Ruta de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Articles .
US agreements with the Northern Triangle may have had a deterrent effect before entering into force
In the first month following the extension of the Asylum Cooperation Agreements (ACA) to the three Northern Triangle countries, apprehensions at the US border have fallen below the levels of recent years. The actual reduction in migrant inflows that this evidences has to do with Mexico's increased control over its border with Guatemala, but may also be due to the deterrent effect of advertisement of the agreements, whose implementation has not yet fully begun and therefore has yet to demonstrate whether they will be directly effective.
![Honduran migrants held by Guatemalan border guards, October 2018 [Wikimedia Commons]. Honduran migrants held by Guatemalan border guards, October 2018 [Wikimedia Commons].](/documents/10174/16849987/tercer-pais-blog.jpg)
▲ Honduran migrants held by Guatemalan border guards, October 2018 [Wikimedia Commons].
article / María del Pilar Cazali
Attempts to entrance attempt to enter the United States through its border with Mexico have not only returned to the levels of the beginning of the year, before the number of migrants soared and each month set a new record high, reaching 144,116 apprehensions and inadmissions in May( USBorder Guard figures that provide an indirect assessment of migration trends), but have continued to fall to below several previous years.
In October (the first month of the US fiscal year 2020), there were 45,250 apprehensions and inadmissions at the US southern border, down from October 2018, 2015 and 2016 (but not 2017). This suggests that the total number of apprehensions and inadmissions in the new fiscal year will be well below the record of 977,509 recorded in 2019. This boom had to do with the caravans of migrants that began at the end of 2018 in the Central American Northern Triangle (Honduras, El Salvador and Guatemala), following a migratory flow that, with different intensities, began in the 1980s due to political and economic instabilities in those countries.
This migration crisis led President Trump's US administration to implement tougher deportation policies, including changing conditions for expedited deportations. In addition, the White House pressured Mexico with the threat of tariffs on its products if it did not help reduce the flow of migrants crossing Mexican soil, prompting President López Obrador to deploy the newly created National Guard to the border with Guatemala. Trump combined these measures with the negotiation of Asylum Cooperation Agreements (ACAs) with the Northern Triangle countries, which were initially improperly referred to as "safe third countries", adding to the controversy they generated.
agreement with Guatemala
Due to US threats to impose tariffs on Guatemala if it failed to reduce the issue of migrants from or through Guatemala on their way to the US, the Guatemalan government accepted the terms of a attention announced by Trump on 26 July 2019. The agreement foresees that those who apply for asylum in the US but have previously passed through Guatemala will be brought back to the US so that they can remain there as asylum seekers if they qualify. The US sees this as a safe third country agreement .
A safe third countryagreement is an international mechanism that makes it possible to host in one country those seeking asylum in another. The agreement signed in July prevents asylum seekers from receiving US protection if they passed through Guatemala and did not first apply for asylum there. The US goal is intended to prevent migrants from Honduras and El Salvador from seeking asylum in the US. Responsibility for processing protection claims will fall to Washington in only three cases: unaccompanied minors, persons with a US-issued visa or document Admissions Office , or persons who are not required to obtain a visa. Those who do not comply with requirements will be sent to Guatemala to await the resolution of their case, which could take years. On the other hand, the agreement does not prevent Guatemalan and Mexican applicants from seeking asylum in the US.
Guatemalan President Jimmy Morales had previously announced that a similar agreement could become part of the migration negotiations with the US. In Guatemala, after advertisement of what had been agreed, multiple criticisms arose, because the security conditions in both countries are incomparable. This was compounded by rumours about the true content of the agreement that Morales had signed, as it was not immediately revealed to the public. Faced with this uncertainty, Interior Minister Enrique Degenhart declared that the agreement was only for Hondurans and Salvadorans, not for nationals of other Latin American countries, and that the text did not explicitly mention the term "safe third country".
In the week following the advertisement, three appeals for amparo against the agreement were lodged with Guatemala's Constitutional Court, arguing that the country is not in a position to provide the protection it supposedly offers and that the resulting expense would undermine the economic status of the population itself. However, Degenhart defended agreement by saying that the economic repercussions would have been worse if the pact with Washington had not been reached, because with the US tariffs, half of Guatemala's exports and the jobs that accompany these sectors would be at risk.
These criticisms came not only from Guatemalan citizens, but also from public figures such as Guatemala's Human Rights Ombudsman, Jordán Rodas, citing a lack of transparency on the part of the government. Rodas insisted that Guatemala is not fit to be a safe third country because of its low indicators of production, Education, public health and security. Similar ideas have also been expressed by organisations such as Amnesty International, for whom Guatemala is not safe and cannot be considered a safe haven.
In its pronouncement, Guatemala's Constitutional Court affirmed that the Guatemalan government needs to submit the agreement to congress for it to become effective. This has been rejected by the government, which considers that international policy is skill directly the responsibility of the country's president and will therefore begin to implement what has been decided with Washington without further delay.
![Apprehensions and inadmissibilities by US Border Guard, broken down by month over the last fiscal years (FY) [Taken from CBP]. Apprehensions and inadmissibilities by US Border Guard, broken down by month over the last fiscal years (FY) [Taken from CBP].](/documents/10174/16849987/tercer-pais-grafico.png)
Apprehensions and inadmissibilities by US Border Guard, broken down by month over the last fiscal years (FY) [Taken from CBP].
Also with El Salvador and Honduras
Despite all the controversy generated since July as a result of the pact with Guatemala, the US developed similar efforts with El Salvador and Honduras. On 20 September 2019, El Salvador's president, Nayib Bukele, signed a agreement similar to the safe third country figure, although it was not explicitly called that either. It commits El Salvador to receive asylum seekers who cannot yet enter the US, similar to the agreement with Guatemala. El Salvador's agreement has the same three assumptions in which the US will have to make position of migrant protection.
The Salvadoran government has received similar criticism, including a lack of transparency in the negotiation and denial of the reality that the country is unsafe. Bukele justified signature by saying it would mean the extension of Temporary Protected Status (TPS) for the more than 190,000 Salvadorans living in the US. In October 2019, the Salvadoran Foreign Ministry said that this agreement is not a safe third country because El Salvador is not in the serious migratory situations in which Guatemala and Honduras are in terms of the flow of people, so it is only a agreement of non-violation of rights to minimise the number of migrants.
On 21 September 2019 the Honduran government also made public the advertisement of a agreement very similar to the one accepted by its two neighbours. It states that the US will be able to deport to Honduras asylum seekers who have passed through Honduras. Like the other two countries, the Honduran government was criticised as not being a safe destination for migrants as it is one of the countries with fees highest homicide rates in the world.
Despite criticism of the three agreements, in late October 2019 the Trump administration announced that it was in final preparations to begin sending asylum seekers to Guatemala. However, by the end of November, no non-Guatemalan asylum seekers had yet been sent. The inauguration in early January of President-elect Alejandro Giammattei, who announced his desire to rescind certain terms of agreement, may introduce some variation, though perhaps his purpose will be to wring some more concessions from Trump, in addition to the agricultural visas that Morales negotiated for Guatemalan seasonal workers.
The avalanche of unaccompanied foreign minors suffered by the Obama Administration in 2014 has been overcome in 2019 with a new migratory peak
In the summer of 2014, the United States suffered a migration crisis due to an unexpected increase in the number of people in the country. issue of unaccompanied foreign minors, mostly Central Americans, who arrived at its border with Mexico. What has happened since then? Although oscillating, the volume of this subject Immigration prices fell, but in 2019 a new record has been recorded, hand in hand with the "caravan crisis", which has led to the rise again in total apprehensions at the border.
![U.S. border agents search unaccompanied minors at Texas-Mexico border in 2014 [Hector Silva, USCBP–Wikimedia Commons] U.S. border agents search unaccompanied minors at Texas-Mexico border in 2014 [Hector Silva, USCBP–Wikimedia Commons]](/documents/10174/16849987/migracion-blog.jpg)
▲ U.S. border agents search unaccompanied minors at Texas-Mexico border in 2014 [Hector Silva, USCBP–Wikimedia Commons]
article/ Marcelina Kropiwnicka
The United States hosts more immigrants than any other country in the world, with more than a million people arriving each year, either as legal permanent residents, asylum seekers and refugees, or in other immigration categories. While there is no exact figure for how many people cross the border illegally, U.S. Customs and Border Control (U.S. Customs and Border Control) measures changes in illegal immigration based on the number of apprehensions made at the border; Such arrests serve as an indicator of the issue total number of attempts to enter the country illegally. As for the data, it can be concluded that there have been notable changes in the demographics of illegal migration at the border with Mexico (southwest border, in official U.S. terms) in recent years.
The peak of apprehensions at the U.S.-Mexico border was during 2000, when 1.64 million people were apprehended trying to enter the United States illegally. The numbers have declined, across the board, since then. In recent years, there have been more apprehensions of non-Mexicans than Mexicans at the border with the neighboring country, reflecting a decrease in issue of unauthorized Mexican immigrants who came to the U.S. in the last decade. The increase, in fact, was largely due to those fleeing violence, gang activity and poverty in Guatemala, Honduras and El Salvador, a region known as Central America's Northern Triangle.
The nations included in the Northern Triangle are among the poorest in Latin America – a high percentage of the population still lives on less than $2 a day (the international poverty line is $1.90); There has been little progress in reducing poverty in recent years. Within Latin America and the Caribbean, Honduras has the second highest percentage of the population living below the poverty line (17%), after Haiti, according to the latest data of the World Bank.
Unaccompanied Alien Minors
While fewer unaccompanied adults have attempted to cross the border without authorization over the past decade, there has instead been a surge of unaccompanied alien minors (MENAs) trying to enter the United States from Mexico. The migration of minors without accompanying adults is not new; What is new now is its volume and the need to implement policies in response to this problem. The increase in apprehensions of MENAs in FY2014 caused alarm and prompted both intense media scrutiny and the implementation of policy responses; Attention was maintained even as the phenomenon declined. The numbers dropped again to just under 40,000 apprehensions of minors the following year.
The international community defines an unaccompanied migrant minor as a person, "who is under eighteen years of age" and who is "separated from both parents and is not being cared for by an adult who by law or custom has the responsibility to do so." Many of these unaccompanied minors report immediately to U.S. border security, while others enter the country unnoticed and undocumented. Not only this, but children have no parents or legal guardians available to provide care or physical custody, which quickly overwhelms the services of local border patrols.
In 2014, many of the unaccompanied children said they were under the false impression that the Obama administration was granting "permits" to children who had relatives in the U.S., as long as they arrived no later than June. These false convictions and hoaxes were even more potent this past year, especially as President Trump continues to reinforce the idea of restricting migrants' access to the United States. The cartels have continued to transport a issue increasing number of Central American migrants from their countries to the United States.
Critical moments of 2014 and 2019
In 2014, during Obama's second term, total apprehensions along the border with Mexico reached 569,237 (this figure includes "inadmissible" people), a record only surpassed now. While the increase over the previous year was 13%, the increase was much more B regarding the arrests of MENAs; These rose from 38,759 in fiscal year 2013 to 68,541 in fiscal year 2014 (in the U.S. the fiscal year runs from October of one year to September of the next), an increase of almost 80%, more than four times those recorded in fiscal year 2011. In the case of minors from Honduras, the figure rose from 6,747 to 18,244 in one year; those of Guatemala rose from 8,068 to 17,057, and those of El Salvador, from 5,990 to 16,404 (those of Mexico, on the other hand, fell from 17,240 to 15,634). The Greatest issue The number of apprehensions occurred in May, a month in which MENA arrests accounted for 17% of total apprehensions.
Since 2014, apprehensions of unaccompanied minors, while fluctuating, have declined by issue. But in 2019 a new record has been recorded, reaching 76,020, with a maximum in the month of May. However, that month they accounted for only 9% of the total apprehensions, because this time it has not been a MENA crisis, but has been inserted into a B peak of total apprehensions. While overall apprehensions decreased significantly during the first six months of Trump's presidency, they then rose, reaching a total of 851,508 in 2019 (with the "inadmissible" the figure reached 977,509), which is more than double the number from 2018. The issue total apprehensions increased by 72% from 2014 to 2019 (in the case of MENAs the increase was 11%).
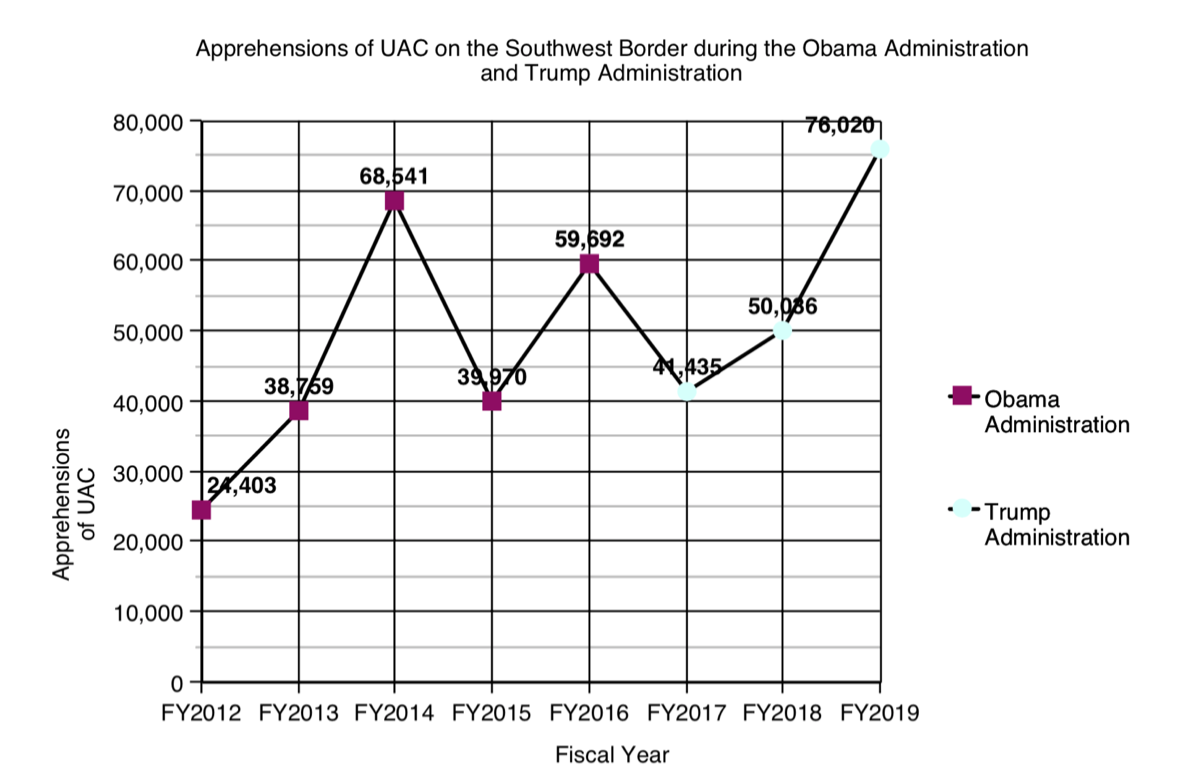 |
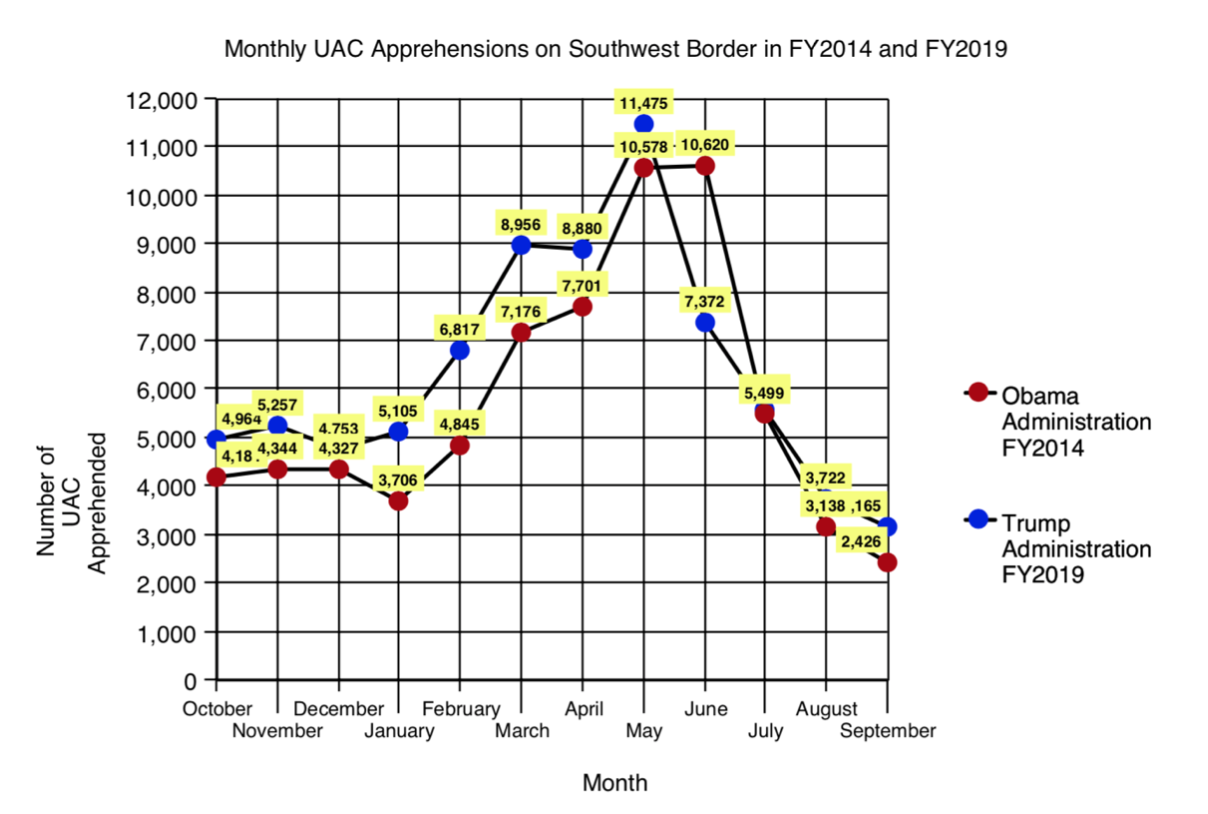 |
Apprehensions of unaccompanied alien minors at the U.S.-Mexico border, between 2012 and 2019 (Figure 1), and comparison of 2014 and 2019 by month (Figure 2). source: US Customs and Border Patrol.
Reaction
The U.S. had a variety of domestic policies aimed at dealing with the massive increase in immigration. However, with the overwhelming peak of 2014, Obama called for funding for a program for "the repatriation and reintegration of migrants to the countries of Central America and to address the root causes of migration from these countries." Although funding for the program has been fairly consistent over the past few years, the budget for 2018 proposed by the President Trump reduced the financial aid to these countries by approximately 30%.
The Trump Administration has made progress in implementing its diary on immigration, from the beginning of the construction of the wall on the border with Mexico to the implementation of new programs, but the hard line already promised by Trump in his degree program The U.S. government has proven ineffective in preventing thousands of Central American families from crossing the southwest border into the United States. With extreme gang violence running rampant and technicalities in the U.S. immigration system, migrants' motivation to leave their countries will remain.
Some U.S. and Canadian diplomats who were in Havana between 2016 and 2018 are still not fully recovered from ailments they suffered
![U.S. Embassy building in Cuba [department de Estado] [ de Estado] U.S. Embassy building in Cuba [department de Estado] [ de Estado]](/documents/10174/16849987/ataques-sonicos-blog.jpg)
▲ Building of the U.S. Embassy in Cuba [department de Estado].
ANALYSIS / Eduardo Villa Corta
Three years ago, staff U.S. diplomats stationed in Cuba began to feel physical discomfort supposedly caused by strange sounds to which they had apparently been exposed; Washington spoke of a "sonic attack. However, although the symptoms suffered by those affected have been determined to be anomalous, it has not been possible to establish what caused them. Was it really an attack? Who was behind it? We review here the main hypotheses and conjectures that have been made, and point out their weaknesses.
In late 2016 and early 2017, several U.S. diplomats stationed in Havana, as well as members of their families, reported suffering from dizziness, vertigo and sharp pains in their ears that could be caused by strange sounds to which they had been exposed. According to their testimonies, the sounds came from a specific direction, and they had heard them in their own residences or, in some cases, in hotel rooms, while people staying in neighboring houses or adjoining rooms had not heard any special sounds. The phenomenon also affected Canadian diplomats in the Cuban capital. In all, some forty people were treated for these symptoms.
Acoustic attack
Echoing the facts reported by its staff in Cuba, in mid-2017 the U.S. State department stated that the symptoms could have been caused by a sonic attack by the Cuban government directed against diplomats and their families. In October 2017, President Donald Trump directly accused Havana: "I believe Cuba is manager; yes, I do."
At the beginning of 2018 the department of State issued a statement alert not to travel to Cuba due to a possible health crisis and withdrew a good part of the staff of the mission statement diplomatic in Havana, reducing the activity of this to the minimum possible. At that time, a total of 24 Americans had been affected.
At the time, the Canadian government also indicated that its diplomats had experienced similar discomfort. Ottawa decided to evacuate the families of its employees in Cuba and in early 2019 proceeded to reduce the staff of the embassy in the face of what appeared to be the appearance of a fourteenth case.
The Cuban government denied from the outset being involved in any harassment operation against the U.S. or Canada. ˝There is no test about the cause of the reported ailments, nor is there any evidence to suggest that these health problems have been caused by an attack of any kind˝, Havana assured. Raul Castro's government offered its cooperation in the research of the facts, with nothing coming to light that could explain the case. No devices that could have provoked the sounds appeared.
Adding confusion to the status, at least two US diplomats stationed in China, busy at the consulate general in Guangzhou, the largest that the US has in the country, presented in early 2018 also the symptoms already described. Washington evacuated them and issued a health warning about missions in mainland China.
The Associated Press published in October 2017 a recording of the alleged sounds causing the reported ailment, and indicated that government agencies had been unable to determine the nature of the noise and explain its relationship to the bodily disorders caused. Months later, he noted that internal FBI reports did not even establish that there had been an "attack". Other media highlighted the poor cooperation in the research, due to jurisdictional zeal, between the department of State, the FBI and the CIA.
Symptoms of "Havana syndrome".
A medical team from the University of Pennsylvania, at the request of the U.S. Government, examined 21 people affected by what the press began to call "Havana syndrome". The research, initially published in March 2018 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), indicated that most of the patients reported problems with report, concentration, and balance, and determined that they appeared to have suffered injuries to extensive brain networks.
data Further MRI scans of the same team extended to 40 patients, released in July 2019, led to the conclusion that the diplomats had experienced some craniocerebral trauma. The results of the MRI scans, compared with those of a group of healthy people, showed differences in the volume of the white and gray substances of the brain, in the integrity of the cerebellar microstructures and in the functional connectivity of the subnetworks for hearing and spatial vision, but not for executive functions.
This report concluded that the staff diplomat had been physically injured, although it could not determine the cause. He also noted that patients do not experience a usual recovery, as they are not recovering quickly from symptoms, as is the case in other cases of similar "concussions" or ear problems.
IF IT WASN'T AN ATTACK, WHAT WAS IT?
As no clear cause has been established as to what caused the ailments suffered by the US and Canadian diplomatic staff and some members of their families, the very reality of an attack has been called into question. Although various alternative explanations have been put forward, none of them are fully convincing.
1) Collective hysteria
Formulation. Some neurologists and sociologists, such as Robert Bartholomew, have suggested that it could be a case of mass hysteria. Given the pressure to which some of the diplomats working in very unfriendly environments are subjected, and the endogamic relationship in which they live, living almost exclusively among themselves, it could explain a mutual conviction of an external attack that even has somatic consequences.
Weak spot. Both the research of the University of Pennsylvania and the doctor of the department of State, Charles Rosenfarb, who appeared before the committee of Foreign Relations of the Senate, came to rule out that the symptoms suffered by the diplomats were due to a mere mental mechanism. It is very difficult that about sixty people, including Americans and Canadians, convinced each other of an aggression of this kind subject and then almost all of them developed the same brain lesions.
2) Microwave
Formulation. The researcher team at the University of Pennsylvania, while not pointing to any possible cause of the ailments, did not rule out certain assumptions, such as that of microwave affectation. This aspect was insisted upon by a research published in 2018 in the journal Neural Computation, which considered the symptoms consistent with exhibition to electromagnetic microwave (RF/MW) radiation.
Weak point. Not all the symptoms shown by patients could be a consequence of the exhibition of such a radiation subject, which also has a diverging literature on its effects on the human body. In addition, there is no known microwave weapon that can affect the brain.
3) Ultrasound
Formulation. A team of computer experts at the University of Michigan suggested in 2018 that it could be a case of exhibition to some subject ultrasound, perhaps coming from malfunctioning listening equipment mixing multiple ultrasonic signals.
Weak point. The recording of one of the sound episodes - the sample broadcast by AP - is not sufficient to be able to determine its nature. It is also possible that the sound was somewhat different in other cases.
4) Crickets
Formulation. A research from the Universities of California-Berkeley and Lincoln, from the existing sound sample , considered in January 2019 that the possible cause of the attacks was made by cricketsThe study, specifically crickets Anurogryllus muticus. The research was a comparative study between the sound emitted by that variant of crickets and the sample of one of the Havana acoustic episodes.
Weak point. The sound perceived by the diplomats was directional, so it was not heard by neighboring people. If they had been crickets in their natural environment, the sound would have spread around.
5) Neurotoxins
Formulation. A joint study by two Canadian research centers in May 2019 attributed the symptoms suffered by diplomats to exhibition to neurotoxins from pesticides used to spray mosquitoes, a internship common occurrence in embassy buildings.
Weak point. The diplomats affected related the beginning of their physical discomfort to situations experienced in their own residences or in hotel rooms, where there was no fumigation.
IF IT WAS AN ATTACK, WHO DID IT?
Given that the previous explanations do not seem entirely solid, the US Government maintains the hypothesis of an attack. If it really happened, who was behind it? Here, too, there are various conjectures.
1) Castro regime
The first option considered, assumed in principle by the US given the public accusations made from Washington, has been to attribute the alleged attacks to the Cuban regime itself. With them, Havana would try to maintain pressure on the Americans, in spite of the formal reestablishment of diplomatic relations, with the goal to mark each other's territory.
Weak point. The incidents began to occur during the Obama Administration, in a context of a ˝honeymoon˝ marked by the reopening of embassies and the visit of Barack Obama to Havana. The normal thing is that at the end of 2016, in view of the U.S. elections, the Castro regime would not want to give reasons to the next U.S. president to twist the diplomatic line opened by Obama. It could make sense that after Donald Tump's later revocation of the previous openness measures, Cuba would want to punish the new Administration, but not before seeing the direction it would take; in any case, the attacks would only justify the hard line followed by Trump, which does not benefit the island.
2) A sector of Castroism
Fidel Castro was attributed with an unaccommodating attitude towards his brother Raul's decision to reestablish diplomatic relations with the United States. Although he died in November 2016, people around him might have tried to torpedo that rapprochement, convinced that hostility with Washington was the best way to ensure the survival of the regime as conceived by its founder.
Weak point. Although Fidel Castro's reluctance towards rapprochement with the U.S. is true, it is difficult to think that the most conservative sector within Castroism would dare to boycott so directly Raul Castro's fundamental political line. It is another thing that, after he handed over the presidency of Cuba to Miguel Díaz-Canel in April 2018, some sectors within the regime could make internal movements to send certain messages, but the changeover occurred when most of the acoustic episodes had already taken place.
3) A third country (Russia, China)
The third option would be that a third country generated the attacks. American intelligence indicates that the most viable option in this case would be Russia. Moscow has been keen to return to operating in the Caribbean, as in the Cold War, and aggression against U.S. diplomats in Cuba would fit in with its strategy. It has also been suggested that China might want to repay Washington in its backyard with the same harassment that the Chinese believe they feel from the US in their nearest seas.
Weak point. The return of Russia to the Caribbean is certainly documented, and it is conceivable that Moscow could have promoted a punctual action against some specific goal , but it seems difficult that it would have sustained over time an operation that harms Cuba's sovereignty. As for China's presence in the US neighborhood, it is a less confrontational move than the one carried out by Russia. Moreover, if Beijing had chosen foreign soil in order to better erase the traces of an action against US diplomats, then the cases recorded in Guangzhou would not have occurred.
With its mega-city and technology zone project , the Saudis are seeking to consolidate an economic alternative to oil.
NEOM, an acronym for New Future, is the name of the new economic-technological city and area , with an area three times the size of Cyprus, which Saudi Arabia is promoting in the north-west of the country, opposite the Sinai Peninsula. In addition to seeking alternatives to oil, with NEOM the Saudis aim to rival the urban innovations of Dubai, Abu Dhabi and Doha. The project also involves shifting Saudi interest from the Persian Gulf to the Red Sea and closer neighbourhoods with Egypt, Jordan and Israel.
![The future NEOM megacity, from agreement with the vision of its promoters [NEOM Project]. The future NEOM megacity, from agreement with the vision of its promoters [NEOM Project].](/documents/10174/16849987/neom-blog.jpg)
▲ The appearance of the future NEOM megacity, from agreement with the vision of its promoters [NEOM Project].
article / Sebastián Bruzzone Martínez
Middle Eastern states are seeking to diversify their revenues and avoid potential collapse of their economies in order to counteract the end-of-oil crisis expected in the mid-21st century. Arabs' preferred sectors are renewable energy, luxury tourism, modern infrastructure and technology. Governments in the region have found ways to unify these four sectors, and Saudi Arabia, along with the United Arab Emirates, seems to want to position itself at the forefront of the Arab technology degree program .
While the world looks towards Sillicon Valley in California, Shenzhen in China or Bangalore in India, the Saudi government has begun preparations for the creation of its first independent economic and technological zone: NEOM (short for the Arabic term Neo-Mustaqbal, New Future). The project was until recently headed by Klaus Kleinfeld, former CEO of Siemens AG, who has been replaced by Nadhmi Al Nasr as CEO of NEOM since his appointment as an advisor to the Saudi Crown.
On 24 October 2017, at the Future Investment Initiative lecture in Riyadh, Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman announced the $500 billionproject , part of the Saudi Vision 2030 policy programme. average The territory where NEOM will be located is in the border area between Saudi Arabia, Egypt and Jordan, on the shores of the Red Sea, through which almost ten percent of world trade flows, has a temperature 10ºC lower than that of the rest of the countries of the Gulf Cooperation committee , and is located less than eight hours' flight from 70% of the world's population, so it could become a major passenger transport hub.
As announced by the Saudi government, NEOM will be a special economic city, with its own civil and tax laws and Western social customs, covering 26,500 square kilometres (the size of Cyprus multiplied by three). The main objectives are to attract foreign investment from multinational companies, diversify the oil-dependent Saudi Economics , create a free market space and home to millionaires, "a land for free and stress-free people; a start-up the size of a country: a blank sheet of paper on which to write the new era of human progress", says a promotional video on project. All this under the slogan: "The world's most ambitious project: an entire new land, purpose-built for a new way of living". According to the website and official accounts of project, the 16 sectors of energy, mobility, water, biotechnology, food, manufacturing, communication, entertainment and fashion, technology, tourism, sport, services, health and wellness, Education, and livability will generate 100 billion dollars a year.
Thanks to a report published by The Wall Street Journal and prepared by the consulting firms Oliver Wyman, Boston Consulting Group and McKinsey & Co., which, according to them, had access to more than 2,300 confidential planning documents, some of the ambitions and luxuries that the futuristic city will have have have have come to light. These include flying cars, holograms, a Jurassic Park-style robot dinosaur theme park and edition Genetics , never-before-seen technologies and infrastructure, luxury hotels, resorts and restaurants, cloud-creating mechanisms to cause rainfall in arid areas, glow-in-the-dark sandy beaches, and even an artificial moon.
Another aim of project is to make NEOM the safest city on the planet, through state-of-the-art surveillance systems including drones, automated cameras, facial and biometric recognition machines and AI capable of reporting crimes without the need for citizens to report them. Similarly, the leaders of the urban development initiative themselves predict that the city will be an ecological centre of great projection, basing its power supply system solely on solar and wind energy obtained from panels and windmills, as they have a whole desert to install them in.
At the moment, NEOM is only a project in its infancy. The land on which the big city will be located is a desert terrain, mountains up to 2,500 metres high and 468 kilometres of pristine coastline of turquoise blue water, with a palace and a small airport. NEOM is being built from scratch, with an initial outlay of $9 billion from the Saudi Arabian sovereign wealth fund Saudi Arabia Monetary Authority (SAMA). Apart from foreign business investment, the Saudi government is looking for workers from all professional sectors to help in their respective fields: Jurists to draft a civil, criminal and tax code; engineers and architects to design a modern, efficient and technological infrastructure and energy plan; diplomats to collaborate in its promotion and cultural coexistence; scientists and doctors to encourage clinical and biotechnological research and welfare; academics to promote Education; economists to make income and expenditure profitable; personalities specialising in tourism, fashion and telecommunications... But, above all, people and families to inhabit and give life to the city.
As reported by the Arabic daily Rai Al Youm, Mohammed bin Salman has C a proposal prepared by a joint Saudi legal committee with the UK, which consists of providing a VIP document that will offer special visas, residency programrights to investors, senior officials and workers in the future city. Contracts business have already been awarded to the US engineering firm Aecom and construction contracts to the UK's Arup Group, Canada's WSP, and the Netherlands' Fugro NV.
However, not everything is as ideal and straightforward as it seems. Despite the strong interest of 400 foreign companies in project, according to the local government, there is uncertainty about its profitability. Problems and scandals related to the Saudi crown, such as the imprisonment of family members and dissidents, corruption, unequal rights, the military intervention in Yemen, the case of the murder of journalist Khashoggi and the possible political crisis following the future death of King Salman bin Abdulaziz, Mohammed's father, have caused investors to tread carefully. Moreover, in the region where the city is to be built there are villages of locals who would be relocated, and "compensated and supported by social programmes", according to the Saudi government, which will be criticised by human rights groups.
In conclusion, NEOM is a unique project and a match for the Arab sheikhs themselves, who have adopted a far-sighted economic vision. It is expected that by 2030 it will be possible to live in the city, even if construction is still underway and not yet fully completed. According to the markets, the project, still far from completion, seems to be on track. It already has a structural financing commitment with BlackStone of 20 billion euros, and a technology financing commitment with SoftBank of 45 billion euros. Because such a project has never been seen before and therefore there are no references, it is difficult to determine whether the visionary plan will be successfully consolidated or whether it will remain just smoke and mirrors and a huge loss of money.
In the largest countries in the region, there are four times as many private guards as police officers and ten times more weapons than in Europe
The high rates of violence in Latin America and the deficient presence of the authority of the respective States in parts of the territory have led to the proliferation of private security companies throughout the region. His issue It now has more than 16,000 companies, in an industry that involves more than 2.4 million people. The sector faces significant challenges, such as vague legality in many cases, a lack of experience, ways that are incompatible with civil and human rights in certain places, and the risk of escalating stockpiles.

article / Martín Biera Muriel
The proliferation of private security companies in Latin America is linked to crime and violence statistics in the region. It is estimated that 19 out of every 20 violent crimes that occur in the world take place in Latin America, where 17 of the 20 most violent cities in the world and 4 of the 5 most violent countries are located.
The status has led to an "explosive growth" in the privatization of security in Latin America, as the report "Security for Sale" by the Inter-American Dialogue. The rise of the issue of Private Defense and Security Companies (PMSCs) has occurred not only in countries with marked conflicts, such as Colombia, where in the last ten years there has been an increase of 126%, but also in countries of greater social peace and institutionality such as Chile, which in five years has seen an increase of 50%. The total number of companies engaged in this function in Latin America reached 16,174 in 2017, as specified at the time by the Center for the Democratic Control of the Armed Forces in Geneva (DCAF).
The PMSC sector
The term PMSC includes both security companies in use in developed countries, normally dedicated to the safekeeping of establishments or individuals, as well as defence companies that can replace functions usually reserved for the State. The latter developed after the end of the Cold War and have become an important player in international relations, with participation in conflicts of interest. leave and even high intensity.
These defence companies operate in a framework The regulation of which was attempted to be standardized in 2008 with the Montreaux Document, a compilation of legal obligations and good practices aimed at guaranteeing the sovereignty of States and protecting Human Rights. While the text applies more directly to situations of armed conflict, it also provides a framework for security companies in general, given the tenuous boundary between a subject Especially in Latin America, where the authority of the State often does not extend to the entire national territory, some civil conflicts are especially virulent and some use the Armed Forces in the fight against criminal violence and the maintenance of public order.
More Guards Than Cops
The more than 16,000 PMSCs in Latin America employ around 2.4 million people. While security guards outperform in issue to members of the police around the world, in many Latin American countries there is a particular imbalance between the issue components of the police forces and that of private agents: in Colombia, Brazil and Mexico, the ratio is one police officer to four members of EMSP; in countries of extreme violence such as Honduras and Guatemala, the ratio is even as high as one to seven. It is also the case that many members of the police resort to moonlighting, acting as police officers during the day and becoming security agents at night in some neighborhood. business or building.
The largest companies are those that are engaged in the surveillance and escort of VIP clients. The largest are of European and American origin and specialise in a part of the sector, especially in the protection of private property. Most of them operate in cities or in centres of natural resource extraction isolated from urban areas. In relation to the frequent criticism that these companies receive, for alleged supplanting of functions proper to the legally constituted authority, it is necessary to emphasize that the framework The legal system in which large companies operate is strict and supervised.
degree program Armament
It can be argued that the skill among operators has generated a kind of degree program armaments in which each business You want to offer more efficient services. At the same time, as there is a greater issue With more modern weapons, criminals also tend to increase their firepower and their capabilities to meet their objectives, which consequently leads companies to also increase the caliber of their weapons, in a spiral that is difficult to control. Statistics show that Latin America has the highest ratio of firearms to security guards in the world outside of conflict-affected areas. This ratio is ten times higher than that of small arms in Europe.
This has led to the fact that certain PMSCs have been criticized in the Latin American scenario for having contributed, directly or indirectly, to illegal arms trafficking and the increase in armed gangs, generating a vicious circle. For example, in 2015 ninety people were arrested in San Francisco (some of them linked to PMSCs) for belonging to a network of arms trafficking linked to the Mara Salvatrucha (MS-13). There have also been cases of theft and loss of weapons imported from the region, both by individual private security contractors and by the military itself; These weapons then enter the black market. Thus, more than 40% of illegal weapons in El Salvador are linked to some 460 private security companies, despite the obligation to have an official registry for their identification.
Challenges
Reducing high levels of insecurity is one of the main challenges for many Latin American countries. The reasons for the persistent violence in their societies are manifold; These include political corruption and economic inequality. The richer classes can be considered targets of attempted robberies or kidnappings, but the working classes also suffer from high crime figures, in their case without the possibility of resorting to private security.
Private security in Latin America faces two major challenges. One is illegality on the part of the sector: illegal companies grow faster than in the legal sector; in Brazil, for example, the issue of guards employed informally outnumbered formal ones. The other is the lack of training or experience of a certain volume of private guards. To meet the need for greater legal regulation, and for a regulation more adjusted to national specificities, and to the convenience of greater training It will help to reduce the grey area in which in many cases it operates and the violations of Human Rights.
The deterioration of recent years seems to have been corrected in several indicators on democratic health and economic environment.
Costa Rica has traditionally been a model of democratic functioning in a region with serious institutional deficits, which has earned it a mediating role in different conflicts. The increase of internal problems -strikes, citizen protests, bipartisan crisis...- have seemed to have diminished Costa Rica's international prestige in recent years. Is Costa Rica suffering from democratic and institutional deterioration?
![Facade of the National Theater of Costa Rica, in San José [Pixabay]. Facade of the National Theater of Costa Rica, in San José [Pixabay].](/documents/10174/16849987/costa-rica-deterioro-blog.jpg)
▲ Facade of the National Theater of Costa Rica, in San José [Pixabay].
article / Ramón Barba
The political unrest of recent years in Costa Rica, in a regional context of the "angry vote" and the consequent "outsider phenomenon", has given the impression of a setback in the country's institutional virtues. The goal of this article is to determine, based on different indicators on democratic health and economic and political satisfaction, if there are objective data that ratify this perception.
For this purpose we will first analyze a set of indicators, elaborated by the World Bank, the Konrad Adenauer Foundation and The Economist magazine, and then we will also take into account some results of the survey Latinobarómetro. We will compare the values recorded in 2010, 2013, 2016 and, when possible, 2018.
Indicators
Regarding the Democracy Index elaborated by The Economist, although Costa Rica maintains its second place among Latin American democracies, behind Uruguay and ahead of Chile (these are the three countries that usually obtain better grade in the different institutional parameters of the region), in the last decade a Costa Rican democratic decline is observed, apparently overcome in the most recent report. From a score of 8.04 achieved in the 2010 Democracy Index, Costa Rica dropped to 8.03 in 2013 and 7.88 in 2016, to regain ground in 2018 with an 8.07. The country remains the best democracy in Central America, followed at a distance by a stable Panama.
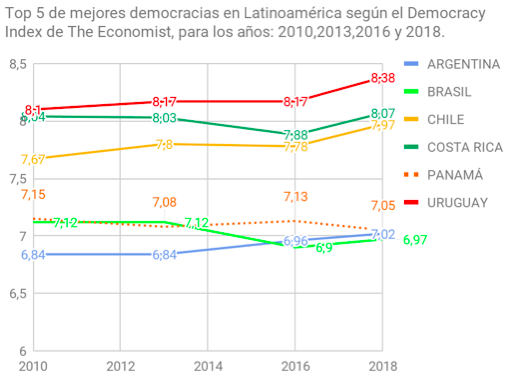 |
The deterioration of recent years has also been picked up by the Index of development of Democracies in Latin America (IDD-LAT), of the Konrad Adenauer Foundation, which has not yet published data referring to 2018, so this index cannot endorse whether there has been a recent recovery. In 2010, Costa Rica had a score average of 9.252; it barely varied in 2013, with a figure of 9.277, but dropped clearly in 2016, with 8.539 points. The components of the index that suffered the most were welfare policy creation and economic efficiency, where it dropped from 1st and 5th place, respectively, to 8th and 12th. The fact that Costa Rica remained between 1st and 3rd place in civil and political rights and in institutional and political efficiency in those years sample shows that the social concern of those years was more in the economic sphere than in the institutional sphere.
The World Bank's Good Governanceindicators also registera small regression in the case of Costa Rica between the years 2013 and 2016 (data more recent ones have not yet been published). Regarding the Rule of Law and Government Effectiveness scales the score dropped from 0.6 and 0.5, respectively, to 0.5 and 0.4. There has been little change in the Control of Corruption scale.
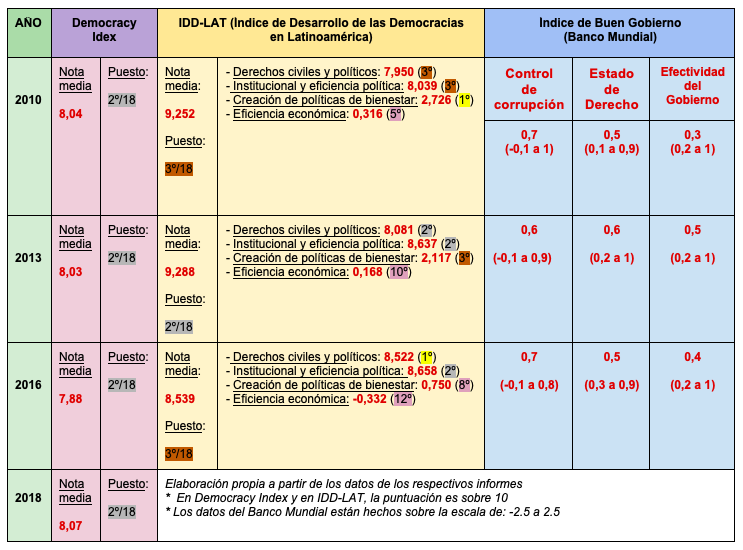 |
evaluation citizen
The above indicators are prepared by experts who, by applying standardized criteria, seek to offer an objective estimate. But we also wanted to take into account the opinion of the citizens themselves, as expressed in the survey Latinobarómetro. These can be useful to indicate the perception that exists among the population regarding the institutional health of the country: the satisfaction that exists regarding the government system and the economic system.
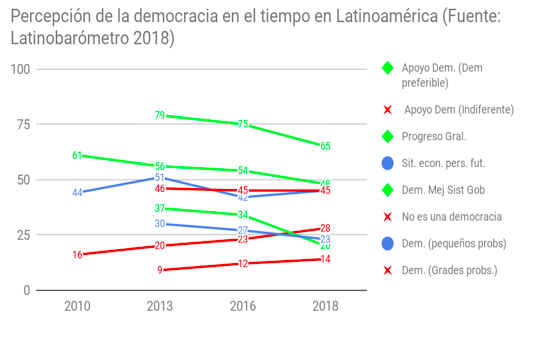 |
The value of democracy is maintained in high percentages in Costa Rica, despite a negative trend in the region as a whole. Attending to four values that Latinobarómetro has included in its surveys corresponding to the years here chosen for our comparison, we see that indeed in 2016 the citizen perception was that of a worsening of status, but in 2018 an improvement is observed, reaching even more positive levels than in 2013. As for the evaluation of democracy, its consideration as the best system of government dropped from 77% to 72% and then has risen again to 77%, while its cataloging as a preferable system has been increasing: 53%, 60% and 63%.
The perception of the economic environment, for its part, had a blip in 2013, but today it is in better condition. The statement "progress is being made" fell from 15% to 12%, but in 2018 it reached 22%, while satisfaction with future personal economic prospects fell from 45% to 20% to stand in 2018 at 52%.
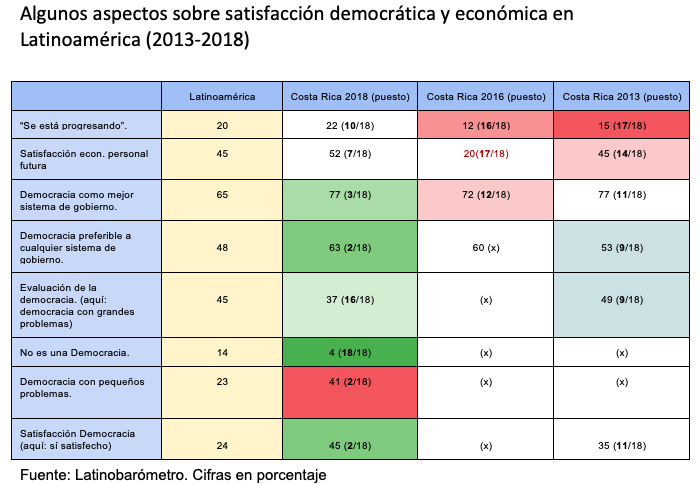
Political unrest
Costa Rica is a country that retains strong institutions, although the political landscape is more divided. test of this is the end of the two-party system (1953-2014), brought about by less support for the National Liberation Party (PLN) and the Social Christian Unity Party (PUSC) and the emergence of the Citizen Action Party (PAC), to which the country's current president, Carlos Alvarado, belongs.
Corruption issues such as the "cimentazo case", the high public debt that has forced cutbacks in a country with certain well-established social benefits and a regional and international environment prone to populist solutions may be behind the political unrest observed in Costa Rica in recent years.
This occurs in a context of the "angry vote" in Latin America, which arises as a consequence of the political actions of the last twenty years in the region and a strengthening of the middle classes. Citizen dissatisfaction has led to the emergence of outsider politicians: people with relative popularity, short degree program political, without a determined strategy and with an "anti-political" speech . This is a patron saint that, although it is in the emergence of the PAC, in any case does not fully correspond to the personality of President Alvarado, who actually seems to have contributed to redirect the Costa Rican restlessness.
Conclusions
Thus, from the analysis of the data observed here, it can be concluded that there was indeed a slight deterioration in both institutional circumstances and especially in economic conditions or expectations between 2013 and 2016, but the different scales have returned in 2018 to previous values, even improving in some cases to levels of ten years ago. This is something that can be observed both in the indicators at position of experts that follow standardized objective procedures and in the surveys of subjective citizen perception.
The sample used and the temporal tastings carried out have not been exhaustive, so it is not possible to specify whether the variations noted here are circumstantial fluctuations or part of a trend pointing in a certain direction.
The management given to a Chinese business prompts US threat not to sell technology to Israel.
The Trump administration's protests over the awarding of management of the port of Haifa to a Chinese business have so far not prompted the Netanyahu government to review the contract, which was dealt with at ministerial level without plenary session of the Executive Council knowledge of its geopolitical implications. China's penetration of Israel - in the wider Middle East context - as well as the US reaction, highlights a complicated triangle of relations: Israel wants Chinese investment, but fears losing US favour.
![management container port in the port of Haifa, northern Israel [Wikipedia]. management container port in the port of Haifa, northern Israel [Wikipedia].](/documents/10174/16849987/haifa-blog.jpg)
▲ management of containers in the port of Haifa in northern Israel [Wikipedia].
article / María Martín Andrade
The port of Haifa is one of the main ports in Israel in terms of volume of goods handled. It also has a strategic character: the port, in the north of the country, hosts the US Sixth Fleet in its movements. The latter could be altered following the announcement of Israel's contract with the Chinese business Shanghai International Port Group (SIPG) to operate the port for the next 25 years from 2021, which has not been very well received by Washington. management The company, which has pledged to invest $2 billion to expand the facility into Israel's largest port, describes its functions as including the construction and installation of equipment and the day-to-day running of port activities, classifying this project as part of the One Belt, One Road initiative.
This initiative has its origins in the Silk Road, a trade pathway linking China with various Asian countries all the way to Europe, dating back to the first centuries BC. The new version is based on the early schemes and aims to boost China by creating a network of infrastructure, investment and trade, and by establishing multilateral and bilateral ties with the various states along the Silk Road, as well as with international companies.
All of the above, added to the growing industrial and transport expansion that China is experiencing, also justifies the Asian country's interest in some of the natural resources that the Middle East offers, such as oil, the import of which amounts to 50%, constituting another of the reasons why China wants to gain a presence in different parts of the region and which is manifested in, among other ways, investment in canals and ports such as those of Haifa and Ashdad in Israel, Cherchell in Algeria, Said and Alexandria in Egypt, and Kumport in Turkey. Specifically, its commitment to the port of Haifa is also contributing to the development of what is known as the Israel-Gulf Economic Corridor (IGEC), whose goal is to create a railway line running from the port of Haifa to the Jordanian-Israeli border, linking up with the Jordanian railway system.
However, China's ambitions to gain a greater presence in the Middle East collide with the pretensions of another "robust rival", the United States, which is also driven by economic and security interests and has no intention of sharing it. Thus, after learning of the plans in the port of Haifa, the US response is manifested in threats that it might stop sharing data intelligence with Israel and reconsider holding future long deadline exercises by the US navy in that port.
It is important to note that this is not the first time that the US has intervened to hinder relations between China and Israel. The conditions under which the latter country was established, coupled with the hostile environment surrounding it and the need to possess weapons to maintain and protect it, have contributed to the development of its technology, especially in subject defence, whose broad scope is due in part to the United States, which has been supplying the country with the latest military technology since the 1960s. This has contributed to Israel's exports of subject technology, mainly defence subject technology, becoming the source main source of revenue for its industry.
During the 1970s, China's Economics began to modernise, and the next step was to extend this modernisation to the military domain, and China began importing defence developments from Israel. These relations continued to expand until 2000, when the Middle Eastern country, due to US pressure, decided to cancel the agreement that allowed China to obtain four Phalcon radar systems. The reason given by the US at the time for opposing the agreement was the possibility that China would benefit from the technology in a military conflict in Taiwan. However, China is not the only country with which Israel has had difficulties exporting its technology. In 2008 Washington denied that it could submit Heron drones to Russia.
Despite all this, Sino-Israeli relations have managed to survive, with China becoming Israel's second largest trading partner in 2012, partner and developing new partnership R&D ties, consisting of a series of agreements and collaborations between academic institutions and companies in both countries.
However, considering the US reaction to China's involvement in the port of Haifa, it is not unthinkable to envisage a scenario in which American pressure would be repeated and in this case would succeed in abolishing the existing agreement with the business Shanghai International Port. If this happens, Israel would lose an important part of the investments it receives and trade relations with China would cool, while Beijing could see one of its plans to create its ambitious Silk Road frustrated, although this would not mean its decline in the Middle East.
What is unquestionable is that the United States no longer enjoys hegemony in this part of the world and has to come to terms with the idea that it will have to share influence with other great powers. It may therefore make more sense to engage in new forms of cooperation with China in order to establish mutually favourable terms.
In conclusion, this new Chinese investment affirms what was already known: China's international presence is growing and increasing in volume, and it is wiser to adapt to the new changes than to get involved in love triangles that never have a happy ending for anyone.
The arrest of Barakat, a major financial operator in the group, was made possible by the partnership from Argentina, Paraguay and Brazil
-
In January 2018, the Trump Administration reconstituted a research about Hezbollah and in October tagged the group of a transnational criminal organization
-
The arrival to the presidency of Abdo Benítez in Asunción and Jair Bolsonaro in Brasilia has activated action against drug trafficking, money laundering and smuggling in the country. area
-
Assad Ahmad Barakat and fifteen members of his clan were arrested throughout 2018, in a "significant milestone" of the action against Hezbollah in Latin America
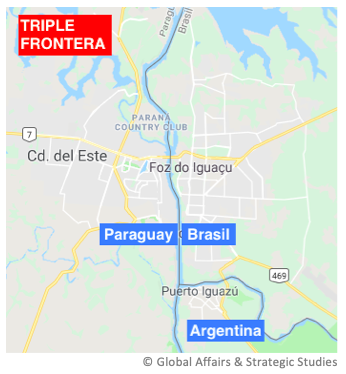
![Friendship Bridge, which connects the Paraguayan town of Ciudad del Este with Brazil's Foz do Iguaçu [BienvenidoaParaguay.com] Friendship Bridge, which connects the Paraguayan town of Ciudad del Este with Brazil's Foz do Iguaçu [BienvenidoaParaguay.com]](/documents/10174/16849987/triple-frontera-blog.jpg)
▲ Friendship Bridge, which connects the Paraguayan town of Ciudad del Este with the Brazilian town of Foz do Iguaçu [BienvenidoaParaguay.com]
report SRA 2019 / Lisa Cubías [PDF Version]
Pressure actions on Hezbollah have increased significantly in the Western Hemisphere over the past year. Both the United States and the countries of the Triple Frontier – a border area between Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay, which shelters a dense network funding of the organization – have taken some measures that, with different Degree have led to the arrest of a number of people and the dismantling of their Structures money laundering.
In the case of the United States, the change in the administration meant a change in policy. Some testimony from Obama-era officials has suggested that the previous presidency had a attention Hezbollah, a Lebanese Shiite organization with a dual political and military facet, is soft on the activities on the continent. The purpose this would have been to avoid inconveniences in the denuclearization negotiation with Iran, one of the organization's most notorious pillars of support. Thus, the Obama Administration would have hindered efforts to implement the "project Cassandra," developed by the DEA, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency, to uncover the sources of Hezbollah's funding in Latin America for its illicit activities.
The "project Cassandra," widely exposed by Politico in late 2017, bore some fruit despite that alleged interference, denied by other Obama administration officials. In March 2017, Kassim Tajideen, a major financier of the terrorist organization, was captured and pleaded guilty in December 2018. In June 2017, Paraguayan Ali Issa Chamas was extradited to the U.S. to face charges of conspiracy to traffic drugs.
The change in the White House, in any case, led to the dismantling of some research that the Trump Administration had reinstated the effort against Hezbollah. Thus, in January 2018 the department announced the Creating a Unit of research Hezbollah's Narco-Terrorism and Financing Team, and later, in October, designated Hezbollah as a transnational criminal organization, considering its drug trafficking and money-laundering activities beyond thelabel terrorist organization that the U.S. already granted him.
For its part, throughout 2018 the department The U.S. Treasury Department has placed 31 individuals and entities linked to Hezbollah on its sanctions list, including Lebanese financier Adham Tabaja, while the U.S. Department of Homeland Security has placed 31 Hezbollah-related individuals and entities on its sanctions list, including Lebanese financier Adham Tabaja. department In November, the U.S. government designated Jawad Nasrallah, the son of Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah, as a terrorist and imposed sanctions on several Iraqi members of the organization.
These actions have basically affected operatives residing in the Middle East, but they have hardly affected the structure of Hezbollah in the Tri-Border Region or in Venezuela, places indicated by the Administration as sites of implantation of that organization. Thus, the Treasury Undersecretary for Terrorist Financing, Marshall Billingslea, spoke at the end of October of a "deep and substantial footprint" of Hezbollah in the Western Hemisphere, with a "very robust presence" in the Tri-Border Area, while Secretary of State Mike Pompeo has repeatedly underlined the relationship between Nicolás Maduro's regime and Hezbollah, affirming in February 2019 that in Venezuela there are "active cells" of that kind of disease. group.
 |
Action in the Tri-Frontier
Nonetheless, the efforts of both the Trump Administration and the governments of Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay, to varying degrees, led to a major operation in 2018 in the Tri-Border, the most significant in a long time: the arrest of Assad Ahmad Barakat, considered one of Hezbollah's main operatives in the area. who had already been sanctioned by the U.S. Treasury in 2004. For expert Joseph Humire, this constituted "a significant milestone in the regional effort against terrorism and transnational crimes practiced by Hezbollah in Latin America."
According to fellow experts Emanuelle Ottolenghi and José Luis Stein, three factors have led to this new emphasis on the risk posed by Hezbollah. First, the clues that the funds that the group The economic crisis obtained from its funding networks in Latin America have grown markedly, both because their needs have increased and because U.S. sanctions on Iran may be restricting the economic support provided by the Iranian regime. Second, Washington is acting in the face of the increased use of its financial system by the amounts generated for Hezbollah in Latin America. And thirdly, the greatest reaction in Brasilia, Asunción and Paraguay is due to the changes of government: in April 2018 Abdo Benítez was elected president of Paraguay and in October Jair Bolsonaro won the elections in Brazil (Mauricio Macri had previously replaced Cristina Fernández de Kirchner in the Casa Rosada).
Hezbollah's beginnings in Latin America are directly related to the civil war in Lebanon, which in the 1980s led to a wave of migration to the American continent, particularly South America, and especially in areas of easy trade, such as the Tri-Border Area, where one of the largest free trade zones on the continent is located. Family and background connections served the group, through infiltrated elements, to carry out recruitment, fundraising and money laundering activities.
It was not until 1994, however, that Hezbollah's presence in Latin America became noticeable. That year saw the attack on the headquarters of the association Mutual Israelita Argentina (AMIA) in Buenos Aires, in which 85 people died. Although it was initially claimed by a group Soon investigations led to the Tri-Border Region and targeted Hezbollah. At the time, it was also suspected that the organization may have been behind the attack two years earlier on the Israeli embassy in the Argentine capital, which killed 22 people. Everything indicates that in both cases the Tri-Border Area was used for the logistics of the attacks and for the refuge of the perpetrators.
That is why the latest security operations in that area are of particular importance. At the request of the United States, Paraguayan police arrested Nader Mohamad Fahrat in May 2018 and Mahmoud Ali Barakat a month later, both for drug trafficking and money laundering, in what would be a year especially concentrated in the clan led by Assad Ahmad Barakat. In July, Argentina's Financial Intelligence Unit froze the assets of 14 Lebanese (eleven with residency program in Brazil and three in Paraguay), all of them belonging to the clan. That network He allegedly laundered money and evaded $10 million worth of foreign currency at a casino in the Argentine border city of Puerto Iguazú. In August, Paraguay's Attorney General's Office issued an arrest warrant for the clan chief, alleging the use of a false Paraguayan passport. Assad Ahmad Barakat was arrested in September by Brazilian police. In Paraguay and Argentina, members of the clan were arrested, played and convicted of crimes of money laundering, smuggling, product evasion and drug trafficking.
Panamanian authorities recorded the transit of 2,100 people of "interest" to Washington in 2018.
-
Of the 8,445 illegal migrants located in Darien (an increase of 20% in two years), 91% were from Asia and Africa, with goal mostly from reaching the US.
-
The US Southern Command deployed helicopters in January and February 2019 to improve surveillance capabilities in the dense jungle area.
-
Washington's awareness of the presence of AIS in the Central American migrant caravans last autumn prompts it to focus on the Darien Gap.
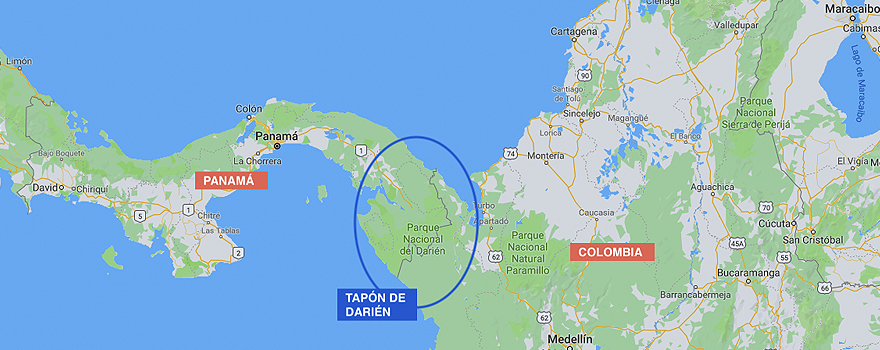
report SRA 2019 / Alex Puigrefagut[PDF version].
One of the best-known icons on the American continent is the Pan-American Highway: network of roads that runs from Argentina to the United States and even goes as far as Alaska. Between one end and the other, there is only one point where you have to get out of your car: 130 kilometres of dense vegetation between Panama and Colombia, which is truly impassable, even difficult to cross on foot. It is the Darién jungle, which is known as the Darién Gap.
Precisely because it blocks land transit between South America and Central America, it has traditionally been a area with little surveillance of migratory flows. This lack of monitoring, however, has led in recent years to a call effect of illegal immigration, mainly from Asia and Africa, which is of concern to the United States. Many of these immigrants are classified by Washington as Special Interest Aliens (SIAs), as they come from countries that, according to the US, show a tendency to promote, produce or protect criminal organisations, mostly terrorist organisations. If they emerge in Panama, they can easily use Central American migratory routes to the US, as has been denounced in the recent crisis of the caravans that departed from Honduras.
Panama' s National Migration Service recorded the passage through Darién of 8,445 illegal immigrants in 2018 (with December still to be counted), of which 5,400 were from Asia and 2,287 from Africa, which together accounted for 91 per cent of the entire contingent. This is an increase of 20 per cent in two years. Of these, 2,123 were nationals from countries the US sees as a potential terrorist threat: most were from Bangladesh (1,440), but also from Eritrea (418), Pakistan (151), Yemen (34), Somalia (32), Afghanistan (10), Iraq (10), Mauritania (10), Syria (7) and Egypt (2). At the end of 2017, the Panamanian National Border Service detained 26 Yemeni nationals with suspected links to terrorist groups.
This migration flow of people labelled as SIAs by Washington was already alerted in 2016 by the US Homeland Securitydepartment , which sent a memo to US border authorities to be vigilant.
With a focus on Darién, in June 2018 the US and Panama agreed to establish a Joint Migration Task Force (JMTF), goal to ensure more effective and comprehensive coordination to address illegal and uncontrolled immigration in the region. Security authorities from both administrations prioritised action against drug trafficking and other types of organised crime that could pose a threat to the security of both Panama and the US, as well as the region as a whole. In January and February 2019, the US Southern Command used helicopters for transports to improve surveillance facilities in Darién.
USA and Colombia
The main purpose of the JMTF created between the two States is that there can be exchange of information and resources to establish strategic border points and thus combat all subject of organised crime on the southern border of Panama, such as drug trafficking, arms trafficking, human trafficking and above all for the comprehensive monitoring of the possible penetration of illegal migrants considered CIS that may be effectively related to international terrorist organisations. In addition, for the proper functioning of the JMTF, the two governments agreed to meet bilaterally twice a year to effectively supervise and coordinate the border security groups.
Already in 2016, the governments of Panama and Colombia implemented further measures in the Binational Border Security Commission (COMBIFRON) to strengthen the fight against drug trafficking and organised crime, as well as illegal migration. These measures included the creation of two shared surveillance points between the two navies in order to control migratory flows along the border of both countries, especially in the Darién region. The area had historically been a place of influence for Colombian cartels and a rearguard for guerrilla forces, so the peace process with the FARC was an opportunity to seek greater state control.
The main problem in the Darién challenge in recent decades, according to some observers, was the passivity shown by Colombia, which gradually decreased patrolling and land control of its part of the border, leaving Panama with limited resources in the face of criminal groups, which led to a considerable increase in the illegal trafficking of drugs, arms and people along the border. This Colombian passivity was mainly due to the fact that the transit of illegal migrants did not create migratory pressure on Colombia, as the flows were towards the northern part of the continent. Although today both countries pay attention to the Darién, control of the area is still deficient, partly because maritime security is prioritised over land security, especially in the case of Colombia.
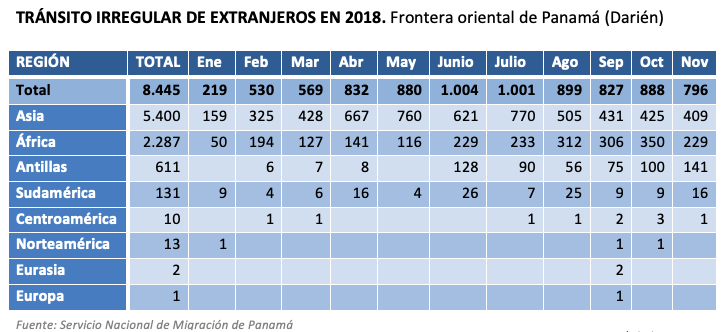 |
Central American caravans
The illegal passage through the Darién of people Washington considers "of interest" because they come from countries that may foment terrorism is part of international routes to the southern border of the United States. Ample evidence sample that the Darién Gap has become a strategic point for regional and US security.
The presence of individuals labelled as SIAs was at the centre of the discussion on the various migrant caravans that in autumn 2018 departed from Central America - emerging in Honduras and increasing in size as they passed through El Salvador and Guatemala - and headed for the US-Mexico border. According to the US think-tank Center for a Secure and Free Society (SFS), these caravans involved individuals from outside Central America, from the Middle East, Asia and Africa, some of whom entered the label of SIA. According to agreement with SFS, these individuals had a privileged attention in the development of the convoys, which could even indicate collusion between SIA networks and certain Central American migration channels. The same centre found that Guatemalan officials detected no less than 157 irregular migrants from other continents, at least 17 of whom were of "special interest" to the US because they came from countries such as Pakistan, Bangladesh and Eritrea.
It is difficult to establish how many people with profile SIAs actually transit through Central America to the US, as their identities are falsified in order to go unnoticed during their journey. On the other hand, the US president exaggerated the state of alarm over the large Central American caravans, because even if there were grounds for the alert, it should not be forgotten that the vast majority of Special Interest Aliens who enter the US and who are highly dangerous because of their direct connections to terrorism arrive by air and not by land. According to an explanatorystatement of the US Homeland Security department , average of ten people on the "terrorist watch list" are apprehended every day (3,700 in the last fiscal year), although few of them enter through the US-Mexico border.
After a record production of opium poppies in Mexico and overdose deaths in the US the problem has stopped growing
-
Less amount of heroin is reaching the US market: Mexican authorites eradicated 29,207 hectares of poppy crops in 2017, and 17,288 hectares in the first half of 2018
-
US President Trump signed in October 2018 the Opioid Crisis Response Act; a National Drug Control Strategy was published in January 2019.
-
Mexico is the main transit route into the US for fentanyl originating from China; Mexican anti-narcotics operations try to exert more control over this trade
![Cultivation of opium poppies (Papaver somniferum), the variety of poppies (Papaver) with the highest concentration of narcotics [DEA]. Cultivation of opium poppies (Papaver somniferum), the variety of poppies (Papaver) with the highest concentration of narcotics [DEA].](/documents/10174/16849987/sra-drugs-blog.jpg)
▲ Cultivation of opium poppies (Papaver somniferum), the variety of poppies (Papaver) with the highest concentration of narcotics [DEA].
ARS 2019 Report / Marcelina Kropiwnicka[PDF version] [PDF version].
The severe opioid crisis experienced by the United States in recent years, with a record number of deaths by drug overdoses in 2017, apparently began to remit in 2018, according to the first available data. Both the efforts of the United States to confront the epidemic and of Mexico in eradicating opium poppy crops seem to be bearing fruit.
The dramatic increase in opium cultivation and heroin production in Mexico in the last years triggered drug consumption in the US. Besides, Mexico is the main route into the US for fentanyl, an opioid narcotic which is behind the US opioid epidemic as well.
After four years of sharp increase, the number of deaths in the United States due to opioid overdose rise in 2017 to 47,600, twice as many as in 2010. The main part of those deaths was due to the consumption of prescription opioids (17,029), followed by overdose deaths involving heroin (15,482). In both cases, the increase was mainly due to the use of synthetic narcotics, basically fentanyl, as prescription drug or mixed with heroin.
The first data referring to 2018 provided by the US health authorities seem to reflect a stabilization in the number of deaths due to opioid overdoses, which would at least indicate that the problem has stopped growing. Along with the efforts of the US administration to put in place a stricter regulation for the prescription of certain medicines, especially affecting synthetic opiates, there is a greater eradication of illicit crops in Mexico, with special emphasis on the cultivation of opioid poppies.
In 2017 the Mexican authorities proceeded to eradicate 29,207 hectares of this crop, thus limiting the heroin that in 2018 could reach the US domestic market. In 2018 eradication accelerated: in the first half of the year, the crop of 17,288 hectares was eliminated. This is a progress highlighted by the latest International Narcotics Control Strategy Report (INCSR), published in Mach 2019 by the US Department of State.
Heroin production
Illicit heroin and fentanyl have been infecting US neighborhoods for years. Initially, the source for almost all heroin found in the US was from Southern Asia. Over the past few decades, however, the trade for heroin has changed drastically. Most of the heroin found in US communities comes from South America, and namely Mexico. This has been fueled by a number of factors, including increased production and trafficking by criminal organizations. These current trends in drug trafficking lead to opioid abuse, and represent a considerable shift in outcomes. This has obliged the governments in both countries to instill and coordinate new law enforcement responses.
The United States is home to the largest heroin market in the Americas. Created from the milky sap scraped from the seedpod of an opium poppy, heroin can be transformed into multiple forms. These include powder, viscous tar, pills, a rock-like black substance and more. In addition to this, the substance has different degrees of purity, with white powder heroin being the purest and black tar-like heroin being the most impure. Heroin can also be administered through a number of means, but most commonly is smoked, injected or snorted.
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), most of the heroin trafficked into the US comes from Mexico. Along with this, Mexican poppy cultivation and heroin production have been on the rise, especially over the past decade, contributing to the ever-increasing threat to the United States. In fact, 2017 was the year Mexican poppy cultivation and heroin production reached a record high, as the Office of National Drug Control Policy of the White House reaffirmed in August 2018: poppy cultivation in Mexico rose 38 percent, from 32,000 hectares in 2016 to 44,100 hectares in 2017; it went from 685 tons to 944 tons of potential opium production, and from 81 tons to 111 tons of potential pure heroin elaboration, almost five times 2012 levels.
Evaluations carried out by the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) in its October 2018 report National Drug Threat Assessment (NDTA) stated that Mexico accounts for 91 percent (by weight) of heroin found in the US. A similar figure is given by the World Drug Report (WDR) published by the UNODC in June 2018: "Analysis of heroin samples in the United States over the past decade shows the increasing predominance of Mexico (90 percent of samples analysed in 2015) as a source country of the drug". According to the INCSR, the Department of State report already mentioned, Mexico is especially focused on producing heroin, marijuana, and methamphetamine that is destined for the US; it is also a main transit route- originating from China-for another important triger of the opioid crisis in the US: fentanyl.
Fentanyl
Fentanyl's availability is widespread and surging. While there are licit forms of the opioid, such as painkillers and anaesthetics, illicit production and trafficking of it are on the rise. The new trend is rooted toward mixing synthetic opiate fentanyl in Mexico's tarry black heroin, without the consumer's knowledge. Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that is approximately 50 times more potent than heroin and 100 times stronger than morphine. The opioid is much cheaper when it comes to production, mainly because rather than being grown on a farm it is manufactured in a laboratory. The decreased cost for the traffickers and increased high for users signifies that drug producers have begun to cut their heroin with fentanyl.
The DEA warns that Mexican cartels present an intense threat to US neighborhoods mainly given their dominance in heroin and fentanyl exports). It also noted that a majority of the samples that were seized and analyzed involved fentanyl in its powder form. The concern arising from this is that fentanyl could be pressed into counterfeit pills, mainly because most drug abusers use prescription pain pills rather than heroin. This means that the creation of such counterfeit pills could ultimately affect a larger population of individuals.
The increase in heroin related deaths has been primarily linked to heroin being combined with fentanyl. The counterfeit pills could increase deaths due to fentanyl and white powder heroin looking alike. Consequently, users are unaware that the heroin they have purchased contains fentanyl, thus removing the user's ability to know the potency of the drug and preventing them from correctly dosing in respect to their tolerance level.
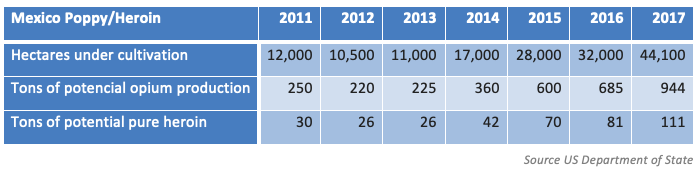 |
Solving the problem
The opioid epidemic suffered by the US in the last years was confronted in 2018 by the Trump administration with some special measures. In October 2018 President Trump signed the Opioid Crisis Response Act, which gave more powers to the US health authorities to monitor the situation and extended the controls on patient access to some specific drugs. In January 2019 a National Drug Control Strategy was published by the White House in order to take extra steps to protecting the public through effective drug abuse prevention, addiction treatment and use of law enforcement actions.
Apart from these new tools, the US relies on a long-standing relationship with Mexico regarding anti-narcotic matters. Both countries set up in 2008 the Merida Initiative, which allows the US to assist the Mexican authorities in different fields. It includes several measures in order to improve law enforcement operations: training and equipment to dismantle covert drug labs, cutting-edge airport security training, advanced inspection tools equipped along border crossings and checkpoints, and so forth in order to improve law enforcement operations, among others. Results have already been seen, as Mexican units trained by US officials have seized more than 300 illicit laboratories since 2015. In addition to this, canines donated by the initiative have helped detect a significant amount of illicit drugs attempting to pass the border.
