Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Trials .
ESSAY / Emilija Žebrauskaitė
Introduction
While the Western Westphalian State - and, consequently, the Western legal system - became the default in most parts of the world, Africa with its traditional ethics and customs has a lot to offer. Although the positive legalism is still embraced, there is a tendency of looking at the indigenous traditions for the inspiration of the system that would be a better fit in an African setting. Ubuntu ethics has a lot to offer and can be considered a basis for all traditional institutions in Africa. A great example of Ubuntu in action is the African Traditional Justice System which embraces the Ubuntu values as its basis. This article will provide a conceptualization of Ubuntu philosophy and will analyse its applications in the real-world scenarios through the case of Gacaca trials in Rwanda.
Firstly, this essay will define Ubuntu: its main tenants, how Ubuntu compares with other philosophical and ethical traditions, and the main criticism of Ubuntu ethics. Secondly, the application of Ubuntu ethics through African Indigenous Justice Systems will be covered, naming the features of Ubuntu that can be seen in the application of justice in the African setting, discussing the peace vs. justice discussion and why one value is emphasized more than another in AIJS, and how the traditional justice in Africa differs from the Western one.
Lastly, through the case study of Gacaca trials in post-genocide Rwanda, this essay seeks to demonstrate that the application of the traditional justice in the post-genocide society did what the Western legalistic system failed to do - it provided a more efficient way to distribute justice and made the healing of the wounds inflicted by the genocide easier by allowing the community to actively participate in the judicial decision-making process.
It is the opinion of this article that while the African Traditional Justice System has it's share of problems when applied in modern-day Africa, as the continent is embedded into the reality of the Westphalian state, each state being a part of the global international order, the Western model of justice is eroding the autonomy of the community which is a cornerstone of African society. However, the values of Ubuntu ethics persist, providing a strong basis for traditional African institutions.
Conceptualization of Ubuntu
The word Ubuntu derives from the Bantu language group spoken widely across sub-Saharan Africa. It can be defined as "A quality that includes the essential human virtues; compassion and humanity" (Lexico, n.d.) and, according to Mugumbate and Nyanguru, is a homogenizing concept, a "backbone of African spirituality" in African ontology (2013). "Umuntu ngumuntu ngabantu" - a Zulu phrase meaning "a person is a person through other persons" is one of the widely spread interpretations of Ubuntu.
In comparison with non-African philosophical thoughts, there can be found similarities between Ubuntu and the traditional Chinese as well as Western ethics, but when it comes to the modern Western way of thought, the contrast is striking. According to Lutz (2009), Confucian ethics, just like Ubuntu ethics, view the institution of family as a central building block of society. An Aristotelian tradition which prevailed in the Western world until Enlightenment had some characteristics similar to Ubuntu as well, namely the idea of Aristotle that human being is a social being and can only reach his true potential through the community (Aristotle, 350 B.C.E.). However, Thomas Hobbes had an opposite idea of human nature, claiming that the natural condition of man is solidarity (Hobbes, 1651). The values that still prevail in Ubuntu ethics, therefore, are rarely seen in modern liberal thought that prevails in the Western World and in the international order in general. According to Lutz (2009) "Reconciling self-realization and communalism is important because it solves the problem of moral motivation" which Western modern ethics have a hard time to answer. It can be argued, therefore, that Ubuntu has a lot to offer to the global ethical thought, especially in the world in which the Western ideas of individualism prevail and the values of community and collectivism are often forgotten.
Criticisms
However, while Ubuntu carries values that can contribute to global ethics, as a philosophical current it is heavily criticised. According to Metz (2011), there are three main reasons why Ubuntu receives criticism: firstly, it is considered vague as a philosophical thought and does not have a solid framework; secondly, it is feared that due to its collectivist orientation there is a danger of sacrificing individual freedoms for the sake of society; and lastly, it is thought that Ubuntu philosophy is applicable and useful only in traditional, but not modern society.
When it comes to the reproach about the vagueness of Ubuntu as a philosophical thought, Thaddeus Metz examines six theoretical interpretations of the concept of Ubuntu:
U1: An action is right just insofar as it respects a person's dignity; an act is wrong to the extent that it degrades humanity.
U2: An action is right just insofar as it promotes the well-being of others; an act is wrong to the extent that it fails to enhance the welfare of one's fellows.
U3: An action is right just insofar as it promotes the well-being of others without violating their rights; an act is wrong to the extent that it either violates rights or fails to enhance the welfare of one's fellows without violating rights.
U4: An action is right just insofar as it positively relates to others and thereby realises oneself; an act is wrong to the extent that it does not perfect one's valuable nature as a social being.
U5: An action is right just insofar as it is in solidarity with groups whose survival is threatened; an act is wrong to the extent that it fails to support a vulnerable community.
U6: An action is right just insofar as it produces harmony and reduces discord; an act is wrong to the extent that it fails to develop community (Metz, 2007).
While arguing that the concept U4 is the most accepted in literature, Matz himself argues in favour of the concept U6 as the basis of the ethics is rooted not in the subject, but in the object (Metz, 2007).
The fear that Ubuntu tenants make people submissive to authority and collective goals, giving them a very strong identity that might result in violence against other groups originates, according to Lutz (2009), from a faulty understanding of Ubuntu. Even though the tribalism is pretty common in the African setting, it does not derive from the tenants of Ubuntu, but a corrupted idea of this ethical philosophy. Further criticism on the idea that collectivism might interfere with individual rights or liberties can also be denied quoting Lutz, who said that "Ethical theories that tell us we must choose between egoism and altruism, between self-love and love of others, between prudence and morality, or one's good and the common good are individualistic ethical theories" and therefore have nothing in common with ideas of Ubuntu, which, unlike the individualistic theories, reconciles the common and staff good and goals.
The third objection, namely the question of whether Ubuntu ethics remain useful in the modern society which functions according to the Westphalian State model is challenged by Metz (2011). While it is true that Ubuntu developed in a traditional setting in which the value of human beings was based on the amount of communal life a human has lived (explaining the respect for the elders and the ancestors in African setting), a variant concept of dignity that in no way can be applied in a modern setting, there are still valuable ethical norms that can be thought by Ubuntu. Metz (2011) provides a concept of human dignity based on Ubuntu ideas, which, as he argues, can contribute to ethics in the modern African setting: "individuals have dignity insofar as they have communal nature, that is, the inherent capacity to exhibit identity and solidarity with others".
The Ubuntu ethics in African Indigenous Justice System
The institutionalisation and centralisation of power in the hands of the Westphalian State takes away the power from the communities which are central to the lifestyle in Africa. However, the communal values have arguably persisted and continue to directly oppose the centralisation. While the Westphalian State model seems to be functioning in the West, there are many good reasons to believe that Africa must look for inspiration in local traditions and customs (Malisa & Nhengeze, 2018). Taking into consideration the Ubuntu values, it is not difficult to understand why institutionalisation has generally not been very successful in African setting (Mugumbate & Nyanguru, 2013), as a place where the community is morally obliged to take care of its members, there is little space for alienated institutions.
Generally, two justice systems are operating alongside each other in many African societies: the state-administered justice system and the African Indigenous Justice System (AIJS). According to Elechi, Morris & Schauer, the litigants can choose between the state tribunal and AIJS, and can apply to be judged by the state if they do not agree with the sentence of the AIJS (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010). However, Ubuntu values emphasise the concept of reconciliation: "African political philosophy responds easily and organically to the demands for the reconciliation as a means of restoring the equilibrium of the flow of life when its disturbed" (Nabudere, 2005). As the national court interventions often disharmonize the community by applying the "winner takes it all" approach, and are sometimes considered to be corrupt, there is a strong tendency for the communities to insist on bringing the offender to the AIJS tribunal (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010).
African Indigenous Justice System is a great example of Ubuntu values in action. The system operates on the cultural norm that important decision should be reached by consensus of the whole group as opposed to the majority opinion. AIJS is characterised by features such as the focus on the effects the offence had on victims and the community, the involvement of the litigants in the active definition of harms and the resolution of the trial, the localisation and decentralisation of authority, the importance of the restoration of harm, the property or relationship, the understanding that the offender might be a victim of the socioeconomic conditions; with the main objective of the justice system being the restoration of relationships, healing, and reconciliation in the community (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010). Underlying this system is the concept of Ubuntu, which "leads to a way of dealing with the social problems which are very different from the Western legalistic, rule-based system which had become the global default" (Baggini, 2018).
One of the reasons why AIJS can be considered exemplary is its ability to avoid the alienation of the Western courts in which the victim, the offender, and everybody else seem to be represented, but neither victim nor offender can directly participate in the decision making. The system which emphasises reconciliation and in which the community is in charge of the process is arguably much more effective in the African setting, where communities are generally familiar and close-knit. As the offender is still considered a part of the community and is still expected to contribute to its surroundings in the future, the participation in the trial and the decision making is important to the reconciliation: "unlike adjudicated justice, negotiated justice is not a winner take it all justice. Resolution can be reached where the offender, the community, and the victim are each partially wrong" (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010). As there is very little hope for an offender to be reintegrated into a close community without forgiving and forgiveness from both parties, this type of approach is pivotal.
Another interesting feature of AIJS is the assumption that the offender is not inherently bad in himself, but is primarily a marginalised victim, who does not have the same opportunities as other members of the community to participate in the economic, political, and social aspects of the group, and who can be made right if both the offender and the community make effort (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010). This concept differs from the Western Hobbesian idea of human beings being inherently corrupt and is much closer to traditional Western Aristotelian ethics. What makes the African concept different, however, is the focus which is not on the virtue of the person himself, but rather on the relationship the offender has with his family and community which, although violated by the offence, can and should be rebuilt by amendments (Elechi, Morris, & Schauer, 2010).
The Gacaca Trials
The Gacaca trials are the state-administered structure which uses communities (around a thousand of them) as a basis for judicial forums (Meyerstein, 2007). They were introduced by the Rwandan government as an alternative to national justice after the Rwandan genocide.
During the colonial times, Rwanda was indirectly ruled by the colonisers through local authorities, namely the Tutsi minority (Uvin, 1999). The Hutu majority were considered second class citizens and by the time of independence were holding deep grievances. The Rwandan Revolution of 1959-1961 overthrew the monarchy and the ruling Tutsi elite. After the independence from the colonial regime, Rwanda was ruled by the Party of Hutu Emancipation Movement, which was supported by the international community on the grounds of the idea that the government is legitimate as it represents the majority of the population - the Hutu (ibid.) During the period of transition, ethnic violence against Tutsi, forcing many of them to leave the country, happened (Rettig, 2008). In 1990 the Rwandan Patriotic Army composed mostly by the Tutsi exiles invaded Rwanda from neighbouring Uganda (ibid.) The incumbent government harnessed the already pre-existing ethnic to unite the Hutu population to fight against the Tutsi rebels. The strategy included finding a scapegoat in an internal Tutsi population that continued to live in Rwanda (Uvin, 1999). The genocide which soon followed took lives of 500,000 to 800,000 people between April and July of the year 1994 when the total population at the time is estimated to have been around 8 million (Drumbl, 2020). More than 100,000 people were accused and waited in detention for trials, creating a great burden on a Rwandan county (Schabas, 2005).
According to Meyerstein (2007), the Gacaca trials were a response to the failure of the Western-styled nation court to process all the suspects of the genocide. Gacaca trials were based on indigenous local justice, with Ubuntu ethics being an underlying element of the system. The trials were traditionally informal, organic, and patriarchal, but the Rwandan government modernised the indigenous justice system by establishing an organisational structure, and, among other things, making the participation of women a requirement (Drumbl, 2020).
The application of Gacaca trails to do justice after the genocide was not always well received by the international community. The trials received criticism for not complying with the international standards for the distribution of justice. For example, Amnesty International invoked Article 14 of the ICCPR and stated that Gacaca trials violated the right of the accused to be presumed innocent and to the free trial (Meyerstein, 2007). There are, undoubtedly, many problems that can be assigned to the system of Gacaca when it comes to the strict norms of the international norms.
The judges are drawn from the community and arguably lack the official legal training, the punitive model of the trials that arguably have served for many as an opportunity for staff revenge, and the aforementioned lack of legal protection for the accused are a few of many problems faced by the Gacaca trials (Rettig, 2008). Furthermore, the Gacaca trials excluded the war criminals from the prosecution - there were many cases of the killings of Hutu civilians by Tutsis that formed the part of the Rwandan Patriotic Front army (Corey & Joireman, 2004). This was seen by many as a politicised application of justice, in which, by creating two separate categories of criminals - the crimes of war by the Tutsis that were not the subject of Gacaca and the crimes of the genocide by the Hutus that were dealt with by the trials - the impunity and high moral ground was granted for the Tutsi (ibid). This attitude might bring results that are contrary to the initial goal of the community-based justice - not the reconciliation of the people, but the further division of the society along the ethnic lines.
However, while the criticism of the Gacaca trials is completely valid, it is also important to understand, that given the limited amount of resources and time, the goal of bringing justice to the victims of the genocide is an incredibly complex mission. In the context of the deeply wounded, post-genocidal society in which the social capital was almost non-existent, the ultimate goal, while having justice as a high priority, was first of all based on Ubuntu ethics and focused more on peace, retribution, and social healing. The utopian perfectness expected by the international community was nearly impossible, and the Gacaca trials met the goal of finding the best possible solutions in the limits of available resources. Furthermore, the criticism of international community often seemed to stem not so much from the preoccupation for the Rwandan citizens, as from the fact that a different approach to justice threatens the homogenising concept of human rights "which lashes out to squash cultural difference and legal pluralism by criticising the Gacaca for failures to approximate canonised doctrine" (Meyerstein, 2007).
While it is true that even Rwandan citizens often saw Gacaca as problematic, whether the problems perceived by them were similar to those criticised by the international community is dubious. For example, Rwanda's Supreme Court's response to the international criticism was the provision of approach to human rights which, while not denying their objectivity, also advocates for the definition that better suits the local culture and unique circumstances of post-genocide Rwanda (Supreme Court of Rwanda, 2003). After all, the interventions from the part of the Western world on behalf of the universal values have arguably created more violence historically than the defended values should ever allow. The acceptance that Gacaca trials, while imperfect, contributed positively to the post-genocide Rwandan society has the grave implications that human rights are ultimately a product of negotiation between global and local actors" (Meyerstein, 2007) which the West has always refused to accept. However, it is the opinion of this article that exactly the opposite attitude, namely that of better intercultural understanding and the search for the solutions that are not utopian but fit in the margins of the possibilities of a specific society, are the key to both the efficiency and the fairness of a justice system.
Conclusion
The primary end of the African Indigenous Justice System is to empower the community and to foster reconciliation through a consensus that is made by the offenders, the victims, and the community alike. It encourages to view victims as people who have valuable relationships: they are someone's daughters, sons, fathers - they are important members of society. Ubuntu is the underlying basis of the Indigenous Justice System and African ethnicity in general. While the AIJS seems to be functioning alongside the state's courts, in the end, the centralization and alienation from the community are undermining these traditional values that flourish in the African setting. The Western legalistic system helps little when it comes to the main goal of justice in Africa - the reconciliation of the community, and more often than not only succeeds in creating further discord. While the criticism of Gacaca trials was undoubtedly valid, it often stemmed from the utopian idealism that did not take the actual situation of a post-genocide Rwanda into consideration or the Western universalism, which was threatened by the introduction of a justice system that in many ways differs from the positivist standard. It is the opinion of this article, therefore, that more autonomy should be granted to the communities that are the basic building blocks of most of the African societies, with the traditional values of Ubuntu being the basis of the African social institutions.
REFERENCES
Lexico. (n.d.). Lexicon. Retrieved from https://www.lexico.com/definition/ubuntu
Mugumbate, J., & Nyanguru, A. (2013). Exploring African Philosophy: The Value of Ubuntu in Social Work. African Journal of Social Work, 82-100.
Metz, T. (2011). Ubuntu as a moral theory and human rights in South Africa. African Human Rights Law Journal, 532-559.
Metz, T. (2007). Towards an African Moral Theory. The Journal of Political Philosophy.
Lutz, D. W. (2009). African Ubuntu Philosophy and Global Management. Journal of Business Ethics, 313-328.
Hobbes, T. (1651). Leviathan.
Aristotle. (350 B.C.E.). Politics.
Malisa, M., & Nhengeze, P. (2018). Pan-Africanism: A Quest for Liberation and the Pursuit of a United Africa. Genealogy.
Elechi, O., Morris, S., & Schauer, E. (2010). Restoring Justice (Ubuntu): An African Perspective. International Criminal Justice Review.
Baggini, J. (2018). How the World Thinks: A Global History of Philosophy. London: Granta Books.
Meyerstein, A. (2007). Between Law and Culture: Rwanda's Gacaca and Postolocial Legality. Law & Social Inquiry.
Corey, A., & Joireman, S. (2004). African Affairs. Retributive Justice: the Gacaca Courts in Rwanda.
Nabudere, D. W. (2005). Ubuntu Philosophy. Memory and Reconciliation. Texas Scholar Works, University of Texas Library.
Rettig, M. (2008). Gacaca: Truth, Justice, and Reconciliation in Postconflict Rwanda? African Studies Review.
Supreme Court of Rwanda. (2003). Developments on the subject of the report and different correspondences of Amnesty International. Départements des Jurisdictions Gacaca.
Drumbl, M. A. (2020). Post-Genocide Justice in Rwanda. Journal of International Peacekeeping.
Uvin, P. (1999). Ethnicity and Power in Burundi and Rwanda: Different Paths to Mass Violence. Comparative Politics, 253-271.
Schabas, W. A. (2005). Genocide Trials and Gacaca Courts. Journal of International Criminal Justice, 879-895.
15 June, 2021
essay / Paula Mora Brito [English version].
Terrorism in the Sahel is a neglected reality that affects millions of people. Not surprisingly, the region is one of the most afflicted by it internship. Its complex geographical features make it difficult to control borders (especially those of the Sahara desert), and the lack of cultural and religious homogeneity, coupled with continuing economic and social challenges, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, make the region a fragile and convenient scenario for terrorist groups. In addition, Western countries (mainly France) are present in the area, provoking a certain rejection of their intervention in the eyes of the Sahelian population. Although data is scarce on this issue, which makes it difficult to study, this article will attempt to broaden the concepts and knowledge of terrorism in the Sahel, extending its geographical scope to show the daily life of its inhabitants over the last few years. The focus of the analysis will be on Western intervention in the fight against terrorism.
The terrorist phenomenon
Terrorism is a controversial concept, as it is subject to individual interpretation: while some condemn a group for the use of indiscriminate violence under a political/social/economic goal , others consider its members to be heroes of freedom. Only its purpose defines this activity: to coerce and intimidate the general intention on an issue. It takes different forms: by geographical scope (regional, national or international) or by its goal (ethno-nationalist, political and/or economic ideology, religious or specific issues). This is why each has different characteristics.
Religious terrorism, as Charles Townshend highlighted in his book Terrorism: A Very Short Introduction, has its own unique characteristics. Quoting Hoffman, he explains that goal transcends politics because it is seen as a theological demand. It is a bilateral relationship between fanatics and God, in which there is no possibility of dialogue or understanding, only the establishment of the demand. This conception leads to international terrorism, even if it starts at the regional or national level, as the group of "enemies" is broader. Messianism is the driving force behind this activity, and martyrdom its most potent weapon. The death that comes from fighting is presented as a sacred act and reflects the certainty of the members of these groups to their ideology.
The West finds it difficult to address these threats because it understands the world in a secular way. However, in the states in which these groups develop, religion represents nationhood, values and lifestyle: the individual is religion and vice versa. As Edward Said said: "The entrenched West is blind to nuance and change in the Islamic world". Indeed, Islamic religious terrorism emerges as a response to colonialism and the internship of soft power in Arab and Islamic cultures, which has been reinforced through the current of Islamic fundamentalism.
Terrorism in the Sahel
The Sahel ("edge, coast" in Arabic) is an ecoregion that transitions between the north and south of the African continent, as well as from west to east, with a total area of 3,053,200 km², constituting a belt of 5,000 km. It is made up of Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Algeria, Burkina-Faso, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, Sudan, Eritrea and Ethiopia. It is a privileged area, as the desert is understood as a pathway to speech.
The area has 150 million inhabitants, 64% of whom are under 25 years old and mostly Sunni Islamic. In 2018, the last year there is data on these countries, the annual mortality rate per 1,000 people was 8.05, a very high rate compared to Spain's 2.59 in 2019. The adult literacy rate (15+), for which there is only data for seven of the ten countries, is 56.06 %. In reality, it is very unequal: while Algeria has 81.40%, Niger or Mali have 35%. The poverty incidence rate based on the national poverty line is 41.15% (only four countries have data from 2018). Life expectancy is 63 years.
The territory faces an economic, political and social crisis. The Sahel is one of the poorest regions in the world, with northern Nigeria as one of the territories with the largest number of extremely poor people in the world. The status worsened this year with a historic drop in the price of raw materials (more than 20%), which account for 89% of its exports. The environmental crisis is hampering the economic development .
Climate change has caused temperatures to rise 1.5 times faster than the global average rate, which has multiplied droughts (from one every ten years to one every two). Political instability in some countries, such as the 2012 coup d'état in Mali, is hampering their economic development development .
In this context, insecurity has increased since the 2004 attacks in Borno, a Nigerian state bordering Cameroon and Chad, by the Islamic terrorist group Boko Haram group . Terrorist activity has spread through the leadership of Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM), present in northern Mali, eastern Mauritania, Niger and western Chad. This has led to a demographic crisis, with 4.2 million people displaced and more than a million unable to find homes work. The UN programme development estimates that between now and 2050, more than 85 million Sahelians will be forced to migrate.
Most attacks take place on the tri-border areas of Mali, Burkina-Faso and Niger; and Niger, Nigeria and Chad. Since the Treaty of Berlin in 1885, African borders have been a serious problem because they were a European imposition that did not respect the tribal and ethnic reality of many regions, forcing and creating a nation that its inhabitants do not feel part of. This reality was reflected in the case of Mali, showing the pre-existing fragility of the region.
AQIM has divided the Sahel into katibas (branches): the Yahia Abou Ammar Abid Hammadu, which is established between southern Algeria and Tunisia and northern Niger; and Tarik Ben Ziyad, active in Mauritania, southern Algeria and northern Mali. The former is known to be more "terrorist", while the latter is more "criminal". This is due to the greater Degree cruelty employee by the Hammadu, as they follow the takfirism (war against "infidel" Muslims) of Zarqawi (ISIS).
They take over territories through negotiations, where they establish a market for illegal trafficking. Once they have acquired a area, they set up their settlements, training camps and prepare their next attacks. Another means of financing is kidnapping. It is a way to subjugate, humiliate and extract revenue from the West. The need for money, unlike in a criminal organisation, is not for the enrichment staff of the components, but to continue financing the activity: buying loyalties, weapons, etc. There is no recruitment data development , no conditions, no age, class or gender targeting.
The geographical and socio-political characteristics of the ecoregion have forced AQIM to develop its capacity to adapt, such as the subdivision of group (Boko Haram), which sample no longer needs a fixed physical base as in the 1990s (AQ in Afghanistan). In addition, there has been a change in strategy, as these groups are increasing their attacks on international organisations or government infrastructure by 250%, and decreasing attacks on civilians. This may be a new way of attracting locals as they promote themselves as protectors against state abuse.
In 2019 there was an average of 69.5 attacks per month in the Sahel and Maghreb, and 438 deaths were recorded last March. In 2020, activity has decreased due to COVID-19. Terrorism brings political and social insecurity, as well as economic insecurity, as investors are not attracted to do business in an unstable area, leading to continued precariousness. This causes and/or maintains the underdevelopment of a state, leading to a large influx of migration. A vicious circle of underdevelopment and poverty then ensues.
For Spain, the most recent and shocking event took place on 28 April 2021, when journalists David Beriain and Roberto Fraile were murdered in Burkina-Faso by the Jama'a Nusrat ul-Islam wa al-Muslimin, group de Apoyo al Islam y a los Musulmanes en español; a terrorist group linked to Al-Qaeda.
The recent sudden death of Chadian President Idris Déby Itno on 19 April 2021 at the hands of the Fighters of the Front for Change and Concord in Chad (FACT) has further increased instability in the region. The president of the last three decades was fighting against this rebel group , created in 2016 in Libya, which sought to oust Déby and the dynastic regime from Chad. Since this event, massive protests have covered the streets of Chad, calling for a democratic transition in the country, to which the army has responded by killing some of the protesters. This uprising is due to what Chadians see as a repetition of their history and a violation of the nation's constitution. The Chadian army had announced the training of an 18-month transitional committee under the leadership of Mahamat Idriss Déby, the son of the former president. The problem is that his father, in 1999, created the same political body and promised the same. However, his promises were not kept. The transitional military committee suspended the constitution, which states at degree scroll Fifteenth that the transnational president must be the president of the National Assembly.
Chad's status is core topic in the fight against terrorism in the Sahel. The country lies between the Sahel and the Horn of Africa. The withdrawal or weakening of troops on the country's borders poses a great risk not only to Chad, but also to its neighbours. Countries bordering Chad will be exposed to violent attacks by terrorist groups, as Chad has the largest combined force in the G5 Sahel. Chad is the stabiliser of the region. To the east, it prevents Sudanese political instability from spilling over the borders. To the south, Chad has been the new home to more than 500,000 refugees from the Central African Republic and its massive migration crisis. To the west, it mainly counters Boko Haram, which is now a major player in Niger and Nigeria. To the north, it counters Libyan rebel groups. It is important to understand that although Libya is not part of the Sahel, its instability resonates strongly in the region, as the country is the new hub for terrorist groups in the Sahel, as the death of the former president seems to demonstrate. The country has become the launching pad for Africa's terrorist groups seeking to impose their will across the continent. What happens in Chad remains to be seen, as it will completely change the current Sahelian paradigm.
The West's fight against terrorism
There are institutional initiatives to address these regional issues jointly, such as the group G5 Sahel, composed of Mauritania, Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso and Chad, with the support of the African Union, the European Union, the United Nations and the World Bank, among others.
There is also financial aid international support to the region, mainly from France and the European Union. Since 2013, at the request of the Malian government, the French government launched Operation 'Serval' with the goal aim of expelling terrorist groups in northern Mali and other Sahel nations. It was followed a year later by Operation Barkhan, which focuses on attendance to the G5 Sahel member states, seeking to provide the resources and training necessary for these countries to manage their own security independently. Spain, Germany, Estonia and the UK also participate in this Operation. Last year, 2020, Task Force "Takuba", composed of French and Estonian special forces, was launched in the Sahara-Sahel belt. To date, France has deployed 5,100 military personnel, trained more than 7,000 G5 Sahel soldiers, deployed 750 training or combat support activities and has 75 cooperation officers in the region.
France has also been at the forefront of international intervention in the Sahel. In 2012, at the UN Security committee it promoted Resolution 2085 to underline the need for international attendance intervention in the region. In 2017, France was the precursor of the mission statement United Nations Multidimensional Integrated Stabilisation Mission in Mali (MINUSMA), created under Resolution 2391 to provide attendance to the Malian government in the stabilisation of its country. It has more than 15,000 civilian and military personnel providing logistical and operational support.
The EU has also been involved through three main missions in the Common Security and Defence Policy (CSDP) framework : mission statement of training of the European Union (EUTM) Mali, EUCAP Sahel Mali and EUCAP Sahel Niger. The first was created in 2013 to train and advise the Malian armed forces. It also cooperates with the G5 Sahel member states to improve border control. The other two are civilian missions whose goal is to train the police, gendarmerie and national guard, as well as to advise on security reforms at government. EUCAP Sahel Niger was created in 2012 and is still in force. As for EUCAP Sahel Mali, it was created in 2014 and has been extended until 2023. In addition, France and the European Union also contribute financially to the region. Last year, the EU contributed €189.4 million to the region. France contributed around €3.97 billion during 2019-2020.
However, the uncertainty over Déby's death has reshaped local perceptions of Western, mainly French, intervention. The protests that have taken place in Chad in recent weeks have also led to an indictment of France for backing the military committee against the will of the people. Together with the African Union and the European Union, Macron declared at Déby's funeral that "France will never be able to make anyone question (...) and threaten, today or tomorrow, the stability and integrity of Chad", following Mahamat's promises to "remain faithful to his father's report". These statements were understood by Chadians to mean that Mahamat will follow his father's style of leadership and that France does not care about the oppression the people have suffered for decades. It is at this point that France risks only caring about the stability that Chad brought to the region, especially in its geopolitical interests regarding Libya and West Africa in particular. Perhaps this is why Macron felt the need to clarify his words a week later: "I will be very clear: I supported the stability and integrity of Chad when I was in N'Djamena. I am in favour of a peaceful, democratic and inclusive transition, I am not in favour of a succession," he said. However, Sahelians are getting tired of being the puppets of Western games, as demonstrated this year in Mali by the protests of the inhabitants against the French military presence in the country. The West must show its real commitment to promoting human rights by pushing for a democratic transition while maintaining its fight against terrorism.
In conclusion, Islamist religious terrorism has been on the rise in recent years as a counterpoint to US power in the Cold War. The Sahel is one of the predominant theatres of these activities, as it is an area with pre-existing political-economic instability that terrorists have taken advantage of. Terrorism is changing its modus operandi, showing its adaptability in terms of geography, methods of operation and resource acquisition. France has shown itself to be the leader of the Western initiative in the region and has made progress in the region. However, the West, especially European countries, must begin to pay more attention to the causes of the region's problems by gathering data and understanding the realities of the region. Only then will they be able to address these problems effectively, assisting existing regional institutions, looking for long-term solutions deadline that satisfy the population.
![Gacaca trials, a powerful instrument of transitional justice implemented in Rwanda [UNDP/Elisa Finocchiaro].](/documents/16800098/0/Foto_Africa-Peacebuilding_larga.png/14888a0b-3a0c-2ee5-71dc-e75c22249faf?t=1621873383792&imagePreview=1)
ESSAY / María Rodríguez Reyero
One of the main questions that arise after a conflict comes to an end is what the reconstruction process should be focused on. Is it more important to forget the past and heal the wounds of a community or to ensure that the perpetrators of violence are fairly punished? Is the concept of peacebuilding in post-conflict societies compatible with justice and the punishment for crimes? Which one should prevail? And most importantly, which one ensures a better and more sustainable future for the already harshly punished inhabitants?
One of the main reasons in defence of the promotion of justice and accountability in post-conflict communities is its significance when it comes to retributive reasons: those who committed such atrocious crimes deserve to get the consequences. The accountability also discourages future degradations, and some mechanisms such as truth commissions and reparations to the victims allow them to have a voice, as potentially cathartic or healing. They may also argue that accountability processes are essential for longer-term peacemaking and peacebuilding. Another reason for pursuing justice and accountability is how the impunity of past crimes could affect the legitimacy of new governments, as impunity for certain key perpetrators will undermine people's belief in reconstruction and the possibilities for building a culture of respect for rule of law.[1]
On the other hand, peacebuilding, which attempts to address the underlying causes of a conflict and to help people to resolve their disputes rather than aiming for accountability, remains a quite controversial term, as it varies depending on its historical and geographical context. In general terms, peacebuilding encompasses activities designed to solidify peace and avoid a relapse into conflict[2]. According to Brahimi, those are undertaken to reassemble the foundations of peace and provide tools for building up those foundations, more than just focusing on the absence of war[3]. Some of the employed tools to achieve said aims typically include rule of law promotion and with the tools designed to promote security and stability: disarmament, demobilization, and reintegration of ex-combatants (DDR), and security sector reform (SSR) and others such as taking custody of and destroying weapons, repatriating refugees, offering advisory and training support for security personnel, monitoring elections, advancing efforts to protect human rights, reforming or strengthening government institutions and promotion of the formal and informal process of political participation.[4]
Those conflict resolution and peacebuilding activities can be disrupted by accountability processes. [5] The concern is that accountability initiatives might even block possible peace agreements and lengthen the dispute as they remove the foundations of the conflict, making flourish bad feelings and resentment amongst the society. The main reason behind this fear is that those likely to be targeted by accountability mechanisms may therefore resist peace deals. This explains why on many occasions and aiming for peace, amnesties have been given to secure peace agreements Likewise, there is a prevailing concern that transitional justice tools may reduce the impact in the short term the durability of a peace settlement as well as the effectiveness of further peace-building actions.
Despite the arguments in favour and against both mechanisms, the reality is that in practice post-conflict societies tend to strike a balance between peacebuilding and transitional justice. Both are multifaceted processes that do not rely on one system to accomplish their ends, that frequently converge. However, their activities on occasions collide and are not complimentary. This essay examines one of the dilemmas in building a just and durable peace: the challenging and complex relationship between transitional justice and peacebuilding in countries emerging from conflict.
To do so, this essay takes into consideration Rwanda, a clear example of the triumph of transitional justice, after a tragic genocide in 1994. From April to July 1994, between 800,000 and one million ethnic Tutsis were brutally killed during a 100-day killing spree perpetrated by Hutus[6]. After the genocide, Rwanda was on the edge of total collapse. Entire villages were destroyed, and social cohesion was in utter deterioration. In 2002, Rwanda boarded on the most arduous practice in transitional justice ever endeavoured: mass justice for mass atrocity, to judge and restart a stable society after the bloody genocide. To do so, Rwanda decided to put most of the nation on trial, instead of choosing, as other post-conflict states did (such as Mozambique, Uganda, East Timor, or Sierra Leone), amnesties, truth commissions, selective criminal prosecutions.[7]
On the other hand, Sierra Leone is a clear example of the success of peacebuilding activities, after a civil war that led to the deaths of over 50,000 people and a poverty-stricken country. The conflict faced the Revolutionary United Front (RUF[8]) against the official government, due to a context of bad governance and extensive injustice. It came to an end with the Abuja Protocols in 2001 and elections in 2002. The armed factions endeavoured to avoid any consequences by requesting an amnesty as well as reintegration assistance to ease possible societal ostracism. It was agreed only because the people of Sierra Leone so severely needed the violence to end. However, the UN representative to the peace negotiations stated that the amnesty did not apply to international crimes, President Kabbah asked for the UN's assistance[9] and it resulted in the birth of Sierra Leone's Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) and the Special Court for Sierra Leone (SCSL or Special Court).[10]
Disarmament, Demobilization and Reintegration (DDR) and transitional justice
Promoting short- and longer-term security and stability in conflict-prone and post-conflict countries in many cases requires the reduction and structural transformation of groups with the capacity to engage in the use of force, including armies, militias, and rebel groups. In such situations, two processes are of remarkable benefit in lessening the risk of violence: DDR (disarmament, demobilization, and reintegration) of ex-combatants; and SSR (security sector reform).
DDR entails a range of policies and programs, supporting the return of ex-combatants to civilian life, either in their former communities or in different ones. Even if not all ex-combatants are turned to civilian life, DDR programs may lead to the transfer and training, of former members of armed groups to new military and security forces. The essence of DDR programming and the guarantees it seeks to provide is of utmost importance to ensuring peacebuilding and the possibility of efficient and legitimate governance.
It is undeniable that soldiers are unquestionably opposing to responsibility processes enshrined in peace agreements: they are less likely to cede arms if they dread arrest, whether it is by an international or domestic court. This intensifies their general security fears after the disarming process. In many instances, ex-combatants are integrated into state security forces, which makes the promotion of the rule of law, difficult, as the groups charged with enforcing new laws may have the most to lose through the implicated reforms. It is also likely to lessen citizen reliance on the security forces. The incorporation of former fighters not only in the new military but also in new civilian security structures is common: for example, in Rwanda, the victorious RPF dominated the post-genocide security forces.
While the spectre of prosecutions most obviously may impede DDR processes, there is a lesser possibility that it might provide incentives for DDR, as might happens where amnesty or reduced sentences are offered as inducements for combatants to take part in DDR processes. For them to be effective, the reliability of both the threat of prosecution and the durability of amnesty or other forms of protection are essentials whether it is in national or international courts. Even if this is not related to the promotion of transitional justice processes, it is another example of how it can have a long-term effect on the respect of human rights and the prevention of future breaches.
As previously stated, some DDR and transitional justice processes may share alike ends and even employ similar mechanisms. A variety of traditional processes of accountability and conflict resolution often also seek to promote reconciliation. DDR programs increasingly include measures that try to encourage return, reintegration, and if possible, reconciliation within communities. This willingness of victims to forgive and forget could in theory be promoted through a range of reconciliation processes like the ones promoted by transitional justice with the assistance of tools like truth commissions, which facilitate a dialogue that allows inhabitants to move forward while accepting the arrival of former perpetrators.
The triumph of the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF) in 1994 finally put an end to the genocide in the country. The new government focused on criminal accountability for the 1994 genocide and as a result of this prioritization, the needs of survivors have not been met completely Rwanda is the paradigm and perfect example of prosecution of perpetrators of mass atrocity by the employment of transitional justice mechanisms, that were kept separated from DDR programs in order not to interfere with the attribution of responsibilities. [11] The Rwandan one is a case where DDR largely worked notwithstanding firmly opposing amnesty. Proof of this outstanding DDR success is how Rwanda has managed to successfully reintegrate around 54,000 combatants since 1995 thanks to the work of the Rwandan Demobilization and Reintegration Commission (RDRC). Another clear evidence of the effectiveness of DDR methods in Rwanda is the reintegration of child soldiers. Released child soldiers were installed in a special school (Kadogo School), which started with 2,922 children. By 1998 when it closed, the RDRC reported that 73% of its students had reunited with one or both parents successfully.[12]
On the other hand, Sierra Leone's case on DDR was quite different from Rwanda's success, as Sierra Leone's conflict involved the prevalence of children associated with armed forces and groups (CAAFG). By the time the civil war concluded in 2002, data from UNICEF estimates that roughly 6,845 children have been demobilized,[13] although the actual number could be way higher. Consequently, the DDR program in Sierra Leone is essentially focused on the reintegration of young soldiers, an initiative led by UNICEF with the backing of some local organisations, such as the National Committee on DDR (NCDDR)of Sierra Leone. Nonetheless, in practice, Sierra Leone's military did not endure these local guidelines, and as a result the participation of children in the process often had to be arranged by UNICEF peacekeepers in most cases. In addition to that initial local reluctance, some major quandaries aroused when it came to the reintegration of children in the new peace era in Sierra Leone, mainly due to the tests and requirements for children to have access to DDR programs, such as to present a weapon and demonstrate familiarity with it. [14] As a result, many CAAFG were excluded from the DDR process, primarily girls who were predominantly charged with non-directly military activities such as "to carry loads, do domestic work, and other support tasks."[15]In addition, many CAAFG were excluded from the DDR process.
Thus, the participation of girls in Sierra Leone's DDR was particularly low and many never even received support. While it is not clear how many girls were abducted during the war, data from UNICEF calculates that out of the 6,845 overall children demobilized, 92% were boys and only 8% were girls. The Women's Commission for Refugee Women and Children has pointed out that as many as 80 per cent of rebel soldiers were between the ages of 7 and 14, and escapes from the rebel camps reported that the majority of camp members were young captive girls. [16] Research also reported that 46% of the girls who were excluded from the program confirmed that not having a weapon was the reason for exclusion. In other cases, girls were not permitted by their husbands to go through the DDR,2 whilst others chose to opt-out themselves due to worry of stigmatization back in their neighbourhoods. [17] It is worth noting that many of those who succeeded to go through the demobilization phase "reported sexual harassment at the ICCs, either by male residents or visiting adult combatants", while others experienced verbal abuse, beatings, and exclusion in their communities.[18]
Another problem that underlines the importance of local leadership in DDR processes is that the UN-driven DDR program lets children decide to receive skill training rather than attending school if they were above 15 years. However, the program provided little assistance with finding jobs upon completion of the apprenticeship. Besides, little market examination was done to learn the demands of the local economy where children were trying to reintegrate into, so they are far more than the Sierra Leonean economy could absorb, which resulted in a lack of long-term employment for demobilized child soldiers. Studies by the Coalition to Stop the Use of Child Soldiers[19] and Human Rights Watch[20] revealed that adolescents who had previouslyhand been part of armed organisations during the war in Sierra Leone were re-recruited in Liberia or Congo because of the frustration and the lack of economic options for them back in Sierra Leone.
Promotion of the rule of law and its contributions to peacebuilding
Amongst many others, the promotion of the rule of law in post-conflict countries is a fundamental factor in peacebuilding procedures. It contributes to eradicating many of the causes of emerging conflicts, such as corruption, disruption of law... Even if it may seem contradictory, peacebuilding activities in support of the rule of law may become contradictory to transitional justice. Sometimes processes of transitional justice may displace resources, both capital, and human, that might otherwise be given to strengthening the rule of law. For instance, in Rwanda, it has been claimed that the resources invested in the development and assistance to national courts should have been equal to those committed to the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda (ICTR), and the extent to which trials at the ICTR have had an impact domestically remains to be seen.
However, transitional justice also presents other challenges to the reconstruction of the rule of law. Transitional justice processes might also destabilize critically imperfect justice sectors, making it more difficult to improve longer-term rule of law. They can stimulate responses from perpetrators which could destabilize the flimsy harmony of nascent governments, as they might question its legitimacy or actively attempt to undermine the authority of public institutions. Judging former perpetrators is an arduous task that is also faced with corruption and lack of staff and resources on many occasions. Additionally, the effort by national courts to prosecute criminals is an undue burden on the judicial system, which is severely damaged after a conflict and in many cases not ready to confront such atrocious crimes and the long processes they entail. Processes to try those accused of genocide in Rwanda, where the national judicial system was devastated after the genocide, have put great pressure on the judicial system, and the lack of capacity has resulted that many arrested remained in custody for years without having been convicted or even having had their cases heard, in the majority of the cases in appalling prison conditions. Such supposed accountability initiatives may have a counterproductive effect, contributing to a sense of impunity and distrust in justice processes.
Despite the outlined tensions, transitional justice and rule of law promotion are also capable to work towards the same ends. A key goal of transitional justice is to contribute to the rebuilding of a society based on the rule of law and respect for human rights, essential for durable peace. The improvement of a judiciary based on transparency and equality is strictly linked to the ability of a nation to approach prior human rights infringements after a conflict. [21] Both are potentially mutually reinforcing in practice if complementarities can be exploited. Consequently, rule of law advancement and transitional justice mechanisms however combine in some techniques.
To start with, the birth of processes to address past transgressions perpetrated during the conflict, both international and domestic processes, can help to restore confidence in the justice sector, especially when it comes to new arising democratic institutions. The use of domestic courts for accountability processes helps to place the judiciary at the centre of the promotion and protection of human rights of the local population, which contributes to the intensification of trust not only in the judicial system but also in public institutions and the government in general. Government initiation of an accountability process may indicate an engagement to justice and the rule of law beforehand. Domestically-rooted judicial processes, as well as other transitional justice tools, such as commissions of inquiry, may also support the development of mechanisms and rules for democratic and fair institutions by establishing regularized procedures and rules and promoting discussions rather than violence as a means of resolving differences and a reassuring population that their demands will be met in independent, fair and unbiased fora, be this a regular court or an ad hoc judicial or non-judicial mechanism. This is not to assume that internationally driven transitional justice mechanisms do not have a role to play in the development of the rule of law in the countries for which they have been established, as the hybrid tribunal of Sierra Leone demonstrates.[22]
In general terms, the refusal of impunity for perpetrators and the reformation of public institutions are considered the basic tools for the success of transitional justice. Transcending the strengthening of the judiciary, different reform processes can strengthen rule of law and accountability: institutions that counteract the influence of certain groups (including the government) like human rights commissions or anti-corruption commissions, may contribute to the establishment of a strong institutional and social structure more capable of confronting social tensions and hence evade the recurrence to conflict.[23]
Achieving an effective transitional justice strategy in Rwanda is an incredible challenge taking into consideration the massive scale as well as the harshness of the genocide, but also because of the economic and geographical limitations that make perpetrators and survivors live together in the aftermath. To facilitate things, other post-conflict states with similarly devastatingly high numbers of perpetrators have opted for amnesties or selective prosecutions, but the Rwandan government is engaged in holding those guilty for genocide responsible, thus strongly advocating for the employment of transitional justice. This is being accomplished through truth commissions, Gacaca traditional courts, national courts, and the international criminal tribunal for Rwanda combined. This underlines the dilemma of whether national or international courts are more efficient in implementing transitional justice.
Gacaca focuses on groups rather than individuals, seeks compromise and community harmony, and emphasizes restitution over forms of punishment. Moreover, it is characterized by accessibility, economy, and public participation. It encourages transparency of proceedings with the participation of the public as witnesses, who gain the truth about the circumstances surrounding the atrocities suffered during the genocide. Also, it provides an economic benefit, as Gacaca courts can try cases at a greater speed than international courts, thus reducing considerably the monetary cost as the number of incarcerated persons waiting for a trial is significantly reduced.
Alongside the strengths of the Gacaca system come flaws that seem to be inherent in the system. Many have come to see the Gacaca as an opportunity to require revenge on enemies or to frighten others with the threat of accusation, instead of injecting a sense of truth and reconciliation: the Gacaca trials have aroused concern and intimidation amongst many sectors of the population. Additionally, the community service prescribed to convicted perpetrators frequently is not done within the community where the crime was committed but rather done in the form of public service projects, which enforces the impression that officials may be using the system to benefit the government instead of helping the ones harmed by the genocide. Another proof of the control of Gacaca trials for benefit of the government is manifested by the prosecutions against critics of the post-genocide regime.
On the other hand, Sierra Leone's situation is very different from the one in Rwanda. To help restore the rule of law, the Special court settled in Sierra Leone must be seen as a role model for the administration of justice, and to promote deterrence it must be deemed credible, which is one of its main problems. [24] There is little confidence in the international tribunals amongst the local population, as the Court's nature makes it non-subordinated to the Sierra Leonean court system, and thus being an international tribunal independent from national control. [25] Nevertheless, it is considered as a "hybrid" tribunal since its jurisdiction extends over both domestic and international crimes and it relies on national authorities to enforce its orders. Still, in practice, there is no genuine cooperation between the government and the international community, as there is a limited extent of government participation in the Special Court's process and the lack of consultation with the Sierra Leonean population before the Court's endowment. This absence of national participation, despite causing scepticism over citizens, has the benefit that it remains more impartial when it comes to the proceedings against CDF leaders.
Another major particularity of the case of Sierra Leone and its process of implementation of transitional justice is once again the high degree of implication of children in the conflict, not only as victims but also as perpetrators of crimes. The responsibility of child soldiers for acts committed during armed conflict is a quite controversial issue. In general, under international law, the prosecution of children is not forbidden. However, there is no agreement on the minimum age at which children can be held criminally responsible for their acts. The Rome Statute, instituting the International Criminal Court (ICC), only provides the Court jurisdiction over people over eighteen years. Although not necessarily directly addressed to the prosecution of child soldiers, Article 40 of the Convention on the Rights of the Child foresees the trials of children (under eighteen), ordering that the process should consider their particular needs and vulnerabilities due to their shortage.
The TRC for Sierra Leone was the first one to focus on children's accountability, directly asserting jurisdiction over any person who committed a crime between the ages of fifteen and eighteen. Concerning child soldiers, the commission treated all children equally, as victims of war, but also studied the double role of children as both victims and perpetrators. It emphasized that it was not endeavouring to guilt but to comprehend how children came to carry out crimes, what motivated them, and how such offences might be prevented. Acknowledging that child soldiers are essentially victims of serious abuses of human rights and prioritizing the prosecution of those who illegally recruited them is of utmost importance. Meticulous attention was needed to guarantee that children's engagement did not put them at risk or expose them to further harm. Proper safeguard and child-friendly procedures were ensured, such as special hearings, closed sessions, a safe and comfortable environment for interviews, preserving the identity of child witnesses, and psychological care, amongst others.
However, shall children that have committed war crimes be prosecuted in the first place? If not, is there a risk that tyrants may assign further slaughter to be performed by child soldiers due to the absence of responsibility they might possess? The lack of prosecution could immortalize impunity and pose a risk of alike violations reoccurring eventually, as attested by the re-recruitment of some child soldiers from Sierra Leone in other armed conflicts in the area, such as in Liberia. Considering the special conditions of child soldiers, it becomes clear that the RUF adult leaders primarily are the ones with the highest responsibility, and hence must be prosecuted.[26]
It is known that both the Sierra Leonean government and the RUF were involved in the recruitment of child soldiers as young as ten years old, which is considered a violation of both domestic and international humanitarian law. Under domestic law, in Sierra Leone, the minimum age for voluntary recruitment is eighteen years. International humanitarian law, (Additional Protocol II) fifteen is established as the minimum age qualification for recruitment (both voluntary or compulsory) or participation in hostilities (includes direct participation in combat and active participation linked to combat such as spying, acting as couriers, and sabotage). Additionally, the African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the Child[27] to which Sierra Leone is a signatory, requires "state parties . . . to take all necessary measures to ensure that no child below age eighteen shall take direct part in hostilities" and "to refrain in particular from recruiting any child."
Nevertheless, victims who have been hurt by children also have the right to justice and reparations, and it also comes to ask whether exempting children of accountability for their crimes is in their best interest. When the child was in control of their actions (not coerced, drugged, or forced) acknowledgement might be an important part of staff healing that also adds to their acceptance back in their communities. The prosecution, however, should not be the first stage to hold child soldiers accountable, as TRC in Sierra Leone also performs alternatives, so the possibility of using those should first be inquired, as these alternatives put safeguards to ensure the best interest of the child and the main aim is restorative justice and not criminal prosecution.
Conclusions
Finally, after parsing where peacebuilding and justice clash and when do they have shared methods, we can assert that establishing an equitable and durable peace requires pursuing both peacebuilding and transitional justice activities, taking into consideration how they interact and the concrete needs of each community, especially when it comes to the needs of former child soldiers and the controversial discussion around the need for their accountability and reinsertion in communities, as despite the pioneer case of Sierra Leone, the unusual condition of a child combatant, which is both victim and perpetrator still presents dilemmas concerning their accountability in international criminal law.[28]
Additionally, it becomes of utmost importance in assessing post-conflict societies, whether it is to implement peacebuilding measures such as DDR or to apply justice and search for accountability, that international led initiatives include in their program's local organisations. Critics of international criminal justice often assume that criminal accountability for genocide, crimes against humanity, and war crimes are better handled at the national level. While this may well hold for liberal democracies, it is far more problematic for post-conflict successor regimes, where the benefits of the proximity to the affected population must be seriously weighed against the challenges facing courts placed in conflict-ridden societies with weak and corrupt judiciaries.
Local systems however have more legitimacy and capacity than devastated formal systems, and they promise local ownership, access, and efficiency, which seems to be the most appropriate way to ensure peace and endurability of peace. Additionally, restorative justice methods put into place thanks to local initiatives emphasize face-to-face intervention, where offenders have the chance to ask for forgiveness from the victims. In many cases restitution replaces incarceration, which facilitates the reintegration of offenders into society as well as the satisfaction of the victims.
To conclude, it has become clear that improving the interaction between peacebuilding and transitional justice processes requires coordination as well as a deep knowledge and understanding of said community. It is therefore not a question of deciding whether peacebuilding initiatives or transitional justice must be implemented, but rather to coordinate their efforts to achieve a sense of sustainable and most-needed peace in post-conflict countries. Taken together, and despite their contradictions, these processes are more likely to succeed in their seek to foster fair and enduring peace.
[1] Sooka, Y., 2006. Dealing with the past and transitional justice: building peace through accountability. [online] International Review of the network Cross. https://www.corteidh.or.cr/tablas/a21925.pdf [Accessed 5 April 2021].
2 Boutros-Ghali, B. (1992). An diary for Peace:Preventive Diplomacy, Peacemaking and peace-keeping.Report of the Secretary-General UN: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/145749 [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[Brahimi (n.d.). Report of the Panel on United Nations Peace Operations. 55th Session: Brahimi Report | United Nations Peacekeeping [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[4] United Nations Secretary General (1992). "An Agenda for Peace, Preventive diplomacy, peacemaking and peace-keeping UN Doc. A/47/277 - S/24111, 17 June.", title VI, paragraph 55.<A_47_277.pdf (un.org)>. [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[5] Sooka, Y., 2006. Dealing with the past and transitional justice: building peace through accountability. [online] International Review of the Red Cross. Available at: < https://www.corteidh.or.cr/tablas/a21925.pdf > [Accessed 5 March 2021].
[6] Roser, M. and Nagdy, M., 2021. Genocides. [online] Our World in Data. Available at: < Genocides - Our World in Data > [Accessed 5 March 2021].
[7] Waldorf, L., 2006. Mass Justice For Mass Atrocity: Rethinking Local Justice As Transitional Justice. [online] Temple Law Review. Available at: < https://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/temple79&div=7 > [Accessed 5 March 2021].
[8] Gibril Sesay, M. and Suma, M., 2009. Transitional Justice and DDR: The Case of Sierra Leone. [online] International Center for Transitional Justice. Available at: < https://www.ictj.org/sites/default/files/ICTJ-DDR-Sierra-Leone-CaseStudy-2009-English.pdf > [Accessed 5 March 2021].
[9] Roht-Arriaza, N., & Mariezcurrena, J. (Eds.). (2006). Transitional Justice in the Twenty-First Century: Beyond Truth versus Justice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Chapter 2, Sigal HOROVITZ: Transitional criminal justice in Sierra Leone. <(PDF) Transitional Criminal Justice in Sierra Leone | Sigall Horovitz - Academia.edu >[Accessed 5 March 2021]
[10] Connolly, L., 2012. Justice and peacebuilding in postconflict situations: An argument for including gender analysis in a new post-conflict model. [online] ACCORD. Available at: < https://www.accord.org.za/publication/justice-peacebuilding-post-conflict-situations/ > [Accessed 5 March 2021].
[11] Waldorf, L., 2009. Transitional Justice and DDR: The Case of Rwanda. [online] Intenational Center for Transitional Justice. Available at: < https://www.ictj.org/sites/default/files/ICTJ-DDR-Rwanda-CaseStudy-2009-English.pdf >[Accessed 5 April 2021].
[13] UNICEF (2004). From Confict to Hope:Children in Sierra Leone's Disarmament, Demobilisation and Reintegration Programme. [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[14] SESAY, M.G & SUMA, M. (2009), "Transitional Justice and DDR: The Case of Sierra Leone", International Centre for Transitional Justice (ICTJ) [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[15] WILLIAMSON, J. (2006), “The disarmament, demobilization and reintegration of child soldiers: social and psychological transformation in Sierra Leone”, Intervention 2006, Vol. 4, No. 3, Available from: < http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.600.1127&rep=rep1&type=pdf> [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[16]: A. B. Zack-Williams (2001) Child soldiers in the civil war in Sierra Leone, Review of African Political Economy, 28:87, 73-82, DOI: 10.1080/03056240108704504 [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[17] MCKAY, S. & MAZURANA, D. (2004), "Where are the girls? Girls in Fighting Forces in Northern Uganda, Sierra Leone and Mozambique: Their Lives During and After War",Rights & Democracy. International Centre for Human Rights & Democratic Development, [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[18] UNICEF (United Nations Children’s Fund) (2005), “The Impact of Conflict on Women and Girls in West and Central Africa and the Unicef Response”, Emergencies, pg.19,Available from: < https://www.unicef.org/emerg/files/Impact_conflict_women.pdf> [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[19] Coalition to Stop the Use of Child Soldiers (2006), "Child Soldiers and Disarmament, Demobilization, Rehabilitation and Reintegration in West Africa". [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[20] HRW (Human Rights Watch) (2005), “Problems in the Disarmament Programs in Sierra Leone and Liberia [1998-2005]”, Reports Section, Available from: <https://www.hrw.org/reports/2005/westafrica0405/7.htm> [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[21] Herman, J., Martin-Ortega, O. and Sriram, C., 2012. Beyond justice versus peace: transitional justice and peacebuilding strategies. 1st ed. Routledge. <Beyond justice versus peace: transitional justice and peacebuilding strategies | Taylor & Francis Group> [Accessed 5 March 2021]
[22] Young, G., n.d. Transitional Justice in Sierra Leone: A Critical Analysis. [online] PEACE AND PROGRESS – THE UNITED NATIONS UNIVERSITY GRADUATE STUDENT JOURNAL. Available at: < https://postgraduate.ias.unu.edu/upp/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/upp_issue1-YOUNG.pdf > [Accessed 5 March 2021].
[23] Herman, J., Martin-Ortega, O. and Sriram, C., 2012. Beyond justice versus peace: transitional justice and peacebuilding strategies. 1st ed. Routledge. <Beyond justice versus peace: transitional justice and peacebuilding strategies | Taylor & Francis Group> [Accessed 5 March 2021]
[24] Stensrud, E., 2009. New Dilemmas in Transitional Justice: Lessons from the Mixed Courts in Sierra Leone and Cambodia. [online] Journal of peace research. Available at: <New Dilemmas in Transitional Justice: Lessons from the Mixed Courts in Sierra Leone and Cambodia on JSTOR> [Accessed 5 March 2021].
[25] Roht-Arriaza, N., & Mariezcurrena, J. (Eds.). (2006). Transitional Justice in the Twenty-First Century: Beyond Truth versus Justice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Chapter 2, Sigal HOROVITZ: Transitional criminal justice in Sierra Leone. <(PDF) Transitional Criminal Justice in Sierra Leone | Sigall Horovitz - Academia.edu >[Accessed 5 March 2021]
[26] Zarifis, Ismene. "Sierra Leone's Search for Justice and Accountability of Child Soldiers." Human Rights Brief 9, no. 3 (2002): 18-21. [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[27] Article 22 of the AFRICAN CHARTER ON THE RIGHTS AND WELFARE OF THE CHILD , achpr_instr_charterchild_eng.pdf (un.org). [Accessed 5 April 2021].
[28] Veiga, T. G. (2019). A New Conceptualisation of Child Reintegration in Conflict Contexts. E International Relations: https://www.e-ir.info/2019/06/21/a-new-conceptualisation-of-child-reintegration-in-conflict-contexts/.[Accessed 5 April 2021].
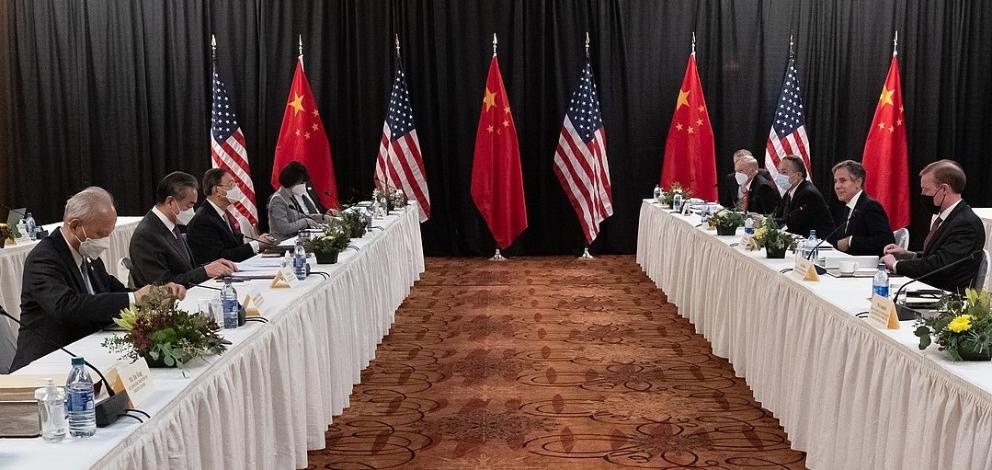

First high-level US-China meeting of the Biden era, to be held in Alaska on 18 March 2021 [State Department].
essay / Ramón Barba
President Joe Biden is cautiously building his Indo-Pacific policy, seeking to build an alliance with India on which to build an order to counter the rise of China. Following his entrance in the White House, Biden has kept the focus on this region, albeit with a different approach than the Trump Administration. While it is true that the main goal is still about containing China and defending free trade, Washington is opting for a multilateral approach that gives greater prominence to QUAD[1] and takes special care over relations with India. As a standard-bearer for the free world and democracy, the Biden Administration seeks to renew US leadership in the world and particularly in this critical region. However, although the relationship with India is at a good moment, especially given the signature of agreement scholarship[2] reached at the end of the Trump Administration, the interaction between the two countries is far from consolidating an alliance.
The new US presidency is faced with a very complicated puzzle to solve in the Indo-Pacific, with China and India as the main players. Generally speaking, of the three powers, only Beijing has successfully managed the post-pandemic status [3], while Delhi and Washington continue to face both a health and economic crisis. All of this may affect the India-US relationship, especially on trade[4], but although Biden has yet to demonstrate his strategy in the region, the relationship between the two powers looks set to go from strength to strength[5]. However, although the US wants to pursue a policy of multilateral alliances and deepen its relationship with India, the Biden administration will have to take into account a number of difficulties before it can talk about an alliance as such.
Biden began to move in this direction from the outset. First up was February's meeting of QUAD[6], which some see as a mini-NATO[7] for Asia, where issues of vaccine distribution in Asia (aiming to distribute one trillion doses by 2022), freedom of navigation in the region's seas, North Korea's denuclearisation and democracy in Myanmar were discussed. In addition, the UK seems to be taking a greater interest in the region and in this dialogue group . On the other hand, in mid-March there was a meeting in Alaska[8] between Chinese and US diplomats (led respectively by Yang Jiechi, director of the Central Foreign Affairs Commission, and Antony Blinken, Secretary of State), in which both countries harshly reproached each other's policies. Washington remains firm in its interests, although open to a certain partnership with Beijing, while China insists on rejecting any interference in what it considers to be its internal affairs. Finally, it is worth mentioning that Biden seems to be willing to organise a summit of democracies[9] in his first year in office.
Following contacts also in Alaska between the Chinese and US defence chiefs, Pentagon chief Austin Lloyd[10] visited India to stress the importance of Indo-US cooperation. In addition, early April saw France's participation in the La Pérouse[11] naval exercises in the Bay of Bengal, raising the possibility of a QUAD-plus involving not only the four original powers but also other countries.
The Indo-Pacific, remember, is the present and the future of the International Office due to its economic importance (its main actors, India, China and the USA, represent 45% of the world's GDP), demographic importance (it is home to 65% of the world's population) and, as we will see throughout this article, geopolitical importance[12].
US-China-India relations
The Biden administration seems to be continuing along the same lines as the Trump administration, as the objectives have not changed. What has changed is the approach to the subject matter, which in this case is none other than the containment of China and freedom of navigation in the region, albeit on the basis of a strong commitment to multilateralism. As George Washington's new successor said at his inauguration[13], the United States wants to resume its leadership, but in a different way from the previous Administration; that is, through a strong policy of alliances, moral leadership and a strong defence of values such as dignity, human rights and the rule of law.
The new presidency sees China as a rival to be reckoned with[14], as does the Trump Administration, but it does not see this as a zero-sum game, since, although it openly declares itself to be against Xi's actions, it opens the door to dialogue[15] on issues such as climate change or healthcare. Generally speaking, in line with what has been seen in New tensions in the Asia-Pacific[16], the United States is committed to a multilateralism that seeks to reduce tension. It should be remembered that the United States advocates the defence of free navigation and the rule of law, as well as democracy in a region in which its influence is being eroded by the growing weight of China.
A good understanding of the state of US-China-India relations goes back to 2005[17], when everything seemed to be going well. As far as the Sino-Indian relationship was concerned, the two nations had resolved their disputes over the 1998 nuclear tests, their presence in regional fora was growing, and it seemed that the issue of cross-border disputes was beginning to be settled. For its part, the United States enjoyed good trade relations with both countries. However, shifting patterns in the global Economics , driven by the rise of China, the 2008 financial crisis in the US, and India's inability to maintain its growth rate upset this balance. Donald Trump's tightening stance contributed to this. However, some argue that the breakdown of the post-Cold War order in the Asia-Pacific began with the Obama administration's 'pivot to Asia'[18]. To this must be added the minor frictions China has had with both nations.
Briefly, it is worth mentioning that there are border problems between India and China[19] that have been flaring up again since 2013. India, in turn, is opposed to Chinese hegemony; it does not want to be subjugated by Beijing and is clearly committed to multilateralism. Finally, there are problems regarding maritime dominance because the Strait of Malacca is at capacity. Moreover, Delhi claims the Adaman and Nicobar Islands, on the Malacca access route, as its own. Moreover, as India is now well below China's military and economic power[20] - the balance that existed between the two powers in 1980 is broken - it is trying to hinder Beijing in order to contain it.
The United States has ideological subject friction with China, due to the authoritarian nature of Xi Jinping's regime[21], and commercial friction, in a dispute[22] that Beijing is trying to take advantage of to reduce US influence in the region. In the middle of this conflict is India, which supports the United States because, although it does not seem to want to be completely against China[23], it rejects a Chinese regional hegemony[24].
According to the CEBR's latest report [25], China will overtake the United States as a global power in 2028, earlier than previous projections, in part because of its handling of the coronavirus emergency: it was the only major country to avoid a crisis after the first wave. On the other hand, the US has lost the battle against the pandemic; economic growth between 2022-2024 is expected to be 1.9% of GDP and to slow to 1.6% in the following years[26], while China, according to report , is expected to grow at 5.7% between 2021-2025[27].
For China the pandemic has been a way of signalling its place in the world[28], a way of warning the United States that it is ready to take over as leader of the international community. This has been compounded by China's belligerent attitude in the Asia-Pacific region, as well as its hegemonic growth in the region and trade projects with Africa and Europe. All of this has led to imbalances in the region that implicate Washington's QUAD moves. Recall that, despite its declining role as a power, the US is interested in freedom of navigation for both commercial and military reasons[29].
China's economic rise has thus led to a worsening of the relationship between Washington and Beijing[30]. Moreover, while Biden is committed to cooperation on the pandemic and climate change, there is talk in some quarters of American politics of inevitable competition between the two countries[31].
The Degree of the US-India alliance
In line with the above, we can see that we are in a delicate situation after the change in the White House. January and February have been months of small moves by the US and India, which have not left China indifferent. Although the Sino-US relationship has benefited both sides since its inception (1979)[32], with trade between the two countries growing by 252% since then, the reality is that trust levels are now at rock bottom, with more than 100 dialogue mechanisms suspended between them. Therefore, although conflict is not foreseeable, tension is predicted to rise as, far from being able to cooperate in broad areas, only light and limited cooperation seems feasible at the moment. At the same time, it should be remembered that China is very much affected by the Malacca Dilemma[33], which is why it is seeking other access to the Indian Ocean, giving rise to territorial disputes with India, with whom it already has the territorial problem of Ladakh[34]. In the midst of this Thucydides Trap[35], in which China seems to threaten to overtake the United States, Washington has been moving closer to New Delhi.
Consequently, both countries have been developing a strategic partnership [36], based essentially on security and defence, but which the United States seeks to extend to other areas. It is true that Delhi's problems are in the Indian Ocean and Washington's in the Pacific; however, both have China[37] as a common denominator. Their relationship, moreover, is strongly marked by the aforementioned "tripartite crisis"[38 ] (health, economic and geopolitical).
Despite the intense cooperation between Washington and New Delhi, there are two different views on thispartnership. While the US claims that India is a very important ally, sharing the same political system and an intense trade relationship[39], India prefers a less strict alliance. Traditionally, Delhi has conveyed a policy of non-alignment[40] in international affairs. Indeed, while India does not want Chinese supremacy in the Indo-Pacific, neither does it want to align itself directly against Beijing, with whom it shares more than 3,000 km of border. Nonetheless, Delhi sees a great need for cooperation with Washington on subject security and defence. Indeed, some argue that India needs the US more than ever.
Although Washington began to review the US Global Posture Strategy last February, everything suggests that the Biden Administration will continue Trump's line on partnership with India as a way of containing China. However, while Washington speaks of India as its ally, Delhi is somewhat reticent, speaking of an alignment[41] rather than an alliance. Although the reality we live in is far from that of the Cold War[42], this new containment[43] in which Delhi is sought as a base, support and banner, is materialised in the following:
(i) Intensive cooperation on subject Security and Defence
There are different forums and agreements here. First, the aforementioned QUAD[44]. This new multilateral cooperation alliance that began to take shape in 2006[45] agreed at its March meeting on the development of its vaccine diplomacy, with India at the centre, in order to counteract Beijing's successful international campaign in this field. In fact, there was a commitment to spend 600 million to deliver 1 billion vaccines[46] by 2022. The idea is that Japan and the US will finance the operation[47], while Australia will provide the logistics. India, however, is committed to greater multilateralism in the Indo-Pacific, giving entrance to countries such as the UK and France[48], which already participated in the last Raisina Dialogues together with QUAD. Other issues such as the denuclearisation of Korea, the restoration of democracy in Myanmar and climate change were also discussed at meeting [49].
India seeks to contain China, but without provoking a direct confrontation with China[50]. In fact, Beijing has intimated that if things go further, it is not only India that knows how to play Realpolitik. Let us recall that New Delhi will chair this year's meeting with the BRICS. Moreover, the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation will host joint military exercises between China and Pakistan, a country with a complex relationship with India.
On the other hand, during his March trip to India, the Pentagon chief[51] discussed with his counterpart Rajnath Singh increased military cooperation, as well as issues related to logistics, exchange information, possible opportunities for mutual attendance and the defence of free navigation. Lloyd said he did not object to Australia and Korea participating as permanent members in the Malabar exercises. Since 2008, military subject trade between Delhi and Washington has totalled $21 billion[52]. In addition, $3,000 has recently been spent on drones and other aerial equipment for reconnaissance and surveillance missions.
A week later this meeting, two Indian and one US ship conducted a maritime exercise of subject PASSEX[53] as a way of consolidating the synergies and interoperability achieved in last November's Malabar exercise.
accredited specialization subject In this context, a special mention should be made of the 2+2 dialogue platform and the aforementioned scholarship (agreement ) ( exchange and Basic and Cooperation for Geospatial Cooperation). The first is a subject of meeting in which the foreign and defence ministers of both countries meet every two years to discuss issues of interest to them. The most recent meeting took place in October 2020[54]. Not only was the scholarship agreed, but the US reaffirmed its support for India on its territorial issues with China. Other memoranda of understanding were also signed on nuclear energy and climate issues.
The scholarship, signed in October 2020 during the final months of the Trump administration, makes it easier for India to better track enemies, terrorists and other subject threats from land or sea. This agreement is intended to consolidate the friendship between the two countries, as well as help India outpace China technologically. This agreement concludes the "troika of foundational pacts" for deep security and defence cooperation between the two countries[55].
Prior to this agreement, the LEMOA (Memorandum of agreement for exchange Logistics) was signed in 2016, and in 2018 the COMCASA (agreement Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement) was signed. The former allows both countries access to each other's instructions for supply and replenishment; the latter allows India to receive systems, information and encrypted communication to communicate with the United States. Both agreements affect land, sea and air forces[56].
(ii) United for Democracy
Washington emphasises that the two powers are very similar, since they share the same political system, and it is emphasised with a certain grandiloquence that they are the oldest and the largest democracy (per issue inhabitants)[57]. Because this presupposes a shared set of values, Washington likes to speak of "likeminded partners"[58].
Tanvi Mandan of the Brookings Institution think tank Tanvi Mandan defends this idea of ideological bonding. The same system of government means that the two countries see each other as natural allies, who think alike and also believe in the value of the rule of law. In fact, in all matters relating to the spread of democracy around the globe, there is strong cooperation between the two nations: for example, supporting democracy in Afghanistan or the Maldives, launching the US-India Global Democracy Initiative, and providing legal and technical assistance on democratic issues to other countries at attendance . Finally, it is worth noting that democracy and its associated values have facilitated the exchange and flow of people from one country to another. As for the economic relationship between the two countries, it has become more viable, given that they are both open economies, share a common language and their legal system has Anglo-Saxon roots.
iii) Growing economic cooperation
partner The United States is India's main trading partner, with which it has a significant surplus[59]. Trade between the two has grown by 10% annually over the last decade, and in 2019 was $115 billion[60]. Around 2,000 US companies are based in India, and some 200 Indian companies are based in the US[61]. There is a Mini-Trade Deal between the two, believed to be signed soon, which aims to deepen this economic relationship. In the context of the pandemic, everything related to the health sector plays an important role[62]. 62] In fact, despite the fact that both countries have recently adopted a protectionist attitude, the idea is to achieve $500 billion in trade.
Divergences, challenges and opportunities for India and the US in the region
Briefly, between the leaders of the two countries there are minor frictions, opportunities and challenges to be nuanced in order to make this relationship a strong alliance. Among the sticking points is India's purchase of S-400 missiles from Russia, which is against CAATSA(Countering America's Adversaries trhough Sanctions Act) [64], for which India may receive a sanction, although in the meeting between Sigh and Lloyd, Lloyd seemed to overlook topic [65]. However, it remains to be seen what happens once the missiles arrive in Delhi. There are also minor divergences on freedom of expression, security and civil rights, and how to engage with non-democratic countries[66]. Among the challenges that both countries must take into account is the possible loss of support in some quarters of US policy for the relationship with India. This is due to India's actions in Kashmir in August 2019, the protection of religious freedom and attention to dissent. On the other hand, there has been no shortage of weakening of democratic norms, immigration restrictions and violence against Indians[67].
Lastly, let us remember that both are facing a profound health and therefore economic crisis, the resolution of which will be decisive in relation to competition with Beijing[68]. The crisis has affected the bilateral relationship since, although trade in services has remained stable (around 50 billion), trade in goods declined from 92 to 78 billion between 2019 and 2020, increasing India's trade deficit[69].
Finally, it is worth mentioning the opportunities. First, both countries can develop democratic resilience in the Indo-Pacific as well as in a rules-based international order[70]. In security and defence, there are also opportunities such as the UK and France's entrance as allies in the region, for example by seeking both countries' entry into the Malabar exercise or France's chairmanship of the Indian Ocean Naval Symposiumin 2022[71]. Although the medium-term trend deadline is for cooperation between the US and India, skill with Russia will be a growing threat[72], so cooperation between the US, India and Europe is very important.
It also opens up the possibility of cooperation in MDA (Maritime Warning Environment) and ASW (Anti-Submarine Warfare) mechanisms, as the Indian Ocean is of general importance to several countries due to the value of its energy transport routes. The possibility of cooperation through the use of the US P-8 "Poseidon" aircraft is opened up. Despite disputes over the Chagos archipelago, India and the US should take advantage of the agreements they have over islands such as the Andaman and Diego Garcia to carry out these activities[73]. Therefore, India should use the regional bodies and groups of work to cooperate with European countries and the US[74].
Europe seems to be gaining increasing importance because of the possibility of entering the Indo-Pacific game through QUAD Plus. European countries are very much in favour of multilateralism, defending freedom of navigation and the role of rules in regulating it. While it is true that the EU has recently signed a trade agreement with China - the IAC - increasing the European presence in the region takes on greater importance, as Xi's authoritarianism and his actions in Tibet, Xinjiang, or central China are not to the liking of European countries[75].
Lastly, it is worth remembering that there are some voices that speak of a decline or weakening of globalisation[76], especially after the coronavirus epidemic[77], so reviving multilateral exchanges through joint action becomes a challenge and an opportunity for both countries. In fact, it is believed that protectionist tendencies, at least in the Sino-Indian relationship, will continue in the short term deadline , despite intense economic cooperation[78].
Conclusion
The geopolitical landscape in the Indo-Pacific is complex to say the least. Chinese expansionism clashes with the interests of the other major regional power, India, which, while avoiding confrontation with Beijing, takes a dim view of its neighbour's actions. In a bid for multilateralism, and with its sights set on its regional waters, threatened by the Malacca Dilemma, India seems to be cooperating with the United States, but sticking to regional forums and groups to make its position clear, while seeming to open the door to European countries, whose interest in the region is growing, despite the recent trade agreement signed with China.
On the other hand, the United States is also threatened by Chinese expansionism and sees the moment of its rival's economic overtaking approaching, which the coronavirus crisis may even have brought forward to 2028. In order to avoid this status, the Biden Administration has opted for multilateralism at the regional level and is deepening its relationship with India, beyond the military aspect. Washington seems to have understood that US hegemony in the Indo-Pacific is far from being real, at least in the medium term deadline, so that only a cooperative and integrating attitude can be adopted. On the other hand, in the midst of this supposed retreat from globalisation, we see how Washington, together with India, and probably halfway through deadline with Europe, are defending the Western values that govern the international sphere, i.e. the defence of human rights, the rule of law and the value of democracy.
There are two factors at play here. On the one hand, India does not want to see an order imposed by any subject, either American or Chinese, hence its reluctance to confront Beijing directly and its preference to expand the QUAD. On the other hand, the United States seems to perceive that it is at a delicate moment, as its competition with China goes beyond the mere substitution of one power for another. Washington is still a traditional power that, for its presence in the Indo-Pacific, has relied primarily on military power, while China has based the extension of its influence on the establishment of strong trade relations that go beyond the belligerent logic of the Cold War. Hence, the United States is seeking to form a front with India and its European allies that goes beyond military cooperation.
REFERENCES
[1] The QUAD (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue) is a dialogue group formed by the United States, India, Japan and Australia. Its members share a common vision of Indo-Pacific security that runs counter to China's; they advocate multilateralism and freedom of navigation in the region.
[2] scholarship (Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement). Treaty signed by India and the United States in October 2019 to improve security in the Indo-Pacific region. Its goal is the exchange of tracking, tracing and intelligence systems.
[3]Chilamkuri Raja Mohan, "Trilateral Perspective". Chinawatch. Connecting Thinkers... http://www. chinawatch.cn/a/202102/05/WS60349146a310acc46eb43e2d.html,(accessed 5 February 2021),
[4] Tanvi Madan, "India and the Biden Administration: Consolidating and Rebalancing Ties," in Tanvi Madan, "India And The Biden Administration: Consolidating And Rebalancing Ties",. German Marshal Found of the United States. https://www.gmfus.org/blog/2021/02/11/india-and-biden-administration-consolidating-and-rebalancing-ties,(accessed 11 February 2021).
[5]DarshanaBaruah, Frédéric Grére, and Nilanthi Samaranayake, "diary 2021: A Blueprint For U.S.-Europe-India Cooperation", US-India cooperation on Indo-Pacific Security. GMF India Trilateral Forum. Pg:1. https://www.gmfus.org/blog/2021/02/16/us-india-cooperation-indo-pacific-security, (accessed 16 February 2021).
[6] "'QUAD' Leaders Pledge New Cooperation on China, COVID-19, Climate". Aljazeera.com. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2021/3/12/quad-leaders-pledge-new-cooperation-on-china-covid-19-climate (accessed March 2021).
[7] Mereyem Hafidi, "Biden Renews 'QUAD' Alliance Despite Pressure From Beijing". Atalayar. https://atalayar.com/content/biden-renueva-la-alianza-de-%E2%80%98QUAD%E2%80%99-pesar-de-las-presiones-de-pek%C3%ADn.(accessed February 2021).
[8] "`Grandstanding`: US, China trade rebukes in testy talks". Aljazeera. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2021/3/19/us-china-top-diplomats-trade-rebukes-in-testy-first-talks (accessed March 2021).
[9] Joseph R. Biden, "Why America Must Lead Again". Foreign Affairs. https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/united-states/2020-01-23/why-america-must-lead-again (accessed February, 2021).
[10] Maria Siow. "India Receives US Defence Secretary With China On Its Mind". South China Morning Post. https://www.scmp.com/week-asia/politics/article/3126091/india-receives-us-defence-secretary-lloyd-austin-china-its-mind.(accessed 19 March 2021).
[11] Seeram Chaulia, "France and sailing toward the 'QUAD-plus'". The New Indian Express. https://www. newindianexpress.com/opinions/2021/apr/06/france-and-sailing-toward-the-QUAD-plus-2286408.html (accessed April 4, 2021).
[12] Juan Luis López Aranguren. "Indo-Pacific: The new order without China at the centre. The Indo-Pacific as a new global geopolitical axis. Global Affairs Journal. P.:2. https://www.unav.edu/web/global-affairs/detalle/-/blogs/indo-pacifico-el-nuevo-orden-sin-china-en-el-centro?_33_redirect=%2Fen%2Fweb%2Fglobal-affairs%2Fpublicaciones%2Finformes.(accessed April 2021).
[13] Biden, "Remarks By President Biden On America's Place In The World | The White House...".
https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/speeches-remarks/2021/02/04/remarks-by-president-biden-on-americas-place-in-the-world/
[14] Ibid.
[15] Derek Grossman, 'Biden's China Reset Is Already On The Ropes'. Nikkei Asia. https://asia.nikkei.com/Opinion/Biden-s-China-reset-is-already-on-the-ropes.(accessed 14 March 2021).
[16] Ramón Barba Castro, 'New tensions in the Asia-Pacific in a scenario of electoral change'. Global Affairs and Strategic Studies. https://www.unav.edu/web/global-affairs/detalle/-/blogs/nuevas-tensiones-en-asia-pacifico-en-un-escenario-de-cambio-electoral-en-eeuu.(accessed, April 2021).
[17] Sankaran Kalyanaraman, "Changing Pattern Of The China-India-US Triangle". Manohar Parrikar Institute For Defence Studies And Analyses. https://www.idsa.in/idsacomments/changing-pattern-china-india-us-triangle-skalyanaram (accessed March 2021).
[18] Pang Zhongying, 'Indo-Pacific Era Needs US-China Cooperation, Not Great Power Conflict'. South China Morning Post. https://www.scmp.com/comment/opinion/article/3125926/indo-pacific-needs-us-china-cooperation-not-conflict-QUAD (accessed 19 March 2021).
[19] Sankaran Kalayanamaran, "Changing Pattern of the China-India-US Triangle".
[20] Chilamkuri Raja Mohan, "Trilateral Perspective".
[21] Joseph R. Biden, "Remarks By President Biden On America's Place In The World
[22]Chilamkuri Raja Mohan, "Trilateral Perspective".
[23] Maria Siow, "India Receives US Defence Secretary With China On Its Mind".
[24]Tanvi Madan, "India and the Biden Administration: Consolidating And Rebalancing Ties".
[25] CEBR (Centre for Economics and Business Research) is an organisation dedicated to the economic analysis and forecasting of companies and organisations. linkhttps://cebr.com/about-cebr/. Every year, this organisation produces an annual report graduate World Economic League Table¸which analyses the position of each country in the world in terms of the state of its Economics. The latest edition(World Economic League Table 2021), published on 26 December 2020, presents a prediction of the state of the world's Economics in 2035, in order to know who will be the world's leading economic powers. (CEBR, "World Economic League Table 2021". Centre for Economics and Business Research (12th edition), https://cebr.com/reports/world-economic-league-table-2021/ (accessed March 2021).
[26] Ibid., 231.
[27] Ibid., 71.
[28] Vijay Gokhale, "China Doesn't Want a New World Order. It Wants This One". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/04/opinion/china-america-united-nations.html(accessed April 2021).
[29] Mereyem Hafidi, "Biden renews 'QUAD' alliance despite pressure from Beijing.
[30] Chilamkuri Raja Mohan, "Trilateral Perspective".
[31] Ibid.
[32] Wang Huiyao, "More cooperation, less competition". Chinawatch. Connecting Thinkers. http://www.chinawatch.cn/a/202102/05/WS6034913ba310acc46eb43e28.html(accessed March 2021).
[33] Chilamkuri Raja Mohan, "Trilateral Perspective".
[34] DarshanaBaruah, Frédéric Grére, and Nilanthi Samaranayake, "US-India cooperation on Indo-Pacific Security". Page 5.
[35] Chilamkuri Raja Mohan, "Trilateral Perspective".
[36] Ibid.
[37] DarshanaBaruah, Frédéric Grére, and Nilanthi Samaranayake, "US-India cooperation on Indo-Pacific Security". Page 5.
[38] Tanvi Madan, "India and the Biden Administration: Consolidating And Rebalancing Ties".
[39] Tanvi Madan, "Democracy and the US-India relationship". Brookings. https://www.brookings.edu/articles/democracy-and-the-us-india-relationship/ (accessed March 2021)
[40] Maria Siow, "India Receives US Defence Secretary With China On Its Mind".
[41] Bilal Kuchay, "India, US sign key military deal, symbolizing closer ties". Aljazeera. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/11/2/india-us-military-deal(accessed March 2021)
[42] Wang Huiyao, "More cooperation, less competition".
[43] Alex Lo, "India-the democratic economic giant that disappoints". South China Morning Post. https://www.scmp.com/comment/opinion/article/3126342/india-democratic-economic-giant-disappoints(accessed 21 March 2021).
[44] Simone McCarthy, "QUAD summit: US, India, Australia and Japan counter China's 'vaccine diplomacy' with pledge to distribute a billion doses across Indo-Pacific". South China Morning Post. https://www.scmp.com/news/china/diplomacy/article/3125344/QUAD-summit-us-india-australia-and-japan-counter-chinas.(accessed 13 March 2021).
[45] MereyemHafidi, "Biden renews 'QUAD' alliance despite pressure from Beijing.
[46] Simone McCarthy, "QUAD summit: US, India, Australia and Japan counter China's 'vaccine diplomacy' with pledge to distribute a billion doses across Indo-Pacific".
[47] Aljazeera, "'QUAD' leaders pledge new cooperation on China, COVID-19, climate".
[48]DarshanaBaruah, Frédéric Grére, and Nilanthi Samaranayake, "US-India cooperation on Indo-Pacific Security". Page 2.
[49]Simone McCarthy, "QUAD summit: US, India, Australia and Japan counter China's 'vaccine diplomacy' with pledge to distribute a billion doses across Indo-Pacific".
[50] Maria Siow, "India Receives US Defence Secretary With China On Its Mind".
[51] "US defense secretary Lloyd Austin says US considers India to be a great partner". Hindustan Times. https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/us-defense-secretary-lloyd-austin-says-us-considers-india-to-be-a-great-partner-101616317189411.html.(accessed 21 March 2021).
[52] Maria Siow, "India Receives US Defence Secretary With China On Its Mind".
[53] The term PASSEX is an abbreviation of the English military jargon, which stands for Passing Exercise. It consists of taking advantage of the fact that a Marine unit is passing through a given area to deepen military cooperation with the army of the area through which it is passing. An example of this is the news item cited in this article article: "India, US begin two-day naval exercise in eastern Indian Ocean region". The Economic Times. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/defence/india-us-begin-two-day-naval-exercise-in-eastern-indian-ocean-region/articleshow/81735782.cms (accessed 28 March 2021).
[54] Annath Krishnan, Dinakar Peri, Kallol Bhattacherjee; India-U.S. 2+2 dialogue: U.S. to support India's defence of territory. The Hindu. https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-us-22-dialogue-rajnath-singh-raises-chinas-action-in-ladakh/article32955117.ece.(accessed, March 2021)
[55] Maria Siow, "India Receives US Defence Secretary With China On Its Mind".
[56] Ibid.
[57] Tanvi Madan, "Democracy and the US-India relationship".
[58] Hindustan Times, "US defense secretary Lloyd Austin says US considers India to be a great partner".
[59] "Committed to achieving goal of $500 bn in bilateral trade with US: Ambassador Sandhu".The Economic Times. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/foreign-trade/committed-to-achieving-goal-of-500-bn-in-bilateral-trade-with-us-ambassador-sandhu/articleshow/80878316.cms.(accessed March 2021).
[60] Joe C. Mathew, "India-US mini trade deal: Low duty on medical devices; pact in final stages". Business Today. https://www.businesstoday.in/current/economy-politics/india-us-mini-trade-deal-low-duty-on-medical-devices-pact-in-final-stages/story/413669.html.(Accessed March 2021).
[61] Economic Times, "Commited to achieving goal of $500 bn in bilateral trade with US: Ambassador Sandhu".
[62] Joe C. Mathew, "India-US mini trade deal: Low duty on medical devices; pact in final stages".
[63] Economic Times, "Commited to achieving goal of $500 bn in bilateral trade with US: Ambassador Sandhu".
[64] Darshana Baruah, Frédéric Grére, and Nilanthi Samaranayake, "US-India cooperation on Indo-Pacific Security". Page 2.
[65] "Hindustan Times "US defense secretary Lloyd Austin says US considers India to be a great partner".
[66] Tanvi Madan, "Democracy and the US-India relationship".
[67] Ibid.
[68] Tanvi Madan, "India and the Biden Administration: Consolidating and Rebalancing Ties".
[69] Economic Times, "Commited to achieving goal of $500 bn in bilateral trade with US: Ambassador Sandhu".
[70] Tanvi Madan, "Democracy and the US-India relationship".
[71] Darshana Baruah, Frédéric Grére, and Nilanthi Samaranayake, "US-India cooperation on Indo-Pacific Security". Page3.
[72] IBIDEM p.3
[73] IBIDEM. Page 6
[74] IBIDEM. Page 7
[75] Seeram Chaulia, "France and sailing toward the 'QUAD-plus'". The New Indian Express
[76] Elisabeth Mearns, Gary Parkinson; "With a pandemic, populism and protectionism, have we passed peak globalization?". China Global Television Network. https://newseu.cgtn.com/news/2020-05-28/With-a-pandemic-populism-and-protectionism-has-globalization-peaked--QOQMPg3ABO/index.html.(accessed April 2021).
[77] Abraham Newman, Henry Farrel; "The New Age of Protectionism". Foreign Affairs. https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/europe/2021-04-05/new-age-protectionism.(accessed 5 April 2021).
[78] Economic Times, "Commited to achieving goal of $500 bn in bilateral trade with US: Ambassador Sandhu".

IDF soldiers during a study tour as part of Sunday culture, at the Ramon Crater Visitor Center [IDF].
ESSAY / Jairo Císcar
The geopolitical reality that exists in the Middle East and the Eastern Mediterranean is incredibly complex, and within it the Arab-Israeli conflict stands out. If we pay attention to History, we can see that it is by no means a new conflict (outside its form): it can be traced back to more than 3,100 years ago. It is a land that has been permanently disputed; despite being the vast majority of it desert and very hostile to humans, it has been coveted and settled by multiple peoples and civilizations. The disputed territory, which stretches across what today is Israel, Palestine, and parts of Lebanon, Jordan, Egypt, and Syria practically coincides with historic Canaan, the Promised Land of the Jewish people. Since those days, the control and prevalence of human groups over the territory was linked to military superiority, as the conflict was always latent. The presence of military, violence and conflict has been a constant aspect of societies established in the area; and, with geography and history, is fundamental to understand the current conflict and the functioning of the Israeli society.
As we have said, a priori it does not have great reasons for a fierce fight for the territory, but the reality is different: the disputed area is one of the key places in the geostrategy of the western and eastern world. This thin strip, between the Tigris and Euphrates (the Fertile Crescent, considered the cradle of the first civilizations) and the mouth of the Nile, although it does not enjoy great water or natural resources, is an area of high strategic value: it acts as a bridge between Africa, Asia and the Mediterranean (with Europe by sea). It is also a sacred place for the three great monotheistic religions of the world, Judaism, Christianity and Islam, the "Peoples of the Book", who group under their creeds more than half of the world's inhabitants. Thus, for millennia, the land of Israel has been abuzz with cultural and religious exchanges ... and of course, struggles for its control.
According to the Bible, the main para-historical account of these events, the first Israelites began to arrive in the Canaanite lands around 2000 BC, after God promised Abraham that land ".... To your descendants ..."[1] The massive arrival of Israelites would occur around 1400 BC, where they started a series of campaigns and expelled or assimilated the various Canaanite peoples such as the Philistines (of which the Palestinians claim to be descendants), until the Kingdoms of Israel and Judah finally united around the year 1000 BC under a monarchy that would come to dominate the region until their separation in 924 BC.
It is at this time that we can begin to speak of a people of Israel, who will inhabit this land uninterruptedly, under the rule of other great empires such as the Assyrian, the Babylonian, and the Macedonian, to finally end their existence under the Roman Empire. It is in 63 BC when Pompey conquered Jerusalem and occupied Judea, ending the freedom of the people of Israel. It will be in 70 AD, though, with the emperor Titus, when after a new Hebrew uprising the Second Temple of Jerusalem was razed, and the Diaspora of the Hebrew people began; that is, their emigration to other places across the East and West, living in small communities in which, suffering constant persecutions, they continued with their minds set on a future return to their "Promised Land". The population vacuum left by the Diaspora was then filled again by peoples present in the area, as well as by Arabs.
The current state of Israel
This review of the historical antiquity of the conflict is necessary because this is one with some very special characteristics: practically no other conflict is justified before such extremes by both parties with "sentimental" or dubious "legal" reasons.
The current state of Israel, founded in 1948 with the partition of the British Protectorate of Palestine, argues its existence in the need for a Jewish state that not only represents and welcomes such a community but also meets its own religious requirements, since in Judaism the Hebrew is spoken as the "chosen people of God", and Israel as its "Promised Land". So, being the state of Israel the direct heir of the ancient Hebrew people, it would become the legitimate occupier of the lands quoted in Genesis 15: 18-21. This is known as the concept of Greater Israel (see map)[2].
On the Palestinian side, they exhibit as their main argument thirteen centuries of Muslim rule (638-1920) over the region of Palestine, from the Orthodox caliphate to the Ottoman Empire. They claim that the Jewish presence in the region is primarily based on the massive immigration of Jews during the late 19th and 20th centuries, following the popularization of Zionism, as well as on the expulsion of more than 700,000 Palestinians before, during and after the Arab-Israeli war of 1948, a fact known as the Nakba[3], and of many other Palestinians and Muslims in general since the beginning of the conflict. Some also base their historical claim on their origin as descendants of the Philistines.
However, although these arguments are weak, beyond historical conjecture, the reality is, nonetheless, that these aspirations have been the ones that have provoked the Palestinian-Israeli conflict. This properly begins in the early 20th century, with the rise of Zionism in response to the growing anti-Semitism in Europe, and the Arab refusal to see Jews settled in the area of Palestine. During the years of the British Mandate for Palestine (1920-1948) there were the first episodes of great violence between Jews and Palestinians. Small terrorist actions by the Arabs against Kibbutzim, which were contested by Zionist organizations, became the daily norm. This turned into a spiral of violence and assassinations, with brutal episodes such as the Buraq and Hebron revolts, which ended with some 200 Jews killed by Arabs, and some 120 Arabs killed by the British army.[4]
Another dark episode of this time was the complicit relations between the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, Haj Almin Al-Husseini, and the Nazi regime, united by a common diary regarding Jews. He had meetings with Adolf Hitler and gave them mutual support, as the extracts of their conversations collect[5]. But it will not be until the adoption of the "United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine" through Resolution 181 (II) of the General Assembly when the war broke out on a large scale. [6] The Jews accepted the plan, but the Arab League announced that, if it became effective, they would not hesitate to invade the territory.
And so, it was. On May 14, 1948, hours after the proclamation of the state of Israel by Ben-Gurion, Israel was invaded by a joint force of Egyptian, Iraqi, Lebanese, Syrian and Jordanian troops. In this way, the 1948 Arab-Israeli War began, beginning a period of war that has not stopped until today, almost 72 years later. Despite the multiple peace agreements reached (with Egypt and Jordan), the dozens of United Nations resolutions, and the Oslo Accords, which established the roadmap for achieving a lasting peace between Israel and Palestine, conflicts continue, and they have seriously affected the development of the societies and peoples of the region.
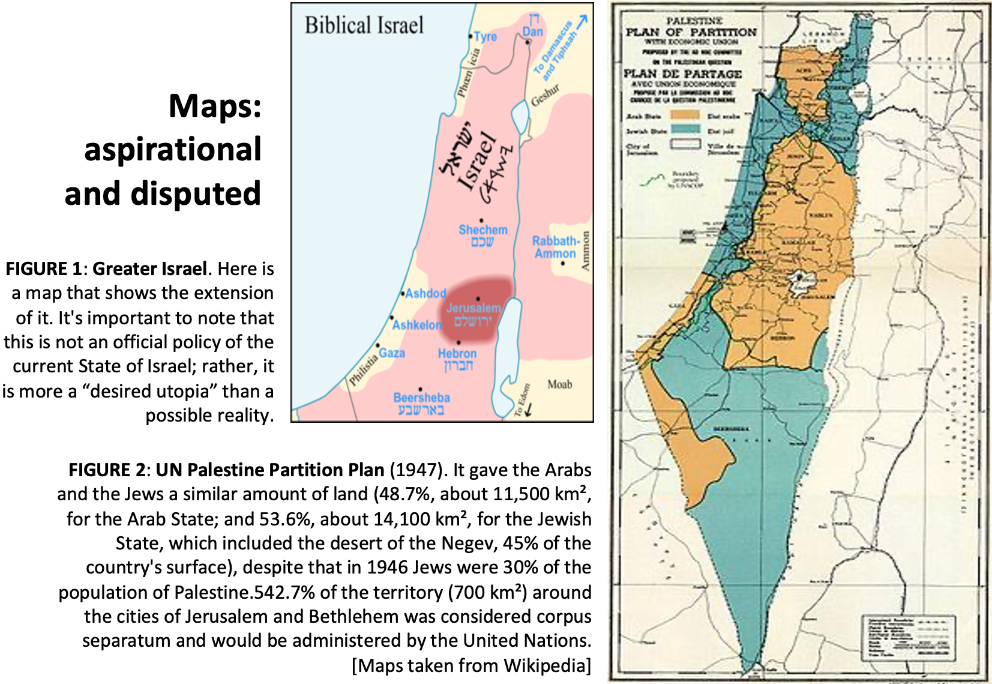
The Israel Defense Forces
Despite the difficulties suffered since the day of its independence, Israel has managed to establish itself as the only effective democracy in the region, with a strong rule of law and a welfare state. It has a Human Development Index of 0.906, considered very high; is an example in education and development, being the third country in the world with more university graduates over the total population (20%) and is a world leader in R&D in technology. Meanwhile, the countries around it face serious difficulties, and in the case of Palestine, great misery. One of the keys to Israel's success and survival is, without a doubt, its Army. Without it, it would not have been able to lay the foundations of the country that it is today, as it would have been devastated by neighbouring countries from the first day of its independence.
It is not daring to say that Israeli society is one of the most militarized in the world. It is even difficult to distinguish between Israel as a country or Israel as an army. There is no doubt that the structure of the country is based on the Army and on the concept of "one people". The Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) act as the backbone of society and we find an overwhelming part of the country's top officials who have served as active soldiers. The paradigmatic example are the current leaders of the two main Knesset parties: Benny Ganz (former Chief of Staff of the IDF) and Benjamin Netanyahu (a veteran of the special forces in the 1970s, and combat wounded).
This influence exerted by the Tzahal[7] in the country is fundamentally due to three reasons. The first is the reality of war. Although, as we have previously commented, Israel is a prosperous country and practically equal to the rest of the western world, it lives in a reality of permanent conflict, both inside and outside its borders. When it is not carrying out large anti-terrorist operations such as Operation "Protective Edge," carried out in Gaza in 2014, it is in an internal fight against attacks by lone wolves (especially bloody recent episodes of knife attacks on Israeli civilians and military) and against rocket and missile launches from the Gaza Strip. The Israeli population has become accustomed to the sound of missile alarms, and to seeing the "Iron Dome" anti-missile system in operation. It is common for all houses to have small air raid shelters, as well as in public buildings and schools. In them, students learn how to behave in the face of an attack and basic security measures. The vision of the Army on the street is something completely common, whether it be armoured vehicles rolling through the streets, fighters flying over the sky, or platoons of soldiers getting on the public bus with their full equipment. At this point, we must not forget the suffering in which the Palestinian population constantly lives, as well as its harsh living conditions, motivated not only by the Israeli blockade, but also by living under the government of political parties such as Al-Fatah or Hamas. The reality of war is especially present in the territories under dispute with other countries: the Golan Heights in Syria and the so-called Palestinian Territories (the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip). Military operations and clashes with insurgents are practically daily in these areas.
This permanent tension and the reality of war not only affect the population indirectly, but also directly with compulsory military service. Israel is the developed country that spends the most defense budget according to its GDP and its population. [8] Today, Israel invests 4.3% of its GDP in defense (not counting investment in industry and military R&D). [9] In the early 1980s, it came to invest around 22%. Its army has 670,000 soldiers, of whom 170,000 are professionals, and 35.9% of its population (just over 3 million) are ready for combat. It is estimated that the country can carry out a general mobilization around 48-72 hours. Its military strength is based not only on its technological vanguard in terms of weapons systems such as the F-35 (and atomic arsenal), material, armored vehicles (like the Merkava MBT), but also on its compulsory military service system that keeps the majority of the population trained to defend its country. Israel has a unique military service in the western world, being compulsory for all those over 18 years of age, be they men or women. In the case of men, it lasts 32 months, while women remain under military discipline for 21 months, although those that are framed in combat units usually serve the same time as men. Military service has exceptions, such as Arabs who do not want to serve and ultra-Orthodox Jews. However, more and more Israeli Arabs serve in the armed forces, including in mixed units with Druze, Jews and Christians; the same goes for the ultra-orthodox, who are beginning to serve in units adapted to their religious needs. Citizens who complete military service remain in the reserve until they are 40 years old, although it is estimated that only a quarter of them do so actively[10].
Social cohesion
Israeli military service and, by extension, the Israeli Defense Forces are, therefore, the greatest factor of social cohesion in the country, above even religion. This is the second reason why the army influences Israel. The experience of a country protection service carried out by all generations creates great social cohesion. In the Israeli mindset, serving in the military, protecting your family and ensuring the survival of the state is one of the greatest aspirations in life. From the school, within the academic curriculum itself, the idea of patriotism and service to the nation is integrated. And right now, despite huge contrasts between the Jewish majority and minorities, it is also a tool for social integration for Arabs, Druze and Christians. Despite racism and general mistrust towards Arabs, if you serve in the Armed Forces, the reality changes completely: you are respected, you integrate more easily into social life, and your opportunities for work and study after the enlistment period have increased considerably. Mixed units, such as Unit 585 where Bedouins and Christian Arabs serve,[11] allow these minorities to continue to throw down barriers in Israeli society, although on many occasions they find rejection from their own communities.
Israelis residing abroad are also called to service, after which many permanently settle in the country. This enhances the sense of community even for Jews still in the Diaspora.
In short, the IDF creates a sense of duty and belonging to the homeland, whatever the origin, as well as a strong link with the armed forces (which is hardly seen in other western countries) and acceptance of the sacrifices that must be made in order to ensure the survival of the country.
The third and last reason, the most important one, and the one that summarizes the role that the Army has in society and in the country, is the reality that, as said above, the survival of the country depends on the Army. This is how the military occupation of territories beyond the borders established in 1948, the bombings in civilian areas, the elimination of individual objectives are justified by the population and the Government. After 3,000 years, and since 1948 perhaps more than ever, the Israeli people depend on weapons to create a protection zone around them, and after the persecution throughout the centuries culminating in the Holocaust and its return to the "Promised Land," neither the state nor the majority of the population are willing to yield in their security against countries or organizations that directly threaten the existence of Israel as a country. This is why despite the multiple truces and the will (political and real) to end the Arab-Israeli conflict, the country cannot afford to step back in terms of preparing its armed forces and lobbying.
Obviously, during the current Covid-19 pandemic, the Army is having a key role in the success of the country in fighting the virus. The current rate of vaccination (near 70 doses per 100 people) is boosted by the use of reserve medics from the Army, as well as the logistic experience and planning (among obviously many other factors). Also, they have provided thousands of contact tracers, and the construction of hundreds of vaccination posts, and dozens of quarantine facilities. Even could be arguable that the military training could play a role in coping with the harsh restrictions that were imposed in the country.
The State-Army-People trinity exemplifies the reality that Israel lives, where the Army has a fundamental (and difficult) role in society. It is difficult to foresee a change in reality in the near future, but without a doubt, the army will continue to have the leadership role that it has assumed, in different forms, for 3,000 years.
[1] Genesis 15:18 New International Version (NIV). 18: "On that day the Lord made a covenant with Abram and said, 'To your descendants I give this land, from the Wadi [a] of Egypt to the great river, the Euphrates'".
[2] Great Israel matches to previously mentioned Bible passage Gen. 15: 18-21.
[3] Independent, JS (2019, May 16). This is why Palestinians wave keys during the 'Day of Catastrophe'. Retrieved March 23, 2020, from https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/middle-east/nakba-day-catastrophe-palestinians-israel-benjamin-netanyahu-gaza-west-bank-hamas-a8346156.html
[4] Ross Stewart (2004). Causes and Consequences of the Arab-Israeli Conflict. London: Evan Brothers, Ltd., 2004.
[5] Record of the Conversation Between the Führer and the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem on November 28, 1941, in Berlin, Documents on German Foreign Policy, 1918-1945, Series D, Vol. XIII, London , 1964, p. 881ff, in Walter Lacquer and Barry Rubin, The Israel-Arab Reader, (NY: Facts on File, 1984), pp. 79-84. Retrieved from https://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/the-mufti-and-the-f-uuml-hrer#2."Germany stood for uncompromising war against the Jews. That naturally included active opposition to the Jewish national home in Palestine. .... Germany would furnish positive and practical aid to the Arabs involved in the same struggle .... Germany's objective [is] ... solely the destruction of the Jewish element residing in the Arab sphere .... In that hour the Mufti would be the most authoritative spokesman for the Arab world. The Mufti thanked Hitler profusely. "
[6] United Nations General Assembly A / RES / 181 (II) of 29 November 1947.
[7] Tzahal is a Hebrew acronym used to refer to the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF).
[8] Newsroom (8th June 2009). Arming Up: The world's biggest military spenders by population. 03-20-2020, by The Economist Retrieved from: https://www.economist.com/news/2009/06/08/arming-up
[9] Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (nd). SIPRI Military Expenditure Database. Retrieved March 21, 2020, from https://www.sipri.org/databases/milex
[10] Gross, JA (2016, May 30). Just a quarter of all eligible reservists serve in the IDF. Retrieved March 22, 2020, from https://www.timesofisrael.com/just-a-quarter-of-all-eligible-reservists-serve-in-the-idf/
[11] AHRONHEIM, A. (2020, January 12). Arab Christians and Bedouins in the IDF: Meet the members of Unit 585. Retrieved March 19, 2020, from https://www.jpost.com/Israel-News/The-sky-is-the-limit-in-the- IDFs-unique-Unit-585-613948

ESSAY / Pablo Arbuniés
Introduction
In 1994 both South Africa and Rwanda embarked on a journey of political change that to this day seems unfinished. The first saw the end of apartheid and the beginning of a transition to non-racial democracy, while the latter saw the end of a civil conflict that sparked a genocide.
Both countries faced fundamental changes of a political and social nature at the same time in two very different ways. South Africa faced such change from the perspective of democracy, while Rwanda saw the collapse of a radical ethnic regime under Habyalimana after the civil war in 1994.
Understanding that countries move in a wide spectrum between democracy and non-democracy, that is, that they often are in a liminal political status, is the very basis to study these processes. Comparing these countries that experienced monumental political change at the same time can be useful to understand how societies can be rebuilt after a dark period. Depending on how the transition started, either through force as is the case in Rwanda or via political consensus or constitutional change as in South Africa, the path that the country will follow can vary greatly. It is also worth exploring how a post-conflict consensus can be the basis of a renewed system. Of key interest is how long such dispensation go uncontested and how stable it can sustain the project.
The case of South Africa and Rwanda
South Africa is classified by some as a Flawed Democracy[1], meaning that there are free and fair elections but there are factors that prevent it from arriving at a full democratic rule. In 1990, the government re-established multi-party politics. Then, the 1992 referendum approved universal suffrage, including black people in the democratic process, and the 1994 general elections were the first democratic and universal vote in the history of the country. The African National Congress (ANC) came to power and has won all the following elections.
The ANC-and similarly, the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF)-has a sense of exceptionalism, a belief that it has an extraordinary mandate to finish the revolution that only it can fulfil[2]. However, recent elections have shown a decrease in popular support for the ANC. Yet the fact that, over time, the ruling party during a transition process eventually loses free elections is a sign of a consolidated democracy[3].
Rwanda on the other hand is deemed an authoritarian regime by the EIU[4]. In the aftermath of the civil war and the genocide, the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF) positioned itself as a guarantor of security, consolidating control over all sectors of society. This provision of security and stability in the wake of a conflict, accompanied by an authoritarian use of power, can be referred to as the authoritarian social contract, prioritising security over democracy and fundamental rights, but with a sufficiently transparent and accountable government.
This article will proceed to explore a few indicators like transitional justice, legal framework and institutions, separation of power and rule of law, transparency and accountability plus civil society to test whether South Africa and Rwanda have attained democratic transition through building sustainable political institutions.
Transitional justice
The South African Constitution highlights the importance of healing the consequences of apartheid and establishing a society based on human rights, democracy and social justice. Thus, in 1995 the Government established the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC), tasked with uncovering past injustices and establishing the truth about the apartheid.
The TRC was composed of three committees: Human rights violations, Reparation and Rehabilitation and Amnesty. Their ultimate goal was to restore the dignity and encourage the spirit of forgiveness between the victims and the perpetrators.
However, in terms of accountability, the TRC has fallen short. The offer of "amnesty for the truth" as well as the de facto back door amnesty provided by the National Prosecuting Authority's Prosecution Policy have meant effective immunity for apartheid-era perpetrators even if they did not apply for amnesty nor helped the TRC. Even after the "back door" was declared unconstitutional in 2008, none of the cases affected has returned to the courts.[5]
In Rwanda, the priority after the civil war and genocide was also rebuilding social peace. Civil war crimes and genocide were treated differently from each other in transitional justice, partly due to the reluctance of the RPF to judge its crimes as a belligerent actor in the civil war, and also because of the prioritising of genocide prosecution.[6]
Rwanda's main challenge for transitional justice was the vast number of people that took part in the genocide. Despite other countries facing similar problems and opting for amnesties or selective prosecution, Rwanda chose the way of accountability through criminal trials. To achieve this, the government had to create community courts (Gacaca) to make accountability possible for low-level genocide suspects.
This choice of criminal prosecution was defended by the RPF as a measure to end impunity culture that led to the genocide. However, the massive prosecutions have ended up overwhelming the system and hindering the rule of law.
Legal framework and institutions
Constitution
In its transition to democracy, South Africa chose to completely re-write its constitution. The 1996 Constitution was promulgated by Nelson Mandela and entered into force in 1997, in place of the 1993 interim constitution. The interim constitution set the instructions for the final one, including universal adult suffrage, the prohibition of discrimination, multi-party democracy, separation of powers, etc.
However, the biggest achievement of the South African transition is how the institutions in charge of the elections have been built on consensus and with the guarantee of non-interference by the ruling party, making the Electoral Commission a body publicly perceived to be neutral and impartial.[7]
Rwanda held a referendum in 2003 to approve a new constitution, after a deep public consultation process. A new constitution was approved, prohibiting ethnic politics along with other forms of discrimination. This clause has been widely used by the government to maintain a one-party system by illegalising opposition parties and attacking any form of political dissent under the façade of preventing another genocide[8]. In 2015 term limits were abolished by referendum, allowing president Kagame to run for a third 7-year term.
Separation of powers and rule of law
In terms of separation of powers and checks and balances, South Africa ranks above the average of its region according to the world justice and rule of law index. Its overall score in the Rule of Law Index is of 0.59, making it the 45th country out of 128. The lowest rated indicators for the country are absence of corruption at 0.48 and criminal justice at 0.53. In terms of fundamental rights, all indicators are above average and above the upper-middle threshold except for no discrimination, valued at 0.54.
Constraints on government powers are measured at 0.63, and all indicators are above average and above the "upper-middle" threshold. Legislative and judiciary checks and balances are valued at 0.58 and 0.67 respectively, meaning that there is an effective separation of powers. However, and despite the absence of corruption ranking above average, in the legislative power is below the upper-middle threshold and valued at a worrying 0.23, and in the executive branch it is also below said threshold at 0.4. Corruption in the executive and the legislative powers can be explained as a consequence of the political dominance of the ANC and its firm grab onto power, and it should eventually fade away when a new party reaches power.
On the other hand, Rwanda is a fascinating case, since it presents a very low score on the democratic index[9] but an overall decent rule of law index. [10] In other words, Rwanda's government might not be democratic, but it does play by the rules, hence reinforcing the idea of an authoritarian social contract that is indeed being fulfilled by the government. In fact, despite being an authoritarian country, Rwanda's rule of law index is higher than South Africa's, and the second highest in Sub-Saharan Africa, only bettered by Namibia (one of the best-ranked democracies in the region).
To further prove the point of the authoritarian social contract, looking at the different indicators of the Rule of Law Index, one can notice that its lowest-rated indicators are the fundamental rights ones (0.51, ranking 81st in the world) and it's best indicator is order and security (0.84, ranking 22nd in the world) with a perfect score in absence of civil conflict (1.00).
Limits to governmental power by the legislative and judiciary powers are worth mentioning too. In the case of legislative checks and balances, the country ranks below the Sub-Saharan average, partly due to the predominance of RPF parliamentarians dominating the legislature. Hence they provide little checks on the executive. On the other hand, Judiciary checks and sanctions for official misconduct are above the Sub-Saharan average, showing a surprising level of judiciary independence for a country deemed as authoritarian.
Transparency and accountability
Transparency indicators show South Africa leading the regional chart, well above the Sub-Saharan average and also above the upper-middle threshold, which means that the government can be considered transparent enough. In the other hand, persistent levels of corruption in the executive and legislative power, as well as in the police and military (ranked above regional average but below the upper-middle threshold) show worrying signs that could obstruct the accountability of those holding power. Indeed, sanctions for official misconduct are the weaker link in constraints on government power, showing a limited action taken against corruption, but still ranking above the Sub-Saharan average.
In Rwanda, judiciary independence and sanctions for official misconduct are also above average for the region, showing an acceptable degree of accountability in the exercise of power that yet again can be surprising in an authoritarian country.
In terms of transparency, Rwanda ranks above the Sub-Saharan average in all indicators: publicized laws and government data (0.60), right to information (0.61), civic participation (0.53) and complaint mechanisms (0.60). Corruption indicators are above regional average as well with corruption in the legislative power being the worst of the lot despite still being better than that of its neighbouring counterparts.
Civil society
The ANC has, in a similar fashion to the RPF, tried to become a gatekeeping power, attempting to draw the limits of what is acceptable opposition or an acceptable discourse. This allows the parties to monopolize the social cohesion discourse by presenting themselves as the only legitimate actor to tackle the issue.
In South Africa, the ANC accuses the opposition parties of trying to bring back apartheid; for instance, it claims that the Democratic Alliance aims to return to a minority rule system. Thus, the party presents itself as the only one that can prevent the Boers from returning to power. A state of constant alert is promoted by the ANC, not only within national politics and against civil society actors, but also claiming that foreign agendas are seeking a regime change in the country and trying to turn the people against their leaders.[11]
In Rwanda, the government took advantage of the post-conflict situation to limit public participation in the political sphere. Those opposed to the government are marginalised and their discourse is rejected as genocide-promoting or supportive of ethnical divisions. This is key for the government to retain popular support, as any dissenting voice will be delegitimized and presented as a call to go back to the worst moments of Rwanda's history, and thus publicly rejected. As for dealing with foreign civil society actors, Kagame tends to delegitimize them by associating any dissenting foreign opinion with colonialism. [12] This overall helps the RPF sustain their rhetoric of the Rwandicity of the people as the only way of keeping social peace and cohesion.
This discourse that attempts to create national unity as well as within the parties, has a constant "rally around the flag" effect, silencing dissenting opinions and deterring potential civil society actors, in fear of being singled out as apartheid or genocide promoters. This results in a weakened civil society often deterred from criticising the government in fear of being marginalised and portrayed as either a colonialist or a promoter of ethnic division and genocide. Dissenting voices are turned into enemies of the nation and used for an "us versus them" political discourse.
Despite this, non-governmental checks on the exercise of power in South Africa are valued at 0.71, well above the Sub-Saharan average as well as the upper-middle threshold. Freedom of expression has the same score and again and both above the regional average and nearly reaching the higher threshold.
Overall, South Africa has a robust civil society that plays a key role in creating and sustaining political culture, tackling the gaps between national and local politics, as well as holding public officials accountable and checking their use of power. This can be seen in the outing of former presidents Thabo Mbeki and Jacob Zuma through consistent mobilisations and lawsuits.[13]
For Rwanda, as expected in an authoritarian country, civil society is not a key actor. Non-governmental checks to the use of power are low (0.45), and likely limited by an also low freedom of expression indicator (0.45).
Conclusions
Treating democracy and non-democracy as a dichotomy instead of the two sides of a wide spectrum would not allow us to look at how different variables are key to understanding national politics. Instead, it is crucial to understand that many countries occupy a liminal space between democracy and non-democracy without necessarily moving towards either. Therefore, it is in that space that they should be analysed in order to be fully understood. That being said, South Africa and Rwanda both occupy very different liminal spaces, with the first being much closer to full democracy than the former.
The civil society indicators, as well as the role of transitional justice, show a very clear difference between South Africa and Rwanda, which is rooted in the legitimation of the power of the ruling party, as well as in the background of their political changes. The RPF came to power by winning the civil war and used transitional justice to whitewash its image as no RPF member has been investigated for alleged war crimes[14]. Thus, the lack of accountability and the militaristic nature of the transition can be seen as factors that discourage citizen participation in politics. On the other hand, South Africa had an easier task with transitional justice, but the result cannot be considered perfect or ideal, and many criticise the South African model of transitional justice for being too superficial and symbolic and not providing the needed social healing. Also, South Africa's transition is built on political consensus instead of the outcome of a civil war, and that spirit of consensus can be seen in the much bigger role of civil society nowadays. The ability of civil society actors to hold political ones to a high enough standard is key in rebuilding a country.
The transparency indicators show that both countries have open and transparent governments, with Rwanda scoring better than South Africa in the publicized laws & government data as well as the right to information indicators, which can be surprising due to the authoritarian nature of the Rwandan government.
Although both countries seem to be in very different positions, they share a political discourse based on party exceptionalism and rejection of dissenting voices as encouragers of genocide or apartheid. The fear of ethnic conflict is the very basis of the traces of an authoritarian social contract that still prevails in the South African and Rwandan politics.
In terms of institutional transformation, South Africa shows how important it is to build trustworthy institutions, with the best example being the Electoral Commission. Also, political trust in pacific transitions of power after an election is a sign of a consolidated democracy and shows the success of South Africa.
The level of transparency of the Rwandan government, added to its success in the accountability and security aspects and the high civil and criminal justice indicators (all above regional average) show how an authoritarian country can effectively deal with a post-conflict situation without abandoning its non-democratic model. Rwanda is a fascinating example of a successfully fulfilled authoritarian social contract in which civil liberties are given up in exchange for a peaceful and stable environment in which the country can heal economically as the quite positive GDP per capita projections show.[15]
[1] The Economist Intelligence Unit; Democracy Index (2019) https://www.eiu.com/topic/democracy-index?&zid=democracyindex2019&utm_source=blog&utm_medium=blog&utm_name=democracyindex2019&utm_term=democracyindex2019&utm_content=top_link
[2] Beresford, A. Liberation movements and stalled democratic transitions: reproducing power in Rwanda and South Africa through productive liminality. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13510347.2018.1461209
[3] Huntington, S. P. (1991). The third wave: Democratization in the late 20th century.
[4] The Economist Intelligence Unit; Democracy Index (2019) https://www.eiu.com/topic/democracy-index?&zid=democracyindex2019&utm_source=blog&utm_medium=blog&utm_name=democracyindex2019&utm_term=democracyindex2019&utm_content=top_link
[5] International Center for Transitional Justice, South Africa https://www.ictj.org/our-work/regions-and-countries/south-africa
[6] Waldorf, L, Transitional Justice and DDR: The Case of Rwanda, International Center for Transitional Justice https://www.ictj.org/sites/default/files/ICTJ-DDR-Rwanda-CaseStudy-2009-English.pdf
[7] Ahere, J. R. (2020). Africa's dalliance with democracy, but whose democracy? In N. Sempijja, & K. Molope, Africa rising? Navigating the nexus between rhetoric and emerging reality (pp. 37-54). Pamplona: Eunsa.
[8] Roth, K. The power of horror in Rwanda, https://www.hrw.org/news/2009/04/11/power-horror-rwanda
[9] The Economist Intelligence Unit; Democracy Index (2019) https://www.eiu.com/topic/democracy-index?&zid=democracyindex2019&utm_source=blog&utm_medium=blog&utm_name=democracyindex2019&utm_term=democracyindex2019&utm_content=top_link
[10] World Justice Project, Rule of Law Index 2020 https://worldjusticeproject.org/our-work/research-and-data/wjp-rule-law-index-2020
[11] Beresford, A. Liberation movements and stalled democratic transitions: reproducing power in Rwanda and South Africa through productive liminality https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13510347.2018.1461209
[12] Beresford, A. Liberation movements and stalled democratic transitions: reproducing power in Rwanda and South Africa through productive liminality. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13510347.2018.1461209
[13] Gumede, W. How civil society has strengthened South Africa' s democracy https://www.corruptionwatch.org.za/civil-society-strengthened-democracy-south-africa/#toggle-id-1
[14] Waldorf, L, Transitional Justice and DDR: The Case of Rwanda, International Center for Transitional Justice https://www.ictj.org/sites/default/files/ICTJ-DDR-Rwanda-CaseStudy-2009-English.pdf
[15] IMF. "Rwanda: Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita in current prices from 1985 to 2025 (in U.S. dollars)." Chart. October 12, 2020. Statista. Accessed January 25, 2021. https://www.statista.com/statistics/452130/gross-domestic-product-gdp-per-capita-in-rwanda/

ESSAY / Álvaro de Lecea Larrañaga
From the moment colonial empires left the African continent and the new republics celebrated their first democratic elections, the issue of election violence has been present in the majority of the countries. It is a problem that has not changed and that keeps disturbing national and international supporters of a peaceful democratization of the African continent. It is not the first time in history we know about election violence in democratic states, such as France during the nineteenth century; nevertheless, the African dynamics are quite peculiar.
Violence, in general terms, has become a political instrument in the African democratic dynamics (Laakso, 2007). Depending on the actor making use of it, the motivation behind it is different. It is also important to take into account the historical, political, partner-cultural and economic context of each country to understand the purposes of the usage of this controversial mechanism. The spur is not the same for the ruling party or the opposition party, or other groups like the youth. Hence the use of violence has a lot of influence in the outcomes of an election process as it is an effective means that shapes the democratic dynamics when it comes to the election of the representatives at all stages of the electoral processes. For example, the ruling parties use it to avoid being removed from their powerful positions and all the benefits that come from them (Mehler, 2007).
This issue of power, with a high level of influence of money, is probably the most common motivation for every actor involved in these dynamics (Muna & Otieno, 2020, pp. 92-111). Not only the ruling powers but the ones trying to substitute them or the ones trying to impose a new order are, in some way, motivated by the powerful positions they could attain. The violence therefore permeates all party structures and is also noticeable within the parties.
The issue of intra-party violence has not received a lot of attention due to more frequency of state inspired violence against the opposition. Yet it is becoming more prevalent especially in political parties that hold power. This is because the belief is usually entrenched that if one represents the ruling party the chances of getting elected get higher. It should also be noted that the risk of intra-party violence increases as inter-party competition decreases, making intra-party violence more common in districts where a single party dominates (Bech Seeberg, Skaaning, & Wahman, 2017).
The timing of the violence is very relevant to understand the problem of election violence. The different three kinds of election violence (pre-election violence, post-election violence and violence during the Election Day) carry different connotations with them (Daxecker, 2013). They are the result of the general context of the country and represent the behaviour of their citizens towards the democratic principles of the nation. This can also be a response to the electoral campaigns of both the ruling and opposition parties, which sometimes involve violent means too.
Pre-election violence is normally recorded within parties as they carry out their primaries to select representatives and during the campaign process in a bid to hinder opponents from getting access to the people. Violence on Election Day is usually designed to disrupt areas where some candidates suspect they will lose or feel the election process has not been fair. While post-election violence is mainly an expression of dissatisfaction with the outcome of the election.
The role of average and international observers are also key for drafting the big picture of the problems involving election violence. These to some extent can escalate the conflict or reduce it. The power of information is huge and these agents are the most reliable sources to the local and international communities. If an international observer, such as a Committee from the United Nations, declares an election fraud, post-election violence is a very possible outcome (Daxecker, 2012). However, the average, and more concretely a trustworthy local average agent, has the power to calm the masses and bring peace.
Finally, the electoral system chosen by each country will also have a direct effect on the violence because of the interests behind the election. The plurality voting is the most used system among African states. These kinds of systems are also known as winner-takes-all, because the winner gets all the power. Even if it is not necessarily a negative system, as successful countries such as France or Brazil also use them, the difference of power between a common citizen and a politician is so big in Africa that the interest of getting those posts is higher (Reynolds, 2009). This will cause that any means justified to get there, including the use of violence.
To further analyse the motivations behind election violence in Africa and the effects it has on the region, and to try to offer a functional solution for this issue the article explores two case studies: Kenya 2007 and Burundi 2010.
African election violence case studies
Kenya 2007
The presidential and parliamentary elections held in Kenya in 2007 are a great example of election violence where external factors had influences on the outcomes. However, these external factors were not the only ones causing the violence. Internal issues such as the historical culture of the country, the electoral system or the will of power were also influential in this case. To understand the big picture, it is always important to analyze every relevant aspect.
Since the first multi-party democratic elections in Kenya, held in 1992, post-election violence has been very present. During the almost thirty years of dictatorship in Kenya after their independence from the British Crown, repression was promoted throughout the whole territory. Abuses of human rights, nepotism, widespread corruption and patronage were very common (Onyebadi & Oyedeji, 2011), therefore Kenyans are used to protest, violently if needed, against political fraud and suppression of their democratic rights.
Mwai Kibaki's victory in the 2007 elections brought a whole wave of violent protests because of the fraudulent accusations the elections received (Odhiambo Owuor, 2013). Not only the opposition leader Raila Odinga denounced the election as massively rigged, but also the international community did so. As they condemned the election as fraudulent, the United Nations intervened and helped reach a deal between both party leaders. In this case, the violence produced arrived after the elections (post-election violence) and was motivated by the fraudulent accusations made by international and national observers.
The solution reached was to recognise Kibaki as president and to create a new position of Executive Prime Minister for Odinga. Furthermore, they stipulated that cabinet positions were to be shared by the disputants and their political parties. This characteristic outcome was accepted with more enthusiasm by the Kenyan people because it divided the power in more than one person and, therefore, the abuse of it as it had happened before was not so probable. The electoral system, which is explained later on, has helped these abuses to be produced, so this different outcome meant a significant change in the Kenyan policy-making.
In the case of Kenya, average is very relevant, as the two most successful newspapers, the "Daily Nation" and "The Standard", with a combined strength of 75% market share, do not receive funding from the government. Without falling into sensationalism, these newspapers were able to become agents of peace and reconciliation. As violence raged in the post-election period, the newspapers adopted a thematic approach to reaching a peaceful outcome (Onyebadi & Oyedeji, 2011).
This conflict, apart from the effects it had on the electoral outcome, influenced the economic situation of the country. The annual percentage growth of GDP fell from 6.8% in 2007 to 0.2% in 2008, the annual percentage of GDP per capita growth was negative (-2.5%) and the growth on the percentage of employment regarding total labour force began increasing again in 2008, going from 2.5% that year to 2.7% in 2009 (World Bank, 2020). However, this data is biased because of the economic recession several countries, including Kenya, suffered due to the 2008 financial crisis.
Finally, Kenya's first-past-the-post single member constituency electoral system gives the electoral winner plenty of power. Moreover, the economic inequality, the domination of the powerful elites of the country who are very influential in the political system and the fact that Kenyan political parties are not usually founded on ideology but serve the ideas of the founders, produce a form of democracy that represents the few rather than the majority. Therefore, it is very complicated to terminate the desire for political power from the Kenyan mindset.
Burundi 2010
Burundi's history has been marked by the Hutu-Tutsi rivalry. Since it got independence in 1962, the ethnic cleavages between the majority Hutu and minority Tutsi have been remarkable. The 2010 elections are not quite different from the rest, as the outcomes resulted in boycotts and violence. Burundi is a country that has used violence as a tool of solving conflicts several times and has a violent historical precedent regarding "democratic" elections (Mehler, 2007). Several prime ministers and presidents from the different ethnic groups have been assassinated throughout Burundi's democratic history, which has led to a series of coups and ethnic clashes.
During the 2010 elections, the United Nations also sent a mission to observe the democratic process followed. They affirmed that the winning party, the National Council for the Defense of Democracy - Forces for the Defense of Democracy (CNDD-FDD), were able to campaign throughout the country, whereas the opposition parties had much less visibility (Palmans, n.d.).
The Independent National Electoral Commission (CENI), which is supposed to organise, conduct and supervise the elections independently from any party were not as transparent as they were meant to and didn't respect the rights of the political parties, which caused the boycott led by the opposition (Niang, n.d.). In Burundi too, elections have mainly been a struggle for power as a means of gaining access to economic resources through control of the state. So, the tensions have always been great during elections. Thus, violence tends to be used by nearly every actor involved.
The peculiarity within this case is that the violence didn't only take place after knowing the results of the elections, but also before the Election Day. Pre-election violence came as a consequence of systematic disagreement between CNDD-FDD and opposition parties. Although several institutions were created to ensure the legality and transparency of the election, such as the CENI, the CNDD-FDD tried to arrange the legal and institutional context to force the process into its advantage and ensure its victory against the opposition.
The pre-election violence transformed into post-election violence leading to the main opposition leader, Agathon Rwasa, having to flee the country. Even though the violence was not as widespread as in Kenya, the situation remained tense in the country. The results didn't change, and the political rivalries were further entrenched. In this case, the use of violence and coupled with display of power won the elections which created more fear and despair within the population.
Conclusion
Election violence is very common in several countries over the world, with an emphasis on Africa. There, it has become some kind of political instrument which, despite being anti-democratic by nature, is part of the policymaking, campaigning and electoral process. It is different depending on the timing it appears and plenty of factors influence its appearance and control. Within the most remarkable we can find the role of international and national observers, the role of the average, both national and international, and the will of power, usually linked to the economic benefits the winner receives. Furthermore, depending on who the actor is making use of it, the factors behind it can change drastically.
After having analysed the two case studies, Kenya 2008 and Burundi 2010, and having interpreted the impact these issues have had in their internal partner-economic parameters, it is also obvious that these anti-democratic practices do have some impact in every aspect of the society involved in it. Its most remarkable influence can be seen on the election outcome. In both cases, violence was key for establishing the results. In the case of Kenya, it was the motor that boosted a change in the policymaking, and in the case of Burundi, it helped the winning party keep the power.
The three main factors that influence this kind of policymaking and that should be reviewed and, if necessary, modified to end the violence are the electoral system most African countries follow, the ethnic nature of violence and the common African mindset regarding power. The majority of the electoral systems followed in Africa are winner-takes-all systems that makes it hard for the loser to give up power and lose the benefits it brings. Also, as the case of Burundi has shown, ethnic rivalries are a very common reason motivating the violent outcomes of elections, even if the state follows a democratic regime. This, together with the great will of power present on the African societies, demonstrated by the intra- and inter-party violence, provokes the unsustainable situation present nowadays.
REFERENCES
Bank, W. (2020). World Bank Database. Retrieved from https://data.bancomundial.org/
Bech Seeberg, M., Skaaning, S.-E., & Wahman, M. (2017). Candidate nomination, Intra-party Democracy, and Election Violence in Africa. ResearchGate.
Daxecker, U. E. (2012). The cost of exposing cheating: International election monitoring, fraud, and post-election violence in Africa. Journal of Peace Research.
Daxecker, U. E. (2013). All quiet on Election Day? International election observation and incentives for pre-election violence in African elections. Electoral Studies, 1-12.
Laakso, L. (2007). Insights into Electoral Violence in Africa. In M. Basedau, G. Erdmann, & A. Mehler, Votes, Money and Violence: Political Parties and Elections in Sub-Saharan Africa (pp. 224-252). South Africa: University of KwaZulu-Natal Press.
Mehler, A. (2007). Political Parties and Violence in Africa: Systematic Reflections against Empirical Background. In M. Basedau, G. Erdmann, & A. Mehler, Votes, Money and Violence: Political Parties and Elections in Sub-Saharan Africa (pp. 194-223). South Africa: University of KwaZulu-Natal Press.
Muna, W., & Otieno, M. (2020). The 'Money Talks Factor' in Kenya's Public Policy and Electoral Democracy.
Niang, M. A. (n.d.). Case study: Burundi. EISA.
Odhiambo Owuor, F. (2013). The 2007 General Elections in Kenya: Electoral Laws and Process. EISA, 113-123.
Onyebadi, U., & Oyedeji, T. (2011). Newspaper coverage of post-political election violence in Africa: an assessment of the Kenyan example. average War & Conflict, 215-230.
Palmans, E. (n.d.). Burundi's 2010 Elections: Democracy and Peace at Risk? European Centre for Electoral Support.
Reynolds, A. (2009). Elections, Electoral Systems, and Conflict in Africa. The Brown Journal of World Affairs, 75-83.
![A B-1B Lancer unleashes cluster munitions [USAF]. A B-1B Lancer unleashes cluster munitions [USAF].](/documents/16800098/0/cluster-bombs-blog.jpg/86c6e39e-4ca3-dac3-dfb3-cdba300bbac2?t=1621877460129&imagePreview=1)
▲ A B-1B Lancer unleashes cluster munitions [USAF].
ESSAY / Ana Salas
The aim of this paper is to study the international contracts on cluster bombs. Before going deeper into this issue, it is important to understand the concept of international contract and cluster bomb. "A contract is a voluntary, deliberate, legally binding, and enforceable agreement creating mutual obligations between two or more parties and a contract is international when it has certain links with more than one State."[1].
A cluster bomb is a free-fall or directed bomb that can be dropped from land, sea, or air. Cluster bombs contain a device that releases many small bombs when opened. These submunitions can cause different damages, they are used against various targets, including people, armored vehicles, and different types of material. It is an explosive charge designed to burst after that separation, in most cases when impacting the ground. But often large numbers of the submunitions fail to function as designed, and instead land on the ground without exploding, where they remain as very dangerous duds.
The main problem with these types of weapons is that they may cause serious collateral damage such as the death of thousands of civilians. Because of that, the legality of this type of weapon is controversial. Out of concern for the civilians affected by artifacts of this type, the Cluster Bomb Convention was held in Dublin, Ireland in 2008. There, a treaty was signed that prohibited the use of these weapons. Not all countries, though, signed the treaty; major arms producers, such as the United States, Russia and China, are not parties in the convention.
Among other things, the Convention proposed a total ban on cluster munitions, the promotion of the destruction of stocks in a period of 8 years, the cleaning of contaminated areas in 10 years, and assistance to the victims of these weapons.
Convention on Cluster Munitions: geopolitical background
The antecedents of this convention are in the recognition of the damage produced by the multiple attacks that have been carried out with cluster munitions. The International Handicap Organization has produced a report that offers concrete and documented data on the victims of cluster bombs around the world. In Laos[2], the attacks were designed to prevent enemy convoys make use of dense vegetation to camouflage among the trees. Furthermore, in this way it was not necessary to use ground troops. In Kosovo (1999), the targets were military posts, road vehicles, troop concentrations, armored units, and telecommunications centers. In Iraq cluster bombs have been used several times. During Operation "Desert Storm" in 1991, US forces dropped almost 50,000 bombs with more than 13 million submunitions on Iraq in air operations alone (not taking into account those dropped from the sea or by artillery). Estimates suggest that a third did not explode, and were found on roads, bridges and other civil infrastructure.
Pressure for an international ban on cluster bombs has recently intensified, following Israel's bombardments with these weapons in southern Lebanon in the summer of 2006. Also, in Afghanistan, in 2001 and 2002, during the US offensive, more than 1,200 cluster bombs with almost 250,000 submunitions were dropped against Taliban military instructions and positions. These targets were near towns and villages, whose civilian population was affected. UN demining teams estimate that around 40,000 munitions did not explode. These have been the main concern of NGOs. On the one hand, because of the large percentage of civilians who have been affected by the cluster bombs and on the other hand, due to the amount of submunitions that did not explode at the time and that are in the affected areas, being an even greater risk for the security of the civilian population or even for their agriculture in those lands.
Due to the great commotion over the death of thousands of civilians and after several attempts, a convention on such munitions was adopted in Dublin, where more than 100 countries had come together for an international agreement. The Convention on Cluster Munitions was adopted on May 30, 2008, in Dublin and signed on December 3-4, 2008 in Oslo, Norway. The Convention on Cluster Munitions entered into force on August 1, 2010.
One of the major problems addressed in the Convention was the threat posed by submunitions that do not explode as expected, and which remain in the area as a mortal danger, turning the affected area into a large minefield where the civilian population is the most vulnerable. A study indicates that 20-30% of these bombs do not explode either due to manufacturing defects, or to falls in soft areas or in trees, for example.
Articles 3 and 4 of the Convention are of great importance. Article 3 refers to the stockpile, storage, and destruction of cluster bombs. Here all Parties haves the obligation of making sure to destroy their stored cluster bombs no later than 8 years. Article 4, on the cleaning and destroying of cluster munition remnants and education on risk reduction, is intended to protect possible victims from the danger of bombs that have not exploded. Article 5 reinforces the obligation of the signatory parties to assist the victims of cluster bombs.
After the convention there is a double deal on cluster bombs. Since the destruction of the entire arsenal of these ammunitions and submunitions was approved, the affected companies and the countries involved will have a new challenge in hiring companies that carry out the extinction of these reserves.
Producers
The main manufacturers of cluster bombs are the United States, Russia, China, Israel, Pakistan, and India. Approximately 16 states are the largest producers of this ammunition and submunition worldwide, and none of these countries adhered to the convention on cluster munitions. Some of the countries involved are Greece, South Korea, North Korea, Egypt, Iran, Poland, Turkey, Brazil, Singapore, Romania, and Poland. The date on which the cluster munitions were produced is not clear because of the lack of transparency and the data available.
A total of 85 companies have produced, along history, cluster bombs or their essential parts. Many of these companies are headquartered in the United States or Europe, but others are state-owned industries located in developing countries. Cluster munition production involves the manufacturing and integration of a large number of parts, including metal parts, explosives, fuses, and packaging materials. All components are seldom produced by a single company in the same state. This makes it difficult to determine the true extent of the international trade in cluster munitions.
International trade on cluster bomb has slackened. As the cluster munition monitor of 2017 states, the US company Textron Systems Corporation, for example, has slowed production of the CBU-105[3] weapon due to "reduced orders, and claimed that the current political environment has made it difficult to obtain sales approvals from the executive branch".
Manufactures are also adapting their production to international regulations. Following a study by Pax[4] on "Worldwide Investments in cluster munitions," Avibras (Brazil), Bharat Dynamics Limited (India), China Aerospace Science and Industry (China) or Hanwha (South Korea) are some of the companies that develop or produce cluster bombs according to the definition given by the Dublin Convention in 2008.
It is important to warn about the existing sensitivity regarding the production of cluster bombs. Undoubtedly, they pose a serious problem from the point of view of civil protection, but many companies engaged in the production and the funders of this kind of weapons have a high interest in keeping them legal.
There are very controversial weapons. Many countries insist on that cluster munitions are legal weapons, that, although not essential, have great military use. Some states believe that submunitions can be accurately targeted to reduce damage to civilians, meaning that military purposes can be isolated in densely populated areas. On the other hand, others believe that the ability of cluster munitions to destroy targets just as effectively throughout the attack area can cause those using them to neglect the target, thus increasing the risk of civilian casualties.
The future of International contracting on cluster bombs
As Jorge Heine defines the "New Diplomacy", it requires the negotiation of a wide range of relationships with the state, NGOs and commercial actors. "As middle powers have demonstrated, through joining forces with NGOs, they have actually succeeded in augmenting their power to project their interests into the international arena."[5] Cluster munition is an example of this case.
Because of this, parties forming international contracts for the purchase and financing of cluster bombs are forced to change the object of the cluster bomb business. As mentioned earlier, the new business will be the destruction of these weapons, rather than their production. Especially munitions with high submunition failure rates. For this reason, countries such as Argentina, Canada, France, UK, Denmark, Norway, Spain and more have promoted a new business on the destruction of the storage of cluster bombs. As a result, cluster munitions move away from their useful life and have more chances of being destroyed than of being sold for profit.
By financing companies that produce cluster munitions, financial institutions (in many cases states themselves) help these companies to produce the weapon. But to achieve an effective elimination of cluster bombs, more than a convention is needed. The effort requires national legislation that reflects that purpose. Domestic governments must provide clear guidelines by introducing and enforcing legislation that prohibits investment in cluster munitions producers.
Conclusion
As a military tactic, the use of cluster bombs provides a high percentage of success. A good number of states and armies defend that they are effective weapons, sometimes even decisive ones, depending on the circumstances and the context. It is often argued that using another type of weapon to achieve the same objective would require more firepower and use more explosives, and that this would cause even greater collateral damage. At the same time, and to avoid the low reliability of these weapons, some armies have begun to modernize their arsenals and to replace older weapons with more modern and precise versions that incorporate, for example, guidance or self-destruct systems. Their main objective in developing cluster bombs is to compensate for precision failures with more munitions and, on the other hand, to allow a greater number of targets to be hit in less time.
Advances in technology can certainly reduce some of the humanitarian problems generated by the less advanced types of cluster bombs but a good number of military operations are currently peace operations, where the risk generated by these products also becomes a military concern, not just humanitarian. For example, to address the issue of unexploded ordnance, weapons are being developed that have self-destruction or, at least, self-neutralization mechanisms[6].
There is great uncertainty about how the norms of International Humanitarian Law (IHL) are interpreted and whether they are applied rigorously in the case of cluster munitions, given the lack of precision and reliability of these weapons. The Convention on Cluster Munitions gives hope, but we must consider the different current situations and how they can change. We also have to take into account that this agreement leaves open many possibilities of circumventing what has been signed. For example, guided or self-destructive cluster bombs do not fall under the umbrella of this pact.
Despite the provisions of International Humanitarian Law, existing cluster munitions have caused large numbers of civilian casualties in various conflicts. A better implementation of the IHL, including the Protocol on Explosive Remnants of War, will not be able to fully address the problems caused by these weapons. There is a need for specific rules on these munitions as outlined above.
[1] Renzo Cavalieri and Vincenzo Salvatore, An introduction to international contract law, Torino: Giappichelli, 2018.
[2] During the years 1964 to 1973, Laos was bombed by the United States. The attacks were intended to cut off North Vietnamese supply lines and support Laotian government forces in their fight against communist rebels.
[3] CBU-105 is a free fall cluster bomb unit of the United States Air Force.
[4] Pax is a peace organisation with the aim of "bringing peace, reconciliation and justice in the world".
[5] Matthew Bolton and Thomas Nash, 'The Role of Middle Powe-NGO Coalitions in Global Policy: The Case of the Cluster Munitions Ban', Global Policy, Vol. 1, No. 2 (May 2010), pp 172-184.
[6] Some essential component for the operation of the bomb is deactivated.
![Bahraini and UAE foreign ministers sign Abraham Accords with Israeli premier in September 2020 [White House]. Bahraini and UAE foreign ministers sign Abraham Accords with Israeli premier in September 2020 [White House].](/documents/16800098/0/acuerdos-blog.jpg/ad268976-c84e-2b4c-d2a5-ca36909e72e2?t=1621877040390&imagePreview=1)
Bahraini and UAE foreign ministers sign Abraham Accords with Israeli premier in September 2020 [White House].
essay / Lucas Martín Serrano
It is interesting to incorporate into any geopolitical analysis subject a touch of history. History is a fundamental financial aid for understanding the present. And most conflicts, problems, frictions or obstacles, whether between nations or public or private entities, always have an underlying historical background. Moreover, taken to the field of negotiation, regardless of the level of negotiation, demonstrating a certain historical knowledge of the adversary is useful because, on the one hand, it is not only a sample of interest and respect for him, which will always place us in an advantageous position, but, on the other hand, any stumbling block or difficulty that appears has ample possibilities of having its historical counterpart, and precisely there the path to a solution can be found. The party that has a greater depth of knowledge will significantly increase the chances of a solution that is more favourable to its interests.
In ancient times, the territory now occupied by the United Arab Emirates was inhabited by Arab tribes, nomadic farmers, craftsmen and traders. Plundering the merchant ships of European powers that sailed along its coasts, coming closer than was advisable, was commonplace. And, in a way, a way of life for some of its inhabitants. It was in the 7th century that Islam took root in the local culture. Of the two currents that emerged after the disputes that followed the death of the Prophet, it was the Sunni current that became dominant from the 11th century onwards.
In order to put an end to piracy and secure the maritime trade routes, the United Kingdom signed a peace treaty with the sheikhs in the area in 1820, signature . In 1853, a further step was taken and another agreement was signed, placing the entire territory under the military protectorate of the United Kingdom.
signature The area attracted the attention of powers such as Russia, France and Germany, and in 1892, to protect their interests, the agreement was set up, guaranteeing the British a monopoly on trade and exports.
The area encompassing today's seven United Arab Emirates plus Qatar and Bahrain became known as the "Trucial States".
During World War I, the Gulf's airfields and ports played an important role in the conflict in favour of the UK, development . At the end of World War II in 1945, the League of Arab States (Arab League) was created, made up of those with some colonial independence. The organisation attracted the attention of the Truce states.
In 1960, the Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) was created, with Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait and Venezuela as founding members and headquartered in Vienna, Austria. The seven emirates, which would later form the United Arab Emirates, joined the organisation in 1967.
Since 1968, nine emirates on the eastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula had begun negotiations to form a federal state. Following the withdrawal of British troops final and after Bahrain and Qatar dissociated themselves from the process and gained independence separately, in 1971, six emirates became independent from the British Empire: Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm al Qaywayn and Fujairah, forming the federation of the United Arab Emirates, with a legal system based on the 1971 constitution. Once consolidated, they joined the Arab League on 12 June. The seventh emirate, Ras Al-Khaimah, joined the following year, with the strongest components being the emirates of Dubai and Abu Dhabi, the capital.
It was the beginning of the exploitation of the huge oil wells discovered years earlier that turned the tide at status. After the 1973 oil crisis, the Emirates began to accumulate enormous wealth, as OPEC members decided not to export any more oil to the countries that supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War.
Oil and tourism based on urban growth and technological development are the main sources of prosperity in the country today, and a very important fact from all points of view is that 80-85% of the UAE's population is currently immigrant.
status current
It has been especially during the last decade, and partly as a consequence of events in the region since what became known as the Arab Spring, that the US has emerged as a regional power with the capacity to influence the region.
The main characteristic that can be attributed to this emergence on the international scene is the transformation of a conservative foreign policy, very much geared towards "self-preservation", towards a more open-minded one with a clear vocation not only to play a relevant role in the region, but also to influence it in order to protect its interests.
What can be seen as Abu Dhabi's main ambition is to become a major player capable of influencing the definition and establishment of governance Structures throughout the region according to its own model, securing and expanding trade routes, bringing in its neighbours to create a sufficiently powerful economic node with the capacity to forge closer ties with the entire East African region and Southeast Asia, in what seems another clear example of how the global geopolitical centre is already shifting definitively towards the Asia-Pacific axis.
The Emirati model has been able to evolve to integrate increasing economic openness with a conservative and strong-government model political whose main speech is built on the foundation of a well-entrenched and secure state. And all of this is coupled with a strong capacity as a service provider provider. Interestingly, the social model is relatively secular and liberal based by regional standards.
But a fundamental fact that cannot be forgotten is the outright rejection of any political or religious ideology that poses the slightest threat to the hegemony and supremacy of the state and its leaders.
It is Abu Dhabi, as the largest and most prosperous of the seven emirates, that exerts the most influence in setting the broad lines of both domestic and foreign policy. Indeed, the evolution of the UAE's established model is firmly associated with Abu Dhabi's crown prince and de facto leader of the emirate, Mohamed bin Zayed (MbZ).
What cannot be lost sight of is that, although MbZ and his inner circle of trust share the same vision of the world and politics, their actions and decisions do not necessarily follow a pre-established plan. There is no basic doctrine with set tactical and strategic objectives and the lines of work to follow in order to achieve them.
Their way of carrying out country strategy, if it can be called that, is based on a small group belonging to that inner circle, which puts on the table a number of usually tactical and reactive options to any problems or issues that arise to carry out. Based on these, the top leadership follows an ad hoc decision-making process that can lead to an excessive need for subsequent corrections and adjustments that in turn lead to missed opportunities.
Threats - status security
Emirati authorities have a clear perception of the main geostrategic threats to their development: on the one hand, the Iranian-promoted transnational spread of Islamist political ideology and, on the other, the influence sought by the Muslim Brotherhood and its promoters and supporters, including Qatar and Turkey, is perceived as an existential threat to their vision of a more secular form of government, as well as to the stability of the current regional status quo, given that it can act as a catalyst for radicalism in the area.
However, Abu Dhabi has been much more belligerent in its speech against the Muslim Brotherhood and its supporters, while remaining cautious in its stance against Iran.
The recent agreement with the State of Israel has served to undermine the credibility of many long-held clichés and has also highlighted the emergence of a Sunni-Jewish bloc as civil service examination to the belligerent and growing Shiite current led by Iran and its proxies, active in virtually every country in the region and in all regional conflicts.
This new status should serve to confirm to Western powers that in the Middle East region the view of their own problems has changed and Iran and its particular way of conducting foreign policy and defending its interests are now seen as a far more destabilising factor than the long-running Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The threat posed by Iran has acted as a catalyst in bringing together views, while Israel is nonetheless seen as providing stability both militarily and economically.
The UAE-Israel Treaty
On 15 September, Israel, the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain formalised the normalisation of their relations. This agreement means that four Arab states have now accepted Israel's right to exist, and this is undoubtedly a real diplomatic success.
The fact that it was precisely the UAE and Bahrain is no coincidence. Neither state has engaged in a direct war against Israel. And, if this characteristic is common to both states, Bahrain's relationship with Israel has been much smoother than that of the UAE. This reality is underpinned by the Jewish community based in Al-Qatif and its integration, which has translated into full and active participation in Bahrain's political life. This has helped to ensure that relations between Manama and Jerusalem have been far from conflictual.
Despite being seen as a novelty in the eyes of the general public, the truth is that the recent agreement is the third 'peace treaty' that signature has reached between the Hebrew country and an Arab nation. However, it is the first that seems to have been born with sufficiently solid foundations to augur a new, much more stable and lasting status , in clear contrast to the relations resulting from the previous agreements with Egypt and Jordan, which were very limited to personal relations and in the field of security and conventional diplomacy.
The new agreement with Israel sets out a new path for partnership affecting the Middle East as a whole, including substantially counterbalancing Iran's influence, fostering trade relations, tourism, partnership in subject military intelligence sharing, cooperation in health area and thereby helping to position the UAE to lead Arab diplomacy in the region by offering a solid civil service examination to Islamist groups such as the Muslim Brotherhood and its Palestinian arm in Gaza, Hamas, and thereby opening the door for other countries in the region to move in the same direction.
Israel's decision to fail the announced annexation under its sovereignty of certain areas of the West Bank is test that these moves in the region are much deeper and much more prepared and agreed in advance than might be imagined.
And this is precisely one of the major differences with previous agreements. The great expectation that has been created and the clear indications that other countries, including Saudi Arabia, will follow the UAE's lead.
In fact, one significant step in this direction was taken, and it was as simple as an Israeli "EI-Al" plane flying over Saudi airspace carrying a large issue group of businessmen, staff officials and investors on its way to the Emirates as a gesture of goodwill. And contrary to what might have been expected at other times, this had no repercussions in the Arab world, nor did it provoke any protests or demonstrations against it, subject .
Places such as Amman, Beirut, Tunis and Rabat, where demonstrations against the Israeli "occupation" and similar accusations are traditionally large in terms of participation, remained largely calm on this occasion.
But if this has gone unnoticed by the general population, it has not gone unnoticed by the leaders of the Middle Eastern powers and the violent organisations they use as proxies.
For those aspiring to follow in the UAE's footsteps and establish relations with Israel, this has served as a spur to reaffirm their decision, as the sense of unease or even danger emanating from the streets in the Arab world regarding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict that such a move might provoke has diminished.
For Iran and its proxies , on the other hand, it has been a hard lesson. Not only has the Palestinian cause, which has been raised and put on the table for so long, been significantly diminished in importance, but it has coincided in time with potestas in both Iraq and Lebanon in the opposite direction, i.e. against Iran's interference in the internal affairs of both countries.
In conclusion, it should be noted that, while this absence of protest at the agreement between Israel and the UAE may seem surprising, it is a clear sign of a long process of political maturation and evolution within the Arab world at large.
The people of the Middle East in general no longer aspire to pan-Arabist, pan-Islamic unity, to the establishment of the Great Caliphate or, in the case of Iran or Turkey, to imperialist dreams that are a thing of the past. What the mass of the people and society really want is to improve their well-being, to have more and more attractive economic opportunities, to have a good system educational, to improve the standards of development in all areas, to have the rule of law, and for the rule of law to be equal for all in their respective countries.
The treaty that is the subject of this point fits perfectly within these aspirations and this mental outline . The masses that once took to the streets no longer believe that the Palestinian cause is worthy of more effort and attention than their own struggle for a better future for their nations.
And, importantly, despite the opacity of the ayatollahs' regime, Iran's population is becoming less and less submissive to policies that are leading the country into a series of permanent conflicts with no end in sight, wasting the country's resources to sustain them.
Just two days after advertisement of agreement , the United Arab Emirates lifted the ban on telephone communication with Israel, with Hebrew Foreign Minister Gabi Ashkenazi and his Emirati counterpart Abdullah binZayed symbolising the opening of this new line of communication.
Almost immediately afterwards, a team from the Israeli Foreign Ministry travelled to Abu Dhabi to begin looking for possible sites for the future Israeli embassy.
A significant flow of investment from the UAE is being channelled to Israeli companies seeking new ways to treat COVID19 and to develop new tests to detect the disease. The increase in business deals between Israeli and Emirati companies has been almost immediate, and the "El-Al" company is already working to open a direct corridor between Tel Aviv and Abu Dhabi.
In view of the new status and the new approaches, Morocco, Oman and other Arab countries are now moving to follow in the UAE's footsteps. Israel's attractiveness is only growing, in a significant evolution from being the most hated country in the region to the most desired partner .
One factor to consider, however, is the impact in the US and Europe. In the West, the Palestinian cause is generally gaining support mainly due to the Boycott, Divestment and Sanctions (BDS) movement. As such, changes in relations with Israel are likely not only to fail to undermine that support, but also to spur increased efforts to prevent normalisation through disinformation campaigns spreading hatred towards Israel.
Finally, the civil service examination by Turkey, Qatar and Iran was predictable, but also clarifying. The Iranian president has called agreement a "grave mistake", while his Turkish counterpart has threatened to close the UAE embassy in Turkey. status In both cases, the ultimate reason for this reaction is the same: the use of the Palestinian cause for their own interests and, coincidentally, both are on this occasion coincidental: to distract public opinion from the difficult economic situation that, for different reasons, the two countries are going through.
Regional policy
The most important and enduring element of the UAE's foreign and security policy is its strategic alliances with the US and Saudi Arabia. Although the UAE has pursued a more independent course over the past decade, developments and this new direction would not have been possible without the support of the US, on whose protection the small but wealthy yet sparsely populated state relies, and who can be counted on to export its energy resources in the event of a conflict.
Even during the Obama administration, when relations were strained by US policy towards the events of the 'Arab Spring' and Iran, the strategic alliance between the two nations was maintained.
The clearly defined anti-Iranian policy of Donald Trump's administration, equivalent to that of the UAE, facilitated a rapid improvement in relations once again, and the new US administration saw the UAE as a fundamental pillar on which to base its Middle East policy. Thus, together with Israel and Saudi Arabia, the UAE is now the main US ally in the region.
In contrast to the US, Saudi Arabia became a strategic partner of the UAE's new regional policy under Obama. Indeed, the two nations have maintained close ties since the birth of the Emirates in 1971, but the new, young state unsurprisingly remained in the shadow of the other, more established nation, following the policies of its 'big brother'.
This status changed with the rise to power of Mohammed Bin Zayed who, since 2011, has been committed to spearheading a political line of joint actions in the region that have ultimately been decisive. MbZ found his perfect counterpart in Saudi Prince Mohammed Bin Salman, who gradually, since 2015, took the reins as the visible head of Saudi Arabia's policy. To such an extent that in certain cases, such as Yemen and Qatar, the UAE's leadership and drive seems to have been the unifying force behind joint regional policies.
Alliances
United States
The US role as an ally of the UAE dates back to the early 1980s, just after the 1979 Iranian revolution, which resulted in the loss of its most important ally in the region and the beginning of the Iran-Iraq war.
However, it was the 1990-1991 Gulf War that, with Iraq's invasion of Kuwait on 2 August 1990, showed the UAE how vulnerable the small Gulf states were to military aggression by any of their powerful neighbours.
In order to ensure its protection, and in common with other countries in the region, the UAE favoured an increased US presence on its territory in the years following the war. This concluded with a bilateral security agreement, agreement , signed in July 1994. This gave the US access to the UAE's air and seaports instructions and, in return, it undertook to protect the country from external aggression. Interestingly, and as a measure of how status has evolved, the agreement remained secret at Abu Dhabi's request because of the UAE's fear of criticism and protest both domestically and from Iran.
Initially, the UAE was no more than a US ally in the Persian Gulf. However, its importance as partner grew between 1990 and 2000, in part due to the port of Jebel Ali, which became the US Navy's most used base outside the country, and the Al Dhafra air base, a facility core topic for US activities in the region.
Moreover, since the late 1990s, the UAE has begun a process of presenting itself to its new ally as a reliable and more relevant partner , increasing the quantity and level of its cooperation. framework In line with this, UAE military forces have participated in all major US operations in the Middle East, from the Gulf War in 1991 to Somalia in 1992, Kosovo in 1999, Afghanistan since 2002, Libya since 2011, and Syria (in the fight against Da'esh) between 2014 and 2015. Only the UAE's participation in the invasion of Iraq in 2003 was vehemently avoided. From this involvement, the UAE Armed Forces have gained a great deal of experience on the ground, which has been beneficial to their effectiveness and professionalism.
This involvement in the often controversial US military actions in Arab countries has undoubtedly been a key element for the United States. Not only because of the image and narrative implications of having at least one Muslim country supporting them, but also because Abu Dhabi's contribution has not been limited to the military aspect. Humanitarian organisations have acted in parallel in order to win the support of the population wherever they have intervened by investing huge amounts of money. The most obvious example is Afghanistan, where the UAE has spent millions of dollars on humanitarian projects and development to help stabilise the country, while providing a small contingent of special operations forces in the particularly dangerous southern part of the country since 2003. In addition, between 2012 and 2014 they expanded their deployment with six F16 aircraft to support air operations against the Taliban. Even when the US began its phased withdrawal after 2014, Emirati troops remained in Afghanistan.
Getting the UAE on board in the fight against jihadists was not difficult at all, as its leaders are particularly averse to any form of religious extremism that affects the political system within Islam. This is the main reason for its air force's involvement in the US-led coalition against Daesh in Syria between 2014 and 2015. To such an extent that, after the US aircraft, it was the UAE aircraft that flew the most sorties against jihadist targets.
But partnership was not limited to the US. Both Australia and France had the emirates' air instructions at their disposal to carry out their operations.
Only the open breakdown of hostilities and the UAE's involvement in the 2015 Yemen War reduced its involvement in the fight against Daesh.
But it has not all been easy. The 2003 invasion of Iraq caused deep misgivings in the UAE, which saw it as a grave mistake. Their fear was that such an intervention would end up increasing Iran's influence over Iraq, or lead to civil war, which would destabilise the entire region.
Fears were realised when in 2005 a Shiite coalition close to Iran won the Iraqi elections and war broke out, leaving the UAE with its hands tied to try to influence status. Their main concern at the time was that a premature withdrawal of all US forces would further complicate status.
The renewed relationship with the Trump administration has led to the signature of a new security and cooperation agreement signed in 2017. reference letter In contrast to what happened in 1994, the contents of the agreement have been made public, and mainly relate to the presence of US troops on Emirati soil on a permanent basis. The agreement also covers the training of Emirati armed forces and regular joint exercises.
Thanks to this agreement, the US presence in the UAE is larger than ever. There are currently some 5,000 men deployed between the Al Dhafra airbase, the port of Jebel Ali and a few other small instructions or naval stations. At Al Dhafra air base alone, 3,500 men operate from F-15, F-22 and F-35 fighter jets, reconnaissance aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
For its part, the UAE has continued to develop its own military capabilities by acquiring US-made material, mainly anti-aircraft systems ("Patriot" and THAAD) and combat aircraft (110 F-16s). In addition, for a couple of years now, the UAE has shown great interest in acquiring the new F-35, although negotiations, not without some reluctance, are still ongoing.
In 2018, problems arose in supplying precision-guided munitions to both the UAE and Saudi Arabia, as both countries were using them in the Yemen War. The murder of Saudi journalist Jamal Kashoggi exacerbated resistance from the US congress , forcing President Trump to use his veto power in order to maintain the supply. This gives a measure of how decisive the current administration's attitude towards both countries is.
Despite all the difficulties mentioned above, the current US administration has redoubled its efforts to support the UAE in its regional policies, as they coincide with US objectives.
The first goal has been to build an anti-Iran alliance among Middle Eastern states that includes the UAE as partner core topic along with Saudi Arabia and Egypt. This plan is entirely in line with Abu Dhabi's aspiration to gain some leadership in the region, and is likely to succeed, as the UAE is likely to support the US in a solution to the Palestinian conflict that is quite in line with the Israeli proposal .
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is currently the UAE's most important ally in the region. Both states are financed by oil exports and both are equally wary of the expansionist ambitions of their powerful neighbours, especially Iran.
However, despite this alliance, the UAE has long feared that Saudi Arabia, using its unequal size in terms of population, military strength and oil production capacity, would seek to maintain a hegemonic position in the Persian Gulf.
In 1981, the Persian Gulf countries seized the opportunity to create an alliance that excluded the then major regional powers. Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the UAE created the committee Cooperation for the Arab States of the Gulf (GCC). This committee had a joint military force that never grew to any significant size. The biggest test of the GCC's weakness and ineffectiveness was Iraq's invasion of Kuwait without civil service examination by the supranational body.
As result of the above, the UAE relied on the US for its protection, the only country with both the will and the capacity to carry out the task of defending the small state against potential foreign aggression.
The consequence at the regional level is marked by the convergence of interests of Saudi Arabia and the UAE which, between 2011 and 2019, have pursued common regional political objectives, relying if necessary on their military capabilities.
For example, Bahrain's request for financial aid to the GCC in 2011 when its rulers felt threatened by Shia protest movements. However, its most significant intervention was its support for the coup d'état in Egypt against President Mohamed Morsi and the Muslim Brotherhood in 2013.
India
Socio-political and economic relations between the GCC members and India have always been very close, and have been based on the understanding that a secure and stable political and social environment in the Persian Gulf and Indian subcontinent are critical factors for the respective countries' development and their trans-regional ties.
From India's perspective, the improvement of its technological and economic development goes hand in hand with New Delhi's ability to strengthen its partnerships around the world. In this regard, the Persian Gulf countries, and especially the UAE, are seen as a bridge to knowledge, capabilities, resources and markets to enhance that development.
In 2016, the hitherto bilateral relations between the two countries were formalised in a strategic cooperation agreement called CSP(Comprehensive Strategic Partnership).
For the UAE, India is a modern country, a political phenomenon independent of the West that maintains strong religious and traditional roots without renouncing its diversity. In some ways, and with some reservations, it is a mirror for the UAE.
The agreement cooperation is cross-cutting and covers issues as diverse as counter-terrorism, exchange information and intelligence, anti-money laundering measures, cyber-security, as well as cooperation on subject defence, financial aid humanitarian, etc.
On the more economic side, the initiative includes concrete actions to facilitate trade and investment, with the UAE committing goal $75 billion to support the development of new generation infrastructure in India, especially railways, ports, roads, airports and industrial parks.
With regard to the energy sector, the agreement envisages the UAE's participation in the modernisation of the oil sector in all its branches, taking into account the development of a strategic reservation .
The part dealing with the development of technology for the peaceful use of nuclear energy, as well as cooperation in the aerospace sector including the development and joint launching of satellites, as well as the necessary ground control infrastructure and all necessary applications, is very significant.
Today, India has growing and multifaceted socio-economic ties with both Israel and the Persian Gulf countries, especially the UAE. The diaspora of Indian workers in the Gulf accounts for annual remittances of nearly $50 billion. Trade relations bring in more than $150 billion to India's coffers, and almost two-thirds of India's hydrocarbon needs come from the region. It is therefore evident that the new status is viewed with special interest from this part of the world, assessing opportunities and possible threats.
Clearly, any such agreement that at least a priori brings more stability and a normalisation of relations will always be beneficial, but its weaknesses and the possible evolution of status must also be taken into account.
Thus, from a geopolitical point of view, India has welcomed the re-establishment of relations between the UAE and Israel, as both are strategic partners.
The new landscape that is opening up between Israel and the GCC seems to bring a moderate and consistent solution to the Palestinian problem closer, making it much easier for Indian diplomacy to work .
But one must be cautious, and especially in this part of the world nothing is of one colour. This hopeful agreement could have a perverse effect, further polarising the jihadist sectors of the Arab world and pitting them even more against each other.
The possibility of the Persian Gulf region becoming the new battleground where Iranian and Israeli proxies clash cannot be completely ruled out, especially in Shia-controlled areas. However, this is not a likely option for the time being.
But for India it is even more important to manage the economic implications of the new treaty. With defence and security cooperation as key pillars, both sides are now beginning to contemplate the real economic potential of complementing their economies.
Reactions to the treaty: scenarios
Faced with an event as important as the one described above, it is to be expected that there will be reactions in various directions, and depending on these, the evolution of status may be different.
Actors likely to play a role in the different scenarios include the UAE and the new alliance, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Turkey, Palestine and the Muslim Brotherhood.
It should not be forgotten that the background to this treaty is economic. subject If its development is successful, it will bring stability to a region that has long been punished by all kinds of conflicts and clashes, and will lead to an exponential increase in trade operations, technology transfer and the opening of new routes and cooperation, mainly with Southeast Asia.
The role of the US will be decisive in any of the scenarios that may arise, but in any of them its position will be to minimise physical presence and support the signatories of the treaty with political, economic and defence actions through the supply of military materiel.
The treaty has a strong economic component fixed on the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. This is but one more sign of how the world's geopolitical centre of gravity is shifting to the Asia-Pacific region and this is one of the main reasons for the US's unconditional support.
Members of the UAE government have traditionally viewed more radical Islamist ideologies and policies as an existential threat to the country's core values. Both the Shiite sectarian regime in Iran and the Sunni Muslim Brotherhood, group , are seen as a constant threat to the stability of the region's powers.
For the UAE these transnational movements are a catalyst for radicalism across the region.
In view of the above, the following scenarios are plausible:
Scenario 1
For the moment, the Palestinians are the ones whose interests have been most harmed by the new status . Prominent figures in Palestinian society, as well as senior officials of the Palestinian Authority, have considered the new treaty a betrayal. As mentioned, the Palestinian issue is taking a back seat in the Arab world.
If, as is predicted, more countries join the new treaty in the coming months, the Palestinian Authority may try by all means to bring its demands and struggle back to the forefront. To this end, it would count on the support of Iran and its proxies and Turkey. This status would begin by delegitimising the governments of the countries that have aligned themselves with the UAE and Israel through a strong information campaign at all levels, with massive use of social networks in order to mobilise the most sensitive and pro-Palestinian population. The goal would be promote demonstrations and/or revolts that would create doubts among those who have not yet joined the pact. These doubts could lead to a change of decision or delay in new accessions, or these new treaty candidates could increase the Palestinian-related conditions for joining the treaty. This option is likely to be the most dangerous because of the possibility of internal dissension or disputes that could lead to an implosion of the pact.
It can be considered a likely scenario of intensity average/leave.
Scenario 2
The position that Saudi Arabia takes is core topic. And it will be decisive in gauging Iran's reaction. In the Middle East ecosystem, Iran is the power that has the most to lose from this new alliance. The struggle for hegemony within the Muslim world cannot be forgotten. And this struggle, which is also a religious one, pitting Shiites against Sunnis, has Iran and Saudi Arabia as its main protagonists.
Saudi Arabia is likely to join the treaty, but given the status, and in an attempt not to further strain relations with its main enemy, it may decide not to join the treaty, but to support it from the outside with specific or bilateral agreements. This would always be done with the rest of the Arab member countries, which would act as a bridge for its relations with Israel. It would be a way to wash its face and avoid express recognition of the state of Israel or direct relations with it. It should be borne in mind that there are pockets of Shiite majority in the country that could be spurred on by Iran.
However, in a worst-case scenario, Iran will react through its proxies, stepping up its activity in Yemen, trying to promote protests and revolts inside Saudi Arabia, reinforcing its support for Hamas in Palestine and Hezbollah in Lebanon and even its militias in Iraq.
Support for the protests that have already taken place in Sudan will also be part of this campaign. Sudan is a very unstable country, with a very weak Structures of power that is unlikely to be able to quell high-intensity revolts.
The goal would be to inflame the region under the cover of support for the Palestinian people in order to dissuade further accessions to the treaty, as well as undermine the treaty's effectiveness, giving the image of instability and insecurity in the region. This will discourage potential investors from approaching the UAE, attracted by the enormous economic possibilities it offers, while keeping Saudi Arabia occupied with its southern flank and its internal problems. Some action without a clear or acknowledged perpetrator against vessels transiting the Gulf, as has already happened, or the boarding of one by Iranian forces under any subject accusation or legal ruse, cannot be ruled out. Direct actions involving Iranian forces are unlikely.
Turkey may become involved by providing weapons, technology and even mercenary fighters to any of the factions acting as Iran's proxy.
This scenario can be considered as possible and of intensity average
Scenario 3
Iran needs either the governments or the populations of the various Middle Eastern countries to continue to see Israel as its main enemy and threat. Among other reasons because it is a narrative for domestic consumption that it uses recurrently to divert the attention of its own population from other subject problems. So far, the unifying element of this view of Israel has been the Palestinian conflict. It is therefore likely that actions will be taken that provoke a reaction from Israel. These actions may come from within the state of Israel itself, from Palestinian or Lebanese territory, always at position from Iran's proxies. A provocation that would result in an Israeli attack on Arab territory, most likely against Iran or Syria, cannot be ruled out: result . The final goal would not be the Hebrew state but undermining the instructions of the treaty, creating social unrest among the signatories, preventing Saudi Arabia's accession and being able to use the Palestinian conflict in its own interests.
This is a possible, high-intensity scenario.
Conclusions
The UAE's emergence as an emerging geopolitical power in the Middle East has been as surprising as it has been precipitous, as not so long ago international observers did not give much hope for the life of the new federation of small states that had just come into being.
By contrast, the UAE and Abu Dhabi, its largest and most prosperous emirate, in particular, has been increasing its position over the last decade, playing a decisive role in the region. To such an extent that, to this day, the UAE's actions are seen as having facilitated to some extent the changes we are witnessing.
Western policymakers are generally dazzled by the UAE's perceived liberalism and the ability of its elites to speak both literally and figuratively their own language. It is important that they familiarise themselves with the UAE's model in all its aspects and, importantly core topic, that they understand that Abu Dhabi expects to be treated by all as an equal. Dealing with the UAE in this way and considering it a robust and reliable partner also means sending them the message of a clear intention to support them.
One of the major consequences of this agreement may be to de-escalate the Palestinian conflict, if not end it, then permanently limit it. For generations, this conflict has been used by political and religious leaders across the Arab and Muslim world to distract their attention from other issues. It was an easy and readily available resource . But it is now recognised that it is a territorial dispute between two peoples, and future negotiations have no choice but to go down that road, with the focus on the outdated Palestinian leadership.
There is the not inconsiderable possibility that the agreement agreement could have a domino effect, leading other states in the region to follow in the UAE's footsteps, which in some cases would only mean publicising the de facto relations they already have with the state of Israel. In this sense, talks between Oman's foreign minister and his Israeli counterpart are known to have taken place just after the signature treaty with the UAE was signed.
The Israeli prime minister also held a meeting meeting with Sudanese leader Abdel Fattah Burhan, which could be a sign of upcoming moves on that flank as well.
Although the leak had consequences for a senior Sudanese official, the government did not deny the contacts. And it has all been confirmed when the US, advertisement of Sudan's forthcoming removal from the list of countries sponsoring terrorism, has followed the agreement between Israel and Sudan to normalise diplomatic relations.
For years, US policy has been to demilitarise its position in the Middle East; the cost of its presence has been very high compared to the benefits it brings, as well as generating some animosity. Both the US and other G8 members support the UAE as the region's economic leader. This support provides them with the ideal position to deploy their economic interests in the region(commodities, research and development & investment).
This position of US/UAE support (plus some G8 countries), strengthens the Arab country's role in the region at subject political and by default military, and in a way allows its new allies and supporters to have some influence in organisations such as OPEC, GCC, Arab League) and in neighbouring countries, but from a more Arab and less Western position.
On the issue of the UAE's purchase of the F-35, it is undeniable that this issue makes Israel uncomfortable despite the change in relations. The main reason for this is the fear of an equalisation in military capabilities that could be dangerous. However, this will not be an obstacle to progress on future peace agreements and on development of this one. Such a major operation would take years to materialise and by then, relations between Jerusalem and Abu Dhabi will have been consolidated. Indeed, it might even be welcomed by Israel, as it would strengthen its military capabilities vis-à-vis its main opponents in the region.
It is increasingly apparent in the Arab world that Israel is too small to harbour imperialist aspirations, in contrast to countries such as Turkey and Iran, both of which formed former empires, and which seem intent on trying to restore what they once achieved or were.
Instead, Israel is increasingly seen as a strong, prosperous and dynamic enough country that cooperation with Jerusalem is a smart move that can provide benefits to both sides.
The agreement between Israel and the UAE may have been driven in part by their fear of Iran's advances and the danger it poses. But the benefits to them go far beyond that issue.
These extend to economic investment possibilities, finance, tourism and especially the sharing of know-how. The UAE can benefit from Israel's technological and scientific edge just as Israel can profit from the UAE's position as an international service centre and a key gateway to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. entrance .
In relation to the entrance gateway to the Indian subcontinent, it should be noted that for India the most important part of agreement is to manage the economic side of the synergies caused by it.
The UAE and Bahrain can become intermediaries for Israeli exports of both commodities and services to various parts of the world.
Israel has a strong defence, security and surveillance equipment industry. It is a leader in dryland farming, solar energy, horticulture, high-tech jewellery and pharmaceuticals.
Moreover, Israel has the capacity to provide highly skilled and semi-skilled labour to GCC countries, especially if they come from Sephardic and Mizrahi ethnic groups, many of whom speak Arabic. Even Israeli Arabs can find opportunities to help further build ties and bridges across the cultural divide.
Israel's incursion into the Gulf has the potential to influence the political-economic architecture that India has been building for years, being, for example, one of the largest suppliers of labour, foodstuffs, pharmaceuticals etc.
The largest customers in Dubai's real estate market, as well as the largest issue of tourists visiting the country, come from India. But in this changing scenario there is scope for three-way synergies, making India a major player in this.
The final conclusion that can be drawn by way of evaluation for the future is that this new relationship will undoubtedly be a model for other Sunni states to follow, transforming a region mired in 19th century conflicts into one of the power centres of the 21st century.
* Lieutenant Colonel of Infantry. Geopolitical Analyst
REFERENCES
Acharya, Arabinda, 'COVID-19: A Testing Time for UAE-India Relations? A Perspective from Abu Dhabi", Strategic Analysis, September 2020.
Arab Center for Research and Policy studies, 'The Abraham Agreement: normalization of relations or announcement of an existing Emirati - Israeli alliance? Qatar, August 2020.
Karsh, Ephraim, ed., "The Israel-UAE Peace: A Preliminary Assessment", Ramat Gan: The Begin-Sadat Center for Strategic Studies, cafeteria-Ilan University, September 2020.
Salisbury, Peter, "Risk Perception and Appetite in UAE Foreign and National Security Policy", The Royal Institute of International Affairs, Chatham House Middle East and North Africa Programme, London: July 2020.
Steinber, Guido, "Regional Powers, United Arab Emirates", German Institute for International and Security Affairs, Berlin, July 2020.
![Nicolás Maduro during a broadcasted speech [Gov. of Venezuela]. Nicolás Maduro during a broadcasted speech [Gov. of Venezuela].](/documents/16800098/0/nicolas-maduro.jpg/61303fce-8b6f-0835-73c1-7dc5fe8e6e8f?t=1621887713513&imagePreview=1)
Nicolás Maduro during a broadcasted speech [Gov. of Venezuela] ▲ Nicolás Maduro during a broadcasted speech [Gov. of Venezuela].
ESSAY / Isabelle León Graticola
It is no secret to anyone that Venezuela is going through the most convoluted economic and social crisis in its history, a crisis in which the creators have manipulated the existence of the people, degrading its integrity, and extinguishing everything that once characterized Venezuela.
The country holds a key geopolitical location that serves as a route for North America and the Caribbean to the rest of South America. Likewise, the country is endowed with abundant natural resources like natural gas, iron ore, diamonds, gold, and oil.1 Venezuela has the largest proven oil reserves in the world, with 302 billion barrels in January 2018, emanating an extremely rich country with astonishing potential.2 However, this crisis has not only hindered people's lives but has ironically dissipated the country's resources to consolidate the pillars of the regime to such an extent that today the government of Nicolás Maduro is importing oil from Iran. Inadequate policies that have weakened the society's sense of responsibility and nationalism, decreased foreign investment out of lack of trust, and annihilated the state-led oil production, therefore reinforcing the country's economic downfall and hyperinflation.
The Venezuelan government, headed by Nicolás Maduro, has managed its way to continue holding power despite accusations of corruption, crimes against humanity, and even drugs trafficking involvement. The perplexing partner-economic and political crisis has created an unsustainable and violent context in which poorly informed people are manipulated by the government through speeches that take big significance on how society perceives the actual situation, as well as other countries' statements on the crisis. Up to this point, it has become difficult to understand what keeps bolstering this regime, but if the situation is analysed from the nucleus, the well-orchestrated rhetoric of Chávez and his successor, Maduro, has contributed to support the ends and sustainment of the regime.
Since Maduro reached power, poverty motivated violence has been rampant in Venezuela and insecurity has become a significant part of society's dynamics. Consequently, many protests against the government demanding for freedom and better living standards have taken place. Maduro's regime has been forced to employ tools such as fake news and hateful rhetoric to soften the anger of the people by manipulating them and brainwashing the armed forces to avoid uprisings.
This article aims to analyse how Maduro's rhetoric has maintained a minority in the wrong side of history and a majority in constant battle by making erroneous accusations to third parties to justify the perturbed situation, while the government keeps enriching its wallet at the cost of the people and its smudged operations. Such feverish society gave rise to pure uncertainty, to a place where disinformation takes the form of a lethal weapon for the dangerous context in which it exists.
The background: Chávez's indoctrinated society
First, it is necessary to clarify that the focus of this article is merely on the rhetorical aspect as a pillar of the regime. However, when it comes to the background that has sustained Maduro's administration up to this day, there is a more complex reality, full of crime, death, manipulation, and corruption. Venezuela is an almost abnormal reality because, after more than twenty years, it is still tied to a group of people who have taken absolutely everything from it. From a man that portrayed nothing but hope for the poor, to one who has managed his way sticking to policies damaging to the very people they mean to help, and which, sooner or later, will make the regime collapse.
Hugo Chávez's presidency was characterized by a tremendous and persuasive oratory; he knew how to get to the people. Chávez's measures and campaigns were based on a psychological strategy that won him the admiration of the most impoverished classes of the country. Chávez arrived and gave importance and attention to the big mass of the population that previous governments had systematically neglected. People felt the time had come for them to have what they never had before. Filled with charisma and political mastery, his speeches always contained jokes, dances, and colloquial phrases that were considered indecent by the country's highest class and often misunderstood abroad.
Chávez always built a drastic separation between the ideals of the United States and Venezuela and looked for ways to antagonize the former with his rhetoric. He began to refer to George W. Bush as "Mr. Danger", an imperial literary character of one of the most famous Venezuelan novels, Doña Bárbara.3
Hugo Chávez is one of the most revolutionary characters in Venezuelan history, one who brought the convoluted situation that today perpetuates in the country. Chávez persecuted journalists and political opponents, expropriated lands, nationalized Venezuela's key industries such as telecommunications, electricity, and the refining processes of heavy crudes, and slowly degraded the society as the exercise of power was directed to hold complete control of Venezuela's internal dynamics.4
Chávez extended education and medical assistance to the least favoured classes and improved the living conditions of the needy. This policy did nothing but create among these classes a culture of dependence on the government. Chávez's supporters or Chavistas were the pillars that buttressed the government, while the wealthy were catalogued as "squealing pigs" and "vampires. "5 The Chavistas admired Chavez's charismatic character and his constant gifts; he gave them fridges and TVs, gadgets that they could never afford on their own. He also constructed buildings, under the "mission statement Vivienda" initiative, to give people living in slums a 'proper' home. All of this was possible because the oil prices at the time were skyrocketing; he used the oil income to buy his support. The general standard of life, however, continued to be poor. The government knew what to give and how to manipulate to stay in power, and that is precisely what made Hugo Chávez so powerful and almost impossible to defeat despite strong opposition.
Historically, the United States has opposed left-wing governments in Latin America, so Chávez condemned the US, by referring to them as an imperialist power, or the "Empire". He disgraced US leaders and actions and transferred that anti-imperialistic and anti-capitalist approach to the population, part of which supported him and was blindly loyal to the cause. Chávez's alliance with Cuba under Fidel Castro led to the supply of oil at cut-rate prices, all related to the desire of reducing US economic influence in South America. Chávez's populist initiatives were the tenets of his administration and controversial foreign policy. These, along with his rhetoric and opposition from the Venezuelan wealthy class, deeply polarized the society and gave rise to what Venezuela has today: a divided society that has suffered from the lack of basic necessities, disinformation, and integrity.
Currently, the spokesmen of the Government of Nicolás Maduro address citizens at all hours from public channels and social networks to stir up the disgruntlement of the population toward the external enemy.6 Despite the poorly prepared speeches, the lack of vocabulary, and the improper formulation of sentences, Maduro has kept the colloquial and unformal rhetoric that characterised Chávez, but has failed to draw the connection that the late president enjoyed. The anti-imperialist strategy has been maintained, and, as the justification of the crisis, it has become the epicenter of the regime's speech. Nicolás Maduro's rhetoric revolves around two words: the US and the "Patria", a word frequently used by Chávez.
The base of Maduro's rhetoric: the love for Chávez
Shortly before dying in March 2013, Hugo Chávez appointed Vice President Nicolás Maduro as his successor. Chávez's charisma and legacy are what somehow ensured him that Maduro would provide a smooth transition. After Chávez's passing, Maduro took advantage of the momentum and sentiment that the Chavistas revealed and ensured that if picked, he would follow the steps of his predecessor and would continue to strengthen the 'Bolivarian Revolution'. Along with the continuity with Chávez's legacy, the defence of Venezuelan sovereignty in front of the US, and the social equality became the key messages of his administration.7 Nevertheless, Maduro had little support from the elites and inherited a country that was already economically weak due to the downfall of the oil prices and corruption.
In Chávez's wake, Maduro appealed to the emotion of the audience. He strongly claimed that the people were there for the 'Comandante' and said that "his soul and his spirit was so strong that his body could not stand it anymore, and he was released and now through this universe expanding filling us with blessings and love". He knew what this meant for the people and a crying audience exclaimed "Chávez lives, the fight goes on".
Maduro filled his rhetoric with the love for Chávez. He acknowledged that the Chavistas worshipped him as if he was God and that for ideological reasons, support for Maduro was guaranteed. Nevertheless, others recognised that the situation in the country was not favourable and questioned Maduro's ability to fill the void left by Chávez. When Maduro took power, the country entered a period of reinforced economic decline accompanied by hyperinflation that nowadays exceeds 10 million percent.8 As it was previously stated, the conditions of poverty surpass anything seen before in the country, which is now on the brink of collapse.
Furthermore, Venezuela went through two rounds of mass protests, in 2014 and 2018, that demanded freedom and change. Unfortunately, and as was expected from the government, thousands of violations of human rights were part of the demonstration's dynamics as brutal repression and the unjust imprisonment of demonstrators took place all along. Simultaneously, Maduro managed to call for rallies on the days of the major opposition's marches and retained the populist speech based on ideological arguments and emotional appeals among the minority of supporters to consolidate his power in Venezuela. Last year, in a regime rally on February 23rd, he condemned the elites as he explained that he was certain that from the bottom of his Chavista sentiment of loyalty to this battle, he was never going to be part of one. He stated that Venezuela will continue to be Patria for more many years to come.
The ongoing crisis has forced many to survive rather than to live, but despite all, Maduro remains in control. Maduro has kept Chávez's anti-imperialist policy and has rejected any minimum support from the United States. The government takes advantage of the hunger and the vulnerable situation of its people and makes sure that it remains as the only source of food. It does not take responsibility and instead, blames the crisis on the 'economic war' that the US has imposed on Venezuela.9 When Juan Guaidó sworn himself the legitimate president, Maduro's supporters started raising firms in a campaign called "Hands off Venezuela", while the US was trying to get humanitarian assistance into Venezuela through the Colombian border in the name of Guaidó.
In this sense, he explained in the same concentration speech that they were defending the national territory and the right to live freely and independently. Although it may seem ironic, because the government has killed hundreds of people with its police brutality and torture, this rhetoric is what has kept him the support of the hardcore revolutionary followers. The "Hands off Venezuela", was shouted and accompanied by the worst English pronunciation -that characterizes Maduro-, and followed with insults to Guaidó.
As Maduro yelled "puppet, clown, and beggar of imperialism and Donald Trump. If he is the President, where are the economic and social measures that he has applied for the people? It is a game to deceive and manipulate, it is a game that has failed, the coup d'état has failed" as the network audience shouted, "jail him, jail him!". He drew his speech to a hardcore anti-imperialist audience and firmly stated that the US intended to invade Venezuela and enslave it. Maduro finalized his speech by shouting "wave up the flag, up the Patria, for the people in defense of the Revolution".
Recently, the US State Department released a price for the capture of Maduro and his cabinet, not only for the crimes committed against the Venezuelan population, but also because of their involvement in a huge drug-trafficking network. With this, the regime's position has become more vulnerable and simultaneously pragmatic, but as tough actions were taken against possible threats and opposing figures, Maduro's rhetoric remains to deny its status and manipulating those that still support him. In another public speech, he stated that "Donald Trump's government, in an extravagant and extreme, vulgar, miserable action, launched a set of false accusations and like a racist cowboy of the 21st century, put a price on the heads of revolutionaries that are still willing to fight them". He one more time accused the US of being the main cause of the economic crisis of Venezuela.
Nicolás Maduro's speech has always been directed to the hardcore revolutionaries, those that worship Chávez since the beginning and who firmly believe in the socialist cause. Maduro has maintained his rhetoric despite the changes in the internal situation of the country; he has held an enduring method for antagonizing the opposition, the Venezuelan upper class, and the United States. On the other hand, regarding the strategic foreign allies, the regime openly gives declarations to support them, but again to somehow antagonize the United States. Indeed, this was the case of the US assassination of Qasem Soleimani, the Iranian top commander, in which government representatives attended the Iranian embassy to give the condolences in the name of the regime and swore to avenge Soleimani's death. The administration of Nicolás Maduro has no gray areas, everything is either black or white; the opposition, the upper class, the US, and the US-influenced countries are the enemies, and the rhetoric rarely leans toward a conciliatory message, rather has always revolved around these conflicting parties.
What is left
Twenty years have passed since the Chavismo arrived in the country. Nowadays, a passionate minority of the population keeps supporting Maduro. His regime continues to train armed groups to combat discontent headed by opposition leader Juan Guaidó. The Chavismo keeps being strong, but it has been fragmented by those who believe that the revolution ended at the moment Chávez died, and the ones that are convinced that supporting Maduro means being loyal to Chávez. In the case of Juan Guaidó, he keeps doing his efforts. He still has relative support and keeps being a source of hope. Nevertheless, many criticize the fact that he let again the people cool down. A close change is expected, but no one knows what the movements behind are. Meanwhile, the people will continue suffering and trying to survive.
Upon reflection, it can be noticed that Maduro's entire argumentation revolves around a confrontational rhetoric: the US and capitalism against Venezuela; Guaidó against the Patria; the elites against the Revolution.10 Far from recognising the reality that the country faces and taking actions to improve it, this confrontational approach simply places the blame on those who have tried to bring a change in the internal dynamics of Venezuela. The regime has managed to construct a national united front against a common foreign enemy and to demonize the opposition.
Chávez and Maduro's rhetoric has followed a tangible objective: the Revolution. Maduro's regime up to this point is searching for a way to consolidate its power and sustain itself as the best way to elude a rather somber future in jail. This never-ending nightmare should have long ago collapsed due to the economic catastrophe, hyperinflation, political repression, human rights violations, and the lack of direction for Venezuela. Behind what maintains this structure there is nothing but the exercise of power and the almost absolute control of society. The Patria that they constantly speak of is running out of fuel to keep going. Nonetheless, the rhetorical deceptions of the Bolivarian revolution, which for two decades have appealed to the popular classes, settled in the collective mindset of the Chavismo and brought space for support in the Venezuelan society.
Chávez and Maduro's presidencies have been based on educating and changing the mindset of the population as they wanted; a population that is content with one box of food a month and which, unfortunately, hunts for the easy means to achieve its goals instead of fighting to improve its lot.
Today, the regime is fed on the memory of Hugo Chávez, on his promises, on his battle. As long as it keeps generating an illusion on the supporters, Maduro will appeal to it as a pillar of his administration and of the Revolution.
1. Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries. Venezuela facts and figures. 2019, https://www.opec.org/opec_web/en/about_us/171.htm. Accessed 28 Nov. 2019.
2. US Energy Information Administration - EIA - Independent Statistics and Analysis. Venezuela. Jan. 2019, https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis.php?iso=VEN. Accessed 28 Nov. 2019.
3. Livingstone, G. (2013, March 10). The secret of Hugo Chavez's hold on his people. Retrieved March 17, 2020, from https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/americas/the-secret-of-hugo-chavezs-hold-on-his-people-8527832.html
4. El País. (2007, January 08). Chávez anuncia la nacionalización del servicio eléctrico y las telecomunicaciones. Retrieved July 01, 2020, from https://elpais.com/internacional/2007/01/08/actualidad/1168210811_850215.html
5. The Guardian (2012, October 08). Hugo Chávez: A victory of enduring charisma and political mastery. Retrieved March 17, 2020, from https://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/oct/08/hugo-chavez-victory-political-venezuela
6. Twitter, F., & Miraflores, P. (2017, July 23). Maduro, his ministers and the corruption of language. Retrieved March 15, 2020, from https://elpais.com/elpais/2017/07/22/opinion/1500746848_239358.html
7. Grainger, S. Hugo Chávez and Venezuela Confront his Succession. Dec. 2012. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-20678634. Accessed 29 Nov. 2019.
8. Sánchez, V. Venezuela hyperinflation hits 10 million percent. 'Shock therapy' may be only chance to undo economic damage. Aug. 2019. https://www.cnbc.com/2019/08/02/venezuela-inflation-at-10-million-percent-its-time-for-shock-therapy.html. Accessed 29 Nov. 2019.
9. TVVenezuela. The CLAP boxes no longer have anything to feed Venezuelans. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MelhZDbiFQQ. Sept. 2019. Accessed 30 Nov. 2019.
10. Delgado, A., & Herrero, J. (2019, February 12). Venezuela rhetorics on Twitter: Guaidó vs. Maduro. Retrieved March 18, 2020, from https://beersandpolitics.com/retoricas-de-venezuela-en-twitter-guaido-vs-maduro
Showing the range 1 - 10 of 52 results.
