-
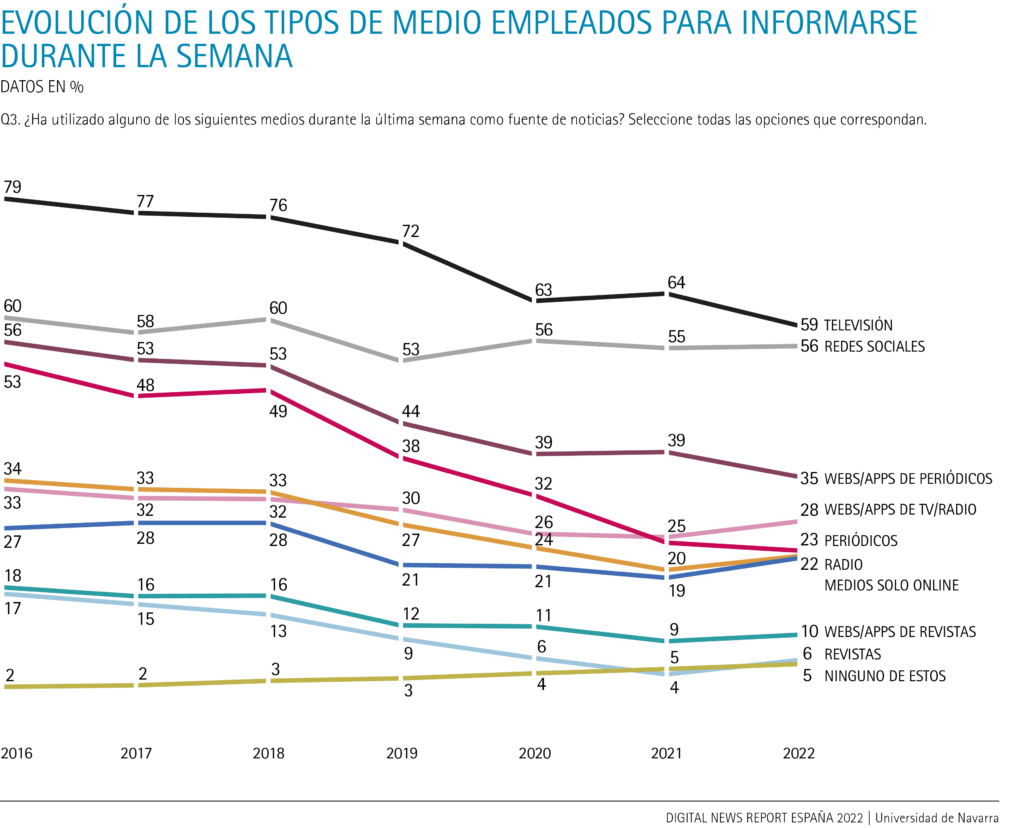
Despite its primacy, television (59%) loses five points and the consumption of information from social networks remains stable (56%).
-
Social networks are the most used news source for six out of ten Internet users up to 44 years of age (60%), 17 points above television (43%).
-
28% of Internet users over the age of 45 read printed newspapers, but only 17% of adults between 18 and 44 are informed by newspapers.
-
Radio stopped its decline and gained 2 points in a year, to 22%, while news magazines recovered two points and reached 6% of weekly reach.
In recent years, the drop in television consumption and the stagnation of newspapers and radios as sources of news for Internet users, together with the increase in news consumption on social networks, have caused the decline of traditional media as a whole, as noted by our report Digital News Report Spain in 2018.
In 2020, the consumption of online media as a whole (79%) exceeded that of traditional offline media (75%) for the first time, due to the drop in television, radio and newspaper users. The data of the survey conducted between January and February 2021 confirmed a slight advantage of the information consumption of the online media group -including social networks- (78%) over the traditional offline media (74%). In 2022, the news consumption of the online media aggregate (79%) stabilizes and, moreover, is 9 points ahead of the consumption of all traditional media (70%), which loses 4 points compared to 2021.
News consumption on social networks (56%, the same as in 2020 and 1 point more than in 2021) and the rebound of TV and radio websites and apps (28%, 3 points more than in 2021) and digital-only media (22%, also 3 points more than in 2021 and obtaining its best record since 2019) contribute to the stability of online media. In contrast, newspaper websites and apps lose 4 percentage points compared to last year (from 39% to 35%) and magazine websites and apps maintain an audience of 10%, 1 point more than in 2021.
However, Spanish Internet users' information consumption of traditional offline media has plummeted since 2016: printed newspapers have lost 30 percentage points; television, 20; radio, 12; and magazines, 11 points.
News consumption on television leave 5 points
The circumstances of the covid-19 pandemic halted in 2021 the sharp decline that television news consumption had been suffering previously. In 2022, however, it will fall again. Despite maintaining its position as the medium most used by Internet users for information, the percentage drops to 59%, 5 points less than last year. As for the other traditional offline media, the drop in the consumption of printed newspapers by Internet users has slowed down: 23% of those surveyed read newspapers, 2 percentage points less than in 2021. In contrast, over the past year radio has gained 2 points (22%) and magazine readership has grown by another 2 percentage points (6%).
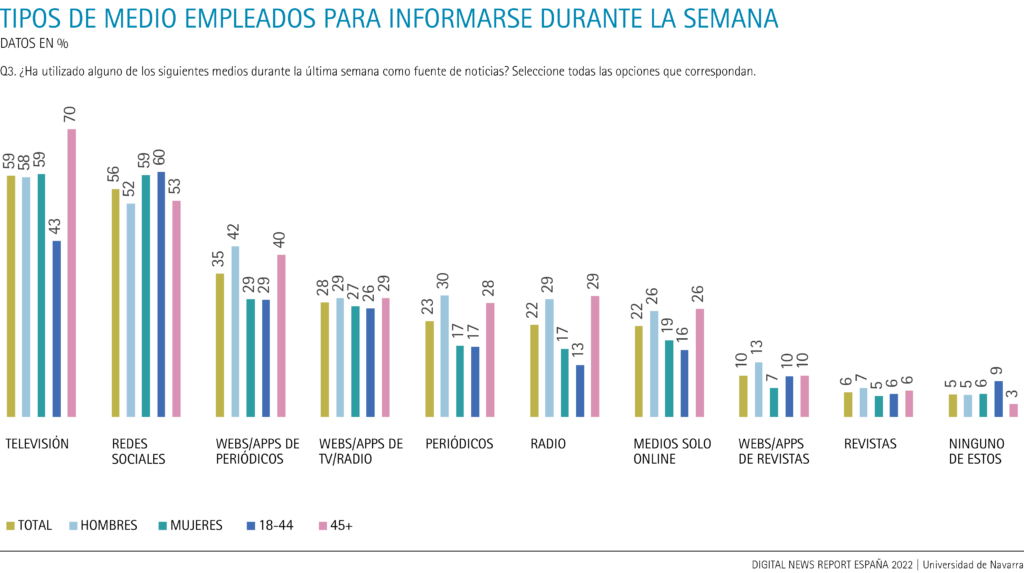
The decline in television consumption is most marked among those under 45 years of age: four out of ten (43%, 51% in 2021), compared with seven out of ten Internet users over 45 years of age who get their information from television (70%, 73% in 2021). The difference between the two groups is significant and is accentuated at the extremes. Television is the second most used medium by 18-24 year olds (42%), behind social networks (65%), while from the age of 55 onwards almost eight out of ten Internet users say they get their information from television (76%). In terms of gender, there are no significant differences in overall consumption (58% of men and 59% of women).
Social networks (56%) are only 3 points behind television. For six out of ten Internet users up to 44 years of age (60%), social networks are the most used news source and are 17 points ahead of television (43%) in this age group ( group ). Among 18 to 34 year olds, the percentage of users of social networks as news source reaches 63%. The proportion of Internet users who use social networks to obtain information drops after the age of 45: five out of ten (53%) use them for this purpose and, for them, they are the second most popular means of information, after television (70%). With respect to gender, there is a higher proportion of women (59%) than men (52%) among those who use social networks for information.
As for newspaper websites and apps, information consumption is down 4 percentage points from last year (from 39% to 35%), which is maintained by men (42%) and, however, down 8 percentage points among women (29%, 37% in 2021). Significant differences in consumption are found in terms of age between the groups of online newspaper users up to 44 years of age (29%) and over 45 (40%); among Internet users over 55, the percentage of those who get their information from newspaper websites and apps reaches 43%.
On the contrary, consumption of TV and radio websites and apps does not seem to have been affected in the last year: it has recovered 3 points and reaches 28% of users. There are no notable differences in consumption by gender (29% among men, 27% among women), nor by age group, with the exception of those over 65, among whom the percentage of users is significantly higher (34%).
However, fewer and fewer Internet users read print newspapers. Despite dropping only 2 points in the last year, the percentage is 23%, 30 points less than in 2016. There is a significant difference by gender (30% of respondents versus 17% of female respondents) and by age. From 45 years of age, almost 3 out of 10 Internet users get their information from newspapers (28%); the proportion barely reaches two out of ten (17%) among users aged 18 to 44. From the age of 55 upwards, 31%, while only 16% of young Internet users aged 18 to 34 read newspapers.
The general decline in traditional media consumption also affects radio, although in 2022 the percentage of users has grown 2 points and stands at 22%. Even so, this is 2 points less than in 2020 (24%) and 11 points less than in 2018 (33%). The proportion of male Internet users who get their information from the radio (29%) is significantly higher than that of women (17%); and information consumption among those over 45 (29%) more than doubles that of Internet users aged 18 to 44 (13%). Among those over 65, four out of ten (39%) listen to the news on the radio. In contrast, only one in ten Internet users aged 18 to 34 (10%) listen to news on the radio.
Internet users prefer online media (49%) almost as much as traditional offline media (51%).
When it comes to getting information, the Internet user's priority choice of one subject medium or another is changing. Since 2016, the preferred consumption of online media as a whole -including social networks- has grown 11 points, while the option for some subject of traditional offline media (television, radio and print media) has lost 10 points. In the last year, the preference for online media as a whole (49%) has risen 3 points and almost equals the priority consumption of traditional media (51%), which has lost 3 points in the last year.
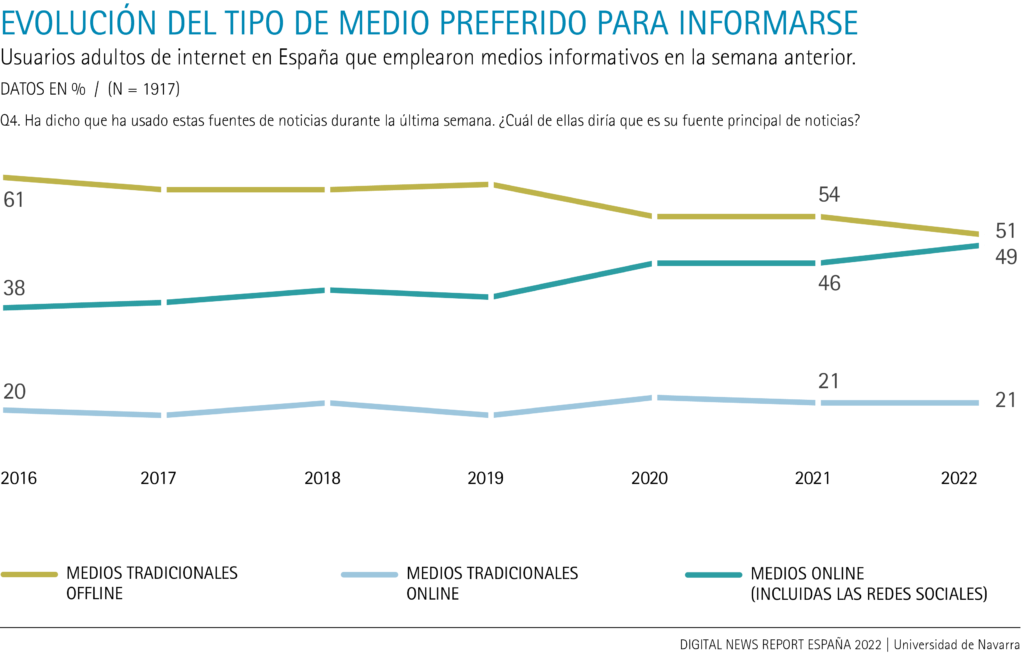
Significant differences in consumption can be found at the 45-year old age group: between 18 and 44 years of age, six out of ten Internet users (63%) prefer online media, while four out of ten (37%) opt for traditional offline media. On the other hand, for those over 45, six out of ten (61%) prefer traditional offline media, and four out of ten (39%) choose online media for their information.
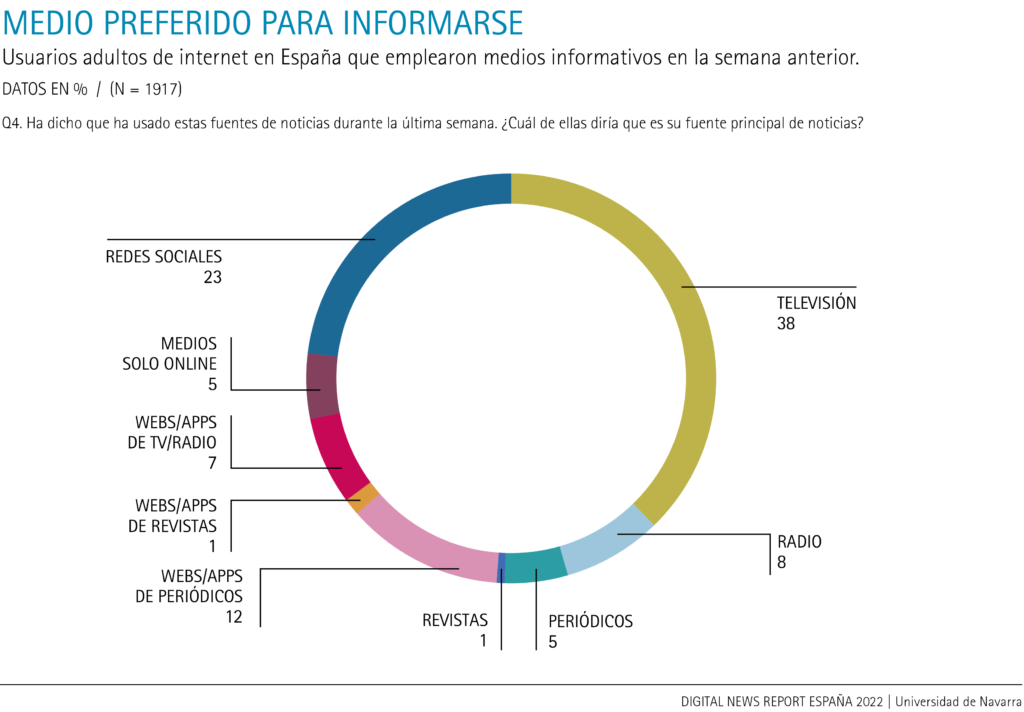
Social networks are growing, but television remains the preferred medium for most people
Despite a drop of 4 points in the last year, television is still the preferred medium for information for almost four out of ten respondents (38%). However, social networks grew 2 percentage points over the previous year, are the preferred medium for 23% of users and occupy second place on the list, closing the gap with television. The other media, both online and traditional offline, obtained very similar results to last year, with differences of 1 percentage point up or down. The exception is radio, which goes from 6% in 2021 to 8% of Internet users who prefer radio for information in 2022.
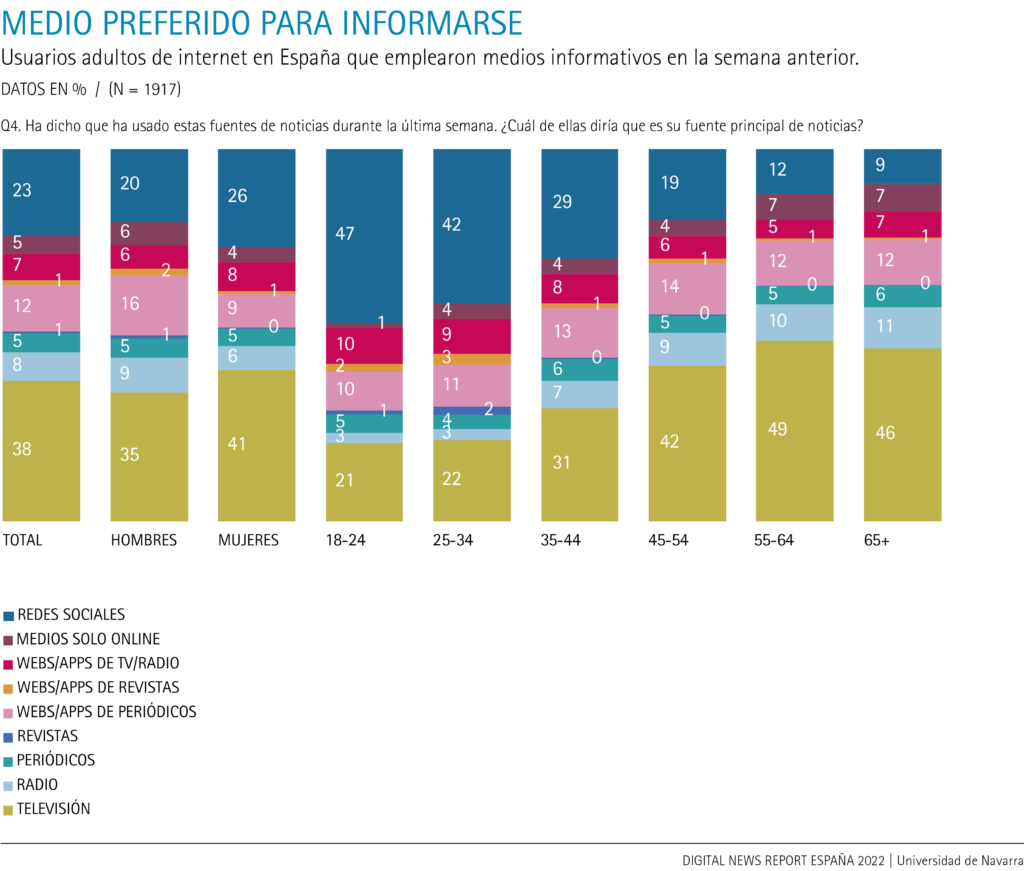
Women's consumption is characterized by their preference for television (41%, compared to 35% of men) and social networks (26%, compared to 20% of men), while men stand out in radio consumption (9%, compared to 6% of women) and newspaper websites and apps (16%, compared to 9% of women); these are significant differences.
Television continues to be the main medium for information for Internet users over 45 years of age: almost five out of ten (46%) prefer television. It is also the preferred medium for 42% of users over the age of 35.
Four out of ten (37%) Internet users aged 18 to 44 prefer social networks for information, compared to 14% of those aged 45 and over. For Internet users up to 44 years of age, television is in second place (26%) as the main medium. On the other hand, social networks are the preferred medium for information for four out of ten young people up to 34 years of age (43%); the percentage is almost double that of television (22%) in this age group ( group ).
Newspaper websites and apps ranked third (12%) as the preferred medium for accessing digital news, and no significant differences in consumption by age were found. As for the rest of the media, the 11% of Internet users over 65 years of age who choose radio as their main medium stand out significantly. There is also a significant difference in preferential consumption of the radio medium between those over 45 (10%) and users between 18 and 44 (5%), among whom only 3% of young people up to 34 years of age prefer radio as their main medium for information. At the other extreme, for 12% of users over 65, radio is their main medium: it is their second preferred medium, behind television (48%).