Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Articles .
The deployment of nearly 19,000 peacekeepers has reduced violence, but human rights violations continue
President Joseph Kabila's leverage of power and social and tribal resentment have fueled violent conflict inside the Democratic Republic of the Congo over the past year and a half. So far, 3.9 million people have been displaced; In 2017 alone, 3,300 deaths were recorded. The UN intervention has reduced the levels of violence, but the conflict in Kasai province is still alive.

▲Forces of the mission statement UN Stabilization Agency in the DRC [MONUSCO/Sylvain Liechti]
article / Eduardo Villa Corta
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is in the midst of a major civil crisis that has been going on for a long time. While this country has had numerous internal problems and conflicts, the one in the Kasai region, in the south-central part of the country, stands out for its high issue of deaths and human rights violations.
The origin of this conflict dates back to 2016, when President Joseph Kabila, in power since 2001, decided to delay the elections in order to remain in power longer. The death of his main opponent, Étienne Tshisekedi, facilitated Kabila's intentions to remain in the presidency, but he has since had to confront a civil service examination Kamuina Nsapu's militia.
To understand the status It is necessary to start from the tribal division present in the DRC. Territorial chiefdoms and divisions are administered by a traditional chief and his committee. These hereditary lines follow a succession process, which must be ratified by the Ministry of the Interior. In the case of the Kamuina Nsapu tribe, in January 2012 there was a problem with the access to the leadership of Jean Pierre Nsapu Pandi, because the Ministry of the Interior (appointed by Kabila) did not recognize the new leader. After some time, he received word that the Ministry had selected another chief from outside the tribe. This selection generated resentment that led to a revolt. From that moment on, Nsapu Pandi decided to start recruiting people in the area.
Among the reasons why this movement grew and expanded in the region is in the first place the status of widespread poverty. Given low living conditions and low economic growth, the leader's promises were a popular incentive. The knowledge of the language Local Tshilub and the Charisma itself staff Nsapu Pandi also helped him gain supporters, so that by the end of July 2016 some 800 young people were following him. It was then that the militia, called Kamuina Nsapu out of devotion to their leader and guide, the revolt began, with the burning of a police station 20 kilometers from the city of Tsimbulu.
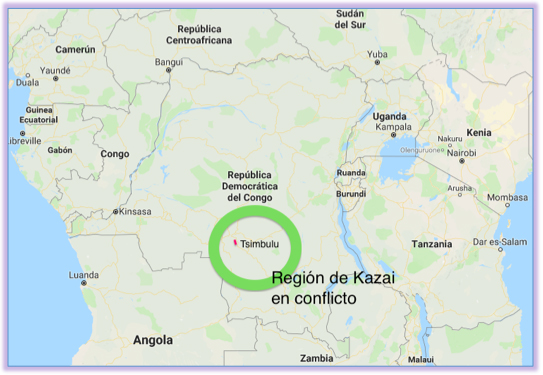 |
The conflict took a leap a few weeks later, when a clash broke out between police and military in Tsimbulu. The episode ended with Pandi's death order in combat, given by the president himself. From that moment on, the newly formed militia was grouped with the civil service examination Kabila and went from being a group to become a national one. It is now a militia in civil war with the government, in a confrontation that has devastated the Congolese population.
The Kamuina Nsapu militia and its atrocities had a swift response from Kabila. The latter responded with disproportionate and disproportionate force, since in their actions against the militia the authorities caused some 400 deaths in the first weeks, both among armed elements and among the civilian population. The group has grown exponentially due to the strong civil service examination Kabila, who nevertheless continues to hold power in Kasai to this day. Both sides of the conflict have been involved in atrocities and serious human rights violations.
The data about deaths and harm to people are not easy to obtain. According to sources in the Catholic Church, in 2017 alone the conflict caused at least 3,300 deaths. That same year, 1.7 million people left their homes and moved to neighbouring countries in search of asylum. To date, a total of 3.9 million people have been displaced. The conflict has exacerbated famine in the country, which has reached 7.7 million people. Of these, 3.3 million are located in the Kasai region, which is the hardest hit by the conflict. In January 2018, it was estimated at 400,000 issue of malnourished children. The numbers are only rising due to migration and the status of danger suffered by thousands of people. The DRC has order the World Bank $1.7 billion to be able to establish and help the population. But this sum has not been delivered nor has there been any financial contribution from any international organization.
The truth is that these atrocities are the responsibility of both sides in the conflict. The involvement of both parties can be seen in the finding of mass graves (80 have been found in the area) following a United Nations initiative. It showed that everything from beheadings to mutilations had been committed, and that the victims ranged from soldiers to children. The UN has sent observers and "blue helmets" to the area: a total of 19,000 troops whose troops are being sent to the area. mission statement It is to try to keep the peace, support civilians and investigate the events that happened. So far, 2,800 human rights violations have been recorded. At least two UN observers were beheaded in the Kasai region, which is difficult for international organisations to access due to government restrictions and the very unfolding of violence.
This conflict is based on social and tribal resentment and the struggle for control of the country. In order for the country to recover, both Kabila and the Kamuina Nsapu would have to reach some point in the country. subject complimentary. To achieve this, the international community should reiterate the pressure exerted in 2016 at the start of a conflict that has escalated over almost two years. The African Union and the UN should push both parties to the dispute towards a ceasefire, in mediation both regionally and extracontinentally. The most conducive solution to the stabilization of the country is the holding of free elections.
Local Tribes Call for Benefit-Sharing and Reduction of Environmental Damage
The social stability of Nigeria, one of the most populous countries in the world and the largest in the world, is the world's largest Economics of Africa, is of international concern because of its potential impact on continental and global security. Hence, a local conflict such as the one between the tribes of the Niger Delta and the Nigerian government, as a result of the exploitation of the abundant oil of the area, be followed closely from the outside.

▲The area of light at the bottom of the satellite image corresponds to the oil facilities of the Niger Delta [NASA]
article / Baltasar Martos
The fierce dispute over energy resources at the mouth of the Niger River in southern Nigeria has been one of Africa's most high-profile conflicts for decades. The marginalization, confinement, and impoverishment of the Ogoni and Ijaw – the name given to the ethnic tribes in the coastal provinces of Rivers, Bayelsa, and Delta – have contributed to an escalation of tension between locals and the federal government.
In order to understand the underlying problem, it is first necessary to take a brief look back in time and discern the three chronological stages that have shaped the current panorama of the conflict, namely: the beginning of oil exploitation, the hegemony of Royal Dutch Shell and the post-independence period.
In 1903, in the southern coastal region of present-day Nigeria, which became a British protectorate (1901) and later a colony (1914), a large deposit of minerals and hydrocarbons, such as coal, bitumen, oil and natural gas, was discovered. The British company Nigeria Properties Ltd. then began oil exploration and extraction, reaching a production of 2,000 barrels per day in 1905. Later, in 1937, and after the succession of several oil companies, the Anglo-Dutch multinational Royal Dutch Shell acquired a monopoly on the exploration of oil sources – and, to a lesser extent, other hydrocarbons – reaching a number of fees production of 5,000 barrels per day.
Three decades later, following independence and the official establishment of the Federal Republic of Nigeria (1960-1963), the military government of Yakubu Gowon embarked on a policy of nationalization and acquisition of foreign firms in the country, forcing them by legal mandate to re-register through joint ventures with state-owned enterprises. In this way, he managed to transform this activity into the main strategic sector for the Economics of the country. In addition, taking into account the entrance Nigeria joined OPEC in 1971, it is not surprising that the federal government currently owns 60% of the capital stake in practically all the oil companies in operation, occupying an important role as a leader in the country. partner majority.
On the contrary, the civilian population in the area has result The big loser. The ethnic minorities most affected by prospecting, extraction and commercialization activities – with the consequent enrichment for some and environmental pollution for others – have been demanding the attention of the government and demanding legislative measures for environmental and social protection for decades [1].
On the one hand, locals demand "environmental justice," defined by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency as "fair treatment and meaningful participation in political decision-making processes about activities that affect the natural environment of all peoples, regardless of race, color, culture... concerning the implementation and enforcement of environmental laws, regulations, and policies."
The Ogoni and Ijaw are peoples dedicated mainly to agriculture and fishing as a means of subsistence, for whom the natural environment is the only and main one source of wealth. They are protesting against the long-standing collusion (since independence) between the government and multinational oil companies, calling them both "expropriators and polluters" and blaming them for the impoverishment of the region and the deplorable state of the rivers that flow through it. They also claim their rights to obtain and use, for their local communities, the corresponding share of the profits derived from the exploitation of energy deposits because they are traditionally located on a large pocket of crude oil [2].
Corruption, clientelism and the structural weakness of the government, added to its great interest in and dependence on this sector – which has come to be a benefit for the Economics The national increase of up to 55% of GDP in the mid-1990s according to World Data Bank statistics – makes it extremely difficult for the president and his cabinet to agree to address the needs of these communities in the Niger River Delta. The growing protests led to a real conflict, which began in the last decade of the last century, pitting the civilian population against the federal government in collusion with the multinationals. This confrontation has taken two forms, one peaceful and the other violent, and has attracted the media attention of a large part of the international community.
International Attention
On the other hand, the conflict in the Niger Delta is a clear case of globalization, since oil extraction involves a set of transnational forces, non-state actors and interdependent processes. Fruit of the prolonged status In response to the discontent of the indigenous tribes of the area, two movements have grown in denunciation of profit by a government that barely invests in the development of this region of the country, mired in poverty and poverty. withdrawal, and degraded by the exploitation of its natural resources.
On the one hand, there is the Movement for the Survival of the Ogoni People (MOSOP), created in the wake of protests in the 1990s and used as a model for other civil associations to publicly express their dissatisfaction with the negative impacts of the oil industry on the quality of life of the inhabitants of the area. This organization, started by writer Ken Saro-Wiwa and composed mainly of academics and teachers, peacefully denounces the joint actions of the government and the corporations installed in the area and advocates for the civil human rights of the Ogoni to decent housing conditions, environmental justice and legislation that respects and protects them from environmental threats.
On the other hand, there is the Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta (MEND). It is made up of an amalgam of armed youth groups organized into local resistance militias, whose goal The main one is to fight for control of the oil benefits for the ethnic minorities settled in the area. This is a military branch of MOSOP that has already sabotaged oil pipelines and kidnapped foreign factory workers, demanding ransom from the government on several occasions.
The most important thing about both movements is that they have caught the attention of a large number of people. issue local and international non-governmental organizations that have partnered with them and have begun to promote and to make their cause visible to the entire international community. Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch and the Niger Delta Human and Environmental Rescue Organization are some of the many organisations that have opened a space for work devoted solely and exclusively to the question of the Niger Delta. They advocate worldwide for the defense of the environmental rights of communities affected by the exploitation of resources and the pollution of the natural environment. They have also been able to partner with transnational media and human rights networks to spread the status from conflict to a global audience.
The joint denunciation of the "alleged violations of human and environmental rights against the members of the Ogoni ethnic group of the Niger Delta" has resonated worldwide and has obtained a significant sum of economic aid aimed at the re-establishment of the settlements from which the indigenous peoples had been displaced, as well as the promotion of environmental justice. the protection and guarantee of the civil rights of locals to take advantage of the natural wealth of their area, the continuation of their economic activities and the safeguarding of their environment. The global impact of this conflict is likely to have an impact on how similar conflicts are resolved.
[1] Obi, Cyril. "Insights from the Niger Delta", Young, Tom. Readings in the International Relations of Africa. Indiana University Press, 2016.
[2] Botchway, Francis N., ed. Natural Resource Investment and Africa's Development. Edward Elgar Publishing, 2011.
China, India and Japan are investing in their respective air forces with an eye on the neighbor
North Korea is making headlines about space-faring weaponry, but it is Asia's great powers – China, India and Japan – that are striving for full air potential.

▲Chinese J-20 Stealth Fighter
article / Sebastian Bruzzone
North Korea is not the most powerful military air power in Asia. The exuberant parades and frequent ballistic missile launches by this nation are certainly far from their actual firepower, although they invest roughly 15% of their GDP in it. Military air hegemony is mainly in three centres-states:
Japan. The Japanese air force, established in 1954, combines its level of technique and sophistication with U.S. aircraft. Both countries, also with South Korea, carry out exercises in the airspace of the Pacific Ocean. Its aviation fleet varies from generation to generation. It has modern F-15 and F-2 aircraft manufactured by Mitsubishi Industries (Japanese, national company) and Lockheed Martin (American company), and older aircraft such as the Phantom F-4. Similarly, it has an early warning team and attendance and another for tanker planes to keep the rest of the aircraft in the air for as long as possible.
India. The Indian Air Force possesses Soviet and domestic technology, as well as a training system and management of the British Royal Air Force. Its fleet has 300 state-of-the-art fighters supplemented by older MiG-21s. In addition, 200 offensive ground attack aircraft and C-17 Globemasters in the field of logistics to ensure cargo transport and refueling and immediate warning.
China. Since the end of World War II, the Chinese government has invested in its aerial weaponry to become the continent's leading military power. Today, it has 600 fighters of the 4th and 4.5th generations, as well as the aircraft of the aforementioned countries. Unlike Japan and India, the main manufacturer of their equipment is the country itself and they have not been imported from any other nation. What stands out most about the Chinese Air Force is the evolution in recent years. It has gone from having a very large and poorly trained fleet to being made up of pilots who can spend more than 24 hours on a plane. However, the Chinese aviation industry still has quality issues in its engines. Still, we may be talking about the most important air power in Asia.
It generates many of the raw materials needed for global technology production.
China not only has significant reserves of mineral resources, but also leads the world in the production of many of them. B This gives it a geopolitical advantage as source of the resources essential for global technological production.

▲Satellite image [NASA].
article / Gabriel Ros Casis [English version].
With such a vast territory as the Asian country, it is obvious to think that it possesses a large amount of raw materials and natural resources. Throughout China's history, this has become a strong geopolitical asset, not only for the country's own development but also for its trading partners through exports. Today, when we talk about these raw materials, China stands out in two main groups: base metals and technological elements.
The group of the base metals essentially comprises five metals from the periodic table, these being: iron, copper, aluminum, magnesium and zinc (sometimes lead and tin are also included). There is no need to recall that we can find all these metals in everyday objects, and that they have been the backbone of industry for a long time. Therefore, every country needs them, placing those with the largest deposits of these metals at a strategic advantage. But a country's mineral wealth is not always given by this condition, as it can also be measured by the ease and feasibility of extracting the product. In the case of China, both arguments would be valid, since the country has the largest deposits of many of these minerals, with magnesium leading the way (79% of global extractions) followed by tin (43%) and zinc (31%).
As far as technological metals are concerned, it is important to note that they include various minerals, such as rare earths, precious metals, as well as semiconductors. From a quantitative approach , the required amount of these metals is minimal, even though their availability is crucial for the production of today's technology. For example, some of the most common technology metals include lithium, yttrium, palladium, cerium and neodymium, which can easily be found in cell phone batteries, medicines, magnets or catalysts. Once again, China leads the way with the largest deposits of several of these elements, especially tungsten (83%), followed by rare earths (78%) and molybdenum (38%).
From this we can conclude that China not only has the largest deposits, but is also the world's leading exporter. In addition to extraction, this country also refines and manufactures components with minerals such as aluminum, copper and certain rare earths, and in some cases even manufactures the final product.
Therefore, it must be taken into account that extraction brings with it certain consequences. Environmentally, extraction always has an impact on the land, perhaps less in China compared to other countries (due to the size of its territory), but equally significant. From an economic approach , these extractions entail a great cost, but which, managed in the right way, can generate an immense benefit. In the political scenario, they are seen as an important geopolitical advantage, creating dependence on the demand of other countries.
As a conclusion, it can be drawn from this that China has great power in terms of raw material resources, but this carries with it a great responsibility, since a substantial part of the raw materials used for almost all the world's technology production depends on this country, which provides the resources, but also manufactures them.
Bulgaria's semester focuses on refugee crisis and Western Balkans
Bulgaria's presidency of the European Union, in addition to advancing in the concretization of the 'Brexit', puts on the table particularly sensitive issues for Central and Eastern Europe, such as the migratory routes that enter Europe through the southeast of the continent and the advisability of the future integration of the states born of the former Yugoslavia, of which so far only Croatia has joined the EU.

▲European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker and Bulgarian Prime Minister Boyko Borissov [Nikolay Doychinov-Bulgarian Presidency].
article / Paula Ulibarrena García
During this first semester of 2018, for the first time, Bulgaria holds the rotating presidency of the committee of the European Union (EU). The Bulgarian presidency has as its main challenges the management of the migration crisis and the 'Brexit' negotiations. As a special goal has been marked to put the focus on the Western Balkans. During the semester, Bulgaria hopes to take the final steps towards the euro and to join the Schengen area.
Under the slogan "Unity is strength", Bulgaria - the poorest country in the EU - has set itself an ambitious diary until June. The Bulgarian government, formed by the conservative populist GERB party and the ultra-nationalist Patriotic Front, has set out to help make the European bloc stronger, more stable and more united.
To this end, Sofia wants to foster consensus, cohesion and competitiveness, with the specific challenge of overcoming existing differences in the handling of the refugee crisis. Given the rejection by several partners of quotas for the relocation of asylum seekers, Bulgaria will seek "a sustainable system for managing immigration," with "common rules that are enforced," the Bulgarian presidency program highlights.
Migration crisis
Dialogue with third countries to facilitate the return of migrants without the right to asylum and the strengthening of external border control are some of the measures planned by the executive led by the Bulgarian Prime Minister, the conservative populist Boiko Borisov.
Bulgaria's position on the Syrian refugee crisis is that the adoption of a mechanism to relocate refugees is only a solution provisional. The government in Sofia believes that a lasting and solid solution must be found under which to limit the pressure on the external borders of the EU and the secondary migration resulting from it. It proposes that the EU should work as a matter of priority and urgency together with its EU partners with a view to stabilizing the countries of origin and helping the transit countries. Bulgaria, which has Turkey as a neighbor, considers Turkey to be core topic for the resolution of the problem and proposes that the EU should forge urgent measures to strengthen Turkey's capacity to receive refugees. Bulgaria has always been keen for the agreements to provide for Turkey to admit the refugees that the EU can refund from Greece.
For Sofia, it is necessary to clarify the distinction between economic migrants and refugees and to move towards "solidarity mechanisms" that are acceptable to all member states, recalling in this regard the failure of the mandatory quota system for the relocation of refugees in Italy and Greece.
Western Balkans
Another priority of the Bulgarian presidency is to place the countries of the Western Balkans in the sights of an EU, which for the time being is not considering any further enlargement. Some countries in the region, such as Serbia and Montenegro, are actively negotiating their entrance, which they hope will take place within the next five years. Meanwhile, Bosnia Herzegovina, Albania, Macedonia and Kosovo are still waiting to formally start negotiations.
Among the nearly 300 meetings planned during the Bulgarian EU presidency, a special summit on May 17-18 between EU leaders and these six aspirants stands out.
"The European project will not be complete without the integration of the Balkans", warned the Minister manager of the Bulgarian Presidency, Lilyana Pavlova. Bulgaria insists on the convenience of helping a European region still marked by the political instability of the new and small states that emerged after the Yugoslav war.
After Croatia's integration into the European Union on July 1, 2013, it is logical that other countries of the former Yugoslavia intend to follow. Montenegro (which even has a bilateral agreement with Bulgaria of technical-political attendance on topic) and Albania are already official candidates, and there will probably soon be an invitation for Serbia and Macedonia.
The Economics, stability of institutions and democratic transparency have always been and will always be decisive factors in the integration process. For this reason, today, the question of the development of the Balkans and the region of southeastern Europe is very present in the European diary since the big donors of the European budgets do not forget the problems caused by the integration of countries such as Poland, Hungary, Romania or Bulgaria itself. In fact, four countries in the area are subject to the economic policy of the Union: Greece, Bulgaria, Romania and Croatia.
Excluded from this possible integration for the time being are Bosnia and Herzegovina, which is still under European protectorate, and Kosovo, without official recognition by several governments, including two members of the committee Security Council (China and Russia) and five EU members (Spain, Greece, Slovakia, Cyprus and Romania). In addition, the level of unemployment in the Western Balkans is quite high compared to Bulgaria and Romania, with a combined average of the four candidates at around 25%.
On the other hand, with the disintegration of the Soviet bloc and the war in the Balkans, the socioeconomic systems collapsed and the transition period resulted not only in growing inequalities, but also in the absence of legality and effective government. The consequence of all this has been in many countries of the area the important role played by black money in the Economics. Bulgaria leads this sad record, with an informal sector accounting for 31% of the Economics, closely followed by Romania and Croatia, whose underground Economics accounts for 28%, and Greece, with 24%. The problem lies in the question of the extent to which the underground Economics and illegal trafficking channels in southeastern Europe can pose a danger to the security of the other countries of the Union. For this reason, the efforts of the candidate countries to improve democratic Structures , governance, transparency and control of capital flows will be an important factor to be taken into account in the negotiations.
Brexit, Schengen and corruption
The decisive phase of negotiations on the UK's exit from the EU is expected to begin under the Bulgarian presidency, following the progress noted in early December by European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker. Sofia wants to become a "neutralcoordinator " in this process, according to Bulgarian President Rumen Radev.
The progress in the digital Economics of the continent after the impulse given to this topic by the outgoing Estonian presidency, as well as in the banking union, are other points core topic of the Bulgarian diary . The Balkan country will also defend the cohesion policy and the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), which will be affected by the loss of funds due to the 'brexit'.
At the same time, Bulgaria aspires to enter during its EU presidency in the "anteroom" of the euro zone and join the Schengen area, of free community circulation, a step blocked until now by the lack of progress of Bulgaria in the fight against corruption and organized crime. The Balkan country, considered the most corrupt in the EU, took eleven years in approve its first anti-corruption law, adopted last December 20, less than two weeks before assuming its presidency of the EU. Unlike what happened in neighboring Romania, so far the Bulgarian justice system has not investigated or convicted any politician for corruption cases.
Air connectivity
association The International Air Transport Association (IATA) called for a renewed policy approach to strengthen Europe's aviation competitiveness at the Bulgarian presidency of the EU. There is an urgent need to strategically plan for the capacity needed to meet the growing demand for global connectivity, environmental improvements and regulation of infrastructure costs.
IATA forecasts a 6 percent expansion of air travel demand in Europe in 2018. "Operating an airline in Europe is challenging. There are high costs and regulatory burdens. Infrastructure capacity is often not sufficient and charges for using airports have doubled across Europe in the last decade. The Bulgarian government has put competitiveness and connectivity at the center of the diary of its EU Presidency. This will drive greater competitiveness and prosperity for European economies, but only if individual EU member states follow through by adopting policies that promote air connectivity," said Rafael Schvartzman, regional vice president of IATA Europe, at the IATA Bulgaria Aviation Day in Sofia.
Bulgaria occupies a strategically important position as the entrance gateway from Europe to Turkey and beyond to Asia. It is also a fast-growing market in its own right, with passenger issue set to double in the next 20 years. This is a challenge for the country's air traffic management , and the Bulgarian air navigation services provider BULATSA.
A country with many conditions to have a great weight in Europe, but weighed down by Russia's proximity to it
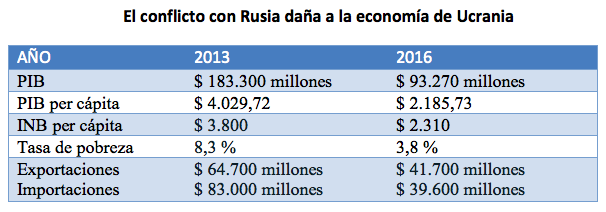
If the border between the West and the Russian-dominated area divided Germany during the Cold War, today that border runs through Ukraine. The open conflict with Russia hampers the objective conditions of great development that Ukraine has. The country is paying a high price for the desire to preserve its independence.

▲Pro-European protesters at place central Kiev, during the riots in late 2013 [Evgeny Feldman].
article / Alona Sainetska [English version].
Ukraine, a sovereign and independent state (since 1991), located in Eastern Europe, with the second largest area (after Russia) of the European countries (576,550 km² without the Crimean peninsula) and with a long history of struggle to preserve its identity, is today the center of tensions between Russia and the West. In 2014 Moscow wanted to compensate for the fall of the pro-Russian government in Kiev by annexing the Crimean peninsula. It was then that Ukraine aroused global interest. The Ukrainians were finally achieving a prominence commensurate with the size of their country, although they would undoubtedly have wanted to do so with another subject headline-grabber.
1. WHAT DRIVES FORWARD
Considering its geographical position and its strategic, economic and military weight, it is difficult to justify that before the outbreak of the conflict Ukraine was not for many more a fuzzy place on the map. The country is surrounded by Russia, Belarus, Moldova, Poland, Slovakia, Hungary and Romania, and has direct access to the Black Sea. This central location makes it very clear that Ukraine should play an important role in the context of the International Office.
Agriculture
Ukraine's rich and fertile soil is known as black soil or "Chornozem". The agricultural area used covers 70% of the arable land, or about 42 million hectares, and is capable of feeding 500 million people. The country, with its 46 million inhabitants, therefore has considerable potential for production, processing, consumption and export of agricultural and organic products. It is already one of the leading countries in the agricultural sector and can be considered a "green vein" in the heart of Europe.
It is the leading producer and exporter of sunflower oil, 30% of whose exports go to India and 16% to China. Ukraine also produces large quantities of wheat, of which it is the world's sixth largest exporter. It produces wheat flour and corn flour for food production, which it exports to France, Poland and Belarus, among others. It is also one of the leaders in poultry production, whose issue grew by more than 55% between 2000 and 2011; its exports go mainly to Iraq and the EU and seventy other countries.
Industry and logistics infrastructure
Ukraine also has an aircraft industry, although lack of investment is holding back its development on a large scale. However, examples such as Antonov's Mriya-225, the world's largest cargo plane built during the Soviet era and capable of carrying up to 250 tons, speak of its potential while awaiting investment.
On the other hand, it is worth mentioning that Ukraine is ideally suited to be a hub for international trade, mainly between the European Union, the Middle East and Asia. Five out of ten European transport corridors cross the Ukrainian territory; Ukraine has the most extensive railway networks in Europe that handle a substantial part of passenger and freight traffic; moreover, its road network covers the entire territory of the country and enables deliveries to any destination point. Last but not least, there is the natural gas transmission system, led by business Ukrtransgas, engaged in natural gas transmission and storage in Ukraine. In 2013 it transported 132 billion cubic meters (bcm), including 86 bcm for the EU and Moldova. Ukrtransgas owns Europe's largest subway gas storage network with a total capacity of 31 bcm and consists of 14 subsidiary units operating in Ukraine.
 |
2. WHAT SLOWS DOWN THE DEVELOPMENT
However, the country continues to be underestimated by other players on the international chessboard and this exposes it to Russian ambitions. These are manifested in numerous obstacles that make it difficult for Ukraine to gain weight in the aforementioned sectors of trade, industry, agriculture and transport. There are also other derived factors that slow down the country's development .
Interest from Russia
Russia's interest in its neighbor to the west is mainly due to strategic reasons, since Ukraine is a fundamental piece for any expansion of the former Russian imperial power. Therefore, Russia seeks to strengthen its influence in Ukraine through economic expansion, control over the maritime border, installation of Russian military instructions and Russian occupation troops in the territory, expansion of interference in the Ukrainian information space, influence of the Russian church, etc. Another of the measures attributed to Moscow is the placement of people with similar interests in positions of power in Ukraine: the Kremlin wanted to take advantage of the presidency of V. Yanukovych, a pro-Russian politician.
Internal instability
Today the future of Ukraine is as uncertain as ever. Economic and political reforms have failed to overcome the country's serious structural problems, the fight against corruption is weak, and the insignificant international support further diminishes the already leave expectation that Ukraine can overcome the crisis in a short time. Given the absence of other means to put pressure on Russia than sanctions, and in view of the fact that those that have been applied have hardly changed the Kremlin's attitude, it is safe to say that normalization of the status is far away on the horizon.
All this is reflected in the growing popular discontent. 90% of Ukrainians disapprove of the current government's management , express the desire for new elections and show their refusal to allow the regions closest to Russia to participate in the country's political life. Desperation means that the only institutions the Ukrainian people trust are the army, the church and volunteers.
The "frozen" conflict
On the other hand, the "frozen conflict" in the east of the country remains and continues to undermine the state's budget . Defense and security spending accounted for 5% of GDP last year, a high figure that includes the government's efforts to create a new army. According to President Petro Poroshenko, this was one of the many reasons for the failure to raise citizens' living standards. Overall, the prospects for a Ukrainian victory in a war to regain full sovereignty over its eastern lands appear dim, given Russia's support for the rebels and Ukraine's fear of an internal counter-reaction. A vicious circle is thus generated, so that as long as there is no successful end to the war, economic and political tension on the Kiev government will increase and could lead to a new Maidan, the popular revolt that collapsed the government in 2014.
The geopolitical standoff between Russia and the West in Ukraine has been detrimental to all parties involved, but most of all to the Ukrainian state. Declining cross-border trade, weakening currencies and stock markets, and increased security risks have affected the entire region. Poverty is growing at the same pace as the standard of living of citizens is declining and market prices are rising. As result, Ukrainians are unable to take advantage of the opportunities granted to them, as is the clear example of the exemption of visas between Ukraine and the European Union (approved in May 2017), which many have not been able to use as they have been unable to finance their travel.
3. THE NECESSARY BALANCE
Ukraine's geopolitical priority is to gain independence from Russia, which means breaking economic ties with it. This is an unbalanced battle with a high cost for the Ukrainians, who face the destruction of Economics, the defeat of the elites and the impoverishment of the population.
This strategy of development of the Ukrainian state is increasingly based on the concepts of radical nationalism. But the report of historical antecedents, such as the Holodomor (the great famine of the 1930s), warns of the enormous power of the Russian "hegemon" and suggests the need to serve the national interest through a sort of balance between ultimate goals and halfway diplomacy deadline.
States are torn between securing national sovereignty and cooperation between neighbours.
No other region of the world is likely to be as important a geopolitical game-changer as the Arctic. The melting ice opens up huge logistical prospects and enhances the value of territories north of the Arctic Circle because of the access they provide to untapped natural resources. Many issues are being agreed by the eight members of the Arctic committee , although of these it is Russia, Canada and the United States that are seeking to exert the most influence in the region. Let us examine the Arctic strategy being pursued by these three countries.

article / Martín Biera Muriel
The Arctic Circle comprises 6% of the Earth's total surface, covering 21 million square kilometres. As temperatures rise and the effects of global warming worsen, the Arctic ice sheet is shrinking, revealing an area rich in raw materials and natural resources, and increasing its strategic importance for the maritime connection between Europe and Asia. This has made the Arctic a region of great geopolitical significance in the 21st century International Office .
Agencies from various countries, such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and the US National Snow & Ice Data Center, as well as international organisations and companies of different nationalities, point out that the ice cover on the Arctic shelf has been considerably reduced due to the consequences of climate change and rising temperatures. This allows states with sovereignty over these waters and islands easy access to the region, providing an opportunity for the exploitation of oil, natural gas, minerals, fisheries, shipping and tourism.
As early as 2008, the US Geological Survey estimated that the Arctic contained approximately 240 billion barrels of oil and natural gas, a figure that constitutes about 10 per cent of the world's existing resources; this does not take into account the amount of resources that, for practical reasons, have not yet been discovered. In total, it is estimated that undiscovered resources would comprise 16% of the world's oil reserves, 30% of the world's gas reserves and 26% of the world's natural gas reserves; about 84% of these resources are offshore. Estimates suggest that 10 trillion barrels of oil and 1.55 quadrillion cubic metres of natural gas may exist in the Arctic subsurface.
The Arctic committee
The Arctic committee , established in 1996, is a high-level intergovernmental forum for policy discussions on issues common to the governments of the Arctic states and their inhabitants. It is the only circumpolar forum for policy discussions on Arctic issues. All Arctic states are members, with the active participation of their indigenous peoples. It has eight members: Iceland, Denmark, Canada, the United States, Russia, Sweden, Norway and Finland. In terms of its functioning, it is divided into different groups of work and task forces, each of which has its own fields of action and functions. Thus, there is the Artic Contaminants Action Program (ACAP), whose function is to promote mechanisms for states to reduce pollutant emissions, or the Emergency Prevention, Preparedness and Response Working Group (EPPR), which seeks to protect the environment from possible accidental releases of pollutants. Although their presence is very limited, it is worth noting that on numerous occasions the different task forces and groups of work have managed to achieve the objectives they had planned, such as, for example, a reduction in CO2 emissions.
Of the eight countries that are part of the Arctic committee , Canada, the United States and Russia have the most influence in the region. What strategies are each of them pursuing?
Canada: more means to patrol the waters
For Canada, the Arctic is not only central to its national identity, but represents a potential for the country's future, especially in subject geopolitics. The Canadian government sees the Arctic as a area of opportunities and challenges, which it groups into four areas: exercising its sovereignty, promote the development economic and social, protecting the environment, and improving its governance in the northern regions. These four pillars of Canada's Arctic policy are manifold: resolving territorial disputes, maintaining sovereignty and security in the Arctic territory, promote the conditions for sustainable development and addressing governance of emerging issues such as public safety or pollution, among others.
Since 2007, Canada has strengthened its defence efforts to ensure sovereignty over its Arctic territory. That year it announced measures to increase its capabilities in the area, which have included the launch of the RADARSAT-2 satellite to monitor the Arctic and the deployment of 1,500 troops to patrol Arctic waters. For the latter role, icebreakers and maritime patrols have been added. The government also announced increased investment in the Canadian Ranger Corps to improve its presence in the area and to work with the North American Aerospace Defence Command to monitor Canada's northern airspace.
United States: Pentagon sets out its Arctic Strategy
US activity in the Arctic, a region to which it has belonged since the purchase of Alaska, encompasses a broad spectrum of activities, from resource extraction and trade to science and national defence operations. The strategy of the US Arctic Defence department is to maintain a secure and stable region, where US interests are safeguarded and its sovereign space protected, and where nations work together to address a range of challenges, including, most notably, climate change. The US strategy has two objectives:
-
Ensuring and supporting security and promote defence cooperation.
-
Prepare for a wide range of challenges and contingencies.
In addition, the department Defence stated in a document called Arctic Strategy that these objectives should be achieved through innovative approaches, with low budget and through multilateral exercises with other countries, such as the Search and Rescue Exercise. To achieve these goals, the Defence department set out a number of strategies: exercising sovereignty in its territory, engaging public and private sector entities to improve domain awareness in the Arctic, partnering with other Departments, agencies and nations to support human and environmental security, and so on. The department Defence, at partnership with the North American Aerospace Defense Command, developed an analysis and reporting programme to monitor regional activity and anticipate future trends so that future investments can sustain human activity in the region over time.
Russia: more coastline, greater access to resources
Russia is the polar state with the longest coastline, which gives it much greater access to certain resources, such as oil, than other countries, including Canada, which is the second most coastal polar state. In recent months Russia has seen an increase in natural resource production in the Arctic, especially hydrocarbons. It is worth noting that international sanctions over the Crimean crisis have meant a challenge for Russian production, which is why the Arctic is core topic for its development. Russia' s policy in the North Pole is based on two levels, military and defence, with the following objectives:
-
Use the resources in the region, mainly oil and gas, to promote Russia's economic development .
-
Maintain the Arctic as a zone of peace and cooperation.
-
Preserving ecology in the Arctic.
-
The northern route to be recognised as a transport route.
On the military side, the need to maintain troops in case of attack in the region continues. instructions In recent years Russia has therefore developed radar systems to monitor its domain, and has also encouraged the construction of small military airfields, ports and airfields to protect its territory. Notably, the port city of Severomorsk is home to the headquarters of the North Sea Fleet, one of the world's largest submarine fleets and the world's only nuclear Wayside Cross , called Peter the Great.
Notwithstanding this emphasis on military and defence issues, Russia also proposes the option of reaching agreements with other Arctic states, regardless of their size, to enhance cooperation.
Environment, development economic, defence
The elaboration of specific Arctic strategies by the countries present in the region shows that area is a relevant scenario for geopolitics and International Office in the 21st century. The states involved move on two levels: that of cooperation with their neighbours, in matters such as environmental protection and commitment to a sustainable economic development , and that of defence of their own interests, particularly in terms of ensuring sovereignty over their Arctic territories and preserving the rights that these may grant them in a future shared exploitation of the area .
If we look at the theories of International Office, the Arctic states play on the realist plane of taking positions vis-à-vis others, thinking about any future competition, and at the same time on the liberal plane of willingness to cooperate and jointly solve problems.
The new EU cooperation programme should lead to increased investment in security and defence.
After seven long years of hibernation, the European Union's Permanent Structured Cooperation (PESCO) was launched on 11 December, with the aim of achieving greater convergence in security and defence matters, mission statement . The initiative represents a leap forward in the process of European integration, overcoming the period of stagnation and hesitation brought about by the last economic and financial crisis.

Soldiers carrying the flag of the European Union in front of the EU institutions, in 2014 [European Parliament].
article / Manuel Lamela Gallego
The very year in which the 60th anniversary of the Treaties of Rome was commemorated ended with a certain sense of vindication and reaffirmation on the part of the European Union and its member states, having succeeded against all odds in generating investment and cooperation in the areas of security and defence. The implementation of Permanent Structured Cooperation (PESCO) is the response to the urgent need for investment in these two areas, a need that the EU has had for decades and that not even the failure in the Balkans managed to address.
We speak of reaffirmation in the face of the evident crisis that the European Union has suffered in recent years, when doubts have been raised about its own continuity. Despite this delicate situation status, the EU has acted with admirable flexibility and has considered its own role on the world stage with the aim of continuing to make a positive difference in the world goal . It is in this context of reflection and change that the launch of PESCO should be framed.
To this recent loss of credibility must be added the collection of 'failures' that the EU has accumulated in generating a common defence strategy. Javier Solana's words in 2003 acknowledging the failure and fracture of the Union in the Iraq crisis management cast a shadow of impotence and ineptitude that the EU has so far been unable to shake off. area The implementation of PESCO represents a great flash of light in Europe's external action, as it demonstrates the unity within the European project in the highly sensitive area of security and defence.
In this way, and in compliance with the provisions of the Lisbon Treaty, on 13 November, and after several months of insistence by the European committee , 23 Member States signed a notification that represents the first step towards the implementation of Permanent Structured Cooperation. This moment was declared "historic" by the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, Federica Mogherini. This is undoubtedly a turning point in the history of the European Union, since after several decades it has managed to break with the tendency to reduce European cooperation to the sphere of economic integration. PESCO aspires to lay the foundations from which, with truly binding projects, common and shared strategies can be generated that will gradually shape the new Europe of security and defence. In its measure, Permanent Structured Cooperation is positioned like the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) Commission, whose decision-making dimension was one of the pillars for the expansion of European supranationalism into other, more ambitious areas.
Legal basis
The legal basis for PESCO is found in Articles 42(6) and 46, together with protocol issue 10, of the Lisbon Treaty (2009).
article 42(6): "Member States which fulfil higher military capability criteria and which have made more binding commitments on subject to perform the most demanding tasks will establish permanent structured cooperation on framework of the Union. This cooperation shall be governed by article 46 and shall not affect the provisions of article 43".
If anything should be emphasised about the Permanent Structured Cooperation it is its binding nature, whereby states will be truly bound by their commitments, as we can see from article 46(4): "If a participating Member State no longer fulfils the criteria or can no longer assume the commitments referred to in Articles 1 and 2 of the protocol on permanent structured cooperation, the committee may adopt a decision suspending the participation of that State".
PESCO's lack of influence over state sovereignty is one of its fundamental characteristics. This is clearly reflected in articles 46(5) and 46(6) of the Lisbon Treaty. The first clarifies the steps to be taken by a Member State to leave project: it need only notify committee of its intention to leave withdrawal. The second deals with decision-making within the Permanent Structured Cooperation: decisions will be taken unanimously, in a unanimity constituted by the votes of the representatives of all Member States participating in PESCO.
expense of 2% of
On 11 December, the European committee finally decided to launch PESCO, an initiative that Ireland and Portugal joined, bringing the issue membership to 25 countries. This led to the adoption of the first 17 projects on which participating states commit to cooperate and which will be formally adopted by committee in 2018. These projects will cover various areas of European security and defence, such as the training of troops or the standardisation and facilitation of cross-border military transport (the latter of which has been in high demand by NATO in recent years). In addition to this list of projects, it is worth highlighting the commitment of states to steadily and continuously increase defence budgets in real terms. After several years of economic and financial recession in most European states, defence spending falls short of the 2% of GDP agreed at the NATO summit in Wales in 2014. This is undoubtedly one of the most important tasks for PESCO to fulfil in order to continue with a stable development .
The Permanent Structured Cooperation initiative was taken by France, Germany, Spain and Italy, which confirms the functioning of the two-speed Europe, although in the end project has been joined by practically the entire Union, with the only absences being Malta, Denmark (which does not participate in European defence) and obviously the United Kingdom, which is planning to leave in March 2019. It remains to be seen whether this high participation does not jeopardise the initial ambition of project. Although the very nature of PESCO facilitates the coexistence of the two Europes as long as the minimum commitments are met.
The friction that PESCO and NATO may have or the future position that the UK will hold in European defence after its exit from the EU are other questions that PESCO raises. Only its implementation will dispel these uncertainties. Leaving these doubts aside for a moment, what can be said is that Permanent Structured Cooperation opens up a wide horizon and that it is exclusively in the hands of European citizens to take advantage of it.
As the current French Minister of Economics and Finance, Bruno le Maire, says: "Europe is not a certainty, it is a fight".
Bibliography
Council of the EU. (11 December 2017). consilium.europa.eu. Retrieved from Cooperation on subject defence: statement press
Council of the European Union (2017). Legislative acts and other instruments (PESCO), (p. 20). Brussels.
European Union (2009). Treaty of Lisbon. Lisbon, Portugal.
The Council and the High Representative of foreign affairs and security policy (2017). Notification on Permanent Structured Cooperation, (p. 10).
Examination of the reformulation of Castro's economic model attempted by Fidel's successor
Next April, a year and a half after Fidel Castro's death, his brother Raúl plans to leave the presidency of Cuba, where he has been for a decade. His bequest is an attempt to lengthen the Castro regime by forcing the island's economic recovery. But the restrictions of the reforms themselves, the slow pace of their implementation and the fact that they are not accompanied by greater political freedom, have limited the effect of the changes. Nevertheless, they may be a good starting point for the next president if he really wants to move towards full openness.
article / Valeria Vásquez
Raúl Castro replaced his brother Fidel as president of Cuba's state committee in 2008. Since then, the island has undergone changes in its organisation, although without abandoning its communist structure or the revolutionary principles set in motion in 1959. On coming to power, Castro decided to embark on a path of structural reforms in order to "update" Cuba's socio-economic model and emerge from the serious economic crisis.
As part of this programme, Raúl Castro approved a series of social and economic reforms of a "transformative" nature, which tended towards the introduction of market mechanisms, while maintaining adherence to socialist principles based on centralised planning (and without accompanying these changes with political liberalisation). Revitalisation was the main goal of the reforms in the economic sphere, turning around what had been a fully socialist approach policy and rejecting free market reforms.
Ten years after the changeover between the Castros brothers, the Cuban regime is preparing for the arrival in April of the first president from outside the family. Although it has not yet been confirmed who the new president will be, it is expected that the current vice-president, Miguel Díaz-Canel, will be appointed as part of a continuity of power.
The country is currently at a disadvantageous status , with political uncertainty over the new phase that is opening up, the serious economic difficulties that Venezuela (the island's main benefactor for more than a decade) is going through, and the truncated foreign expectations that the arrival of Donald Trump in the White House a year ago brought with it.
update from model economic
Since 1959, Cuba's economic model has been based on revolutionary socialist principles. Since Raúl Castro came to power, however, a process of transformation has been undertaken, considered necessary to move forward a Economics that was stagnating and immersed in a serious crisis.
In reality, there was no substantial modification of the economic model , but rather a update of it, maintaining the predominance of central state planning and state ownership over the laws of the free market. The goal of this process has been to guarantee the continuity and irreversibility of socialism, as the Cuban authorities have declared, as well as to promote the country's economic development and improve the standard of living of the population.
The framework reforms were approved at the VI congress of the Cuban Communist Party, held in 2011. Among other points, the approved agreements established the submission of a usufruct to peasants and cooperatives, and opened the door to the mass dismissal of hundreds of state employees. The reform guidelines, however, did not set out the specific role that the state and state-owned sector should play in the Economics.
The so-called update of Cuba's model has led to the expansion of the market and non-state ownership, but in a Economics that is still conditioned by state planning this measure is still inefficient, as it was in China or Vietnam. While the state business still prevails (in a more decentralised form, through self-financing and without fiscal subsidies), the private sector has become more flexible, but heavy taxation of the private sector still hampers development.
Land in usufruct
One of the main pillars of the Castro government's reforms was the submission usufruct of idle state land to peasants and cooperatives, with the purpose aim of reducing imports and increasing production. The usufructuaries have obtained the right to cultivate the land and to keep what they harvest, but the state retains ownership and can terminate the contract for reasons of public interest.
Regulation was carried out through two laws: a first, in 2008, subject to many restrictions and actually disadvantageous for farmers; and a second, in 2012, more flexible, whereby the government expanded the size of the plot (from 13 to 67 hectares), approved the planting of orchards and forests, and also allowed the construction of houses next to the land (previously forbidden).
In March 2011, the government reported that 128,000 usufructs, totalling 1.2 million hectares, had already been handed over. However, although the 2012 law was less restrictive than the previous one, as mentioned above, it still included certain hurdles that discouraged farmers from getting involved: farmers made gains, but only after overcoming various obstacles.
Mass dismissal of civil servants and self-employment
At the beginning of 2011, the state payroll presented an "inflated" rate, with millions of state employees in precarious positions and conditions at work . For this reason, Raúl Castro promoted the dismissal of 500,000 surplus state workers between October 2010 and March 2011, which raised the unemployment rate to 12%. To counteract this measure, 250,000 self-employed jobs were initially created and other private activities were also promoted.
This was necessary to raise labour productivity, reduce costs and increase wages. The agreements of the CCP's VI congress allowed for the approval of 178 self-employed activities: many of them were very specific and unskilled (such as forklift drivers or bath attendants), and a few were skilled (such as translators or insurance agents). This made the private work more flexible.
Thus, in a country with a labour force of 5 million people, out of the total of 11.2 million people living on the island, a total of 4.2 million of those working are state employees and the rest are in the non-state sector, consisting of agricultural cooperatives, private farmers and the self-employed [1]. The latter now number 500,000 people. Despite this development of what is known in Cuba as "cuestapropismo", there are restrictions that prevent most professionals from working on their own in their profession, and this reduces the human capital available to boost the country's Economics .
Openness to foreign investment
The flow of investment from abroad has not accompanied the reforms promoted by Raúl Castro, which has been one of the biggest obstacles to the desired success. In order to attract foreign investment, the Special Zone of development Mariel (ZEDM) was inaugurated in 2013. The port of Mariel, located 45 kilometres west of Havana, was allocated a 465.4 square kilometre industrial zone and an advanced ship terminal. entrance The purpose was to convert the ZEDM, through the existence of incentives to attract investment, into the main gateway for foreign trade and the largest industrial structure in Cuba [2]. However, four years after its inauguration, the results have not been as expected. In an administrative process that has followed an extraordinarily slow pace, today only 33 companies have been set up at C , a far cry from the 2.5 billion dollars that the ZEDM was intended to attract annually.
The restoration of diplomatic relations with Washington at the end of the Obama administration has not accelerated investment from the US or other Western countries. In addition to the US embargo remaining in place, the Trump administration has reversed provisions passed by his predecessor that opened a timid door to greater economic engagement.
status economic
Raúl Castro's reform plan has not been as successful as expected, mainly because of the restrictive Degree that regulates them. The lack of the intended economic revitalisation has manifested itself in the poor performance of Cuba's Economics in recent years. In 2016, Cuba fell into recession, with an economic decline of 0.9%. In 2017, it was able to recover slightly (figures that have not yet been finalised speak of a 1.6% increase in GDP) thanks to a boom in tourism and better agricultural results.
In the last decade, tourism has been precisely one of the assets of the Cuban Economics . agreement According to an ECLACreport , tourism to the island grew by 11.9% in 2017, with 4.7 million visitors. This increase accounts for the largest issue of visits from the United States, made possible by the elimination of restrictions approved by Obama, but which Trump has reimposed.
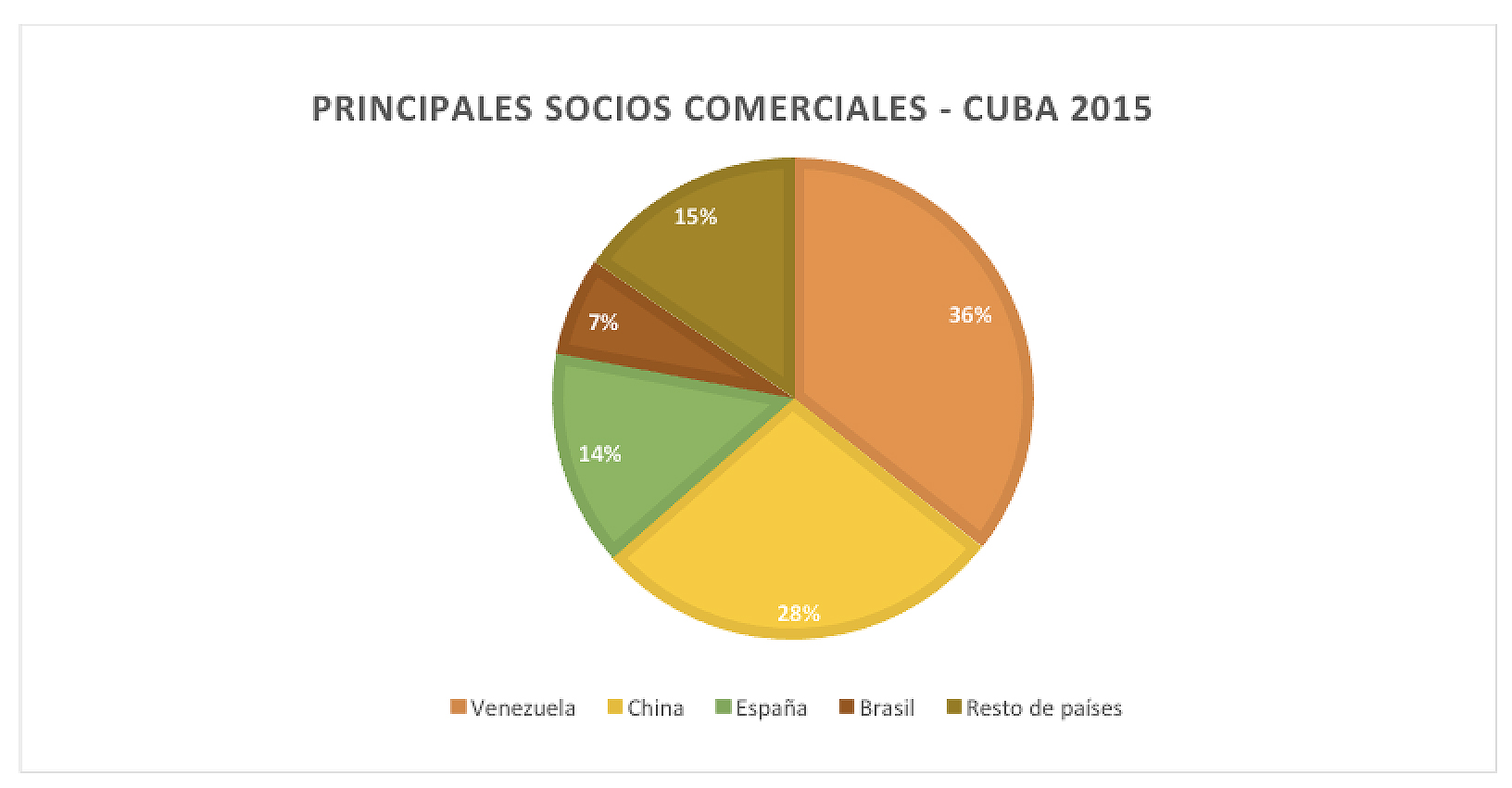
On the other hand, Cuba maintains its chronic trade deficit. Although in 2016 it managed to reduce it to 9.6 per cent of GDP, the outlook is not good, given Venezuela's difficulties in continuing to supply oil, practically on a non-repayable basis. In 2015, Venezuela was Cuba's main trade partner , with which it maintains 36% of its foreign trade, in a exchange valued at 4 billion dollars. It is followed by China, with 28%, a country that sells under soft credit conditions to the island.
|
sourceSOURCE: ONEI. yearbook Estadístico de Cuba 2015, external sector. |
bequest and new challenges
As Raúl Castro's presidency draws to a close, Cuba finds itself in an unfavourable status , with a Economics that is struggling to emerge from stagnation and with a programme of structural reforms that have been insufficient to resolve the problems accumulated over more than 60 years of centralised state socialism. partner-economic problems. The timid nature and slow pace of economic reforms have not helped to revive Economics.
However, during his decade in power, Castro has led changes in the management of model, something that should be taken into account even though in the political sphere he has perpetuated the lack of freedom and the persecution of opposition activity, without undervaluing the moral guilt of the dictatorship. Among the changes that have taken place are the opening up to foreign investment, new diplomatic relations, participation in Latin American forums and the immersion of Cubans in work on their own account.
Probably forced by circumstances, Raúl Castro was able to break down some of the obstacles and ideological barriers that his brother Fidel had implemented on the island for more than 40 years in power. The outgoing president's bequest marks some progress, but it will be the actions of the incoming president that will indicate whether Cuba is truly moving towards the economic - and political - opening that Cubans have longed for.
[1] VIDAL, P. and PÉREZ Villanueva, Omar E. "Se extiende el cuentrapropismo en Cuba". Espacio Laical, vol. 6, n. 3 (2010), p. 53-58.
[2] HERSHBERG, E., & LEOGRANDE, W. M. (2016). A new chapter in US-Cuba relations: social, political, and economic implications. New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
Introduction to the project cooperation of 12 EU countries located between the Baltic, Adriatic and Black Seas.
In addition to the East-West integration efforts of EU enlargement, a number of North-South linking initiatives have been added between the countries of Central and Eastern Europe, such as the Three Seas Initiative. The goal is aimed at overcoming the road infrastructure deficit and improving connectivity between these nations, which will enhance cooperation in the region and in the EU as a whole.

▲First meeting of the new forum, in the Croatian city of Dubrovnik, in August 2016 [i3].
article / Paula Ulibarrena
What is it and what does it aim to achieve?
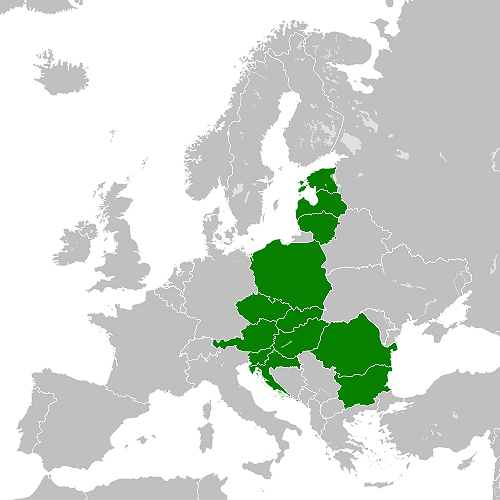
It is an initiative of Poland and Croatia that brings together 12 countries located between the Baltic, Adriatic and Black Seas and is therefore also known as the Baltic, Adriatic, Black Sea (BABS) Initiative.
The key goal is promote that these countries of the European Union have greater cooperation in infrastructure development , economic development , economic cooperation and above all in energy resources. Polish President Andrzej Duda expressed the hope that the Three Seas Initiative would contribute to the modernisation, integration and unification of Central Europe, Eastern Europe and the entire European Union.
How and where was this forum born?
Since the fall of the Berlin Wall, much progress has been made towards a united, free and peaceful Europe. The entrance of Central European countries in the European Union and NATO has contributed to the security, stability and prosperity of the entire continent. But this work is far from complete. And the cohesive role of infrastructure will be crucial in achieving this.
For more than half a century, efforts to develop European connections and infrastructure focused on the East-West axis. After the fall of the Wall, governments in the region focused on integrating their economies into Western markets, leaving the development of a North-South interregional infrastructure on the back burner. After decades of disinvestment, a major effort has been made in the last twenty years to catch up: 5,600 kilometres of motorway have been built. But the imbalance between the two Europes is still glaring: a citizen of old Europe has twice as many kilometres of motorway as a citizen of central Europe, average.
|
▲Wikimedia Commons [JayCoop]. |
goal With the aim of reversing status, the presidents of Poland and Croatia, Andrzej Duda and Kolinda Grabar-Kitarović, respectively, launched in 2015 a project for the construction of energy, transport and telecommunications infrastructure in Central Europe. They called it the Three Seas Initiative.
By whom is it formed?
The initiative aims to modernise economic links between the twelve EU nations located between the Baltic, the Black Sea and the Adriatic Sea (Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia). This region accounts for 28% of the European Union's territory and 22% of its population. But it accounts for only 10% of its GDP.
In 2016, Poland and Croatia were joined by most Eastern European countries: Austria, Bulgaria, Slovakia, Slovenia, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Czech Republic and Romania. Thus a north-south axis that, with the exception of Austria, corresponds to the former communist countries.
The so-called Three Seas Initiative held its first session on 25-26 August 2016 in Dubrovnik and ended with a declaration of cooperation on subject economic cooperation, particularly in the fields of energy, transport and communications. In addition to the member states, representatives of the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the US Homeland Security committee attended as guests.
The second meeting took place on 6-7 July 2017 in Warsaw, with US President Donald Trump as a guest. In fact, this visit was a slight snub to other EU countries.
The third meeting will take place in Romania in 2018, although the city has not yet been fixed.
How is it financed?
150 billion from the Structural Funds, plus additional money from the Connecting Europe Facility and the European Investment Bank. However, more than 384 billion still needs to be invested in another 2,000 projects to fill in or modernise these corridors.
An investment of this size is beyond the possibilities of public institutions, so infrastructure companies and financial institutions will have to play a key role. Up to now, this subject of financing has been much less important than state contributions. However, the increase in public debt makes it increasingly interesting to have sources that minimise the impact on public accounts.
Screening
Faced with this magnitude of resource requirements, the question arises as to whether Central Europe is really an attractive market for investment. In this respect, two points can be made. This is a region with, firstly, very good economic growth prospects (expected to outpace Old Europe over the next five years), and secondly, with a construction sector that is expected to grow at a rate of 3.1% per annum average (compared to 2.3% for Western Europe), according to data by BMI Research. This is certainly attractive for investors.
The other side of the story is that we are still an emerging region. And, of course, this, in addition to generating reserves, brings with it a higher level of risk. In this sense, we also have very different situations depending on which country in the region we are looking at. For example, Estonia right now is what investors call a "sweet spot", with very high returns and low risk. But it is the only country in the region in this category. There are countries - such as Lithuania, Croatia, Slovakia and Slovenia - where the risks are equivalent to those of Greece or Italy, but the returns are relatively low. And others have the opposite problem: high returns but too much risk.
The experience of those players already present in this area -some of them Spanish, such as Ferrovial, Bankia or BBVA-, shows that although each country has significant peculiarities, there are some common risks. To mention them briefly: lack of political support; regulatory regimes that lack transparency; very complex contracting processes - such as PPPs and concessions -; lack of projects with the necessary level of maturity to arouse investor appetite, and the lack of skill in the public sector in these countries to take advantage of private-sector funding schemes, among others.
In an increasingly competitive and global Economics , the prosperity and well-being of a united Europe will depend on how quickly it adapts to today's world. In that process, building a connected, safe, affordable and sustainable transport network connecting the EU from north to south is core topic. Doing so will have a direct impact on increasing the competitiveness of all European countries, and consequently on the economic growth of Europe as a whole.