Ruta de navegación
Blogs
Entries with label nafta .
The changes, although significant in some cases, will not substantially alter trade flows between the three countries.
The new Free Trade Agreement between the United States, Canada and Mexico is now ready for implementation, following ratification by the congresses of the three countries. The revision of the previous treaty, which came into force in 1994, was called for by Donald Trump on his arrival at the White House, citing the trade deficit generated for the US in relation to Canada and especially Mexico. Although some significant corrections have been introduced, following the main American approaches, it does not seem that the revised agreement will substantially modify trade flows between the three countries.
![Presidents Peña Nieto, Trump and Trudeau sign the agreement free trade agreement in November 2019 [US Gov.] Presidents Peña Nieto, Trump and Trudeau sign the agreement free trade agreement in November 2019 [US Gov.]](/documents/10174/16849987/tmec-blog-pyn6UhDC.jpg)
▲ Presidents Peña Nieto, Trump and Trudeau sign the free trade agreement in November 2019 [US Gov.]
article / Marcelina Kropiwnicka
On 1 January 1994, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) entered into force. More than twenty years later and under the administration of President Donald Trump, the three partner countries opened a review process of agreement, now called the Free Trade Agreement between the United States, Canada and Mexico (to which each country has given a different acronym: the Mexicans call it T-MEC or TMEC, the Americans USMCA and the Canadians CUSMA).
The text of the TMEC finally ratified by the three countries is broadly consistent with the old NAFTA. However, there are particular distinctions. Thus, it includes stricter rules of origin in the automotive and textile sectors, an updated labour value content requirement in the automotive sector, increased US access to Canadian supply-managed markets, novel provisions related to financial services, and a specification on the establishment of free trade agreements with non-market economies. The joint goal is to encourage production in North America.
New developments negotiated in 2017-2018
The three parties began negotiations in the summer of 2017 and after just over a year they concluded a agreement, signed by the presidents of the three countries in November 2018. The main novelties introduced until then were the following:
1) The agreement revises the regional value content (RVC) percentage for the automotive industry. Under NAFTA, at least 62.5% of an automobile had to be made from North American parts. The TMEC raises the percentage to 75% with the intention of strengthening the countries' manufacturing capacity and increasing the strength of work in the automotive industry.
2) Along the same lines, to support employment in North America, the agreement contains new trade rules of origin to boost higher wages by mandating that 40-45% of auto manufacturing be done by workers earning at least $16 per hour on average by 2023; that's roughly three times the pay a Mexican worker normally receives today.
3) Apart from the automotive industry, the dairy market will be opened to ensure greater access for US dairy products , a demand core topic for Washington. Currently, Canada has a system of domestic quotas that were put in place to protect its farmers from foreign skill ; however, under the new TMEC agreement , changes will allow the US to export up to 3.6% of Canada's dairymarket ,an increase of 2.6% from the original NAFTA provision. Another achievement core topic for Trump was the negotiation of Canada's elimination of what are known as itsmilk classes 6 and 7.
4) Another new aspect is the sunset clause. NAFTA had an automatic sunset clause or a pre-determined end date for the agreement, which meant that any of the three parties could withdraw from the agreement, after a six-month notice of withdrawal notice ; if this did not occur, the agreement remained indefinite. However, the TMEC foresees a duration of 16 years, with the option to meet, negotiate and revise the document after six years, as well as the possibility to renew the agreement after 16 years.
5) The three-country pact also includes a chapter on work that anchors labour obligations at the core of agreement , making enforcement more demanding.
Reforms in Mexico
Precisely to make that last point more credible, US and Canadian negotiators demanded that Mexico make changes to its labour laws to speed up the process of approval and ratification of the TMEC by lawmakers in Washington and Ottawa. US House leaders had doubted Mexico's ability to comply specifically with the labour rights points of agreement. One of President Trump's main objectives in the renegotiation was to reassure US workers that the status of skill would be overcome.
Mexican President Andrés Manuel López Obrador sent a letter to the US congress guaranteeing the implementation of a four-year plan to ensure the achievement of adequate labour rights. López Obrador committed to an outlay of $900 million over the next four years to change the labour justice system and ensure that disputes between workers and employers are resolved in a timely manner. Mexico has also invested in the construction of a Federal Centre for Labour Conciliation and Registration, where labour disputes will be addressed prior to a court hearing.
Obrador showed his commitment to labour reforms by ensuring at least a 2% increase in theminimum wage in Mexico. Most importantly B is that the requirement for direct voting of union leaders will change the way workers' organisations function. With direct elections, decisions on collective agreements will be more transparent. Mexico's plan to improve the working environment will start in 2020.
What's new in 2019 to facilitate ratification
Faced with demands on the US congress , especially from the Democratic majority, to ratify the treaty, negotiators proceeded with two major revisions to NAFTA. One of them aimed primarily at revising a large number of provisions relating to intellectual property, pharmaceuticals and the digital economy:
6) The intellectual property rights chapter seeks to address US concerns to spur innovation, generate economic growth and support jobs work. For the first time, according to the US Trade Representative, the additions include: strict rules against circumvention of technological protection measures for music, movies and digital books; strong protections for pharmaceutical and agricultural innovation; broad protections against theft of trade secrets; and authority for officials to stop suspected counterfeit or pirated goods from official document .
7) A new chapter on digital trade has also been included that contains stricter controls than any other international agreement , strengthening the foundation for the expansion of trade and investment in areas where the US has a competitive advantage.
8) The final draft removes a 10-year guarantee of intellectual property protection for biological medicines, which are some of the most expensive medicines on the market. It also removes granting an additional three years of IP exclusivity for medicines for which a new use is found.
A second group of last minute changes makes reference letter for greater environmental and labour protections:
9) Environment covers 30 pages, outlining obligations to combat trafficking in wildlife, timber and fish; strengthen law enforcement to stop such trafficking; and address critical environmental issues such as air quality and marine litter. New obligations include: protection of various marine species, implementation of appropriate methods for environmental impact assessments, and alignment with obligations under seven multilateral environmental agreements. In particular, Mexico is agreement to improve surveillance to stop illegal fishing, and the three countries agree to stop subsidize fishing for overfished species. To increase environmental accountability, Democrats in the US House of Representatives called for the creation of an inter-agency oversight committee. However, the treaty does not address climate change issues.
10) To ensure that Mexico delivers on its labour promises, House Democrats forced the creation of an interagency committee to monitor the implementation of Mexico's labour reform and compliance with labour obligations. Despite the new and unique 'LVC' requirement, a labour value content rule, it will still be difficult to impose a minimum wage on Mexican automakers. However, US Democrats hope that the condition will force automakers to buy more supplies from Canada or the US, or cause automakers' wages in Mexico to rise.
The finally ratified agreement will replace the one that has been in force for 25 years. Overall, the move from NAFTA to the TMEC should not have a drastic effect on the three countries. It is a progressive agreement that will entail slight changes: certain industries will be affected, such as the automotive and dairy industries, but only to a small extent. In the long run deadline, given the changes introduced, wages should increase in Mexico, which would reduce Mexican migration to the US. Businesses will be affected in the long run deadline, but with back-up plans and new redesigns, the transition process will hopefully be smooth and mutually beneficial.
▲Enrique Peña Nieto and Donald Trump at the July 2017 G20 summit in Hamburg [Presidency of Mexico].
ANALYSIS / Dania Del Carmen Hernández [English version].
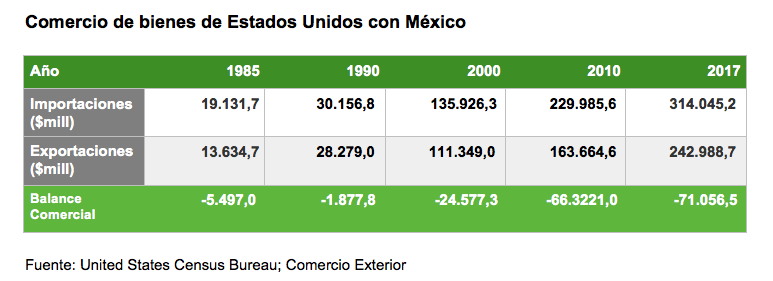
Canada, the United States and Mexico are immersed in the renegotiation of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). The trade agreement between these three countries has been somewhat controversial in recent years, especially in the US, where its advisability has been questioned. During the presidential campaign, Donald Trump defended the cancellation of the treaty; later, already in the White House, he accepted that there would be a renegotiation. Trump argued that the pact has reduced US manufacturing jobs and generated a trade deficit of more than $60 billion with Mexico ($18 billion with Canada), so unless new conditions substantially reduced that deficit, the US would withdraw from agreement.
Overall, Americans have positive views of the treaty, with 56% of the population saying NAFTA is beneficial to the country, and 33% saying it is detrimental, from agreement with a November 2017 Pew Researchsurvey . Among those who hold a negative view, the majority are Republicans, with 53% saying Mexico benefits the most, while Democrats overwhelmingly support the pact and only 16% view it negatively.
 |
Regardless of public acceptance, opinion about the treaty has not always been so dubious. When President Bill Clinton ratified the treaty, it was considered one of the greatest achievements of his presidency. Just as globalization has liberalized trade around the world, NAFTA has also expanded trade very effectively and presented a great issue of opportunities for the U.S., while strengthening the U.S. Economics .
Under NAFTA, trade in U.S. goods and services with Canada and Mexico grew from $337 billion in 1994, when the treaty entered into force, to $1.4 trillion in 2016. The impact has been even greater when taking into account cross-border investments between the three countries, which went from $126.8 billion in 1993 to $731.3 billion in 2016.
Washington's concern is that, despite this increase in trade volume, in relative terms the United States is not achieving sufficiently fruitful results compared to what its neighbors are getting from the treaty. In any case, Canada and Mexico accept that, after almost 25 years in force, the treaty must be revised to adapt it to the new productive and commercial conditions, marked by technological innovations that, as is the case of the Internet development , were not contemplated when the agreement was signed.
Round-by-round examination
The discussion of the three countries touches on numerous aspects, but three blocks can be mentioned, which have to do with certain red lines set by the different parties to the negotiation: the rules of origin; the desire of the United States to end the independent arbitration system, through which Canada and Mexico have the ability to end measures that violate the trade agreement (elimination of Chapter 19), and finally proposals, perhaps less decisive but equally important, aimed at the general update of the treaty.
When negotiations began in August 2017, it was expressed that they could be concluded by January 2018, with six rounds of meetings planned. This issue is already being exceeded, with a seventh round at the end of February, possibly to be followed by others. Now that the initial deadline has been reached, however, it is time to review the status of the discussions. A good way to do this is to follow the evolution of the talks through the rounds of meetings held and thus be able to assess the results that have been recorded so far.
|
Last North American Summit, with Peña Nieto, Trudeau and Obama, held in Canada in June 2016 [Presidency of Mexico]. |
1st Round (Washington, August 16-20, 2017)
The first round of negotiations put on the table the priorities of each of the three countries; it served to set the diary of the main issues to be discussed in the future, without yet addressing concrete measures.
agreement First of all, Donald Trump already made it clear during his election campaign that he considered NAFTA to be unfair to the United States due to the trade deficit that the United States has mainly with Mexico and, to a lesser extent, with Canada.
According to figures from the Office of the US Trade Representative, the US went from a surplus of $1.3 billion in 1994 to a deficit of $64 billion in 2016. Most of this deficit comes from the automotive industry. For the new U.S. Administration, this calls into question whether the agreement will have beneficial effects for the domestic Economics . Mexico, less inclined to introduce major changes, insists that NAFTA has been good for all parties.
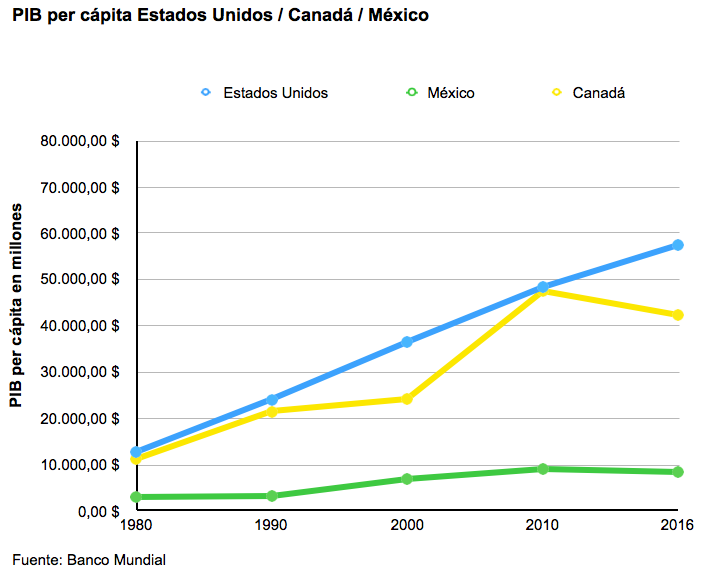
Another topic was the wage gap between Mexico and the United States and Canada. Mexico argues that, despite having one of the lowest minimum wages in Latin America, and having had a stagnant average wage for the last two decades, this should not be taken into account in the negotiations, as it believes that Mexican wages will gradually catch up with those of its trading partners. On the contrary, for the US and Canada it is a topic of concern; both countries warn that a wage increase would not harm the growth of the Mexican Economics .
Rules of origin was one of the main topics of discussion. The United States is seeking to increase the percentage of content required to consider a product as originating so that it is not necessary to pay tariffs when moving it between any of the three countries. This was controversial in this first round, as it could negatively affect Mexican and Canadian companies. Specialists warn that the minimum national content requirement does not exist in any free trade agreement in the world.
Finally, the Trump administration hinted at its intentions to eliminate Chapter 19, which guarantees equality in resolving disputes between countries, so that it is not the national laws of each country that resolve the conflict. The United States sees this as a threat to its sovereignty and believes that conflicts should be resolved in such a way that its own democratic processes are not ignored. Canada has conditioned its continued membership in the treaty on the maintenance of this chapter. Mexico also defends guarantees of independence in conflict resolution, although so far in this discussion it was not categorical.
 |
2nd Round (Mexico City, September 1-5, 2017)
Although considered successful by many analysts, the second round of renegotiation continued at a slow pace. Some of the issues that advanced were: wages, market access, investment, rules of origin, trade facilitation, environment, digital trade, SMEs, transparency, anti-corruption, agriculture and textiles.
The president of committee coordinator Mexican Businessmen, Juan Pablo Castañón, insisted that for the moment the wage issue was not subject to negotiation, and denied that any of the parties had any intention of leaving the treaty, despite threats to that effect from the Trump Administration. Castañón said he was in favor of Mexico supporting the maintenance of Chapter 19 or the establishment of a similar instrument for the settlement of trade disputes between the three countries.
Round 3 (Ottawa, September 23-27, 2017)
The delegates made important advances in policies on skill, digital commerce, state-owned enterprises and telecommunications. The main progress was on some aspects related to SMEs.
Canadian Foreign Minister Chrystia Freeland complained that the United States had not made any formal or written proposals in the most complex areas, which in her opinion demonstrates a passive attitude on the part of that country in the context of the negotiations.
U.S. Trade Secretary Robert Lighthizer said that his country is interested in increasing wages in Mexico, under the logic that this is unfair skill , as Mexico has attracted factories and investment with its low wages and weak union rules. However, Mexican business and union leaders are resisting such pressures.
Canada stood firm on its position on Chapter 19, which it considers one of the great achievements of the current agreement. "Our government is absolutely committed to defending it," Freeland said. Washington raised, although without presenting a formal proposal , the modification of the rules of origin to make them stricter and prevent imports from other nations from being considered "made in North America", just because they were assembled in Mexico.
This round took place as the United States slapped a tariff of nearly 220% on C Series aircraft made by Canadian aircraft manufacturer Bombardier, which it considered that business had used a government subsidy to sell its aircraft to the U.S. at artificially low prices.
Round 4 (Virginia, October 11-17, 2017)
The United States presented its formal proposal to raise the rules of origin for the automotive industry and its suggestion to introduce a sunset clause to agreement.
The United States proposed raising from 62.5% to 85% the percentage of components of national origin from one of the three countries in order for the automotive industry to benefit from NAFTA, and that 50% be of U.S. production. association The Mexican Automotive Industry Association (AMIA) rejected proposal.
Washington's interest in weakening the dispute settlement system within the treaty (Chapter 19) was also debated, without a rapprochement of positions.
Finally, there was talk of including a sunset clause, which would cause the treaty to cease to exist after five years, unless the three countries decide to renew it. This proposal was widely criticized, warning that this would go against the essence of agreement and that every five years it would generate uncertainty in the region, as it would affect the investment plans of companies.
These proposals add to the tough negotiating climate, as already in the third round the United States had begun to defend difficult proposals, on issues such as lawsuits for dumping (selling a product below its normal price) in the importation of perishable Mexican products (tomatoes and berries), government purchases and the purchase of textiles.
 |
Round 5 (Mexico City, November 17-21, 2017)
The fifth round took place without much progress. The U.S. maintained its demands and this generated great frustration among the representatives of Mexico and Canada.
The United States received no alternatives to its proposal of wanting to increase the regional composition from 62.5% to 85%, with at least 50% being U.S.-based. On the contrary, its trading partners put on the table data showing the damage that this proposal would cause to the three economies.
Faced with the U.S. desire to limit the issue of concessions that its federal government offers to Mexican and Canadian companies, Mexican negotiators responded with a proposal to limit the country's public contracts to issue of contracts reached by Mexican companies with other governments under NAFTA. Given that the issue of these contracts is quite small, U.S. companies would be restricted in their contracting.
At the end of this fifth round, the most advanced issues are the regulatory improvement of telecommunications and the chapter on sanitary and phytosanitary measures. With the latter, the Americans seek to establish new transparent and non-discriminatory rules, allowing each country to establish the Degree protection it deems appropriate.
Round 6 (Montreal; January 23-29, 2018)
The sixth negotiation showed some progress. The chapter on corruption was finally closed, and there was progress in other areas. Some of the important issues that had been left aside in the previous negotiations were discussed. Progress is slow, but seems to be making headway.
Robert Lightizer rejected the compromise on rules of origin that Canada had previously proposed. The framework was based on the idea that rules of origin should be calculated to include the value of software, engineering and other high-value work, facets that today are not taken into account with a view to goal regional content.
As a form of pressure, Canada threatened to reserve the right to treat its neighboring countries worse than other countries if they enter into agreements. One of them could be China. The proposal was not considered, as the United States and Mexico found it unacceptable.
Beyond the deadline
After more than seven months of meetings, as reflected in this round-by-round review of the talks, the negotiations between the three countries have still not reached the threshold of a pre-agreement that, while awaiting the resolution of more or less important points, would confirm the shared will to continue NAFTA. The hard stances of the United States and the pressure from Canada and Mexico to save the treaty have so far resulted in a "tug of war" that has allowed some partial, but not decisive result . Thus, it is yet to be determined whether the treaty has actually reached its expiration date or whether it can be reissued. For the time being, the three countries are at agreement working towards a renewed treaty.
From what has been seen so far in the negotiations, it is difficult to determine which country will be more willing to yield to the pressure exerted by the others. The most controversial issues have hardly been addressed until recently, so it is not possible to say what each country has achieved in this negotiation process.
The two neighbors of the United States, but especially Canada, continue to warn of the risk of Trump wanting to kill the treaty. An acceleration of the negotiations could help the positive resolution of the process, but the electoral calendar rather threatens postponements. On March 30, campaigning begins for Mexico's presidential election, which will take place on July 1. In September, the U.S. will begin to look more closely at the November congressional elections. A substantial breakthrough before the Mexican presidential elections could put agreement back on track, even if some issues remain to be closed, but if no breakthrough is made in the next meetings, the three countries could be getting used to the idea of the end of NAFTA, which would weigh down the negotiations.

