Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
After four years of board The upcoming elections open up the possibility of a return to a legitimacy too interrupted by coups d'état
Thailand has seen several coups d'état and attempts to return to democracy in its most recent history. The board The military that seized power in 2014 has called elections for March 24. The unsuccessful desire of the king's sister Maha Vajiralongkorn to run for prime minister has drawn global attention to a political system that fails to meet the political aspirations of Thais.
![Bangkok Street Scene [Pixabay] Bangkok Street Scene [Pixabay]](/documents/10174/16849987/tailandia-elecciones-blog.jpg)
▲ Bangkok Street Scene [Pixabay]
article / María Martín Andrade
Thailand is one of the fastest developing ASEAN countries in economic terms. However, these advances come up against a difficult obstacle: the political instability that the country has been dragging since the beginning of the 20th century and that opens a new chapter now, in 2019, with the elections that will take place on March 24. These elections mark a turning point in recent Thai politics, after General Prayut Chan-Ocha staged a coup d'état in 2014 and became Prime Minister of Thailand at the head of the NCPO (committee National Institute for Peace and Order), the board of government formed to run the country.
However, there are many who are sceptical about this new development. entrance of democracy. To begin with, the elections were initially set for 24 February, but shortly afterwards the government announced a change of date and called them for a month later. Some have expressed suspicions about a strategy to prevent the elections from taking place, since, according to the law, they cannot be held once one hundred and fifty days have elapsed since the publication of the last ten organic laws. Others fear that the NCPO has given itself more time to buy votes, while also raising concerns that the Electoral Commission, which is an independent administration, could be manipulated into a success that would in turn be a success. board It's going to be hard for you to insure.
Focusing this analysis on what the future holds for Thai politics, it is necessary to go back to its trajectory in the last century to realize that it follows a circular path.
Coups d'état are not new in the country (1). There have been twelve since the first constitution was signed in 1932. It all responds to an endless struggle between the "military wing", which sees constitutionalism as a Western import that does not quite fit in with the Structures Thai (it also defends nationalism and venerates the image of the king as a symbol of the nation, Buddhist religion and ceremonial life), and the "leftist orbit", originally composed of Chinese and Vietnamese emigrants, which perceives the country's institutionality as similar to that of "pre-revolutionary China" and which throughout the twentieth century expressed itself through guerrillas. To this last ideology must be added the student movement, which since the early 1960s has criticized "Americanization," poverty, the traditional order of society, and the military regime.
With the urban boom that began in the 1970s, the gross domestic product increased fivefold and the industrial sector became the fastest growing, thanks to the production of technological goods and the investments that Japanese companies began to make in the country. During this period, there were coups d'état, such as the one in 1976, and numerous student demonstrations and guerrilla actions. After the 1991 coup and new elections, a new discussion on how to create an efficient political system and a society adapted to globalization.
These efforts were cut short when the economic crisis of 1997 hit, which generated divisions and aroused rejection of globalization, considering it the evil force that had led the country to misery. It is at this point that someone who has since been core topic in Thai politics and who will undoubtedly mark the March elections: Thaksin Shinawatra.
Shinawatra, a prominent businessman, created the Thai Rak Thai (Thai loves Thai) party as a nationalist reaction to the crisis. In 2001 he won the elections and bet on economic growth and the creation of large companies, but at the same time he exercised intense control over the media, attacking those who dared to criticize him and allowing only the publication of positive news. In 2006, there was a coup d'état to overthrow Shinawatra, who was accused of serious corruption offences. However, Shinawatra won the election again in 2007, this time with the People Power Party.
In 2008 there was a new uprising, but the Shinawatra brand, represented by the sister of the former prime minister, won the elections in 2011, this time with the Pheu Thai party. Yingluck Shinawatra thus became the first woman to head the Government of Thailand. In 2014, another coup pushed her aside and set up a board who has ruled until now, with a speech based on the fight against corruption, the protection of the monarchy, and the rejection of electoral politics, considered as the national epidemic.
In this context, all the efforts of the board, running in March under the party name Palang Pracharat, has focused on weakening Pheu Thai and thus wiping out any remaining trace of Shinawatra from the map. To achieve this, the board it has proceeded to reform the electoral system (in 2016 a new constitution replaced the 1997 one), so that the Senate is no longer elected by the citizens.
Despite all the efforts made in vote-buying, the possible manipulation of the Electoral Commission and the reform of the electoral system, it is intuited that Thai society can make its voice heard in the weariness of the military government, which is also losing support in Bangkok and in the south. Added to this is the collective conviction that, rather than pursuing economic growth, the board has focused on achieving stability by doing the more unequal the Economics of Thailand, according to data of Credit Suisse. For this reason, the rest of the parties running in these elections, Prachorath, Pheu Thai, and Bhumjaithai, agree that Thailand has to rejoin the skill and that the capitalist market has to grow.
At the beginning of February, the context became even more complicated, when Princess Ulboratana, the sister of the current king, Maha Vajiralongkorn, announced the presentation of his candidacy in the elections as a representative of the Thai Raksa Chart party, an ally of Thaksin Shinawatra. This news was a great anomaly, not only because a member of the monarchy showed his intention to participate actively in politics, something that had not happened since the end of the absolute monarchy in 1932, but also because all the coups d'état that have taken place in the country have had the support of the royal family. The last one, in 2014, had the blessing of the then King Bhumibol. Likewise The Royal Family has always had the support of the board military.
In order to avoid a confrontation that would damage the monarchy, the king reacted quickly and publicly showed his rejection of his sister's candidacy; finally, the Electoral Commission decided to withdraw it from the election process.
Poor governance
Over the last few years, the board military has been manager poor governance, the country's weak institutions, and a Economics threatened by international sanctions that seek to punish the lack of internal democracy.
To begin with, following the article 44 of the Constitution proclaimed in 2016, the NCPO has the legitimacy to intervene in the legislative, judicial and executive branches under the pretext of protecting Thailand from threats to public order, the monarchy or the judiciary. Economics. Not only does this preclude any possibility of interaction and effective conflict resolution with other actors, but it is an unmistakable feature of an authoritarian system.
It has been precisely its characteristics as an authoritarian regime, which is how its governmental system can be described, that have made the international community react since the 2014 coup, imposing various sanctions that may seriously affect Thailand. The U.S. suspended $4.7 million from attendance while Europe has objected to the negotiation of a agreement as Pirkka Tappiola, the EU's representative to Thailand, has pointed out, it will only be possible to establish a agreement of that subject with a democratically elected government. In addition, Japan, the main investor in the country, has begun to look for alternative routes, setting up factories in other parts of the region such as Myanmar or Laos.
Faced with the questioning of his managementthe board It reacted by devoting $2.7 billion to programs aimed at the poorest sections of the population, especially peasants, and investing nearly $30 billion in building infrastructure in unexploited areas.
Given that Thailand's exports account for 70 per cent of its GDP, the Government cannot afford to have the international community at loggerheads. That explains why the board create a committee to deal with human rights problems that have been reported from abroad, although the goal of the initiative seems to have been rather public.
In the face of a new democratic stage, the board He has a strategy. Having put most of its efforts into the creation of new infrastructure, it hopes to open an economic corridor, the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC), with which to convert the three main coastal provinces (Chonburi, Rayong, and Chachoengsao) into special economic zones where industries such as automobiles or aviation are enhanced, and which will be attractive to foreign investment once democratic legitimacy is cleared.
It is difficult to predict what will happen in Thailand in the March 24 elections. Although almost everything speaks of a new return to democracy, it remains to be seen what will happen. result of the party created by the military (Pralang Pracharat) and its steadfastness in its commitment to a really honest institutional game. If Thailand wants to continue to grow economically and attract foreign investors again, the military should soon give way to a completely civilian process. Possibly it will not be a smooth road, since democracy is a dress that until now has been somewhat tight for the country.
(1) Baker, C., Phongpaichit, P. (2005). A History of Thailand. Cambridge, Univeristy Press, New York.

▲ Protest in London in October 2018 after the disappearance of Jamal Khashoggi [John Lubbock, Wikimedia Commons]
ANALYSIS / Naomi Moreno Cosgrove
October 2nd last year was the last time Jamal Khashoggi—a well-known journalist and critic of the Saudi government—was seen alive. The Saudi writer, United States resident and Washington Post columnist, had entered the Saudi consulate in the Turkish city of Istanbul with the aim of obtaining documentation that would certify he had divorced his previous wife, so he could remarry; but never left.
After weeks of divulging bits of information, the Turkish president, Recep Tayyip Erdogan, laid out his first detailed account of the killing of the dissident journalist inside the Saudi Consulate. Eighteen days after Khashoggi disappeared, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) acknowledged that the 59-year-old writer had died after his disappearance, revealing in their investigation findings that Jamal Khashoggi died after an apparent "fist-fight" inside the Saudi consulate in Istanbul; but findings were not reliable. Resultantly, the acknowledgement by the KSA of the killing in its own consulate seemed to pose more questions than answers.
Eventually, after weeks of repeated denials that it had anything to do with his disappearance, the contradictory scenes, which were the latest twists in the "fast-moving saga", forced the kingdom to eventually acknowledge that indeed it was Saudi officials who were behind the gruesome murder thus damaging the image of the kingdom and its 33-year-old crown prince Mohammed bin Salman (MBS). What had happened was that the culmination of these events, including more than a dozen Saudi officials who reportedly flew into Istanbul and entered the consulate just before Khashoggi was there, left many sceptics wondering how it was possible for MBS to not know. Hence, the world now casts doubt on the KSA's explanation over Khashoggi's death, especially when it comes to the shifting explanations and MBS' role in the conspiracy.
As follows, the aim of this study is to examine the backlash Saudi Arabia's alleged guilt has caused, in particular, regarding European state-of-affairs towards the Middle East country. To that end, I will analyse various actions taken by European countries which have engaged in the matter and the different modus operandi these have carried out in order to reject a bloodshed in which arms selling to the kingdom has become the key issue.
Since Khashoggi went missing and while Turkey promised it would expose the " naked truth" about what happened in the Saudi consulate, Western countries had been putting pressure on the KSA for it to provide facts about its ambiguous account on the journalist's death. In a joint statement released on Sunday 21st October 2018, the United Kingdom, France and Germany said: "There remains an urgent need for clarification of exactly what happened on 2nd October – beyond the hypotheses that have been raised so far in the Saudi investigation, which need to be backed by facts to be considered credible." What happened after the kingdom eventually revealed the truth behind the murder, was a rather different backlash. In fact, regarding post-truth reactions amongst European countries, rather divergent responses have occurred.
Terminating arms selling exports to the KSA had already been carried out by a number of countries since the kingdom launched airstrikes on Yemen in 2015; a conflict that has driven much of Yemen's population to be victims of an atrocious famine. The truth is that arms acquisition is crucial for the KSA, one of the world's biggest weapons importers which is heading a military coalition in order to fight a proxy war in which tens of thousands of people have died, causing a major humanitarian catastrophe. In this context, calls for more constraints have been growing particularly in Europe since the killing of the dissident journalist. These countries, which now demand transparent clarifications in contrast to the opacity in the kingdom's already-given explanations, are threatening the KSA with suspending military supply to the kingdom.
COUNTRIES THAT HAVE CEASED ARMS SELLING
Germany
Probably one of the best examples with regards to the ceasing of arms selling—after not been pleased with Saudi state of affairs—is Germany. Following the acknowledgement of what happened to Khashoggi, German Chancellor Angela Merkel declared in a statement that she condemned his death with total sharpness, thus calling for transparency in the context of the situation, and stating that her government halted previously approved arms exports thus leaving open what would happen with those already authorised contracts, and that it wouldn't approve any new weapons exports to the KSA: "I agree with all those who say that the, albeit already limited, arms export can't take place in the current circumstances," she said at a news conference.
So far this year, the KSA was the second largest customer in the German defence industry just after Algeria, as until September last year, the German federal government allocated export licenses of arms exports to the kingdom worth 416.4 million euros. Respectively, according to German Foreign Affair Minister, Heiko Maas, Germany was the fourth largest exporter of weapons to the KSA.
This is not the first time the German government has made such a vow. A clause exists in the coalition agreement signed by Germany's governing parties earlier in 2018, which stated that no weapons exports may be approved to any country "directly" involved in the Yemeni conflict in response to the kingdom's countless airstrikes carried out against Iranian-backed Houthi rebels in the area for several years. Yet, what is clear is that after Khashoggi's murder, the coalition's agreement has been exacerbated. Adding to this military sanction Germany went even further and proposed explicit sanctions to the Saudi authorities who were directly linked to the killing. As follows, by stating that "there are more questions unanswered than answered," Maas declared that Germany has issued the ban for entering Europe's border-free Schengen zone—in close coordination with France and Britain—against the 18 Saudi nationals who are "allegedly connected to this crime."
Following the decision, Germany has thus become the first major US ally to challenge future arms sales in the light of Khashoggi's case and there is thus a high likelihood that this deal suspension puts pressure on other exporters to carry out the same approach in the light of Germany's Economy Minister, Peter Altmaier's, call on other European Union members to take similar action, arguing that "Germany acting alone would limit the message to Riyadh."
Norway
Following the line of the latter claim, on November 9th last year, Norway became the first country to back Germany's decision when it announced it would freeze new licenses for arms exports to the KSA. Resultantly, in her statement, Norwegian Minister of Foreign Affairs, Ine Eriksen Søreide, declared that the government had decided that in the present situation they will not give new licenses for the export of defence material or multipurpose good for military use to Saudi Arabia. According to the Søreide, this decision was taken after "a broad assessment of recent developments in Saudi Arabia and the unclear situation in Yemen." Although Norwegian ministry spokesman declined to say whether the decision was partly motivated by the murder of the Saudi journalist, not surprisingly, Norway's announcement came a week after its foreign minister called the Saudi ambassador to Oslo with the aim of condemning Khashoggi's assassination. As a result, the latter seems to imply Norway's motivations were a mix of both; the Yemeni conflict and Khashoggi's death.
Denmark and Finland
By following a similar decision made by neighbouring Germany and Norway—despite the fact that US President Trump backed MBS, although the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) had assessed that the crown prince was responsible for the order of the killing—Denmark and Finland both announced that they would also stop exporting arms to the KSA.
Emphasising on the fact that they were "now in a new situation"—after the continued deterioration of the already terrible situation in Yemen and the killing of the Saudi journalist—Danish Foreign Minister, Anders Samuelsen, stated that Denmark would proceed to cease military exports to the KSA remarking that Denmark already had very restrictive practices in this area and hoped that this decision would be able to create a "further momentum and get more European Union (EU) countries involved in the conquest to support tight implementation of the Union's regulatory framework in this area."
Although this ban is still less expansive compared to German measures—which include the cancellation of deals that had already been approved—Denmark's cease of goods' exports will likely crumble the kingdom's strategy, especially when it comes to technology. Danish exports to the KSA, which were mainly used for both military and civilian purposes, are chiefly from BAE Systems Applied Intelligence, a subsidiary of the United Kingdom's BAE Systems, which sold technology that allowed Intellectual Property surveillance and data analysis for use in national security and investigation of serious crimes. The suspension thus includes some dual-use technologies, a reference to materials that were purposely thought to have military applications in favour of the KSA.
On the same day Denmark carried out its decision, Finland announced they were also determined to halt arms export to Saudi Arabia. Yet, in contrast to Norway's approach, Finnish Prime Minister, Juha Sipilä, held that, of course, the situation in Yemen lead to the decision, but that Khashoggi's killing was "entirely behind the overall rationale".
Finnish arms exports to the KSA accounted for 5.3 million euros in 2017. Nevertheless, by describing the situation in Yemen as "catastrophic", Sipilä declared that any existing licenses (in the region) are old, and in these circumstances, Finland would refuse to be able to grant updated ones. Although, unlike Germany, Helsinki's decision does not revoke existing arms licenses to the kingdom, the Nordic country has emphasized the fact that it aims to comply with the EU's arms export criteria, which takes particular account of human rights and the protection of regional peace, security and stability, thus casting doubt on the other European neighbours which, through a sense of incoherence, have not attained to these values.
European Parliament
Speaking in supranational terms, the European Parliament agreed with the latter countries and summoned EU members to freeze arms sales to the kingdom in the conquest of putting pressure on member states to emulate the Germany's decision.
By claiming that arms exports to Saudi Arabia were breaching international humanitarian law in Yemen, the European Parliament called for sanctions on those countries that refuse to respect EU rules on weapons sales. In fact, the latest attempt in a string of actions compelling EU foreign policy chief Federica Mogherini to dictate an embargo against the KSA, including a letter signed by MEPs from several parties.
Rapporteur for a European Parliament report on EU arms exports, Bodil Valero said: "European weapons are contributing to human rights abuses and forced migration, which are completely at odds with the EU's common values." As a matter of fact, two successful European Parliament resolutions have hitherto been admitted, but its advocates predicted that some member states, especially those who share close trading ties with the kingdom are deep-seated, may be less likely to cooperate. Fact that has eventually occurred.
COUNTRIES THAT HAVE NOT CEASED ARMS SELLING
France
In contrast to the previously mentioned countries, other European states such as France, UK and Spain, have approached the issue differently and have signalled that they will continue "business as usual".
Both France and the KSA have been sharing close diplomatic and commercial relations ranging from finance to weapons. Up to now, France relished the KSA, which is a bastion against Iranian significance in the Middle East region. Nevertheless, regarding the recent circumstances, Paris now faces a daunting challenge.
Just like other countries, France Foreign Minister, Jean-Yves Le Drian, announced France condemned the killing "in the strongest terms" and demanded an exhaustive investigation. "The confirmation of Mr. Jamal Khashoggi's death is a first step toward the establishment of the truth. However, many questions remain unanswered," he added. Following this line, France backed Germany when sanctioning the 18 Saudi citizens thus mulling a joint ban from the wider visa-free Schengen zone. Nevertheless, while German minister Altmeier summoned other European countries to stop selling arms to Riyadh—until the Saudi authorities gave the true explanation on Khashoggi's death—, France refused to report whether it would suspend arms exports to the KSA. "We want Saudi Arabia to reveal all the truth with full clarity and then we will see what we can do," he told in a news conference.
In this context, Amnesty International France has become one of Paris' biggest burdens. The organization has been putting pressure on the French government for it to freeze arms sales to the realm. Hence, by acknowledging France is one of the five biggest arms exporters to Riyadh—similar to the Unites States and Britain—Amnesty International France is becoming aware France's withdrawal from the arms sales deals is crucial in order to look at the Yemeni conflict in the lens of human rights rather than from a non-humanitarian-geopolitical perspective. Meanwhile, France tries to justify its inaction. When ministry deputy spokesman Oliver Gauvin was asked whether Paris would mirror Berlin's actions, he emphasized the fact that France's arms sales control policy was meticulous and based on case-by-case analysis by an inter-ministerial committee. According to French Defence Minister Florence Parly, France exported 11 billion euros worth of arms to the kingdom from 2008 to 2017, fact that boosted French jobs. In 2017 alone, licenses conceivably worth 14.7 billion euros were authorized. Moreover, she went on stating that those arms exports take into consideration numerous criteria among which is the nature of exported materials, the respect of human rights, and the preservation of peace and regional security. "More and more, our industrial and defence sectors need these arms exports. And so, we cannot ignore the impact that all of this has on our defence industry and our jobs," she added. As a result, despite President Emmanuel Macron has publicly sought to devalue the significance relations with the KSA have, minister Parly, seemed to suggest the complete opposite.
Anonymously, a government minister held it was central that MBS retained his position. "The challenge is not to lose MBS, even if he is not a choir boy. A loss of influence in the region would cost us much more than the lack of arms sales". Notwithstanding France's ambiguity, Paris' inconclusive attitude is indicating France's clout in the region is facing a vulnerable phase. As president Macron told MBS at a side-line G20 summit conversation in December last year, he is worried. Although the context of this chat remains unclear, many believe Macron's intentions were to persuade MBS to be more transparent as a means to not worsen the kingdom's reputation and thus to, potentially, dismantle France's bad image.
United Kingdom
As it was previously mentioned, the United Kingdom took part in the joint statement carried out also by France and Germany through its foreign ministers which claimed there was a need for further explanations regarding Khashoggi's killing. Yet, although Britain's Foreign Office said it was considering its "next steps" following the KSA's admission over Khashoggi's killing, UK seems to be taking a rather similar approach to France—but not Germany—regarding the situation.
In 2017, the UK was the sixth-biggest arms dealer in the world, and the second-largest exporter of arms to the KSA, behind the US. This is held to be a reflection of a large spear in sales last year. After the KSA intervened in the civil war in Yemen in early 2015, the UK approved more than 3.5billion euros in military sales to the kingdom between April 2015 and September 2016.
As a result, Theresa May has been under pressure for years to interrupt arms sales to the KSA especially after human rights advocates claimed the UK was contributing to alleged violations of international humanitarian law by the Saudi-led coalition in Yemen. Adding to this, in 2016, a leaked parliamentary committee report suggested that it was likely that British weapons had been used by the Saudi-led coalition to violate international law, and that manufactured aircraft by BAE Systems, have been used in combat missions in Yemen.
Lately, in the context of Khashoggi's death things have aggravated and the UK is now facing a great amount of pressure, mainly embodied by UK's main opposition Labour party which calls for a complete cease in its arms exports to the KSA. In addition, in terms of a more international strain, the European Union has also got to have a say in the matter. Philippe Lamberts, the Belgian leader of the Green grouping of parties, said that Brexit should not be an excuse for the UK to abdicate on its moral responsibilities and that Theresa May had to prove that she was keen on standing up to the kind of atrocious behaviour shown by the killing of Khashoggi and hence freeze arms sales to Saudi Arabia immediately.
Nonetheless, in response and laying emphasis on the importance the upholding relation with UK's key ally in the Middle East has, London has often been declining calls to end arms exports to the KSA. Foreign Secretary Jeremy Hunt defended there will be "consequences to the relationship with Saudi Arabia" after the killing of Khashoggi, but he has also pointed out that the UK has an important strategic relationship with Riyadh which needs to be preserved. As a matter of fact, according to some experts, UK's impending exit from the EU has played a key role. The Campaign Against Arms Trade (CAAT) claims Theresa May's pursuit for post-Brexit trade deals has seen an unwelcome focus on selling arms to some of the world's most repressive regimes. Nevertheless, by thus tackling the situation in a similar way to France, the UK justifies its actions by saying that it has one of the most meticulous permitting procedures in the world by remarking that its deals comprehend safeguards that counter improper uses.
Spain
After Saudi Arabia's gave its version for Khashoggi's killing, the Spanish government said it was "dismayed" and echoed Antonio Guterres' call for a thorough and transparent investigation to bring justice to all of those responsible for the killing. Yet, despite the clamour that arose after the murder of the columnist, just like France and the UK, Spain's Prime Minister, Pedro Sánchez, defended arms exporting to the KSA by claiming it was in Spain's interest to keep selling military tools to Riyadh. Sanchez held he stood in favour of Spain's interests, namely jobs in strategic sectors that have been badly affected by "the drama that is unemployment". Thusly, proclaiming Spain's unwillingness to freeze arms exports to the kingdom. In addition, even before Khashoggi's killing, Sanchez's government was subject to many critics after having decided to proceed with the exporting of 400 laser-guided bombs to Saudi Arabia, despite worries that they could harm civilians in Yemen. Notwithstanding this, Sánchez justified Spain's decision in that good ties with the Gulf state, a key commercial partner for Spain, needed to be kept.
As a matter of fact, Spain's state-owned shipbuilder Navantia, in which 5,500 employees work, signed a deal in July last year which accounted for 1.8 billion euros that supplied the Gulf country with five navy ships. This shipbuilder is situated in the southern region of Andalusia, a socialist bulwark which accounts for Spain's highest unemployment estimates and which has recently held regional elections. Hence, it was of the socialist president's interest to keep these constituencies pleased and the means to this was, of course, not interrupting arms deals with the KSA.
As a consequence, Spain has recently been ignoring the pressures that have arose from MEP's and from Sanchez's minorities in government—Catalan separatist parties and far-left party Podemos— which demand a cease in arms exporting. For the time being, Spain will continue business with the KSA as usual.
CONCLUSION
All things considered, while Saudi Arabia insists that MBS was not aware of the gruesome murder and is distracting the international attention towards more positive headlines—such as the appointment of the first female ambassador to the US—in order to clear the KSA's image in the context of Khashoggi's murder, several European countries have taken actions against the kingdom's interests. Yet, the way each country has approached the matter has led to the rise of two separate blocks which are at discordance within Europe itself. Whereas some European leaders have shown a united front in casting blame on the Saudi government, others seem to express geopolitical interests are more important.
During the time Germany, Norway, Denmark and Finland are being celebrated by human rights advocates for following through on their threat to halt sales to the kingdom, bigger arms exporters—like those that have been analysed—have pointed out that the latter nations have far less to lose than they do. Nonetheless, inevitably, the ceasing carried out by the northern European countries which are rather small arms exporters in comparison to bigger players such as the UK and France, is likely to have exacerbated concerns within the European arms industry of a growing anti-Saudi consensus in the European Union or even beyond.
What is clear is that due to the impact Saudi Arabia's state of affairs have caused, governments and even companies worldwide are coming under pressure to abandon their ties to the oil-rich, but at the same time, human-rights-violating Saudi Arabian leadership. Resultantly, in Europe, countries are taking part in two divergent blocks that are namely led by two of the EU's most compelling members: France and Germany. These two sides are of rather distant opinions regarding the matter, fact that does not seem to be contributing in terms of the so-much-needed European Union integration.
ESSAY / Marina Díaz Escudero
Since 2015, Europe has been dealing with an unprecedented scale of migration from different parts of the world, mainly from MENA (Middle East and North Africa). People flee their countries due to war, bad living conditions or a lack of opportunities for wellbeing.
Although Europe characterises itself for its solidarity, liberty, values and respect for other countries and cultures, such a large flow of immigration seriously tests the European project. For instance, the Schengen system of passport-free travel could collapse as fearful countries enhance their border controls, to the disadvantage of European citizens. "The Schengen system is being more and more questioned and most opinion polls highlight the correlation between the fear of immigration and the distrust of the citizens of the member states towards European institutions. "1 The migration crisis is also considered a "threat for the European project's constitutional stability and for its fundamental values" (Spijkerboer, 2016). 1
Divisions between northern and southern EU countries, and between them and the Visegrad countries have clearly intensified due to this problem, especially after the approval, in 2015, of some quotas of relocation of refugees that were critisised and voted against by Hungary, the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Due to this lack of consensus but also due to the delay of other EU countries in complying with the quotas, a treaty was signed between the EU and Turkey in March 2016 so that most refugees arriving to Europe through Greece would be immediately returned to Turkey2.
Understandably, EU countries are mostly concerned with the prevention of illegal immigration and with border-control policies, as well as with the need of reaching an agreement for an egalitarian distribution of arriving migrants, most of them being asylum seekers and refugees. Nevertheless, this will probably not be enough to satisfy both the European citizens and the migrants: root causes of migration may need to be solved as soon as possible to prevent people from fleeing their homes. This gives the EU food for thought: addressing the migration problem without focusing on the prevention of migration in the countries of origin may not be a lasting, long-term solution. "The instability, insecurity, terrorism, poverty, famine and climate change besetting large parts of Africa and the Middle East are the root causes of migration, but the European Union (EU) governments have come around to this too late, engaging essentially in damage-limitation exercises at our borders. "3
According to World Bank data, in 2017 over 8 million migrants came from "the Arab world" and from these, 6 million fleed the Syrian Arab Republic4. The war in Syria, originally between Bashar al Assad's regime and the rebel opposition, and currently a proxy war involving various international actors, turns the country into one of the greatest sources of migrants. The fact that over a million of them live in Lebanon (currently accounting for a 30% of the population) , a country who didn't sign the 1951 Refugee Convention and who has been trying to deport the migrants for years now, is worrying. Due to the "fuelling tensions between Lebanese host communities and the Syrian refugees" the Lebanese government has taken some more restrictive measures towards migrants, such as the banning of the construction of formal refugee camps. This for sure puts additional pressure on the EU5.
In order to comprehend the European Union's vision and strategy on Syria, and whether the institution and its members are willing to fight the root causes of its situation, one must consider the words of the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, Federica Mogherini, in her speech at the Conference of Brussels in April 2018:
"[In this conference] we had representatives of over 85 countries and international organizations, international and Syrian civil society. [...] We identified common ground on at least 2 or 3 issues: one is that there is no military solution to the war in Syria and that there is a need that everyone recognizes to relaunch the political process. The second element on which I have not found any divergent view is the key role of the United Nations in leading this political process. This is extremely important for us, the European Union, because we have always consistently identified in the UN and in Staffa de Mistura the only legitimate leadership to ensure that the political process represents all Syrians in intra-Syrian talks and happens along the lines of the United Nations Security Council resolutions already adopted. The third element is the need to support Syrians inside Syria and in the neighbouring countries, with humanitarian aid, financial support but also to support hosting communities, in particular neighbouring countries".6
The Vice-President of the European Commission basically makes three clear statements: the European institution will by no means intervene militarily in Syria, neither will it take the initiative to start a political process or peaceful negotiation in the country (it will only support the UN-led process), but it will clearly invest economically both in the country and in its citizens to improve their conditions.
Defence of the UN-led political process
Once a solely-European military intervention has been discarded (due to a lack of consensus among countries on a common defense policy and to the already effective existence of NATO in this regard), the EU considers its role in a political solution to the Syrian conflict, which would clearly reduce migration numbers.
According to the European Council in its conclusions on Syria of April 2018, "the momentum of the current situation should be used to reinvigorate the process to find a political resolution of the Syrian conflict [...] A lasting peace in Syria is the ultimate objective of the EU".7 The Council makes clear that it will not create a new EU-led political process but that it will support the UN's: "...any sustainable solution to the conflict requires a genuine political transition in line with UNSCR 2254 and the 2012 Geneva Communique negotiated by the Syrian parties within the UN-led Geneva process."
The UN currently takes part in two parallel processes: inter-Syrian conversations in Geneva and the Conversations in Astana. The first looks for a dialogue solution to the conflict and participants are the Syrian government, a delegation from the opposition and the UN Special Envoy for Syria. Until now, 9 rounds of talks have taken place, the last focused on the elaboration of a new constitution for the country. The second process is promoted by Russia, Iran and Turkey, guarantors of the peace process in Syria. Conversations started in 2017 with the aim of consolidating the cease-fire and preparing the way for a political solution to the war. The last round of talks took place in Sochi this past July8.
But things aren't as easy as they seem.
UN special envoy for Syria will soon be replaced by the Norwegian Geir Pedersen making future lines of action unpredictable for us. We know, however, what the starting point will be. In the ordinary UN session held on the past 20th December, de Mistura stated that they had "almost completed the job of starting a constitutional commitee to write a constitutional reform, as a contribution to the political process, but still have to go one more mile. "9
Such a commiteee would be composed of 150 persons, a third of which should be appointed by the Syrian regime, another third by the opposition and the last one by UN designated persons. This last point has been repeatedly opposed by Syria. The biggest problem at the moment is that the UN is not fully comfortable with the 50-name list proposed by Iran, Russia and Turkey9.
On the other hand, the strategy of the US, a very relevant actor in this process due to its position in the UN as a permanent member of the Security Council (with veto power on resolutions), has been unclear for a long time. US Special Envoy to Syria Joel Rayburn stated in November that the objectives of the US in Syria were three: the defeat of the Islamic State, the withdrawal of all Iranian-commanded forces and "a political settlement under the auspices of the UNSC Resolution 2254 and the political process supported by the UN in Geneva. "10
In other words, it seemed that unless the first two objectives were covered the US wouldn't wholeheartedly compromise for a definitive political settlement in Syria and given US relevance, the UN would have it very difficult to advance the political process anytime soon. Most recently however, there was a turn of events: in December the US declared its intention of gradually withdrawing its troops from Syria. "We have defeated ISIS in Syria, my only reason for being there during the Trump presidency. "11
Does this mean that the US is finally willing to head its efforts towards the third objective? US diplomat Rodney Hunter said: "the US is ready to impulse the political process, to isolate more the regime diplomatic and economically, we are willing to do it". 9
Although a positive answer would facilitate discussions for peace and thus, EU involvement, a reduction of violence in the region (and therefore a reduction of migration to Europe) is not assured for two reasons: the US now leaves Turks with free hands to attack Kurdish militants and, although ISIS has lost 95% of its territory, "2,500 Isis fighters remain [...] The group retains the capacity to do even more damage, especially if let off the hook now." 11
Soft power: humanitarian aid and investment
Given the fact that the EU can not really influence the military and political/diplomatic decisions regarding the Syrian conflict, it has been focusing, since the beginning of the war in 2011, on delivering humanitarian aid and development support to the country and its nationals. The next phrase from the European External Action Service summarises very well the EU's aims on this respect: "Our objective is to bring an end to the conflict and enable the Syrian people to live in peace in their own country. "12
Although bilateral, regional and technical assistance cooperation between the EU and the Syrian government came to an end due to the violent situation that was emerging in the country, the international organization directly supports the Syrian population and its neighbours13.
Through the European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP), the EU worked hand in hand with its neighbours to the East and South (including Syria) with the aim of fostering stabilization, security and prosperity and achieving cooperation in key areas like the "promotion of democracy, rule of law, respect for human rights and social cohesion. "14 After the cease of cooperation between the EU and the regime, support to the ENP countries is given through the European Neighbourhood Instrument (ENI), with a predicted budget of 15 billion dollars (2014-2020)15.
Under the financing og the ENI, the Commission approved in November a special measure "to help the Syrian population to cope with the effects of the crisis and prepare the grounds for a sustainable peace. "16 The main action has been entitled as "Preserving the prospects for peace and stability in Syria through an inclusive transition" and counts with a maximum contribution of EUR 31 million. According to the European Commission, if the Syrian situation turns into a "post-crisis state-building and reconstruction scenario," special measures will be revised in order to suit the new needs of the population14.
The ENP is part of the EUGS or European Union Global Strategy (for the European Union's Foreign and Security Policy) presented by Federica Mogherini to the EU Council in 2016, and whose main aim is to achieve an integrated approach and a "coherent perspective for EU's external action. "15 As part of this broader strategy, the EU wishes to prevent fragile contexts from becoming serious humanitarian crises17.
Within this, another particular strategy for Syria was developed in 2015, the EU Strategy for Syria. Some of its most important objectives are "saving lives by addressing the humanitarian needs of the most vulnerable Syrians across the country," "promoting democracy, human rights and freedom of speech by strengthening Syrian civil society organisations" and "supporting the resilience of the Syrian population and Syrian society. "18 The European Council, in its Conclusions on Syria of 2018, agreed that the objectives of the "European Union Strategy on Syria" remain valid.
Although all these initiatives are well-intentioned and show that the EU is not only concerned about the end of the war but also with how it will be done and its aftermath, history has proved that Western political intervention in the Middle East is far from optimum for the region. In the 1916 the Sykes-Picot agreement between France and the UK drew an artificial political line on the territory that would later trigger the Arab-Israeli conflict and promote present ISIS action. Later on, the US-leaded intervention in Iraq in 2003 (one of its objectives being the "liberation" of the Iraqi people) has caused an increase of Sunni-Shiite tension, the rise of Al-Qaeda and the strenghtening of Iran in the region.
The point here is that the EU might be interested in helping Syria and its citizens in ways that improve living conditions and welfare opportunities without messing up with the country's cultural, social and political system. Imposing the notion of democracy in these states, knowing that they have a completely different historical and cultural background, might not be a feasible solution.
Thus, other types of EU initiatives like the New Partnership Framework (NPF, June 2016), focused on the role of economic development in fighting the root causes of migration, might be more effective in the long-term. "It will address all aspects of this migration crisis, from its root causes to the daily tragedies that occur in the Mediterranean. These ambitions [...] illustrate EU's willingness to address specific migratory challenges, but also the long-term drivers of migration. "19
Through the NPF, the EU explains how private investment can be a very useful tool for promoting the economic growth and development of Syria, which would in turn improve the living conditions of its citizens making it less necessary to flee their homes in search of a better place to be. "Instead of letting irregular migrants risk their lives trying to reach European labour markets, European private and public resources should be mobilised for investment in third countries of origin. If deployed intelligently, leveraged use of the limited budget resources available will generate growth and employment opportunities in source as well as transit countries and regions [...] This should address the root causes of migration directly, given the high impact of those investments in terms of employment and inequality reduction". This is what the EU calls innovative financing mechanisms.
This project is called the External Investment Plan and is being organized in three steps. First, the mobilization of scarce public resources in an attractive way to attract private investment. Then, helping local authorities and private companies to be known in the international investor community. Finally, the EU would try to improve the general business government by putting a solution to some corruption issues as well as some market distortions. "The EU, Member States, third countries, International Financial Institutions, European bilateral development institutions, as well as the private sector, should all contribute." The EU hopes to collect, through this External Investment Fund, a total of 62 billion euros.
Long story short, European countries believe in the expansion of this type of innovative financing "in those fragile and post-conflict countries which are often important for migration flows but where the potential for direct private or public investment is currently limited."
An interesting factor to take into account in this matter is who will be the most involved international actor in the project. Will it be the US, allowing us to compare the current situation with the 20th century Marshall Plan? (where investments in infrastructure and the spread of domestic management techniques was also a key element). Or could it be Russia? As the President of the Russian Chamber of Commerce stated in March 2018, "$200 billion to $500 billion will be needed for the reconstruction of the Syrian economy, and the first priority will, as President Bashar al-Assad has said, be given to Russian businesses. "20 What is clear is that investing in Syria will clearly give the investor country some important influence on the newly-recovered state.
Conclusions and forecast for the future
Since the beginning of the crisis in 2011, Syria has been one of the major sources of migration towards Europe. Although EU members currently need to discuss the prevention of illegal immigration and the distribution of legally coming asylum seekers, some attention must also be given to the elimination of factors that activate migration in the country of origin.
While it is true that a definitive end to the war between the regime and the opposition would be the best and most immediate solution for disproportionate fleeing from Syria, the EU doesn't seem to be able to intervene more than it already does.
Not having an army of itself (and not seeming to want it in the near future) and being the "assistant" of the UN in the political and diplomatic resolution of the conflict, it can only apply its soft power tools and instruments to help to the country and its citizens.
Although humanitarian aid is essential and the EU is sparing no expense on it, the institution has come to realise that the real key to improving Syria's situation and the wellbeing of its citizens may be investment and development. This investment could be "short-term", in the sense that foreign countries directly invest in Syria and decide what the money will be used for (i.e reconstruction of buildings, construction of new infrastructure...) or "long-term", in the sense that the main role of the EU is improving the country's business governance to facilitate the attraction of private investors in the long-term.
Regarding the last option it is very important that "the recipient countries establish transparent policies, broad and effective that propitiate an appropiate atmosphere for investment, with the consequent formation of human resources and the establishment of an appropiate institutional climate. "21 Taking this into account, Syria will be a difficult challenge for the EU, as in order to achieve an appropiate institutional climate, a diplomatic solution to the conflict and a peaceful political transition will be required, as well as the collaboration of the future government in promoting political transparency.
All in all, the EU is clearly aware of the root causes of migration and is developing feasible strategies to counter them. The rate of progress is still slow and it may be due to the fact that, in order to effectively apply many of these soft power strategies (except for the humanitarian aid), the recipient country must be stable and ready to collaborate. In other words, EU investment and development plans will most probably bear fruit when the war is over, a peaceful political transition is on the move and the general atmosphere is favorable for economic growth and innovation.
Political stability in Syria could be achieved through two scenarios: the success of the UN-led process and the drafting of new constitution for the country; or the victory of one of the sides (most probably the Syrian regime) and its establishment in power. Meanwhile, the EU and its members will have three challenges: developing the forementioned long-term investment strategies in the view of a future peace (while maintaining already-functioning soft power initiatives), dealing with the refugee crisis at the European borders, and preserving the European project and unity by avoiding major disagreements on migration policy and an exacerbated fear of immigration.
Moreover, one of the key issues that will need to be followed closely in the following months is the effect that the, maybe early, withdrawal of US troops can have on the region and on the power dynamic between the actors, together with the potential changes in US strategy with regards to the UN-led process.
References
-
CIDOB - "Immigration and asylum: at the center of the political arena". yearbook CIDOB on Immigration 2018. (2018). Retrieved from
-
López, E. (2018). Refugee crisis: The divergence between the European Union and the Visegrad Group/ GLOBAL AFFAIRS, UNAV. Retrieved from
-
Tajani, A. (2018). The migration crisis threatens to destroy the EU. We must not let it | Antonio Tajani. Retrieved from
-
Refugee population by country or territory of origin | Data. (2017). Retrieved from
-
Lebanon - European Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations - European Commission (2019). Retrieved from
-
Photos and videos of the conference - Consilium (2018). Retrieved from
-
Battu, V. (2018). Syria: Council adopts conclusions - Consilium. Retrieved from.
-
Syria. Retrieved from
-
UN still stuck for a solution in Syria as US announces withdrawal (2018). Retrieved from
-
Elgeneidy, S. (2018). INTERVIEW: 'We need a political settlement of the conflict', US Special Envoy to Syria says - Region - World - Ahram Online. Retrieved from.
-
Chulov, M. (2018). Has Isis been defeated in Syria, as Trump claims?. Retrieved from.
-
Syria and the EU - EEAS - European External Action Service - European Commission (2016). Retrieved from
-
Syria - European Neighbourhood Policy And Enlargement Negotiations - European Commission (2018). Retrieved from
-
European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP) - Commission européenne (2016). Retrieved from
-
European Neighbourhood Policy - European Neighbourhood Policy And Enlargement Negotiations - European Commission.(2018). Retrieved from
-
Commission implementing decision on the special measure in favour of the Syrian population for 2018. (2018). Retrieved from
-
EUGS at 1 - EU Global Strategy - European Commission (2019). Retrieved from
-
Battu, V. (2017). Council adopts EU strategy on Syria - Consilium. Retrieved from
-
Communication on establishing a new Partnership Framework with third countries under the European diary on Migration. (2016). Retrieved from
-
"Russian business first in line for spoils of Syrian war/Subscribe to read | Financial Times. Retrieved from
-
Foreign Direct Investment for Development: Maximising Benefits, Minimising Costs (2002). Retrieved from
Strategic bombers will continue to matter in the geopolitical balance as "weapons of mass deterrence"
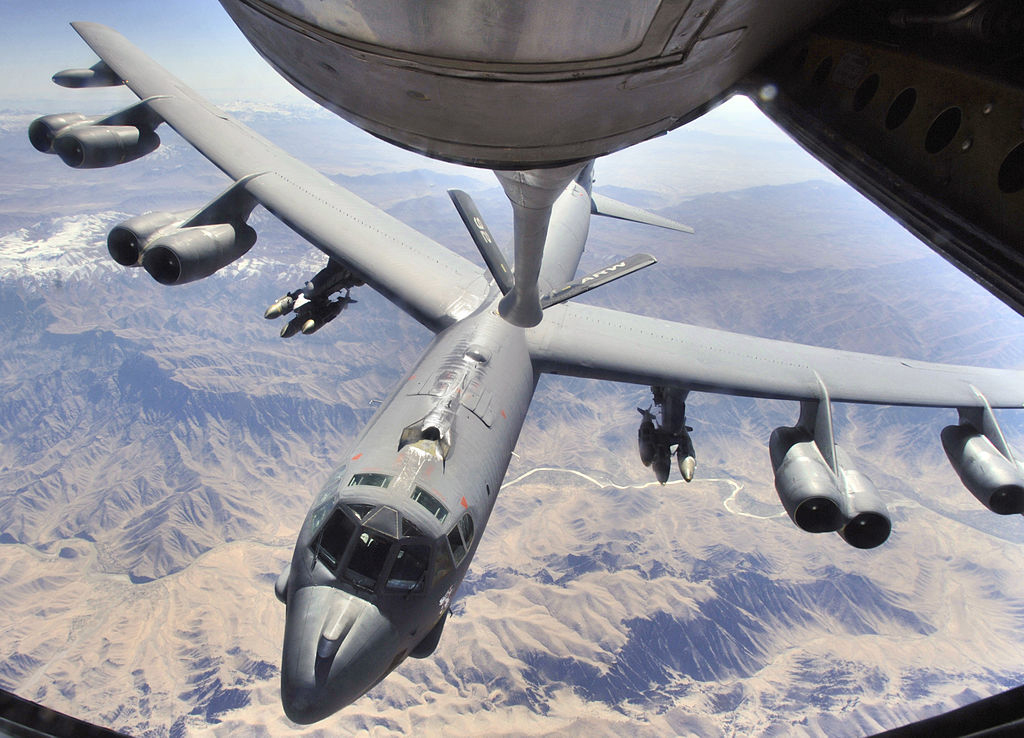
The U.S. fleet of B-52 bombers is set to receive a series of upgrades that will boost its working life at least until the 2050s. By then, the B-52 will have been flying for nearly 90 years, since its takeoff during Eisenhower's presidency. This will make him, by far, the model of the aircraft that will have been flying the longest with its main operator, in this case the USAF.

▲ A B-52G when in service [USAF]
article / Jairo Císcar Ruiz
The words "strategic bomber" may sound like the Cold War, the Soviet Union, and spy planes, but today it's a concept that's at its disposal. agenda despite sounding very far away. It is true that the status strategic aviation is constrained by the agreement of 2010 (START III), which restricts deployed nuclear weapon delivery to 700. These means of delivery include strategic bombers, ICBMs (intercontinental missiles) and SLBMs (submarine launches). Despite the fact that both Russia and the U.S. have now significantly reduced the issue of its bombers (the US has "only" 176), strategic weapons (and with it, bombers) will continue to be a fundamental part of the geopolitical balance in international relations.
There are only 3 countries in the world that have strategic bombers in their arsenal, the US, Russia and China (although the Chinese Xian H-6 is well below its Russian and American counterparts), and this shortage of aircraft makes them so prized and a differentiator on the battlefield. But it is not only on the battlefield that these aircraft cause an imbalance, but they especially stand out in the field of international relations as "weapons of mass deterrence".
A strategic bomber is an aircraft designed not for the battlefield directly, but to penetrate enemy territory and attack both strategic targets (instructions military headquarters, bunkers...) as critical locations for a country's war effort. The fact that a country has such an aircraft in its fleet of aircraft is clearly a deterrent to potential enemies. Both Russia and the U.S. – especially the latter country – are able to permanently have their bombers in the air (thanks to in-flight refueling) loaded with up to almost 32 tons of weaponry, with a flight duration only restricted to the endurance capacity of the crew. In this "diplomacy of fear", strategic bombers will continue to be prominent elements in the field of geostrategy and the balance of forces at the global level. The US is fully aware of this and is therefore embarking on a series of ambitious plans to continue to enjoy air and geostrategic superiority. Of these plans, one of the newest and, perhaps, most eagerly awaited is the advertisement that American B-52s will continue to fly until at least 2050.
Although it was assumed that this would be the case, the confirmation given by the US Air Force is no less surprising: the fleet of active B-52s is going to receive a series of improvements that will boost its active life until at least the 2050s. It wouldn't be too much news B taking into account that it is common to approve improvement packages, either avionics or software to increase the useful life of aircraft in service, but the reality is that the last B-52 Stratofortress left the Boeing assembly plant in Wichita (Kansas) in 1962. In other words, by 2050 the entire fleet would have been flying for nearly 90 years, which would make it by far the world's largest fleet in the world. model of the aircraft that will have been flying the longest with its main operator, in this case the USAF.
Versatility, deterrent effect and lower operating cost
But can an aircraft that was put into service from 1955, with Eisenhower as president, stand up to new bomber models, such as the B-2 or the future B-21 Raider? Is the enormous outlay that the government intends to make justifiable? congress of the U.S.? It is estimated that it could spend 11,000 million on engines alone; Almost €300 million have been approved for the 2019 financial year.
The answer is yes. Due to its strategic versatility, its deterrent effect and its comparatively low operating cost, the B-52 has become a vital aircraft for the United States.
Its versatility in combat has been long tested, since its "debut" in the Vietnam War, where it was the protagonist of carpet bombings (it is capable of launching more than 32 tons of explosives). As time progressed, it proved that it could not only drop bombs, but also long-range missiles such as the AGM-158 JASSM or the Harpoon anti-ship missile. Its great weapons capacity makes it one of the flagship long-range attack aircraft of the United States. This has been attested in the mission statement In which, until being relieved by the B-1, the B-52s flew 1,850 combat missions, dropping some 12,000 bombs, something that was fundamental to the victory over Daesh in Mosul.
Speaking of long distance is precisely where the B-52 is overwhelming: without refueling, a B-52 can fly more than 15,000 km, having flown 20,000 km in extraordinary situations. This offers a global attack capability, since in the event of refueling, only the crew's own endurance would prevent them from being in flight indefinitely. This capability makes them ideal not only for bombing from instructions Not only to participate in search tasks, being able to carry out a "scan" of 364,000 km2 between two aircraft in two hours. This is vital for use by the U.S. Navy in anti-submarine missions or to detect enemy navies.
The same parameters and advantages apply to the use of the B-52 as a "massive" deterrent. Initially created to permanently have a squadron in flight armed with nuclear bombs, and thus guarantee an immediate response to any aggression, the aircraft stationed in Guam are now used as part of the U.S. tactic of free passage through the international waters of the South China Sea. There have also been employee as permanent air support in areas of particular risk such as the Korengal Valley, in Afghanistan, or at the beginning of the war itself, in Tora Bora. By having a B-52 on standby, troops could have air support that would otherwise take time to arrive in a few moments (and for a long time).
Another indisputable advantage of these aircraft is their relatively low cost in proportion to the other bombers in the U.S. fleet. First of all, it should be clarified that the cost per flight hour is not only the fuel used, but also the cost of maintenance, spare parts, etc. It is true that these theoretical prices are not added to the cost of ammunition (which can amount to tens of millions) or other variables such as the salary of pilots, mechanics, insurance costs, cost of insurance, etc. car park in hangars or other variables that are classified, but they do serve to give us a global view of their operating cost. The B-52s cost the U.S. taxpayer about $70,000 per hour. It may seem like an extraordinarily high price, but its "sibling" the B-2 fetches $130,000 an hour. Despite being exorbitant prices for an army like the Spanish (Eurofighters cost about $15,000/hour), for the budget is not significant (Trump aims to reach $680 billion in U.S. dollars). budget).
|
A B-52H after being in-flight refueled by a KC-135 Stratotanker over Afghanistan [USAF] |
Engine refurbishment
We have seen that the B-52, that Big Ugly Fat Fellow as it is affectionately nicknamed by its crews, may continue to be a vector to be reckoned with in the air for years to come, but the USAF does not want it to become a supporting actor, but to remain the main actor. To this end, it has created the Commercial Engine Reengineering Program (CERP) to replace the old original engines. The TF33 is now more than 50 years old, and in the last 20 years its cost has doubled, due to the lack of spare parts (currently they have to cannibalize the parts of retired engines) and their inefficient consumption. It should not be forgotten that it has 8 engines, so consumption is not a trivial matter. To replace them, the USAF has opened a competition that should be decided from mid-2019. At the moment, the USAF's specifications aim to achieve engines that are at least 25% more efficient and take 5 times longer to need repair, which would mean a 30-year saving (until 2050) of about 10,000 million dollars. With a very juicy contract (there is talk of the order of 11,000 million dollars to replace the 650 engines of the B-52 fleet), the large military aviation companies have begun to present their proposals, including Pratt & Whitney (with the PW815), General Electric (with the new Passport Advanced Turbofan) and Rolls-Royce (with the Pearl or the BR735). Other flagships of the aeronautical industry are pending their proposals.
But not only the engines will benefit from the improvements and investment, but precisely the purchase of new engines will make it necessary to change the instrumentation of the cockpit: in this way, they will also take advantage of the remodeling to change the old analogue indicators and cathode ray screens for the modern multifunctional screens that we see in any fighter today. USAF assistant secretary for procurement William Roper has also commented that new ejection seats are being considered.
Beyond speculation, it is certain that in the framework of the Radar Modernization Program (RMP), $817 million will be invested between fiscal years 2019 and 2023 in the purchase of new radar systems to replace the APQ-166 from the 1960s. New tactical software will also be purchased. data Link 16, as it is the only USAF aircraft that does not have it incorporated and is vital to carry out joint operations, both within the US military itself and with European NATO armies.
In the future, the software and the aircraft itself will be adapted to increase its offensive capabilities, as was already done with the IWBU program, which increased its cargo capacity in the hold by 67%. One of the main goals of offensive remodeling is to be able to carry at least one GBU-43/b (or MOAB; Mother of all bombs; the world's most powerful non-nuclear bomb). To this end, a new wing pylon is being designed that can support 9,000 kilos of weight. Looking ahead, the B-52 will be able to carry hypersonic missiles, but that won't be seen until the mid-2020s at the earliest.
In this way, the USAF aims to ensure that the B-52 Stratofortress remains the A option in its fleet when it comes to heavy bombing. Therefore, the B-52 will continue to be a fundamental strategic-military factor for understanding international relations in the years to come. No one would have claimed in 1955 that that plane, no matter how good it was, could still fly until a hundred years later. There are still 31 years to go, but we'll see what the B-52 has in store for us. subject fat and ugly" that he has become, thanks to his magnificent design and construction, in the Dean of bomber planes: the B-52 (arguably) the best bomber in the world.
From Soviet assistance to the race with the US to take advantage of the mineral wealth of asteroids
The arrival of a Chinese artifact on the hidden side of the Moon has led world public opinion to focus on the Chinese space program, more developed than many imagined. Assisted by the Soviets in their beginnings, the Chinese have ended up taking a lead in some programs (probably more apparent than real, due to some setbacks), such as the development of their own permanent space station, and compete with the United States in the desire to take advantage of the mineral wealth of asteroids.

▲ Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center [CNSA]
ARTICLE / Sebastián Bruzzone [Spanish version]
The Chinese space program started at the beginning of the Cold War, in the midst of a direct struggle between the United States and the Soviet Union for the control of international politics. Since 1955, Chairman Mao Zedong looked for the respect of the world powers and decided to follow in the footsteps of the neighboring country, the USSR. In March of the following year, the Fifth Academy of the Ministry of National Defense began the development of a first ballistic missile (Twelve Year Chinese Aerospace Plan). After the launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union in 1957, Mao embarked on the development of a Chinese artificial satellite that would be active in space two years later (Project 581), an effort materially and economically supported by the Soviet Union. However, in the early 1960s, all economic and technological assistance by the USSR stopped after Beijing accused Nikita Khrushchev of being a revisionist leader who wanted to restore capitalism.
The China National Space Administration (CNSA) is in charge of the Chinese space program. The first Chinese manned space flight took place in 2003, with Yang Liwei, aboard the Shenzhou 5 spacecraft, which was docked to the Tiangong-1 space station. In this way, China became the third nation to send humans out of Earth. The main objective of the Shenzhou missions is the establishment of a permanent space station. Up to now, there have been nine Chinese men and seven women in space.
Since 2007, China put its focus on the Moon. The Chinese lunar exploration program has been developed in four phases. The first (Chang'e 1 and 2), that took place in 2007 with CZ-3A, was the launching of two unmanned lunar orbital probes. The second (Chang'e 3 and 4), conducted in 2013 with CZ-5/E, was the first moon landing of two rovers. The third one (Chang'e 5 and 6), executed in 2017 with CZ-5/E, consisted of a moon landing and return of samples. And the fourth, scheduled for 2024 with CZ-7, will consist of a manned mission and the implementation of permanent instructions on the lunar surface.
The Chang'e 4 mission was launched on December 8, 2018; the landing took place on 3rd January 2019 in the crater Von Kárman (186 kilometers of diameter), in the southern hemisphere of the hidden face of the Moon. The landing was a success, according to Sun Zezhou, chief engineer of the mission. The images transmitted by the Yutu-2 rover showed that this lunar surface never before explored is densely perforated by impact craters and that its crust is thicker than the visible side. As part of a biological project a cotton seed sprouted, but the high levels of radiation, lower gravity than terrestrial and sudden changes in temperature killed the cotton plant some days later. Given that the hidden side of the Moon is protected from any interference from the Earth, according to astronomers, it should be a good place to better study the evolution of stars and galaxies.
In mid-2017, Chinese intentions to search for scarce minerals on Earth on the surface and, if possible, inside asteroids, were made public. Within China's space program, this particular issue occupies an important place. According to Ye Peijan, head of the lunar exploration program, in recent years his country has been studying the possibility of executing a mission that captures an asteroid to place it in the orbit of the Moon, and thus be able to mine it, or even use it as a permanent space station, according to the South China Morning Post. The same official highlighted that in the Solar System and near our planet there are asteroids and stars with a large amount of precious metals and other materials. This plan could be launched as soon as 2020. To do this, the CNSA will use the Tianzhou position ships, unlike the Shenzhou manned exploration vessels whose main objective is the establishment of a permanent space station, or the Chang'e of lunar missions.
The cost of this futuristic plan would be very high and it would involve the organization of complex and high-risk missions, but the interest will not decline, since it could be very profitable in the long term and would provide billionaire benefits. Goldman Sachs analyst Noah Poponak has pointed out that a single asteroid could have more than 50 billion dollars in platinum, as well as water or other precious metals.
The capture of an asteroid requires, first, that a ship land on its surface, to anchor itself. The ship must have incredibly powerful engines, so that, being anchored, it may be able to drag the entire asteroid into the Moon's orbit. These thrusters, with enough power to move a rock of thousands of tons, still do not exist. Ye Peijan has warned that this technology needed for such a space experience could take approximately 40 years to develop. For the moment, in March 2017 China announced in the official press that it had the intention of sending probes to the cosmos to study trajectories and characteristics of some objective asteroids. Thus China goes to direct competition with NASA, which is developing a program to reach an asteroid as well.
Tiangong-1 was the first space laboratory that China put into orbit, in 2011, measuring 10.5 meters in length, 3.4 meters in diameter and weighing 8.5 tons, with the objective of carrying out experiments within the Chinese space program and starting the permanent station that the CNSA seeks to have in orbit by 2023. Against all speculations, in 2016 the digital control of the ship was lost and it ended destroyed in pieces over the Pacific Ocean, northwest of New Zealand. Subsequently, that very year a second module, Tiangong-2, was launched with the same objectives. On the other hand, China is making progress in the plan to establish a permanent space station. According to Yang Liwei, the central capsule will be launched in 2020 and the two experimental modules in the two subsequent years, with manned missions and position spacecraft.
From Soviet Aid to the degree program with the U.S. to take advantage of asteroid mineral wealth
The arrival of a Chinese device on the far side of the Moon has led world public opinion to focus on China's space program, which is more developed than many imagined. Aided by the Soviets in their early days, the Chinese have ended up taking the lead in some programs (probably more apparent than real, given certain setbacks suffered), such as the development of a permanent space station of their own, and compete with the United States in the desire to harness the mineral wealth of asteroids.

▲ Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center [CNSA]
article / Sebastián Bruzzone [English version]
The origin of China's space program1 can be traced back to the early Cold War, at the height of tension between the United States and the Soviet Union over control of international politics. Since 1955, Chairman Mao Zedong sought the respect of world powers and decided to follow in the footsteps of the neighboring country, the USSR. In March of the following year, the Fifth Academy of the Ministry of National Defense began the development of a first ballistic missile (China's Twelve-Year Aerospace Plan). After the launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union in 1957, Mao threw himself into the development of a Chinese artificial satellite that would be active in space two years later (project 581), in an effort materially and economically supported by the Soviet Union. However, in the early 1960s, the USSR withdrew all its attendance economic and technological crisis following Beijing's accusation that the first secretary of the committee The Central of the CPSU, Nikita Khrushchev, was a revisionist and wanted to restore capitalism.
The China National Space Administration (CNSA) is the manager of space programs. The first Chinese manned spaceflight took place in 2003, with Yang Liwei, aboard the Shenzhou 5 spacecraft, which docked with the Tiangong-1 space station. In doing so, China became the third nation to send men off Earth. The main goal One of the Shenzhou missions is the establishment of a permanent space station. To date, nine Chinese men and seven women have traveled into space.
Since 2007, China has shown a special interest in Luna. China's lunar exploration program consists of four phases. In the first (Chang'e 1 and 2), carried out with CZ-3A, two unmanned lunar orbital probes were launched. In the second (Chang'e 3 and 4), in 2013, with CZ-5/E, the first moon landing of two rovers took place. The third (Chang'e 5 and 6) was executed in 2017 with CZ-5/E, consisting of a moon landing and sample return. The fourth, with CZ-7, is scheduled for 2024; will consist of a mission statement manned and the implementation of instructions on the lunar surface.
The mission statement Chang'e 4 was launched on December 8, 2018, and landed on the lunar surface on January 3, 2019, in the crater Von Kárman (186 kilometers in diameter), in the southern hemisphere of the far side of the satellite. Images transmitted by the Yutu-2 rover showed that this never-before-explored lunar surface is densely pierced by impact craters and that its crust is thicker than the visible side. As part of a essay A cotton seed could be sprouted, but high levels of radiation, gravity lower than Earth's, and sudden changes in temperature caused the cotton plant to succumb a few days later. Astronomers believe that the far side is protected from interference from Earth, so from there it would be possible to better study the evolution of stars and galaxies.
In mid-2017, Chinese intentions to search for minerals scarce on Earth on the surface of asteroids, and if possible in their interiors, were made public. Within China's space program, this topic Concrete occupies an important place. Of agreement with Ye Peijan, Maxim manager of the lunar exploration programme, his country had been studying in recent years the possibility of carrying out a mission statement to capture an asteroid to place it in the orbit of the Moon, so that it can be exploited minerally, or even used as a permanent space station, according to the South China Morning Post. The same manager He pointed out that in the Solar System and near our planet there are asteroids and stars with a large amount of precious metals and other materials. This plan will be implemented from 2020. To do this, the CNSA will use the Tianzhou cargo ships, as opposed to the manned Shenzhou exploration ships whose goal The main one is the establishment of a permanent space station, or the Chang'e lunar missions.
The cost of this futuristic plan would be very high, as it would involve the organization of complex and high-risk missions, but interest will not wane, as it could be very profitable in the long term and would give billions of dollars in profits. According to Noah Poponak, an analyst at Goldman Sachs, a single asteroid could have more than $50 billion worth of platinum, as well as other precious metals and water.
Capturing an asteroid requires, first, that a spacecraft land on its surface, in order to anchor itself. The spacecraft will need to have extremely powerful engines, so that, being anchored, it can be able to drag the entire asteroid into the orbit of the Moon. These thrusters, powerful enough to move a rock weighing thousands of tons, do not yet exist. Ye Peijan has warned that this technology needed for such a space experience could take approximately 40 years to develop. For the time being, in March 2017 China announced in the official press that it intended to send probes into the cosmos to study the trajectories and characteristics of some asteroids. With this, it goes live skill with NASA, which is also developing a program aimed at an asteroid.
Tiangong-1 was the first laboratory It is a space telescope that China launched into orbit in 2011, with a length of 10.5 meters, a diameter of 3.4 meters and a weight of 8.5 tons. His goal was to carry out experiments within the Chinese space program and launch the permanent station that the CNSA seeks to have in orbit by 2023. Against all odds, in 2016 digital control of the ship was lost and destroyed in pieces over the Pacific Ocean, northwest of New Zealand. That same year, 2016, a second module, Tiangong-2, with the same objectives. On the other hand, China is making progress on the plan to establish a permanent space station. According to Yang Liwei, the core capsule will be launched in 2020 and the two experimental modules in the following two years, with manned missions and cargo spacecraft.
[Bruno Maçães, The Dawn of Eurasia. On the Trail of the New World Order. Allen Lane. Milton Keynes, 2018. 281 pp]
review / Emili J. Blasco
 |
The discussion on the emergence of Eurasia as an increasingly compact reality, no longer as a mere geographical description that was conceptually a chimera, owes much to the contribution of Bruno Maçães; particularly to his book The Dawn of Eurasia, but also to his continuous proselytizing to different audiences. This Portuguese diplomat with research activity in Europe notes the consolidation of the Eurasian mass as a single continent (or supercontinent) to all intents and purposes.
"One of the reasons we have to start thinking about Eurasia is because this is how China is increasingly looking at the world (...) China is already living a Eurasian age," says Maçães. What is new about it, he says, "is not that there are such connections between continents, but that, for the first time, they work both ways. Only when the influence flows in both directions can we speak of an integrated space." The Silk Belt and Road Initiative, especially its overland route, sample that China is no longer looking only to the Pacific, but is also contemplating new routes to Europe.
Maçães urges Europe to adopt a Eurasian perspective, for three reasons: because Russia and China have one; because most of the big foreign policy issues of our time have to do with how Europe and Asia are connected (Ukraine, refugee crisis, energy and trade); and because all the security threats of the coming decades will play out in a Eurasian context. Maçães adds a final reason why Europe should become more actively involved in the Eurasian integration project : it is the way to combat the forces of disintegration that exist within Europe itself.
From the various considerations included in the book, some suggestive ideas could be highlighted. One is that Russia's historic problems of identity, straddling Europe and Asia - seeing itself as different from the Europeans and at the same time being attracted by the modernity of the West - are now being replicated in the East, where China is on its way to creating a second pole of economic growth and integration in the supercontinent. If Europe is one of the poles and Asia (China and the other successful countries of the Far East) the other, then what is Russia, if it does not fully respond to the European and Asian identities?
The Silk Belt and Road Initiative gives geopolitical importance to Central Asia, as Maçães reviews. Thus, China needs a clear dominance of Xinjiang, its westernmost province and the gateway to the Central Asian republics. The land route to Europe cannot exist without the Xinjinag segment, but at the same time the exhibition of this Uyghur-majority territory to trade and modernization could accentuate its separatist aspirations. Just northwest of Xinjiang is the ex-Soviet republic of Kazakhstan, a vast country of great agricultural value, where Chinese attempts to buy land are being viewed with high suspicion from its capital, Astana. Maçães estimates that if Russia were to try to reintegrate Kazakhstan into its sphere of influence, as vehemently as it has done with Ukraine, "China would not stand aside."
Not only are the East Coast (European peninsula) and the West Coast (Pacific coast) moving closer together, but the connections between the two also improve logistical conditions in the interior of the supercontinent. This is precisely one of the objectives of the Silk Belt and Road Initiative: as Chinese companies have moved away from coastal business hubs to lower labor costs, they are moving farther away from ports and therefore need better land connections, thus contributing to the shrinking of Eurasia.
Beijing accelerates its change in economic strategy as Germany tries to reinvent itself as a manufacturing powerhouse with its 'Industry 4.0'
From being the great factory of the lowest products in the world price chain to becoming a manufacturing powerhouse appreciated by the added value that China can contribute to its production. The 'Made in China 2025' plan is underway with the purpose to operate change in a few decades. The Chinese push is intended to be countered by Germany with its 'Industry 4.0', in order to preserve international recognition of what is produced by German industry.

▲ Huawei Booth at Mobile World Congress 2017 [Huawei]
article / Jimena Puga
"Made in China 2025" is a political-economic plan presented by Chinese Premier Li Keqiang in May 2015. The main goal of this initiative is the growth of Chinese industry, and in turn to foster the development in China's poorest areas in the interior of the country, such as Qinghai, Xinjiang and Tibet provinces. One of the goals is to increase the domestic content of basic materials to 40% by 2020 and 70% by 2025.
But what does the People's Republic want to achieve with this initiative? As Mu Ronping announced, director of the Innovation Center and development According to the Chinese Academy of Science, "I don't think the Made in China 2025 plan and other industry-related plans pose a threat to the Economics and innovation. These industrial policies derive from traditional Chinese culture. In China, whenever we set a new political or economic measure, we have high expectations. So, if we get only half of it, we will be satisfied. This view has led China to change and, to some extent, innovation."
China's economic developments
In 1978 Deng Xiaoping came to power and changed all the Structures Maoists. Thus, from an economic perspective, law has become a decisive element in resolving conflicts and maintaining social order in China. Deng tried to establish a socialist system, but with "Chinese characteristics." In this way, a Economics and, consequently, the obligation to develop new rules and Structures. In addition, the president introduced the concept of democracy as a necessary instrument for the new socialist China. The most important legal reform was the possibility of creating private businesses. In 1992, the expression "Economics of the socialist market", a label to hide a real capitalism (1).
The current president of the People's Republic, Xi Jinping, has spoken out against economic protectionism and in favor of balancing globalization to "make it more inclusive and equitable." It also added an increase in the study of current capitalism and capitalism. development socialism with Chinese characteristics is typical of the country, since if the party were to abandon Marxism it would lose "its soul and leadership", in addition to describing it as "irreplaceable to understand and transform the world".
The Made in China 2025 plan and Industry 4.0
Over the past decade, China has emerged as one of the most significant manufacturing miracles in history since the Industrial Revolution began in Britain in the 18th century. By the end of 2012, China had become a global leader in manufacturing operations and the world's second-largest economic power ahead of Germany. The Made in China paradigm has been evidenced by products made in China, from high-tech products such as computers or mobile phones to consumer goods such as air conditioners. The goal of the Central Empire is to extend this plan to three phases. In the first, from 2015 to 2025, China aims to be on the list of global manufacturing powers. In the second, from 2026 to 2035, China expects to position itself at a medium level in terms of global manufacturing power. And finally, in the third phase, from 2036 to 2049, the year in which the People's Republic will celebrate its centenary, China wants to become the world's leading manufacturing country.
In 2013, Germany, a world leader in industrialization, published its Industry 4.0 strategic plan. Known for its prestigious brands such as Volkswagen or BMW, the country's leading industries have emphasized its innovative strength that allows them to reinvent themselves again and again. The Industry 4.0 plan is another example of the German country's manufacturing strategy to compete in a new industrial revolution based on industrial integration, the integration of industrial information, the Internet and artificial intelligence. Germany is known worldwide for thedesign and quality of their products. The Industry 4.0 plan, presented in 2013 by the German government, focuses on the smart factory, i.e. making the factories of the future more sustainable and intelligent; in cyber-physical systems, which integrate advanced technologies such as automotive, exchange of data in manufacturing technology and 3D printing, and in goods and people.
Both plans, Industry 4.0 and Made in China 2025 , focus on the new industrial revolution and employ elements of manufacturing digitalization. The core of the German plan is the cyber-physical system, i.e. a mechanism controlled or monitored by algorithms closely linked to the Internet and its users, and integration into dynamic value creation mechanisms. The Chinese plan, in addition to the "Internet Plus Industry" action plan, has a goal Particular focus is on consolidating existing industries, promoting diversity and widening the scope for action of many industries, enhancing regional cooperation through the use of the Internet for borderless manufacturing, innovation of new products and improvement of product quality.
By 2020, the United States will be the most competitive country in manufacturing in the world, followed by China, Germany, Japan, India, South Korea, Mexico, Taiwan, Canada, and Singapore. Of these ten countries, six are Asian countries, one is European and the remaining three are members of NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement).
This new shift in industrial strategy translates into a world anticipation of a fourth industrial revolution brought about by technological advances. China will undoubtedly be one of the international leaders of this revolution thanks to the Made in China 2025 and One Belt One Road plans, however, the new emerging economies such as South Africa, Vietnam or Hungary that have contributed to the Economics in recent years will require more attention.
(1) Vid. ARANZADI, Iñigo González Inchaurraga, Derecho Chino, 2015, p. 197 et seq.
The need for close air support in the fight against ISIS has led to a rethink of the preference of technology over effectiveness
In recent decades, the constant commitment to technological improvement has led to the discarding of old models of combat aircraft that, properly equipped, are proving to be more effective in counterinsurgency operations. The urgencies posed especially by the fight against the Islamic State have turned these old models into a kind of Special Operations capability of the Air Force.

▲ OV-10 Bronco [USAF, TSgt Bill Thompson]
article / Ignacio Yárnoz
August 2015. In the framework of the "Combat Dragon II" Special Operations Program, two OV-10G+ Bronco jets take off from a U.S. air base in northern Iraq. The mission statement of these twin-engine aircraft from the time of the Vietnam War is double. Firstly, to help Peshmerga fighters in the face of attacks by Daesh insurgents (al-Dawla al-Islamiya al-Iraq al-Sham); the second, to demonstrate the effectiveness of low-cost propeller aircraft in COIN (Counter Insurgency) operations. The mission statement It turned out to be a success and made many things rethink in the Pentagon, where astonishment flooded the offices at the mission statement counterinsurgency with aircraft from 50 years ago.
It is important to highlight the three fundamental pillars that made this mission statement a success. First of all, there is the human factor that was part of the mission statement. The brave pilots who embarked on it were carefully chosen for their experience in special missions, as well as being instructor officers of the USAF Weapons School. This was of great importance given the delicacy of the mission statement and the precision it required. Here's why.
The second pillar to highlight is the weaponry and material used. More specifically, these are the new, but very promising APKWS (Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System) laser-guided rockets and multiple modern infrared surveillance systems such as the MX-15HD FLIR. The first are 70 mm rockets similar to the "Hydra" (an American system of air-to-air/air-to-ground rockets known to be the most widely used in the world as helicopter weapons) to which a laser guidance and control system can be incorporated. They are rockets that can be fired either from very close or at longer distances at all angles you want, giving a very wide margin of fire to the pilot that gives him a significant tactical advantage. In addition, its high accuracy means that it can eliminate enemies or destroy lightly armored vehicles with an efficiency that other systems would not be able to achieve, at least not without causing greater collateral damage. There's the core topic Discussed in the first pillar: pilots experienced in the handling of precision weapons accompanied by the appropriate means make this a perfect combination that turned the OV-10G+ Bronco into true precision weapons.
Finally, and as a third pillar, there is the aircraft itself: the OV-10G+ Bronco (or "Black Pony"). This Vietnam War veteran is an aviation legend. The Bronco was born after the U.S. Navy and Air Force approved a triple-duty specification called "LARA" (Light Armed Reconnaissance Aircraft), issued in late 1963 and designed for that war. LARA was based on the need for a new subject light attack aircraft and observation for "jungle fighting". During the conflict, the Broncos conducted observation operations, forward air control, helicopter escort, armed reconnaissance, light transport services, and limited ground attack actions. The Broncos also conducted airborne radiological reconnaissance, tactical aerial observation and for naval artillery, as well as aerial control of tactical support operations and, on the battlefront, aerial photography of leave height.
However, doctrines have changed since smart bombs were integrated into air forces. Advanced air control, one of the primary missions of this aircraft, passed into the hands of elite ground troops with laser designators and digital transmissions. The concept of using Broncos to loiter over an area and drop ammo was not explored. Finally, the apparatus was given the necessary leave in July 1994.
|
A-10 Thunderbolt [USAF, MSgt William Greer] |
OV-10 Bronco and A-10 Thunderbolt
It is a light attack and observation aircraft powered by two turboprops that, although it is a fixed-wing aircraft, meets the capabilities of a helicopter and a drone. Like drones, the OV-10 can hover over the battlefield for hours, but with greater visibility than an RQ9 Reaper and with greater weaponry capacity. The model The original was capable of flying at a speed of up to 560 km/h, carrying up to 3 tons of external ammunition and staying hover over an area for more than three hours. Finally, this versatile device is capable of operating from short or semi-prepared tracks (STOL) with low operating and maintenance costs. In most cases it can fly with only one engine. The latter makes the OV-10 Bronco and all its counterparts a great asset given that while jet aircraft have great fuel consumption on each flight (starting at $20,000 for the cheapest jet, the F16), light attack jets only cost a few thousand dollars per operation. In addition, the aircraft currently available can only take off and land on long, expensive runways that must be located hundreds of kilometres from the front line and, as a result, the effective time of their missions is shorter and their fuel consumption is higher.
However, the USAF's trend has always tipped the scales toward high-tech rather than effectiveness. Since World War II and the beginning of the Cold War, the American way of fighting has been to rely on superior technology. There has been a constant approach in the most important technological advances in which it is at the forefront. However, these effective aircraft have found a niche within the Army, possibly the Air Force Special Operations. The need for close air support in the fight against ISIS has led many commanders to rethink their strategy. In fact, it also helped convince the Air Force to reconsider its plans to retire the A-10 Thunderbolt II (A-10 Warthog as it is nicknamed in the USAF). The reasons turn out to be analogous to the start-up of aircraft such as the OV-10 Bronco: the need for effectiveness, experience, close air support and advanced air control, all combined with low maintenance costs.
In the case of the A-10 Thunderbolt II, it is an aircraft designed specifically around its main weapon, a 30mm GAU-8/A cannon mounted directly under the fuselage. With a 540 kg titanium armor, it incorporates two General Electric TF34-GE-100 turbines mounted in an elevated position, so that the aircraft can land in austere environments such as difficult, dirty or sandy terrain. In addition, the aerodynamics and technology of the engines allow the A-10 to fly slower and lower, and therefore closer to forces on the ground and enemy targets, specifically at 555 km/h and at an altitude of 30 meters. Last but not least, it's cheap to buy (a average $11 million for each of the 715 built) and operating (about $17,000 per flight hour).
Although the OV-10 Bronco was not ultimately selected by the USAF in the framework of the Combat Dragon II, has marked a milestone in aeronautical history. The USAF has finally decided to opt for the model Brazil's A29 SuperTucano, a two-seater aircraft that speeds around 580 km per hour and possesses the sophisticated avionics typical of fourth-generation fighters, including radar warning receivers, front-scan infrared sensors, and the ability to launch bombs and precision-guided missiles. In final, an aircraft with the same advanced air control and tactical observation capabilities as the OV-10 Bronco. This model it is already part of the Afghan, Lebanese and Nigerian air forces (countries with insurgency threats such as Boko Haram, Hezbollah and Al-Qaeda) as well as being in the process of replacing the Broncos in the Philippines, where the same counterinsurgency techniques used in Iraq to fight Daesh in this region are also being applied. Regardless of whether it's the legendary Bronco, the paradigm is still latent. It has been proven that light aviation can be able to establish itself as a powerful ally in today's COIN operations.
The Trump Administration endorses fill in in the European theater the deployment of the Aegis system put in place by Obama.
The main defense deployment in Europe is the Ballistic Missile Defense System, a NATO capability that has been completed following the so-called European Phased Adaptive approach (EPAA). Put in place during the Obama Administration, the Trump Administration has just ratified it in its Missile Defense Review. The withdrawal of the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Weapons Treaty (INF Treaty), which bound the United States and Russia, puts the missile defense system on the diary of European priorities.

▲ Launching of the ESSM missile from the Spanish frigate Álvaro de Bazán [Armada].
article / Martín Biera
In the pre-industrial era, battles were largely fought face to face, but in the technological era the line of defense can be placed at a great distance. Thus, in Europe the main defense deployment is the Ballistic Missile Defense System. This is a NATO capability that integrates the Aegis naval system and the Patriot land-based system, produced by Lockeed Martin and Raytheon, respectively, which can be used in the same scenario.
Its deployment in Europe was proposed by the Obama Administration in 2009 in what is known as approach European Phased Adaptive Approach (EPAA). This program aims to progressively develop anti-ballistic capabilities that will assist in the defense of NATO allies in the European theater.
The Missile Defense Review document, released by the Pentagon in January, reiterates the U.S. commitment to the planned program. "The United States is committed to fill in the deployment of the EPAA," the text states.
If in other respects, the Trump Administration has shown signs of a certain withdrawal of its military deployment in the world, on this point it maintains its technological and operational contribution so that NATO can sustain in the European theater its missile defense architecture. "The United States will strengthen regional missile defense capabilities and cooperative relations with its allies and partners," the document adds. It calls, however, as it has already done in relation to overall contributions to NATO by its member states, for "additional allied investment in missile defense, including development and joint production, to better share the common defense burden."
Phased implementation
The EPAA is planned in four phases, from agreement with the Polish Foreign Ministry and the administration of former President Obama in the strategy of implementing advanced anti-ballistic missile systems in Europe.
The first phase, implemented in 2011, included the deployment in the Mediterranean Sea of ships equipped with the Aegis Anti-Ballistic Missile System (SAMB) and SM-3 IA missile launchers capable of intercepting short and medium range missiles (up to 3,000 kilometers). The frigate Álvaro de Bazán is equipped with the Aegis combat system (the Spanish Navy is the only one in Europe, besides the Norwegian Navy, integrated in this system). It also included the installation of a radar device located in Turkey, the AN/TPY-2, which operates in the X-band (microwave section of the electromagnetic spectrum, used by communication satellites).
The second phase was implemented in 2015. It additionally covers the deployment in Romania of a surface-to-air missile launch system subject IB-SM-3 capable of countering short- and medium-range missiles of more than 500 kilometers effective range, and the deployment of the four ships with the Aegis AMB capability. AN/TPY-2 radar capabilities were enhanced with an additional network of sensors.
The third phase, in 2018, consisted of the deployment in Poland of a ground-based subject II-SMA missile launcher capable of combating intermediate-range missiles (IRBM up to 5,500 km). The launchers are located at the Redzikowo base.
The last phase will take place in 2020 and will allow U.S. allies to improve anti-missile systems against medium- and long-range missiles and ICMBs, culminating in the implementation of SM-3 Block IIB systems that will also include a command and control system.
Thus, the SAMB Aegis system includes the capabilities deployed on the two permanent instructions (in Poland and Romania) and on board four Aegis BMD ships (in the Mediterranean Sea, based in Rota), as well as a radar operating in the X-band and a network of sensors, which makes it possible to defend the European continent against short, medium and long-range missiles.
Operation
First, infrared and communication satellites provide early warning. When a ballistic missile is launched, it is detected by the infrared satellite; the information it picks up is sent to a communications satellite, which notifies a NATO headquarters, where it is analyzed. In the case of Europe, this information is sent to the Ramstein base in Germany, where it is confirmed whether the projectile is a threat. It is then communicated to all appropriate forces, both commanders and defense systems.
When the engine finishes burning the fuel on the missile's upward trajectory, the infrared satellite can no longer detect it, so long-range sensors, such as the AN/TPY-2 system or the Smart-L Radar naval system located in Holland, are used. These sensors detect and continue analyzing the missile so that it can be intercepted. The process also integrates the Aegis system, which consists of AN/SPY-1 radars capable of tracking more than 100 objects. Together, these systems perform a more detailed analysis of the tracking and possible consequences of a ballistic missile.
All systems, on land, at sea and in the air, have the ability to share and update instantly share information. The core topic of this system is the ability to destroy the missile outside the atmosphere, largely thanks to the Aegis system, although systems such as THAAD can also provide additional capabilities. The Aegis system provides cover for missiles that have passed through the atmosphere; in the event that a missile re-enters the atmosphere, the Patriot system, which is used by France, Germany, Spain and other countries, comes into operation.
Patriot System
Following Poland's decision to allocate a higher percentage of GDP to defense, the country is expected to increase its military capacity. On March 28, Poland signed a $4.75 billion agreement with the United States for the purchase of the Patriot missile system. Its manufacturer, Raytheon, undertook to build in Poland parts core topic of the system, creating "new high-tech jobs", as required by Polish law.
Poland will join fifteen other countries in Europe, the Pacific and the Middle East that share and operate with this system This agreement comes after Poland signed a ten-year agreement with Raytheon to facilitate the introduction of Patriot missiles among the country's defensive capabilities. In mid-2018 Warsaw ran into some complications in acquiring the Patriots, as the civil service examination put up roadblocks to the approval of the purchase. Finally, the Polish government and Raytheon signed the project at the agreed value of €4.75 billion.
In November 2017 Romania and Sweden also showed interest in purchasing Patriots. In the case of the Middle East, the countries that mainly use this system are Israel and Qatar, although the Pentagon has expressed its desire to withdraw its batteries from the region.
|
outline of the Ballistic Missile Defense System [Ministry of Defense of Japan]. |
Russian alternative
The Polish purchase of Patriot missiles was criticized by Russia. Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova condemned the "progressive militarization" of that country. Moscow sees such "militarization" moves as an element of destabilization of the military and political apparatus in Europe and a threat to Russia.
The Kremlin criticized the deployment of the Patriot missile system batteries as a violation of the arms control treaty signed in 1987 between Mikhail Gorbachev and Ronald Reagan. This Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF Treaty) is about to be abandoned by the United States on the grounds that Russia has been violating it with some of its missile developments.
In response to degree program for advances in surface-to-air missile technology, the Russian arms industry developed the S-400 Triumf, which NATO designates as the SA-21 Growler. The S-400 system is a mobile defense system, which offers greater versatility and firepower. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, Turkey and India have shown interest in purchasing this system despite US sanctions. The fact that major users and customers of U.S. weapons are interested in competing companies poses a problem for the U.S. military industry. The S-400 is capable of reaching a flight ceiling of 185 kilometers and an effective range distance of 120, 250 and 400 kilometers depending on the missile employee. By 2020 the Russian Army will have a new generation missile system, the S-500, a more advanced and more powerful version than the current ones.
Deterrence
"Invincibility is in oneself, vulnerability is in the adversary.
Invincibility is a matter of defense, vulnerability is a matter of attack. As long as you have not observed vulnerabilities in the order of battle of the adversaries, hide your own attack training , and prepare to be invincible, in order to preserve yourself. When adversaries have vulnerable orders of battle, it is time to go out and attack them." The Art of War, Sun Tzu.
Both NATO and Russian systems clearly have a deterrent facet. Every military operation has a relevant diplomatic, political and interest role. After the Russian annexation of Crimea and the Vostok 2018 and Trident Juncture maneuvers, missile defense systems appear to be the future of European and international security. In recent years, in a context of militarization of space by the world's military powers, a update of missile systems is underway that not only makes it possible to reach farther but also to be more precise. From agreement with the defense strategy of both the European and the Atlantic organization has led its partners to have better capabilities than their competitors to ensure the security of States. Consequently, a progressive but effective modernization of anti-missile systems.
In recent years, in the face of Russia's and China's advancement and modernization of weapons, the United States has seen the need to develop space-based systems capable of shooting down missiles, with some resemblance to the cancelled Pebbles Program. The Pebbles program sought to put into orbit autonomous systems capable of intercepting any missile launched by U.S. competitors. These systems would provide the U.S. and its allies with a capability to counter almost any subject projectile, giving them an unprecedented advantage. The employment of anti-missile systems strengthens the bond between the United States and its allies, thus enabling more effective defense and cooperation as a necessary relationship.
On the other hand, there are analysts who can see this escalation in the purchase and use of AMB systems as a new cold war, at least on a smaller scale, mainly because it is taking place in Europe and in new facets such as the economic one, manifested through the influence that arms companies exert over national governments.
Showing the range 271 - 280 of 427 results.