Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs World order, diplomacy and governance .
[John West, Asian Century on A Knife Edge: A 360 Degree Analysis of Asia's Recent Economic Development. Palgrave Macmillan. Singapore, 2018. 329 p.]
REVIEW / Gabriela Pajuelo

The degree scroll of this book seems to contribute to the generalised chorus that the 21st century is Asia's century. In reality, the book's thesis is the opposite, or at least puts this claim "on a knife's edge": Asia is a continent of great economic complexity and competing geopolitical interests, posing a series of challenges whose resolution will determine the region's place in the world in the coming decades. For now, argues John West, a university professor in Tokyo, nothing is certain.
The book begins with a preamble on the recent history of Asia, from the Second World War to the present day. Already at the beginning of this period, economic liberalism was established as the standard doctrine in much of the world, including most Asian countries, in a process driven by the establishment of international institutions.
China joined this system, without renouncing its domestic doctrines, when it joined the World Trade Organisation in 2001. Since then, there have been some shocks such as the financial crisis of 2007-2008, which severely affected the US economy and had repercussions in the rest of the world, or the recent tariff tensions between Washington and Beijing, as well as the current global crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic.
The principles of protectionism and nationalism deployed by Donald Trump and an increased US resource to the hard power in the region, as well as a more assertive policy by Xi Jinping's China in its geographical surroundings, also resorting to positions of force, such as in the South China Sea, have damaged the multilateralism that had been built up in that part of the world.
The author provides some thought-provoking insights into the challenges that Asia will face, given that the factors core topic that favoured its development have now deteriorated (mainly due to the stability provided by international economic interdependence).
West examines seven challenges. The first is to gain a better position in global value chains, as since the 1980s the manufacture of components and the production of final products has taken place in different parts of the world. Asia is heavily involved in these supply chains, in fields such as technology or apparel production, but is subject to business decisions by multinationals whose practices are sometimes not socially responsible and allow abuse of labour rights, which are important for the middle classes development .
The second challenge is to maximise the potential of urbanisation, which has grown from 27% of the population in 1980 to 48% in 2015. The region is known for its densely populated mega-cities. This brings with it some challenges: people migrating to industrial centres generally move from leave productivity jobs to high productivity jobs, and health care capacity is put at test . But it is also an opportunity to improve environmental practices or encourage innovation through green technologies, even though much of Asia today still faces high levels of pollution.
Another challenge is to give all Asians equal opportunities in their respective societies, from LGBT people to women and indigenous communities, as well as ethnic and religious minorities. The region also faces a major demographic challenge , as many populations either age (such as China's, despite the correction of the "two-child policy") or continue to expand with presumed future supply problems (such as India's).
West also points to reference letter, the barriers to democratisation in the region, with China's notable immobility, and the spread of economic crime and corruption (counterfeiting, piracy, drug trafficking, human trafficking, cybercrime and money laundering).
Finally, the author speaks of challenge that Asian countries can live together in peace and harmony, while China consolidates its position as a regional leader: if there is a Chinese commitment to thesoft powerThrough the Belt and Road initiative, there is also a more confrontational attitude on the part of Beijing towards Taiwan, Hong Kong and the South China Sea, while actors such as India, Japan and North Korea want a greater role.
Overall, the book provides a comprehensive analysis of Asia's economic and social development and the challenges ahead. In addition, the author offers some thought-provoking insights, arguing that the proclaimed "Asian century" is unlikely due to the region's lagging economic development , as most countries have not caught up with their Western counterparts in terms of GDP per capita and technological sophistication. However, it leaves the future open: if the challenges are successfully met, the time may indeed come for an Asian century.
![Rice terraces in Vietnam [Pixabay]. Rice terraces in Vietnam [Pixabay].](/documents/10174/16849987/vietnam-blog.jpg)
▲ Rice field terraces in Vietnam [Pixabay].
COMMENT / Eduardo Arbizu
The combination of a market Economics and an authoritarian regime dominated by the Communist Party of Vietnam (VCP) has led Vietnam, a country of over 90 million people, to become a key player in the future of Southeast Asia.
Today's Vietnam is the consequence of a confusing and contradictory process of change that has transformed not only the country's Economics but has also had a profound impact on social life, urban configuration, environment, domestic and foreign policies and whose final effects will be seen in the long term deadline.
An impressive economic turnaround
The transformation of the economic model in Vietnam derives formally from the decision taken at the VCP's sixth congress in December 1986 to open the country to the market Economics , but its roots lie earlier, in the economic crisis that followed the war, in the collapse of agricultural production that the radical implementation of a communist model brought about in 1979. This debacle forced the private trading of any surplus production that exceeded the targets set by the state for public land or enterprises. This kind of state capitalism paved the way for the liberalisation that followed the death of Stalinist leader Le Duan in 1986. The approval of the do-moi or renovation policy meant the withdrawal of planning and the choice for the free market. It was not an ideological decision but an instrumental one. work If the CP wanted to maintain control of the country it needed to generate one million jobs a year, guarantee food for 90 million people and reduce poverty.
It has been an economic and social success: per capita income has increased dramatically and the population below the poverty line has been reduced from 60% to 20%. The US embargo ended in 1993 and in 1997 the two countries signed a new agreement trade agreement. In 2007 Vietnam was admitted to the WTO. In this context of openness, more than 150,000 new businesses were set up under the new enterprise law and major international companies such as Clarks, Canon, Samsung and Intel set up production facilities in Vietnam.
The achievements of the process, however, should not hide its weaknesses: a state-controlled Economics through joint ventures and state-owned enterprises, a fragile rule of law, massive corruption, a web of families loyal to the VCP accumulating wealth and owning most private businesses, growing inequality and deep ecological degradation.
Agriculture has evolved from the sudden drop in production that followed communist collectivisation to the current status where Vietnam is the second largest exporter of rice in the world, a crop that accounts for 20% of its exports. The industrialisation of Economics has meant that agriculture, which used to account for 40% of GDP, is now only 20%. Livelihoods still depend on rice cultivation, still the main source of income for rural households, where half of the population lives. source . Rice exports are managed by a combination of free market and corrupt officialdom, with the negative consequences experienced in the speculative crisis of 2008. There has been an intense migration from the countryside to the big cities where wages are five times higher. The pressure for wealth is converting agricultural land into residential or industrial plots. Every year 10,000 new hectares are re-zoned. The transformation of the rural world is pushing away the old Structures that provided security, meaning and purpose and it remains to be seen how it affects future stability.
Social and environmental change
The construction of proletarian towns after the war, under the communist housing programme, has not prevented overcrowding and the continuation of communal life. Migrants continue to arrive in search of work, money and protection. Tons of industrial waste remains untreated; the rivers around Ho Chi Min City are biologically dead and pollution in Hanoi is well above internationally accepted levels. Problems such as prostitution, with more than 1% of women working in the illicit sex trade, or abandoned children on the streets are a reality. However, while doubling or tripling its urban population, Vietnam has managed these problems better than neighbouring countries, largely avoiding the ghost cities and their problems of crime, extreme poverty and drug addiction so common in the rest of Asia.
Commercial and urban dynamism is reflected in thousands of illegal street food shops and small businesses, pioneers of small-scale capitalism, which are now a tourist symbol of Vietnam. In cities full of young people who identify freedom with a polluting motorbike, youth rebels against years of communist austerity but not against family traditions.
Vietnam is a country where a natural wonder like Ha Long Bay, one of the country's iconic images, is simultaneously a tourist attraction and an environmental disaster. It is also one of the areas most exposed to the effects of climate change, due to its low altitude and reliance on agricultural production in the Mekong Delta and tourism. Respect for wildlife and the environment are issues of high priority for the authorities leave .
The VCP remains in control
There are issues that have not changed with the same intensity. Vietnam still lives under a "natural system of control", the deep surveillance system put in place by the communist regime to control the values and behaviour of its people. A system in which one in six Vietnamese ended up working in the security forces and which resulted in the control of "cultivated families", those who behave in accordance with the values set by the party. agreement . Although it has proven its effectiveness in crises such as avian flu and now partly in the Covid-19 crisis, the system is now controversial due to the spread of the internet and social networks and radical social changes that call for more freedom. Despite this control, corruption is widespread and damaging to the country's future.
The VCP is still in power. Retaining its Leninist roots, it is now an elitist and intelligent organisation in search of its own survival. A new mandarinate that has evolved from a centralised power present in all aspects of public and social life to a fragile and partial control; from a "petty legal system", where decisions were taken directly by the VCP and their compliance with the law was irrelevant, to a "State based on Law", where rules are the tool to supervise entrepreneurs and investors, allowing them to create wealth and employment but simultaneously comply with the VCP's expectations. Similarly, the party controls the legislature, the courts and indirectly the press, media and news coverage, which prevents Vietnam from being considered a truly free country.
Life has been difficult and lonely for those few who tried to oppose the regime and promote real democracy. The name of the Catholic priest Father Ly and his followers, brutally repressed, tried and convicted in March 2007, once the country was admitted to the WTO, casts a shadow over the hope for a transition to effective political freedom.
Foreign policy and the future
Vietnam's foreign policy seeks to strike a balance in its relations with two main actors: the US and China, counterbalanced by a set of alliances with third countries. Overcoming war wounds and establishing trusting cooperation on subject security is the goal of the policy of rapprochement with the US, which is already a significant investor in the country. The special relationship with China, the largest importer of Vietnamese goods, an industrial giant and Asia's largest military, is the other axis of its policy despite long-standing territorial disputes.
The overexploited environment, inequality, elite entrenchment and, above all, uncertainty about the evolution of the Communist Party of Vietnam and the political system are aspects that are weighing on the outlook. However, a young and well-educated population, as well as the inflow of foreign investment, are reasons for optimism about further liberalisation of the country, including political liberalisation.
[A. Patanru, M. Pangestu, M.C. Basri (eds), Indonesia in the New World: Globalisation, Nationalism and Sovereignty. ISEAS Yusof Ishak Institute. Singapore, 2018. 358 p.]
review / Irati Zozaya
 The book consists of fifteen articles, written by different experts, on how Indonesia has dealt with globalisation and what effect it has had on the country. The texts have been coordinated by Arianto A. Patunru, Mari Pangestu and M. Chatib Basri, Indonesian academics with experience also in public management having served as ministers in different governments. The articles combine general approaches with specific aspects, such as the consequences of the opening up to international trade and investment in the mining industry or the nationalisation of foodstuffs.
The book consists of fifteen articles, written by different experts, on how Indonesia has dealt with globalisation and what effect it has had on the country. The texts have been coordinated by Arianto A. Patunru, Mari Pangestu and M. Chatib Basri, Indonesian academics with experience also in public management having served as ministers in different governments. The articles combine general approaches with specific aspects, such as the consequences of the opening up to international trade and investment in the mining industry or the nationalisation of foodstuffs.
To explain Indonesia's present-day status , the book occasionally recapitulates periods of its history. In fact, one of the concepts that crops up frequently in the book is that of nationalism: it could be said, according to the authors, that this is what has most marked Indonesia's relationship with the world, beyond who has led this country of 260 million inhabitants at any given time.
The first part of the book reference letter looks more generally at Indonesia's experience with globalisation, nationalism and sovereignty. It begins by showing the colonial era and how, under Dutch and British pressure to open up to the world, a strong nationalist sentiment began to emerge. After the occupation by Japan during World War II, total autarchy was introduced, leading to a problem that is still very present in Indonesia today: internship smuggling. In 1945 the country achieved its long-awaited independence under President Sukarno, who closed Indonesia to the rest of the world in order to focus on reasserting national identity and developing its capabilities. This led to the deterioration of the Economics and subsequent hyperinflation, which ushered in a new era: the New Order.
In 1967, with Suharto's accession to the presidency, a cautious opening to foreign trade and investment flows began. However, Suharto repressed political activity and during his rule the military gained much influence and the government retained control over Economics. Moreover, the end of his presidency coincided with the Asian financial crisis (1997-1998), which led to a fall in the country's economic growth and a slowdown in poverty reduction, and consequently a growth in inequality. The financial crisis undermined confidence in the president and culminated in the collapse of the New Order.
The next period covered is the Reformasi, an era that marked the beginning of a more open and democratic political climate. The next two presidents, Abdurrahman Wahid (1999-2001) and Megawati Soekarnoputri (2001-2004), were more concerned with economic recovery and democratic consolidation, and a protectionist system endured in terms of Economics. The book does not focus much on the next president, Yudhoyono (2004-2014), noting only that he was an internationalist who maintained a more cautious and ambivalent stance on economic issues.
Finally, in the 2014 elections, Joko Widodo came to power and holds the position presidency today. Under him, Indonesia has returned to the path of economic growth and stabilised as a reasonably successful democracy. As the president, commonly known as Jokowi, has taken further steps to emphasise political sovereignty and promote economic autarky and national cultural renaissance, his term has been characterised as 'new nationalism'. In his political speech , Jokowi puts Indonesia as goal of foreign conspiracies and calls for vigilance against such threats. However, the country maintains an ambivalent stance towards international openness and cooperation since, although trade restrictions have increased again in recent decades, Jokowi emphasises global engagement and has revived regional negotiations.
All this has led to public dissatisfaction with globalisation, with up to 40% of citizens believing that globalisation threatens national unity. One of the most negative and important effects in Indonesia is that of workers who have been forced to migrate and work abroad under very poor conditions. However, the later parts of the book also show the positive consequences of globalisation in Indonesia, including higher productivity, increased wages and economic growth. The authors therefore emphasise the importance of constructing a narrative that can generate public and political support for the country's openness and counter the growing anti-globalisation sentiment.
As is the case with a book that is the sum of articles by different authors, its reading can be somewhat tiresome due to a certain reiteration of content. However, the variety of signatures also means a plurality of approaches, which undoubtedly provides the reader with a wealth of perspectives.
[Ming-Sho Ho, Challenging Beijing's Mandate of Heaven. Taiwan's Sunflower and Hong Kong's Umbrella Movement. Temple University Press. Philadelphia, 2019. 230 p.]
review / Claudia López
 Taiwan's Sunflower Movement and Hong Kong's Umbrella Movement achieved international notoriety during 2014, when they challenged the Chinese regime's 'Mandate of Heaven', to use the image that gives degree scroll to the book. The book analyses the origins, processes and also the outcomes of both protests, at a time of consolidation of the rise of the People's Republic of China. Challenging Beijing's Mandate of Heaven provides a detailed overview of where, why and how these movements came into being and achieved relevance.
Taiwan's Sunflower Movement and Hong Kong's Umbrella Movement achieved international notoriety during 2014, when they challenged the Chinese regime's 'Mandate of Heaven', to use the image that gives degree scroll to the book. The book analyses the origins, processes and also the outcomes of both protests, at a time of consolidation of the rise of the People's Republic of China. Challenging Beijing's Mandate of Heaven provides a detailed overview of where, why and how these movements came into being and achieved relevance.
Taiwan's Sunflower Movement developed in March and April 2014, when citizen demonstrations protested against the approval of a free trade agreement with China. Between September and December of the same year, the Umbrella Movement staged 79 days of protests in Hong Kong demanding universal suffrage to elect the highest authority in this enclave of special status within China. These protests attracted international attention for their peaceful and civilised organisation.
Ming-Sho Ho begins by describing the historical background of Taiwan and Hong Kong from their Chinese origins. He then analyses the status of the two territories so far this century, when Taiwan and Hong Kong have begun to face increased pressure from China. It also reviews the similar economic circumstances that produced the two waves of youth revolts. The second part of the book analyses the two movements: the voluntary contributions, the decision-making process and its improvisation, the internal power shift, the political influences and the challenges of the initiative. The book includes appendices with the list of Taiwanese and Hong Kong people interviewed and the methodology used for the analysis of the protests.
Ming-Sho Ho was born in 1973 in Taiwan and has been a close observer of the island's social movements; during his time as a student of doctorate in Hong Kong he also closely followed the political discussion in the former British colony. He is currently researching initiatives for promote renewable energy in East Asian nations.
Being from Taiwan gave him access to the Sunflower Movement and allowed him to build close relationships with several of its key activists. He was able to witness some of the students' internal meetings and conduct in-depth interviews with students, leaders, politicians, NGO activists, journalists and university professors. This provided him with a variety of sources for his research.
Although they are two territories with different characteristics - Hong Kong is under the sovereignty of the People's Republic of China, but enjoys autonomy management assistant; Taiwan remains independent, but its statehood is challenged - both represent a strategic challenge for Beijing in its consolidation as a superpower.
The author's sympathy for these two movements is obvious throughout the book, as is his admiration for the risk taken by these student groups, especially in Hong Kong, where many of them were convicted of 'public nuisance' and 'disturbing the peace' and, in many cases, sentenced to more than a year in prison.
The two movements had a similar beginning and a similar development beginning, but each ended in a very different way. In Taiwan, thanks to the initiative, the free trade agreement with China failed and was withdrawn, and the protesters were able to call hold a farewell rally to celebrate this victory. In Hong Kong, police repression succeeded in stifling the protest and a final massive raid brought a disappointing end for the protesters. However, it is possible that without the experience of those mobilisations, the new student reaction that throughout 2019 and early 2020 in Hong Kong has put the highest Chinese authorities on the ropes would not have been possible.
ESSAY / Emilija Žebrauskaitė
Introduction
While the Western Westphalian State - and, consequently, the Western legal system - became the default in most parts of the world, Africa with its traditional ethics and customs has a lot to offer. Although the positive legalism is still embraced, there is a tendency of looking at the indigenous traditions for the inspiration of the system that would be a better fit in an African setting. Ubuntu ethics has a lot to offer and can be considered a basis for all traditional institutions in Africa. A great example of Ubuntu in action is the African Traditional Justice System which embraces the Ubuntu values as its basis. This article will provide a conceptualization of Ubuntu philosophy and will analyse its applications in the real-world scenarios through the case of Gacaca trials in Rwanda.
Firstly, this essay will define Ubuntu: its main tenants, how Ubuntu compares with other philosophical and ethical traditions, and the main criticism of Ubuntu ethics. Secondly, the application of Ubuntu ethics through African Indigenous Justice Systems will be covered, naming the features of Ubuntu that can be seen in the application of justice in the African setting, discussing the peace vs. justice discussion and why one value is emphasized more than another in AIJS, and how the traditional justice in Africa differs from the Western one.
Lastly, through the case study of Gacaca trials in post-genocide Rwanda, this essay seeks to demonstrate that the application of the traditional justice in the post-genocide society did what the Western legalistic system failed to do - it provided a more efficient way to distribute justice and made the healing of the wounds inflicted by the genocide easier by allowing the community to actively participate in the judicial decision-making process.
It is the opinion of this article that while the African Traditional Justice System has it's share of problems when applied in modern-day Africa, as the continent is embedded into the reality of the Westphalian state, each state being a part of the global international order, the Western model of justice is eroding the autonomy of the community which is a cornerstone of African society. However, the values of Ubuntu ethics persist, providing a strong basis for traditional African institutions.
Conceptualization of Ubuntu
The word Ubuntu derives from the Bantu language group spoken widely across sub-Saharan Africa. It can be defined as "A quality that includes the essential human virtues; compassion and humanity" (Lexico, n.d.) and, according to Mugumbate and Nyanguru, is a homogenizing concept, a "backbone of African spirituality" in African ontology (2013). "Umuntu ngumuntu ngabantu" - a Zulu phrase meaning "a person is a person through other persons" is one of the widely spread interpretations of Ubuntu.
In comparison with non-African philosophical thoughts, there can be found similarities between Ubuntu and the traditional Chinese as well as Western ethics, but when it comes to the modern Western way of thought, the contrast is striking. According to Lutz (2009), Confucian ethics, just like Ubuntu ethics, view the institution of family as a central building block of society. An Aristotelian tradition which prevailed in the Western world until Enlightenment had some characteristics similar to Ubuntu as well, namely the idea of Aristotle that human being is a social being and can only reach his true potential through the community (Aristotle, 350 B.C.E.). However, Thomas Hobbes had an opposite idea of human nature, claiming that the natural condition of man is solidarity (Hobbes, 1651). The values that still prevail in Ubuntu ethics, therefore, are rarely seen in modern liberal thought that prevails in the Western World and in the international order in general. According to Lutz (2009) "Reconciling self-realization and communalism is important because it solves the problem of moral motivation" which Western modern ethics have a hard time to answer. It can be argued, therefore, that Ubuntu has a lot to offer to the global ethical thought, especially in the world in which the Western ideas of individualism prevail and the values of community and collectivism are often forgotten.
Criticisms
However, while Ubuntu carries values that can contribute to global ethics, as a philosophical current it is heavily criticised. According to Metz (2011), there are three main reasons why Ubuntu receives criticism: firstly, it is considered vague as a philosophical thought and does not have a solid framework; secondly, it is feared that due to its collectivist orientation there is a danger of sacrificing individual freedoms for the sake of society; and lastly, it is thought that Ubuntu philosophy is applicable and useful only in traditional, but not modern society.
When it comes to the reproach about the vagueness of Ubuntu as a philosophical thought, Thaddeus Metz examines six theoretical interpretations of the concept of Ubuntu:
U1: An action is right just insofar as it respects a person's dignity; an act is wrong to the extent that it degrades humanity.
U2: An action is right just insofar as it promotes the well-being of others; an act is wrong to the extent that it fails to enhance the welfare of one's fellows.
U3: An action is right just insofar as it promotes the well-being of others without violating their rights; an act is wrong to the extent that it either violates rights or fails to enhance the welfare of one's fellows without violating rights.
U4: An action is right just insofar as it positively relates to others and thereby realises oneself; an act is wrong to the extent that it does not perfect one's valuable nature as a social being.
U5: An action is right just insofar as it is in solidarity with groups whose survival is threatened; an act is wrong to the extent that it fails to support a vulnerable community.
U6: An action is right just insofar as it produces harmony and reduces discord; an act is wrong to the extent that it fails to develop community (Metz, 2007).
While arguing that the concept U4 is the most accepted in literature, Matz himself argues in favour of the concept U6 as the basis of the ethics is rooted not in the subject, but in the object (Metz, 2007).
The fear that Ubuntu tenants make people submissive to authority and collective goals, giving them a very strong identity that might result in violence against other groups originates, according to Lutz (2009), from a faulty understanding of Ubuntu. Even though the tribalism is pretty common in the African setting, it does not derive from the tenants of Ubuntu, but a corrupted idea of this ethical philosophy. Further criticism on the idea that collectivism might interfere with individual rights or liberties can also be denied quoting Lutz, who said that "Ethical theories that tell us we must choose between egoism and altruism, between self-love and love of others, between prudence and morality, or one's good and the common good are individualistic ethical theories" and therefore have nothing in common with ideas of Ubuntu, which, unlike the individualistic theories, reconciles the common and staff good and goals.
The third objection, namely the question of whether Ubuntu ethics remain useful in the modern society which functions according to the Westphalian State model is challenged by Metz (2011). While it is true that Ubuntu developed in a traditional setting in which the value of human beings was based on the amount of communal life a human has lived (explaining the respect for the elders and the ancestors in African setting), a variant concept of dignity that in no way can be applied in a modern setting, there are still valuable ethical norms that can be thought by Ubuntu. Metz (2011) provides a concept of human dignity based on Ubuntu ideas, which, as he argues, can contribute to ethics in the modern African setting: "individuals have dignity insofar as they have communal nature, that is, the inherent capacity to exhibit identity and solidarity with others".
The Ubuntu ethics in African Indigenous Justice System
The institutionalisation and centralisation of power in the hands of the Westphalian State takes away the power from the communities which are central to the lifestyle in Africa. However, the communal values have arguably persisted and continue to directly oppose the centralisation. While the Westphalian State model seems to be functioning in the West, there are many good reasons to believe that Africa must look for inspiration in local traditions and customs (Malisa & Nhengeze, 2018). Taking into consideration the Ubuntu values, it is not difficult to understand why institutionalisation has generally not been very successful in African setting (Mugumbate & Nyanguru, 2013), as a place where the community is morally obliged to take care of its members, there is little space for alienated institutions.
Generally, two justice systems are operating alongside each other in many African societies: the state-administered justice system and the African Indigenous Justice System (AIJS). According to Elechi, Morris & Schauer, the litigants can choose between the state tribunal and AIJS, and can apply to be judged by the state if they do not agree with the sentence of the AIJS (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010). However, Ubuntu values emphasise the concept of reconciliation: "African political philosophy responds easily and organically to the demands for the reconciliation as a means of restoring the equilibrium of the flow of life when its disturbed" (Nabudere, 2005). As the national court interventions often disharmonize the community by applying the "winner takes it all" approach, and are sometimes considered to be corrupt, there is a strong tendency for the communities to insist on bringing the offender to the AIJS tribunal (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010).
African Indigenous Justice System is a great example of Ubuntu values in action. The system operates on the cultural norm that important decision should be reached by consensus of the whole group as opposed to the majority opinion. AIJS is characterised by features such as the focus on the effects the offence had on victims and the community, the involvement of the litigants in the active definition of harms and the resolution of the trial, the localisation and decentralisation of authority, the importance of the restoration of harm, the property or relationship, the understanding that the offender might be a victim of the socioeconomic conditions; with the main objective of the justice system being the restoration of relationships, healing, and reconciliation in the community (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010). Underlying this system is the concept of Ubuntu, which "leads to a way of dealing with the social problems which are very different from the Western legalistic, rule-based system which had become the global default" (Baggini, 2018).
One of the reasons why AIJS can be considered exemplary is its ability to avoid the alienation of the Western courts in which the victim, the offender, and everybody else seem to be represented, but neither victim nor offender can directly participate in the decision making. The system which emphasises reconciliation and in which the community is in charge of the process is arguably much more effective in the African setting, where communities are generally familiar and close-knit. As the offender is still considered a part of the community and is still expected to contribute to its surroundings in the future, the participation in the trial and the decision making is important to the reconciliation: "unlike adjudicated justice, negotiated justice is not a winner take it all justice. Resolution can be reached where the offender, the community, and the victim are each partially wrong" (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010). As there is very little hope for an offender to be reintegrated into a close community without forgiving and forgiveness from both parties, this type of approach is pivotal.
Another interesting feature of AIJS is the assumption that the offender is not inherently bad in himself, but is primarily a marginalised victim, who does not have the same opportunities as other members of the community to participate in the economic, political, and social aspects of the group, and who can be made right if both the offender and the community make effort (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010). This concept differs from the Western Hobbesian idea of human beings being inherently corrupt and is much closer to traditional Western Aristotelian ethics. What makes the African concept different, however, is the focus which is not on the virtue of the person himself, but rather on the relationship the offender has with his family and community which, although violated by the offence, can and should be rebuilt by amendments (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010).
The Gacaca Trials
The Gacaca trials are the state-administered structure which uses communities (around a thousand of them) as a basis for judicial forums (Meyerstein, 2007). They were introduced by the Rwandan government as an alternative to national justice after the Rwandan genocide.
During the colonial times, Rwanda was indirectly ruled by the colonisers through local authorities, namely the Tutsi minority (Uvin, 1999). The Hutu majority were considered second class citizens and by the time of independence were holding deep grievances. The Rwandan Revolution of 1959-1961 overthrew the monarchy and the ruling Tutsi elite. After the independence from the colonial regime, Rwanda was ruled by the Party of Hutu Emancipation Movement, which was supported by the international community on the grounds of the idea that the government is legitimate as it represents the majority of the population - the Hutu (ibid.) During the period of transition, ethnic violence against Tutsi, forcing many of them to leave the country, happened (Rettig, 2008). In 1990 the Rwandan Patriotic Army composed mostly by the Tutsi exiles invaded Rwanda from neighbouring Uganda (ibid.) The incumbent government harnessed the already pre-existing ethnic to unite the Hutu population to fight against the Tutsi rebels. The strategy included finding a scapegoat in an internal Tutsi population that continued to live in Rwanda (Uvin, 1999). The genocide which soon followed took lives of 500,000 to 800,000 people between April and July of the year 1994 when the total population at the time is estimated to have been around 8 million (Drumbl, 2020). More than 100,000 people were accused and waited in detention for trials, creating a great burden on a Rwandan county (Schabas, 2005).
According to Meyerstein (2007), the Gacaca trials were a response to the failure of the Western-styled nation court to process all the suspects of the genocide. Gacaca trials were based on indigenous local justice, with Ubuntu ethics being an underlying element of the system. The trials were traditionally informal, organic, and patriarchal, but the Rwandan government modernised the indigenous justice system by establishing an organisational structure, and, among other things, making the participation of women a requirement (Drumbl, 2020).
The application of Gacaca trails to do justice after the genocide was not always well received by the international community. The trials received criticism for not complying with the international standards for the distribution of justice. For example, Amnesty International invoked Article 14 of the ICCPR and stated that Gacaca trials violated the right of the accused to be presumed innocent and to the free trial (Meyerstein, 2007). There are, undoubtedly, many problems that can be assigned to the system of Gacaca when it comes to the strict norms of the international norms.
The judges are drawn from the community and arguably lack the official legal training, the punitive model of the trials that arguably have served for many as an opportunity for staff revenge, and the aforementioned lack of legal protection for the accused are a few of many problems faced by the Gacaca trials (Rettig, 2008). Furthermore, the Gacaca trials excluded the war criminals from the prosecution - there were many cases of the killings of Hutu civilians by Tutsis that formed the part of the Rwandan Patriotic Front army (Corey & Joireman, 2004). This was seen by many as a politicised application of justice, in which, by creating two separate categories of criminals - the crimes of war by the Tutsis that were not the subject of Gacaca and the crimes of the genocide by the Hutus that were dealt with by the trials - the impunity and high moral ground was granted for the Tutsi (ibid). This attitude might bring results that are contrary to the initial goal of the community-based justice - not the reconciliation of the people, but the further division of the society along the ethnic lines.
However, while the criticism of the Gacaca trials is completely valid, it is also important to understand, that given the limited amount of resources and time, the goal of bringing justice to the victims of the genocide is an incredibly complex mission. In the context of the deeply wounded, post-genocidal society in which the social capital was almost non-existent, the ultimate goal, while having justice as a high priority, was first of all based on Ubuntu ethics and focused more on peace, retribution, and social healing. The utopian perfectness expected by the international community was nearly impossible, and the Gacaca trials met the goal of finding the best possible solutions in the limits of available resources. Furthermore, the criticism of international community often seemed to stem not so much from the preoccupation for the Rwandan citizens, as from the fact that a different approach to justice threatens the homogenising concept of human rights "which lashes out to squash cultural difference and legal pluralism by criticising the Gacaca for failures to approximate canonised doctrine" (Meyerstein, 2007).
While it is true that even Rwandan citizens often saw Gacaca as problematic, whether the problems perceived by them were similar to those criticised by the international community is dubious. For example, Rwanda's Supreme Court's response to the international criticism was the provision of approach to human rights which, while not denying their objectivity, also advocates for the definition that better suits the local culture and unique circumstances of post-genocide Rwanda (Supreme Court of Rwanda, 2003). After all, the interventions from the part of the Western world on behalf of the universal values have arguably created more violence historically than the defended values should ever allow. The acceptance that Gacaca trials, while imperfect, contributed positively to the post-genocide Rwandan society has the grave implications that human rights are ultimately a product of negotiation between global and local actors" (Meyerstein, 2007) which the West has always refused to accept. However, it is the opinion of this article that exactly the opposite attitude, namely that of better intercultural understanding and the search for the solutions that are not utopian but fit in the margins of the possibilities of a specific society, are the key to both the efficiency and the fairness of a justice system.
Conclusion
The primary end of the African Indigenous Justice System is to empower the community and to foster reconciliation through a consensus that is made by the offenders, the victims, and the community alike. It encourages to view victims as people who have valuable relationships: they are someone's daughters, sons, fathers - they are important members of society. Ubuntu is the underlying basis of the Indigenous Justice System and African ethnicity in general. While the AIJS seems to be functioning alongside the state's courts, in the end, the centralization and alienation from the community are undermining these traditional values that flourish in the African setting. The Western legalistic system helps little when it comes to the main goal of justice in Africa - the reconciliation of the community, and more often than not only succeeds in creating further discord. While the criticism of Gacaca trials was undoubtedly valid, it often stemmed from the utopian idealism that did not take the actual situation of a post-genocide Rwanda into consideration or the Western universalism, which was threatened by the introduction of a justice system that in many ways differs from the positivist standard. It is the opinion of this article, therefore, that more autonomy should be granted to the communities that are the basic building blocks of most of the African societies, with the traditional values of Ubuntu being the basis of the African social institutions.
REFERENCES
Lexico. (n.d.). Lexicon. Retrieved from https://www.lexico.com/definition/ubuntu
Mugumbate, J., & Nyanguru, A. (2013). Exploring African Philosophy: The Value of Ubuntu in Social Work. African Journal of Social Work, 82-100.
Metz, T. (2011). Ubuntu as a moral theory and human rights in South Africa. African Human Rights Law Journal, 532-559.
Metz, T. (2007). Towards an African Moral Theory. The Journal of Political Philosophy.
Lutz, D. W. (2009). African Ubuntu Philosophy and Global Management. Journal of Business Ethics, 313-328.
Hobbes, T. (1651). Leviathan.
Aristotle. (350 B.C.E.). Politics.
Malisa, M., & Nhengeze, P. (2018). Pan-Africanism: A Quest for Liberation and the Pursuit of a United Africa. Genealogy.
Elechi, O., Morris, S., & Schauer, E. (2010). Restoring Justice (Ubuntu): An African Perspective. International Criminal Justice Review.
Baggini, J. (2018). How the World Thinks: A Global History of Philosophy. London: Granta Books.
Meyerstein, A. (2007). Between Law and Culture: Rwanda's Gacaca and Postolocial Legality. Law & Social Inquiry.
Corey, A., & Joireman, S. (2004). African Affairs. Retributive Justice: the Gacaca Courts in Rwanda.
Nabudere, D. W. (2005). Ubuntu Philosophy. Memory and Reconciliation. Texas Scholar Works, University of Texas Library.
Rettig, M. (2008). Gacaca: Truth, Justice, and Reconciliation in Postconflict Rwanda? African Studies Review.
Supreme Court of Rwanda. (2003). Developments on the subject of the report and different correspondences of Amnesty International. Départements des Jurisdictions Gacaca.
Drumbl, M. A. (2020). Post-Genocide Justice in Rwanda. Journal of International Peacekeeping.
Uvin, P. (1999). Ethnicity and Power in Burundi and Rwanda: Different Paths to Mass Violence. Comparative Politics, 253-271.
Schabas, W. A. (2005). Genocide Trials and Gacaca Courts. Journal of International Criminal Justice, 879-895.
![Insight into mineral extraction on an asteroid, from ExplainingTheFuture.com [Christopher Barnatt]. Insight into mineral extraction on an asteroid, from ExplainingTheFuture.com [Christopher Barnatt].](/documents/10174/16849987/gaj-foto-4.jpg)
▲ Vision for mineral extraction on an asteroid, from ExplainingTheFuture.com [Christopher Barnatt].
GLOBAL AFFAIRS JOURNAL / Mario Pereira
 [14-page document. downloadin PDF]
[14-page document. downloadin PDF]
INTRODUCTION
The American astrophysicist Michio Kaku recalls that when President Thomas Jefferson bought Louisiana from Napoleon (in 1803) for the astronomical sum of 15 million dollars, he spent a long period of time in deep fear. The reason for this lay in the fact that he did not know for a long time whether the territory (mostly unexplored) hid fabulous riches or, on the contrary, was a worthless wasteland... The passage of time proved the former, as well as proving that it was then that the march of the American pioneers began: those people who - like the "Adelantados" of Castile and Extremadura in the 16th century - set out for the unknown in order to make their fortune, discover new wonders and improve their social position.
The Jeffersons of today are the Musks and the Bezos, American businessmen, owners of huge financial, commercial and technological empires, who, hand in hand with new "pioneers" (a mix between Jules Verne/Arthur C. Clark and Neil Armstrong/John Glenn) seek to reach the new frontier of Humanity: the commercial and mining exploitation of Outer Space.
Faced with such a challenge, many questions can (and should) be asked. Here we will try to answer (at least briefly) whether the existing international and national rules and regulations on the mining of the Moon and celestial bodies constitutes - or does not constitute - a sufficient framework for the regulation of such planned activities.
![Prime Minister Imran Kahn, at the United Nations General Assembly, in 2019 [UN]. Prime Minister Imran Kahn, at the United Nations General Assembly, in 2019 [UN].](/documents/10174/16849987/pakistan-introduccion-blog.jpg)
Prime Minister Imran Kahn, at the United Nations General Assembly, in 2019 [UN].
ESSAY / M. Biera, H. Labotka, A. Palacios
The geographical location of a country is capable of determining its destiny. This is the thesis defended by Whiting Fox in his book "History from a Geographical Perspective". In particular, he highlights the importance of the link between history and geography in order to point to a determinism in which a country's aspirations are largely limited (or not) by its physical place in the world.[1]
Countries try to overcome these limitations by trying to build on their internal strengths. In the case of Pakistan, these are few, but very relevant in a regional context dominated by the balance of power and military deterrence.
The first factor that we highlight in this sense is related to Pakistan's nuclear capacity. In spite of having officially admitted it in 1998, Pakistan has been a country with nuclear capacity, at least, since Zulfikar Ali Bhutto's government started its nuclear program in 1974 under the name of Project-706 as a reaction to the once very advanced Indian nuclear program.[2]
The second factor is its military strength. Despite the fact that they have publicly refused to participate in politics, the truth is that all governments since 1947, whether civilian or military, have had direct or indirect military support. [3] The governments of Ayub Khan or former army chief Zia Ul-Haq, both through a coup d'état, are faithful examples of this capacity for influence.[4]
The existence of an efficient army provides internal stability in two ways: first, as a bastion of national unity. This effect is quite relevant if we take into account the territorial claims arising from the ethnic division caused by the Durand Line. Secondly, it succeeds in maintaining the state's monopoly on force, preventing its disintegration as a result of internal ethnic disputes and terrorism instigated by Afghanistan in the Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA region).[5]
Despite its internal strengths, Pakistan is located in one of the most insecure geographical areas in the world, where border conflicts are intermingled with religious and identity-based elements. Indeed, the endless conflict over Kashmir against India in the northeastern part of the Pakistani border or the serious internal situation in Afghanistan have been weighing down the country for decades, both geo-politically and economically. The dynamics of regional alliances are not very favourable for Pakistan either, especially when US preferences, Pakistan's main ally, seem to be mutating towards a realignment with India, Pakistan's main enemy.[6]
On the positive side, a number of projects are underway in Central Asia that may provide an opportunity for Pakistan to re-launch its economy and obtain higher standards of stability domestically. The most relevant is the New Silk Road undertaken by China. This project has Pakistan as a cornerstone in its strategy in Asia, while it depends on it to achieve an outlet to the sea in the eastern border of the country and investments exceeding 11 billion dollars are expected in Pakistan alone[7]. In this way, a realignment with China can help Pakistan combat the apparent American disengagement from Pakistani interests.
For all these reasons, it is difficult to speak of Pakistan as a country capable of carving out its own destiny, but rather as a country held hostage to regional power dynamics. Throughout this document, a review of the regional phenomena mentioned will be made in order to analyze Pakistan's behavior in the face of the different challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
History
Right after the downfall of the British colony of the East Indies colonies in 1947 and the partition of India the Dominion of Pakistan was formed, now known by the title of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. The Partition of India divided the former British colony into two separate territories, the Dominion of Pakistan and the Dominion of India. By then, Pakistan included East Pakistan (modern day) Pakistan and Oriental Pakistan (now known as Bangladesh).
It is interesting to point out that the first form of government that Pakistan experienced was something similar to a democracy, being its founding father and first Prime Minister Muhammad Ali Jinnah. Political history in Pakistan consists of a series of eras, some democratically led and others ruled by the military branch which controls a big portion of the country.
-The rise of Pakistan as a Muslim democracy: 1957-1958. The era of Ali Jinnah and the First Indo-Pakistani war.
-In 1958 General Ayub Khan achieved to complete a coup d'état in Pakistan due to the corruption and instability.
-In 1971 General Khan resigned his position and appointed Zulfikar Ali Bhutto as president, but, lasted only 6 years. The political instability was not fruitful and rivalry between political parties was. But in 1977 General Zia-ul-Haq imposed a new order in Pakistan.
-From 1977 to 1988 Zia-ul-Haq imposed an Islamic state.
-In the elections of 1988 right after Zia-ul-Haq's death, President Benazir Bhutto became the very first female leader of Pakistan. This period, up to 1999 is characterized by its democracy but also, by the Kargil War.
-In 1999 General Musharraf took control of the presidency and turned it 90º degrees, opening its economy and politics. In 2007 Musharraf announced his resignation leaving open a new democratic era characterized by the War on Terror of the United States in Afghanistan and the Premiership of Imran Khan.
Human and physical geography
The capital of Pakistan is Islamabad, and as of 2012 houses a population of 1.9 million people. While the national language of Pakistan is English, the official language is Urdu; however, it is not spoken as a native language. Afghanistan is Pakistan's neighbour to the northwest, with China to the north, as well as Iran to the west, and India to the east and south.[8]
Pakistan is unique in the way that it possesses many a geological formation, like forests, plains, hills, etcetera. It sits along the Arabian Sea and is home to the northern Karakoram mountain range, and lies above Iranian, Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates. There are three dominant geographical regions that make up Pakistan: the Indus Plain, which owes its name to the river Indus of which Pakistan's dominant rivers merge; the Balochistan Plateau, and the northern highlands, which include the 2nd highest mountain peak in the world, and the Mount Godwin Austen. [9] Pakistan's traditional regions are a consequence of progression. These regions are echoed by the administrative distribution into the provinces of Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa which includes FATA (Federally Administered Tribal Areas) and Balochistan.
Each of these regions is "ethnically and linguistically distinct."[10] But why is it important to understand Pakistan's geography? The reason is, and will be discussed further in detail in this paper, the fact that "terror is geographical" and Pakistan is "at the epicenter of the neo-realist, militarist geopolitics of anti-terrorism and its well-known manifestation the 'global war on terror'..."[11]But why is it important to understand Pakistan's geography?
Punjabi make up more than 50% of the ethnic division in Pakistan, and the smallest division is the Balochi. We should note that Balochistan, however small, is an antagonistic region for the Pakistani government. The reason is because it is a "base for many extremist and secessionist groups". This is also important because CPEC, the Chinese-Pakistan Economic Corridor, is anticipated to greatly impact the area, as a large portion of the initiative is to be constructed in that region. The impact of CPEC is hoped to make that region more economically stable and change the demography of this region.[12]
The majority of Pakistani people are Sunni Muslims, and maintain Islamic tradition. However, there is a significant number of Shiite Muslims. Religion in Pakistan is so important that it is represented in the government, most obviously within the Islamic Assembly (Jamāʿat-i Islāmī) party which was created in 1941.[13]The Islamic Assembly is the largest Islamic party in Pakistan.
This is important. The reason being is that there is a history of sympithism for Islamic extremism by the government, and giving rise to the expansion of the ideas of this extremism. Historically, Pakistan has not had a strict policy against jihadis, and this lack of policy has poorly affected Pakistan's foreign policy, especially its relationship with the United States, which will be touched upon in this paper.
Current Situation: Domestic politics, the military and the economy
Imran Khan was elected and took office on August 18th, 2018. Before then, the previous administrations had been overshadowed by suspicions of corruption. What also remained important was the fact that his election comes after years of a dominating political power, the Pakistan Muslim League-Nawaz (PML-N) and Pakistan People's Party (PPP). Imran Khan's party, the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) surfaced as the majority in the Pakistan's National Assembly. However, there is some discussion by specialists on how prepared the new prime minister is to take on this extensive task.
Economically, Pakistan was in a bad shape even before the global Coronavirus-related crisis. In October 2019, the IMF predicted that the country's GDP would increase only 2.4% in 2020, compared with 5.2% registered in 2017 and 5.5% in 2018; inflation would arrive to 13% in 2020, three times the registered figure of 2017 and 2018, and gross debt would peak at 78.6%, ten points up from 2017 and 2018.[14] This context led to the Pakistani government to ask for a loan to the IMF, and a $6 billion loan was agreed in July 2019. In addition, Pakistan got a $2 billion from China. Later on, because of the Covid-19 pandemic, the IMF worsened its estimations on Pakistan's economy, and predicted that its GDP would grow minus 1.5% in 2020 and 2% in 2021.
Throughout its history, Pakistan has been a classic example of a "praetorian state", where the military dominates the political institutions and regular functioning. The political evolution is represented by a routine change "between democratic, military, or semi military regime types". There were three critical pursuits towards a democratic state that are worth mentioning, that started in 1972 and resulted in the rise of democratically elected leaders. In addition to these elections, the emergence of new political parties also took place, permitting us to make reference to Prime Minister Imran Khan's party, the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI).[16]
Civilian - military relations are characterized by the understanding that the military is what ensures the country's "national sovereignty and moral integrity". There resides the ambiguity: the intervention of the military regarding the institution of a democracy, and the sabotage by the same military leading it to its demise. In addition to this, to the people of Pakistan, the military has retained the impression that the government is incapable of maintaining a productive and functioning state, and is incompetent in its executing of pertaining affairs. The role of the military in Pakistani politics has hindered any hope of the country implementing a stable democracy. To say the least, the relationship between the government and the resistance is a consistent struggle.[17]
The military has extended its role today with the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. The involvement of the military has affected "four out of five key areas of civilian control". Decision making was an area that was to be shared by the military and the people of Pakistan, but has since turned into an opportunity for the military to exercise its control due to the fact that CPEC is not only a "corporate mega project" but also a huge economic opportunity, and the military in Pakistan continues to be the leading force in the creation of the guidelines pertaining to national defense and internal security. Furthermore, accusations of corruption have not helped; the Panama Papers were "documents [exposing] the offshore holdings of 12 current and former world leaders."[18] These findings further the belief that Pakistan's leaders are incompetent and incapable of effectively governing the country, and giving the military more of a reason to continue and increase its interference. In consequence, the involvement of civilians in policy making is declining steadily, and little by little the military seeks to achieve complete autonomy from the government, and an increased partnership with China. It is safe to say that CPEC would have been an opportunity to improve military and civilian relationships, however it seems to be an opportunity lost as it appears the military is creating a government capable of functioning as a legitimate operation.[19]
[1] Gottmann, J., & Fox, E. W. (1973). History in Geographic Perspective: The Other France. Geographical Review.
[2] Tariq Ali (2009). The Duel: Pakistan on the Flight Path of American Power.
[3] Marquina, A. (2010). The European Union's Security and Defence Policy. 28, 441-446.
[4] Tariq Ali (2009). Ibid.
[5] Sánchez de Rojas Díaz, E. (2016).Is Pakistan one of the most conflictive countries in the world? The origins of terrorism in Pakistan.
[6] Ríos, X. (2020). India aligns with the US.
[7] Economic corridor: China to extend assistance at 1.6 percent interest rate. (2015). Business Recorder.
[8] Szczepanski, Kallie,"Pakistan: Facts and History". ThoughtCo.
[9] Pakistan Insider. "Pakistan's Geography, Climate, and Environment."Pakistan Insider, February 9, 2012.
[10] Burki, Shahid Javed, and Lawrence Ziring. "Pakistan." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, inc., March 6, 2020.
[11] Mustafa, Daanish, Nausheen Anwar, and Amiera Sawas. "Gender, Global Terror, and Everyday Violence in Urban Pakistan." Elsevier. Elsevier Ltd., December 4, 2018.
[12] Bhattacharjee, Dhrubajyoti. "China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC)." Indian Council of World Affairs, May 12, 2015.
[13] Burki, Shahid Javed, and Lawrence Ziring. Ibid.
[14] IMF, "Economic Outlook", October 2019.
[15] IMF, "World Economic Outlook", April 2020.
[16] Wolf, Siegfried O. "China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, Civil-Military Relations and Democracy in Pakistan." SADF Working Paper, no. 2 (September 13, 2016).
[17] Ibid.
[18] "Giant Leak of Offshore Financial Records Exposes Global Array of Crime and Corruption." The International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, April 3, 2016.
[19] Wolf, Siegfried O. Ibid.
[Joseph S. Nye. Do Morals Matter? Presidents and Foreign Policy from FDR to Trump. Oxford University Press. New York, 2020. 254 pp.]
review / Emili J. Blasco
 The question that serves as degree scroll for the new book by Jospeh Nye, known to the public at large for having coined the term "the question of the future". soft powerThe author's argument is not so much a concession to secularist thinking as a lack of boldness in asserting from entrance the desirability of ethical reflection in foreign policy decisions, an importance that, despite the question mark, one senses is defended by the author.
The question that serves as degree scroll for the new book by Jospeh Nye, known to the public at large for having coined the term "the question of the future". soft powerThe author's argument is not so much a concession to secularist thinking as a lack of boldness in asserting from entrance the desirability of ethical reflection in foreign policy decisions, an importance that, despite the question mark, one senses is defended by the author.
In fact, the question itself is a question core topic at discipline of International Office. A common approach is to see the world scenario as a conjunction of competing states, in an anarchic dynamic where the law of the strongest prevails. Internally, the state can be driven by criteria of the common good, addressing the different needs of its inhabitants and making decisions at the national or local level through democratic processes. But beyond one's own borders, does the legitimacy granted by one's own electorate not require the ruler above all to guarantee the security of his citizens against external threats and to safeguard the national interest against that of other states?
The fact that the state is the basic subject in the International Office of course marks a dividing line between the two spheres. And so the question of whether the ethical discernment that is demanded of the mandatary in the internal sphere should also be demanded of him in the external sphere is fully relevant.
Only from extreme positions that consider the state to be a wolf for the state, applying the Hobbesian principle to international order (disorder) (and here there would be no supra-state to discipline this tendency of the state-individual), can it be argued that amorality rules all against all. On a lower rung is so-called offensive realism, and on a lower rung, defensive realism.
Nye, a scholar of International Office, believes that realist theory is a good starting point for any president when it comes to defining a country's foreign policy, given that he must be guided especially by the ethics of responsibility, as he fulfils a 'fiduciary role'. "A president's first moral duty is that of a trustee, and this begins with ensuring the survival and security of the democracy that elected him. But from here it should also be explored what possibilities exist for partnership and international mutual benefit, not closing the door on entrance to approaches of liberalism or cosmopolitanism.
"When survival is at stake, realism is a necessary but not sufficient basis for a moral foreign policy," says Nye, for whom it is a "question of Degree". "Given that there is never perfect security, the moral question is what Degree security should be assured before other values such as welfare, identity or rights are part of a president's foreign policy". He adds: "Many of the most difficult moral decisions are not all-or-nothing [...] The difficult moral decisions are in the middle. While it is important to be cautious about the dangers of a slippery slope, moral decisions rest on matching ends and means with each other'. He concludes that "the maintenance of international institutions and regimes is part of moral leadership".
From the very beginning of the book, Nye uses the three conditions that have traditionally been used in moral treatises to judge an action as ethically good: that the intention, the means and the consequences are good at the same time.
Using these three yardsticks, the author analyses the foreign policy of each of the US presidents since World War II and establishes a final ranking that combines both the morality of their actions on the international stage and the effectiveness of their policy (because an ethical foreign policy can be the case, but one that does little to further a country's national interests).
Thus, of the fourteen presidents, he considers that the four with the best grade in that combination are Roosevelt, Truman, Eisenhower and Bush I. In the middle he places Reagan, Kennedy, Ford, Carter, Clinton and Obama. And as the four worst he lists Johnson, Nixon, Bush II and ("tentatively incomplete") Trump. Having done the ranking, Nye warns that he may have given precedence to the Democratic administrations he worked for.
The book is a quick overview of the foreign policy of each presidency, highlighting the presidents' doctrines, their successes and failures (as well as examining the ethical component), so it is also interesting as a succinct history of the US International Office of the last eighty years.
The aspect of morality perhaps lacks a more academic foundation, as it is an discipline especially studied since the scholastic era. But Nye's purpose was not intended to delve into this subject, but to offer a brief study of applied morality.
Reading Nye is always thought-provoking. Among his other reflections might be the idea of the new prospects that would have opened up for the world if particularly propitious times had coincided in the calendar. In particular, he suggests that if Brezhnev and his gerontocratic generation had left earlier and the USSR had been beset by severe economic problems earlier, Gorbachev might have come to power at the same time as Carter's presidency; what they would have achieved together is, however, a matter for speculation.
![A view of the Badshahi Mosque, in Lahore, capital of the Punjab province [Pixabay]. A view of the Badshahi Mosque, in Lahore, capital of the Punjab province [Pixabay].](/documents/10174/16849987/pakistan-mayo-2020-blog.jpg)
▲ A view of the Badshahi Mosque, in Lahore, capital of the Punjab province [Pixabay].
STRATEGIC ANALYSIS REPORT / Naomi Moreno, Alejandro Puigrefagut, Ignacio Yárnoz
 Download the document [pdf. 1,4MB] [pdf. 1,4MB
Download the document [pdf. 1,4MB] [pdf. 1,4MB
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
This report has been aimed at examining the future prospects for Pakistan in the 2025 horizon in relation to other States and to present various scenarios through a prospective strategic analysis.
The research draws upon the fact that, despite the relatively short space of time, Pakistan is likely to undergo several important changes in its international affairs and thus feel forced to rethink its foreign policy. This strategic analysis suggests there could be considerable estrangement between the U.S. and Pakistan and, therefore, the American influence will decrease considerably. Their security alliance could terminate, and Pakistan would cease to be in U.S.' sphere of influence. Moreover, with the new BRI and CPEC projects, China could move closer to Pakistan and finally become its main partner in the region. The CPEC is going to become a vital instrument for Pakistan, so it could significantly increase Chinese influence. Yet, the whole situation risks jeopardizing Pakistan's sovereign independence.
India-Pakistan longstanding dispute over Kashmir seems to be stagnated and will possibly remain as such in the following years. India has taken steps to annex its administered territory in Jammu and Kashmir and Pakistan could potentially follow. The possibility of an open conflict and a nuclear standoff remains possible as both nuclear powers have very different strategies and conceptions which could lead to misinterpretation and a nuclear escalation.
In the quest to rethink its foreign policy, the U.S.-Taliban peace and the empowerment of the group has come as a bolt from the sky for Pakistan. Through its ties with the Taliban, Pakistan could gain itself a major presence in the region namely by reaching out to Central Asia and advance its interest to curtail India's influence. Amid a dire economic crisis, with regards to the Saudi Iranian Cold War, Pakistan could seek a way in which it can recalibrate its stance in favour of the resource-rich Saudi alliance while it appeases sectarian groups who could strongly oppose this potential policy.
Pakistan ought to acknowledge that significant changes ought to be made in both the national and international sphere and that decisive challenges lay ahead.
Beijing has announced the construction of a fifth base, matching the US base at issue .
While there is widespread international monitoring of the major powers' position-taking in the Arctic, given that global warming opens up trade routes and possibilities for resource exploitation, geopolitical movements around Antarctica go more unnoticed. With any national claims to the South Pole continent frozen by existing agreements, the steps taken by the superpowers are minor but significant. As in the Arctic, China is a new player, and is stepping up its stakes.
![Shared camp for research scientists in Antarctica [Pixabay]. Shared camp for research scientists in Antarctica [Pixabay].](/documents/10174/16849987/antartida-china-blog.jpg)
▲ Shared camp for research science in Antarctica [Pixabay].
article / Jesús Rizo
Antarctica is the southernmost continent and at the same time the most extreme due to its geographical and thermal conditions, which seriously limit its habitability. Human presence is almost impossible in the so-called East Antarctic, which is two thousand metres above sea level and makes up more than two thirds of the continent, making it the highest altitude continent average. Moreover, since Antarctica is not an ocean, as is the Arctic, it is not affected, except in its continental perimeter, by the increase in sea temperatures due to climate change.
To these difficulties for human presence are added the limitations imposed by international provisions, which have applied a moratorium on any claim to sovereignty or commercial exploitation, something that does not happen in the Arctic. Action in Antarctica is strongly determined by the Antarctic Treaty (Washington, 1959) which, in its articles I and IX, reservation the continent for research scientific and peaceful purposes. In addition, it prohibits nuclear explosions and the disposal of radioactive waste (article V), and any non-peaceful military action (article I).
protocol This treaty is complemented and developed by three other documents: the Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR, Canberra, 1980), the Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Seals (CCFA, London, 1988) and the Antarctic Treaty on Environmental Protection (Madrid, 1991), which prohibits "any activity related to mineral resources, except for scientific research " until 2048. At final, the so-called Antarctic Treaty System (ATS) "shields" the Antarctic region from exploitation of its resources and increased international tensions, as it also freezes territorial claims for as long as it is in force. However, this does not prevent global powers from also seeking a foothold in Antarctica.
The most recent action corresponds to the People's Republic of China, which aspires to play a major role in the area, as is the case in the Arctic. Already with four scientific instructions sites on the southern continent (the Antarctic instructions Great Wall, Zhongshan, Kunlun and Taishan, the first two permanent and the last two functional in summer), last November it announced the construction of its fifth base (thus equalling the United States at issue ). The new facility, in the Ross Sea, would be operational by 2022.
In relation to these scientific stations, since Xi Jinping came to power in 2013, China has been seeking to create a Specially Managed Antarctic Zone for the protection of the environment around the Kunlun base, something resisted by its regional neighbours, as it would give Beijing dominion over the activities carried out there. This is China's most important base, essential for its programs of study at subject astronomy and, therefore, for the development of the BeiDou, China's satellite navigation system, which is essential for the expansion and modernisation of its armed forces and rivals the GPS (US), Galileo (EU) and GLONASS (Russia) systems. In this respect, and in view of the military implications of Antarctica, the Treaty established the possibility for any country to carry out inspections of any of the instructions sites there, as a way of ensuring compliance with the provisions of agreement (article VII). However, the danger and cost of these inspections have meant that they have been considerably reduced, not to mention that the Kunlun base is located in one of the most climatically hostile regions of the continent.
On the other hand, China currently has two icebreakers, the Xue Long I and the Xue Long II, the latter built entirely on Chinese territory with the Finnish Aker Arctic attendance . Experts believe that, following the construction of this vessel, the People's Republic could be close to building nuclear-powered icebreakers, something that is currently only undertaken by Russia and which would have global consequences.
But the importance of Antarctica for China is not only reflected in the technical and technological advances it is making, but also in its bilateral relations with countries close to the southern continent such as Chile and Brazil, the former with original consultative status and with a territorial claim in the ATS, and the latter with consultative status only. Last September, the Andean country held the first meeting of the Joint Antarctic Cooperationcommittee with the People's Republic, in which, among other matters, the use of the port of Punta Arenas by China as a base for the supply of staff and materials to its Antarctic installations was discussed, conversations that will require further deepening. business As for Brazil, China's CEIEC (China National Electronics Import & Export Corporation) financed a new Brazilian Antarctic base worth $100 million in January.
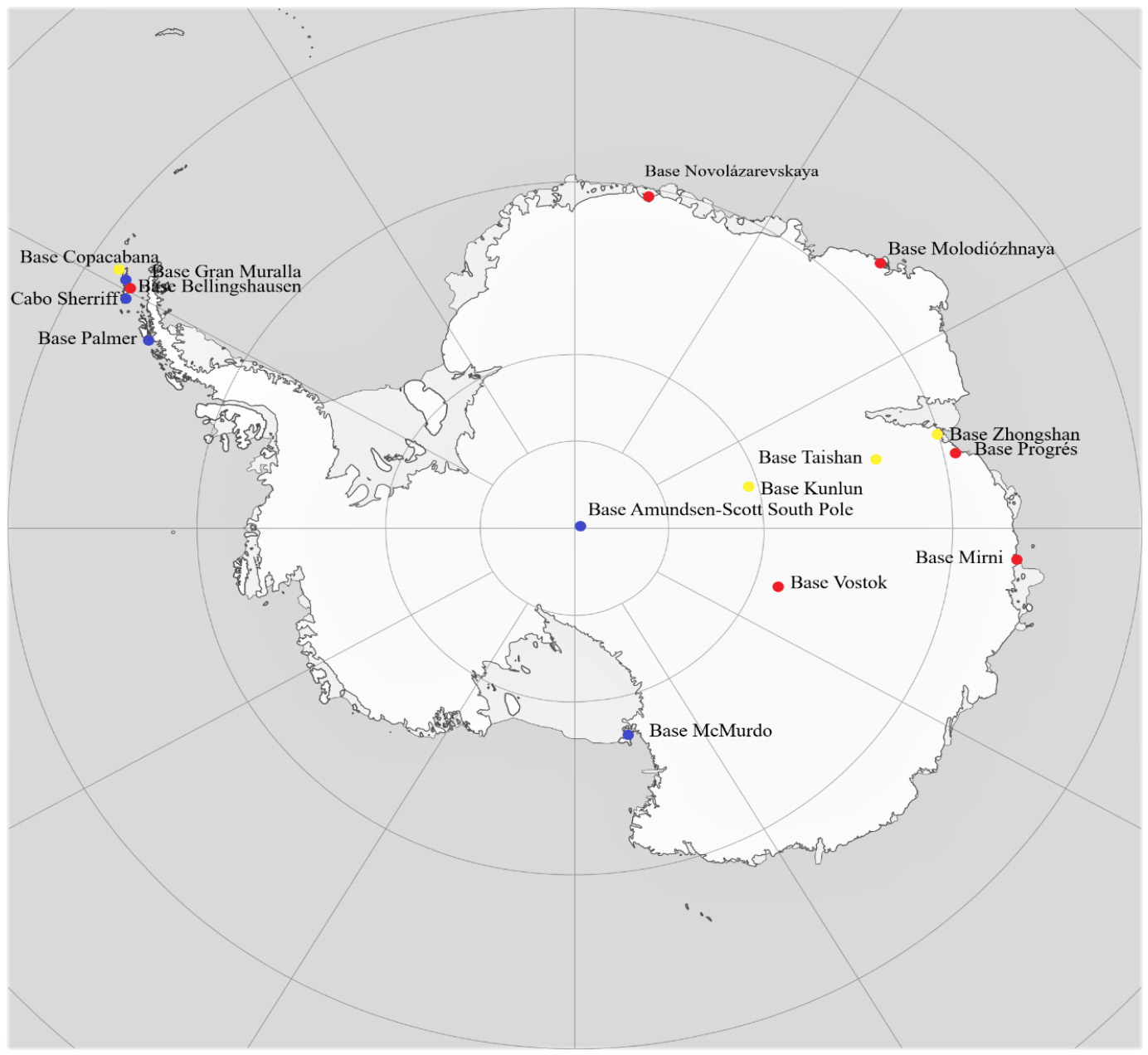
Approximate location of the main Antarctic instructions . In blue, the US instructions , in red, the Russian , and in yellow, the Chinese .
Finally, it is worth analysing the weight of the US and Russia in Antarctica, although China is likely to be the most important player in the region, at least until the opening of the Madrid protocol for review in 2048. The United States has three permanent instructions (the instructions McMurdo, Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station and Palmer) and two summer only (the instructions Copacabana and Cape Shirreff), so the construction of the new Chinese base will equal the issue total of the instructions US bases.
For its part, Russia, the dominant power in the Arctic, is also the dominant power in its southern counterpart, at least in terms of issue of instructions, since it has six, four of which operate annually (Mirni, Novolazarevskaya, Progrés and Vostok) and the other two only during the summer (Bellingshausen and Molodiózhnaya). However, it should be noted that Russia has not opened any Antarctic bases since the collapse of the USSR, the most recent being Progrés (1988), although it has tried, for example, to reopen the Soviet base Russkaya, without success. The United States also established most of its Antarctic instructions at the height of the Cold War, in the 1950s and 1960s, except for the two summer ones (Copacabana in 1985 and Cape Shirreff in 1991).
China, by contrast, opened the Great Wall base in 1985, the Zhongshan base in 1989, the Kunlun base in 2009 and the Taishan base in 2014 and, as mentioned above, has a new one pending for 2022.
In addition to the countries mentioned above, another twenty countries have instructions of research in Antarctica, including Spain, which has consultative status in the Antarctic Treaty. Spain has two summer instructions sites in the South Shetland Islands, the Juan Carlos I base (1988) and the Gabriel de Castilla base (1998). It also has a temporary scientific camp located on the Byers Peninsula of Livingston Island.
