Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with label Bigfoot .
The United States remains attentive to the innovation of methods that can also serve to introduce terrorist cells or even weapons of mass destruction.
In the last ten years, the proliferation of submersible and semi-submersible, with difficult detection, has monopolized a third of the drug transport from South America to the United States. The incorporation of GPS systems by the cartels also makes the global fight against narcotics difficult. A possible use of these new methods for terrorist purposes keeps the United States on high alert.

▲ A narco-submarine found in the jungle of Ecuador in 2010 [DEA].
ARTICLE / Marcelina Kropiwnicka[English version] [Spanish version].
Drug trafficking to large consumer markets, especially the United States and Europe, is especially innovative: the magnitude of the business leads to attempts in overcoming any barriers placed by the States to prevent their penetration and distribution. In the case of the United States, where the illicit arrival of narcotics dates back to the 19th century-from opium to marijuana and cocaine-, authorities have continuously managed to intercept many shipments of drugs, but traffickers find new ways and methods to introduce significant volumes of narcotics.
The most disturbing method in the last ten years has been the use of boat submersibles and semi-submersibles, which have commonly been given the name of narco-submarines. They allow several tons of substances to be transported-five times more than a fishing boat can transport-dodging the US Coast Guard's surveillance [1]. Satellite technology has also led traffickers to drop drug loads into the sea, then be collected by recreational boats without raising suspicion. Those methods are referenced in recent reports from the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), the US anti-narcotics agency.
Through the waters of Central America
For many years, the conventional way of transporting drugs that leave South America to the United States has been through fishing boats, speedboats and light aircraft. Advances in airborne detection and tracking techniques have pushed drug traffickers to look for new ways to take their loads to the North. Hence the development of narco-submarines, whose number, from a first interception in 2006 by the US authorities, has seen a rapid progression.
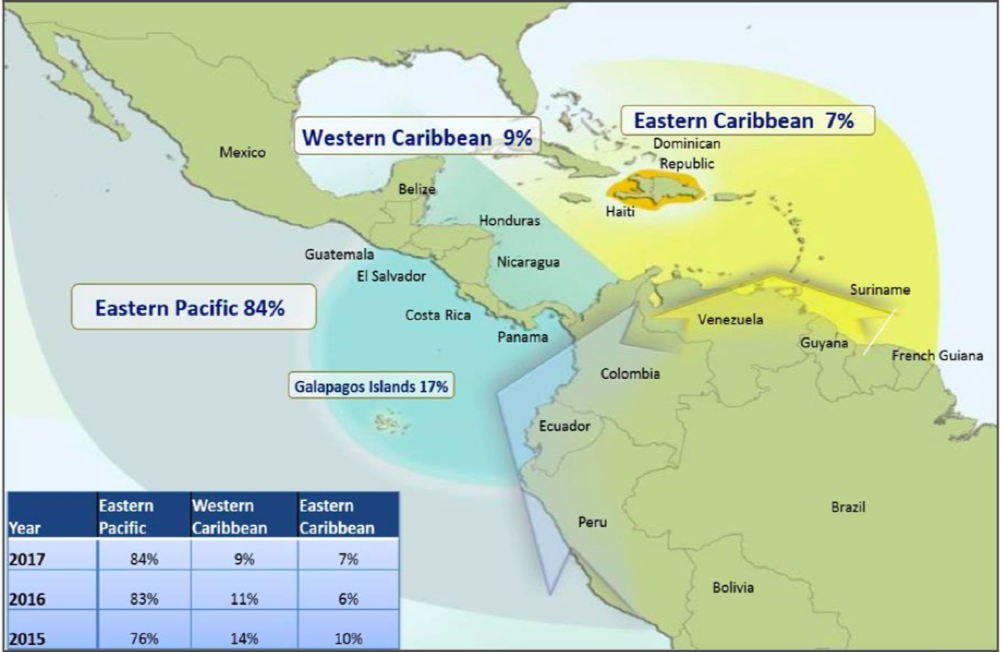
This means of transport is one of the reasons that since 2013 there has been a 10% increase in trafficking of drugs that travel from Colombia (the country that produces 93% of the cocaine consumed in the US) to Central America and Mexico, the location where the shipments are introduced to the US. According to the DEA, this corridor today represents an estimated 93% of the movement of cocaine from South America to North America, compared to 7% of the route that passes through the Caribbean islands (mainly the Dominican Republic) to reach Florida or other places on the East American coast.
For a while, among US Coast Guard service members spread a rumor that the drug cartels were using narco-submarines. Without having seen one up to that moment, the agents gave it the name of 'Bigfoot' (like the supposed ape-like animal that would inhabit Pacific forests in the US).
The first sighting occurred in November 2006, when a patrolman from the US Coast Guard detected a blurred shape in the ocean, about a hundred miles off the coast of Costa Rica. As the agents approached the blur, they discovered three tubes of plastic that emerged from the water, which came from a submersible ship that was two meters below the surface. Inside the submersible they found three tons of cocaine and four men armed with an AK-47 rifle. The coastguard named the discovery as 'Bigfoot I'.
Two years later there would be detection of a 'Bigfoot II'. In September 2008, a frigate of the US Navy working with the Coast Guard seized a similar apparatus 350 miles from the border between Mexico and Guatemala. The crew consisted of four men and the position reached 6.4 tons of cocaine.
By then, the US authorities calculated that more than one hundred submersibles or semi-submersibles had been crafted. In 2009 they estimated that they were only able to stop 14% of shipments, and that this method of transport provided at least one third of the total cocaine shipment reaching the US market. The Colombian, Mexican and Guatemalan armies have also confiscated some of these narco-submarines. In addition to being located in the Pacific, they have also been detected in the Caribbean and the Atlantic. Crafted in the jungle, perhaps the most striking discovery was in the interior of Ecuador, in the waters of a river.
Its technical innovation has often surprised counter-narcotics officials. Many of these self-propelled narco-submarines measure fifteen meters, are made of synthetic materials and fiberglass and have been designed to reduce their detection by radar or infrared. There have also been models with systems of GPS navigation to refuel and receive food at agreed points along their established route.
GPS tracking
The development and generalization of the GPS system has also served drug traffickers to introduce greater innovations. One procedure, for example, has been to fill a vessel shaped like a torpedo with drugs-like a submersible, but without a crew-, and attached to a buoy and a signal emitter. The container can hold up to seven tons of cocaine and be fastened to the bottom of a ship by a cable. If the boat is intercepted, the container can simply be dropped deeper into the water, and can later be recovered by another boat thanks to satellite locators. This makes it extremely difficult for authorities to seize the drugs and stop the traffickers.
The GPS navigation system is also used to deposit drug cargos at points in the territorial waters of the United States, where they can be collected by recreational craft or by a small group of people without raising suspicion. The package containing the cocaine is coated with several layers of material and then waterproofed with a type of foam. The package is placed inside of a canvas bag that is then deposited into the bottom of the sea to be recovered by others later on.
As indicated by the DEA in its 2017 report, "this demonstrates how trafficking organizations have evolved their methods for conducting cocaine transactions through technology Organizations transport kilograms of cocaine in waterproof packaging to a predetermined location, anchor it to the ocean floor for retrieval by other DTO [Drug Trafficking Organization] members who have the contraband GPS location. This allows members of trafficking organizations to compartmentalize, as it separates maritime transporters from land-based cocaine distributors."
|
Cocaine routes from South America to the United States in 2017 [DEA]. |
Terrorist risk
The possibility that these difficult detection methods are being used to introduce weapons or for terrorist operations worries the United States authorities. Retired Vice Admiral James Stravidis, former commander of US Southern Command, has warned of the potential use, especially of the submersibles, "to transport more than just narcotics: the movement of cash, weapons, violent extremists, or, at the dark end of the spectrum, weapons of mass destruction".
This risk was also referred to by Rear Admiral Joseph Nimmich when, as commander of the Joint Interagency Task Force South, he faced the emergence of submersibles. "If you can carry 10 tons of cocaine, you can carry 10 tons of anything," he told The New York Times.
According to this newspaper, the furtive elaboration of homemade submarines was developed first in Sri Lanka, where the rebel group of the Tamil Tigers used them in confrontation with government forces. "Tamil will go down in history as the first terrorist organization to develop underwater weapons," said the Ministry of Defense of Sri Lanka. In 2006, as the NYT states, "a Pakistani and a Sri Lankan provided plans to the Colombians for building semisubs quickly, stealthily and out of cheap, commonly available materials."
Despite its origin, related to the Tamil rebels, and the terrorist potential presented by the submersibles used by the drug cartels, the fact is that Washington has not yet reported evidence that these new methods of drug transport developed by organized crime groups are being used by other extremist actors. Nevertheless, the US maintains on high alert due to an increased rate of shipments arriving to their destination without detection.
[1] REICH, S., & Dombrowski, P (2017). The End of Grand Strategy. US Maritime Pperations in the 21st Century. Cornell Univesity Press. Ithaca, NY. Pages 143-145.
The U.S. is keeping an eye on the innovation of methods that could also be used to introduce terrorist cells or even weapons of mass destruction
In the last ten years, the proliferation of submersible and semi-submersible vessels, which are difficult to detect, has accounted for a third of drug transport from South America to the United States. The incorporation of GPS systems by the cartels also hinders the global fight against narcotics. A possible use of these new methods for terrorist purposes keeps the United States on its toes.

▲ Narco-submarine found in the jungle of Ecuador in 2010 [DEA]
article/ Marcelina Kropiwnicka
Drug trafficking to large consumer markets, especially the United States and Europe, is particularly innovative: the magnitude of the business means that attempts are made to overcome any barriers put in place by States to prevent its penetration and distribution. In the case of the United States, where the illicit arrival of narcotics dates back to the 19th century – from opium to marijuana to cocaine – the authorities' continued efforts have succeeded in intercepting many drug shipments, but traffickers are finding new ways and methods to smuggle a significant volume of drugs into the country.
The most disturbing method in the last ten years has been the use of submersible and semi-submersible vessels, commonly referred to as narco-submarines, which allow several tons of substances to be transported – five times more than a fishing boat did – evading the surveillance of the coast guard [1]. Satellite technology has also led traffickers to leave loads of drugs at sea, then picked up by pleasure boats without arousing suspicion. These methods make reference letter recent reports from the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
Through the waters of Central America
For many years, the usual way to transport drugs out of South America to the United States has been by fishing boats, speedboats, and light aircraft. Advances in airborne detection and tracking techniques have pushed drug traffickers to look for new ways to get their loads north. Hence the development of the narco-submarines, whose issue, since a first interception in 2006 by the US authorities, has seen a rapid progression.
This means of transport is one of the reasons why since 2013 there has been a 10% increase in trafficking on the drug route that goes from Colombia (a country that produces 93% of the cocaine consumed in the United States) to Central America and Mexico, from where the shipments are introduced into the United States. According to the DEA, this corridor now accounts for an estimated 93 percent of the movement of cocaine from South America to North America, compared to 7 percent of the route that seeks the Caribbean islands (mainly the Dominican Republic) to reach Florida or other places along the U.S. coast.
For a while, rumors spread among the U.S. Coast Guard that drug cartels were using narco-submarines. Without having seen any of them so far, the agents gave him the name 'Bigfoot' (as an alleged ape-like animal that would inhabit forests in the US Pacific is known).
The first sighting occurred in November 2006, when a U.S. Coast Guard patrol boat detected a blurred shape in the ocean, about 100 miles off the coast of Costa Rica. When agents approached, they discovered three plastic tubes emerging from the water, which came from a submersible craft that was making its way two meters below the surface. Inside they found three tons of cocaine and four men armed with an AK-47 rifle. The Coast Guard dubbed it 'Bigfoot I'.
Two years later there would be a 'Bigfoot II'. In September 2008, a U.S. Navy Coast Guard frigate seized a similar aircraft 350 miles from the Mexico-Guatemala border. The crew consisted of four men and the cargo was 6.4 tons of cocaine.
By then, U.S. authorities estimated that more than 100 submersibles or semi-submersibles had already been manufactured. In 2009, they estimated that they were only able to stop 14 percent of shipments and that this mode of transport supplied at least a third of the cocaine reaching the U.S. market. The navies of Colombia, Mexico and Guatemala have also seized some of these narco-submarines, which in addition to having been located in the Pacific have also been detected in the Caribbean and the Atlantic. Made by hand in the jungle, perhaps the most striking episode was that of having found one of them in the interior of Ecuador, in the waters of a river.
Its technical innovation has frequently surprised counternarcotics officials. Many of these self-propelled narco-submarines are up to fifteen meters long, made of synthetic materials and fiberglass, and have been designed to reduce radar or infrared detection. There have also been models with GPS navigation systems to be able to refuel and receive food at agreed appointments along the way.
GPS Tracking
The development and the generalization of GPS has also helped drug traffickers to introduce greater innovations. One procedure, for example, has been to fill a torpedo-shaped container – like a submersible, but this time without a crew – with drugs, attached to a buoy and a signal emitter. The container can hold up to seven tons of cocaine and is attached to the bottom of a ship by a cable. If the ship is intercepted, it can simply drop the container deeper, and then be retrieved by another vessel thanks to the satellite locator. This makes it extremely difficult for authorities to capture the drugs and apprehend traffickers.
The GPS navigation system is also used to deposit drug loads at points in U.S. territorial waters, where they can be picked up by pleasure boats or a small number of people. group of people without arousing suspicion. The package containing the cocaine is coated with several layers of material and then waterproofed with a subject foam. The package is placed inside a duffel bag that is deposited on the seabed to be later retrieved by other people.
As indicated by the AED in its report from 2017, "This demonstrates how drug trafficking organizations have evolved their methods of carrying out cocaine transactions using technology." And quotation the example of organizations that "transport kilos of cocaine in waterproof packages to a predetermined location and attach it to the ocean floor to be later removed by other members of the organization who have GPS location," which "allows members of drug trafficking organizations to compartmentalize their work, separating those who do the sea transport from the distributors on land."
|
Cocaine Journey from South America to the United States in 2017 [DEA] |
Terrorist risk
The possibility that these hard-to-detect methods could be used to smuggle weapons or could be part of terrorist operations worries U.S. authorities. Retired Vice Admiral James Stravidis, former head of the U.S. Southern Command, has warned of the potential use of submersibles especially "to transport more than just narcotics: the movement of cash, weapons, violent extremists or, at the worst end of the spectrum, weapons of mass destruction."
This risk was also referred to by Rear Admiral Joseph Nimmich when, as commander of the group South of work A joint Inter-Agency Agency, it faced the rise of submersibles. "If you can transport ten tons of cocaine, you can transport ten tons of anything," he told The New York Times.
According to this newspaper, the stealth production of homemade submarines was first developed in Sri Lanka, where the group Tamil Tiger rebels used them in their confrontation with government forces. "The Tamils will go down in history as the first terrorist organization to develop underwater weapons," Sri Lanka's Defense Ministry said. In 2006, as the NYT states, "a Pakistani and a Srinlancan provided Colombians with blueprints to build semi-submersibles that were fast, quiet, and made of cheap materials that were commonly within reach."
Despite that origin, ultimately written request In light of the Tamil rebels, and the terrorist potential of the submersibles used by drug cartels, Washington has reported no evidence that the new methods of drug transportation developed by organized crime groups are being used by extremist actors of a different nature. However, the U.S. is keeping its guard up given the high rate of shipments arriving at their destination undetected.
[1] REICH, S., & Dombrowski, P (2017). The End of Grand Strategy. US Maritime Pperations in the 21st Century. Cornell University Press. Ithaca, NY. Pg. 143-145