Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs North America .
![US border patrol vehicle near the fence with Mexico [Wikimedia Commons]. US border patrol vehicle near the fence with Mexico [Wikimedia Commons].](/documents/10174/16849987/us-border-blog.jpg)
▲ US border patrol vehicle near the fence with Mexico [Wikimedia Commons].
ESSAY / Gabriel de Lange
I. Current issues in the Northern Triangle
In recent years, the relationship between the Northern Triangle Countries (NTC) -Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador- and it's northern neighbours Mexico and the United States has been marked in mainstream average for their surging migration patterns. As of 2019, a total of 977,509 individuals have been apprehended at the Southwest border of the US (the border with Mexico) as compared to 521,093 the previous year (years in terms of US fiscal years). Of this number, an estimated 75% have come from the NTC[1]. These individuals are typically divided into three categories: single adults, family units, and unaccompanied alien children (UAC).
As the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) reports, over 65% of the population of the NTC are below 29 years of age[2]. This is why it is rather alarming to see an increasing number of the youth population from these countries leaving their homes and becoming UAC at the border.
Why are these youths migrating? Many studies normally associate this to "push factors. The first factor being an increase in insecurity and violence, particularly from transnational organised crime, gangs, and narco-trafficking[3]. It is calculated that six children flee to the US for every ten homicides in the Northern Triangle[4]. The second significant factor is weak governance and corruption; this undermines public trust in the system, worsens the effects of criminal activity, and diverts funds meant to improve infrastructure and social service systems. The third factor is poverty and lack of economic development; for example in Guatemala and Honduras, roughly 60% of people live below the poverty line[5].
The other perspective to explain migration is through what are called "pull factors." An example would be the lure of economic possibilities abroad, like the high US demand for low-skilled workers, a service that citizens of NTC can provide and be better paid for that in their home countries. Another pull factor worth mentioning is lax immigration laws, if the consequences for illegal entry into a country are light, then individuals are more likely to migrate for the chance attaining better work, educational, and healthcare opportunities[6].
II. US administrations' strategies
A. The Obama administration (2008-2015)
The Obama administration for the most part used the carrot and soft power approach in its engagement with the NTC. Its main goals in the region being to "improve security, strengthen governance, and promote economic prosperity in the region", it saw these developments in the NTC as being in the best interest of US national security[7].
In 2014, in the wake of the massive surge of migrants, especially UACs, the administration launched the reform initiative titled the Plan of the Alliance for Prosperity (A4P). The plan expanded across Central America but with special focus on the NTC. This was a five year plan to address these "push factors" that cause people to migrate. The four main ways that the initiative aims to accomplish this is by promoting the following: first, by fostering the productivity sector to address the region's economic instability; second, by developing human capital to increase the quality of life, which improves education, healthcare and social services; third, improving citizen security and access to justices to address the insecurity and violence threat, and lastly, strengthening institutions and improving transparency to address the concerns for weak governance and corruption[8].
This initiative would receive direct technical support and financing from the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB). In addition, major funding was to be provided by the US, which for the fiscal years of 2015-2018 committed $2.6 billion split for bilateral assistance, Regional Security Strategy (RSS), and other regional services[9]. The NTC governments themselves were major financiers of the initiative, committing approximately $8.6 billion between 2016-2018[10].
The administration even launched programs with the US Agency for International Development (USAID). The principle one being the Central American Regional Security Initiative (CARSI), with a heavy focus on the NTC and it's security issues, which allotted a budget of $1.2 billion in 2008. This would later evolve into the larger framework of US Strategy for Engagement in Central America in 2016.
The Obama administration also launched in 2015 the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA), which currently allows individuals who were brought to the US as children, and have unlawful statuses to receive a renewable two-year period of deferred action from deportation[11]. It is a policy that the Trump administration has been fighting to remove these last few years.
Although the Obama administration was quite diplomatic and optimistic in its approach, that didn't mean it didn't make efforts to lessen the migration factors in more aggressive ways too. In fact, the administration reportedly deported over three million illegal immigrants through the Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), the highest amount of deportations taking place in the fiscal year of 2012 reaching 409,849 which was higher than any single one of the Trump administration's reported fiscal years to date[12].
In addition, the Obama administration used educational campaigns to discourage individuals from trying to cross into the US illegally. In 2014 they also launched a Central American Minors (CAM) camp targeting children from the NTC and providing a "safe, legal and orderly alternative to US migration"[13]. This however was later scrapped by the Trump Administration, along with any sense of reassessment brought about by Obama's carrot approach.
![Number of apprehensions and inadmissibles on the US border with Mexico [Source: CBP]. Number of apprehensions and inadmissibles on the US border with Mexico [Source: CBP].](/documents/10174/16849987/us-border-grafico.png)
Number of apprehensions and inadmissibles on the US border with Mexico [Source: CBP].
B. The Trump administration (2016-present)
The Trump administration's strategy in the region has undoubtedly gone with the stick approach. The infamous "zero tolerance policy" which took place from April-June 2018 is a testimony to this idea, resulting in the separation of thousands of children from their parents and being reclassified as UAC[14]. This was in an attempt to discourage individuals in the NTC from illegally entering the US and address these lax immigration laws.
From early on Trump campaigned based on the idea of placing America's interests first, and as a result has reevaluated many international treaties and policies. In 2016 the administration proposed scaling back funds for the NTC through the A4P, however this was blocked in Congress and the funds went through albeit in a decreasing value starting with $754 million in 2016 to only $535 million in 2019.
Another significant difference between the two administrations is that while Obama's focused on large multi-lateral initiatives like the A4P, the Trump administration has elected to focus on a more bilateral approach, one that goes back and forth between cooperation and threats, to compliment the existing strategy.
Towards the end of 2018 the US and Mexico had announced the concept of a "Marshal Plan" for Central America with both countries proposing large sums of money to be given annually to help improve the economic and security conditions in the NTC. However in this last year it has become more apparent that there will be difficulties raising funds, especially due to their reliance on private investment organisations and lack of executive cooperation. Just last May, Trump threatened to place tariffs on Mexico due to its inability to decrease immigration flow. President López Obrador responded by deploying the National Guard to Mexico's border with Guatemala, resulting in a decrease of border apprehensions by 56%[15] on the US Southwest border. This shows that the stick method can achieve results, but that real cooperation cannot be achieved if leaders don't see eye to eye and follow through on commitments. If large amount of funding where to be put in vague unclear programs and goals in the NTC, it is likely to end up in the wrong hands due to corruption[16].
In terms of bilateral agreements with NTC countries, Trump has been successful in negotiating with Guatemala and Honduras in signing asylum cooperative agreements, which has many similarities with a safe third country agreement, though not exactly worded as such. Trump struck a similar deal with El Salvador, though sweetened it by granting a solution for over 200,000 Salvadorans living in US under a Temporary Protection Status (TPS).[17]
However, Trump has not been the only interested party in the NTC and Mexico. The United Nations' ECLAC launched last year its "El Salvador-Guatemala-Honduras-Mexico Comprehensive Development Program", which aims to target the root causes of migration in the NTC. It does this by promoting policies that relate to the UN 2030 diary and the 17 sustainable development goals. The four pillars of this initiative being: economic development, social well-being, environmental sustainability, and comprehensive management of migratory patters[18]. However the financing behind this initiative remains ambiguous and the goals behind it seem redundant. They reflect the same goals established by the A4P, just simply under a different entity.
The main difference between the Obama and Trump administrations is that the A4P takes a slow approach aiming to address the fundamental issues triggering migration patterns, the results of which will likely take 10-15 years and steady multi-lateral investment to see real progress. Meanwhile the Trump administration aims to get quick results by creating bilateral agreements with these NTC in order to distribute the negative effects of migration among them and lifting the immediate burden. Separately, neither strategy appears wholesome and convincing enough to rally congressional and public support. However, the combination of all initiatives -investing effort both in the long and short run, along with additional initiatives like ECLAC's program to reinforce the region's goals- could perhaps be the most effective mechanism to combat insecurity, weak governance, and economic hardships in the NTC.
[1] Nowrasteh, Alex. "1.3 Percent of All Central Americans in the Northern Triangle Were Apprehended by Border Patrol This Fiscal Year - So Far". Cato at Library. June 7, 2019. Accessed November 8, 2019.
[2] N/A. "Northern Triangle: Building Trust, Creating Opportunities." Inter-American Development Bank. Accessed November 5, 2019.
[3] Orozco, Manuel. "Central American Migration: Current Changes and Development Implications." The Dialogue. November 2018. Accessed November 2019.
[4] Bell, Caroline. "Where is the Northern Triangle?"The Borgen Project. October 23, 2019. Accessed November 6, 2019.
[5] Cheatham, Amelia. "Central America's Turbulent Northern Triangle." Council on Foreign Relations. October 1, 2019. Accessed November 6, 2019.
[6] Arthur, R. Andrew. "Unaccompanied Alien Children and the Crisis at the Border." Center for Immigration Studies. April 1, 2019. Accessed November 9, 2019.
[7] Members and Committees of Congress. "U.S. Strategy for Engagement in Central America: Policy Issues for Congress." Congressional Research Service. Updated November 12, 2019. November 13, 2019.
[8] N/A. "Strategic Pillars and Lines of Action." Inter-American Development Bank. 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[9] N/A. "Budgetary Resources Allocated for the Plan of the Alliance for Prosperity." Inter-American Development Bank. N/A. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[10] Schneider, L. Mark. Matera, A. Michael. "Where Are the Northern Triangle Countries Headed? And What Is U.S. Policy?" Centre for Strategic and International Studies. August 20, 2019. Accessed November 11, 2019.
[11] N/A. "Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA)." Department of Homeland Security. N/A. Accessed November 12, 2019.
[12] Kight, W. Stef. Treene, Alayna. "Trump isn't Matching Obama deportation numbers." Axios. June 21, 2019. Accessed November 13, 2019.
[13] N/A. "Unaccompanied Alien Children: An Overview." Congressional Research Service. October 9, 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[14] N/A. "Unaccompanied Alien Children: An Overview." Congressional Research Service. October 9, 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[15] Nagovitch, Paola. "Explainer: U.S. Immigration Deals with Northern Triangle Countries and Mexico." American Society/Council of Americans. October 3, 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[16] Berg, C. Ryan. "A Central American Martial Plan Won't Work." Foreign Policy. March 5, 2019. Accessed November 11, 2019.
[17] Nagovitch, Paola. "Explainer: U.S. Immigration Deals with Northern Triangle Countries and Mexico." American Society/Council of Americans. October 3, 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[18] Press Release. "El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras and Mexico Reaffirm their Commitment to the Comprehensive Development Plan." ECLAC. September 19,2019. Accessed November 11, 2019.
US agreements with the Northern Triangle may have had a deterrent effect before entering into force
In the first month following the extension of the Asylum Cooperation Agreements (ACA) to the three Northern Triangle countries, apprehensions at the US border have fallen below the levels of recent years. The actual reduction in migrant inflows that this evidences has to do with Mexico's increased control over its border with Guatemala, but may also be due to the deterrent effect of advertisement of the agreements, whose implementation has not yet fully begun and therefore has yet to demonstrate whether they will be directly effective.
![Honduran migrants held by Guatemalan border guards, October 2018 [Wikimedia Commons]. Honduran migrants held by Guatemalan border guards, October 2018 [Wikimedia Commons].](/documents/10174/16849987/tercer-pais-blog.jpg)
▲ Honduran migrants held by Guatemalan border guards, October 2018 [Wikimedia Commons].
article / María del Pilar Cazali
Attempts to entrance attempt to enter the United States through its border with Mexico have not only returned to the levels of the beginning of the year, before the number of migrants soared and each month set a new record high, reaching 144,116 apprehensions and inadmissions in May( USBorder Guard figures that provide an indirect assessment of migration trends), but have continued to fall to below several previous years.
In October (the first month of the US fiscal year 2020), there were 45,250 apprehensions and inadmissions at the US southern border, down from October 2018, 2015 and 2016 (but not 2017). This suggests that the total number of apprehensions and inadmissions in the new fiscal year will be well below the record of 977,509 recorded in 2019. This boom had to do with the caravans of migrants that began at the end of 2018 in the Central American Northern Triangle (Honduras, El Salvador and Guatemala), following a migratory flow that, with different intensities, began in the 1980s due to political and economic instabilities in those countries.
This migration crisis led President Trump's US administration to implement tougher deportation policies, including changing conditions for expedited deportations. In addition, the White House pressured Mexico with the threat of tariffs on its products if it did not help reduce the flow of migrants crossing Mexican soil, prompting President López Obrador to deploy the newly created National Guard to the border with Guatemala. Trump combined these measures with the negotiation of Asylum Cooperation Agreements (ACAs) with the Northern Triangle countries, which were initially improperly referred to as "safe third countries", adding to the controversy they generated.
agreement with Guatemala
Due to US threats to impose tariffs on Guatemala if it failed to reduce the issue of migrants from or through Guatemala on their way to the US, the Guatemalan government accepted the terms of a attention announced by Trump on 26 July 2019. The agreement foresees that those who apply for asylum in the US but have previously passed through Guatemala will be brought back to the US so that they can remain there as asylum seekers if they qualify. The US sees this as a safe third country agreement .
A safe third countryagreement is an international mechanism that makes it possible to host in one country those seeking asylum in another. The agreement signed in July prevents asylum seekers from receiving US protection if they passed through Guatemala and did not first apply for asylum there. The US goal is intended to prevent migrants from Honduras and El Salvador from seeking asylum in the US. Responsibility for processing protection claims will fall to Washington in only three cases: unaccompanied minors, persons with a US-issued visa or document Admissions Office , or persons who are not required to obtain a visa. Those who do not comply with requirements will be sent to Guatemala to await the resolution of their case, which could take years. On the other hand, the agreement does not prevent Guatemalan and Mexican applicants from seeking asylum in the US.
Guatemalan President Jimmy Morales had previously announced that a similar agreement could become part of the migration negotiations with the US. In Guatemala, after advertisement of what had been agreed, multiple criticisms arose, because the security conditions in both countries are incomparable. This was compounded by rumours about the true content of the agreement that Morales had signed, as it was not immediately revealed to the public. Faced with this uncertainty, Interior Minister Enrique Degenhart declared that the agreement was only for Hondurans and Salvadorans, not for nationals of other Latin American countries, and that the text did not explicitly mention the term "safe third country".
In the week following the advertisement, three appeals for amparo against the agreement were lodged with Guatemala's Constitutional Court, arguing that the country is not in a position to provide the protection it supposedly offers and that the resulting expense would undermine the economic status of the population itself. However, Degenhart defended agreement by saying that the economic repercussions would have been worse if the pact with Washington had not been reached, because with the US tariffs, half of Guatemala's exports and the jobs that accompany these sectors would be at risk.
These criticisms came not only from Guatemalan citizens, but also from public figures such as Guatemala's Human Rights Ombudsman, Jordán Rodas, citing a lack of transparency on the part of the government. Rodas insisted that Guatemala is not fit to be a safe third country because of its low indicators of production, Education, public health and security. Similar ideas have also been expressed by organisations such as Amnesty International, for whom Guatemala is not safe and cannot be considered a safe haven.
In its pronouncement, Guatemala's Constitutional Court affirmed that the Guatemalan government needs to submit the agreement to congress for it to become effective. This has been rejected by the government, which considers that international policy is skill directly the responsibility of the country's president and will therefore begin to implement what has been decided with Washington without further delay.
![Apprehensions and inadmissibilities by US Border Guard, broken down by month over the last fiscal years (FY) [Taken from CBP]. Apprehensions and inadmissibilities by US Border Guard, broken down by month over the last fiscal years (FY) [Taken from CBP].](/documents/10174/16849987/tercer-pais-grafico.png)
Apprehensions and inadmissibilities by US Border Guard, broken down by month over the last fiscal years (FY) [Taken from CBP].
Also with El Salvador and Honduras
Despite all the controversy generated since July as a result of the pact with Guatemala, the US developed similar efforts with El Salvador and Honduras. On 20 September 2019, El Salvador's president, Nayib Bukele, signed a agreement similar to the safe third country figure, although it was not explicitly called that either. It commits El Salvador to receive asylum seekers who cannot yet enter the US, similar to the agreement with Guatemala. El Salvador's agreement has the same three assumptions in which the US will have to make position of migrant protection.
The Salvadoran government has received similar criticism, including a lack of transparency in the negotiation and denial of the reality that the country is unsafe. Bukele justified signature by saying it would mean the extension of Temporary Protected Status (TPS) for the more than 190,000 Salvadorans living in the US. In October 2019, the Salvadoran Foreign Ministry said that this agreement is not a safe third country because El Salvador is not in the serious migratory situations in which Guatemala and Honduras are in terms of the flow of people, so it is only a agreement of non-violation of rights to minimise the number of migrants.
On 21 September 2019 the Honduran government also made public the advertisement of a agreement very similar to the one accepted by its two neighbours. It states that the US will be able to deport to Honduras asylum seekers who have passed through Honduras. Like the other two countries, the Honduran government was criticised as not being a safe destination for migrants as it is one of the countries with fees highest homicide rates in the world.
Despite criticism of the three agreements, in late October 2019 the Trump administration announced that it was in final preparations to begin sending asylum seekers to Guatemala. However, by the end of November, no non-Guatemalan asylum seekers had yet been sent. The inauguration in early January of President-elect Alejandro Giammattei, who announced his desire to rescind certain terms of agreement, may introduce some variation, though perhaps his purpose will be to wring some more concessions from Trump, in addition to the agricultural visas that Morales negotiated for Guatemalan seasonal workers.
The avalanche of unaccompanied foreign minors suffered by the Obama Administration in 2014 has been overcome in 2019 with a new migratory peak
In the summer of 2014, the United States suffered a migration crisis due to an unexpected increase in the number of people in the country. issue of unaccompanied foreign minors, mostly Central Americans, who arrived at its border with Mexico. What has happened since then? Although oscillating, the volume of this subject Immigration prices fell, but in 2019 a new record has been recorded, hand in hand with the "caravan crisis", which has led to the rise again in total apprehensions at the border.
![U.S. border agents search unaccompanied minors at Texas-Mexico border in 2014 [Hector Silva, USCBP–Wikimedia Commons] U.S. border agents search unaccompanied minors at Texas-Mexico border in 2014 [Hector Silva, USCBP–Wikimedia Commons]](/documents/10174/16849987/migracion-blog.jpg)
▲ U.S. border agents search unaccompanied minors at Texas-Mexico border in 2014 [Hector Silva, USCBP–Wikimedia Commons]
article/ Marcelina Kropiwnicka
The United States hosts more immigrants than any other country in the world, with more than a million people arriving each year, either as legal permanent residents, asylum seekers and refugees, or in other immigration categories. While there is no exact figure for how many people cross the border illegally, U.S. Customs and Border Control (U.S. Customs and Border Control) measures changes in illegal immigration based on the number of apprehensions made at the border; Such arrests serve as an indicator of the issue total number of attempts to enter the country illegally. As for the data, it can be concluded that there have been notable changes in the demographics of illegal migration at the border with Mexico (southwest border, in official U.S. terms) in recent years.
The peak of apprehensions at the U.S.-Mexico border was during 2000, when 1.64 million people were apprehended trying to enter the United States illegally. The numbers have declined, across the board, since then. In recent years, there have been more apprehensions of non-Mexicans than Mexicans at the border with the neighboring country, reflecting a decrease in issue of unauthorized Mexican immigrants who came to the U.S. in the last decade. The increase, in fact, was largely due to those fleeing violence, gang activity and poverty in Guatemala, Honduras and El Salvador, a region known as Central America's Northern Triangle.
The nations included in the Northern Triangle are among the poorest in Latin America – a high percentage of the population still lives on less than $2 a day (the international poverty line is $1.90); There has been little progress in reducing poverty in recent years. Within Latin America and the Caribbean, Honduras has the second highest percentage of the population living below the poverty line (17%), after Haiti, according to the latest data of the World Bank.
Unaccompanied Alien Minors
While fewer unaccompanied adults have attempted to cross the border without authorization over the past decade, there has instead been a surge of unaccompanied alien minors (MENAs) trying to enter the United States from Mexico. The migration of minors without accompanying adults is not new; What is new now is its volume and the need to implement policies in response to this problem. The increase in apprehensions of MENAs in FY2014 caused alarm and prompted both intense media scrutiny and the implementation of policy responses; Attention was maintained even as the phenomenon declined. The numbers dropped again to just under 40,000 apprehensions of minors the following year.
The international community defines an unaccompanied migrant minor as a person, "who is under eighteen years of age" and who is "separated from both parents and is not being cared for by an adult who by law or custom has the responsibility to do so." Many of these unaccompanied minors report immediately to U.S. border security, while others enter the country unnoticed and undocumented. Not only this, but children have no parents or legal guardians available to provide care or physical custody, which quickly overwhelms the services of local border patrols.
In 2014, many of the unaccompanied children said they were under the false impression that the Obama administration was granting "permits" to children who had relatives in the U.S., as long as they arrived no later than June. These false convictions and hoaxes were even more potent this past year, especially as President Trump continues to reinforce the idea of restricting migrants' access to the United States. The cartels have continued to transport a issue increasing number of Central American migrants from their countries to the United States.
Critical moments of 2014 and 2019
In 2014, during Obama's second term, total apprehensions along the border with Mexico reached 569,237 (this figure includes "inadmissible" people), a record only surpassed now. While the increase over the previous year was 13%, the increase was much more B regarding the arrests of MENAs; These rose from 38,759 in fiscal year 2013 to 68,541 in fiscal year 2014 (in the U.S. the fiscal year runs from October of one year to September of the next), an increase of almost 80%, more than four times those recorded in fiscal year 2011. In the case of minors from Honduras, the figure rose from 6,747 to 18,244 in one year; those of Guatemala rose from 8,068 to 17,057, and those of El Salvador, from 5,990 to 16,404 (those of Mexico, on the other hand, fell from 17,240 to 15,634). The Greatest issue The number of apprehensions occurred in May, a month in which MENA arrests accounted for 17% of total apprehensions.
Since 2014, apprehensions of unaccompanied minors, while fluctuating, have declined by issue. But in 2019 a new record has been recorded, reaching 76,020, with a maximum in the month of May. However, that month they accounted for only 9% of the total apprehensions, because this time it has not been a MENA crisis, but has been inserted into a B peak of total apprehensions. While overall apprehensions decreased significantly during the first six months of Trump's presidency, they then rose, reaching a total of 851,508 in 2019 (with the "inadmissible" the figure reached 977,509), which is more than double the number from 2018. The issue total apprehensions increased by 72% from 2014 to 2019 (in the case of MENAs the increase was 11%).
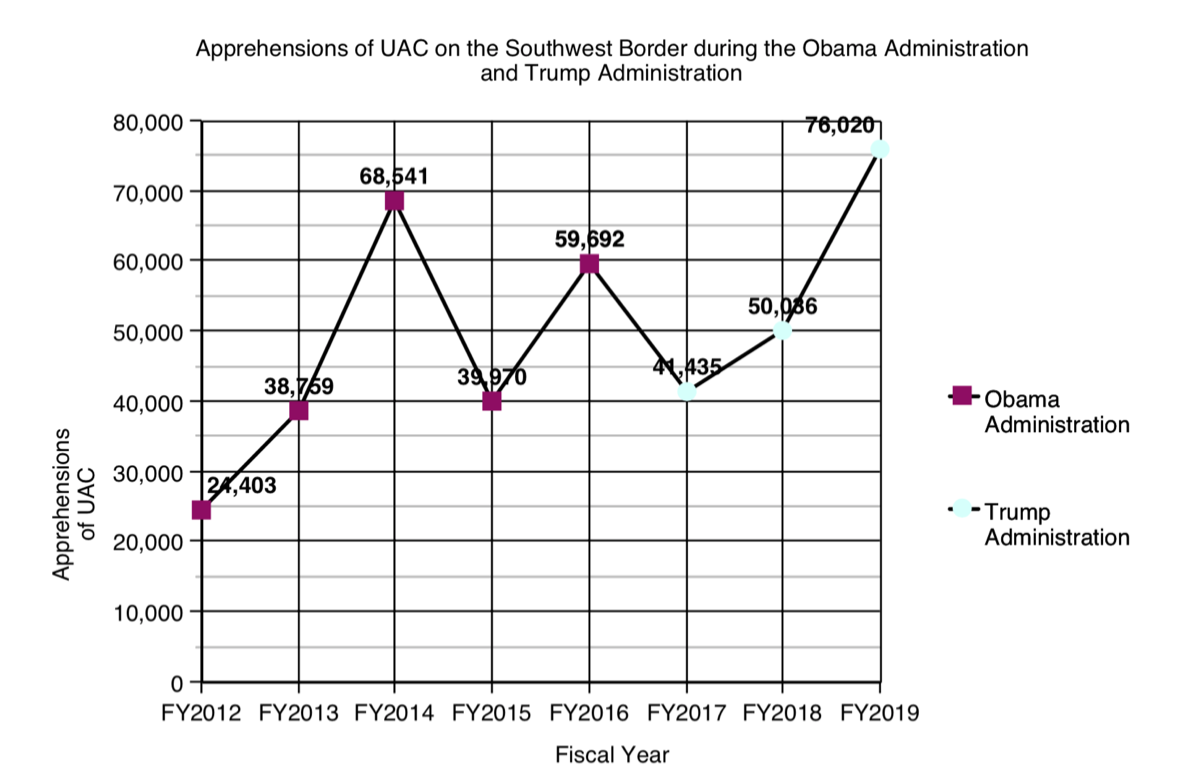 |
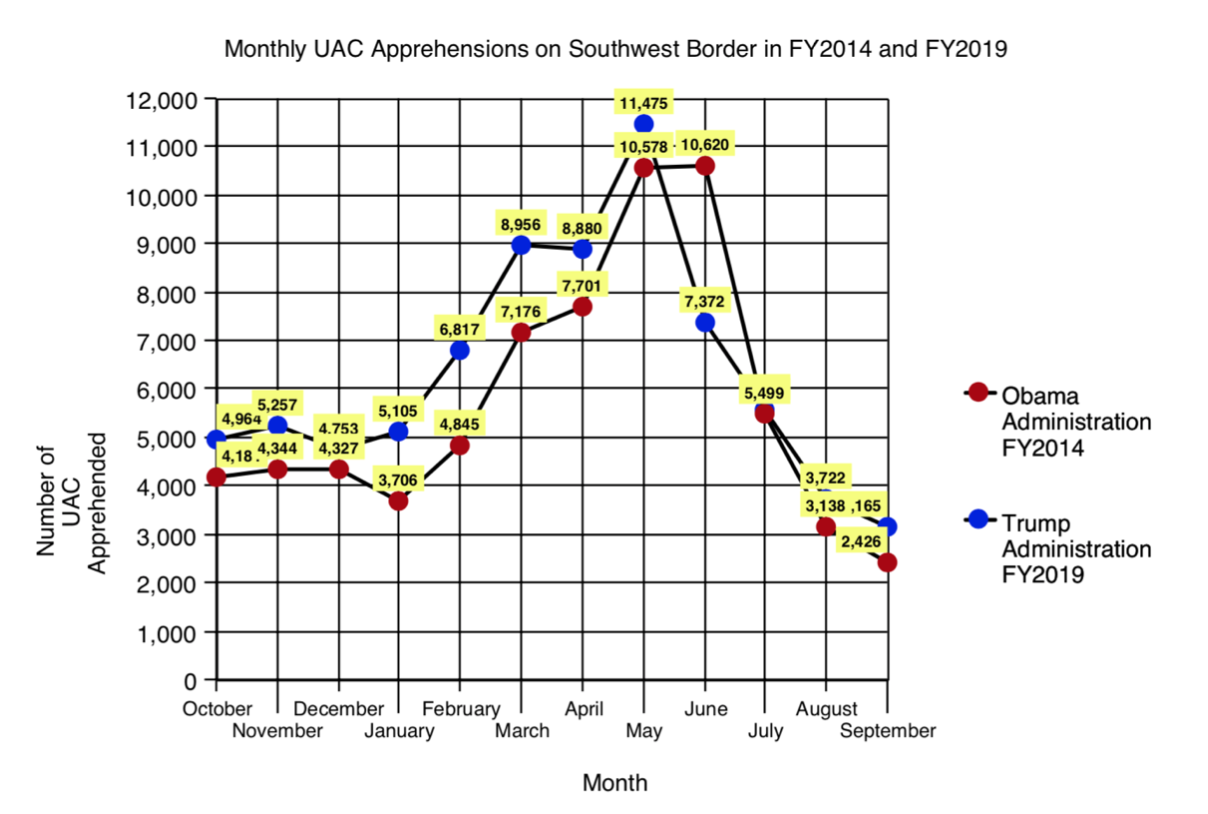 |
Apprehensions of unaccompanied alien minors at the U.S.-Mexico border, between 2012 and 2019 (Figure 1), and comparison of 2014 and 2019 by month (Figure 2). source: US Customs and Border Patrol.
Reaction
The U.S. had a variety of domestic policies aimed at dealing with the massive increase in immigration. However, with the overwhelming peak of 2014, Obama called for funding for a program for "the repatriation and reintegration of migrants to the countries of Central America and to address the root causes of migration from these countries." Although funding for the program has been fairly consistent over the past few years, the budget for 2018 proposed by the President Trump reduced the financial aid to these countries by approximately 30%.
The Trump Administration has made progress in implementing its diary on immigration, from the beginning of the construction of the wall on the border with Mexico to the implementation of new programs, but the hard line already promised by Trump in his degree program The U.S. government has proven ineffective in preventing thousands of Central American families from crossing the southwest border into the United States. With extreme gang violence running rampant and technicalities in the U.S. immigration system, migrants' motivation to leave their countries will remain.
Some U.S. and Canadian diplomats who were in Havana between 2016 and 2018 are still not fully recovered from ailments they suffered
![U.S. Embassy building in Cuba [department de Estado] [ de Estado] U.S. Embassy building in Cuba [department de Estado] [ de Estado]](/documents/10174/16849987/ataques-sonicos-blog.jpg)
▲ Building of the U.S. Embassy in Cuba [department de Estado].
ANALYSIS / Eduardo Villa Corta
Three years ago, staff U.S. diplomats stationed in Cuba began to feel physical discomfort supposedly caused by strange sounds to which they had apparently been exposed; Washington spoke of a "sonic attack. However, although the symptoms suffered by those affected have been determined to be anomalous, it has not been possible to establish what caused them. Was it really an attack? Who was behind it? We review here the main hypotheses and conjectures that have been made, and point out their weaknesses.
In late 2016 and early 2017, several U.S. diplomats stationed in Havana, as well as members of their families, reported suffering from dizziness, vertigo and sharp pains in their ears that could be caused by strange sounds to which they had been exposed. According to their testimonies, the sounds came from a specific direction, and they had heard them in their own residences or, in some cases, in hotel rooms, while people staying in neighboring houses or adjoining rooms had not heard any special sounds. The phenomenon also affected Canadian diplomats in the Cuban capital. In all, some forty people were treated for these symptoms.
Acoustic attack
Echoing the facts reported by its staff in Cuba, in mid-2017 the U.S. State department stated that the symptoms could have been caused by a sonic attack by the Cuban government directed against diplomats and their families. In October 2017, President Donald Trump directly accused Havana: "I believe Cuba is manager; yes, I do."
At the beginning of 2018 the department of State issued a statement alert not to travel to Cuba due to a possible health crisis and withdrew a good part of the staff of the mission statement diplomatic in Havana, reducing the activity of this to the minimum possible. At that time, a total of 24 Americans had been affected.
At the time, the Canadian government also indicated that its diplomats had experienced similar discomfort. Ottawa decided to evacuate the families of its employees in Cuba and in early 2019 proceeded to reduce the staff of the embassy in the face of what appeared to be the appearance of a fourteenth case.
The Cuban government denied from the outset being involved in any harassment operation against the U.S. or Canada. ˝There is no test about the cause of the reported ailments, nor is there any evidence to suggest that these health problems have been caused by an attack of any kind˝, Havana assured. Raul Castro's government offered its cooperation in the research of the facts, with nothing coming to light that could explain the case. No devices that could have provoked the sounds appeared.
Adding confusion to the status, at least two US diplomats stationed in China, busy at the consulate general in Guangzhou, the largest that the US has in the country, presented in early 2018 also the symptoms already described. Washington evacuated them and issued a health warning about missions in mainland China.
The Associated Press published in October 2017 a recording of the alleged sounds causing the reported ailment, and indicated that government agencies had been unable to determine the nature of the noise and explain its relationship to the bodily disorders caused. Months later, he noted that internal FBI reports did not even establish that there had been an "attack". Other media highlighted the poor cooperation in the research, due to jurisdictional zeal, between the department of State, the FBI and the CIA.
Symptoms of "Havana syndrome".
A medical team from the University of Pennsylvania, at the request of the U.S. Government, examined 21 people affected by what the press began to call "Havana syndrome". The research, initially published in March 2018 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), indicated that most of the patients reported problems with report, concentration, and balance, and determined that they appeared to have suffered injuries to extensive brain networks.
data Further MRI scans of the same team extended to 40 patients, released in July 2019, led to the conclusion that the diplomats had experienced some craniocerebral trauma. The results of the MRI scans, compared with those of a group of healthy people, showed differences in the volume of the white and gray substances of the brain, in the integrity of the cerebellar microstructures and in the functional connectivity of the subnetworks for hearing and spatial vision, but not for executive functions.
This report concluded that the staff diplomat had been physically injured, although it could not determine the cause. He also noted that patients do not experience a usual recovery, as they are not recovering quickly from symptoms, as is the case in other cases of similar "concussions" or ear problems.
IF IT WASN'T AN ATTACK, WHAT WAS IT?
As no clear cause has been established as to what caused the ailments suffered by the US and Canadian diplomatic staff and some members of their families, the very reality of an attack has been called into question. Although various alternative explanations have been put forward, none of them are fully convincing.
1) Collective hysteria
Formulation. Some neurologists and sociologists, such as Robert Bartholomew, have suggested that it could be a case of mass hysteria. Given the pressure to which some of the diplomats working in very unfriendly environments are subjected, and the endogamic relationship in which they live, living almost exclusively among themselves, it could explain a mutual conviction of an external attack that even has somatic consequences.
Weak spot. Both the research of the University of Pennsylvania and the doctor of the department of State, Charles Rosenfarb, who appeared before the committee of Foreign Relations of the Senate, came to rule out that the symptoms suffered by the diplomats were due to a mere mental mechanism. It is very difficult that about sixty people, including Americans and Canadians, convinced each other of an aggression of this kind subject and then almost all of them developed the same brain lesions.
2) Microwave
Formulation. The researcher team at the University of Pennsylvania, while not pointing to any possible cause of the ailments, did not rule out certain assumptions, such as that of microwave affectation. This aspect was insisted upon by a research published in 2018 in the journal Neural Computation, which considered the symptoms consistent with exhibition to electromagnetic microwave (RF/MW) radiation.
Weak point. Not all the symptoms shown by patients could be a consequence of the exhibition of such a radiation subject, which also has a diverging literature on its effects on the human body. In addition, there is no known microwave weapon that can affect the brain.
3) Ultrasound
Formulation. A team of computer experts at the University of Michigan suggested in 2018 that it could be a case of exhibition to some subject ultrasound, perhaps coming from malfunctioning listening equipment mixing multiple ultrasonic signals.
Weak point. The recording of one of the sound episodes - the sample broadcast by AP - is not sufficient to be able to determine its nature. It is also possible that the sound was somewhat different in other cases.
4) Crickets
Formulation. A research from the Universities of California-Berkeley and Lincoln, from the existing sound sample , considered in January 2019 that the possible cause of the attacks was made by cricketsThe study, specifically crickets Anurogryllus muticus. The research was a comparative study between the sound emitted by that variant of crickets and the sample of one of the Havana acoustic episodes.
Weak point. The sound perceived by the diplomats was directional, so it was not heard by neighboring people. If they had been crickets in their natural environment, the sound would have spread around.
5) Neurotoxins
Formulation. A joint study by two Canadian research centers in May 2019 attributed the symptoms suffered by diplomats to exhibition to neurotoxins from pesticides used to spray mosquitoes, a internship common occurrence in embassy buildings.
Weak point. The diplomats affected related the beginning of their physical discomfort to situations experienced in their own residences or in hotel rooms, where there was no fumigation.
IF IT WAS AN ATTACK, WHO DID IT?
Given that the previous explanations do not seem entirely solid, the US Government maintains the hypothesis of an attack. If it really happened, who was behind it? Here, too, there are various conjectures.
1) Castro regime
The first option considered, assumed in principle by the US given the public accusations made from Washington, has been to attribute the alleged attacks to the Cuban regime itself. With them, Havana would try to maintain pressure on the Americans, in spite of the formal reestablishment of diplomatic relations, with the goal to mark each other's territory.
Weak point. The incidents began to occur during the Obama Administration, in a context of a ˝honeymoon˝ marked by the reopening of embassies and the visit of Barack Obama to Havana. The normal thing is that at the end of 2016, in view of the U.S. elections, the Castro regime would not want to give reasons to the next U.S. president to twist the diplomatic line opened by Obama. It could make sense that after Donald Tump's later revocation of the previous openness measures, Cuba would want to punish the new Administration, but not before seeing the direction it would take; in any case, the attacks would only justify the hard line followed by Trump, which does not benefit the island.
2) A sector of Castroism
Fidel Castro was attributed with an unaccommodating attitude towards his brother Raul's decision to reestablish diplomatic relations with the United States. Although he died in November 2016, people around him might have tried to torpedo that rapprochement, convinced that hostility with Washington was the best way to ensure the survival of the regime as conceived by its founder.
Weak point. Although Fidel Castro's reluctance towards rapprochement with the U.S. is true, it is difficult to think that the most conservative sector within Castroism would dare to boycott so directly Raul Castro's fundamental political line. It is another thing that, after he handed over the presidency of Cuba to Miguel Díaz-Canel in April 2018, some sectors within the regime could make internal movements to send certain messages, but the changeover occurred when most of the acoustic episodes had already taken place.
3) A third country (Russia, China)
The third option would be that a third country generated the attacks. American intelligence indicates that the most viable option in this case would be Russia. Moscow has been keen to return to operating in the Caribbean, as in the Cold War, and aggression against U.S. diplomats in Cuba would fit in with its strategy. It has also been suggested that China might want to repay Washington in its backyard with the same harassment that the Chinese believe they feel from the US in their nearest seas.
Weak point. The return of Russia to the Caribbean is certainly documented, and it is conceivable that Moscow could have promoted a punctual action against some specific goal , but it seems difficult that it would have sustained over time an operation that harms Cuba's sovereignty. As for China's presence in the US neighborhood, it is a less confrontational move than the one carried out by Russia. Moreover, if Beijing had chosen foreign soil in order to better erase the traces of an action against US diplomats, then the cases recorded in Guangzhou would not have occurred.
![Almagro's remarks at the opening of the 49th OAS General Assembly, in Medellín, Colombia, in June 2019 [OAS] Almagro's remarks at the opening of the 49th OAS General Assembly, in Medellín, Colombia, in June 2019 [OAS]](/documents/10174/16849987/reeleccion-almagro-blog.jpg)
▲ Almagro's remarks at the opening of the 49th OAS General Assembly, in Medellín, Colombia, in June 2019 [OAS]
COMMENTARY / Ignacio Yárnoz
At the General Assembly of the Organization of American States (OAS) held in Medellín last June, the tensions and division that currently exist within this international organization were confirmed. In the first place, these discrepancies were evident in the question of the Venezuelan question, an issue that was the protagonist of the meeting with the presentation of migration reports, criticism of the Bolivarian regime and the presence of the Venezuelan delegation representing the Government of Guaidó led by Ambassador Gustavo Tarre.
These events were met with the rejection of a large part of the Caribbean countries, who abandoned the conference room In the presentation and declared their refusal to comply with any OAS resolution that the Venezuelan delegation voted in favor of. In the opinion of Caribbean countries, Venezuela formally left the organization in March and the presence of Guaidó's delegation as the legitimate representative of Venezuela contravenes international law and the principles of the OAS Charter, since it represents a government without effective control of the territory or legal legitimacy. But the Caricom countries were not the only ones to express their protest, the delegation of Uruguay also left the meeting. conference room and that of Mexico expressed its displeasure with the Venezuelan opposition presence as a delegation of plenary session of the Executive Council right.
The controversy, however, not only revealed the discrepancies on how to deal with the Venezuelan crisis, but also reflected another underlying reality, and that is that the candidacy of Luis Almagro to be re-elected as president of the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela. University Secretary of the organization hangs in the balance.
In December of last year, Uruguay's Almagro formally announced that, at the request of Colombia and the United States, he had decided to run for re-election with the certainty of having the necessary votes. Since then, however, the landscape of re-election has darkened. Voting will take place on the first semester Almagro needs at least 18 votes from the 35 countries of the OAS (if we include Cuba, even if he does not actively participate).
Variables
The future of Almagro, who arrived at the position In May 2015, it depends on several factors that will be developed this year. Mainly, the general elections in Argentina, Canada, Uruguay and Bolivia, which will be held between October and November. However, there are other variables that can also affect your re-election, such as the support you get from the countries of the United States. group or the possible division among CARICOM members on the matter. Below, we will review these assumptions one by one.
In the case of the Bolivian elections, Almagro has already played his cards and has been accused of having used a double standard by harshly criticizing the Maduro regime, but then not being critical of the possibility of Evo Morales being re-elected for a third time. Such re-election is supposedly not legal according to the Bolivian Constitution and was vetoed by the population in a referendum, but President Evo Morales has ignored it under the pretext that it prevents him from being elected. candidate once again, it goes against human rights, an argument later endorsed by the Supreme Court of Bolivia. The administrative office General of the OAS, despite not being in the agreement with the "right to be re-elected", he did not raise any criticism or position himself against said election supposedly because of Bolivia's possible vote in favor of Almagro, something that could happen if Evo Morales is finally re-elected but that is not completely certain either. Otherwise, however, he has already earned the animosity of the candidates of the civil service examination such as Carlos Mesa or Óscar Ortiz and the opposition leader Samuel Doria Medina who, if elected, would not vote in favor of him.
Regarding Guatemala, the first round of the presidential elections gave victory to Sandra Torres (22.08% of the votes) and Alejandro Giammattei (12.06% of the votes), who will face each other in the second round on Sunday, August 11. In the event that Torres is elected, she may align her position with that of Mexico, adopting a less interventionist policy towards Venezuela and therefore against Almagro. In the event of the victory of Giammattei, a center-right politician, it is likely that he will align his positions with Almagro and vote in favor of him. Guatemala has always been aligned with U.S. positions, so it is doubtful that the country will vote against a U.S.-backed candidacy, though not impossible.
As for Argentina and Canada, the position will depend on whether the candidate The winner in their respective elections is either conservative or progressive. Even in the case of Canada, the possibility of a rejection of Almagro is open regardless of the political orientation of the new government, since while Canada has been critical of the Maduro regime, it has also criticized the internal organization of the OAS under the command of the current one University Secretary. As far as Argentina is concerned, there is a clear difference between the presidential candidates: while Mauricio Macri would represent continuity in support for Almagro, the Alberto Fernández-Cristina Kirchner ticket would clearly be a rejection.
Uruguay represents a curious case of how internal politics and political games affect even members of the same party. We must not forget that Luis Almagro was a minister in the government of Pepe Mujica and that his first candidacy for University Secretary was submitted by Uruguay. However, given the division in the training The policy to which he belonged, Frente Amplio, won some enemies such as those of the current government of Tabaré Vázquez. That is why Uruguay has been so critical of Luis Almagro despite being a compatriot and party colleague. However, we should not doubt that he will also have his friends in the party who will change Uruguay's stance. If so, it wouldn't matter what the candidate (Luis Lacalle Pou for the National Party or Daniel Martinez for the Broad Front) that Almagro would be assured of the vote: that of the right wing of the National Party by having some thesis more critical of Maduro (in fact, they recognized Guaidó's government as a party and criticized Uruguay's neutrality), or that of the left of the Frente Amplio because of the contacts that Almagro may have, although the latter is still a hypothesis given that the most extreme wing of the party is the one that still has the majority of votes within the Frente Amplio.
Another Challenger
However, Almagro's chances for re-election could be thwarted if another candidate who could win the sympathy of the government presents his candidacy. group of Lima, created in August 2017 and made up of a dozen countries in the Americas to coordinate their strategy in relation to Venezuela. Peru sounds like the one that is likely to present a candidate: Hugo de Zela, a 42-year-old Peruvian diplomat degree program who in April was appointed Peru's ambassador to Washington and who has played a very important role within the group of Lima as coordinator. In addition, De Zela knows the structure of the OAS since he has served as chief of staff of the administrative office General on two occasions: first, between 1989 and 1994, when the head of the agency was the Brazilian Joao Clemente Baena Soares; and then between 2011 and 2015, with the Chilean José Miguel Insulza. This candidate, apart from his extensive political experience, has as his trump card the fact that he has been a coordinator of the group of Lima, which could provide assurances about the partnership between that group and the OAS on the Venezuelan question.
If De Zela were to decide to run, the group Lima could split its votes, which could favor the interests of the 14 Caribbean Community (CARICOM) countries, which usually vote as a bloc and have been unhappy with the management on the Venezuelan crisis. In fact, Caricom is already thinking about introducing a candidate that takes into account the interests of those countries, mainly climate change. The names that sound among the members of Caricom are the ambassador to the OAS of Antigua and Barbuda, Ronald Sanders, or the representative of Barbados to the UN, Liz Thompson.
However, there remains hope in the Caricom community for Almagro. Saint Lucia, Haiti, Jamaica and the Bahamas broke ranks at the time of voting on the admission of Ambassador Gustavo Tarre appointed by the Guaidó government to represent Venezuela at the OAS (although technically what they supported is that he be designated as "designated permanent representative of the National Assembly, pending new elections and the appointment of a democratically elected government"). These four countries, although with a more moderate position than that of the group of Lima, joined his position by accepting the appointment of such a representative with the aforementioned qualification. This is the third time so far this year that they have broken ranks in Caricom in the topic Venezuelan. This could give the University Secretary A trump card with which to be able to play in order to achieve the support of one of these four countries, although it will require skillful negotiation techniques and to give something in return to these countries, whether they are put in the position of the administrative office benefits in new programs and scholarships from development or climate change, for example.
In conclusion, in the best possible scenario for Almagro and assuming that no country in the group of Lima will present a candidate alternatively, the candidacy for re-election of the current University Secretary it would have 12 votes secured, 4 negotiable from Saint Lucia, Jamaica, Haiti and the Bahamas and 5 pending elections (Guatemala, Canada, Uruguay, Argentina and Bolivia). It is clear that Mexico, a large part of Caricom (Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago) and Nicaragua will vote against. In addition, we must add the fact that any candidacy can be submitted up to 10 minutes before the extraordinary General Assembly, which gives rise even more to shadow political games and last-minute surprises. As we can see, it's a status very difficult for him University Secretary And it's surely going to be more than one headache in this arithmetic of votes to get the position. Without a doubt, a fight for the position that will give a lot to talk about between now and February 2020.
[I. H. Daalder & James M. Lindsay, The Empty Throne. America's Abdication of Global Leadership. Public Affairs. New York, 2018. 256 p.]
review / Salvador Sánchez Tapia
 |
The arrival of Donald Trump to the presidency of the United States in January 2017 has unleashed a significant flow of publishing house that continues to this day, and in which numerous pens question, in substance and form, the new occupant of the White House from different angles.
In this case, two authors from the field of American think tanks , close to Barack Obama – one of them served during his presidency as US ambassador to NATO – offer us a very critical view of President Trump and his management at the head of the U.S. executive branch. With the solid support of numerous quotes, statements and testimonies collected from the media, and in an agile and attractive language, they compose the portrait of an erratic, ignorant president – in one passage his "ignorance on many issues, his unwillingness to accept the advice of others, his impulsiveness, and his lack of critical thinking capacity" are unmitigated. arrogant and irresponsible.
The authors of The Empty Throne argue that President Trump's actions and words show how he has broken with the traditional line of U.S. foreign policy since Franklin Delano Roosevelt, based on the exercise of leadership oriented to collective security, the opening of global markets and the promotion of democracy. of human rights and the rule of law, and that it has result very beneficial for the United States. Trump, they argue, would have abdicated that leadership, embracing instead another purely transactional policy, made out of a simple calculation of self-interest.
This new way of conceiving international politics, based on the logic of competition and domination, would be justified by the Trump administration with the argument that the old one has been highly pernicious for the United States, since it has led to friends and allies obtaining significant profits at the expense of American prosperity.
Paraphrasing Trump's campaign slogan America First, the authors argue that this new policy will result in an America Alone, and that it will benefit China instead, assuming that it will be China that nations look to for a new leader.
To support your thesis , the authors take a look at the management of Donald Trump in the year and a half between his inauguration in early 2017 and the book's publication date in 2018. In their arguments, they review the management of the presidents the nation has had since the end of World War II, and compare it to the internship by the Trump administration.
An important part of the criticism is directed at the controversial presidential style deployed by Donald Trump, exhibited even before the elections, and which is evident in events such as the withdrawal of the label accustomed in the world of international relations, especially hurtful in its relations with friends and allies; the lack of interest shown in coordinating with the Obama administration an orderly transition, or the making of certain decisions against its national security team or even without consulting its members.
Not acknowledging these facts would be to deny the evidence and call into question the inescapable reality of the uneasiness that this new way of treating nations with which North America shares so many interests and values, such as those of the European Union, or others such as Japan, Canada or Australia, firm allies of the United States for decades, produces for many. There is, however, some criticism of the arguments.
First of all, and leaving aside the lack of time perspective to make a evaluation final of Trump's presidency, the authors make a comparison between the first year and a half of the current president's term and those of all his predecessors since the end of World War II to demonstrate Trump's return to the America First policy that prevailed until Roosevelt. This contrast requires certain nuances because, based on the common denominator of the international leadership strategy that all of Trump's predecessors practiced, the country experienced during this time moments of greater unilateralism such as that of George W. Bush's first term, along with others of less global presence of the country such as, perhaps, those of the Eisenhower presidencies. Ford, Carter, and even Obama.
In the case of Obama, moreover, the fundamental differences with Trump are not as many as they seem. Both presidents are trying to manage, in order to mitigate it, the loss of relative American power caused by the long years of military presence in the Middle East and the rise of China. It's not that Trump believes the U.S. should abandon ideas of global leadership and multinational interaction; in fact, while he is accused of leaving traditional allies to their fate, he is reproached for his rapprochement, almost complicity, with others such as Saudi Arabia and Israel. Rather, what he intends is to exercise leadership, but, yes, dictating his conditions so that they are favorable to the United States. From inspirational leadership to leadership by imposition.
The question would be: is it possible to maintain leadership under these conditions? According to the authors, no. In fact, as a consequence of this U.S. "abdication of leadership," they offer two scenarios: a return to a world in which no nation leads, or the irruption of another nation – China, of course – that will fill the vacuum created by that abdication.
The authors do not consider a third option: that of traditional allies adapting to the new style of leadership, even if it is reluctantly, out of necessity, and in the confidence that one day, Trump's presidency will be history. This idea would be consistent with the premise set forth in the book, and with which we agree, that American leadership continues to be essential, and with the very acknowledgment made at the end of it, that there is some basis in the grievances that Trump presents and that the president's attitude is leading many of America's friends and allies to reconsider their defense spending. to rethink the rules of international trade to make them more palatable to North America, and to take a more active role in solving the most important global challenges.
Time will tell which of the three options will prevail. Even considering the challenges involved in the attention With the current head of the White House, the United States continues to be united with its traditional partners and allies by a dense network of common interests and, above all, shared values that transcend people and that will endure beyond them.

essay / Jairo Císcar Ruiz [English version].
In recent months, the open trade hostilities between the United States of America and the People's Republic of China have dominated the main general headlines and specialized economic publications around the world. The so-called "trade war" between these two superpowers is nothing more than the successive escalation of the imposition of tariffs and special levies on original products and manufactured goods from the countries in confrontation. This, in economic figures, means that the US imposed in 2018 special tariffs on US$250 billion of imported Chinese products (out of a total of US$539 billion), while China for its part imposed tariffs on 110 out of US$120 billion of US import products [1]. These tariffs meant an increase of US$3 billion in additional taxes for American consumers and businesses. This analysis is therefore intended to explain and show the position and future of the European Union in this trade war in a general way.
This small reminder of the figures illustrates the magnitude of the challenge for the global Economics posed by this clash between the world's two economic locomotives. It is not China who is paying the tariffs, as Trump literally said on May 9 during a meeting with journalists [2], but the reality is much more complex, and, evidently, as in the case of the inclusion of Huawei in the trade blacklist (and therefore the prohibition to purchase any item on US soil, whether hardware or software, without a prior agreement with the Administration), which may affect more than 1.200 American companies and hundreds of millions of customers globally according to the BBC [3], the economic war may soon start to be a great burden for Economics globally. On June 2, Pierre Moscovici, European Commissioner for Economic Affairs, predicted that if the confrontation continues, both China and the USA could lose between 5 and 6 tenths of GDP, stressing in particular that "protectionism is the main threat to world growth" [4].
As can be inferred from Moscovici's words, the trade war is not only of concern to the countries directly involved in it, but is closely followed by other actors in international politics, especially the European Union.The European Union is the largest Single Market in the world, this being one of the premises and fundamental pillars of the EU's very existence. But it is no longer focused on internal trade, but is one of the major trading powers for exports and imports, being one of the main voices advocating healthy trade relations that are of mutual benefit to the different economic actors at global and regional level. This openness to business means that 30% of the EU's GDP comes from foreign trade and makes it the main player when it comes to doing import and export business. To illustrate briefly, from agreement with the data of the European Commission [5] in the last year (May 2018-April 2019), the EU made imports worth €2,022 billion (a growth of 7%) and exported 4% more, with a total of €1,987 billion. The trade balance is therefore a negative balance of €35 billion, which, due to the large volume of imports and exports and the nominal GDP of the EU (taking the figure of 18.8 trillion euros) is only 0.18% of the EU's total GDP. The USA was the main place of export from the EU, while China was the first place of import. These data are revealing and interesting: an important part of the EU's Economics depends on business with these two countries and a bad performance of their Economics could weigh down the EU member countries' own.
Another data that illustrates the importance of the EU in subject trade is that of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). In 2018, 52% of global FDI came from countries within the EU and the EU received 38.5% of total investment globally, leading on both indicators. It can therefore be said that the current trade war may pose a serious problem for the future European Economics , but, as we will see below, the Union can emerge strengthened and even benefit from this status if it manages to mediate well between the difficulties, businesses and strategies of the two countries. But let us first look at the EU's relations with both the US and China.
The US-EU relationship has traditionally been (albeit with ups and downs) the strongest in the international sphere. The United States is the main ally in defense, politics, Economics and diplomacy of the European Union and vice versa. They share the economic, political and cultural model , as well as the main world collective defense organization, NATO. However, in the so-called transatlantic relationship, there have always been clashes, accentuated in the recent times of the Obama Administration and habitual with Trump. With the current Administration, not only have reproaches to the EU arisen within NATO (regarding the failure of member countries to invest the required budget ; shared criticism with the United Kingdom), but a full-fledged tariff war has begun.
In barely two years we have gone from the TTIP (Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership) negotiations, the announced basis for 21st century trade that finally failed in the final stages of Obama in the White House, to the current status of extreme US protectionism and EU response. Particularly illustrative is the succession of events that have taken place in the last year: at the stroke of Twitter, in March 2018 the US unilaterally imposed global tariffs on steel (25%) and aluminum (10%) to protect American industry [6]. These tariffs did not only affect China, they also inflicted great damage on companies in European countries such as Germany. Tariffs of 25% on European vehicles were also in the air. After a harsh climate of mutual reproaches, on July 25, Jean Claude Juncker, President of the European Commission, announced together with Trump a agreement to lower tariffs on agricultural products and services, and the US committed itself to review the imposition of metallurgical tariffs on the EU, as well as to support within the World Trade Organization the European calls for a reform of Intellectual Property laws, which China does not respect [7]. However, after the reiteration of the transatlantic friendship and Trump's advertisement of "we are heading towards zero tariffs" [8], soon the intemperate boxes have been rung again. In April this year, on April 9, Trump announced on Twitter the imposition of tariffs on the EU worth US$11 billion for the EU's support to Airbus (skill of the American Boeing, Lockheed Martin...), blowing up the principle of agreement of July last year. The EU, for its part, threatened to impose tariffs of €19 billion for the US state support to Boeing. As can be seen, the EU, despite its traditional conciliatory role and often subjugated to the US, has decided to fight back and not allow any more outbursts on the American side. The latest threat, in mid-July, is against French wine (and due to the European mechanism, against all wines of European origin, including Spanish wines). This threat has been described as "ridiculous" [9], since the USA consumes more wine than it produces (it is the world's largest consumer) and therefore, the supply available could be considerably reduced.
It is still too early to see the real impact that the trade war is having on the US, beyond the 7.4% drop in US exports to China [10] and the damage that consumers are suffering, but the Nobel laureate of Economics Robert Schiller, in an interview for CNBC [11] and the president of the World Trade Organization, Roberto Azevedo, for the BBC; have already expressed their fears that if status and protectionist policies continue, we could be facing the biggest economic crisis since the end of the Second World War. It is difficult to elucidate what the future relationship between Europe and its main exporter partner , the USA, will be like. All indications are that friction and escalation will continue if the US Administration does not decide to tone down its rhetoric and actions against free trade with Europe. Finally, it must be clear (and in the spirit of lowering the sometimes excessively alarmist tone of the news) that between the threats (either by Twitter or spokespersons) from both sides and the actual imposition of tariffs (in the US after the relevant advertisement from the Office of the US Trade Representative; in the EU through the approval of the 28) there is a long way to go, and we must not confuse potential acts and facts. It is clear that despite the harsh tone, the negotiating teams on both sides of the Atlantic are still at contact and are trying to avoid as far as possible actions detrimental to both sides.
On the other hand, the relationship between China and Europe is frankly different from the one with the USA. The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) (to which Italy has formally adhered) is the confirmation of China's bid to be the next leader of the world's Economics . Through this initiative, President Xi Jinping aims to redistribute and streamline trade flows to and from China by land and sea. To this end, the stability of South Asian countries such as Pakistan and Afghanistan is vital, as is the ability to control vital maritime traffic points such as the Strait of Malacca and the South China Sea. The Asian "dragon" has an internal status that favors its growth (6.6% of its GDP in 2018 which, being the worst figure for 30 years, is still an overwhelming figure), as the relative efficiency of its authoritarian system and, especially, the great support of the State to companies boost its growth, as well as possessing the largest foreign currency reserves, especially dollars and euros, which allow a great stability of the country's Economics . The Chinese currency, the Renminbi, has been declared by the IMF as a world currency reservation , which is another indicator of the good health that is predicted for the future of the Chinese Economics .
For the EU, China is a competitor, but also a strategic partner and a negotiator partner [12]. China is the EU's main importer partner , accounting for 20.2% of imports (€395 billion) and 10.5% of exports (€210 billion). The volume of imports is such that, although the vast majority reach the European continent by sea, there is a railway connection that, under the BRI, links the entire Eurasian continent, from China's manufacturing capital, Yiwu, and the last stop at the southernmost tip of Europe, Madrid. Although some of the imports are still so-called "low-end" goods, i.e. products of basic manufacture and cheap unit price, since China joined the WTO at entrance in December 2001, the concept of material produced in China has changed radically: the great abundance of rare earths in Chinese territory, together with the progress in its industrialization and investment in new technologies (in which China is a leader) have meant that China is no longer thought of only as a mass producer of bazaars; on the contrary, the majority of imports into the EU from China were high-end, high-tech machinery and products (especially telecommunications and processing equipment from data).
In the aforementioned statement press release from the European Commission, China is warned to comply with the commitments made in the Kyoto Protocols and Paris Agreements regarding greenhouse gas emissions; and urges the Asian country to respect the dictates of the WTO, especially in subject on technology transfer, state subsidies and illegal practices such as dumping.
These aspects are vital for economic relations with China. At a time when most countries in the world signed or are part of the Paris Agreements for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, while the EU is making efforts to reduce its pollution (closing coal plants and mines; putting special taxes on energy obtained from non-renewable sources...), China, which totals 30% of global emissions, increased in 2018 by 3% its emissions. This, beyond the harmful effects for the climate, has industrial and economic benefits: while in Europe industries are narrowing their profit margins due to the rise in energy prices; China, which is fueled by coal, provides cheaper energy to its companies, which, without active restrictions, can produce more. An example of how the climate affects economic relations with China is the recent advertisement [13] of AcerlorMittal to reduce by 3 million tons its total steel production in Europe (out of 44 million tons of usual production) due to high electricity costs and increased imports from countries outside the EU (especially China) which, with excess production, are lowering prices worldwide. This internship, which is especially used in China, consists in flooding the market with an overproduction of a certain product (this overproduction is paid with government subsidies) to lower prices. As of December 2018, in the last 3 years, the EU has had to impose more than 116 sanctions and anti-dumping measures against Chinese products [14]. Which sample that, despite the EU's attempts to negotiate on mutually satisfactory terms, China does not comply with the stipulations of the agreements with the EU and the WTO. Particularly thorny is the problem with government-controlled companies (a ban on 5G networks in Europe, controlled by Chinese providers, is being considered for security reasons), which have a virtual monopoly inside the country; and above all, the distorted reading of legality by the Chinese authorities, who try to use all possible mechanisms in their favor, making it difficult or hindering direct investment by foreign capital in their country, as well as imposing requirements (need to have Chinese partners, etc.) that hinder the international expansion of small and medium-sized companies. However,
The biggest friction with the EU, however, is the forced transfer of technology to the government, especially by companies of strategic products such as hydrocarbons, pharmaceuticals and the automotive industry [15], imposed by laws and conditio sine qua non companies cannot land in the country. This creates a climate of unfair skill and direct attack on international trade laws. The direct investment of Chinese capital in critical industries and producers in the EU has caused voices to be raised calling for greater control and even vetoes on these investments in certain areas due to Defense and Security issues. The lack of protection of intellectual rights or patents are also important points of complaint by the EU, which aims to create through diplomacy and international organizations a favorable climate for the promotion of equal trade relations between the two countries, as reflected in the various European guidelines and plans concerning topic.
As we have seen, the trade war is not only limited to the US and China, but third parties are suffering from it and even actively participating in it. The question arises here: can the EU benefit in any way and avoid a new crisis? Despite the pessimistic mood, the EU can derive multiple benefits from this trade war if it manages to maneuver properly and avoid as far as possible further tariffs against its products and keeps the market open. If the trade war continues and the positions of the US and China harden, the EU, being partner the main beneficiary of both, could benefit from a redistribution of trade flows. Thus, to avoid the loss due to tariffs, both China and the US could sell heavily taxed products to the European market, but especially import products from Europe. If a agreement is reached with the US to lift or minimize tariffs, the EU would find itself facing a huge market niche left by Chinese products vetoed or taxed in the US. The same in China, especially in the automotive sector, from which the EU could benefit by selling to the Chinese market. Alicia Garcia-Herrero, of the Belgian think tank Bruegel, states that the benefit for Europe will only be possible if it does not lean towards any of the contenders and remains economically neutral [16]. He also stresses, like the European Commission, that China must adopt measures to guarantee reciprocity and market access, since the European Union still has a greater volume of business and investments with the USA, so that the Chinese offer should be highly attractive for European producers to consider directing products to China instead of the USA. The UN itself estimates at US$70 billion the benefits that could be absorbed by the EU thanks to the trade war [17]. Definitely, if the right measures are taken and the 28 draw up an adequate road map, the EU could benefit from this war, without forgetting that, as the EU itself advocates, coercive measures are not the solution to the trade problem, and hopes that, due to their ineffectiveness and damage caused to both consumers and producers, the tariff war will come to an end and, if differences persist, they will be resolved in the WTO Appellate Body, or in the Permanent Court of Arbitration of the United Nations.
This trade war is a highly complex and nuanced topic ; this analysis has attempted to address many of the issues, data and problems facing the European Union in this trade war. It has been generally analyzed what the trade war consists of, as well as the relations between the EU, China and the USA. We are facing a gray future, with the possibility of multiple and quick turns (especially on the part of the US, as seen after the G20 summit in Osaka, after which it has allowed the sale of components to Huawei, but has not removed the company from its blacklist) and from which, if the requirements and the conditions set out above are met, the EU will definitely benefit, not only economically, but if it remains united and making a common front, it will be an example of negotiation and economic freedom for the whole world.
REFERENCES
Thomas, D. (14-5-2019) Who loses in the China-US trade war. BBC. Retrieved from.
Blake, A. (9-5-2019) Trump's rambling, disappointing Q&A with reporters, annotated. The Washington Post. Retrieved from.
3. Huawei: US blacklist will harm billions of consumers (29-5-2019) BBC. Retrieved from
4. EU warns China and the US: a trade war would subtract 0.6 points of GDP(3-6-2019) El Confidencial. Retrieved from
5. European Union Trade Statistics. (18-6-2019) European Commission.Retrieved from: http://ec.europa.eu/trade/policy/eu-position-in-world-trade/statistics/
6. Pozzi, S. (2-3-2018) Trump reaffirms protectionism by raising tariffs on imported steel and aluminum. El País (New York correspondent)Retrieved from.
7. Inchaurraga, I. G. (2013). China and GATT (1986-1994): Causes and consequences of the failure of a negotiation. Cizur Menor, Navarra: Aranzadi. pp. 204-230.
8. Tejero, M. (25-7-2018) agreement EU-US: "zero tariffs" on industrial goods; more soybeans and liquefied gas. El Confidencial. Retrieved from.
9. Pardo,P. & Villaécija, R. (17-6-2019) Trump threatens Spanish wine. El Mundo. Retrieved from.
10. A quick guide to US-China Trade War (14-5-2019) BBC. Retrieved from
11. Rosenfeld, E. & Soong, M. (25-3-2018) Nobel-winner Robert Shiller warns of an 'economic crisis' from trade war threats. CNBC. Retrieved from.
12. EU reviews relations with China and proposes 10 actions. (12-3-2019) European Commission- statement de Prensa.
13. Asturias takes 23% of Arcelor's new EU production cut.(6-5-2019) 5 Days Retrieved from.
14. Morales, R. (26-12-2018) EU increased 28.3% its antidumping measures in 3 years: WTO. El Economista Mexico. Retrieved from
15. Warning about forced technology transfer to Chinese government.(20-5-2019) Infobae. Retrieved from
16. García-Herrero, A.; Guardans, I. & Hamilton, C. (28-6-2018) Trade War Trinity: analysis of global consequences. Bruegel (lecture). Retrieved from.
17. European Union, the big beneficiary of the trade war between China and the U.S.(4-2-2019) UN News . Retrieved from
[Condoleezza Rice, Amy B. Zegart, Political Risk: How Businesses and Organizations can Anticipate Global Insecurity. Hachette Book Group. New York, May 2019]
REVIEW / Rossina Funes Santimoni
 |
Every year Stanford Graduate School of Business offers their students a seminar in Political Risk. The classes are taught by former U.S. Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice and the renowned academic Amy B. Zegart. Motivated by their students, they decided to turn their classes into a book in order to allow more people and organizations to navigate the waters of political risk.
The work titled Political Risk: How Businesses and Organizations can Anticipate Global Insecurity is divided into ten chapters. The authors start by explaining the contemporary concept of political risk. Consequently, theoretical framework is added as they advance in the explanation, in this way making it useful for the reader in order to understand, analyze, mitigate and answer efficiently to political risks. Their ultimate objective is to provide functional framework that can be utilized in any organization or by any person to improve political risk management.
Rice and Zegart define the twenty-first-century political risk as the probability that a political action could significantly affect a company's business. Nowadays, the public and the private sphere are constantly changing and evolving. Everything is more complex and intertwined. Governments are no longer the only ones playing an important role in business decisions. The authors emphasize how companies need to efficiently deal with the political risks spawn by an increasing diversity of actors, among which is anyone with access to social average. In order to illustrate the latter, the authors make use of real-life examples, for instance the Blackfish Effect. It is named after a low-budget investigative documentary with the same title that depicted how SeaWorld Entertainment's treatment of orcas harmed both the animals and their human trainers. The film that started with one woman reading a story about orcas triggered political action at the grassroots, state and federal levels, ending up with devastating consequences from which the company has still have not recovered up to now. These cascading repercussions of the film have been denominated the Blackfish Effect.
The work is well equipped with more examples about distinguished companies' experience. Among the organizations cited are Lego Company Group, FedEx, Royal Caribbean and Nike. Some have excelled in dealing with political risk and some have failed. However, both sides of the coin are useful to learn and to understand how the convoluted world of political risks management work.
Nowadays, risk generators perform at five intersecting levels including individuals, local organizations and governments, national governments, transnational organizations, and supranational and international institutions. Therefore, today's risks are different from the old ones, even if those still persist. With this in mind, Rice and Zegart shed a light on these days' top ten political risks: geopolitics, internal conflict, policy change, braches of contract, corruption, extraterritorial reach, natural resource manipulation, social activism, terrorism and cyber threats.
Nevertheless, even if the theory is laid out, the question still haunts us: Why is good political risk management so hard? The authors dedicate a whole chapter investigating it and conclude that there are "Five Hards". Political risk is hard to reward, hard to understand, hard to measure, hard to update, and hard to communicate. Therefore, in order to succeed at its management, one must get right the four basics: understanding, analyzing, mitigating and responding to risks. Rice and Zegart dedicate the remaining four chapters of the book expanding on each basic and, again, employing examples to better illustrate their knowledge.
The thing about political risks is that they are always there. They are imminent and we can do nothing more than try to prevent them and learn from them, to use the present in order to make the best of it for the future. It is not about predicting the future, which is impossible. "No one ever builds a disaster recovery plan that allows for the destruction of everybody in the office at 8:45 am. That is never the plan," assures Howard W. Lutnick, CEO at Cantor Fitzgerald on the how the company dealt with the 9/11 terrorist attack aftermath. Paradoxically, Rice and Zegart maintain that the best way to deal with crises is not having them. Henceforth, they dedicate a whole chapter to providing key takeaways in order to better respond to crises. Politics has always been an unpredictable business. There is no one that can discern accurately how human history is going to unfold. However, the authors are convinced that managing political risks does not have to be pure guesswork and that being prepare is essential and can improve companies performances in a great deal.
Political Risk: How Businesses and Organizations can Anticipate Global Insecurity completely revamps the way we reflect on the topic. It is easy to notice both authors proficiency in the field. On one hand, the past experiences of former U.S Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice serve as anecdotes to elucidate the build-up of the theoretical framework. It is valuable to have such a persona to act as a primary source that has lived among other high-end characters and important people in history. On the other hand we have Professor Amy B. Zegart, who with her natural eloquence excels in conveying the importance of political risk management nowadays. Consequently, everyone can get a precious lesson from this book, ranging from students that are interested in navigating the sphere, to everyday workers, company owners and public servants.
[Winston Lord, Kissinger on Kissinger. Reflections on Diplomacy, Grand Strategy, and Leadership. All Points Books. New York, 2019. 147 p.]
review / Emili J. Blasco
 |
At 96 years old, Henry Kissinger sees the publication of another book largely his own: the transcription of a series of long interviews related to the main foreign actions of the Nixon Administration, in which he served as national security adviser and secretary of state. Although he himself has already written extensively about those moments and has provided documentation for others to write about – as in the case of the biography of Niall Ferguson, whose first volume appeared in 2015 – Kissinger wanted to return to that period of 1969-1974 to offer a synthesis of the strategic principles that motivated the decisions taken at the time. There are no new developments, but there are details that may be of interest to historians of that time.
The work does not respond to Kissinger's last-minute desire to influence a particular reading of his work. bequest. In fact, the initiative to maintain the dialogues transcribed here did not come from him. It is, however, part of a wave of vindication of the presidency of Richard Nixon, whose strategic vision in international politics was tarnished by Watergate. The Nixon Foundation promoted the making of a series of videos, including various interviews with Kissinger, carried out throughout 2016. These were led by Winston Lord, partner during his time in the White House and in the department of State, together with K. T. McFarland, would then be a civil servant under him (and, for a few months, issue two of the committee of Homeland Security under Donald Trump). More than two years later, that conversation with Kissinger is now published in a small-format and short work. His last books had been "China" (2011) and "World Order" (2014).
Kissinger's oral history here deals with a few issues that focused his activity as a great architect of American foreign policy: the opening to China, the détente with Russia, the end of the Vietnam War, and the greater involvement in the Middle East. Although the conversation goes into detail and provides various anecdotes, what is substantial is what can be extracted beyond these specifics: they are the "reflections on diplomacy, grand strategy and leadership" indicated by the subtitle of the book. It might be tiresome to re-read the intra-history of a diplomatic action about which the protagonist himself has already been prolific, but on this occasion reflections are offered that transcend the specific historical period, which for many may already be very far away, as well as interesting recommendations on the decision-making processes in leadership positions.
Kissinger provides some clues, for example, on why the United States has consolidated the committee of National Security as an instrument of the president's foreign action, with an autonomous – and sometimes conflictive – life with respect to the department of State. The Nixon Administration was its great promoter, following the suggestion of Eisenhower, for whom Nixon had been vice president: interdepartmental coordination in foreign policy could hardly be done from a single point of view. department –the administrative office of state, but had to be carried out from the White House itself. While the National Security Adviser can concentrate on those actions that are most in the president's interest, the Secretary of State is obliged to disperse further, having to attend to a multitude of fronts. Moreover, unlike the greater promptness of the department in support of the Commander-in-Chief, the department The State of State, accustomed to elaborating multiple alternatives for each international issue, may take time to fully assume the direction imposed by the White House.
In terms of negotiating strategy, Kissinger rejects the idea of privately setting a maximum goal and then trim it little by little, like slices of a salami, as you reach the end of the negotiation. Instead, he proposes to set from the beginning the basic goals that one would like to achieve – perhaps adding 5% because something will have to be given – and to spend a lot of time explaining them to the other party, with the idea of reaching a conceptual understanding. Kissinger advises a good understanding of what motivates the other party and what their own objectives are, because "if you impose your interests, without linking them to the interests of others, you will not be able to sustain your efforts," since at the end of the negotiation the parties have to be willing to support what has been achieved.
As on other occasions, Kissinger does not take sole credit for the Nixon Administration's diplomatic successes. While the press and a certain part of academia have given greater recognition to the former Harvard professor, Kissinger himself has insisted that it was Nixon who decisively set the policies, the maturation of which had previously been carried out separately, before collaborating in the White House. However, it is perhaps in this book that Kissinger's words most praise the former president, perhaps because he was made in the framework of an initiative born from the Nixon Foundation.
"Nixon's fundamental contribution was to establish a patron saint of foreign policy thinking, which is seminal," Kissinger says. According to him, the traditional way of approaching U.S. foreign action had been to segment issues in order to try to solve them as individuated problems, making their resolution the question itself. "Nixon was – apart from the Founding Fathers and, I would say, Teddy Roosevelt – the American president who thought of foreign policy as grand strategy. For him, foreign policy was the structural improvement of the relationship between countries so that the balance of their self-interests promoted global peace and the security of the United States. And he thought about this in terms of relative long-range."
Those who have little sympathy for Kissinger – a character of passionate defenders but also staunch critics – will see in this work another exercise in self-congratulation and self-aggrandizement typical of the former adviser. To stay at that stage would be to waste a work that contains interesting reflections and I think that it completes well the thought of someone of such relevance in the history of international relations. What Affirmation staff Rather, the publication refers to Winston Lord, who here claims to be Kissinger's right-hand man at the time: in the first pages the complete photo of the interview between Nixon and Mao appears, the margins of which were cut off at the time by the White House so that Lord's presence would not disturb the secretary of state. who was not invited to the historic trip to Beijing.
After a record production of opium poppies in Mexico and overdose deaths in the US the problem has stopped growing
-
Less amount of heroin is reaching the US market: Mexican authorites eradicated 29,207 hectares of poppy crops in 2017, and 17,288 hectares in the first half of 2018
-
US President Trump signed in October 2018 the Opioid Crisis Response Act; a National Drug Control Strategy was published in January 2019.
-
Mexico is the main transit route into the US for fentanyl originating from China; Mexican anti-narcotics operations try to exert more control over this trade
![Cultivation of opium poppies (Papaver somniferum), the variety of poppies (Papaver) with the highest concentration of narcotics [DEA]. Cultivation of opium poppies (Papaver somniferum), the variety of poppies (Papaver) with the highest concentration of narcotics [DEA].](/documents/10174/16849987/sra-drugs-blog.jpg)
▲ Cultivation of opium poppies (Papaver somniferum), the variety of poppies (Papaver) with the highest concentration of narcotics [DEA].
ARS 2019 Report / Marcelina Kropiwnicka[PDF version] [PDF version].
The severe opioid crisis experienced by the United States in recent years, with a record number of deaths by drug overdoses in 2017, apparently began to remit in 2018, according to the first available data. Both the efforts of the United States to confront the epidemic and of Mexico in eradicating opium poppy crops seem to be bearing fruit.
The dramatic increase in opium cultivation and heroin production in Mexico in the last years triggered drug consumption in the US. Besides, Mexico is the main route into the US for fentanyl, an opioid narcotic which is behind the US opioid epidemic as well.
After four years of sharp increase, the number of deaths in the United States due to opioid overdose rise in 2017 to 47,600, twice as many as in 2010. The main part of those deaths was due to the consumption of prescription opioids (17,029), followed by overdose deaths involving heroin (15,482). In both cases, the increase was mainly due to the use of synthetic narcotics, basically fentanyl, as prescription drug or mixed with heroin.
The first data referring to 2018 provided by the US health authorities seem to reflect a stabilization in the number of deaths due to opioid overdoses, which would at least indicate that the problem has stopped growing. Along with the efforts of the US administration to put in place a stricter regulation for the prescription of certain medicines, especially affecting synthetic opiates, there is a greater eradication of illicit crops in Mexico, with special emphasis on the cultivation of opioid poppies.
In 2017 the Mexican authorities proceeded to eradicate 29,207 hectares of this crop, thus limiting the heroin that in 2018 could reach the US domestic market. In 2018 eradication accelerated: in the first half of the year, the crop of 17,288 hectares was eliminated. This is a progress highlighted by the latest International Narcotics Control Strategy Report (INCSR), published in Mach 2019 by the US Department of State.
Heroin production
Illicit heroin and fentanyl have been infecting US neighborhoods for years. Initially, the source for almost all heroin found in the US was from Southern Asia. Over the past few decades, however, the trade for heroin has changed drastically. Most of the heroin found in US communities comes from South America, and namely Mexico. This has been fueled by a number of factors, including increased production and trafficking by criminal organizations. These current trends in drug trafficking lead to opioid abuse, and represent a considerable shift in outcomes. This has obliged the governments in both countries to instill and coordinate new law enforcement responses.
The United States is home to the largest heroin market in the Americas. Created from the milky sap scraped from the seedpod of an opium poppy, heroin can be transformed into multiple forms. These include powder, viscous tar, pills, a rock-like black substance and more. In addition to this, the substance has different degrees of purity, with white powder heroin being the purest and black tar-like heroin being the most impure. Heroin can also be administered through a number of means, but most commonly is smoked, injected or snorted.
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), most of the heroin trafficked into the US comes from Mexico. Along with this, Mexican poppy cultivation and heroin production have been on the rise, especially over the past decade, contributing to the ever-increasing threat to the United States. In fact, 2017 was the year Mexican poppy cultivation and heroin production reached a record high, as the Office of National Drug Control Policy of the White House reaffirmed in August 2018: poppy cultivation in Mexico rose 38 percent, from 32,000 hectares in 2016 to 44,100 hectares in 2017; it went from 685 tons to 944 tons of potential opium production, and from 81 tons to 111 tons of potential pure heroin elaboration, almost five times 2012 levels.
Evaluations carried out by the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) in its October 2018 report National Drug Threat Assessment (NDTA) stated that Mexico accounts for 91 percent (by weight) of heroin found in the US. A similar figure is given by the World Drug Report (WDR) published by the UNODC in June 2018: "Analysis of heroin samples in the United States over the past decade shows the increasing predominance of Mexico (90 percent of samples analysed in 2015) as a source country of the drug". According to the INCSR, the Department of State report already mentioned, Mexico is especially focused on producing heroin, marijuana, and methamphetamine that is destined for the US; it is also a main transit route- originating from China-for another important triger of the opioid crisis in the US: fentanyl.
Fentanyl
Fentanyl's availability is widespread and surging. While there are licit forms of the opioid, such as painkillers and anaesthetics, illicit production and trafficking of it are on the rise. The new trend is rooted toward mixing synthetic opiate fentanyl in Mexico's tarry black heroin, without the consumer's knowledge. Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that is approximately 50 times more potent than heroin and 100 times stronger than morphine. The opioid is much cheaper when it comes to production, mainly because rather than being grown on a farm it is manufactured in a laboratory. The decreased cost for the traffickers and increased high for users signifies that drug producers have begun to cut their heroin with fentanyl.
The DEA warns that Mexican cartels present an intense threat to US neighborhoods mainly given their dominance in heroin and fentanyl exports). It also noted that a majority of the samples that were seized and analyzed involved fentanyl in its powder form. The concern arising from this is that fentanyl could be pressed into counterfeit pills, mainly because most drug abusers use prescription pain pills rather than heroin. This means that the creation of such counterfeit pills could ultimately affect a larger population of individuals.
The increase in heroin related deaths has been primarily linked to heroin being combined with fentanyl. The counterfeit pills could increase deaths due to fentanyl and white powder heroin looking alike. Consequently, users are unaware that the heroin they have purchased contains fentanyl, thus removing the user's ability to know the potency of the drug and preventing them from correctly dosing in respect to their tolerance level.
 |
Solving the problem
The opioid epidemic suffered by the US in the last years was confronted in 2018 by the Trump administration with some special measures. In October 2018 President Trump signed the Opioid Crisis Response Act, which gave more powers to the US health authorities to monitor the situation and extended the controls on patient access to some specific drugs. In January 2019 a National Drug Control Strategy was published by the White House in order to take extra steps to protecting the public through effective drug abuse prevention, addiction treatment and use of law enforcement actions.
Apart from these new tools, the US relies on a long-standing relationship with Mexico regarding anti-narcotic matters. Both countries set up in 2008 the Merida Initiative, which allows the US to assist the Mexican authorities in different fields. It includes several measures in order to improve law enforcement operations: training and equipment to dismantle covert drug labs, cutting-edge airport security training, advanced inspection tools equipped along border crossings and checkpoints, and so forth in order to improve law enforcement operations, among others. Results have already been seen, as Mexican units trained by US officials have seized more than 300 illicit laboratories since 2015. In addition to this, canines donated by the initiative have helped detect a significant amount of illicit drugs attempting to pass the border.
