In the picture
Training of Ukrainian military personnel at the Toledo Training Coordination Center, as part of the mission statement of attendance EU Military to Ukraine or EUMAM [Defense].
The outbreak of Russia's war of aggression against Ukraine has marked a significant turning point in the European Union's foreign policy and common security and defense policy. This drastic change in the continent's unstable geopolitical balance has marked a turning point in the partnership between member states at subject defense.
This process has contributed to the consolidation of a European strategic compass, which emerged in 2014 after the Russian invasion of Crimea. This has as goal addressing conflicts and crises, safeguarding the interests of the European Union and its citizens, strengthening peace and security at the international level and, as an ultimate goal, achieving strategic autonomy.
Approved in 2022, the Strategic Compass is an action plan developed by the European Union to guide and strengthen its security and defense. Through a shared assessment of the strategic environment and an analysis of the threats and challenges facing the EU, it seeks to develop greater coherence and cohesion in the actions of member states in the field of security.
This project is based on the definition of four very concrete areas: action, which involves the development of a rapid and decisive response to crises and threats, using military and civilian means in all operational areas; the stimulation of investment and innovation with the goal to reduce strategic dependencies and improve the military mobility ; the guarantee of security in the face of dynamic and changing threats; and cooperation with various strategic partners.
At final, the Strategic Compass serves as guide for the development of the EU's security and defense diary for the next ten years, with a view to making it a stronger and more capable global security provider while reducing its dependence on other actors.
Under this umbrella, between March and April 2023, the first step towards strengthening defense was taken with the approval by the European Parliament of the creation of an exclusive European Union Rapid Action Force (EU RDC). This instrument, core topic to strengthen the EU's strategic autonomy, should be capable of agile and effective deployment of up to 5,000 troops by land, sea and air, to respond to imminent threats, both in entrance and sortie phases. In principle, the full operational capability of the EU DRC should be achieved by 2025, having completed a series of military exercises to serve as a basis for action in order to mobilize the capabilities of the Member States in a coordinated manner.
Thus, on September 18, 2023, the director general of the European Union Military Staff (DG EUMS), Lieutenant General Michiel van der Laan, opened the management Military Crisis Exercise (MILEX23) at the MPCC's Operational Headquarters (OHQ) in Brussels.
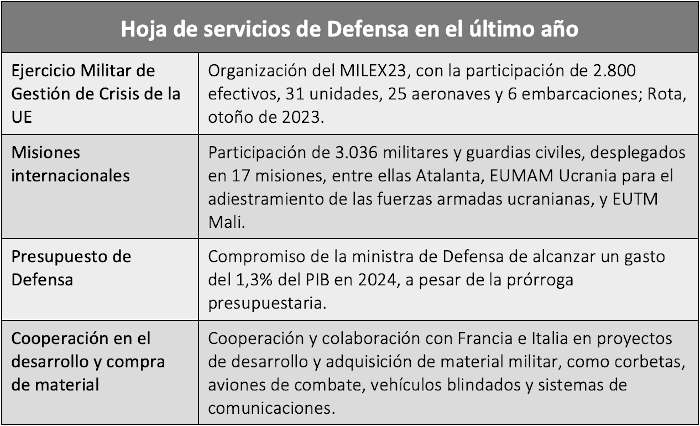
MILEX23 marks a milestone in the EU security and defense field as, during the exercise, consisting of a Command Post Phase (CPX) followed by a Force Phase (LIVEX), the concept reached Initial Operating Capability (IOC). For the first time, a simulation of a crisis operation was conducted in all its phases by 2,800 troops, 31 units, 25 aircraft and 6 vessels from 19 member states. For the execution phase of the exercise, the Rota naval base in Cadiz, Spain, was chosen.
The exercise scenario envisaged a stabilization mission statement in a fictitious country called 'Seglia', in which an amphibious assault had been carried out in order to, after securing a port of disembarkation (SPOD), proceed to insert land forces into the territory; the three phases of the exercise were successfully carried out in Spanish territory.
Spain's leadership in the organization of such a crucial and important exercise is of great significance for its Armed Forces. Both the Minister of Defense, Margarita Robles, and the EU High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Foreign Policy, Josep Borrell, agreed in highlighting the strategicimportance of this event.
Borrell underlined the importance of this exercise taking place during the Spanish presidency of the EU committee , a fact that reflects the confidence placed in Spain to lead an initiative of such great magnitude, especially in a context where other issues of the European diary could have less impact for the country. The fact of being host demonstrates the capacity and level of excellence that Spain possesses in the military field, becoming a leading figure at European level.
The trust placed in Spain to organize and lead this exercise not only highlights the quality of its Armed Forces, but also positions the country as an actor core topic in the implementation of the objectives of the Strategic Compass. This achievement contributes to consolidate Spain's reputation as a reliable, competent partner , and as a reference in cooperation on defense and security issues in the EU.