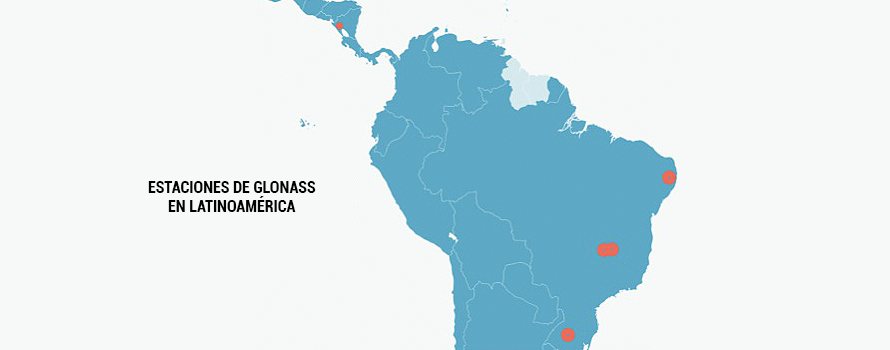
Russia's GLONASS positioning system has placed ground stations in Brazil and Nicaragua; the Brazilian ones are accessible, but the Nicaraguan one is open to conjecture.
At a time when Russia has declared its interest in having military facilities in the Caribbean again, the opening of a Russian station in the Managua area has raised some suspicions. Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, has opened four stations in Brazil, managed with transparency and easy access; in contrast, the one it has built in Nicaragua is shrouded in secrecy. The little that is known about the Nicaraguan station, strangely larger than the others, contrasts with how openly data can be gathered about the Brazilian stations.
article / Jakub Hodek [English version].
It is well known that information is power. The more information one has and manages, the more power one enjoys. This approach should be taken when examining the station facilities that support the Russian satellite navigation system and their construction in close proximity to the United States. Of course, we are no longer in the Cold War period, but some traumas of those old days can perhaps help us to better understand the cautious position of the United States and the importance Russia sees in having its facilities in Brazil and especially in Nicaragua.
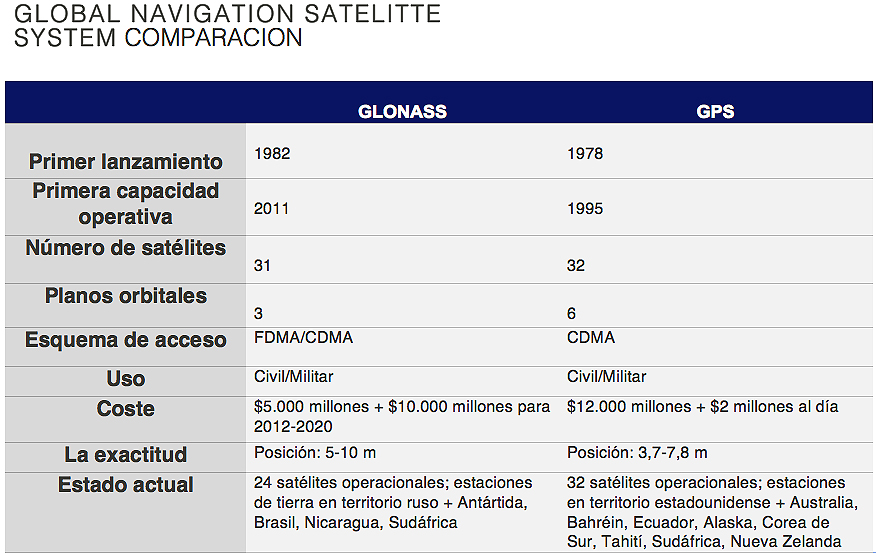
This historical background of the Cold War is at the origin of the two major navigation systems we use today. The United States launched the Global Positioning System (GPS) project in 1973, and possibly in response, the Soviet Union introduced its own positioning system (GLONASS) three years later. [ 1] Almost 45 years have passed, and these two systems no longer serve the purpose of Russians and Americans trying to obtain information about the opposing side, but are collaborating and thus providing a more accurate and faster navigation system for consumers who purchase a smartphone or other electronic device. [2]
However, to achieve global coverage both systems need not only satellites, but also ground stations strategically located around the world. For this purpose, the Russian Federal Space Agency Roscosmos has erected stations for the GLONASS system in Russia, Antarctica and South Africa, as well as in the Western Hemisphere: it already has four stations in Brazil and since April 2017 it has one in Nicaragua, which due to the secrecy surrounding its function has caused mistrust and suspicion in the United States [3] (USA, for its part, has ground stations for GPS in its territory and in Australia, Argentina, Argentina, the United Kingdom, the United States and the United States), for its part, has GPS ground stations in its territory and in Australia, Argentina, United Kingdom, Bahrain, Ecuador, South Korea, Tahiti, South Africa and New Zealand).
The Russian Global Navigation Satellite System(Globalnaya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema or GLONASS) is a positioning system operated by the Russian Aerospace Defense Forces. It consists of 28 satellites, allowing real-time positioning and speed data for surface, sea and airborne objects around the world. [ 4] In principle GLONASS does not transmit any staff identification information; in fact, user devices only receive signals from the satellites, without transmitting anything back. However, it was originally developed with military applications in mind and carries encrypted signals that are supposed to provide higher resolutions to authorized military users (same as US GPS). [5]
In Brazil, there are four ground stations used to track signals from the GLONASS constellation. These stations serve as correction points in the western hemisphere and help to significantly improve the accuracy of navigation signals. Russia is in close and transparent partnership with the Brazilian space agency (AEB), promoting research and development of the South American country's aerospace sector.
 |
In 2013, the first station was installed, located on the campus of the University of Brasilia, which was also the first Russian station of that subject abroad. It was followed by another station at the same location in 2014, and then, in 2016, a third one was placed at the Federal Institute of Education Sciences and Technology of Pernambuco, in Recife. The Russian Federal Space Agency Roscosmos built its fourth Brazilian station on the territory of the Federal University of Santa Maria, in Rio Grande do Sul. In addition to fulfilling its main purpose of increasing the accuracy and improving the performance of GLONASS, the facility can be used by Brazilian scientists to carry out other types of scientific research . [6]
The level of transparency that surrounded the construction and then prevailed in the management of the stations in Brazil is definitely not the same applied to the one opened in Managua, the capital of Nicaragua. There are several pieces of information that sow doubts regarding the real use of the station. To begin with, there is no information on the cost of the facilities or on the specialization of the staff. The fact that it is located a short distance from the U.S. Embassy has given rise to speculation about its use for eavesdropping and espionage.
In addition, the vague answers from representatives of Nicaragua and Roscosmos about the use of the station have failed to convey confidence about the project. It is a "strategicproject " for both Nicaragua and Russia, concluded Laureano Ortega, the son of the Nicaraguan president. Both countries claim to have a very fluid and close cooperation in many spheres, such as in projects related to health and development, however none of them have materialized with such speed and dedication. [7]
Given Russia's increased military presence in Nicaragua, empowered by the agreement facilitating the docking of Russian warships in Nicaragua announced by Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu during his visit to the Central American country in February 2015, and also concretized in the donation of 50 Russian T-72B1 tanks in 2016 and the growing movement of Russian military staff , it can be concluded that Russia clearly sees strategic importance in its presence in Nicaragua. [ 8] [ 9] All this is viewed with suspicion by the U.S. The head of the U.S. Southern Command, Kirt Tidd, warned in April that "the Russians are pursuing a disturbing attitude" in Nicaragua, which "impacts the stability of the region".
Undoubtedly, when world powers such as Russia or the United States act outside their territory, they are always guided by a combination of motivations. Strategic moves are essential in the game of world politics. For this very reason, the financial aid a country receives or the partnership it can establish with a major power is often subject to political conditionality. In this case, it is difficult to know for sure what exactly is the goal of the station in Nicaragua or even those in Brazil. At first glance, the goal seems neutral - to offer a higher quality navigation system and provide a different option to GPS - but given the new value Russia is placing on its geopolitical capabilities, there is the possibility of a more strategic use.