both of which were linked to the pre-existing Mexican Mafia (La M).
When peace came to Central America in the 1990s, many of these young people returned to their countries, following their families or being expelled by U.S. authorities because of their criminal activities. In this way, the maras began to operate in the Northern Triangle, where they constitute a serious social problem.
Transnationality
According to the department According to the U.S., there are about 33,000 violent street gangs, with a total of 1.4 million members. MS-13, with about 10,000 young people enrolled, accounts for only 1% of that total and in 2017 only 17 of its members were prosecuted, and yet it deserves the full attention of the White House. Apart from the possible political interests of the Trump Administration, the truth is that the US authorities have been highlighting its increase and its danger, in addition to warning that certain orders are issued from El Salvador. This transnationality is viewed with concern.
The United States does not recognize MS-13 as a terrorist organization, and therefore has not included it in its National Counterterrorism Strategy released in October 2018. It is, on the other hand, classified as a transnational criminal organization, as described by adocument of the department April 2017. According to the report, several of the gang leaders are incarcerated in El Salvador and are sending representatives to cross illegally into the United States in order to unify the gangs operating in the United States, while forcing the U.S. MS-13 organization to send its illegal profits to the leaders of the United States. group in El Salvador and to exert more control and violence over their territories.
The FBI says MS-13 and Barrio 18 "continue to expand their influence in the United States." These transnational gangs "are present in almost every state and continue to grow in the United States." issue of members, now targeting recruits younger than ever before." As indicated by the grade of the department of Justice, the Attorney General warned that "in the last five years alone" the issue "has gone up significantly." "Transnational criminal organizations like MS-13 pose one of the most serious threats to U.S. security," he said.
Stephen Richardson, director attachment of the Division of research FBI criminal,told the congressIn January 2018, the mass arrests and imprisonment of MS-13 members and mid-level leaders over the past year in the United States have caused frustration for MS-13 leaders in El Salvador. "They're very interested in sending younger, more violent offenders through their channels into this country to be gang thugs," he told the committee House of Representatives.
The transnational nature of MS-13 is questioned by expert Roberto Valencia, author of articles and books on the maras. She works as a journalist at El Faro, one of El Salvador's leading digital media outlets; his latest book, graduate Letter from Zacatraz, was published a few months ago.
"In the beginning, Los Angeles gangs served as moral guides for those who immigrated to El Salvador during the 1990s. Some of the veteran leaders now living in El Salvador grew up in Los Angeles and have maintained personal and emotional ties with the Structures of the gangs they belonged to," Valencia tells Global Affairs. "However," he adds, "that doesn't imply an international connection: everyone, no matter where they live, believes they are the essence of the gang and are not subordinate to another country's organization." "Some leaders in El Salvador share a very close relationship. staff with the organization in which they started in the United States, and that doesn't dissolve so easily, but the link as a single organization was broken a long time ago," he says.
Valencia firmly rejects any interference by the U.S. MS-13 in El Salvador. He admits, instead, that there may be some subject Salvadoran gang members in the United States "can be deported to El Salvador and end up in Salvadoran prisons, where they can be punished by prison mafias."
Migrants: Cause or Consequence?
Roberto Valencia also speaks out about Donald Trump's references to gangs: "Trump talks about MS-13 to win votes under the premise of an immigration policy that ends up criminalizing all immigrants. It is outrageous that Trump presents them as the cause, when gangs started in the United States. In fact, the vast majority of migrants from the Northern Triangle come to the U.S. escaping gangs."
In Central America, gang control over a society that is poor ranges from demanding "rent" (extortion) from companies and people who have small businesses, to forcing older women to take care of babies that gang members have had, to "asking" young girls to be girlfriends of the gang's main leader if they don't want to be killed themselves and their families. The application of young girls is an extremely common cause of migration, which also denotes the misogynistic culture in rural areas of Latin American countries.
In most of his comments, Trump has described MS-13 as a threat to public safety and the stability of American communities. However, the programs of study of Immigration, a leading organization of research independent and non-profit, conducted aresearch on the impact of MS-13 in the United States and addressed the immigration measures that the Administration should take to control its presence. He considered that MS-13 and other gangs are certainly a threat to public safety, thus sharing Trump's point of view, but he disagreed with him by not linking immigration to the impact of gangs.
U.S. attorney Greg Hunter, who has been a member of the panel for Criminal Justice Law in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Virginia since 2001 and has worked on gang-related matters, says that shoplifting and illegal immigration cases are far more prevalent than those that can be categorized as threats to public safety or the "American community." such as drug trafficking and murders. It also alludes to the fact that these organizations are not centralized, and although they operate under the same identity, they do not follow the same orders. He says the gangs have made efforts to centralize operations, but they haveresult Ineffective.
It is crucial to take into account the statistics on the influx of immigrants when assessing the recent caravans of migrants from the Northern Triangle that Trump has sought to link to gangs. The U.S. president called those migrants "stone-cold criminals."
However, the U.S. Customs and Border Protection record does not suggest this. In hisreport The 2017 Security Agency counts a total of 526,901 illegal immigrants who were denied entrance, of whom 310,531 were arrested and 31,039 arrested; of the latter, only 228 belonged to MS-13 and as many were members of other gangs (61 of them from Barrio-18).
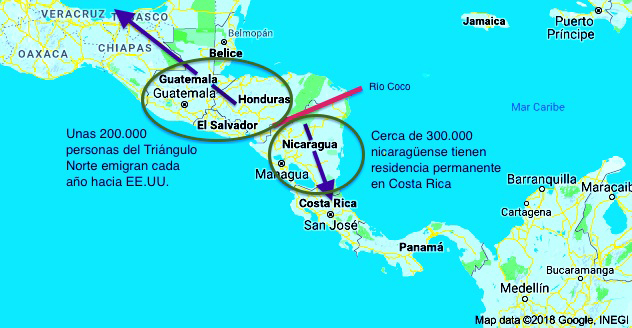
Central America's Northern Triangle migrants look to the U.S., Nicaragua's to Costa Rica
While migrants from Guatemala, El Salvador and Honduras continue to try to reach the United States, those from Nicaragua have preferred to travel to Costa Rica in recent years. The restrictions put in place by the Trump Administration and the deterioration of the Costa Rican economic boom are reducing the flows, but this migratory divide in Central America remains for the time being.

▲Belize-Mexico border crossing [Marrovi/CC].
article / Celia Olivar Gil
When comparing the Degree of development of the Central American countries, the different human flows operating in the region are well understood. The United States is the great migratory magnet, but Costa Rica is also to some extent a pole of attraction, evidently to a lesser extent Degree. Thus, the five Central American countries with the highest poverty rates -Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua and Belize- share their migratory orientation: the first four maintain important flows to the United States, while in recent years Nicaragua has opted more for Costa Rica, given its proximity.
Migration from the Northern Triangle to the U.S.
Nearly 500,000 people try every year to cross Mexico's southern border with the goal to reach the United States. Most of them come from Guatemala, El Salvador and Honduras, the Central American region known as the Northern Triangle, which is currently one of the most violent in the world. The reasons that lead this high issue number of citizens from the Northern Triangle to migrate, many illegally, are various:
On the one hand, there are reasons that could be described as structural: the porousness of the border, the complexity and high costs of regularization processes for migration, the lack of commitment by employers to regularize migrant workers, and the insufficient capacity of governments to establish migration laws.
There are also clear economic reasons: Guatemala, Honduras and El Salvador have high poverty rates, at 67.7%, 74.3% and 41.6%, respectively, of their inhabitants. presentation Difficulties in budgetary income and pronounced social inequality mean that public services, such as Education and healthcare, are deficient for a large part of the population.
Perhaps the most compelling reason is the lack of security. Many of those leaving these three countries cite insecurity and violence as the main reason for their departure. The level of criminal violence in the Northern Triangle reaches levels similar to those of an armed conflict. In El Salvador, a total of 6,650 intentional homicides were registered in 2015; in Honduras, 8,035, and in Guatemala, 4,778.
All these reasons push Guatemalans, Salvadorans and Hondurans to migrate to the United States, who on their journey north use three main routes to cross Mexico: the one that crosses the country diagonally until reaching the area of Tijuana, the one that advances through central Mexico to Ciudad Juarez and the one that seeks to enter the US through the Rio Bravo valley. subject Along these routes, migrants face many risks, such as falling victim to criminal organizations and suffering all kinds of abuses (kidnapping, torture, rape, robbery, extortion...), which can not only cause immediate physical injuries and trauma, but can also leave serious long-term consequences deadline.
Despite all these difficulties, citizens of the Northern Triangle continue to choose the United States as their migration destination. This is mainly due to the attraction of the economic potential of a country like the USA, at status of plenary session of the Executive Council employment ; to its relative geographic proximity (it is possible to arrive by land crossing only one or two countries), and to the human relations created since the 1980s, when the USA began to be goal for those fleeing the civil wars of a politically unstable Central America with economic difficulties, which created a migratory tradition, consolidated by family connections and the protection offered to the newcomers by the already established nationals. During this period, the Central American population in the U.S. tripled. Today, 82.9% of Central American immigrants in the U.S. live in the United States.
|
The American immigration 'watershed' [with ABC's authorization]. |
Migration from Nicaragua to Costa Rica
If emigration from northern Central America has been directed towards the United States, emigration from southern Central America has had more destinations. If Hondurans have looked to the north, in recent years their Nicaraguan neighbors have looked somewhat more to the south. The Coco River, which divides Honduras and Nicaragua, has become a sort of migratory'watershed'.
Certainly there are more Nicaraguans officially residing in the U.S. (over 400,000) than in Costa Rica (close to 300,000), but in recent years the issue of new residents has increased more in Costa Rican territory. In the last decade, from agreement with an OAS report (pages 159 and 188), the US has granted permanent residency program permission to a average of 3,500 Nicaraguans each year, while Costa Rica has granted about 5,000 from average, reaching a record 14,779 in 2013. Moreover, the proportional weight of Nicaraguan migration in Costa Rica, a country of 4.9 million inhabitants, is large: in 2016, some 440,000 Nicaraguans entered the neighboring country, and as many exits were recorded, indicating a significant cross-border mobility and suggesting that many workers temporarily return to Nicaragua to circumvent the requirements de extranjería.
Costa Rica is seen in certain aspects in Latin America as Switzerland in Europe, that is, as an institutionally solid, politically stable and economically favorable country. This means that the emigration of Costa Ricans is not extreme and that people come from other places, so that Costa Rica is the country with the highest net migration in Latin America, with 9% of the Costa Rican population of foreign origin.
Since its independence in the 1820s, Costa Rica has remained one of the Central American countries with the least amount of serious conflicts. For this reason, during the 1970s and 1980s it was a refuge for many Nicaraguans fleeing the Somoza dictatorship and the Sandinista revolution. Now, however, they do not emigrate for security reasons, since Nicaragua is one of the least violent countries in Latin America, even below Costa Rica's figures. This migratory flow is due to economic reasons: Costa Rica's higher development is reflected in the poverty rate, which is 18.6%, compared to Nicaragua's 58.3%; in fact, Nicaragua is the poorest country in the Americas after Haiti.
Likewise, Nicaraguans have a special preference for choosing Costa Rica as a destination because of its geographic proximity, which allows them to move frequently between the two countries and to maintain to a certain extent family coexistence; the use of the same language, and other cultural similarities.