Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Middle East .
Iran Country Risk Report (May 2019)
The sanctions that the United States is implementing against the Islamic Republic of Iran since November 2018 are the toughest sanctions ever imposed on Iran. They threaten to cut off foreign countries and companies dealing with Iran from the US financial system in order to deter business with Iran so to curtail the impact of proxy groups on the Middle East's security and stability. The aim of this country report is to provide the most recent analysis of the Iran's economic and political situation, and estimate its evolution in the short and medium term. It presents an overlook of specific clues about matters related to political risk, as well as the effect that sanctions may have on the Iranian economy, and the prospects for political stability all over the region.
Alona Sainetska
 Report [pdf. 13,5MB] [pdf. 13,5MB
Report [pdf. 13,5MB] [pdf. 13,5MB
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Effects of sanctions
The re-imposition of US sanctions will maintain the Iranian economy in recession during the remaining months of 2019. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the economic meltdown will be very unlikely to happen, as the volume of oil exports is still significant, crude prices are going to continue to rise and other major powers' opinion will still differ from the US's. The multinational companies dependent on US financial system will continue leaving the Iranian market, partially leading to declining of the foreign investment, but SMEs will be almost unaffected and new forms of trading are likely to emerge soon.
Iran is likely to build stronger economic and political ties with India, China and Russia, thus giving them more power and openness to new trading opportunities, basically due to lack of any other possible partner on the horizon in the mid-term.
The prices are likely to keep growing up in the following months reaching the average inflation of 31.2% in 2019-20; still the risk of hyperinflation is discarded due to the fact that Iran is able to meet a significant share of local demand through local production.
Backed by support from the EU, Iran is promised to obtain in the mid-term a special mechanism of payments (Special Purpose Vehicle) for its oil and other exports (possibly through a barter system) in order to conduct trading outside of the competence of the US sanctions. This is likely to create some tensions between Europe and the US but they will not be powerful enough to split the long-lasting alliance between the two.
Oil and gas
The Iran's production of oil will probably continue to decrease affecting the world's oil price.
Five from the eight initial major buyers (Italy, Greece and Taiwan have already stopped their purchases from Iran) are and will be buying Iranian oil now that the waivers have been extended for the following 90 days. Thereby, the Iranian oil will still remain in demand during the following years, and Iran's government is likely to find solutions for its selling and exportation, even though illegally, in the mid and long-term. Thus, the United States is unlikely to meet its earlier target of driving Iranian oil exports to zero.
Iraq will continue to buy natural gas from Iran in order to use it in the production of electricity, becoming the second largest customer. Taking into account the fact that there is a sort of competence between US and Iran for the influence over Iraq, it can fuel a further deterioration of their relations. It is also plausible that more buyers will emerge if some new forms of trading, which do not rely on dollar, appear soon.
Even though the modest production growth is likely to continue, Iran won't be able to unilaterally monetise its natural gas resources due to lack of financial partners and investment, especially from the West. However, it will be able to fulfil its domestic demand and sustain trade with Turkey.
Iran's ability to increase production and exports of natural gas will be almost improbable, unless the relations with the United States are improved or support from international partners in defiance of sanctions is reinforced. Nevertheless, if Iran manages to accomplish current development projects, its export pipeline capacity will increase from 46.4 bcm/year in 2018, to 119.7 bcm/year to the regional and global markets in a long run. China, India and Pakistan will play a significant role in Iran's natural gas sector.
The domestic scene
Iran will continue demonstrating considerable resilience in coping with US sanctions, and is likely to continue to fully implement the commitments of JCPOA as long as China, Russia, or countries which are non-members of the deal, such as India, continue to trade with it, and if EU continues maintaining its constructive attitude. In this case, even a greater international support and United Nations diplomatic intervention is expected in the mid-term. However, on a longer run, the JCPOA future will depend upon the economic situation and complex political battles between moderates and hardliners in Tehran.
The current deterioration of the economic conditions in Iran, the rial devaluation and growing inflation, together with already-high unemployment will provoke a further popular discontent which is likely to maintain the protests but without any considerable probability to threaten the Iranian political stability or lead to leadership's rupture during the upcoming years.
The sanctions are likely to produce some adverse effects on the local political scene over the longer term, as Iranian hardliners may take advantage of them and the popular frustration and obtain the victory in the coming 2020 parliamentary elections and the 2021 presidential poll. As a result, any possibility for future cooperation with US will equal zero.
The struggle for power has already started in the Islamic Republic in the midst of US sanctions and ahead a new electoral cycle.
![Ayatollah Ali Khamenei speaking to Iranian Air Force personnel, in 2016 [Wikipedia]. Ayatollah Ali Khamenei speaking to Iranian Air Force personnel, in 2016 [Wikipedia].](/documents/10174/16849987/khamenei-blog.jpg)
▲ Ayatollah Ali Khamenei speaking to Iranian Air Force personnel, in 2016 [Wikipedia].
ANALYSIS / Rossina Funes and Maeve Gladin
The failing health of Supreme Leader Sayyid Ali Hosseini Khamenei, 89, brings into question the political aftermath of his approaching death or possible step-down. Khamenei's health has been a point of query since 2007, when he temporarily disappeared from the public eye. News later came out that he had a routine procedure which had no need to cause any suspicions in regards to his health. However, the question remains as to whether his well-being is a fantasy or a reality. Regardless of the truth of his health, many suspect that he has been suffering prostate cancer all this time. Khamenei is 89 years old -he turns 80 in July- and the odds of him continuing as active Supreme Leader are slim to none. His death or resignation will not only reshape but could also greatly polarize the successive politics at play and create more instability for Iran.
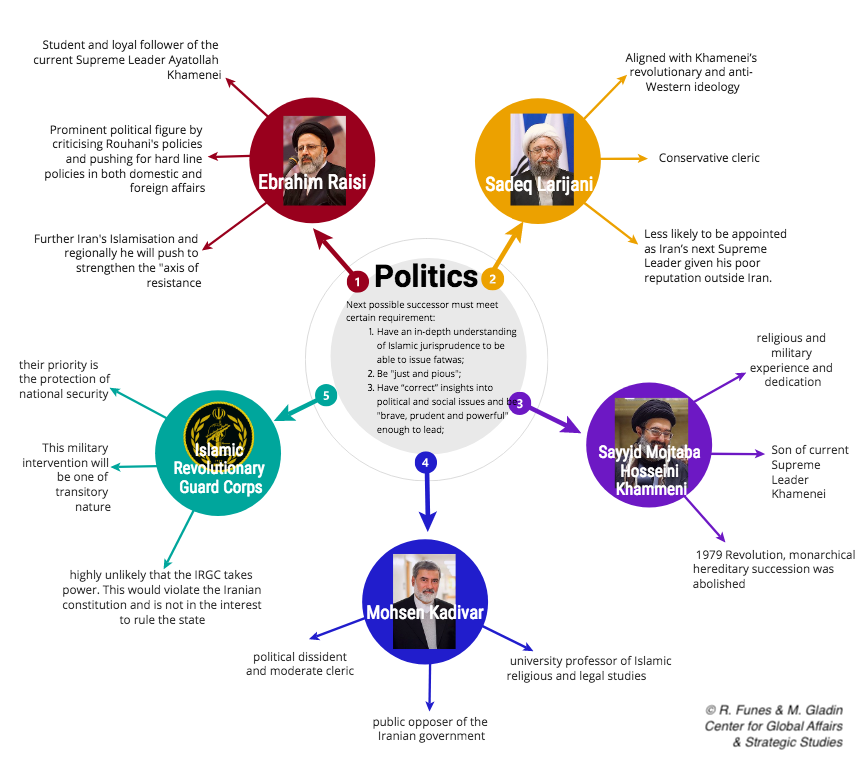
The next possible successor must meet certain requirements in order to be within the bounds of possible appointees. This political figure must comply and follow Khamenei's revolutionary ideology by being anti-Western, mainly anti-American. The prospective leader would also need to meet religious statues and adherence to clerical rule. Regardless of who that cleric may be, Iran is likely to be ruled by another religious figure who is far less powerful than Khamenei and more beholden to the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC). Additionally, Khamenei's successor should be young enough to undermine the current opposition to clerical rule prevalent among many of Iran's youth, which accounts for the majority of Iran's population.
In analyzing who will head Iranian politics, two streams have been identified. These are constrained by whether the current Supreme Leader Khamenei appoints his successor or not, and within that there are best and worst case scenarios.
Mahmoud Hashemi Shahroudi
Mahmoud Hashemi Shahroudi had been mentioned as the foremost contender to stand in lieu of Iranian Supreme Leader Khamenei. Shahroudi was a Khamenei loyalist who rose to the highest ranks of the Islamic Republic's political clerical elite under the supreme leader's patronage and was considered his most likely successor. A former judiciary chief, Shahroudi was, like his patron, a staunch defender of the Islamic Revolution and its founding principle, velayat-e-faqih (rule of the jurisprudence). Iran's domestic unrest and regime longevity, progressively aroused by impromptu protests around the country over the past year, is contingent on the political class collectively agreeing on a supreme leader competent of building consensus and balancing competing interests. Shahroudi's exceptional faculty to bridge the separated Iranian political and clerical establishment was the reason his name was frequently highlighted as Khamenei's eventual successor. Also, he was both theologically and managerially qualified and among the few relatively nonelderly clerics viewed as politically trustworthy by Iran's ruling establishment. However, he passed away in late December 2018, opening once again the question of who was most likely to take Khamenei's place as Supreme Leader of Iran.
However, even with Shahroudi's early death, there are still a few possibilities. One is Sadeq Larijani, the head of the judiciary, who, like Shahroudi, is Iraqi born. Another prospect is Ebrahim Raisi, a former 2017 presidential candidate and the custodian of the holiest shrine in Iran, Imam Reza. Raisi is a student and loyalist of Khamenei, whereas Larijani, also a hard-liner, is more independent.
1. MOST LIKELY SCENARIO, REGARDLESS OF APPOINTMENT
1.1 Ebrahim Raisi
In a more likely scenario, Ebrahim Raisi would rise as Iran's next Supreme Leader. He meets the aforementioned requirements with regards to the religious status and the revolutionary ideology. Fifty-eight-years-old, Raisi is a student and loyal follower of the current Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei. Like his teacher, he is from Mashhad and belongs to its famous seminary. He is married to the daughter of Ayatollah Alamolhoda, a hardline cleric who serves as Khamenei's representative of in the eastern Razavi Khorasan province, home of the Imam Reza shrine.
Together with his various senior judicial positions, in 2016 Raisi was appointed the chairman of Astan Quds Razavi, the wealthy and influential charitable foundation which manages the Imam Reza shrine. Through this appointment, Raisi developed a very close relationship with the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), which is a known ideological and economic partner of the foundation. In 2017, he moved into the political sphere by running for president, stating it was his "religious and revolutionary responsibility". He managed to secure a respectable 38 percent of the vote; however, his contender, Rouhani, won with 57 percent of the vote. At first, this outcome was perceived as an indicator of Raisi's relative unpopularity, but he has proven his detractors wrong. After his electoral defeat, he remained in the public eye and became an even more prominent political figure by criticizing Rouhani's policies and pushing for hard-line policies in both domestic and foreign affairs. Also, given to Astan Quds Foundation's extensive budget, Raisi has been able to secure alliances with other clerics and build a broad network that has the ability to mobilize advocates countrywide.
Once he takes on the role of Supreme Leader, he will continue his domestic and regional policies. On the domestic front, he will further Iran's Islamisation and regionally he will push to strengthen the "axis of resistance", which is the anti-Western and anti-Israeli alliance between Iran, Syria, Hezbollah, Shia Iraq and Hamas. Nevertheless, if this happens, Iran would live on under the leadership of yet another hardliner and the political scene would not change much. Regardless of who succeeds Khamenei, a political crisis is assured during this transition, triggered by a cycle of arbitrary rule, chaos, violence and social unrest in Iran. It will be a period of uncertainty given that a great share of the population seems unsatisfied with the clerical establishment, which was also enhanced by the current economic crisis ensued by the American sanctions.
1.2 Sadeq Larijani
Sadeq Larijani, who is fifty-eight years old, is known for his conservative politics and his closeness to the supreme guide of the Iranian regime Ali Khamenei and one of his potential successors. He is Shahroudi's successor as head of the judiciary and currently chairs the Expediency Council. Additionally, the Larijani family occupies a number of important positions in government and shares strong ties with the Supreme Leader by being among the most powerful families in Iran since Khamenei became Supreme Leader thirty years ago. Sadeq Larijani is also a member of the Guardian Council, which vetos laws and candidates for elected office for conformance to Iran's Islamic system.
Formally, the Expediency Council is an advisory body for the Supreme Leader and is intended to resolve disputes between parliament and a scrutineer body, therefore Larijani is well informed on the way Khamenei deals with governmental affairs and the domestic politics of Iran. Therefore, he meets the requirement of being aligned with Khamenei's revolutionary and anti-Western ideology, and he is also a conservative cleric, thus he complies with the religious figure requirement. Nonetheless, he is less likely to be appointed as Iran's next Supreme Leader given his poor reputation outside Iran. The U.S. sanctioned Larijani on the grounds of human rights violations, in addition to "arbitrary arrests of political prisoners, human rights defenders and minorities" which "increased markedly" since he took office, according to the EU who also sanctioned Larijani in 2012. His appointment would not be a strategic decision amidst the newly U.S. imposed sanctions and the trouble it has brought upon Iran. Nowadays, the last thing Iran wants is that the EU also turn their back to them, which would happen if Larijani rises to power. However it is still highly plausible that Larijani would be the second one on the list of prospective leaders, only preceded by Raisi.
 |
2. LEAST LIKELY SCENARIO: SUCCESSOR NOT APPOINTED
2.1 Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps
The IRGC's purpose is to preserve the Islamic system from foreign interference and protect from coups. As their priority is the protection of national security, the IRGC necessarily will take action once Khamenei passes away and the political sphere becomes chaotic. In carrying out their role of protecting national security, the IRGC will act as a support for the new Supreme Leader. Moreover, the IRGC will work to stabilize the unrest which will inevitably occur, regardless of who comes to power. It is our estimate that the new Supreme Leader will have been appointed by Khamenei before death, and thus the IRGC will do everything in their power to protect him. In the unlikely case that Khamenei does not appoint a successor, we believe that there are two unlikely options of ruling that could arise.
The first, and least likely, being that the IRGC takes rule. Moreover, it is highly unlikely that the IRGC takes power. This would violate the Iranian constitution and is not in the interest to rule the state. What they are interested in is having a puppet figure who will satisfy their interests. As the IRGC's main role is national security, in the event that Khamenei does not appoint a successor and the country goes into political and social turmoil, the IRGC will without a doubt step in. This military intervention will be one of transitory nature, as the IRGC does not pretend to want direct political power. Once the Supreme Leader is secured, the IRGC will go back to a relatively low profile.
In the very unlikely event that a Supreme Leader is not predetermined, the IRGC may take over the political regime of Iran, creating a military dictatorship. If this were to happen, there would certainly be protests, riots and coups. It would be very difficult for an opposition group to challenge and defeat the IRGC, but there would be attempts to overcome it. This would be a regime of temporary nature, however, the new Supreme Leader would arise from the scene that the IRGC had been protecting.
2.2 Mohsen Kadivar
In addition, political dissident and moderate cleric Mohsen Kadivar is a plausible candidate for the next Supreme Leader. Kadivar's rise to political power in Iran would be a black swan, as it is extremely unlikely, however, the possibility should not be dismissed. His election would be highly unlikely due to the fact that he is a board member critic of clerical rule and has been a public opponent of the Iranian government. He has served time in prison for speaking out in favor of democracy and liberal reform as well as publicly criticizing the Islamic political system. Moreover, he has been a university professor of Islamic religious and legal studies throughout the United States. As Kadivar goes against all requirements to become successor, he is highly unlikely to become Supreme Leader. It is also important to keep in mind that Khamenei will most likely appoint a successor, and in that scenario, he will appoint someone who meets the requirements and of course is in line with what he believes. In the rare case that Khamenei does not appoint a successor or dies before he gets the chance to, a political uprising is inevitable. The question will be whether the country uprises to the point of voting a popular leader or settling with someone who will maintain the status quo.
In the situation that Mohsen Kadivar is voted into power, the Iranian political system would change drastically. For starters, he would not call himself Supreme Leader, and would instill a democratic and liberal political system. Kadivar and other scholars which condemn supreme clerical rule are anti-despotism and advocate for its abolishment. He would most likely establish a western-style democracy and work towards stabilizing the political situation of Iran. This would take more years than he will allow himself to remain in power, however, he will probably stay active in the political sphere both domestically as well as internationally. He may be secretary of state after stepping down, and work as both a close friend and advisor of the next leader of Iran as well as work for cultivating ties with other democratic countries.
2.3 Sayyid Mojtaba Hosseini Khamenei
Khamenei's son, Sayyid Mojtaba Hosseini Khamenei is also rumored to be a possible designated successor. His religious and military experience and dedication, along with being the son of Khamenei gives strong reason to believe that he may be appointed Supreme Leader by his father. However, Mojtaba is lacking the required religious status. The requirements of commitment to the IRGC as well as anti-American ideology are not questioned, as Mojtaba has a well-known strong relationship with the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps. Mojtaba studied theology and is currently a professor at Qom Seminary in Iran. Nonetheless, it is unclear as to whether Mojtaba's religious and political status is enough to have him considered to be the next Supreme Leader. In the unlikely case that Khamenei names his son to be his successor, it would be possible for his son to further commit to the religious and political facets of his life and align them with the requirements of being Supreme Leader.
This scenario is highly unlikely, especially considering that in the 1979 Revolution, monarchical hereditary succession was abolished. Mojtaba has already shown loyalty to Iran when taking control of the Basij militia during the uproar of the 2009 elections to halt protests. While Mojtaba is currently not fit for the position, he is clearly capable of gaining the needed credentials to live up to the job. Despite his potential, all signs point to another candidate becoming the successor before Mojtaba.
3. PATH TO DEMOCRACY
Albeit the current regime is supposedly overturned by an uprising or new appointment by the current Supreme Leader Khamenei, it is expected that any transition to democracy or to Western-like regime will take a longer and more arduous process. If this was the case, it will be probably preceded by a turmoil analogous to the Arab Springs of 2011. However, even if there was a scream for democracy coming from the Iranian population, the probability that it ends up in success like it did in Tunisia is slim to none. Changing the president or the Supreme Leader does not mean that the regime will also change, but there are more intertwined factors that lead to a massive change in the political sphere, like it is the path to democracy in a Muslim state.
Interview with Ambassador Francisco Pascual de la Parte, author of "The Returning Empire. The 2014-2017 War in Ukraine"
![Francisco Pascual de la Parte, during the presentation from his book [Manuel Castells] Francisco Pascual de la Parte, during the presentation from his book [Manuel Castells]](/documents/10174/16849987/noticia-donbass-blog.jpg)
▲ Francisco Pascual de la Parte, during the presentation from his book [Manuel Castells]
INTERVIEW / Vitaliy Stepanyuk
Few have a knowledge as direct of Russia's relations with Ukraine and other territories of the former USSR as Francisco Pascual de la Parte, who has been minister-counselor of the Spanish Embassy in Moscow, ambassador to Kazakhstan and consul general in St. Petersburg, among other destinations. He is the author of the book "The Returning Empire. The Ukraine War 2014-2017." During your presentation at the University of Navarra, Global Affairs was able to talk at length with the Spanish diplomat about the Ukrainian crisis and Russian foreign policy.
1. From the point of view of the geopolitics of the region, who are the main actors?
The main actors in the Ukrainian crisis are divided into two groups: those who are directly involved in the armed conflict and those who are not involved in it but are involved in the crisis. The main actors, obviously, are the Ukrainian government and the separatists of the self-proclaimed pro-Russian Republics of Donbass (Donetsk and Luhansk regions), backed and armed by Russia.
In a second concentric circle, the actors are Ukraine and Russia, which has annexed Crimea in response to the overthrow of pro-Russian Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych, and which, as I say, also supports Ukrainian separatists.
In a third concentric circle, there is the discrepancy between Russia and the European Union (EU), which considers the annexation of Crimea and the Russian intervention in the Donbass illegal, for which it has imposed economic sanctions, responded to by Russia.
In a fourth concentric circle we have a rivalry between Russia and the United States, which accuses Moscow of violating Ukraine's territorial integrity and thereby undermining security in Europe. This confrontation has consequences for the entire planet, as it generates mistrust and hostility between the two superpowers that has repercussions on their mutual relations, fundamentally on disarmament treaties and on their positions in crises such as those of Syria, North Korea, Venezuela and anywhere in the world.
Finally, there is the confrontation between Russia and NATO, which Russia blames for the hostile initiative of having spread eastwards, thereby provoking the Russian reaction when, theoretically, after the fall of the USSR, NATO had promised not to carry out its enlargement.
These are all the actors. Some participate in the first concentric circle, others in the second, and others in all.
2. In relation to the previous question, what is the main goal in this fight?
The answer to this question will depend on the actor we are focusing on. Obviously, the leaders of the rebel republics do not pursue the same thing as the Ukrainian government or the Russian government. In my opinion, the Russian regime seeks to ensure its security by regaining great power status. By controlling the post-Soviet space and promoting the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU) including Ukraine, Russia planned to strengthen its international position. But when Ukraine refuses to join the EEU and prefers a association with the EU in Brussels, Russia's plan was badly damaged. In other words, as Brzezinski, former U.S. National Security Advisor, said, Russia with Ukraine is an empire, but without Ukraine it is a normal state. But because it is not resigned to being a normal state, it does not want to lose control over Ukraine. Russia believes that this is the only way it can guarantee its security.
The purpose of the self-proclaimed Donetsk and Luhansk Republics is not very clear, because it has changed over time. First it was autonomy, then independence, then annexation to Russia, and then autonomy again. Several of the leaders who proclaimed independence have disappeared under strange circumstances, being replaced by other leaders.
At the moment the leadership of these republics is entirely under Moscow's control. Theoretically, one would have to conclude from this that the end of the Donetsk and Luhansk Republics is the same as the end of the Russian leadership. But I'm not so sure, since there were leaders in the governments of those republics who, at first, wanted another one subject of State. That is, not to be part of Ukraine, but neither to be part of Russia, even if they gave primacy to the relationship with it. A kind of state that would be autonomous from both Russia and Ukraine, but within the so-called "Russian world": a set of cultural patterns, beliefs and customs that identify the Russian people, based on the traditional values of the Russia of the tsars. Some of its most national-patriotic leaders advocated, after proclaiming secession, fidelity to orthodoxy, protection of the family, prohibition of abortions, gambling, prostitution, divorce... In short, a government that would not have found a place either in a Ukraine integrated into the EU, open, therefore, to assimilating gender ideology and other values contrary to the "Russian world", or in a Russia like the current one, which they considered to be governed by disbelieving ex-communists and former heads of the Soviet intelligence services. The first separatist leaders renamed their new state "Novorrossiya", resuming the name of Eastern Ukraine in tsarist times, whose territories had been conquered by Catherine the Great from the Turks and Ukrainian Cossacks in the 18th century.
But that plan didn't seem to suit Russia. At one point, Moscow stopped supporting the "project Novorrossiya" and brought about the replacement of the leaders who advocated it. Why? Many analysts believe that the emergence of a state like Novorossiya would have given wings to the already powerful Russian far-right nationalist current (advocated, among others, by Alexander Dugin) that accused Putin of treason for not having unceremoniously invaded all of Ukraine, and would encourage the emergence within Russia itself of similar initiatives in other territories of the Russian Federation where national-patriotic traditionalist elements had popular support. As a result, Russia appeared to choose to keep those republics inside Ukraine, but controlled by it or, in the extreme case, to proceed with a de facto annexation. Both solutions benefited him, as they prevented Ukraine from joining NATO and from having enough room for manoeuvre as a sovereign state, as it had within it the Trojan horse of those republics, controlled by leaders close to the Kremlin.
The EU's aim is stability and prosperity on its eastern border, exporting its economic and political reform programmes to the former Soviet republics. To this end, the EU launched its so-called "Eastern Partnership" programme with several of these republics. The more countries of the former Soviet Union assimilate the principles of the EU (human rights, transparent elections, equality before the law, absence of caste privileges, etc.), the more secure the eastern border will be and the more the European market will be able to extend to these countries, gradually incorporating them. In final, for the EU the aim would be the stability of the eastern border, the extension to the countries of Eastern Europe of the principles which gave rise to the EU and the extension of its power to them. area of security and prosperity.
For the U.S., the main goal it would be to prevent the USSR from rebuilding itself under another name and from once again being a factor of instability for democracies. The U.S. has seen how little by little Russian control or influence in former Soviet regions and republics has increased and how these have been regained by Moscow, one after the other. First it was Abkhazia, then Transnistria, then South Ossetia..., as well as Russian influence in Belarus, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and, now, Ukraine, after the annexation of Crimea and control of the Donbass. Some analysts see this process as a reconstruction of Moscow's control over the post-Soviet space, as was the case under the USSR. In the face of this, Washington maintains that each country has the right to freely choose the international organization and the collective security system to which it wants to belong, so Russia does not have the right of veto over the free choice of a given Eastern European country to become a member of NATO, or to cease to be one. a decision to be made by its own citizens, as would be the case in Ukraine. In short, each side in this crisis is pursuing a goal different.
3. The conflict in Ukraine erupted unexpectedly. Hundreds of people took to the streets calling for better living conditions and an end to corruption. How could we explain the fact that the conflict arose so suddenly?
In reality, this is not an isolated conflict, nor did it come as a surprise, but since the dissolution of the USSR, Western chancelleries and embassies have already received up to eight warnings of what was going to happen and did not know how to interpret those warnings.
The first notice It took place in December 1986, in Kazakhstan, with a series of popular revolts that already indicated what was going to happen. Serious riots broke out there when the President of the Kazakhstan Soviet Socialist Republic, President Kunayev, resigned and was replaced by a Russian, Gennady Kolbin. At that time, young Kazakhs took to the streets to protest against Moscow's decision to appoint a president who was not ethnically Kazakh and who did not even know the language, or the particularities of the country. To this day, the issue of deaths in the repression of the KGB troops, the army and the police, who were urgently sent from Russia to crush the insurrection.
The second notice It consisted of the 1988 war in Nagorno-Karabakh (an autonomous mountainous region, populated by Armenians, of Orthodox religion, nestled in the middle of the Islamic Republic of Azerbaijan). When the inhabitants and authorities of Nagorno-Karabakh saw the USSR disintegrating, they feared that in the chaos of the disintegration they would suffer repression and settling scores from the vast Muslim majority around them. Consequently, the parliament of that autonomous region requested annexation to Russia. When this happened, the Azerbaijani authorities sent their troops to prevent secession. A war has ensued that has not yet ended.
The third notice, which occurred in 1989, was the "Tbilisi Massacre" (Georgia), when thousands of Georgians took to the streets in favor of Georgia's independence from the USSR. The Soviet army sent special troops to suppress the uprising, as had happened in Kazakhstan. Many civilians were killed there. That massacre gave rise to the Tbilisi Syndrome: no position From then on, the Soviet Union wanted to take responsibility for having given the order for the intervention. From that moment on, the army would not intervene against the people again unless it received a written order to signature of the person who decided the intervention.
The Fourth notice It dates back to 1990 with the civil war in Transnistria, an ethnic Russian-majority eastern fringe of the Romanian-majority republic of Moldova. It so happened that after Moldova's independence in 1991, the inhabitants of Transnistria feared that they would be oppressed in the new country, which was the only way to achieve it. language and mainly Romanian traditions. Therefore, they declared their own independence from Moldova, consequently starting a conflict that would leave more than 20,000 dead.
In all these cases and in others that would come later, Russia always supported the secessionists, since this was a way of keeping the republics that wanted to secede from the USSR controlled by a minority within them, which prevented their consolidation as sovereign and independent.
Next notice consisted of the failed coup attempt in Moscow in August 1991. Although it failed, this attempt opened the eyes of other republics to the danger of regression and return to the USSR and, from that moment on, the secessionist process accelerated.
The Sixth notice consisted of the referendum held in Ukraine in December 1991. Under the question "Are you agreement for Ukraine to secede from the USSR and become an independent state?", 98% of the Ukrainian population voted yes, including Crimea.
Along with these warnings, there had been other indicators, such as the separatist movement in Abkhazia (a region of northwestern Georgia), which in 1992 declared its independence from Georgia, which wanted to gain complete independence from Russia. Russia supported the separatists here as well.
The last notice took place in 2007, in South Ossetia. It followed an attempt by the Georgian government to bring the breakaway region of South Ossetia back under its control by using its army. Russia, which had peacekeeping forces stationed in Ossetia since a previous conflict, intervened on behalf of the separatists, forcing Georgia to relinquish control of the region.
4. Although the U.S. is concerned about the Ukrainian conflict, it is not as concerned as other issues. In fact, the U.S. is not acting and is only verbalizing its concern. Is it possible that he is not giving a clear answer because he thinks that it is fundamentally a European problem?
The U.S. is concerned for the simple reason that the solution to other crises in the world, mainly those in Syria, Venezuela and North Korea, depends on trust and good relations between Moscow and Washington. And there will never be if the problem is not first resolved. topic of Ukraine. What is poisoning relations is Ukraine. In fact, I very much doubt that without the war in Ukraine there would have been a Russian intervention in the war in Syria as there has been.
When the West tries to isolate Russia by imposing sanctions, Russia has to get out somewhere. Therefore, to show that it cannot be isolated and that it is a protagonist on the international stage, Russia intervenes in Syria, Venezuela or wherever it can stand up to the United States. He would be sending a message similar to this: "Even if you want to isolate me and reduce me to a second-rate regional power, I can show you that without me there is no solution to any world crisis. What's more, if I want to, I'll provoke other crises for you."
5. What do Russian citizens themselves think about the annexation of the Crimean peninsula?
The intervention and consequent annexation of Crimea by Russia, within the Ukrainian conflict, is the point that most poisons relations between Russia and the West, but also has an impact on Russian public opinion.
Because, of course, Russia has a GDP the size of Italy's and is maintaining interventions abroad that cost it a lot of money. Their hospitals are in a pitiful condition, the teaching It is going through a great lack of resources and a decline in quality, pensions are very low, the retirement age has been delayed... Many in Russia are disgusted that, under these circumstances, enormous resources are devoted to subsidize Crimea. Because Crimea does not stand on its own. Before, when she was at peace and thanks to tourism, she could sustain herself. But now, who goes to Crimea? Who invests in Crimea? Everything is subsidized by the Russian government. That would be within the reach of a country with a gigantic GDP, but hardly a country that has a GDP like that of Italy or Spain and that dedicates, directly or indirectly, a third of its GDP to its armed forces and police. In addition to having to subsidize Crimea, Russia has to subsidize Abkhazia, Transnistria, Ossetia and the Donbass. For this reason, there are those in Russia who are already wondering whether the annexation of Crimea was not a mistake, such as, for example, one of its most influential newspapers, "Vedomosti".
On the other hand, a major reason why the Russian leadership does not look favorably on discussing this issue could be Chechnya. According to some international law experts, such as Araceli Mangas Martín, professor of international law at the Complutense University, all the arguments that Russia uses to justify the secession of Crimea from Ukraine would be valid to justify a future secession of Chechnya from Russia. What would happen, some analysts ask, if in 10 or 20 years a Chechen majority were formed to demand secession from Russia in a referendum invoking the precedent of Crimea?
The topic of the legitimacy of the annexation of Crimea is a topic taboo in Russian society, for many reasons. You can't talk about it calmly. In fact, the only member of the Duma (Russian parliament) who voted against the incorporation of Crimea into Russia has had to go into exile because he has been threatened. Debates about the existence and legitimacy of the annexation of Crimea are usually not allowed on TV programmes, and when they are discussed, it must always be from the official point of view.
|
Deployment of Ukrainian troops, June 2014 [Wikipedia] |
6. Do you think it is possible that Russia will end up abandoning the war in Ukraine? Also, could Crimea become part of Ukrainian territory again?
Russia has made one thing very clear: it will never allow Ukrainian rebels and separatists in the Donetsk and Luhansk Republics to be defeated by the Ukrainian army. He's not going to allow it.
The only possibility for Russia to abandon its military intervention in Ukraine would be for the secessionists to win their confrontation with the Ukrainian government and consolidate an independence from the Ukrainian government under Moscow's undisputed control.
Second, I see the return of Crimea to Ukraine as very difficult, practically impossible. Because Russia is turning Crimea into a huge military base that it considers essential in the face of an expansive NATO. It is equipping it with the most modern weapons systems: radars, rockets, a modern fleet...
7. Demographically, is the percentage of Russians in Crimea as high as claimed?
According to some analysts, the Kremlin is playing with numbers. Sometimes he speaks of ethnic Russians, sometimes of Russian speakers. Odessa or Kharkiv, for example, are large Ukrainian cities that speak Russian, but are on the side of the Kiev government. What does Russia mean by "Russian"? The Russian authorities say: "The majority of the inhabitants of Crimea legitimately voted for secession and incorporation into Russia in a referendum by an affirmative majority of around 90%, with Russians also constituting the vast majority of the population on the peninsula." Define that to me. What about the 13% of Tatars, what about the 20% of Ukrainians? And what Moscow calls Russians in Crimea, what exactly are they: ethnic Russians, Russian speakers, Russian passport holders, Russians by choice, by birth, by marriage? With what electoral documentation and with what control of the votes was the referendum made? Were troops from the Russian base in Sevastopol counted as registered voters, or were they not counted? How were the votes inside the military barracks controlled? In short, it's like saying "Spaniards" referring to any Ibero-American country. In Argentina or Cuba there may be 700,000 Spaniards. Do we accept then that in a territory of Argentina, Cuba or Venezuela, where the majority are Spanish, they organize a referendum for secession and their reincorporation into Spain and we arm them clandestinely?
The question that should concern us is: what is the difference between citizenship and nationality? In Western countries, citizenship and nationality are the same. However, this is not the case in Russia, and here we go to the heart of the problem. In the countries of the former Soviet orbit, nationality means "belonging to a group ethnic." Citizenship, on the other hand, means "submission to the political, legal and administrative regime of a given State, regardless of the ethnic group to which one belongs".
In Russia it's completely different things. So much so that on the identity cards of Russia and Ukraine, until recently, the "nationality" of the Russian and Ukrainian countries was listed as the name "nationality". group Headline ethnicity: Jewish, Tatar, Russian... That is why, when Russia annexed Crimea, the main reason President Putin gave for doing so was that he had to protect the "Russians" in Ukraine, "his" nationals in Ukraine, from the "board Fascist" in Kiev that threatened them. For a Russian, you can change citizenship; on the other hand, nationality was never lost, and Russia must protect those who held its own.
All this explains why before intervening in an ex-Soviet republic that wants to separate itself from Moscow's orbit, the first thing Russia does is to distribute Russian passports to citizens of those republics whom, from that moment on, it considers Russians, and then argues that it has to protect them.
Of the Ukrainians who lived in Crimea, many have left it. Others have remained in Crimea, of course, but without being able to question that Crimea belongs to Russia, submitting to the Russian authorities, having to, in many cases, obtain new documentation, different from the one they had before, and lending allegiance and submission to another state other than the one in which they lived until recently.
8. Could we say that Russia and the West have different interpretations of the principles that should govern international relations?
This fundamental principle for the Kremlin of militarily defending Russians wherever they are, including the territory of another ex-Soviet republic, clashes with other basic principles for the EU, the US and Western countries: the territorial integrity of the state, the sovereignty of the state and the equality of all before the law... If you want to protect Russians living in Ukraine by annexing Crimea because it has a Russian majority, you are obviously violating the principle of territorial integrity of the state. However, Russia thinks that it has respected Ukraine's territorial integrity, because territorial integrity has a different meaning for the Russian leadership than ours. For them, territorial integrity refers to the state apparatus, but not to territory. Russia gives priority to other principles, such as the protection of its nationals.
For all these reasons, this conflict is so dangerous, because neither the West nor Russia can renounce principles that they consider basic. That is why, when we talk about EU-US dialogue with Russia to resolve this conflict, we are asking for a dialogue between two parties who speak a different language, because Russia attributes a completely different meaning to the concepts than we attribute to them.
9. Russia's policy of protecting ethnic Russians may be very reminiscent, to a large extent, of Nazi Germany's policy of the 1930s of attempting to unite all ethnic Germans. Do you think that the status Is it similar?
Not only to the 1930s, but also to the time of World War I, which broke out because Serbia wanted to protect Serbs living outside Serbian territory, who considered themselves oppressed and mistreated by the authorities of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, when it annexed Bosnia-Herzegovina. One of those who felt oppressed, the student Gavrilo Princip, with the logistical help of the Serbian secret police, killed the heir to the throne of Austria-Hungary during his visit to Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia and Herzegovina. That set off a chain reaction and a World War.
In World War II, Germany demanded that all Germans live within the same state. Unfortunately, not all Germans lived in Germany. The Nazis then decided to ensure that all Germans of the superior Aryan race were placed in a single state, led by a single Führer. To do this, they annex Austria. The Western powers are perplexed. It turned out that there were also Germans in Czechoslovakia, who were not treated well by the Czechoslovak authorities, according to the Nazis. The Führer then forces the Czechoslovaks to cede the Sudetenland to him. Then Germany annexes other territories and the Western powers give in. Later, Hitler claimed the Polish corridor and the German city of Danzig, also a territory with a German population, but located in Poland, and it was there that, definitely, England and France, who had offered guarantees to Poland, reacted.
For some Western analysts, the status it is very reminiscent of what is happening now in the former USSR. First, Russia annexes a part of another country, then settles in a part of another, with the same justification: that there are Russians in them who must be protected. In my opinion, the status It's not exactly the same, but it has alarming similarities.
10. The lesson of the 1930s is that the policy of appeasement did not prevent war, but merely postponed it and made it more difficult to fight. So what is the recommended attitude to Russian policy?
There are two fundamental tendencies: the first comprises the tendencies to appeasement and the second the tendencies to firmness. Among the tendencies towards appeasement we find, in turn, three distinct currents:
–A first group of experts draws attention to a fundamental fact: that Russia is willing to go further than the West in the conflict in Ukraine, because for Russia Ukraine is a vital issue, while for the West it is not. A territorial review would have to be carried out. We're going to give in and let Russia keep its Russians, and that's the end of the problem. We signed a agreement, and Russia has its zone of influence.
The second school of thought defends the idea of turning Ukraine into a neutral state so that Russia does not perceive a threat. This would imply a decision to freeze NATO expansion, which would no longer extend to any other country in Eastern Europe; the regions of eastern Ukraine populated mostly by Russians should be granted very broad autonomy, and Crimea should be admitted to be part of Russia in compensation for NATO's eastward expansion.
According to the third current, Russia, in annexing Crimea and intervening in eastern Ukraine, did not observe aggressive behavior. On the contrary, it was acting in self-defence, and no country can be denied self-defence. We say that because if the Maidan revolution had triumphed throughout Ukraine, including Crimea, and a Western-leaning regime had been installed throughout Ukraine, it would have been a matter of very little time before the new Ukrainian government would have applied for NATO membership. That would have meant that NATO's borders would have moved even closer to Russia, endangering the country's security. Therefore, Russia, in acting in Ukraine, is only doing so in self-defence. This third current advocates the demilitarization of the Donbass, the security of the borders to be guaranteed by a peacekeeping force under the command of the UN, and the admission of Crimea as part of Russia, in compensation for the fact that NATO has incorporated countries that formerly belonged to the USSR.
As we mentioned earlier, there is a second trend that advocates firmness: "We are not going to repeat the Munich mistake of giving in, giving in and giving in, because if we continue like this, next time we will find that Russia is trying to annex a Baltic country", where, by the way, in Estonia and Latvia it has very important minorities. The main stream of this group he thinks that we cannot repeat the mistake of Yalta, of allowing Europe to be divided into zones of influence and, above all, of imposing neutrality on a country that does not want it. On the other hand, what would be done by allowing Russia to keep all these regions is to deny Ukraine, precisely, its right to self-defense.
Other group of this tendency argues that the supporters of the appeasement strategy do not offer any solution as to how the security of the countries of Eastern Europe would then be guaranteed. Moreover, the fact of not extending NATO and of being condescending to Russia to avoid provoking Russia is a false dilemma, because Russia is already doing everything it can to annoy the West, the whole limit of provocation is already exceeded. If you want to achieve stability in Europe by turning a blind eye and allowing Russia to control areas that formerly belonged to the USSR, there is a risk that Russia will continue to occupy territories. How far do Russia's borders have to go for Russia to feel safe?
In addition to the two previous tendencies, there is a third school of thought that is striking. He says that in the case of Nazi Germany there is a differentiating fact with respect to the status Nuclear weapons did not exist at that time. At the time, it might have been a priority to stop Hitler at the cost of paying a heavy price, otherwise the consequences would have been catastrophic. It was a lesser evil in the face of a greater evil. However, now this dilemma does not exist, as now the dilemma is between reaching an understanding with Russia or a nuclear war.
The question posed by this third position is: what is our priority, to punish Russia or to achieve stability in Europe? If we choose the first option, then what we should do is arm Ukraine. However, if our priority is to restore stability in Europe, then we need to start talks with Russia. Actually, in the long run, the West is much stronger than Russia, but the drawback it has in the long run is that you don't know if in that long period of time we will all be dead. If Russia sees that it is weaker in the long run, it will obviously try to take advantage of the status while it's still going strong.
|
Troops of the self-proclaimed Donetsk People's Republic in May 2015 [Mstyslav Chernov] |
11. There may be an interpretation that what happened in Crimea was a self-defence reaction by Russia to prevent its naval base in Sevastopol from becoming a NATO base. Russia would have interpreted that as a threat to its security and would therefore have intervened to protect its security. With this in mind, let's take the Cuban crisis of 1962 as an example. Cuba decided to buy weapons to place Soviet atomic missiles on Cuban territory. They could do it from the point of view of international law, they were two sovereign countries that could sell arms to each other. The U.S. felt attacked by the possibility of rockets in Cuba and intervened in Cuba. Hasn't the same thing happened with Crimea and the USSR? In a second scenario, let's imagine that an anti-American government enters Mexico, which feels very insecure towards the United States and decides to install nuclear missiles on the border of the Rio Grande. Would the U.S., in the interest of international law of territorial integrity, allow rocket batteries to be aimed at U.S. cities? What do you think about this?
There are similarities in those cases, but they can't be compared. The differences that I see are, first of all, that the United States imposed a blockade on Cuba, but it did not invade Cuba, as you say, nor did it annex any region of Cuba. Kennedy screwed up with his Bay of Pigs invasion, withdrew his troops from there, and publicly apologized for the initiative. I can't imagine a Russian leader publicly apologizing for the illegal invasion by the USSR or Russia of a sovereign country without a declaration of war: Finland in 1939, the Baltics in 1940, Hungary in 1956, Czechoslovakia in 1968, Afghanistan in 1979, Ukraine in 2014....
Second, the missiles installed in Cuba were very powerful offensive nuclear weapons, installed clandestinely, while the US does not install comparable offensive nuclear weapons near Russia nor has it done so clandestinely. Moscow believes that U.S. anti-missile systems in Poland and Romania can easily become offensive, but such Russian misgivings would be solved with an effective system of inspections and verification. Moreover, Russia's leadership is well aware that such systems do not constitute any effective threat to its massive nuclear arsenal. The test it is that they boast about it and consider it invulnerable, in the words of President Putin himself.
Thirdly, Mexico is political fiction. It is inconceivable that the U.S. would militarily invade Mexico to protect U.S. minorities settled in that country, as has happened with Crimea or the Donbass. On the other hand, I doubt that it would be possible for nuclear weapons to be installed in Mexico with the bilateral and regional agreements that are in force between the United States and Mexico and in the United States. framework of the free trade agreement between the United States, Mexico and Canada. Let's not forget that, although imperfect, both Mexico and the U.S. are democratic regimes. Their leaders are accountable to their constituents and to their people, and are elected by them. This is not the case of Cuba or the USSR, communist dictatorships, nor, according to some authors, of today's Russia, an authoritarian nationalist regime. Democracies don't usually wage wars with each other.
The only U.S. behavior similar to what is happening in Crimea was the invasion of the Caribbean island of Grenada. When a Marxist regime came to power in Grenada, the U.S. argued the need to protect the American students who were there to intervene, even though they were not in danger.
Another difference is that what happened in Ukraine is part of a process or trend (Kazakhstan, Transnistria...), which seems to have been perfectly planned since 1990, as we have mentioned before. It is not a one-off, surprising and improvised case, as was the reaction of the United States to the installation of missiles in Cuba in 1962.
12. What you have said above about Russia's aggressive reaction to avoid the long term is very reminiscent of the direct strategy of US containment during the Cold War. The U.S. response was precisely that it was necessary to rearm and have a sufficiently intimidating military capacity so that the USSR would not dare to act aggressively. That would be another possible conclusion: Do we have to rearm?
In fact, we're doing it. For me, Putin's biggest mistake has been to make it possible for the US to achieve in 20 days the consensus for a rearmament and strengthening of NATO that it had not achieved in 20 years. Now that they have a cohesive and organized NATO, they have secured a commitment to increased military spending by NATO allies who were previously reluctant to do so.
13. Crimea was part of Russia until Khrushchev ceded it to Ukraine in 1954. In addition, the Russian Empire had thousands of deaths for regaining that peninsula in the Crimean War. Is the fact that this territory belongs to Ukraine or Russia something that could be debatable?
First of all, the claim that Khrushchev gave away Crimea to Ukraine is, according to documented authors, one of the great falsehoods spread by Russian intelligence centers, which has been believed by almost everyone in the West. Although it is true that the resolution of the Presidium of the CPSU of 1954 made Crimea dependent on Ukraine, on the occasion of the 300th anniversary of the incorporation of Ukraine into the Russian Empire, this was not the only reason, since Crimea is a very arid area, and the supply of water, manpower, infrastructure... it's a lot easier from Ukraine than from Russia. For all practical purposes, it is much more profitable, as we are currently seeing, to hold Crimea from Ukraine than from Russia.
Second, the Taganrog region, richer and larger than Crimea, which previously belonged to Ukraine, was allocated to Russia. For this reason, some analysts think that what happened was a kind of territorial compensation, because holding Taganrog from Ukraine is very difficult as well.
Thirdly, the change of administrative boundaries between the different regions of the USSR in the time of Stalin and Khrushchev was a matter of course and frequent. If we consider Khrushchev's transfer of Crimea to Ukraine unconstitutional or illegal, we must also consider illegal dozens of similar territorial modifications that were made at that time in the USSR.
Fourth, Crimea has been part of Russia for 250 years (Cuba was Spanish about 400 years) and all of western Ukraine was Poland until 1939. Poland would then have an equal right to claim its share of Ukraine as Russia would to claim its share. If we are going to justify the annexation of territories on the basis of historical ties without respecting current international treaties, then we would have to remake the entire world map and we would provoke an escalation of war. By this rule of three, the Spaniards should reclaim Cuba tomorrow, because it was a trauma for us to lose it, thousands of Spaniards reside there and it was much longer Spanish than Russian Crimea.
Fifth, and most importantly, in the 1997 Treaty of Amity and Cooperation between Russia and Ukraine, Russia recognized the independence and territorial integrity of Ukraine, including Crimea.
We cannot be immersed in a continuous process of historical demands. To prevent this, there are international treaties that set the borders and prevent us from returning to the forest.
14. A few years ago we witnessed how the United States fought for the independence of Kosovo, which it recognized. So, could we say that the case of Kosovo constitutes a precedent that legitimizes Russia to defend the separation of Crimea?
For many analysts, the case of Kosovo and the case of Crimea have no relation to each other. First, they say, the U.S. was not seeking to annex Kosovo, unlike what Russia did with Crimea. Secondly, the recognition of Kosovo's independence came after 10 years of ethnic cleansing carried out by Serbian troops in Kosovo against the Albanian population. The topic it was taken to the UN and discussed for a long time. Nothing of the sort happened in Crimea: there was no conflict between Russians and Ukrainians, no topic to the UN, it wasn't even taken to the International Court of Justice (Kosovo was). They are completely different things. There had been no serious inter-ethnic incidents in Crimea that would justify annexation by Russia. In Kosovo, there were, with thousands of deaths.
This is, according to many authors, another success of Russian propaganda, which has led many people in the West to consider them to be similar cases. In addition, it would be necessary to see under what conditions the referendum was held in Crimea: there were no debates on television, there were no different political parties to present their positions, there were no international observers, there was no reliable census, the polling stations were taken over by the Russian army... We don't know what the majority that voted in favour looks like.
15. How can one explain Putin's enormous power and popularity in a country that is considered democratic and where there are regular elections?
One issue worth commenting on is the failure of democratic reforms in Russia. When communism disintegrated in the USSR and Russia opted for the Economics for free trade and for liberal democracy, expects to receive a model civilized of all that. What he gets, on more than one occasion, are real Western gangsters doing business, appropriating Russia's economic and cultural resources, and Russia's brains... The version of the Economics The market share that Russia receives after the implementation of liberal democracy in the country is horrific and, from that moment on, the words "democracy" and "reforms" are totally discredited in Russia. They have an idea of reform and democracy that is totally harmful and fatal. That was precisely what catapulted leaders like Vladimir Putin to power.
One thing we didn't understand in the West is that, for a Russian, stability is much more important than freedom. Above all, we did not understand a very important thing, which was the astonishing ease of the transition from communism to nationalism. It was astonishing naivety on the part of Western diplomats to think that post-communist leaders were going to build democracy on the ruins of the USSR and against their own interests.
The transition from communism to nationalism is, in fact, very easy, because its basic elements are the same: primacy of the leader over institutions, dogma over principles, loyalty over merit, slogans over reasoning, propaganda over information, virtual history over real history, etc.
|
Parade of rebel troops in Donetsk, May 2015 [Wikipedia] |
16. The population of the Baltic countries has a significant Russian minority. In these countries, the status also because there has been a NATO deployment. Could Ukraine join NATO and that would stabilize the status Or would Russia never allow Ukraine to join NATO?
There was a time when Russia was proposed to join NATO. But Russia didn't want to be just another member of NATO, it didn't want to be subject to the US, it wanted to play a leading role. For its part, Ukraine is not the same as the Baltic countries. I believe that Ukraine cannot, for the time being, join NATO. However, there are already partnership between NATO and the Ukrainian government. For me, it is a consequence of President Putin's actions, because what good is it for him to win Crimea if he loses Ukraine, where, moreover, he has stirred up anti-Russian sentiment? With this policy, Russia has managed to wake up and strengthen NATO (which the US had never achieved before), and to make the majority of Ukraine have a pro-Western feeling. Quite a balance.
In my opinion, Russia will do everything possible to prevent Ukraine from joining NATO. However, if Ukraine were admitted to NATO, Russia would respond asymmetrically. In my view, the world would be on the brink of nuclear war.
17. Do you think that the Crimea issue can have a wider impact, set a precedent?
In the opinion of many analysts, including Russians, what Putin has done there is a very dangerous thing. Because the arguments he gives to justify the secession of Crimea from Ukraine would be valid, according to these experts, to justify the secession of other regions of Russia. Not now, but in the future. Russia has about 120 different ethnicities, let's imagine that one decides to apply the arguments used in the case of Crimea to justify its own secession.
There is also another issue to take into account, and that is that Russia has presented itself as the redeemer of humanity throughout history (with the fall of Constantinople, establishing itself as the third Rome and redeemer of what was left of civilization, and with the expansion of communism after the Revolution of 1917, with the redemption of the oppressed), and now Russia presents itself again for the third time as the redeemer of humanity. For Russia, the moral standards that are now part of the basic principles of our civilization in the West are inadmissible. She thinks that our society is dissolving and that it is totally corrupt. For example, gender ideology will never be allowed in Russia and is seen as a plague that is dissolving Western society. This trend, which is known as "Russian messianism", which takes different forms throughout history, is a constant to be reckoned with. Russia thinks that it is not only fighting for Ukraine and Crimea, but for the whole of civilization.

▲ Protest in London in October 2018 after the disappearance of Jamal Khashoggi [John Lubbock, Wikimedia Commons]
ANALYSIS / Naomi Moreno Cosgrove
October 2nd last year was the last time Jamal Khashoggi—a well-known journalist and critic of the Saudi government—was seen alive. The Saudi writer, United States resident and Washington Post columnist, had entered the Saudi consulate in the Turkish city of Istanbul with the aim of obtaining documentation that would certify he had divorced his previous wife, so he could remarry; but never left.
After weeks of divulging bits of information, the Turkish president, Recep Tayyip Erdogan, laid out his first detailed account of the killing of the dissident journalist inside the Saudi Consulate. Eighteen days after Khashoggi disappeared, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) acknowledged that the 59-year-old writer had died after his disappearance, revealing in their investigation findings that Jamal Khashoggi died after an apparent "fist-fight" inside the Saudi consulate in Istanbul; but findings were not reliable. Resultantly, the acknowledgement by the KSA of the killing in its own consulate seemed to pose more questions than answers.
Eventually, after weeks of repeated denials that it had anything to do with his disappearance, the contradictory scenes, which were the latest twists in the "fast-moving saga", forced the kingdom to eventually acknowledge that indeed it was Saudi officials who were behind the gruesome murder thus damaging the image of the kingdom and its 33-year-old crown prince Mohammed bin Salman (MBS). What had happened was that the culmination of these events, including more than a dozen Saudi officials who reportedly flew into Istanbul and entered the consulate just before Khashoggi was there, left many sceptics wondering how it was possible for MBS to not know. Hence, the world now casts doubt on the KSA's explanation over Khashoggi's death, especially when it comes to the shifting explanations and MBS' role in the conspiracy.
As follows, the aim of this study is to examine the backlash Saudi Arabia's alleged guilt has caused, in particular, regarding European state-of-affairs towards the Middle East country. To that end, I will analyse various actions taken by European countries which have engaged in the matter and the different modus operandi these have carried out in order to reject a bloodshed in which arms selling to the kingdom has become the key issue.
Since Khashoggi went missing and while Turkey promised it would expose the " naked truth" about what happened in the Saudi consulate, Western countries had been putting pressure on the KSA for it to provide facts about its ambiguous account on the journalist's death. In a joint statement released on Sunday 21st October 2018, the United Kingdom, France and Germany said: "There remains an urgent need for clarification of exactly what happened on 2nd October – beyond the hypotheses that have been raised so far in the Saudi investigation, which need to be backed by facts to be considered credible." What happened after the kingdom eventually revealed the truth behind the murder, was a rather different backlash. In fact, regarding post-truth reactions amongst European countries, rather divergent responses have occurred.
Terminating arms selling exports to the KSA had already been carried out by a number of countries since the kingdom launched airstrikes on Yemen in 2015; a conflict that has driven much of Yemen's population to be victims of an atrocious famine. The truth is that arms acquisition is crucial for the KSA, one of the world's biggest weapons importers which is heading a military coalition in order to fight a proxy war in which tens of thousands of people have died, causing a major humanitarian catastrophe. In this context, calls for more constraints have been growing particularly in Europe since the killing of the dissident journalist. These countries, which now demand transparent clarifications in contrast to the opacity in the kingdom's already-given explanations, are threatening the KSA with suspending military supply to the kingdom.
COUNTRIES THAT HAVE CEASED ARMS SELLING
Germany
Probably one of the best examples with regards to the ceasing of arms selling—after not been pleased with Saudi state of affairs—is Germany. Following the acknowledgement of what happened to Khashoggi, German Chancellor Angela Merkel declared in a statement that she condemned his death with total sharpness, thus calling for transparency in the context of the situation, and stating that her government halted previously approved arms exports thus leaving open what would happen with those already authorised contracts, and that it wouldn't approve any new weapons exports to the KSA: "I agree with all those who say that the, albeit already limited, arms export can't take place in the current circumstances," she said at a news conference.
So far this year, the KSA was the second largest customer in the German defence industry just after Algeria, as until September last year, the German federal government allocated export licenses of arms exports to the kingdom worth 416.4 million euros. Respectively, according to German Foreign Affair Minister, Heiko Maas, Germany was the fourth largest exporter of weapons to the KSA.
This is not the first time the German government has made such a vow. A clause exists in the coalition agreement signed by Germany's governing parties earlier in 2018, which stated that no weapons exports may be approved to any country "directly" involved in the Yemeni conflict in response to the kingdom's countless airstrikes carried out against Iranian-backed Houthi rebels in the area for several years. Yet, what is clear is that after Khashoggi's murder, the coalition's agreement has been exacerbated. Adding to this military sanction Germany went even further and proposed explicit sanctions to the Saudi authorities who were directly linked to the killing. As follows, by stating that "there are more questions unanswered than answered," Maas declared that Germany has issued the ban for entering Europe's border-free Schengen zone—in close coordination with France and Britain—against the 18 Saudi nationals who are "allegedly connected to this crime."
Following the decision, Germany has thus become the first major US ally to challenge future arms sales in the light of Khashoggi's case and there is thus a high likelihood that this deal suspension puts pressure on other exporters to carry out the same approach in the light of Germany's Economy Minister, Peter Altmaier's, call on other European Union members to take similar action, arguing that "Germany acting alone would limit the message to Riyadh."
Norway
Following the line of the latter claim, on November 9th last year, Norway became the first country to back Germany's decision when it announced it would freeze new licenses for arms exports to the KSA. Resultantly, in her statement, Norwegian Minister of Foreign Affairs, Ine Eriksen Søreide, declared that the government had decided that in the present situation they will not give new licenses for the export of defence material or multipurpose good for military use to Saudi Arabia. According to the Søreide, this decision was taken after "a broad assessment of recent developments in Saudi Arabia and the unclear situation in Yemen." Although Norwegian ministry spokesman declined to say whether the decision was partly motivated by the murder of the Saudi journalist, not surprisingly, Norway's announcement came a week after its foreign minister called the Saudi ambassador to Oslo with the aim of condemning Khashoggi's assassination. As a result, the latter seems to imply Norway's motivations were a mix of both; the Yemeni conflict and Khashoggi's death.
Denmark and Finland
By following a similar decision made by neighbouring Germany and Norway—despite the fact that US President Trump backed MBS, although the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) had assessed that the crown prince was responsible for the order of the killing—Denmark and Finland both announced that they would also stop exporting arms to the KSA.
Emphasising on the fact that they were "now in a new situation"—after the continued deterioration of the already terrible situation in Yemen and the killing of the Saudi journalist—Danish Foreign Minister, Anders Samuelsen, stated that Denmark would proceed to cease military exports to the KSA remarking that Denmark already had very restrictive practices in this area and hoped that this decision would be able to create a "further momentum and get more European Union (EU) countries involved in the conquest to support tight implementation of the Union's regulatory framework in this area."
Although this ban is still less expansive compared to German measures—which include the cancellation of deals that had already been approved—Denmark's cease of goods' exports will likely crumble the kingdom's strategy, especially when it comes to technology. Danish exports to the KSA, which were mainly used for both military and civilian purposes, are chiefly from BAE Systems Applied Intelligence, a subsidiary of the United Kingdom's BAE Systems, which sold technology that allowed Intellectual Property surveillance and data analysis for use in national security and investigation of serious crimes. The suspension thus includes some dual-use technologies, a reference to materials that were purposely thought to have military applications in favour of the KSA.
On the same day Denmark carried out its decision, Finland announced they were also determined to halt arms export to Saudi Arabia. Yet, in contrast to Norway's approach, Finnish Prime Minister, Juha Sipilä, held that, of course, the situation in Yemen lead to the decision, but that Khashoggi's killing was "entirely behind the overall rationale".
Finnish arms exports to the KSA accounted for 5.3 million euros in 2017. Nevertheless, by describing the situation in Yemen as "catastrophic", Sipilä declared that any existing licenses (in the region) are old, and in these circumstances, Finland would refuse to be able to grant updated ones. Although, unlike Germany, Helsinki's decision does not revoke existing arms licenses to the kingdom, the Nordic country has emphasized the fact that it aims to comply with the EU's arms export criteria, which takes particular account of human rights and the protection of regional peace, security and stability, thus casting doubt on the other European neighbours which, through a sense of incoherence, have not attained to these values.
European Parliament
Speaking in supranational terms, the European Parliament agreed with the latter countries and summoned EU members to freeze arms sales to the kingdom in the conquest of putting pressure on member states to emulate the Germany's decision.
By claiming that arms exports to Saudi Arabia were breaching international humanitarian law in Yemen, the European Parliament called for sanctions on those countries that refuse to respect EU rules on weapons sales. In fact, the latest attempt in a string of actions compelling EU foreign policy chief Federica Mogherini to dictate an embargo against the KSA, including a letter signed by MEPs from several parties.
Rapporteur for a European Parliament report on EU arms exports, Bodil Valero said: "European weapons are contributing to human rights abuses and forced migration, which are completely at odds with the EU's common values." As a matter of fact, two successful European Parliament resolutions have hitherto been admitted, but its advocates predicted that some member states, especially those who share close trading ties with the kingdom are deep-seated, may be less likely to cooperate. Fact that has eventually occurred.
COUNTRIES THAT HAVE NOT CEASED ARMS SELLING
France
In contrast to the previously mentioned countries, other European states such as France, UK and Spain, have approached the issue differently and have signalled that they will continue "business as usual".
Both France and the KSA have been sharing close diplomatic and commercial relations ranging from finance to weapons. Up to now, France relished the KSA, which is a bastion against Iranian significance in the Middle East region. Nevertheless, regarding the recent circumstances, Paris now faces a daunting challenge.
Just like other countries, France Foreign Minister, Jean-Yves Le Drian, announced France condemned the killing "in the strongest terms" and demanded an exhaustive investigation. "The confirmation of Mr. Jamal Khashoggi's death is a first step toward the establishment of the truth. However, many questions remain unanswered," he added. Following this line, France backed Germany when sanctioning the 18 Saudi citizens thus mulling a joint ban from the wider visa-free Schengen zone. Nevertheless, while German minister Altmeier summoned other European countries to stop selling arms to Riyadh—until the Saudi authorities gave the true explanation on Khashoggi's death—, France refused to report whether it would suspend arms exports to the KSA. "We want Saudi Arabia to reveal all the truth with full clarity and then we will see what we can do," he told in a news conference.
In this context, Amnesty International France has become one of Paris' biggest burdens. The organization has been putting pressure on the French government for it to freeze arms sales to the realm. Hence, by acknowledging France is one of the five biggest arms exporters to Riyadh—similar to the Unites States and Britain—Amnesty International France is becoming aware France's withdrawal from the arms sales deals is crucial in order to look at the Yemeni conflict in the lens of human rights rather than from a non-humanitarian-geopolitical perspective. Meanwhile, France tries to justify its inaction. When ministry deputy spokesman Oliver Gauvin was asked whether Paris would mirror Berlin's actions, he emphasized the fact that France's arms sales control policy was meticulous and based on case-by-case analysis by an inter-ministerial committee. According to French Defence Minister Florence Parly, France exported 11 billion euros worth of arms to the kingdom from 2008 to 2017, fact that boosted French jobs. In 2017 alone, licenses conceivably worth 14.7 billion euros were authorized. Moreover, she went on stating that those arms exports take into consideration numerous criteria among which is the nature of exported materials, the respect of human rights, and the preservation of peace and regional security. "More and more, our industrial and defence sectors need these arms exports. And so, we cannot ignore the impact that all of this has on our defence industry and our jobs," she added. As a result, despite President Emmanuel Macron has publicly sought to devalue the significance relations with the KSA have, minister Parly, seemed to suggest the complete opposite.
Anonymously, a government minister held it was central that MBS retained his position. "The challenge is not to lose MBS, even if he is not a choir boy. A loss of influence in the region would cost us much more than the lack of arms sales". Notwithstanding France's ambiguity, Paris' inconclusive attitude is indicating France's clout in the region is facing a vulnerable phase. As president Macron told MBS at a side-line G20 summit conversation in December last year, he is worried. Although the context of this chat remains unclear, many believe Macron's intentions were to persuade MBS to be more transparent as a means to not worsen the kingdom's reputation and thus to, potentially, dismantle France's bad image.
United Kingdom
As it was previously mentioned, the United Kingdom took part in the joint statement carried out also by France and Germany through its foreign ministers which claimed there was a need for further explanations regarding Khashoggi's killing. Yet, although Britain's Foreign Office said it was considering its "next steps" following the KSA's admission over Khashoggi's killing, UK seems to be taking a rather similar approach to France—but not Germany—regarding the situation.
In 2017, the UK was the sixth-biggest arms dealer in the world, and the second-largest exporter of arms to the KSA, behind the US. This is held to be a reflection of a large spear in sales last year. After the KSA intervened in the civil war in Yemen in early 2015, the UK approved more than 3.5billion euros in military sales to the kingdom between April 2015 and September 2016.
As a result, Theresa May has been under pressure for years to interrupt arms sales to the KSA especially after human rights advocates claimed the UK was contributing to alleged violations of international humanitarian law by the Saudi-led coalition in Yemen. Adding to this, in 2016, a leaked parliamentary committee report suggested that it was likely that British weapons had been used by the Saudi-led coalition to violate international law, and that manufactured aircraft by BAE Systems, have been used in combat missions in Yemen.
Lately, in the context of Khashoggi's death things have aggravated and the UK is now facing a great amount of pressure, mainly embodied by UK's main opposition Labour party which calls for a complete cease in its arms exports to the KSA. In addition, in terms of a more international strain, the European Union has also got to have a say in the matter. Philippe Lamberts, the Belgian leader of the Green grouping of parties, said that Brexit should not be an excuse for the UK to abdicate on its moral responsibilities and that Theresa May had to prove that she was keen on standing up to the kind of atrocious behaviour shown by the killing of Khashoggi and hence freeze arms sales to Saudi Arabia immediately.
Nonetheless, in response and laying emphasis on the importance the upholding relation with UK's key ally in the Middle East has, London has often been declining calls to end arms exports to the KSA. Foreign Secretary Jeremy Hunt defended there will be "consequences to the relationship with Saudi Arabia" after the killing of Khashoggi, but he has also pointed out that the UK has an important strategic relationship with Riyadh which needs to be preserved. As a matter of fact, according to some experts, UK's impending exit from the EU has played a key role. The Campaign Against Arms Trade (CAAT) claims Theresa May's pursuit for post-Brexit trade deals has seen an unwelcome focus on selling arms to some of the world's most repressive regimes. Nevertheless, by thus tackling the situation in a similar way to France, the UK justifies its actions by saying that it has one of the most meticulous permitting procedures in the world by remarking that its deals comprehend safeguards that counter improper uses.
Spain
After Saudi Arabia's gave its version for Khashoggi's killing, the Spanish government said it was "dismayed" and echoed Antonio Guterres' call for a thorough and transparent investigation to bring justice to all of those responsible for the killing. Yet, despite the clamour that arose after the murder of the columnist, just like France and the UK, Spain's Prime Minister, Pedro Sánchez, defended arms exporting to the KSA by claiming it was in Spain's interest to keep selling military tools to Riyadh. Sanchez held he stood in favour of Spain's interests, namely jobs in strategic sectors that have been badly affected by "the drama that is unemployment". Thusly, proclaiming Spain's unwillingness to freeze arms exports to the kingdom. In addition, even before Khashoggi's killing, Sanchez's government was subject to many critics after having decided to proceed with the exporting of 400 laser-guided bombs to Saudi Arabia, despite worries that they could harm civilians in Yemen. Notwithstanding this, Sánchez justified Spain's decision in that good ties with the Gulf state, a key commercial partner for Spain, needed to be kept.
As a matter of fact, Spain's state-owned shipbuilder Navantia, in which 5,500 employees work, signed a deal in July last year which accounted for 1.8 billion euros that supplied the Gulf country with five navy ships. This shipbuilder is situated in the southern region of Andalusia, a socialist bulwark which accounts for Spain's highest unemployment estimates and which has recently held regional elections. Hence, it was of the socialist president's interest to keep these constituencies pleased and the means to this was, of course, not interrupting arms deals with the KSA.
As a consequence, Spain has recently been ignoring the pressures that have arose from MEP's and from Sanchez's minorities in government—Catalan separatist parties and far-left party Podemos— which demand a cease in arms exporting. For the time being, Spain will continue business with the KSA as usual.
CONCLUSION
All things considered, while Saudi Arabia insists that MBS was not aware of the gruesome murder and is distracting the international attention towards more positive headlines—such as the appointment of the first female ambassador to the US—in order to clear the KSA's image in the context of Khashoggi's murder, several European countries have taken actions against the kingdom's interests. Yet, the way each country has approached the matter has led to the rise of two separate blocks which are at discordance within Europe itself. Whereas some European leaders have shown a united front in casting blame on the Saudi government, others seem to express geopolitical interests are more important.
During the time Germany, Norway, Denmark and Finland are being celebrated by human rights advocates for following through on their threat to halt sales to the kingdom, bigger arms exporters—like those that have been analysed—have pointed out that the latter nations have far less to lose than they do. Nonetheless, inevitably, the ceasing carried out by the northern European countries which are rather small arms exporters in comparison to bigger players such as the UK and France, is likely to have exacerbated concerns within the European arms industry of a growing anti-Saudi consensus in the European Union or even beyond.
What is clear is that due to the impact Saudi Arabia's state of affairs have caused, governments and even companies worldwide are coming under pressure to abandon their ties to the oil-rich, but at the same time, human-rights-violating Saudi Arabian leadership. Resultantly, in Europe, countries are taking part in two divergent blocks that are namely led by two of the EU's most compelling members: France and Germany. These two sides are of rather distant opinions regarding the matter, fact that does not seem to be contributing in terms of the so-much-needed European Union integration.
[Bruce Riedel, Kings and Presidents. Saudi Arabia and the United States since FDR. Brookings Institution Press. Washington, 2018. 251 p.]
review / Emili J. Blasco
Oil in exchange for protection is the pact sealed in early 1945 between Franklin D. Roosevelt and King Abdulaziz bin Saud on board the USS Quincy, in the waters off Cairo, when the American president was returning from the Yalta lecture . Since then, the special relationship between the United States and Saudi Arabia has been one of the key elements of international politics. Today, fracking makes Arabian oil less necessary for Washington, but cultivating Saudi friendship continues to be of interest to the White House, even in an unorthodox presidency in diplomatic matters: the first country that Donald Trump visited as president was precisely Saudi Arabia.
The ups and downs in this relationship, due to the vicissitudes of the world, especially in the Middle East, have marked the tenor of the contacts between the various presidents of the United States and the corresponding monarchs of the House of Saud. This book by Bruce Riedel, a former CIA analyst and member of the U.S. National Security committee as a specialist on the region, now directs project Intelligence at the Brookings Institution think tank, is dedicated to analyzing the content of these relations, following the successive pairs of interlocutors between Washington and Riyadh.
In this relationship, the central position occupied by the Palestinian question is surprising. One might sometimes think that many Arab countries' invocation of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is rhetorical, but Riedel notes that in the case of Saudi Arabia the issue is fundamental. It was part of the initial pact between Roosevelt and Abdulaziz bin Saud (the U.S. president pledged not to support the partition of Palestine to create the State of Israel without Arab consent, something that Truman did not respect, aware that Riyadh could not break with Washington because it needed U.S. oil companies) and since then it has appeared on every occasion.
 |
Progress or stalemates in the Arab-Israeli peace process, and the differing passion of Saudi kings on this issue, have directly shaped the relationship between U.S. administrations and the Saudi Monarchy. For example, Washington's support for Israel in the 1967 war resulted in the 1973 oil embargo; George Bush senior and Bill Clinton's efforts for a peace agreement helped a close relationship with King Fahd and Crown Prince Abdullah; the latter, on the other hand, led to a cooling off in the face of the disinterest shown by George Bush junior. "A vibrant and effective peace process will help cement a strong relationship between king and president; a stalled and exhausted process will damage their connection."
Will this issue continue to be a defining one for the new generations of Saudi princes? "The Palestinian cause is deeply popular in Saudi society, especially in the clerical establishment. The House of Saud has made the creation of a Palestinian state, with Jerusalem as its capital, emblematic of its policy since the 1960s. A generational change is unlikely to alter that fundamental stance."
In addition to this, there are two other aspects that have proven to be disruptive in the Washington-Riyadh entente: Wahhabism promoted by Saudi Arabia and the US demand for political reforms in the Arab world. Riedel asserts that, given the foundational alliance between the House of Saud and this strict Sunni variant of Islam, which Riyadh has promoted in the world to ingratiate itself with its clerics, as compensation each time it has had to bow to the demands of the impious United States, there is no room for a rupture between the two bodies. "Saudi Arabia cannot abandon Wahhabism and survive in its present form," he warns.
Thus, the book ends with a rather pessimistic outlook on the change -democratization, respect for human rights- that Saudi Arabia is facing from the international community (certainly without much insistence, in the case of the United States). Not only was Riyadh the "major player" in the counter-revolution at the time of the Arab Spring, but it may be a factor going against a positive evolution of the Middle East. "Superficially it appears that Saudi Arabia is a force for order in the region, someone who is trying to prevent chaos and disorder. But in the long run deadline, by trying to maintain an unsustainable order, forcibly enforced by a police state, the kingdom could, in fact, be a force for chaos."
Riedel has personally dealt with prominent members of the Saudi royal family. Despite a close relationship with some of them, especially Prince Bandar bin Sultan, who served as ambassador to the United States for more than twenty years, the book does not patronize Saudi Arabia in the disputes between Washington and Riyadh. More critical of George W. Bush than of Barack Obama, Riedel also points out the latter's inconsistencies in his Middle East policies.
![Satellite imagery of the Jordan River [NASA]. Satellite imagery of the Jordan River [NASA].](/documents/10174/16849987/jordan-river-blog.jpg)
▲Satellite imagery of the Jordan River [NASA].
ANALYSIS / Marina Díaz Escudero
Water is an essential natural resource, not only for individual survival on Earth, but also for nation-states and their welfare; having an effect on partner-economic development, trade, health and population productivity.
As a natural determinant of power, its accessibility must be considered by states in their policies on national security; "hydropolitics" being the branch of study for this phenomenon. Although it has been, and continues to be, a major source of inter-state conflict, it is an arena in which cooperation and diplomacy between rival countries can set the ground for further political agreements, effectively leading to more stable and peaceful relations.
On the other hand, when water is used as a natural border or must be shared between various countries, concurrent cooperation between all of them is essential to find an effective and non-violent way to approach the resource. Otherwise, an overlapping of different, and potentially contradictory, bilateral agreements may lead to frictions. If one of the concerned countries is not present in negotiations, as some historical events suggest (e.g. 1992 multilateral negotiations in Moscow, where Lebanon and Syria where not present), this will always constitute an obstacle for regional stability.
Moreover, although 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by water, factors such as economic interests, climate change, and explosive population growth are also challenging the sustainable distribution of water sources among countries. The future effects of this scarcity in the region will demand consistent political action in the long-term and current leaders should bear it in mind.
Water availability and conflict in the MENA region
The Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region is known as an arid and semi-arid region, with only 1% of the world's renewable water resources. On average, water availability is only 1,200 cubic meters, around six times less than the worldwide average of 7,000 cubic meters.
As global temperatures rise, more frequent and severe droughts will take place in the region and this will make countries which already have partner-economic rivalries more prone to go to war with each other. According to the World Resources Institute, thirteen of the thirty three states that will suffer from worse water scarcity in the twenty-first century will be Middle Eastern countries.
To quote the findings of the National Intelligence Council (NIC) report, Global Trends: Paradox of Progress, more than thirty countries - nearly half of them in the Middle East - will experience extremely high water stress by 2035, increasing economic, social, and political tensions.
Although claims to the land were and are the main motives for much of the current conflict, water, as part of the contested territories, has always been considered as a primary asset to be won in conflict. In fact, recognition of the importance of water lent the term, the "War over Water", to conflicts in the region, and control over the resource constitutes a significant advantage.
Despite there being several water bodies in the Middle East (Nile, Euphrates, Tigris...), the Jordan River basin is one of the most significant ones today in terms of its influence on current conflicts. The Jordan River Basin is a 223 km long river with an upper course from its sources up to the Galilee Sea, and a lower one, from the latter to the Dead Sea. Territories such as Lebanon, Israel and the West Bank are situated to its West, while Syria and Jordan border it to the East. Water scarcity in the Jordan watershed comes from many different factors, but the existence of cultural, religious and historical differences between the riparian countries (situated on the banks of the river) has led to a centuries-long mismanagement of the source.
Tensions between Zionism and the Arab world on regards to the Jordan River became noticeable in the 1950s, when most Arab countries rejected the Johnston Plan that aimed at dividing the water by constructing a number of dams and canals on the different tributaries of the river. The plan was based on an earlier one commissioned by the United Nations Relief and Works Agency (UNWRA) and was accepted by the water technical committees of the five riparian countries. Nevertheless, the Arab League didn't give the go-ahead and even hardened its position after the Suez Crisis.
In spite of this, Jordan and Israel decided to abide by their allocations and developed two projects, the Israeli National Water Carrier (to transport water from the north to the center and south) and Jordan's East Ghor Main Canal (King Abdullah Canal). In retaliation and with severe consequences, Arab states reunited in an Arab Summit (1964) and decided to divert Jordan's headwaters to the Yarmouk river (for the Syrian Arab Republic and Jordan), depriving Israel of 35% of its Water Carrier capacity.
This provocation led to a series of military clashes and prompted Israel's attack on Arab construction projects; a move that would help precipitate the 1967 Six-Day War, according to some analysts. As a result of the war, Israel gained control of the waters of the West Bank (formely Jordan-annexed in the 1948 war and today still controlled by the Israeli Civil Administration) and the Sea of Galilee (today constituting about 60% of the country's fresh water).
Later, in 1995, by the Article 40 of the Oslo II political agreement, [...] Israel recognized Palestinian water rights in the West Bank and established the Joint Water Committee to manage and develop new supplies and to investigate illegal water withdrawals. Nevertheless, the loss of control over water in the West Bank has never been accepted by neighboring Arab countries as, despite the agreement, much of the water coming from it is still directly given to Israeli consumers (and only a smaller fraction to Palestinians living under their control).
Role of water in Syrian-Israeli hostilities
Hostilities have been covering the diary of Syrian-Israeli relationships ever since the Armistice Agreements signed by Israel with each of the four neighboring Arab countries in 1949. This is compounded by the fact that there is seldom mutual agreement with resolutions proposed by the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
The Golan Heights, a rocky plateau in south-western Syria, was taken away by Israel in the aftermath of the Six-Day War and is still considered an Israeli-occupied territory. In 1974 the Agreement on Disengagement was signed, ending the Yom Kippur War and resulting in the formation of the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF), a buffer zone separating the Israeli portion of the Golan Heights and the rest of Syria. Although Israel kept most of the Golan Heights territory, in 1981 it unilaterally passed the Golan Heights Law to impose its jurisdiction and administration on the occupied territory (refusing to call it "annexation"). These laws did not receive international recognition and were declared void by the UNSC.
The fact that Israel's Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu stated in April 2016 in a weekly cabinet meeting that "the Golan Heights will remain forever in Israeli hands" has once again triggered the rejection of UNSC's members, who have declared that the status of the Heights "remains unchanged."
Rainwater catchment in the Golan Heights feeds into the Jordan River and nowadays provides a third of Israel's water supply. Although "Syria has built several dams in the Yarmouk river sub-basin, which is part of the Jordan River basin", the Golan Heights are likely to remain an important thorn in future Israeli-Syrian relations.
|
Map of the Jordan River Basin [Palestinian Authority]. |
Water as a casus belli between Lebanon and Israel
In March 2002, Lebanon decided to divert part of the Hasbani (a major tributary of the Jordan upper course) to supply the Lebanese Wazzani village. Ariel Sharon, the former Prime Minister of Israel, said that the issue could easily become a "casus belli". According to Israel, Lebanon should have made consultations before pumping any water from the Springs, but both the Lebanese government and Hezbollah (a shi'a militant group) condemned the idea.
The Wazzani project, according to Lebanon, only aimed to redevelop the south by extracting a limited amount of water from the Hasbani; 300 MCM per year (they drew 7 MCM by the time). The actual conflict with Israel began when Lebanon started constructing the pumping station very close to the Israeli border.
The United States (US) decided to establish a State Department water expert in order to assess the situation "and cool tempers" but in 2006, during the Lebanon war, the pumping station and other infrastructures, such as an underground water diversion pipe which run Letani river water to many villages, were destroyed.
Although Israeli-Lebanese tensions have continued due to other issues, such as spying, natural gas control and border incidents, water source domination has been a significant contributor to conflict between the two states.
Inter-Arab conflicts on water allocation
Some inter-Arab conflicts on regards to water distribution have also taken place, but they are small-scale and low level ones. In 1987, an agreement was signed between Jordan and Syria which allowed the latter to build twenty five dams with a limited capacity in the Yarmouk River. Later on it was proved that Syria had been violating the pact by constructing more dams than permitted: in 2014 it had already constructed forty two of them. New bilateral agreements were signed in 2001, 2003 and 2004, but repeated violations of these agreements by Syria in terms of water-allocation became unsustainable for Jordan. Most recently (2012), former Jordan's water minister Hazim El Naser stressed the necessity "to end violations of the water-sharing accords."
Although these are low-level tensions, they could quickly escalate into a regional conflict between Jordan, Syria and Israel, as a decrease of water from the Yarmouk released by Syria to Jordan may prevent Jordan to comply with its commitments towards Israel.
Regional cooperation: from multilateralism to bilateralism
Since the beginning of the last century, attempts to achieve multilateral cooperation and a basin-wide agreement between the five co-riparian countries have been hindered by regional political conflict. Boundary definition, choices about decision-making arrangements, and issues of accountability, together with other political divisions, can help explain the creation of subwatershed communities of interest instead of a major watershed agreement between all neighboring countries.
The Israeli-Palestine peace process began in 1991 with the Conference in Madrid, attended by all riparians: Israel, Jordan, Palestine, Lebanon and Syria. Co-sponsored by the US and the Soviet Union as representatives of the international community, it addressed several regional issues, such as environment, arms control, economic development and, of course, water distribution (in fact, water rights became one of the trickiest areas of discussion).
In 1992, multilateral negotiations about regional cooperation continued in Moscow but this time they were only attended by Israel, the Jordanian-Palestinian delegation and the international community; Syria and Lebanon were not present. "After the failed Johnston plan, external efforts to achieve a multilateral agreement through cooperation on water sources were attempted by the Centre for Environmental Studies and Resource Management (CESAR) [...] As Syria and Lebanon did not want to participate in a process involving Israel, (it) ran parallel processes for Israel, the Palestinian Authority and Jordan on the one hand, and Syria and Lebanon on the other hand."
As a matter of fact, bilateral instruments grew in importance and two treaties, between Israel and Jordan/Palestine respectively, were signed: The Treaty of Peace between The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan and The State of Israel (1994) and The Israeli-Palestinian Interim Agreement on the West Bank and the Gaza Strip (Oslo II, 1995). Discussions about water use and joint water management played an important role and were included in the annexes.
In 1996, the Trilateral Declaration on Principles for Cooperation on Water-Related Matters and New and Additional Water Resources was signed by Israel, Jordan and the Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) and in 2003 the first two initiated a plan called Roadmap for Peace which included the revival of cooperation on regional issues like water.
Although Israel and Syria started some negotiations to solve the Golan Heights' problem in 2008, after the break out of the Syrian civil war distrust between both actors has increased, leaving the most important thorn in multilateral regional negotatiations still unsolved. Nevertheless, "a new government in Syria after the end of the war may provide new opportunities for improved bi- and ultimately multilateral cooperation," says the FAO. The previous year (2007) Jordan and the Syrian Arab Republic also signed some agreements "in regard to shared water in the Yarmouk river basin."
Role of Non-Governmental Organizations
Civil society has also been an important platform for resource-management discussions between riparian countries.
Middle Eastern rhetoric, according to the BBC, "often portrays the issue of water as an existential, zero-sum conflict - casting either Israel as a malevolent sponge sucking up Arab water resources, or the implacably hostile Arabs as threatening Israel's very existence by denying life-giving water."
For this reason, in 2010, Friends of the Earth Middle East (FoEME, also called EcoPeace Middle East) stressed the importance of replacing this win-lose approach for a compromising perspective of mutual gains for all. In this way, their proposals don't "include quantitative water allocations, but the implementation of a joint institutional structure that is continuously tasked with peaceful conflict resolution over water resources; [...] defining water rights not as the access to a certain water quantity, but as a broader bundle of rights and duties to access and use the available water and to uphold quality and quantity standards."
Through "The Good Water Neighbors" project (2001), the NGO tried to raise awareness about the negative consequences of leaving this issue unmanaged and reiterated its willingness to strenghten "institutional capacities for collaboration in the region." According to the staff, Israel, Jordan and Palestine could develop a certain interdependence, focused on water (Israel to Jordan/Palestine) and solar-generated electricity (Jordan to Palestine/Israel), in order to facilitate the powering of desalination plants and produce more cleanwater for sale.
The use of this type of political support for transboundary cooperation, based on water access but focused on solving less cultural and sensitive problems (like environmental sustainability), as a means to opening up avenues for dialogue on other political issues, could be the key for a lasting peace in the region.
According to Gidon Brombert, cofounder and Israeli director of FoEME, adopting "healthy interdependencies is a powerful way to promote regional water and energy stability as a foundation for long-lasting peace between our people."
A testament to the success of these initiatives is the fact that Jordan and Israel scored 56.67 under the Water Cooperation Quotient (WCQ) 2017, which means that there is currently zero risk of a water-related war between both states (50 is the minimum score for this to apply).
Final key points and conclusions
There is no doubt that water issues have been a key discussion point between riparian countries in the Jordan River watershed since the late nineteenth century, and rightly so, as the only way to achieve a long-lasting peace in the region is to accept that water management is an integral part of political discourse and decisions. Not only because it is an essential factor in the conflicts that arise between states, but because agreements on other political matters could be furthered through the establishment of sound agreements in the hydropolitical arena.
In other words, a "baby-step" approach to politics should be applied: peaceful discussions on this and other matters leveraged to talk about other sources of conflict and utilized to improve political relations between two parties. The Korean conflict is a good example: although both Koreas are far from agreeing with regards to their political outlook, they have been able to cooperate in other fields, such as the Winter Olympic games. Communication during the games was used to subtly suggest avenues for a political reapproachment, which now seems to be progressing satisfactorily.
As for multilateral-bilateral conditions of negotiations, it is important to take into account the fact that the Jordan River basin, mainly due to its geological condition as a watershed, has to be shared by several different countries, five to be exact. This may seem obvious but clearly many actors don't see its implications.
Understandably, it is very difficult for a state to manage various bilateral agreements concerning the same asset with countries that are mutually at odds with one another. Their contents can overlap, creating contradictions and making the achievement of a general arrangement not only disorganized, but also challenging. Notwithstanding, a multilaterally agreed distribution of the basin's water - taking into account the necessities of all riparians simultaneously, could more easily pave the way for further cooperation on other, pressing, political issues.
Last but not least, it is important not to forget about policies related to other regional affairs, and their potential effect on water management. Climate change, for instance, will certainly affect water availability in the MENA region and the Jordan River basin, easily disrupting and modifying past and future agreements on the resource's allocation and distribution. Attention should also be paid to interest groups and to the economic situation of the countries involved in the negotiations, as these will be determinant in states' decisions about the implementation of certain future projects.
![Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman and President Donald Trump during a meeting in Washington in 2017 [White House] Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman and President Donald Trump during a meeting in Washington in 2017 [White House]](/documents/10174/16849987/women-arabia-saudi-blog.jpg)
▲Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman and President Donald Trump during a meeting in Washington in 2017 [White House]
ANALYSIS / Naomi Moreno
Saudi Arabia used to be the only country in the world that banned women from driving. This ban was one of the things that the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) was best known for to outsiders not otherwise familiar with the country's domestic politics, and has thus been a casus belli for activists demanding reforms in the kingdom. Last month, Saudi Arabia started issuing the first driver's licenses to women, putting into effect some of the changes promised by the infamous Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman (MBS) in his bid to modernize Saudi Arabian politics. The end of the ban further signals the beginning of a move to expand the rights of women in KSA, and builds on piecemeal developments that took place in the realm of women's rights in the kingdom prior to MBS' entrance to the political scene.
Thus, since 2012, Saudi Arabian women have been able to do sports as well as participate in the Olympic Games; in the 2016 Olympics, four Saudi women were allowed to travel to Rio de Janeiro to compete. Moreover, within the political realm, King Abdullah swore in the first 30 women to the shura council − Saudi Arabia's consultative council − in February 2013, and in the kingdom's 2015 municipal elections, women were able to vote and run for office for the first time. Finally, and highlighting the fact that economic dynamics have similarly played a role in driving progression in the kingdom, the Saudi stock exchange named the first female chairperson in its history − a 39-year-old Saudi woman named Sarah Al Suhaimi − last February.
Further, although KSA may be known to be one of the "worst countries to be a woman", the country has experienced a B breakthrough in the last 5 years and the abovementioned advances in women's rights, to name some, constitute a positive development. However, the most visible reforms have arguably been the work of MBS. The somewhat rash and unprecedented decision to end the ban on driving coincided with MBS' crackdown on ultra-conservative, Wahhabi clerics and the placing of several of the kingdom's richest and most influential men under house arrest, under the pretext of challenging corruption. In addition, under his leadership, the oil-rich kingdom is undergoing economic reforms to reduce the country's dependency on oil, in a bid to modernize the country's economy.
Nonetheless, despite the above mentioned reforms being classified by some as unprecedented, progressive leaps that are putting an end to oppression through challenging underlying ultra-conservatism traditions (as well as those that espouse them), a measure of distrust has arisen among Saudis and outsiders with regards the motivations underlying the as-of-yet seemingly limited reforms that have been introduced. While some perceive the crown prince's actions to be a genuine move towards reforming Saudi society, several indicators point to the possibility that MBS might have more practical reasons that are only tangentially related to progression for progression's sake. As the thinking goes, such decrees may have less to do with genuine reform, and more to do with improving an international image to deflect from some of the kingdom's more controversial practices, both at home and abroad. A number of factors drive this public scepticism.
Reasons for scepticism
The first relates to the fact that KSA is a country where an ultraconservative form of shari'a or Islamic law continues to constitute the primary legal framework. This legal framework is based on the Qur'an and Hadith, within which the public and many private aspects of everyday life are regulated. Unlike in other Muslim majority countries, where only selective elements of the shari'a are adopted, Wahhabism – which is identified by the Court of Strasbourg as a main source of terrorism − has necessitated the strict adherence to a fundamentalist interpretation of shari'a, one that draws from the stricter and more literal Hanbali school of jurisprudence. As such, music and the arts have been strictly controlled and censored. In addition, although the religious police (more commonly known as the Committee for the Promotion of Virtue and the Prevention of Vice) have had their authority curbed to a certain degree, they are still given the authority to enforce Islamic norms of conduct in public by observing suspects and forwarding their findings to the police.
In the past few years, the KSA has been pushing for a more national Wahhabism, one that is more modern in its outlook and suitable for the kingdom's image. Nevertheless, the Wahhabi clergy has been close to the Al Saud dynasty since the mid-18th century, offering it Islamic legitimacy in return for control over parts of the state, and a lavish religious infrastructure of mosques and universities. Therefore, Saudi clerics are pushing back significantly against democratization efforts. As a result, the continuing prevalence of a shari'a system of law raises questions about the ability of the kingdom to seriously democratise and reform to become moderate.
Secondly, and from a domestic point of view, Saudi Arabia is experiencing disharmony. Saudi citizens are not willing to live in a country where any political opposition is quelled by force, and punishments for crimes such as blasphemy, sorcery, and apostasy are gruesome and carried out publicly. This internal issue has thus embodied an identity crisis provoked mainly by the 2003 Iraq war, and reinforced by the events of the Arab Spring. Disillusionment, unemployment, religious and tribal splits, as well as human rights abuses and corruption among an ageing leadership have been among the main grievances of the Saudi people who are no longer as tolerant of oppression.
In an attempt to prevent the spill over of the Arab Spring fervor into the Kingdom, the government spent $130 billion in an attempt to offset domestic unrest. Nonetheless, these grants failed to satisfy the nearly 60 percent of the population under the age of twenty-one, which refused to settle. In fact, in 2016 protests broke out in Qatif, a city in Saudi Arabia's oil-rich, eastern provinces, which prompted Saudis to deploy additional security units to the region. In addition, in September of last year, Saudi authorities, arguing a battle against corruption and a crack down on extremism, arrested dozens of people, including prominent clerics. According to a veteran Saudi journalist, this was an absurd action as "there was nothing that called for such arrests". He argued that several among those arrested were not members of any political organization, but rather individuals with dissenting viewpoints to those held by the ruling family.
Among those arrested was Sheikh Salman al-Awdah, an influential cleric known for agitating for political change and for being a pro-shari'a activist. Awdah's arrest, while potentially disguised as part of the kingdom's attempts to curb the influence of religious hardliners, is perhaps better understood in the context of the Qatar crisis. Thus, when KSA, with the support of a handful of other countries in the region, initiated a blockade of the small Gulf peninsula in June of last year, Awdah welcomed a report on his Twitter account suggesting that the then three-month-old row between Qatar and four Arab countries led by Saudi Arabia may be resolved. The ensuing arrest of the Sheikh seems to confirm a suspicion that it was potentially related to his favouring the renormalization of relations with Qatar, as opposed to it being related to MBS' campaign to moderate Islam in the kingdom.
A third factor that calls into question the sincerity of the modernization campaign is economic. Although Saudi Arabia became a very wealthy country following the discovery of oil in the region, massive inequality between the various classes has grown since, as these resources remain to be controlled by a select few. As a result, nearly one fifth of the population continues to live in poverty, especially in the predominantly Shi'a South where, ironically, much of the oil reservoirs are located. In these areas, sewage runs in the streets, and only crumbs are spent to alleviate the plight of the poor. Further, youth opportunities in Saudi Arabia are few, which leaves much to be desire, and translates into occasional unrest. Thus, the lack of possibilities has led many young men to join various terrorist organizations in search of a new life.
|
Statement by MBS in a conference organized in Riyadh in October 2017 [KSA] |
Vision 2030 and international image
In the context of the Saudi Vision 2030 , the oil rich country is aiming to wean itself of its dependence on the natural resource which, despite its wealth generation capacity, has also been one of the main causes of the country's economic problems. KSA is facing an existential crisis that has led to a re-think of its long-standing practice of selling oil via fixed contracts. This is why Vision 2030 is so important. Seeking to regain better control over its economic and financial destiny, the kingdom has designed an ambitious economic restructuring plan, spearheaded by MBS. Vision 2030 constitutes a reform programme that aims to upgrade the country's financial status by diversifying its economy in a world of low oil prices. Saudi Arabia thus needs overseas firms' investments, most notably in non-oil sectors, in order to develop this state-of-the-art approach. This being said, Vision 2030 inevitably implies reforms on simultaneous fronts that go beyond economic affairs. The action plan has come in at a time when the kingdom is not only dealing with oil earnings and lowering its reserves, but also expanding its regional role. As a result, becoming a more democratic country could attract foreign wealth to a country that has traditionally been viewed in a negative light due to its repressive human rights record.
This being said, Saudi Arabia also has a lot to do regarding its foreign policy in order to improve its international image. Despite this, the Saudi petition to push the US into a war with Iran has not ceased during recent years. Religious confrontation between the Sunni Saudi autocracy and Iran's Shi'a theocracy has characterized the geopolitical tensions that have existed in the region for decades. Riyadh has tried to circumvent criticism of its military intervention in the Yemen through capitalizing on the Trump administration's hostility towards Iran, and involving the US in its campaign; thus granting it a degree of legitimacy as an international alliance against the Houthis. Recently, MBS stated that Trump was the " best person at the right time" to confront Iran. Conveniently enough, Trump and the Republicans are now in charge of US' foreign affairs. Whereas the Obama administration, in its final months, suspended the sale of precision-guided missiles to Saudi Arabia, the Trump administration has moved to reverse this in the context of the Yemeni conflict. In addition, in May of this year, just a month after MBS visited Washington in a meeting which included discussions regarding the Iran accords, the kingdom has heaped praise on president Trump following his decision to withdraw from the Iran nuclear deal.
All things considered, 2018 may go down in history as the irreversible end of the absolute archaic Saudi monarchy. This implosion was necessitated by events, such as those previously mentioned, that Saudi rulers could no longer control or avoid. Hitherto, MBS seems to be fulfilling his father's wishes. He has hand-picked dutiful and like-minded princes and appointed them to powerful positions. As a result, MBS' actions suggest that the kingdom is turning over a new page in which a new generation of princes and technocrats will lead the breakthrough to a more moderate and democratic Saudi Arabia.
New awareness
However, although MBS has declared that the KSA is moving towards changing existing guardianship laws, due to cultural differences among Saudi families, to date, women still need power of attorney from a male relative to acquire a car, and risk imprisonment should they disobey male guardians. In addition, this past month, at least 12 prominent women's rights activists who campaigned for women's driving rights just before the country lifted the ban were arrested. Although the lifting of the ban is now effective, 9 of these activists remain behind bars and are facing serious charges and long jail sentences. As such, women continue to face significant challenges in realizing basic rights, despite the positive average endorsement that MBS' lifting of the driving ban has received.
Although Saudi Arabia is making an effort in order to satisfy the public eye, it is with some degree of scepticism that one should approach the country's motivations. Taking into account Saudi Arabia's current state of affairs, these events suggest that the women's driving decree was an effort in order to improve the country's external image as well as an effort to deflect attention from a host of problematic internal and external affairs, such as the proxy warfare in the region, the arrest of dissidents and clerics this past September, and the Qatari diplomatic crisis, which recently "celebrated" its first anniversary. Allowing women to drive is a relatively trivial sacrifice for the kingdom to make and has triggered sufficient positive reverberations globally. Such baby steps are positive, and should be encouraged, yet overlook the fact that they only represent the tip of the iceberg.
As it stands, the lifting of the driving ban does not translate into a concrete shift in the prevailing legal and cultural mindsets that initially opposed it. Rather, it is an indirect approach to strengthen Saudi's power in economic and political terms. Yet, although women in Saudi Arabia may feel doubtful about the government's intentions, time remains to be their best ally. After decades of an ultraconservative approach to handling their rights, the country has reached awareness that it can no longer sustain its continued oppression of women; and this for economic reasons, but also as a result of global pressures that affect the success of the country's foreign policies which, by extension, also negatively impact on its interests.
The silver lining for Saudi woman is that, even if the issue of women's rights is being leveraged to secure the larger interests of the kingdom, it continues to represent a slow and steady progression to a future in which women may be granted more freedoms. The downside is that, so long as these rights are not grafted into a broader legal framework that secures them beyond the rule of a single individual − like MBS − women's rights (and human rights in general) will continue to be the temporary product of individual whim. Without an overhaul of the shari'a system that perpetuates regressive attitudes towards women, the best that can be hoped for is the continuation of internal and external pressures that coerce the Saudi leadership into exacting further reforms in the meantime. As with all things, time will tell.
![ISIS Toyota convoy in Syria [ISIS video footage] ISIS Toyota convoy in Syria [ISIS video footage]](/documents/10174/16849987/toyota-blog.jpg)
▲ISIS Toyota convoy in Syria [ISIS video footage]
ANALYSIS / Ignacio Yárnoz
When you go to a Toyota distributor to buy a Toyota Land Cruiser or a Toyota Hilux, what they proudly tell you is how resistant, fast and reliable the truck is. However, what they do not tell you is how implicated in wars and conflicts the truck has been due to the very same characteristics. We have seen in recent newscasts that in many of today's conflicts, there's a Toyota truck; no matter how remote the country is. This is because, if the AK47 is the favourite weapon for militias in developing countries, the Toyota Hilux and Land Cruiser are the militia's trucks of choice.
This is no surprise when one considers that the Toyota Land Cruiser was initially designed to be a military car inspired by the famous Jeep Willis at the time Japan was occupied by the US after Japan's defeat in World War II. However, its popularity among terrorist groups, militias, as well as developing countries' national armies only gained ground in the 80's when a conflict between Chad and Libya proved the trucks' effectiveness as war machines; simultaneously calling into question the efficacy of traditional war strategies and military logistics.
This little-known story is about how an army comprising 400 Toyota pickups of the Chadian army outmanoeuvred and overwhelmed a vastly superior force equipped with soviet-era tanks and aircrafts of the Libyan army. The historical event demonstrated how a civilian truck was able to shape international borders, tipping the balance in favour of the inferior party to the conflict.
The Toyota War
The Toyota War is the name given to the last phase of the Chad-Libyan War that raged on for almost a decade, yet did not have relevance until its last phase. This last phase began in 1986 and ended a year later with a heavy defeat inflicted on the Libyan army by the Chadians. In total, 7,500 men were killed and 1.5 billion dollars worth of military equipment was destroyed or captured. Conversely, Chad only lost 1,000 men and very little military equipment (because they hardly had any).
The last phase of the conflict developed in the disputed area of the North of Chad, an area that had been occupied by Libyan forces in 1986 due to its natural resources such as uranium (highly interesting for Gadhafi and his nuclear armament project). At the beginning of 1987, the last year of the war, the Libyan expeditionary force comprised 8,000 soldiers, 300 T-55 battle tanks, multiple rocket launchers and regular artillery, as well as Mi-24 helicopters and sixty combat aircrafts. However, the Libyan soldiers were demotivated and disorganized. The Chadians, on the other hand, had nothing but 10,000 brave and motivated soldiers with neither air support nor armoured tanks. However, by 1987, Chad could count on the French Air Force to keep Libyan aircraft grounded but, perhaps more importantly, a 400 Toyota pickups fleet equipped with MILAN (Missile d ́infanterie léger antichar) anti-tank guided missiles sent by the French Government. Additionally, it could also be equipped with .50 calibre machine guns, with archaic flak cannons for anti-air purposes or even rocket clusters to be used as WWII-style artillery.
This logistical combination proved to be superior to that employed by the Libyan army as Toyota pickup trucks could easily outmanoeuvre the heavily armoured Russian tanks. Whereas the latter consumed around 200 L/100 km, the Toyota trucks consumed a fraction, at 10L/100 km. In addition, Toyota Trucks could mobilize groups of 20 people in a single truck, enabling faster transport and deployment of troops to the conflict scene; an advantage the Russian tanks did not have.
Reminiscent of the Maginot line when the Nazi army challenged the old trenches system utilizing a fixed artillery method with the innovative Thunder war strategy, the Chad Army emerged victorious over the Libyans through a simple strategic innovation in military logistics. Something clearly demonstrated in the Battle of Fada. In this instance, a Libyan armoured brigade defending Fada was almost annihilated: 784 Libyans and CDR (Democratic Revolutionary Council) militiamen died, 92 T-55 tanks and 33 BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicles were destroyed, and 13 T-55s and 18 BMP-1s were captured, together with the 81 Libyan soldiers operating them. Chadian losses, on the other hand, were minimal: only 18 soldiers died and three Toyotas were destroyed.
All in all, this situation was one of the first deployments of the Toyota Hilux in a conflict zone, demonstrating the reliability of the truck and its high performance in harsh environments. A testament to the Toyota's endurance was its featuring in the famous TV show "Top Gear" where a 1980's Toyota Hilux was put to a wrecking ball, set on fire, submerged in a sea bay for 5 hours, then left on the top of a building waiting its final demolishment, yet still rolled.
Ever since, Toyota trucks have been sighted in conflicts in Nicaragua, Ethiopia, Rwanda, Liberia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (CDR), Lebanon, Yemen, Sudan, and Pakistan and as the New York Times has reported, the Hilux remains the pirates' 'ride of choice.' The deployment of Daesh of a fleet of hundreds of Toyotas in Mosul in 2014 was a lasting testament of the trucks' durability.
|
Chad's troops during the war against Libya in the 1980s [Wikimedia Commons] |
Adaptability
How could the West deal with this issue? To deploy a massive fleet of Humvees? It would be naïve to attack an enemy with their own means. This hardly appears to constitute an effective solution. Humvees are already being substituted by JLTV (Joint Light Tactical Vehicle) due to their vulnerability to IED's (Improvised Explosive Devices); something insurgents are allowed to use but western countries are not due to international treaties and ethical values (how can a mine be designed such that it can distinguish a civilian truck from a Toyota driven by insurgents?). This proves the challenge that counterinsurgency policies (COIN) entail and the need to move to a next generation as far as COIN strategies are concerned.
The Toyota example is one of many that clearly signals a need for conventional state armies to adapt their logistical capabilities to better match the challenges of non-conventional warfare and insurgencies; the primary forms of conflict in which our nations are today engaged. The first lesson is clearly that the traditional focus on high power and the availability of resources is poorly suited to respond to contemporary insurgencies and military engagement with primarily non-state entities. Rather, there is a growing need for logistical versatility, combining both attack power and high manoeuvrability. The Toyota issue is an interesting example that illustrates how groups like Daesh have been able to mobilize an easily accessible, relatively non-expensive market commodity that has proven to be effective in lending the group precisely the kind of logistical aid required to successfully wage its insurgency. This being said, there are a number of dilemmas posed to nation states engaging in COIN strategies that prevent them from being able to employ the same methodology. Clearly there is a need to constantly engage in the adaptation of COIN strategies to respond to new threats and the surprising innovation of the adversary. However, COIN campaigns have been difficult to manage, and even harder to win, since time immemorial.
Recent research in political science and economics investigates a number of difficulties security forces face during conflicts with insurgent actors (Trebbi et al., 2017). Development and military aid spending have uneven effects, and conventional military strategies, including aerial bombardment, can erode civilian support for the COIN. Although states have historically used mass killings of non-combatants to undermine logistical support for guerrilla actors, evidence from modern insurgencies indicates that these measures may have the opposite effect: in some cases, such measures may encourage recruitment and mobilization (Trebbi et al., 2017). As such, the challenge is to constantly adapt to meet the requirements of contemporary warfare, whilst simultaneously assessing and remaining cognizant of the effects that COIN measures have on the overall campaign.
Adaptation through learning and innovation occurs on a much different time-scale than evolution. Although both involve information exchange with the environment and with elements within the system, evolution occurs over long periods of time through successive generations that have been able to successfully survive to changes (Hayden, 2013). Learning is the process of modifying existing knowledge, behaviours, skills, values, or preferences, and innovation involves the incorporation of a previously unused element into the system, or the recombination of existing elements in new ways.
Airstrikes
In the previous example of the conflict between Chad and Libya, it was mentioned that the Libyan army had its air force inoperative due to the presence of French air support. Another important point to make is that Toyotas may have been effective war machines for the terrain and surrounding environment, yet would nevertheless have been vulnerable to airstrikes had the Libyan army been able to engage air power against the Chadians. Air and space are part of the future of COIN strategies, despite composing only one element of them. They are our eyes (UAV systems), our way to get away or deploy forces (Chinook helicopters for example) and also the sword that can eliminate the threat (e.g. Predator drones). However, maintaining complete dominance over the battle space does not guarantee victory.
Due to the success of the air campaign in Operation Desert Storm, airpower seemed to be the predominating weapon of choice for future warfare. Yet, recent operations in Afghanistan and Iraq have called that assertion into question. Airstrikes in ground operations have proven to be controversial in small wars, especially when it comes to civilian casualties and its impact on civilian morale (an element that could enhance local support to insurgents). This is why, to win popular support, the US air force had to rethink its operations in Afghanistan and Iraq to win popular support (this also a result of Taliban and Pakistani propaganda and political pressure). Most recently, the US, along with France and the UK, have engaged in massive airstrikes on strategic infrastructure devoted to chemical development supposedly for a military use. Although being calibrated, proportional and targeted, those attacks have created a lot of internal discussion in the West and have divided society. As such, the future environment seems certain to further limit the kind of strikes it can make with airpower and missiles.
Consequently, technologically superior air assets nowadays face significant challenges in engaging dispersed and oftentimes unseen opponents. The Air Force must determine how modern airpower can successfully engage an irregular opponent. Air power, the "strategic panacea" of Western policymakers (Maxey, 2018), will no longer maintain the same utility that it does against rural insurgents. Although tactical Predator strikes and aerial reconnaissance may have shifted the street-to-street fighting against Daesh, such operations are severely limited within expansive megacities. The threat of civilian casualties is often too high, even for precision-guided munitions with limited blast radius. Further. buildings and layers of infrastructure often obscure a clear overhead view.
For 2030, the United Nations (UN) suggests that around 60 percent of global population will live in urban areas. There are 512 cities of at least one million inhabitants around the world, and this is expected to grow to 662 cities by 2030. Many of the megacities that will emerge will come from the developing world. That is why it is so urgent to design strategies to adapt to operating within metropolitan environments where small roads prevent large tanks to manoeuvre, where buildings give cover to heavy cannon targets and where one is more exposed to the crosshairs of insurgents taking cover in civilian infrastructure.
As U.S. Army Chief of Staff Gen. Mark Milley remarked in 2016; "In the future, I can say with very high degrees of confidence, the American Army is probably going to be fighting in urban areas. We need to man, organize, train and equip the force for operations in urban areas, highly dense urban areas, and that's a different construct. We're not organized like that right now".
In addition to this, National armies must be able to work through host governments, providing training, equipment and on-the-ground assistance to their local partners. The mere presence of a foreign army in the area often creates a negative perception among the local population and, unfortunately, in other cases, violent opposition. However, if the army patrolling the city wears the national flag, things change. Defeating an insurgency depends upon effective state building.
REFERENCES
Engel, P. (2018). These Toyota trucks are popular with terrorists — here's why. Business Insider. [Accessed 21 Apr. 2018].
S.L.P., I. (2018). The Toyota War in Syria. Instituto de Estrategia S.L.P. [Accessed 21 Apr. 2018].
Wang, A. (2018). How did the Toyota pickup become terrorists' favorite truck?. Quartz.
Maxey, L. (2018). Preparing for the Urban Future of Counterinsurgency.
Smallwarsjournal.com. (2018). Air and Space Power COIN / IW | Small Wars Journal.
Costas, J. (2018). The dark and warlike side of the Toyota Land Cruiser. Motorpasion.com.
Tomes, R. R. (2004). Relearning counterinsurgency warfare. Parameters, 34(1), 16-29.
Hayden, N. K. (2013). Innovation and Learning in Terrorist Organizations: Towards Adaptive Capacity and Resiliency. System Dynamics Society.
Ryan, A., & Dila, M. (2014). Disruptive Innovation Reframed: Insurgent Design for Systemic Transformation.
Trebbi, F., Weese, E., Wright, A. L., & Shaver, A. (2017). Insurgent Learning (No. w23475). National Bureau of Economic Research.
essay / Túlio Dias de Assis [English version].
The President of the United States, Donald Trump, surprised in December with another of his statements, which, like many previous ones, was not without controversy. This time the surprise topic was the advertisement of the opening of the US embassy in Jerusalem, thus consummating the recognition of the ancient city as the capital of the only Jewish state in the world today: Israel.
Trump's controversial advertisement , on an issue as controversial as it is sensitive, was criticized internationally and had little foreign support. Nevertheless, a few countries joined the U.S. initiative, and a few others expressed ambiguity. Among these, several European Union countries were singled out by the media. Has there really been a lack of internal cohesion within the Union on this issue?
Why Jerusalem matters
First of all, it is worth analyzing status in more detail, starting with a simple question: Why is Jerusalem so important? There are several factors that make Hierosolyma, Yerushalayim, Al-quds or simply Jerusalem so important not only regionally, but also globally, among which the following three stand out: its historical relevance, its religious importance and its geostrategic value.
Historical relevance. It is one of the oldest human settlements in the world, tracing its earliest origins to the fourth millennium BC. Apart from being the historical capital of both the region of Palestine or Canaan, as well as of the various Jewish kingdoms established throughout the first millennium BC in that part of the Levant.
Religious importance. It is a very sacred city for the three major monotheistic religions of the world, each for its own reasons: for Christianity, mainly because it is where the crucifixion of Christ took place; for Islam, apart from being the city of several prophets - shared in the beliefs of the other Abrahamic religions - and a place of pilgrimage, it is also where Muhammad made his well-known night journey; and obviously, for Judaism, for historical reasons and also because it is where the sacred Temple of Solomon was built.
Geostrategic value. At the geostrategic level it also has a great relevance, since it is a crucial point that connects the Levantine Mediterranean coast with the Jordan Valley. Therefore, its owner would have under its control a great geostrategic advantage in the Levant region.
It is not surprising, then, that the status of this city is one of the main points of conflict in the peace negotiations between the two peoples, as is well known. Hence, Trump's intervention has not been of great financial aid help in resuming the peace process; rather, it could be argued, it has been quite the opposite: it has provoked an outcry not only from the local Palestinians, but from the entire Arab world, thus further destabilizing the region. There have been counter-reactions from Hamas, Hezbollah and also from several Islamic governments in the Middle East (among them even Erdogan's, despite the fact that the Republic of Turkey is de jure a secular state). Hamas called for an intifada against Israel: the multiple demonstrations in the Palestinian territories ended with several hundred wounded and a dozen dead, due to clashes with Israeli police forces.
Europe's position
Europe, for its part, is trying to maintain a rather more neutral and balanced position, aimed at achieving regional peace. The European Union's willingness to mediate mainly takes into account the resolutions passed by the UN on this problematic issue topic. The European declarations, considered somewhat unrealistic and utopian from the perspective of many Israelis, are based on four essential points: the two states, refugees, security and the status of Jerusalem.
The existence of two states. According to the EU, a one-state solution would be contrary to the interests of both parties, since it would impose the sovereignty of one of the peoples over that of the other. Therefore, Brussels believes that a two-state solution would be more appropriate: each nation would have its own state and the borders between the two would be based on those in force on June 4, 1967, before the Six-Day War. Even so, changes to these sovereignty boundaries would be allowed, provided both sides so desired and approved.
The refugee issue. The EU believes that durable measures should be taken on the issue of Palestinian refugees outside their homeland (especially in neighboring countries such as Lebanon and Jordan), with the goal that they can return to their country.
Security. Another key issue for the Europeans would be the question of security, for both sides: On the one hand, measures should be put in place to put an end to the Israeli occupation of the Palestinian territories. On the other hand, the problem of Palestinian terrorism in the area should be tackled with effective measures.
Status of Jerusalem. Taking into account the importance of this city, Brussels considers that there would be no better solution than a resolution in which there would be shared sovereignty between the two hypothetical states. In addition, the holy city of the three religions would also be the capital of both states simultaneously.
However, as previously mentioned, the position of several member states was mistrusted, even to the point of suspecting possible support for the American decision. This was inferred from states such as the Czech Republic or Hungary, due to some statements taken out of context or poorly explained, which made it appear that the dissidence between Brussels and Visegrad continued to grow. However, if there is one thing that stands out in the European response, it is unity and internal coherence.
The Czech government did no more than recognize West Jerusalem as the capital of Israel, just as it will do with East Jerusalem once Palestine regains sovereignty over its territory. The Magyar government did not contradict the European positions either, as its only statements were that Europe should not have to pronounce itself on US diplomatic actions. Subsequently, the Hungarian prime minister clarified that the EU should stand firm on the policy it has defended so far and that this is de facto the Magyar position on the matter. Furthermore, French President Emmanuel Macron, during his meeting with Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu, already mentioned that France did not support Trump's decision on Jerusalem, and likewise Federica Mogherini, the High Representative for Foreign Affairs of the European Union, spoke to him, maintaining the neutral mediating stance that the EU has assumed so far.
Therefore, neither the EU nor any of its member states have shown any sign of support for the unilateral American decision. Europeans remain united in their diversity, quoniam "In varietate concordia".
Bibliography
European Union External Action, Middle East Peace process, 15/06/2016 - 12:32
European Council on Foreign Relations, EU backed into a corner on Israel-PalestineCommentary by Hugh Lovatt, 12th December, 2017
Politico, EU dismisses Netanyahu's Jerusalem prediction, by Jacopo Barigazzi, 12/11/17, 12:29 PM CET
EU Observer, Two EU states break ranks on Jerusalem, by Andrew Rettman, 7th Dec 2017, 16:36
Website of the Hungarian Government, Hungary has successfully represented its position on the issue of Jerusalem, December 15th, 2017
France Diplomacy, Israel/Palestinian Territories - Relations with the European Union
Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic, Position of MFA to Issue of Jerusalem, 06.12.2017 - 20:00
European Union External Action, Netanyahu realised there is full EU unity on Jerusalem, Mogherini says after EU Foreign Affairs Council, 12/12/2017 - 18:06
European Union External Action, Middle East: EU stands by two-State solution for Israel and Palestine; Iran nuclear deal, 05/12/2017 - 18:22
European Union External Action, EU won't give up on peace in the Middle East, says Mogherini, 19/09/2017 - 18:33
The Guardian, Death toll rises to 12 in violence after Trump's Jerusalem recognition, Associated Press in Gaza, Sun 24 Dec 2017 18.55 GMT
El País, Hamas announces a third intifada over recognition of Jerusalem as Israeli capital, Madrid 7 DEC 2017 - 17:49 CET
Le Parisien, Trump sur Jérusalem : "C'est une nouvelle nouvelle humiliation inflicée au monde arabe"., International, par Myriam Encaoua, 08 décembre 2017, 9h47
Radio France Internationale, Vives reacts to Trump's announcement on Jerusalem, 06-12-2017
BBC, Muslim nations urge recognition of East Jerusalem as Palestinian capital, 13 December 2017
[Javier Lesaca, Weapons of mass seduction. Ediciones Península, 2017. 312 pages]
review / Alejandro Palacios Jiménez
What is it that drives a young man to abandon his friends and family and freely give up his dreams to join the Islamic State? With this question in mind, Javier Lesaca immerses us in this narrative in which he dissects the communicative apparatus used by ISIS to gain followers and spread its ideas and influence through the virtual Caliphate.
Thanks to his extensive professional career, the author sample in Armas de seducción masiva has a high Degree of depth and analysis, which is not incompatible with an entertaining and convincing narrative. Javier Lesaca Esquiroz (Pamplona, 1981), graduate in Journalism at the University of Navarra, works as researcher at the International Observatory of programs of study on Terrorism. His extensive knowledge on topic has allowed him to work in organisations such as the World Bank, the Inter-American Bank development and the Government of Navarre. Education Her work experience is complemented by her participation in forums such as the United Nations (UN) Security committee or the Euro-Arab Dialogue of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO).
His main hypothesis is that the crisis of credibility in traditional institutions, which has been fuelled by the economic and financial crisis of 2008 and is palpable in the 15-O movement, coupled with the technological revolution of the 21st century, has allowed the Islamic State (ISIS, or Dáesh, by its Arabic nomenclature) to influence the perceptions of Western citizens, in particular millennials, in a way never seen before. Millennials, who do not feel represented by their respective state institutions, seek to feel important and to participate in a new project that helps them to make sense of their lives and to stand up every day for a cause worth fighting for. And ISIS offers them just that.
 |
But what is Dáesh? Far from historical and religious explanations, Lesaca presents us with an unprecedented answer: the Islamic State embodies what is called modern terrorism, which uses the instruments of the new generations to get its messages across. In other words, Daesh presents itself as a global social movement that uses local communication campaigns that are disseminated throughout the world and whose terrorist acts are used as a mere "performance" within a broader communication strategy. Thus, Daesh defines itself as a leaderless movement that, paradoxically, moves away from the more purely religious elements to suit the concerns of the youth audience it plans to seduce.
The fact that it is a headless movement does not imply that it is internally unorganised. On the contrary, ISIS is a terrorist group that uses social networks very effectively and whose internal structure allows it not only to influence, but also to be in possession of some of the media. Its strategy consists of both developing its own media and using what is called "earned media". reference letter The former refers to Daesh's large communication structure based on: press releases, infographics, photographic reports, magazines in different languages, the Al Amaaq news agency, Al Bayan radio, Ajnabah music productions, the Isdarat website (now closed), audiovisual production companies and offline marketing in some parts of Iraq and Syria (billboards, posters and cybercafés). The media won is measured in terms of the number of times the terrorist group has succeeded in having its actions condition the diary of the traditional media.
The use of such a multitude of communication channels with the goal to create a parallel world, which its activists call the Caliphate, and to geographically segment the audience to modify the framing of the message - all under the cover of twisted interpretations of the Koran - is what is known as transmedia terrorism. To make this strategy as effective as possible, nothing is left to chance. One example given in the book, sample , is the control that the all-powerful Syrian executive producer Abu Mohamed Adnani, a friend of the caliphate's leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, exercised over his subordinates, supervising and approving the content and messages that ISIS transmitted to the public. So much so that Adnani was considered by the West to be the de facto man who exercised the real day-to-day leadership within the terrorist organisation until his death in 2016.
All of this communicative strategy is precisely described in the book thanks to the large number of concrete examples that the author provides of massacres that Dáesh has carried out since its existence and the way in which these have been transmitted. In this sense, Lesaca emphasises the effectiveness with which ISIS, making use of the new media, camouflages real executions among images of video games(Call of Duty) or fictional films(Saw, Hunger Games, Sin City) in order to blur the line between reality and fiction, creating what is called a transmedia narrative. The idea is simple: how are these images going to seem cruel to you if they are similar to the ones you see in a cinema conference room eating popcorn?
In written request, Javier Lesaca attempts to define a useful strategy for dealing with the terrorism of the future. He argues that it is unclear what tools states should equip themselves with to confront this new form of terrorism. However, a good way to do so would be to make democracy fashionable, that is, to reinforce the values that have allowed the construction of the welfare society and development the greatest period of prosperity in our history. "The Islamic State has managed to win the victory of aesthetics, which is why we must make values such as democracy, freedom and equality attractive cultural products," says Lesaca. But this is not enough, he says. In addition, "we must promote institutional strengthening by eradicating corruption and implementing policies to create a Economics capable of absorbing all the talent of the new generations and achieving an effective management of public services".
At summary, this is a book that is a must-read for all those who want to familiarise themselves with the internal organisation and Structures of the power of Daesh, its objectives and the means it uses to achieve them group . It is also an invaluable guide for the study and subsequent reaction of the West to the communication campaigns not only of the Islamic State, but also of subsequent terrorist organisations that will form part of what is already known as modern terrorism.

![Deployment of Ukrainian troops, June 2014 [Wikipedia] Deployment of Ukrainian troops, June 2014 [Wikipedia]](/documents/10174/16849987/noticia-donbass-2.jpg)
![Troops of the self-proclaimed Donetsk People's Republic in May 2015 [Mstyslav Chernov] Troops of the self-proclaimed Donetsk People's Republic in May 2015 [Mstyslav Chernov]](/documents/10174/16849987/noticia-donbass-3.jpg)
![Parade of rebel troops in Donetsk, May 2015 [Wikipedia] Parade of rebel troops in Donetsk, May 2015 [Wikipedia]](/documents/10174/16849987/noticia-donbass-4.jpg)
![Map of the Jordan River Basin [Palestinian Authority]. Map of the Jordan River Basin [Palestinian Authority].](/documents/10174/16849987/jordan-river-mapa.jpg)
![Statement by MBS in a conference organized in Riyadh in October 2017 [KSA] Statement by MBS in a conference organized in Riyadh in October 2017 [KSA]](/documents/10174/16849987/women-arabia-saudi-blog-2.jpg)
![Chad's troops during the war against Libya in the 1980s [Wikimedia Commons] Chad's troops during the war against Libya in the 1980s [Wikimedia Commons]](/documents/10174/16849987/toyota-blog-2.jpg)