Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with label dominican republic .
Pandemic reinforces value of production centres in the same sub-regions
Free trade zones in Central America and the Caribbean have been an important engine for the region's economies. Favoured by the increasing globalisation of recent decades, they could now be boosted by a phenomenon in the opposite direction: "glocalisation", the desirability of having production centres in the same sub-region, close to major markets, in order to avoid the problems in distant supply chains seen during this Covid-19 crisis that has affected transport and communications so much. The two leading Latin American free trade zone countries, the Dominican Republic and Costa Rica, offer affordable and sufficiently skilled labour at the doorstep of the United States.
![One of the Dominican Republic's free trade zones [CNZFE]. One of the Dominican Republic's free trade zones [CNZFE].](/documents/10174/16849987/zonas-francas-blog.jpg)
One of the free trade zones of the Dominican Republic [CNZFE] ▲ One of the free trade zones of the Dominican Republic [CNZFE].
article / Paola Rosenberg
The so-called free trade zones, also known in some countries as free zones, are strategic areas within a national territory that have certain tax and customs benefits. In these zones, commercial and industrial activities are carried out under special export and import rules. It is a way of boosting investment and employment, as well as production and exports, thus achieving the economic development of a part of the country or of the country as a whole.
Free trade zones are important in Latin America, and in the case of the smaller economies they are the main production and export hubs. According to agreement with the association of Free Trade Zones of the Americas (AZFA), there are some 3,500 free trade zones in the world, of which 400 are in Latin America, representing 11.4% of the total. Within this region, they are particularly important in the countries of Central America and the rest of the Caribbean basin. They are particularly important in the Dominican Republic and Costa Rica, as well as in Nicaragua, El Salvador, Colombia and Uruguay (also in Puerto Rico).
These countries benefit from having abundant (especially trained in the Costa Rican case) and low-cost labour (especially in the Nicaraguan case), and this close to the United States. For manufacturers wishing to enter the US market, it may be interesting to invest in these free trade zones, taking advantage of tax benefits and labour conditions, while their production will be geographically very close to their destination.
The latter is gaining ground in a post-Covid-19 world. The trend towards sub-regionalisation, in the face of the fractured dynamics of globalisation, has been highlighted for other areas of the American continent, as in the case of the Andean Community, but it also makes a great deal of sense for greater integration between the United States and the Greater Caribbean. Insofar as the US moves towards a certain decoupling from China, the free trade zones of this geographic area may also become more relevant.
Reproduced from report graphic of the association Free Trade Zones of the Americas (AZFA), 2018
Export processing zones
Free zones can be export-oriented (external market), import substitution-oriented (internal market) or both. The former may have a high industrial component, either seeking diversification or relying on maquilas, or emphasising logistics services (in the case of Panama's free zones).
Free zones for exporting products have been particularly successful in the Dominican Republic and Costa Rica. As the AZFA indicates, of the 31,208 million dollars exported from Latin American free zones in 2018, the first place went to the Dominican Republic, with 5,695 million, and the second to Costa Rica, with 4,729 million (the third place went to Puerto Rico, with 3,000 million). Exports from the Dominican Republic's free trade zones accounted for 56% of all exports from that country; in the case of Costa Rica it was 48% (third in the ranking was Nicaragua, with 44%).
The Dominican Republic is the country with the largest issue number of free zones (71 multi-company zones) and its 665 companies generated the largest number of direct jobs (165,724). Costa Rica has 48 free zones (in third position, after Nicaragua), and its 343 companies generated 93,496 direct work jobs (in fifth position).
In terms of the profitability for the country of this economic modality , for every dollar exempted between 2010 and 2015, Costa Rica's free trade zones generated an average of 6.2 dollars and those of the Dominican Republic 5 dollars (El Salvador ranked second with 6 dollars).
As regards Costa Rica specifically, a late 2019report by the Costa Rican foreign trade promotion agency, Procomer, put the contribution of free trade zones at 7.9% of GDP, generating a total of 172,602 jobs work, both direct and indirect, with an annual growth of issue jobs averaging 10% per year between 2014 and 2018. These areas account for 12% of the country's formal private sector employment . An important fact about the contribution to development of the local Economics is that 47% of the purchases made by firms located in free trade zones were from national companies. An important social dimension is that the zones contributed 508 million dollars to the Costa Rican Social Security Fund in 2018.
The Dominican Republic's free trade zone regime is particularly applauded by the World Bank, which describes the country as a pioneer in this subject instrument of productive and commercial promotion, presenting it as "the best known success story in the western hemisphere". agreement According to the statistics of the committee National Free Trade Zones Export Zones (CNZFE), these have contributed 3.3% of GDP in recent years, thereby contributing to the significant growth of the country's Economics in recent years (one of the highest fees in the region, with an average of over 6% until the onset of the current global crisis). The geographical proximity to the United States makes its free trade zones ideal for US companies (almost 40% of investment comes from the US) or for companies from other countries that want to export to the large North American market (34% of exports go to the US).
High levels of corruption and impunity in the region make it difficult to eradicate millionaire bribes in public procurement contracts
The confession of the construction and engineering company Odebrecht, one of the most important in Brazil, of having delivered large sums as bribes to political leaders, parties and public officials for the awarding of works in various countries in the region has been the biggest corruption scandal in the history of Latin America. The B budget increase during the "golden decade" of raw materials occurred in a framework of little improvement in the effectiveness of the rule of law and control of corruption, which led to high levels of illicit deviations in public contracts.

article / Ximena Barría [English version].
Odebrecht is a Brazilian company that conducts business in multiple industries through several operating sites. It is engaged in areas such as engineering, construction, infrastructure and energy, among others. Its headquarters in Brazil are located in the city of Salvador de Bahia. The business operates in 27 countries in Latin America, Africa, Europe and the Middle East. Over the years, the construction company has participated in public works contracts in most Latin American countries.
In 2016, the U.S. Justice department published a research denouncing that the Brazilian company had bribed public officials in twelve countries, ten of them Latin American: Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guatemala, Mexico, Panama, Peru, Dominican Republic and Venezuela. The research was developed from the confession made by Odebrecht's own top executives once they were discovered.
The company provided officials in these countries with millions of dollars in exchange for obtaining public works contracts and benefiting from the payment for their execution. The business agreed to submit millions of dollars to political parties, public officials, public candidates or persons related to the Government. Its purpose was to have a competitive advantage that would allow it to retain public business in different countries.
In order to cover up these illicit capital movements, business created fictitious corporations in places such as Belize, the Virgin Islands and Brazil. The business developed a secret financial structure to cover up these payments. The research of the U.S. Justice department established that bribes in the aforementioned countries totaled US$788 million (almost half in Brazil alone). Using this illegal method, contrary to all business and political ethics, Odebrecht obtained the commissioning of more than one hundred projects, the execution of which generated profits of US$ 3,336 million.
Lack of an effective judiciary
This matter, known as the Odebrecht case, has created consternation in Latin American societies. Its citizens consider that in order for acts of this nature subject not to go unpunished, countries must have greater efficiency in the judicial sphere and take more accelerated steps towards a true Rule of Law.
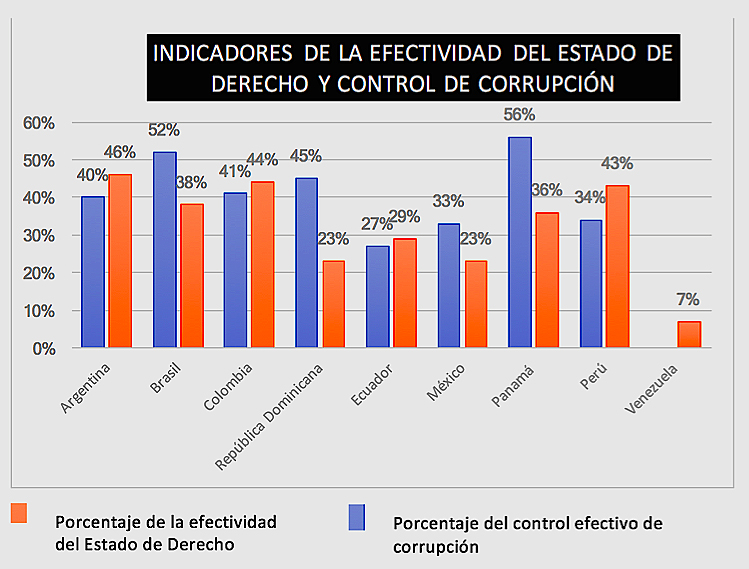
From agreement with World Bank indicators, none of the ten Latin American countries affected by this bribery network reaches 60% of effectiveness of the rule of law and corruption control. This would explain the success of the Brazilian construction company in its bribery policy.
|
source: World Bank, 2016 |
Judicial independence and its effectiveness is essential for the resolution of facts of these characteristics. The proper exercise of justice shapes a proper rule of law, preventing the occurrence of illicit acts or other political decisions that may violate it. Although this is the ideal, the countries involved in the Odebrecht case do not fully comply with this due judicial independence.
Indeed, according to the Global Competitiveness Report for 2017-2018, most of the affected countries obtain a leave grade regarding the independence of their courts, which indicates that they lack an effective judiciary to judge the alleged people involved in this case. This is the case, for example, with Panama and the Dominican Republic, ranked 120th and 127th, respectively, in terms of judicial independence, out of a list of 137 countries.
One of the problems suffered by the Judicial Branch of the Republic of Panama is the high issue of files handled by the Supreme Court of Justice. This congestion makes it difficult for the Supreme Court to work effectively. The high number of processed files doubled between 2013 and 2016: the conference room Criminal Court processed 329 files in 2013; in 2016 there were 857. Although the Panamanian Judicial Branch has improved its budget, that has not represented a qualitative increase in its functions. These difficulties could explain the Court's decision to reject an extension of the research, even though this could mean some impunity. In 2016, there were only two detainees for the Odebrecht case. In 2017, of the 43 defendants who could be involved in the acceptance of bribes valued at US$60 million, only 32 were prosecuted.
The Dominican Republic is also at a similar status . According to a survey of 2016, only 38% of Dominicans trust the judicial institution. This low percentage may have been contributed to by the fact that active members of political parties were elected to serve as Supreme Court judges, something that tarnishes the credibility of the judiciary and its independence. In 2016, Dominican courts only inquired about one person, when the U.S. Supreme Court estimated that the Brazilian business had given $92 million in political bribes, one of the highest amounts outside Brazil. In 2017, the Supreme Court of the Dominican Republic ordered the release from prison of 9 out of 10 allegedly involved in the case due to insufficient evidence.
Need for greater coordination and reform
In October 2017, public prosecutors from Latin America met in Panama City to share information on money laundering, especially in relation to the Odebrecht case. Officials expressed the need to leave no case unpunished, thereby contributing to solving one of the biggest political, economic and judicial problems in the region. Some prosecutors reported having suffered threats in their investigations. All of them valued positively the meeting, as it highlighted the need for greater fiscal coordination and legislative harmony in Latin America. However, it is important to note that the Dominican Republic was absent from meeting.
Any awareness of public ministries in Latin America is essential given the correlation observed between the countries affected by Odebrecht bribes and their poor ranking in indexes provided by different international organizations and centers of research. Ineffective rule of law and lack of control of corruption enable companies like Odebrecht to succeed in their bribery policy to gain a competitive advantage.
The shortcomings of the judicial systems in countries such as Panama and the Dominican Republic, in particular, may make it possible for public officials to go unpunished for crimes committed. In addition, the Odebrecht case, of great magnitude in the region, could further congest judicial activity if effective reforms are not made in each country.