-
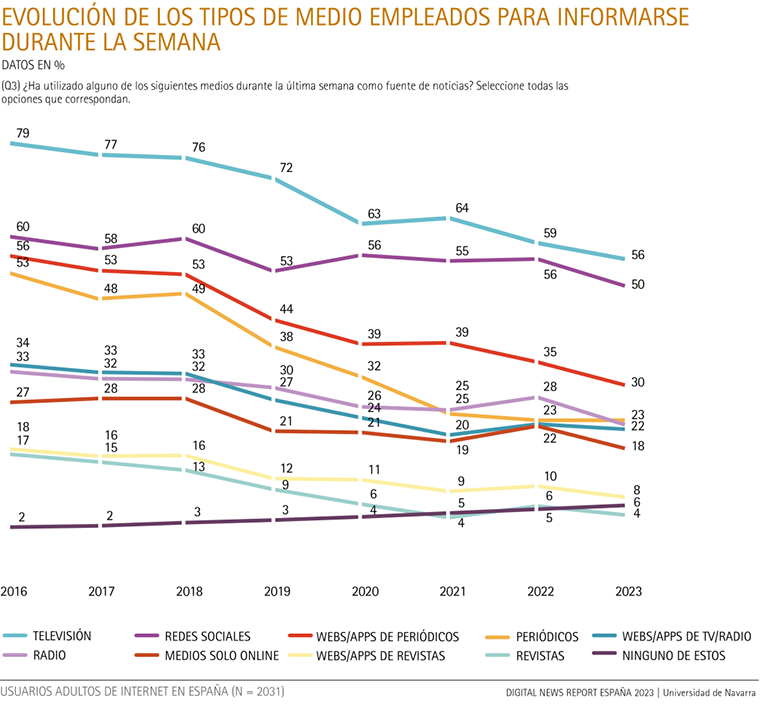
Television continues to be the most used medium for information (56%), although leave three points more in the last year.
-
After remaining stable during the pandemic, the percentage of Internet users who consult news on social networks (50%) lost six points in the last year.
-
Social networks are the most used news source by those under 44 years of age (56%), compared to 43% who opt for television.
-
Newspaper websites and apps are gradually declining, losing five points in the last year, from 35% to 30%.
-
Newspaper (23%) and radio (22%) audiences are maintained and give stability to the traditional offline media as a whole (69%).
The advantage gained since 2018 by the consumption of news in the set of digital media over the total of traditional offline media has narrowed in the last year. In 2022, the difference in the percentage of Internet users who were informed by online media - including social networks - (79%) over those who were informed by offline media (70%) reached nine percentage points. In 2023, this difference is reduced: the proportion of users who get their information online has lost five points to 74%, while the audience of traditional offline media as a whole leave only one point (69%). In 2022, the proportion of users who get their information from social networks (56%) was close to that of those who get their information from television (59%). But in 2023, the percentage of users of social networks dropped six points, and that of television dropped only three points, with television's lead widening slightly from last year.
leave digital media consumption and lose the stability achieved during the pandemic.
Social networks are the second most used media subject among Spanish users (50%). Between 2020 and 2022, the informative use of social networks remained between 55% and 56%. TV and radio websites and apps also held steady (between 26% and 28%) and online-only media (from 21% to 22%), while newspaper websites and apps went from 39% in 2020 and 2021 to 35% in 2022. However, online media as a whole experienced an overall decline in the last year.
In 2023, 50% of Internet users say they get their information from social networks; the percentage is six points lower than last year, and three points lower than in 2019 (53%), before the pandemic. Between 2018 (60%) and 2019 (53%), the decrease had been seven points. In other words, the percentage of those who now get their information from social networks is ten points lower than in 2018.
On the other hand, newspaper websites and apps (30%) have also lost the stability achieved in 2020 and 2021, dropping nine percentage points since then, five in the last year. Despite this drop, online newspapers continue to occupy third place among the various types of source information in this ranking.
The audience of TV and radio websites and apps falls since 2016, and this past year they also lose six points (from 28% to 22%). Their position in the table drops below print newspapers (23%) by a minimal difference.
Finally, there was a four-point drop in online-only media, from 22% to 18%, and a two-point drop in magazine websites and apps, from 10% to 8%.
Newspapers (23%) and radio (22%) maintained last year's records, while television news consumption (56%) continues to fall.
The continued decline in the consumption of traditional media as a whole has been attenuated in the last year by the sustained growth of newspaper and radio audiences.
Television has been falling progressively since 2016, although it remains the medium most used by Internet users to get information (56%). During the pandemic, in 2020 (63%) and 2021 (64%), the decline in TV news consumption seemed to have stopped, although it dropped again in 2022 (59%); and this last year it has lost three more points (56%).
In 2023, the decline in the consumption of newspapers (23%) and radio (22%) slowed down. Lastly, magazines again lost two percentage points, with only 4% of Internet users claiming to read them for information.
Despite the balance of these last two years, it is observed that, since 2016, news consumption of traditional media in Spain has plummeted: printed newspapers lose thirty percentage points; television, twenty-three; radio, twelve; and magazines, thirteen points.
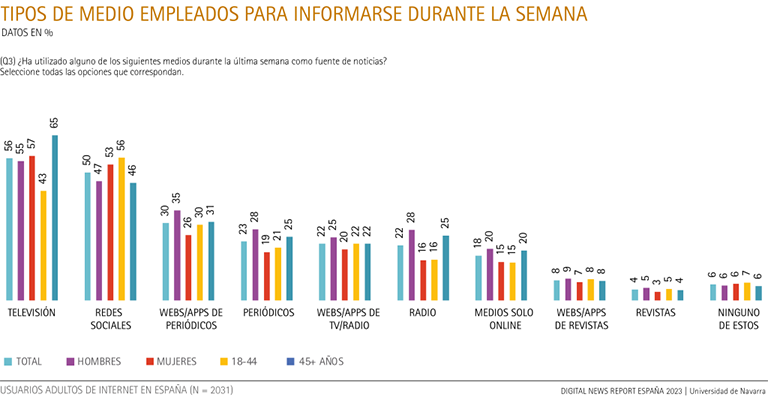
TV continues to be the source most used by those over 45 years of age (65%), while social networks triumph among those under that age (56%).
Television continues to be the medium most used by those over 45 years of age, with 65% stating that they get their information from television. The difference is significant with respect to the audience between 18 and 44 years of age (43%). For those between 45 and 54, 57% get their information from television. And, from 55 years of age, the percentage rises to 69%, seven out of ten respondents (76% in 2022). On the other hand, there are no significant differences in consumption according to gender: 55% among men and 57% among women.
Social networks are the medium in which users between 18 and 44 years of age use the most (56%). There is also a significant difference in the use of this medium with respect to those over 45 (46%). The differences in use are accentuated at the extremes: the percentage rises to 60% among adults up to 34 years of age, while the proportion drops to 42% after 65 years of age. In terms of gender, a higher percentage of women (53%) use social networks than men (47%); this is five points more and the difference is significant.
As for newspaper websites and apps, information consumption has dropped five percentage points compared to last year (from 35% to 30%). By gender, more men (35%) than women (26%) are informed in digital newspapers, there is a significant difference in consumption. By age, no significant difference is found in favor of any group, although news consumption in this media subject is slightly higher among Internet users over 55 years old (32%).
In 2023, newspapers (23%) regain the fourth place lost last year among the various types of media considered in this study, and outperform TV and radio websites and apps by one percentage point (22% in 2023; 28% in 2022). Newspapers repeat the percentage obtained in 2022, after having accumulated nine points of decline during the first two pandemic years (32% in January-February 2020). By age, there is a higher proportion of users among those over 45 (25%), compared to 21% among Internet users aged 18 to 44. However, the group 35 to 44 year-olds account for 25% of newspaper readers. As might be expected, the highest percentage of users is among those over 65, with 33%: this is almost double the percentage of newspaper readers among those under 35 (17%). By gender, the significant difference is in favor of men, with 28% of newspaper readers, compared to 19% among women.
As we have seen, although in 2022 the consumption of TV and radio websites and apps had a rebound in audience, in the last year it has lost six points and stands at 22%. In addition, there are significant differences in consumption by gender (25% among men, 20% among women), but not by age. News consumption of this source is slightly higher among those over 65 years of age, reaching 26%.
As for radio, the proportion of men who get their news from the radio (28%) is significantly higher than that of women (16%); and news consumption among those over 45 years of age (25%) far exceeds that of Internet users aged 18 to 44 (16%). Radio news listening reaches almost three out of every ten Internet users (27%) in the 55 and over age group ( group ), while among those over 65 the percentage is 30%, twice as high as among 18 to 24 year olds (15%).
Since 2019, surveys record about 20% in Internet users' responses about online-only media information use, 18% in 2023. This subject of source gets a higher percentage of responses among men (20%) than among women (15%). By age, 20% among adult users aged 45 and over, while the proportion of users between 18 and 44 is 15%; the difference in favor of older users is significant.
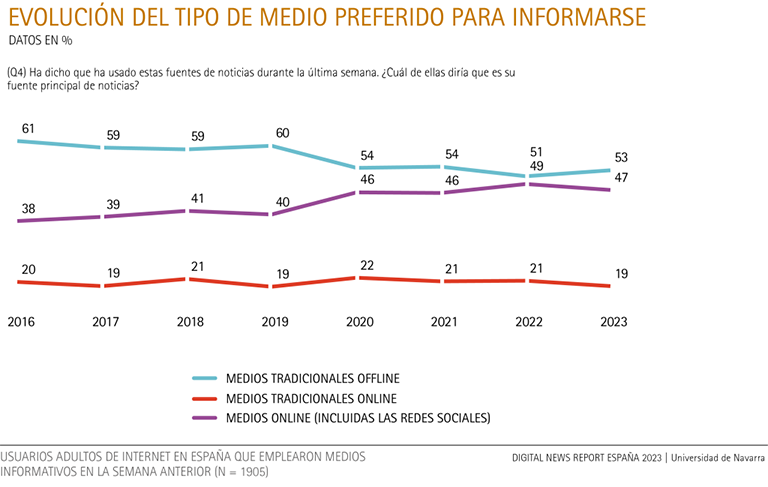
source Traditional, non-digital media are the main source of information for Spaniards (53%), compared to digital media (47%).
While since 2016 there has been a growing preference for group digital media -including social networks-, the choice for the traditional offline media conglomerate has declined. This past year, the decline in online media consumption (from 49% to 47%) and the slight recovery of traditional offline media (from 51% to 53%) have been reflected in the priority choice of subject media by the Internet user. In addition, leave the preference for online traditional media as a whole (from 21% to 19%), which equals the result of 2019.
With regard to the age variable, significant differences in consumption are found at the 45-year age limit: while between 18 and 44 years of age, six out of ten Internet users prefer online media (59%) and four out of ten opt for traditional offline media (41%), for those over 45, six out of ten prioritize traditional offline media (62%) for information, and four out of ten (38%) choose online media.
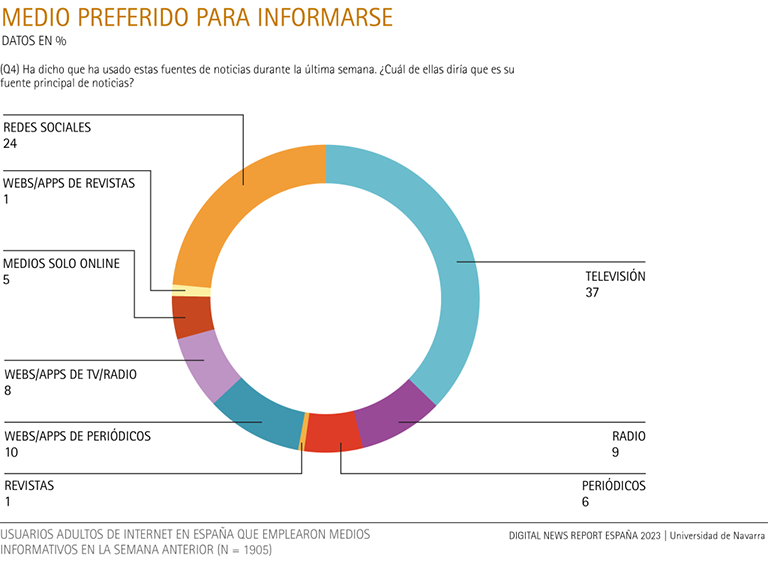
Television (37%) continues to be the preferred medium for the majority, although the gap with social networks (24%) is narrowing.
In general, the question about the preferred means of obtaining information received practically the same answers as last year, with differences of only one percentage point up or down.
Nearly four out of ten respondents (37%) still prefer television, but social networks are up one point this year (three points over the last two years) to 24%. Once again, social networks are closing the gap with respect to television.
Among online media, TV and radio websites and apps added one point (8%), while online-only media (5%) and magazine websites and apps (1%) repeated result. On the other hand, newspaper websites and apps dropped two points.
As for the other traditional media, radio (9%) and newspapers (6%) both added points, while magazines remained the same (1%) as last year.
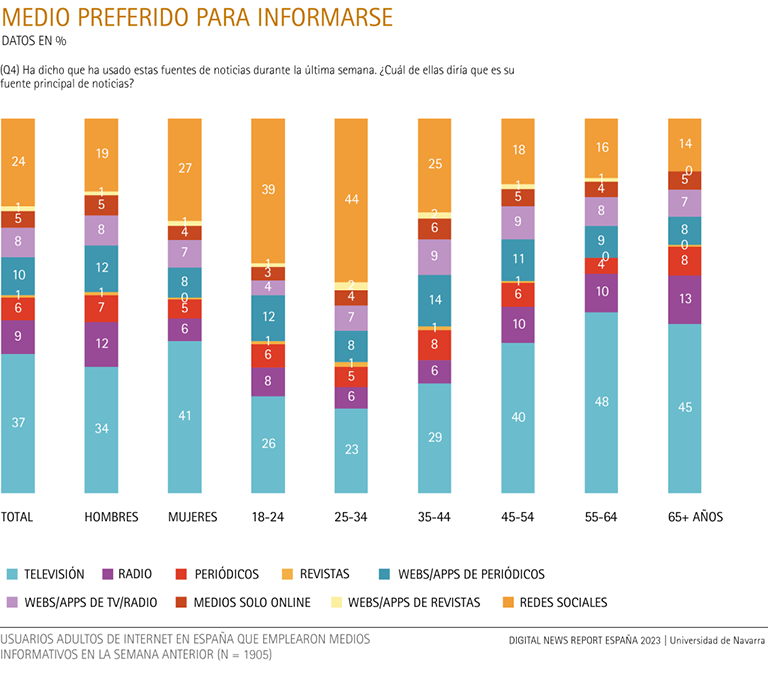
Social networks are the preferred means of information for the majority of Internet users up to 44 years of age (34%).
Social networks are the preferred medium for adults up to 44 years of age (34%). This percentage is double that of users over 45 who prefer social networks (16%). Compared to other media, the preference for social networks is even greater for young people up to 34 years of age: four out of ten prefer them for information (42%), while two out of ten users between 18 and 34 years of age choose television (24%). There is also a higher proportion of those who prefer social networks among women (27%) than among men (19%).
Television is the main medium for information for Internet users over 45 years of age, with almost five out of ten (45%). However, television occupies second place in the preference of adults up to 44 years of age, and the difference is significant (26%). As for the gender variable, four out of ten women (41%) prefer television, compared to three out of ten men (34%).
Newspaper websites and apps obtain third place (10%) as the preferred medium for getting information (12% among men, 8% among women) and, except in the group 35 to 44 year-olds (14%) no significant differences in consumption by age are found, although among users aged 18 to 44 (12%) this subject medium is preferred more than among those aged 45 and older (9%).
As for the preference for radio as an information medium (9%), the proportion of listeners who prefer it among men (12%) is double that of women (6%). By age, the 11% of users over 45 years of age also stands out significantly (reaching 13% among those aged 65 and over), compared to 6% of adults up to 44 years of age.