Ruta de navegación
Blogs
Entries with label bolivia .
The upcoming gas self-sufficiency of its two major buying neighbors forces the Bolivian government to look for alternative markets
![Yacimientos Pretrolíferos Fiscales Bolivianos (YPFB) gas plant [Corporación YPFB]. Yacimientos Pretrolíferos Fiscales Bolivianos (YPFB) gas plant [Corporación YPFB].](/documents/10174/16849987/bolivia-gasnatural-blog.jpg)
▲ Yacimientos Pretrolíferos Fiscales Bolivianos (YPFB) gas plant [Corporación YPFB].
ANALYSIS / Ignacio Urbasos Arbeloa
Bolivia, under Evo Morales, is the only economic success story of all the Latin American countries that embraced left-wing populism at the beginning of this century. Together with Panama and the Dominican Republic, Bolivia has achieved the highest GDP growth in the region in the last five years, and all this in a difficult context of decline on the part of its main trading partners: Argentina and Brazil[1]. The political stability brought by Evo Morales since 2006, coupled with prudent counter-cyclical macroeconomic policies and a new hydrocarbons management are part of the formula for this success. Nevertheless, there are enormous economic and political risks for Bolivia. On the one hand, natural gas accounts for 30% of exports and its destination is exclusively Brazil and Argentina, countries that are close to gas self-sufficiency. Finding alternative routes is not an easy task for a landlocked state, with a diplomatic conflict with Chile and separated by the Andes Mountains from Peru. Moreover, the Bolivian government's bid to exploit lithium through national companies that integrate its processing to favor industrialization is a risky strategy that could leave the country out of the growing world lithium market. Finally, Evo Morales and the MAS have followed a growing authoritarian trend, allowing the reelection of the president, undermining the separation of powers and the recent 2009 constitution. The new Bolivia faces in the next decade the challenge of reorienting its natural gas exports, diversifying its Economics and consolidating a real democracy that will allow a sustained growth of its Economics and its role as a regional actor.
Natural Gas: at the center of the 21st century political discussion
During the failed oil explorations in the Chaco in the 1960's, abundant natural gas reserves of great economic potential were found at finding . Although it was a resource of lesser value than crude oil, an incipient gas industry was soon developed by foreign companies, mainly American, such as Standard Oil. In 1972 a first nationalization took place, with the emergence of YPFB as the state-owned business in charge of the exploration, production, transportation and refining of Bolivian energy resources in partnership with foreign companies. That same year, the first export gas pipeline to Argentina was built. By 1999, Bolivia will export natural gas to Brazil through the Santa Cruz-Sao Paulo pipeline, whose project took more than eight years of negotiations and construction work and introduced Petrobras as an important player in the sector. Thus, Bolivia enters the 21st century with a growing gas industry, mostly privatized by the first government of Gonzalo Sánchez de Lozada, and boosted by a very favorable fiscal model for foreign companies[2].
The year 2001 marks the beginning of a convulsive political stage in Bolivia with the so-called Water War. A wave of protests arose from the privatization of municipal water services in the framework of financial negotiations between the IMF and the government of Hugo Banzer. At the nerve center of these protests in Cochabamba emerged the figure of Evo Morales, a coca growers' leader who will increase his popularity unstoppably. Gas became the protagonist in 2003, with a new wave of protests against the construction of a natural gas pipeline from Tarija to Mejillones (Chile) for consumption by the Chilean mining industry and export to Mexico and the USA in the form of LNG. The civil service examination at project argued the historical incoherence of contributing Bolivian resources to the exploitation of the mining region lost to Chile in the War of the Pacific (1879-1883) and which deprived Bolivia of an outlet to the sea. In addition, an alternative, more costly gas pipeline through Peru was proposed, but which would supposedly benefit the northern region of Bolivia and would not be a national humiliation. The protests took a nationalist and indigenist turn and became a real revolution that blocked La Paz, the international airport and plunged the whole country into violence and shortages. President Lozada resigned and most of his government fled abroad, while the project was cancelled and buried forever.
The new president Mesa comes to power with the promise to call for a binding referendum on gas, the establishment of a Constituent Assembly and a reform of the Hydrocarbons Law, including a review of the privatization processes. The referendum ended up giving the victory to Carlos Mesa's proposals, although with a leave participation and a confusing essay of the questions. President Mesa, unable to capitalize on the legitimacy granted by the plebiscite Withdrawal to position and called early presidential elections in 2005, which brought to power the first indigenous president in the history of Bolivia, Evo Morales, with an absolute majority. Natural gas thus became the main catalyst for political change in Bolivia.
Hydrocarbon reform
The arrival of Evo Morales brought about a profound change in the hydrocarbons legal framework . In 2006 the new hydrocarbons law "Heroes del Chaco" was enacted, nationalizing Bolivia's energy resources, expropriating 51% of the shares of companies involved in the sector and establishing a direct tax on hydrocarbons of 50% subject to an extra royalty of 32% to YPFB in those fields with more than 100 mcf of annual production[3]. This legislation, in the words of Evo Morales "turned the tables, going from 18% to 82% of the State's income on hydrocarbons"[4]. The legislation, although adorned with a radical revolutionary rhetoric, has proven to be moderate and viable in the medium term, since it allows in the internship much less burdensome tax formulas for energy multinationals and did not imply large expropriations of assets. As can be seen in the graph below, tax revenues from natural gas have grown enormously since 2005, the year of the reform, without dramatically affecting natural gas production. Moreover, this reform was accompanied by record highs in the price of raw materials in 2006, 2007 and 2008, cushioning the percentage reduction in foreign companies' revenues. In 2009 Bolivia included in article 362 the primacy of oil service contracts, a formula in which multinationals do not obtain any rights over the hydrocarbons extracted, but are remunerated for the services rendered.
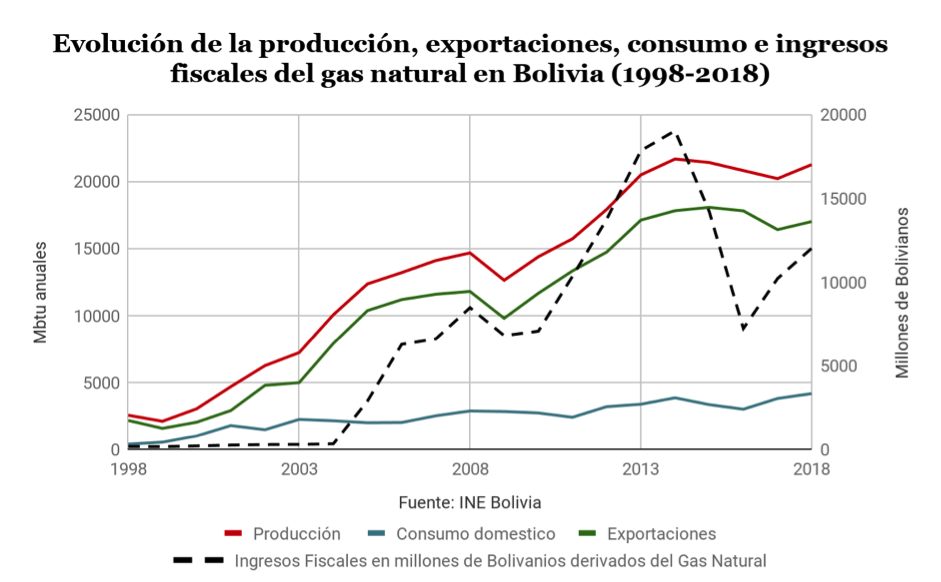
Since the reform, exports have been relatively stable, buoyed by growing demand in both Brazil and Argentina. The most controversial case occurred in the particularly cold winter of 2016, when Bolivia halted exports due to maintenance work at the Margarita field. This event unmasked a stubborn reality about Bolivia's proven natural gas reserves and the need to increase exploration and drilling work in the country. Bolivia's current reserves amount to 283 bcm (10 tcf), enough for only 10 years of export activity at the current rate. Aware of this status limit, the YPFB corporation has launched an investment campaign for 2019 amounting to 1.45 billion dollars, of which 450 million dollars will be dedicated to exploration work[5]. Much of the investment in the sector in recent years has been aimed at industrializing natural gas production instead of exploration work, building refining plants such as the Bulo Bulo ammonia and urea plant[6]. Total, Shell, Repsol and Petrobras are currently working in exploration and production[7]. This effort is intended to answer the IMF's report , which considered Bolivia's natural gas reserves to be too scarce to turn the country into a regional energy center, Evo Morales' greatest aspiration[8]. For YPFB, there are probable reserves of 850 bcm (35 tfc) that would guarantee a long life for the gas sector, but it should rethink its fiscal policy in order to attract foreign companies, which currently account for only 20% of total investment[9].
The future of Bolivian natural gas
From agreement with the contracts signed with Brazil (1999) and Argentina (2005) export prices are indexed to a basket of hydrocarbons, which in general has guaranteed Bolivia a very favorable price, higher than the Henry Hub, but which makes the country equally dependent on fluctuations in international commodity prices. However, the revolution of non-conventional technology and new forms of transportation, now more economical, such as LNG, are transforming the reality of the natural gas market in the Southern Cone. This new situation, linked to the end of the contracts with Brazil in 2019 and Argentina in 2026, puts in check the future of the main asset of the Bolivian Economics .
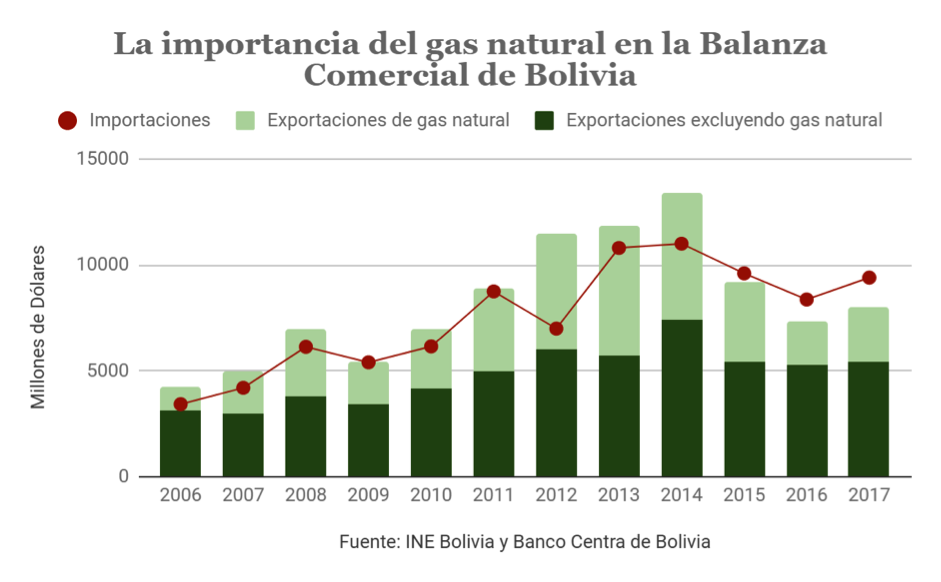
As shown in the graph sample , the Bolivian trade balance and its fiscal stability depend on the exported volumes of natural gas and its international price. The survival of the current Bolivian economic model and the presidency of Evo Morales depend to a great extent on the income derived from this hydrocarbon, being a fundamental factor for the future of the Plurinational Republic of Bolivia.
Brazil
Since 1999, Brazil has become the main destination for natural gas exports, being Bolivia's only client in the 2001-2005 period. This position allowed the entrance of Petrobras as the main investor in the sector until the year of the nationalization, which meant an important diplomatic friction between both countries. It was the complicity between Morales and Lula, as well as the importance of maintaining harmony between the leftist governments in the region, which allowed avoiding a major confrontation between the two countries. Despite the words of Petrobras' president in 2006, Sergio Gabrielli, announcing the end forever of the company in Bolivia, it has continued to be an important investor due to the profitability of its activities and the strategic importance of Bolivian gas for Brazil.
It seems clear that natural gas will play an important role in Brazil's future, since the main source source of electricity in the country, hydroelectric power, requires other sources to replace it when there is a shortage of rainfall, as occurred between 2012 and 2014. This context favored the entrance of natural gas in the electricity mix, which went from 5% in 2011 to 25% by 2015[10]. However, Brazil started a decade ago with the revolutionary pre-salt hydrocarbon exploitations, which have allowed the country to increase its crude oil production from 1.8 mbd in 2008 to 2.6 mbd in 2018. Natural gas production associated with these fields is expected to enter the Brazilian market as the necessary infrastructure connecting the off-shore fields to the still insufficient network of gas pipelines is built, something that is expected to improve with the entrance of private players to the sector following the 2016 energy reform. Likewise, Brazil already has 3 plants to import LNG, allowing it to diversify its imports, as it did during 2018 when Bolivia was unable to supply the 26 million cubic meters per day agreed in 1999. All this puts Petrobras and Bolsonaro, located in the ideological antipodes of Morales, in a privileged position for negotiation, and who could bet on increasing imports of the increasingly cheaper North American LNG and reducing the volume of Bolivian gas. In any case, due to certain non-compliances in the supply of gas from Bolivia, the contract will be extended for at least two more years until the pending volumes of submit , which Brazil has already paid for, are reached.
Argentina
The other natural gas market for Bolivia is also undergoing profound transformations, in this case derived from unconventional shale and tight oil techniques. The Vaca Muerta field, considered one of the largest shale deposits in the world, has begun to produce the first returns after years of investments by YPF and other multinationals. Despite Argentina's economic instability and the fiscal reforms demanded by the IMF that will delay the total development of this giant field[11], it is expected that by 2022 its production will cover approximately 80% of Bolivian imports, returning to the path of self-sufficiency achieved in much of the 1990s and 2000s[12]. For the time being, Argentina has already managed to renegotiate the volumes of natural gas imported in summer and winter in a way that is more favorable to domestic demand[13]. In addition, Argentina authorized natural gas exports to Chile after 12 years of interruption[14] and made its first LNG export in May 2019[15], which are early signs of growing domestic production.
It seems clear that the Argentine market will not have a long run for Bolivian natural gas and will probably put an end to its imports when the contract ends in 2026. Other options are to use the complete network of Argentine pipelines as transit to other destinations via LNG or to neighbors such as Uruguay, Paraguay or even Chile.
Peru
For some months now, Bolivia has been engaged in a public diplomacy campaign to extend a gas export pipeline to Puno, a Peruvian city located on Lake Titikaka. Although Peru has significant natural gas production in Camisea that allows it to export large quantities of LNG, the country launched a program known as Siete Regiones (Seven Regions) to universalize access to natural gas. Southern Peru can be supplied more economically through Bolivian imports due to the proximity of the La Paz pipeline, but there is reluctance, especially in the pro-Fujimori civil service examination , to import a surplus good in the country. This formula would be integrated into a plan to export liquefied petroleum gas from Bolivia to the same area, while Peru would build a gas pipeline to import oil and derivatives from the Pacific port of Ilo to La Paz. For Bolivia, the Peruvian market may be a temporary solution while exports continue to diversify, but it will have an early expiration date given the Peruvian natural gas reserves, double the Bolivian reserves, and the logical trend towards greater domestic production to cover the demand of the entire country. Likewise, it seems sensible to think that the Peruvian coast will in the future be one of the points through which Bolivia could export its natural gas in the form of LNG if the regional market is saturated.
Chile
From an economic point of view, Chile is the most attractive country for Bolivian exports. It lacks natural gas reserves and its mining area, with high energy demand, is located in an area relatively close to Bolivia's gas pipelines and fields network . However, the now century-old dispute over Bolivia's original territories annexed by Chile in the War of the Pacific (1879-1883) has been an insurmountable obstacle in the present century. It is worth mentioning that during the 50's and 60's Bolivia exported oil to Chile and the USA through the Sica Sica-Arica pipeline; that is to say, the refusal to export natural gas to Chile has been a flag used by Evo Morales and not a historical tradition in the relationship between these countries.
After the huge mobilizations caused by the Gas War, Evo Morales was able to catalyze popular fervor and use the territorial dispute to increase his popularity. In fact, a good part of his efforts in the previous legislature were focused on achieving the longed-for exit to the sea through the International Court of Justice in The Hague. In 2018 this court ruled favorably for Chile, ruling that this country has no duty to negotiate with Bolivia a territorial settlement. Morales' refusal to export natural gas to Chile looks set to continue for the duration of his presidency.
However, the 1904 Treaty of Peace and Friendship signed by both states grants Bolivia full customs autonomy in the Chilean ports of Arica and Antofagasta and the right to keep goods in transit for 12 months, with free storage for its imports, and 60 days of free storage for its exports. These conditions seem ideal for the construction of an LNG plant in Arica or Antofagasta to export natural gas by sea while supplying the Chilean north, in need of cheap natural gas to displace coal. The difficult political relations between both countries complicate the viability of this project, which should not be discarded when Morales leaves the presidency and there is greater harmony, as happened with Pinochet and Banzer in power.
Domestic consumption
Domestic consumption of natural gas in Bolivia has grown at an annual rate of 4.5% in the 2008-2018 period driven by subsidized prices for consumption and the implementation of state projects that aim to provide added value natural gas extraction such as the Bulo Bulo urea plant or the Mutun steel industry. It is expected that per capita income in Bolivia and electricity consumption will continue to increase over the next decade. If the volume of natural gas subsidies grows similarly while export revenues decline, Bolivia's delicate fiscal balance could take a similar path to that of Argentina. The process of domestic industrialization through natural gas does not seem far-fetched either, as long as it is based on market rules and not at the expense of public finances. The country has already achieved self-sufficiency in fertilizers and is already a growing exporter, an example of the economic diversification pursued by the Morales government.
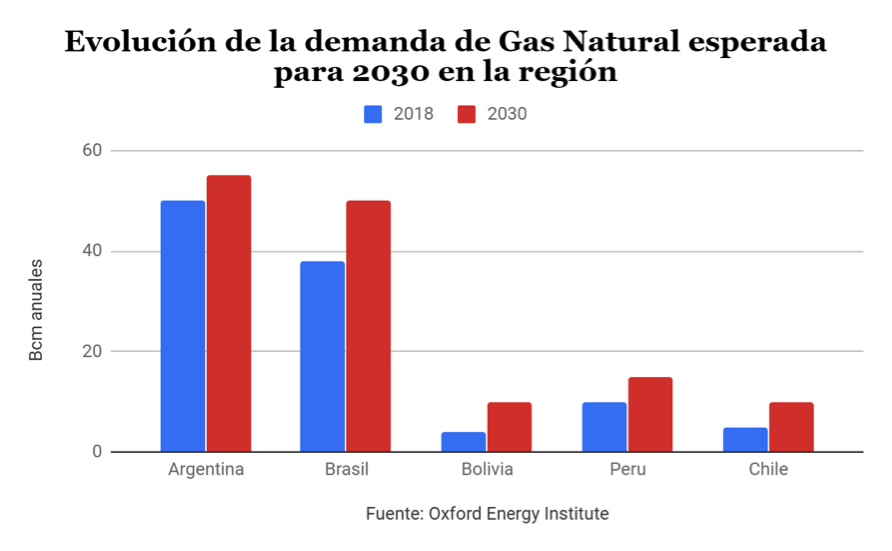
The question: Is there a market for everyone?
After reviewing the regional context, it may appear that the natural gas market in South America will be saturated by future oversupply. As can be seen in the graph, natural gas demand in the Bolivian neighborhood will increase from 107 bcm to 140 bcm per year by 2030. Peru, Argentina and Brazil are likely to increase their production and may reach self-sufficiency during the 2020s. This complicates the commercialization of Bolivian gas, but does not make it impossible. In the first place, the geographical reality of South America makes certain cross-border projects more economical than other internal ones, as in the case of southern Peru. Likewise, the increasingly lower costs of exporting gas by sea make it possible to find a market for surplus regional production, as in the case of Peru, which concentrates its gas exports to Spain. In a context of increasing energy interconnection, Bolivia will be able to continue exporting natural gas, albeit from a less privileged position and having to invest in export infrastructure. The major challenges are focused on increasing exploration activities by attracting more foreign and private investment, as well as the search for new markets, with the Chilean issue being a central element in this discussion.
[2] http://www.realinstitutoelcano.org/wps/portal/rielcano_en/content?WCM_GLOBAL_CONTEXT=/elcano/elcano_en/zones_en/ARI%20130-2006
[5] https://www.efe.com/efe/english/business/bolivia-to-spend-450-mn-in-2019-exploring-for-natural-gas/50000265-3881056
[6] https://www.ypfb.gob.bo/es/14-noticias/332-planta-de-amoniaco-y-urea-registra-avance-del-64.html
[7] https://www.petroleum-economist.com/articles/midstream-downstream/pipelines/2018/weighing-bolivias-gas-export-options
[9] https://www.petroleum-economist.com/articles/politics-economics/south-central-america/2017/bolivia-another-strike-from-the-resources-curse
[11] http://ieefa.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Financial-Risks-Cloud-Development-of-Vaca-Muerta_March-2019.pdf
[13] https://www.reuters.com/article/us-argentina-energy-gas/argentina-renegotiates-key-gas-supply-contract-with-bolivia-idUSKCN1Q402O
The constant expansion of soy production within the MERCOSUR countries exceeds 50% of total world production
While many typically associate South American commodities with hydrocarbons and minerals, soy or soybean is the other great commodity of the region. Today, soy is the agricultural product with the highest commercial growth rate in the world. China and India lead world consumption of this oleaginous plant and its byproducts, thus making South America a strategic supplier. Soy profitability has encouraged the expansion of crop production, especially in Brazil and Argentina, as well as in Paraguay, Bolivia and Uruguay. However, such expansion comes at an environmental cost; such as recent deforestation in the Amazon and the Gran Chaco.

ARTICLE / Daniel Andrés Llonch [English version] [Spanish version].
Soy has been cultivated in Asian civilizations for thousands of years; today its cultivation is also widespread in other parts of the world. It has become the most important oilseed for human consumption and animal feed. Of great nutritional properties, due to its high protein content, soybeans are sold both in grain and in their oil and flour derivatives.
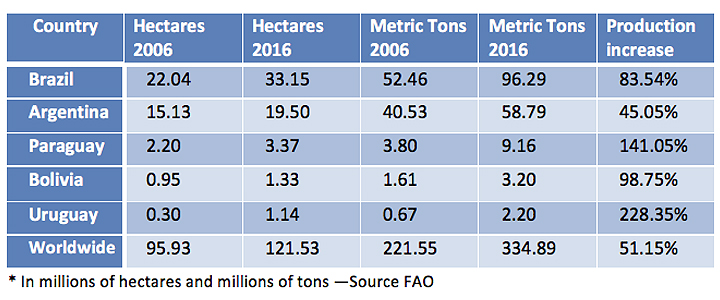
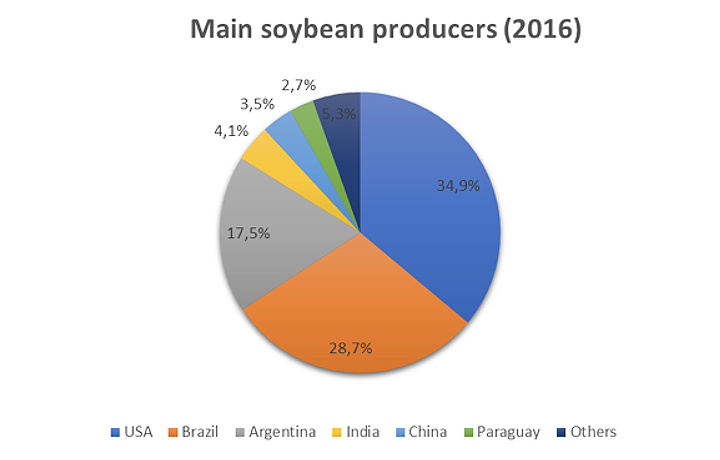
Among the eleven largest soybean producers, five are in South America: Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, Bolivia and Uruguay. In 2016, these countries were the origin of 50.6% of world production, whose total reached 334.8 million tons, according to FAO data. The first producer was the United States (34.9% of world production), followed by Brazil (28.7%) and Argentina (17.5%). India and China follow the list, although what is significant about this last country is its large consumption, which in 2016 forced it to import 83.2 million tons. Much of these import needs are covered from South America. Furthermore, the South American production focuses on the Mercosur nations (in addition to Brazil and Argentina, also Paraguay and Uruguay) and Bolivia.
The strong international demand and the high relative profitability of soybean in recent years has fueled the expansion of the cultivation of this plant in the Mercosur region. The price boom for raw materials, which also involved soy, led to benefits that were directed to the acquisition of new land and equipment, which allowed producers to increase their scale and efficiency.
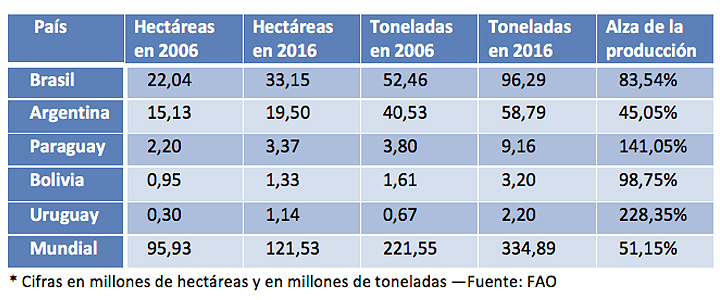
In Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay the area planted with soybeans represents the majority (it constitutes more than 50% of the total area sown with the five most important crops in each country). If we add Uruguay, where soybean has enjoyed a later expansion, we have that the production of these five South American countries has gone from 99 million tons in 2006 to 169.7 million in 2016, which constitutes a rise of 71%. In addition, the production of Brazil and Bolivia has almost doubled their production, somewhat exceeded by Paraguay and Uruguay, where it has tripled. In the decade, this South American area has gone from contributing 44.7% of world production to 50.6%. At that time, the cultivated area increased from 40.6 million hectares to 58.4 million.
 |
Countries
As the second largest producer of soybeans in the world, Brazil reached 96.2 million tons in 2016 (28.7% of the world total), with a cultivation area of 33.1 million hectares. Its production has been in a constant increasement, so that in the last decade the volume of the harvest has increased by 83.5%. The jump has been especially B in the last four years, in which Brazil and Argentina have experienced the highest growth rate of the crop, with an annual average of 936,000 and 878,000 hectares, respectively, according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Argentina is the second largest producer of Mercosur, with 58.7 million tons (17.5% of world production) and a cultivated area of 19.5 million hectares. Soybeans began to be planted in Argentina in the mid-70s, and in less than 40 years it has had an unprecedented advance. This crop occupies 63% of the areas of the country planted with the five most important crops, compared to 28% of the area occupied by corn and wheat.
Paraguay, for its part, had a harvest of 9.1 million tons of soybeans in 2016 (2.7% of world production). In recent seasons, soy production has increased as more land is allocated for cultivation. According to the USDA, in the last two decades, the land dedicated to the cultivation of soybeans has constantly increased by 6% annually. Paraguay currently has 3.3 million hectares of land dedicated to this activity, which constitutes 66% of the land used for the main crops.
As far as Bolivia is concerned, soybeans are grown mainly in the Santa Cruz region. According to the USDA, it represents 3% of the country's Gross Domestic Product, and employs 45,000 workers directly. In 2016, the country harvested 3.2 million tons (0.9% of world production), in an area of 1.3 million hectares.
Soybean plantations occupy more than 60 percent of Uruguay's arable land, where soybean production has been increasing in recent years. In fact, it is the country where production has grown the most in relative terms in the last decade (67.7%), reaching 2.2 million tons in 2016 and a cultivated area of 1.1 million hectares.
 |
Increase of the demand
The production of soy represents a very important fraction in the agricultural GDP of the South American nations. The five countries mentioned together with the United States make up 85.6% of global production, so they are the main suppliers of the growing global demand.
This production has experienced a progressive increase since its insertion in the market, with the exception of Uruguay, whose product expansion has been more recent. In the period between 1980 and 2005, for example, the total world demand for soybean expanded by 174.3 million tons, or what is the same, 2.8 times. In this period, the growth rate of global demand accelerated, from 3% annually in the 1980s to 5.6% annually in the last decade.
In all the South American countries mentioned, the cultivation of soy has been especially encouraged, because of the benefits that it entails. Thus, in Brazil, the largest regional producer of oilseed, soybean provides an estimated income of 10,000 million dollars in exports, representing 14% of the total products marketed by the country. In Argentina, soybean cultivation went from representing 10.6% of agricultural production in 1980/81 to more than 50% in 2012/2013, generating significant economic benefits.
The outlook for growth in demand suggests a continuation of the increase in production. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization estimates that global production will exceed 500 million tons in 2050, which doubles the volume harvested in 2010 and clearly, much of that demand will have to be met from South America.
The constant expansion of the crop in Mercosur countries has led them to exceed 50% of world production.
Soybean is the agricultural product with the highest commercial growth in the world. The needs of China and India, major consumers of the fruit of this oleaginous plant and its derivatives, make South America a strategic granary. Its profitability has encouraged the extension of the crop, especially in Brazil and Argentina, but also in Paraguay, Bolivia and Uruguay. Its expansion is behind recent deforestation in the Amazon and the Gran Chaco. After hydrocarbons and minerals, soybeans are the other major commodity in South America subject .

article / Daniel Andrés Llonch [English version].
Soybean has been cultivated in Asian civilizations for thousands of years; today its cultivation is also widespread in other parts of the world. It has become the most important oilseed grain for human consumption and animal feed. With great nutritional properties due to its high protein content, soybeans are marketed both in grain and in their oil and meal derivatives.
Of the eleven largest soybean producers, five are in South America: Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, Bolivia and Uruguay. In 2016, these countries were the origin of 50.6% of world production, whose total reached 334.8 million tons, according to FAO's data . The first producer was the United States (34.9% of world production), followed by Brazil (28.7%) and Argentina (17.5%). India and China follow on the list, although what is significant about the latter country is its large consumption, which in 2016 forced it to import 83.2 million tons. A large part of these import needs are covered from South America. South American production is centered in the Mercosur nations (in addition to Brazil and Argentina, also Paraguay and Uruguay) and Bolivia.
Strong international demand and the high relative profitability of soybeans in recent years have fueled the expansion of soybean cultivation in the Mercosur region. The commodity price boom, in which soybeans also participated, led to profits that were directed to the acquisition of new land and equipment, allowing producers to increase their scale and efficiency.
In Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay, the area planted with soybean is the majority (it constitutes more than 50% of the total area planted with the five most important crops in each country). If to group we add Uruguay, where soybean has enjoyed a later expansion, we have that the production of these five South American countries has gone from 99 million tons in 2006 to 169.7 million in 2016, which is an increase of 71.2% (Brazil and Bolivia have almost doubled their production, somewhat surpassed by Paraguay and Uruguay, a country where it has tripled). In the decade, this South American area has gone from contributing 44.7% of world production to total 50.6%. In that time, the cultivated area increased from 40.6 million hectares to 58.4 million hectares.
 |
Countries
As the second largest soybean producer in the world, Brazil reached in 2016 a production of 96.2 million tons (28.7% of the world total), with a crop area of 33.1 million hectares. Its production has known a constant increase, so that in the last decade the volume of the crop has increased by 83.5%. The jump has been especially B in the last four years, in which Brazil and Argentina have experienced the highest rate of increase of the crop, with an annual average of 936,000 and 878,000 hectares, respectively, from agreement with the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) department .
Argentina is the second largest producer in Mercosur, with 58.7 million tons (17.5% of world production) and a cultivated area of 19.5 million hectares. Soybean began to be planted in Argentina in the mid 1970s, and in less than 40 years it has made unprecedented progress. This crop occupies 63% of the country's areas planted with the five most important crops, compared to 28% of the area occupied by corn and wheat.
Paraguay, meanwhile, had a 2016 harvest of 9.1 million tons of soybeans (2.7% of world production). In recent seasons, soybean production has increased as more land is allocated for its cultivation. From agreement with the USDA, over the last two decades, land devoted to soybean cultivation has steadily increased by 6% annually. There are currently 3.3 million hectares of land in Paraguay dedicated to this activity, which constitutes 66% of the land used for the main crops.
In Bolivia, soybeans are grown mainly in the Santa Cruz region. According to the USDA, it accounts for 3% of the country's Gross Domestic Product, and employs 45,000 workers directly. In 2016, the country harvested 3.2 million tons (0.9% of world production), on an area of 1.3 million hectares.
Soybean plantations occupy more than 60 percent of the arable land in Uruguay, where soybean production has been increasing in recent years. In fact, it is the country where production has grown the most in relative terms in the last decade (67.7%), reaching 2.2 million tons in 2016 and a cultivated extension of 1.1 million hectares.
 |
Increased demand
Soybean production represents a very important fraction of the agricultural GDP of South American nations. The five countries mentioned above, together with the United States, account for 85.6% of global production, making them the main suppliers of the growing world demand.
This production has experienced a progressive increase since its insertion in the market, with the exception of Uruguay, whose expansion of the product has been more recent. In the period between 1980 and 2005, for example, total world soybean demand expanded by 174.3 million tons, or 2.8 times. During this period, the growth rate of global demand accelerated from 3% per year in the 1980s to 5.6% per year in the last decade.
In all the South American countries mentioned above, soybean cultivation has been especially encouraged, due to the benefits it brings. Thus, in Brazil, the largest regional producer of the oleaginous grain, soybeans contribute revenues estimated at 10 billion dollars in exports, representing 14% of the total products marketed by the country. In Argentina, soybean cultivation went from representing 10.6% of agricultural production in 1980/81 to more than 50% in 2012/2013, generating significant economic benefits.
The outlook for growth in demand suggests that production will continue to rise. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations estimates that global production will exceed 500 million tons in 2050, double the volume harvested in 2010. Much of this demand will have to be met from South America.
