Ruta de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Middle East .
COMMENTARY / Marina G. Reina
After weeks of rockets being fired from Gaza and the West Bank to Israel and Israeli air strikes, Israel and Hamas have agreed to a ceasefire in a no less heated environment. The conflict of the last days between Israel and Palestine has spread like powder in a spiral of violence whose origin and direct reasons are difficult to draw. As a result, hundreds have been killed or injured on both sides.
What at first sight seemed like a Palestinian protest against the eviction of Palestinian families in the Jerusalem's neighbourhood of Sheikh Jarrah, is connected to the pro-Hamas demonstrations held days before at Damascus Gate in Jerusalem. And even before that, at the beginning of Ramadan, Lehava, a Jewish far-right extremist organisation, carried out inflammatory anti-Arab protests at the same Damascus Gate. Additionally, the upcoming Palestinian legislative elections that Palestinian PM Mahmoud Abbas indefinitely postponed must be added to this cocktail of factors. To add fuel to the flames, social average have played a significant role in catapulting the conflict to the international arena-especially due to the attack in Al-Aqsa mosque that shocked Muslims worldwide-, and Hamas' campaign encouraging Palestinian youth to throw into the streets at point of rocks and makeshift bombs.
Sheikh Jarrah was just the last straw
At this point in the story, it has become clear that the evictions in Sheikh Jarrah have been just another drop of water in a glass that has been overflowing for decades. The Palestinian side attributes this to an Israeli state strategy to expand Jewish control over East Jerusalem and includes claims of ethnic cleansing. However, the issue is actually a private matter between Jews who have property documents over those lands dating the 1800s, substantiated in a 1970 law that enables Jews to reclaim Jewish-owned property in East Jerusalem from before 1948, and a group of Palestinians, not favoured by that same law.
The sentence ruled in favour of the right-wing Jewish Israeli association that was claiming the property. This is not new, as such nationalist Jews have been working for years to expand Jewish presence in East Jerusalem's Palestinian neighbourhoods. Far from being individuals acting for purely private purposes, they are radical Zionist Jews who see their ambitions protected by the law. This is clearly portrayed by the presence of the leader of the Jewish supremacist Lehava group-also defined as opposed to the Christian presence in Israel-during the evictions in Sheikh Jarrah. This same group marched through Jerusalem's downtown to the cry of "Death to Arabs" and looking for attacking Palestinians. The fact is that Israel does not condemn or repress the movements of the extreme Jewish right as it does the Islamic extremist movements. Sheikh Jarrah is one, among other examples, of how, rather, he gives them legal space.
Clashes in the streets of Israel between Jews and Palestinians
Real pitched battles were fought in the streets of different cities of Israel between Jewish and Palestinians youth. This is the case in places such as Jerusalem, Acre, Lod and Ashkelon -where the sky was filled with the missiles coming from Gaza, that were blocked by the Israeli anti-missile "Iron Dome" system. Palestinian neighbors were harassed and even killed, synagogues were attacked, and endless fights between Palestinians and Israeli Jews happened in every moment on the streets, blinded by ethnic and religious hatred. This is shifting dramatically the narrative of the conflict, as it is taking place in two planes: one militarised, starring Hamas and the Israeli military; and the other one held in the streets by the youth of both factions. Nonetheless, it cannot be omitted the fact that all Israeli Jews receive military training and are conscripted from the age of 18, a reality that sets the distance in such street fights between Palestinians and Israelis.
Tiktok, Instagram and Telegram groups have served as political loudspeakers of the conflict, bombarding images and videos and minute-by-minute updates of the situation. On many occasions accused of being fake news, the truth is that they have achieved an unprecedented mobilization, both within Israel and Palestine, and throughout the world. So much so that pro-Palestinian demonstrations have already been held and will continue in the coming days in different European and US cities. Here, then, there is another factor, which, while informative and necessary, also stokes the flames of fire by promoting even more hatred. Something that has also been denounced in social networks is the removal by the service of review of the videos in favour of the Palestinian cause which, far from serving anything, increases the majority argument that they want to silence the voice of the Palestinians and hide what is happening.
Hamas propaganda, with videos circulating on social average about the launch of the missiles and the bloodthirsty speeches of its leader, added to the Friday's sermons in mosques encouraging young Muslims to fight, and to sacrifice their lives as martyrs protecting the land stolen from them, do nothing but promote hatred and radicalization. In fact,
It may be rash to say that this is a lost war for the Palestinians, but the facts suggest that it is. The only militarized Palestinian faction is Hamas, the only possible opposition to Israel, and Israel has already hinted to Qatari and Egyptian mediators that it will not stop military deployment and attacks until the military wing of Hamas surrenders its weapons. The US President denied the idea of Israel being overreacting.
Hamas' political upside in violence and Israel's catastrophic counter-offensive
Experts declare that it seems like Hamas was seeking to overload or saturate Israel's interception system, which can only stand a certain number of attacks at once. Indeed, the group has significantly increased the rate of fire, meaning that it has not only replenished its arsenal in spite of the blockade imposed by Israel, but that it has also improved its capabilities. Iran has played a major role in this, supplying technology in order to boost Palestinian self-production of weapons, extend the range of rockets and improve their accuracy. A reality that has been recognised by both Hamas and Iran, as Hamas attributes to the Persian country its success.
This translates into the bloodshed of unarmed civilians to be continued. If we start from the basis that Israeli action is defensive, it must also be said that air strikes do not discriminate against targets. Although the IDF has declared that the targets are instructions of Hamas, it has been documented how buildings of civilians have been destroyed in Gaza, as already counted by 243 the numbers of dead and those of injured are more than 1,700 then the ceasefire entered into effect. On the Israeli side, the wounded reported were 200 and the dead were counted as 12. In an attempt to wipe out senior Hamas officials, the Israeli army was taking over residential buildings, shops and the lives of Palestinian civilians. In the last movement, Israel was focusing on destroying Hamas' tunnels and entering Gaza with a large military deployment of tanks and military to do so.
Blood has been shed from whatever ethnical and religious background, because Hamas has seen a political upside in violence, and because Israel has failed to punish extremist Jewish movements as it does with Islamist terrorism and uses disproportionate defensive action against any Palestinian uprising. A sea of factors that converge in hatred and violence because both sides obstinately and collectively refuse to recognize and legitimate the existence of the other.
[Mondher Sfar, In search of the original Koran: the true history of the revealed text (New York: Prometheus Books, 2008) 152pp].
REVIEW / Marina G. Reina

Not much has been done regarding research about the authenticity of the Quranic text. This is something that Mondher Sfar has in mind throughout the book, that makes use of the scriptural techniques of the Koran, the scarce research material available, and the Islamic tradition, to redraw the erased story of the transmission of the holy book of Muslims. The same tradition that imposes "a representation of the revelation and of its textual product-which (...) is totally alien to the spirit and to the content of the Quranic text".
The work is a sequencing of questions that arise from the gaps that the Islamic tradition leaves regarding the earliest testimony about the Koran and the biography of Prophet Muhammad. The result is an imprecise or inconclusive answer because it is almost impossible to trace the line back to the very early centuries of the existence of Islam, and due to an "insurmountable barrier" that "has been established against any historical and relativized perception of the Koran (...) to consecrate definitively the new orthodox ideology as the only possible and true one".
As mentioned, Sfar's main sources are those found in the tradition, by which we mean the records from notorious personalities in the early years of the religion. Their sayings prove "the existence in Muhammad's time of two states of the revealed text: a first state and a reworked state that have been modified and corrected". This fact "imperils the validity and identity of Revelation, even if its divine authenticity remains unquestioned."
The synthesis that the author makes on the "kinds of division" (or alterations of the Revelation), reducing them to three from certain ayas in the Koran, is also of notorious interest. In short, these are "that of the modification of the text; that of satanic revelations; and finally, that of the ambiguous nature of the portion of the Revelation". The first one exemplifies how the writing of the Revelation was changed along time; the second is grounded on a direct reference to this phenomenon in the Koran, when it says that "Satan threw some [false revelations] into his (Muhammad's) recitation" (22:52), something that, by the way, is also mentioned in the Bible in Ezekiel 13:3, 6.
Another key point in the book is that of the components of the Koran (the surahs and the ayas) being either invented or disorganised later in time. The manuscripts of the "revealed text" vary in style and form, and the order of the verses was not definitively fixed until the Umayyad era. It is remarkable how something as basic as the titles of the surahs "does not figure in the first known Koranic manuscript", nor was it reported by contemporaries to the Prophet to be ever mentioned by him. The same mystery arises upon the letters that can be read above at the beginning of the preambles in the surahs. According to the Tradition, they are part of the Revelation, whilst the author argues that they are linked to "the process of the formation of surahs", as a way of numeration or as signatures from the scribes. As already mentioned, it is believed that the Koran version that we know today was made in two phases; in the second phase or correction phase surahs would have been added or divided. The writer remarks how a few surahs lack the common preambles and these characteristic letters, which leads to think that these elements were added in the proofreading part of the manuscript, so these organisational signals were omitted.
It may seem that at some points the author makes too many turns on the same topic (in fact, he even raises questions that remain unresolved throughout the book). Nonetheless, it is difficult to question those issues that have been downplayed from the Tradition and that, certainly, are weighty considerations that provide a completely different vision of what is known as the "spirit of the law". This is precisely what he refers to by repeatedly naming the figure of the scribes of the Prophet, that "shaped" the divine word, "and it is this operation that later generations have tried to erase, in order to give a simplified and more-reassuring image of the Quranic message, that of a text composed by God in person," instead of being "the product of a historical elaboration."
What the author makes clear throughout the book is that the most significant and, therefore, most suspicious alterations of the Koran are those introduced by the first caliphs. Especially during the times of the third caliph, Uthman, the Koran was put on the diary again, after years of being limited to a set of "sheets" that were not consulted. Uthman made copies of a certain "compilation" and "ordered the destruction of all the other existing copies". Indeed, there is evidence of the existence of "other private collections" that belonged to dignitaries around the Prophet, of whose existence, Sfar notes that "around the fourth century of the Hijra, no trace was left."
The author shows that the current conception of the Koran is rather simplistic and based on "several dogmas about, and mythical reconstructions of, the history." Such is the case with the "myth of the literal 'authenticity'," which comes more "from apologetics than from the realm of historical truth." This is tricky, especially when considering that the Koran is the result of a process of wahy (inspiration), not of a literal transcription, setting the differentiation between the Kitab ( "the heavenly tablet") and the Koran ("a liturgical lesson or a recitation"). Moreover, Sfar addresses the canonization of the Koran, which was made by Uthman, and which was criticized at its time for reducing the "several revelations without links between them, and that they were not designed to make up a book" into a single composition. This illustrates that "the principal star that dominated the period of prophetic revelation was to prove that the prophetic mission claimed by Muhammad was indeed authentic, and not to prove the literal authenticity of the divine message," what is what the current Muslim schools of taught are inclined to support.
In general, although the main argument of the author suggests that the "Vulgate" version of the Koran might not be the original one, his other arguments lead the reader to deduce that this first manuscript does not vary a lot from the one we know today. Although it might seem so at first glance, the book is not a critique to the historicity of Islam or to the veracity of the Koran itself. It rather refers to the conservation and transmission thereof, which is one of the major claims in the Koran; of it being an honourable recitation in a well-guarded book (56:77-78). Perhaps, for those unfamiliar with the Muslim religion, this may seem insignificant. However, it is indeed a game-changer for the whole grounding of the faith. Muslims, the author says, remain ignorant of a lot of aspects of their religion because they do not go beyond the limits set by the scholars and religious authorities. It is the prevention from understanding the history that prevents from "better understanding the Koran" and, thus, the religion.
An update on the Iranian nuclear accord between 2018 and the resumed talks in April 2021
The signatories of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), reached in 2015 to limit Iran's nuclear program, met again on April 6 in Vienna to explore the possibility of reviving the accord. The US withdrawal after Donald Trump becoming president put the agreement on hold and lead Tehran to miss its commitments. Here we offer an update on the issue until the international talks resumed.
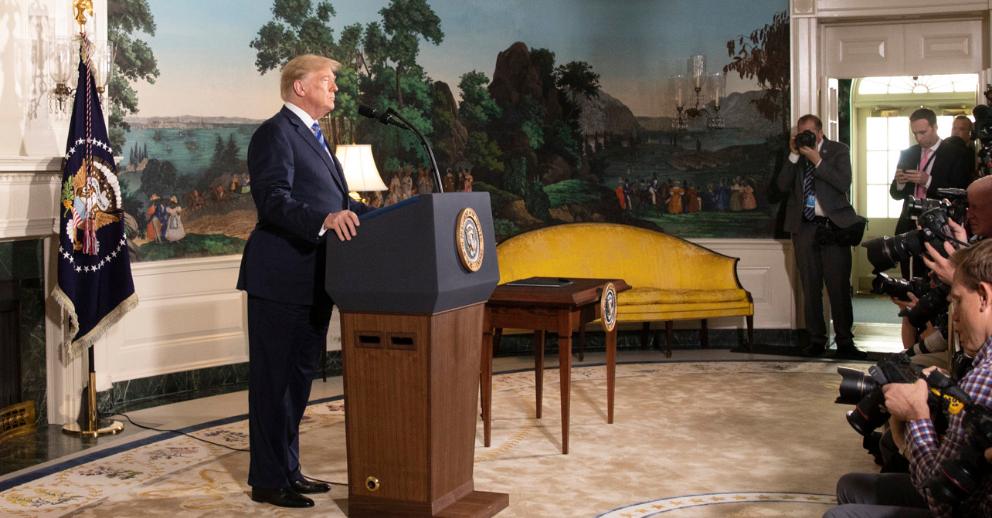

Trump's announcement of the US withdrawal from the JCPOA on May 8, 2018 [White House].
ARTICLE / Ana Salas Cuevas
The Islamic Republic of Iran is a key player in the stability of its regional environment, which means that it is a central country worth international attention. It is a regional power not only because of its strategic location, but also because of its large hydrocarbon reserves, which make Iran the fourth country in oil reserves and the second one in gas reserves.
In 2003, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) brought to the light and warned the international community about the existence of nuclear facilities, and of a covert program in Iran which could serve a military purpose. This prompted the United Nations and the five permanent members of the UN Security Council (the P5: France, China, Russia, the United States and the United Kingdom) to take measures against Iran in 2006. Multilateral and unilateral economic sanctions (the UN and the US) were implemented, which deteriorated Iran's economy, but which did not stop its nuclear proliferation program. There were also sanctions linked to the development of ballistic missiles and to the support of terrorist groups. These sanctions, added to the ones the United States imposed on Tehran in the wake of the 1979 revolution, and together with the instability that cripples the country, caused a deep deterioration of Iran's economy.
In November 2013, the P5 plus Germany (P5+1) and Iran came to terms with an initial agreement on Iran's nuclear program (a Joint Plan of Action) which, after several negotiations, translated into a final pact, the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), signed in 2015. The European Union adhered to the JCPOA.
The focus of Iran's motives for succumbing and accepting restrictions on its nuclear program lies in the Iranian regime's concern that the deteriorating living conditions of the Iranian population due to the economic sanctions could result in growing social unrest.
The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action
The goal of these negotiations was to reach a long-term comprehensive solution agreed by both parties to ensure that Iran's nuclear program would be completely peaceful. Iran reiterated that it would not seek or develop any nuclear weapons under any circumstances. The real aim of the nuclear deal, though, was to extend the time needed for Iran to produce enough fissile material for bombs from three months to one year. To this end, a number of restrictions were reached.
This comprehensive solution involved a mutually defined enrichment plan with practical restrictions and transparent measures to ensure the peaceful nature of the program. In addition, the resolution incorporated a step-by-step process of reciprocity that included the lifting of all UN Security Council, multilateral and national sanctions related to Iran's nuclear program. In total, these obligations were key to freeze Iran's nuclear program and reduced the factors most sensitive to proliferation. In return, Iran received limited sanctions relief.
More specifically, the key points in the JCPOA were the following: Firstly, for 15 years, Iran would limit its uranium enrichment to 3.67%, eliminate 98% of its enriched uranium stocks in order to reduce them to 300 kg, and restrict its uranium enrichment activities to its facilities at Natanz. Secondly, for 10 years, it would not be able to operate more than 5,060 old and inefficient IR-1 centrifuges to enrich uranium. Finally, inspectors from the IAEA would be responsible for the next 15 years for ensuring that Iran complied with the terms of the agreement and did not develop a covert nuclear programme.
In exchange, the sanctions imposed by the United States, the European Union and the United Nations on its nuclear program would be lifted, although this would not apply to other types of sanctions. Thus, as far as the EU is concerned, restrictive measures against individuals and entities responsible for human rights violations, and the embargo on arms and ballistic missiles to Iran would be maintained. In turn, the United States undertook to lift the secondary sanctions, so that the primary sanctions, which have been in place since the Iranian revolution, remained unchanged.
To oversee the implementation of the agreement, a joint committee composed of Iran and the other signatories to the JCPOA would be established to meet every three months in Vienna, Geneva or New York.
United States withdrawal
In 2018, President Trump withdrew the US from the 2015 Iran deal and moved to resume the sanctions lifted after the agreement was signed. The withdrawal was accompanied by measures that could pit the parties against each other in terms of sanctions, encourage further proliferation measures by Iran and undermine regional stability. The US exit from the agreement put the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action on hold.
The United States argued that the agreement allowed Iran to approach the nuclear threshold in a short period of time. With the withdrawal, however, the US risked bringing this point closer in time by not waiting to see what could happen after the 10 and 15 years, assuming that the pact would not last after that time. This may make Iran's proliferation a closer possibility.
Shortly after Trump announced the first anniversary of its withdrawal from the nuclear deal and the assassination of powerful military commander Qasem Soleimani by US drones, Iran announced a new nuclear enrichment program as a signal to nationalists, designed to demonstrate the power of the mullah regime. This leaves the entire international community to question whether diplomatic efforts are seen in Tehran as a sign of weakness, which could be met with aggression.
On the one hand, some opinions consider that, by remaining within the JCPOA, renouncing proliferation options and respecting its commitments, Iran gains credibility as an international actor while the US loses it, since the agreements on proliferation that are negotiated have no guarantee of being ratified by the US Congress, making their implementation dependent on presidential discretion.
On the other hand, the nuclear agreement adopted in 2015 raised relevant issues from the perspective of international law. The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action timeline is 10 to 15 years. This would terminate restrictions on Iranian activities and most of the verification and control provisions would expire. Iran would then be able to expand its nuclear facilities and would find it easier to develop nuclear weapons activities again. In addition, the legal nature of the Plan and the binding or non-binding nature of the commitments made under it have been the subject of intense discussion and analysis in the United States. The JCPOA does not constitute an international treaty. So, if the JCPOA was considered to be a non-binding agreement, from the perspective of international law there would be no obstacle for the US administration to withdraw from it and reinstate the sanctions previously adopted by the United States.
The JCPOA after 2018
As mentioned, the agreement has been held in abeyance since 2018 because the IAEA inspectors in Vienna will no longer have access to Iranian facilities.
Nowadays, one of the factors that have raised questions about Iran's nuclear documents is the IAEA's growing attention to Tehran's nuclear contempt. In March 2020, the IAEA "identified a number of questions related to possible undeclared nuclear material and nuclear-related activities at three locations in Iran". The agency's Director General Rafael Grossi stated: "The fact that we found traces (of uranium) is very important. That means there is the possibility of nuclear activities and material that are not under international supervision and about which we know not the origin or the intent".
The IAEA also revealed that the Iranian regime was violating all the restrictions of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action. The Iranian leader argued that the US first violated the terms of the JCPOA when it unilaterally withdrew the terms of the JCPOA in 2018 to prove its reason for violating the nuclear agreement.
In the face of the economic crisis, the country has been hit again by the recent sanctions imposed by the United States. Tehran ignores the international community and tries to get through the signatory countries of the agreement, especially the United States, claiming that if they return to compliance with their obligations, Iran will also quickly return to compliance with the treaty. This approach has put strong pressure on the new US government from the beginning. Joe Biden's advisors suggested that the agreement could be considered again. But if Washington is faced with Tehran's full violation of the treaty, it will be difficult to defend such a return to the JCPOA.
In order to maintain world security, the international community must not succumb to Iran's warnings. Tehran has long issued empty threats to force the world to accept its demands. For example, in January 2020, when the UK, France and Germany triggered the JCPOA's dispute settlement mechanism, the Iranian Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a direct warning, saying: "If Europeans, instead of keeping to their commitments and making Iran benefit from the lifting of sanctions, misuse the dispute resolution mechanism, they'll need to be prepared for the consequences that they have been informed about earlier".
Conclusions
The purpose of the agreement is to prevent Iran from becoming a nuclear power that would exert pressure on neighbouring countries and further destabilize the region. For example, Tehran's military influence is already keeping the war going in Syria and hampering international peace efforts. A nuclear Iran is a frightening sight in the West.
The rising in tensions between Iran and the United States since the latter unilaterally abandoned the JCPOA has increased the deep mistrust already separating both countries. Under such conditions, a return to the JCPOA as it was before 2018 seems hardly imaginable. A renovated agreement, however, is baldly needed to limit the possibilities of proliferation in an already too instable region. Will that be possible?
Qatar's economic strengthening and expanding relations with Russia, China and Turkey have made the blockade imposed by its Gulf neighbours less effective.
It is a reality: Qatar has won its battle against the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia after more than three years of diplomatic rupture in which both countries, along with other Arab neighbours, isolated the Qatari peninsula commercially and territorially. Economic and geopolitical reasons explain why the imposed blockade has finally faded without Qatar giving in to its autonomous diplomatic line.
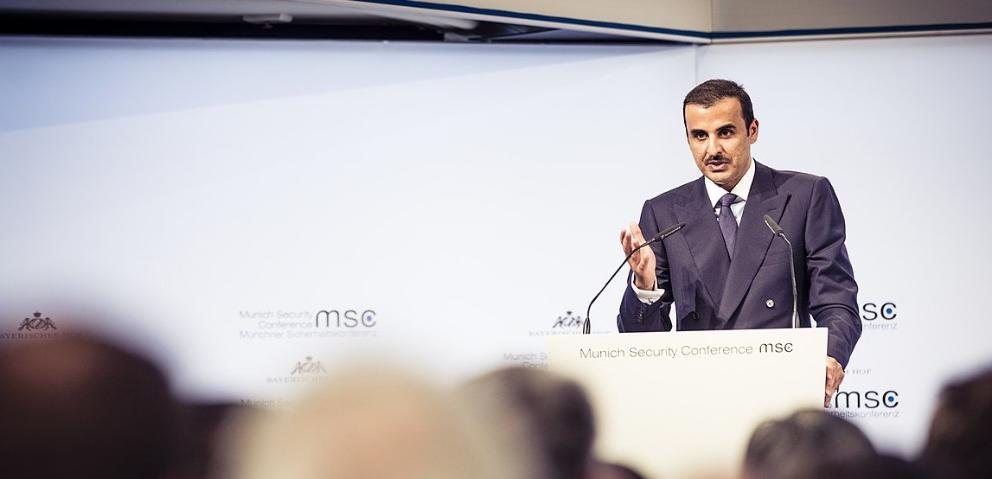

Qatar's Emir Tamim Al Thani at lecture Munich Security 2018 [Kuhlmann/MSC].
article / Sebastián Bruzzone
In June 2017, Egypt, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, Libya, Yemen and the Maldives accused the Al Thani family of supporting Islamic terrorism and the Muslim Brotherhood and initiated a total blockade on trade to and from Qatar until Doha met thirteen conditions. On 5 January 2021, however, Saudi Arabia's Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman welcomed Qatar's Emir Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani with an unexpected embrace in the Saudi city of Al-Ula, sealing the end of yet another dark chapter in the modern history of the Persian Gulf. But how many of the thirteen demands has Qatar met to reconcile with its neighbours? None.
As if nothing had happened. Tamim Al Thani arrived in Saudi Arabia to participate in the 41st Summit of the committee Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) where member states pledged to make efforts to promote solidarity, stability and multilateralism in the face of the challenges in the region, which is confronted by Iran's nuclear and ballistic missile programme, as well as its plans for sabotage and destruction. In addition, the GCC as a whole welcomed the mediating role of Kuwait, then US President Donald J. Trump and his son-in-law, Jared Kushner.
The Gulf Arab leaders' meeting has been a thaw in the political desert after a storm of mutual accusations and instability in what was called the "Qatar diplomatic crisis"; this rapprochement, as an immediate effect, clears the way for the normal preparation of the football World Cup scheduled to take place in Qatar next year. The return of regional and diplomatic understanding is always positive in emergency situations such as an economic crisis, a global pandemic or a common Shia enemy arming missiles on the other side of the sea. In any case, the Al Thani's Qatar may be crowned as the winner of the economic pulse against the Emirati Al Nahyan and the Saudi Al Saud unable to suffocate the tiny peninsula.
The factors
The relevant question brings us back to the initial degree scroll before these lines: how has Qatar managed to withstand the pressure without buckling at all in the face of the thirteen conditions demanded in 2017? Several factors contribute to explaining this.
First, the capital injection by the QIA (Qatar Investment Authority). At the beginning of the blockade, the banking system suffered a capital flight of more than 30 billion dollars and foreign investment fell sharply. The Qatari sovereign wealth fund responded by pumping in $38.5 billion to provide liquidity to banks and revive Economics. The sudden trade blockade by the UAE and Saudi Arabia led to a financial panic that prompted foreign investors, and even Qatari residents, to transfer their assets out of the country and liquidate their positions in fear of a market collapse.
Second, rapprochement with Turkey. In 2018, Qatar came to Turkey's rescue by pledging to invest $15 billion in Turkish assets across subject and, in 2020, to execute a currency swap agreement to raise the value of the Turkish lira. In reciprocity, Turkey increased commodity exports to Qatar by 29 per cent and increased its military presence in the Qatari peninsula against a possible invasion or attack by its neighbours, building a second Turkish military base near Doha. In addition, as an internal reinforcement measure, the Qatari government has invested more than $30 billion in military equipment, artillery, submarines and aircraft from American companies.
Third, rapprochement with Iran. Qatar shares with the Persian country the South Pars North Dome gas field, considered the largest in the world, and positioned itself as a mediator between the Trump administration and the Ayatollah government. Since 2017, Iran has supplied 100,000 tonnes of food daily to Doha in the face of a potential food crisis caused by the blockade of the only land border with Saudi Arabia through which 40 per cent of the food enters.
Fourth, rapprochement with Russia and China. The Qatari sovereign wealth fund acquired a 19% stake in Rosneft, opening the door to partnership between the Russian oil company and Qatar Petroleum and to more joint ventures between the two nations. In the same vein, Qatar Airways increased its stake in China Southern Airlines to 5%.
Fifth, its reinforcement as the world's leading exporter of LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas). It is important to know that Qatar's main economic engine is gas, not oil. That is why, in 2020, the Qatari government launched its expansion plan by approving a $50 billion investment to expand its liquefaction and LNG carrier capacity, and a $29 billion investment to build more offshore offshore platforms at North Dome. The Qatari government has forecast that its LNG production will grow by 40% by 2027, from 77 million tonnes to 110 million tonnes per year.
We should bear in mind that LNG transport is much safer, cleaner, greener and cheaper than oil transport. Moreover, Royal Dutch Shell predicted in its report "Annual LNG Outlook Report 2019" that global LNG demand would double by 2040. If this forecast is confirmed, Qatar would be on the threshold of impressive economic growth in the coming decades. It is therefore in its best interest to keep its public coffers solvent and maintain a stable political climate in the Middle East region at status . As if that were not enough, last November 2020, Tamim Al Thani announced that future state budgets will be configured on the basis of a fictitious price of $40 per barrel, a much smaller value than the WTI Oil Barrel or Brent Oil Barrel, which is around $60-70. In other words, the Qatari government will index its public expense to the volatility of hydrocarbon prices. In other words, Qatar is seeking to anticipate a possible collapse in the price of crude oil by promoting an efficient public expense policy.
And sixth, the maintenance of the Qatar Investment Authority's investment portfolio , valued at $300 billion. The assets of the Qatari sovereign wealth fund constitute a life insurance policy for the country, which can order its liquidation in situations of extreme need.
Qatar has a very important role to play in the future of the Persian Gulf. The Al Thani dynasty has demonstrated its capacity for political and economic management and, above all, its great foresight for the future vis-à-vis the other countries of the Gulf Cooperation committee . The small peninsular "pearl" has struck a blow against Saudi Arabia's Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman and Abu Dhabi's Crown Prince Mohammed bin Zayed, who did not even show up in Al-Ula. This geopolitical move, plus the Biden administration's decision to maintain a hardline policy towards Iran, seems to guarantee the international isolation of the Ayatollah regime from the Persian country.

IDF soldiers during a study tour as part of Sunday culture, at the Ramon Crater Visitor Center [IDF].
ESSAY / Jairo Císcar
The geopolitical reality that exists in the Middle East and the Eastern Mediterranean is incredibly complex, and within it the Arab-Israeli conflict stands out. If we pay attention to History, we can see that it is by no means a new conflict (outside its form): it can be traced back to more than 3,100 years ago. It is a land that has been permanently disputed; despite being the vast majority of it desert and very hostile to humans, it has been coveted and settled by multiple peoples and civilizations. The disputed territory, which stretches across what today is Israel, Palestine, and parts of Lebanon, Jordan, Egypt, and Syria practically coincides with historic Canaan, the Promised Land of the Jewish people. Since those days, the control and prevalence of human groups over the territory was linked to military superiority, as the conflict was always latent. The presence of military, violence and conflict has been a constant aspect of societies established in the area; and, with geography and history, is fundamental to understand the current conflict and the functioning of the Israeli society.
As we have said, a priori it does not have great reasons for a fierce fight for the territory, but the reality is different: the disputed area is one of the key places in the geostrategy of the western and eastern world. This thin strip, between the Tigris and Euphrates (the Fertile Crescent, considered the cradle of the first civilizations) and the mouth of the Nile, although it does not enjoy great water or natural resources, is an area of high strategic value: it acts as a bridge between Africa, Asia and the Mediterranean (with Europe by sea). It is also a sacred place for the three great monotheistic religions of the world, Judaism, Christianity and Islam, the "Peoples of the Book", who group under their creeds more than half of the world's inhabitants. Thus, for millennia, the land of Israel has been abuzz with cultural and religious exchanges ... and of course, struggles for its control.
According to the Bible, the main para-historical account of these events, the first Israelites began to arrive in the Canaanite lands around 2000 BC, after God promised Abraham that land ".... To your descendants ..."[1] The massive arrival of Israelites would occur around 1400 BC, where they started a series of campaigns and expelled or assimilated the various Canaanite peoples such as the Philistines (of which the Palestinians claim to be descendants), until the Kingdoms of Israel and Judah finally united around the year 1000 BC under a monarchy that would come to dominate the region until their separation in 924 BC.
It is at this time that we can begin to speak of a people of Israel, who will inhabit this land uninterruptedly, under the rule of other great empires such as the Assyrian, the Babylonian, and the Macedonian, to finally end their existence under the Roman Empire. It is in 63 BC when Pompey conquered Jerusalem and occupied Judea, ending the freedom of the people of Israel. It will be in 70 AD, though, with the emperor Titus, when after a new Hebrew uprising the Second Temple of Jerusalem was razed, and the Diaspora of the Hebrew people began; that is, their emigration to other places across the East and West, living in small communities in which, suffering constant persecutions, they continued with their minds set on a future return to their "Promised Land". The population vacuum left by the Diaspora was then filled again by peoples present in the area, as well as by Arabs.
The current state of Israel
This review of the historical antiquity of the conflict is necessary because this is one with some very special characteristics: practically no other conflict is justified before such extremes by both parties with "sentimental" or dubious "legal" reasons.
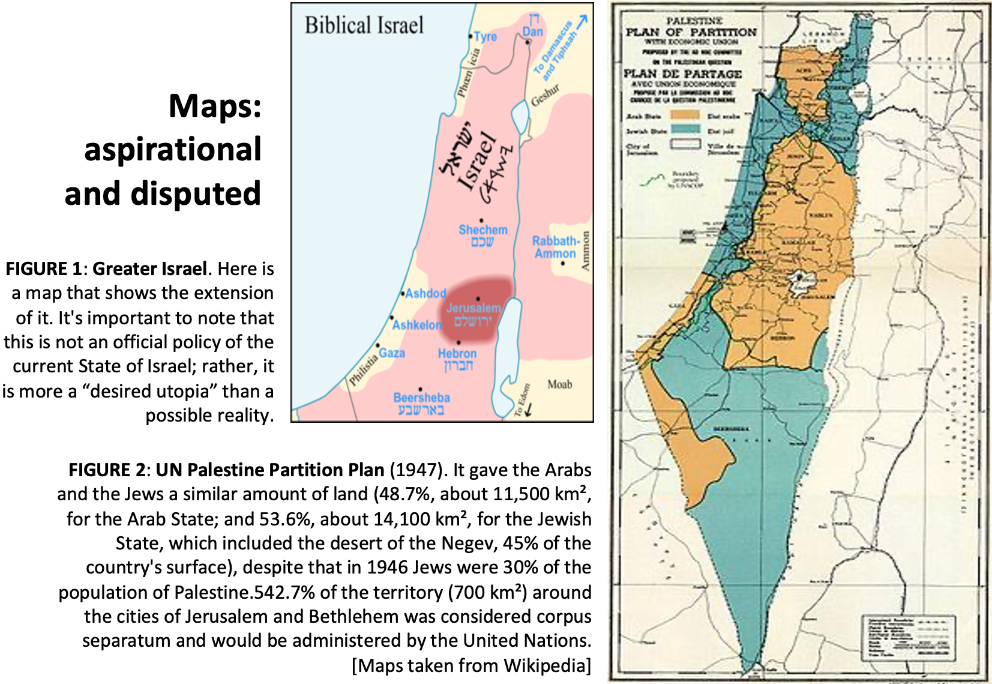
The current state of Israel, founded in 1948 with the partition of the British Protectorate of Palestine, argues its existence in the need for a Jewish state that not only represents and welcomes such a community but also meets its own religious requirements, since in Judaism the Hebrew is spoken as the "chosen people of God", and Israel as its "Promised Land". So, being the state of Israel the direct heir of the ancient Hebrew people, it would become the legitimate occupier of the lands quoted in Genesis 15: 18-21. This is known as the concept of Greater Israel (see map)[2].
On the Palestinian side, they exhibit as their main argument thirteen centuries of Muslim rule (638-1920) over the region of Palestine, from the Orthodox caliphate to the Ottoman Empire. They claim that the Jewish presence in the region is primarily based on the massive immigration of Jews during the late 19th and 20th centuries, following the popularization of Zionism, as well as on the expulsion of more than 700,000 Palestinians before, during and after the Arab-Israeli war of 1948, a fact known as the Nakba[3], and of many other Palestinians and Muslims in general since the beginning of the conflict. Some also base their historical claim on their origin as descendants of the Philistines.
However, although these arguments are weak, beyond historical conjecture, the reality is, nonetheless, that these aspirations have been the ones that have provoked the Palestinian-Israeli conflict. This properly begins in the early 20th century, with the rise of Zionism in response to the growing anti-Semitism in Europe, and the Arab refusal to see Jews settled in the area of Palestine. During the years of the British Mandate for Palestine (1920-1948) there were the first episodes of great violence between Jews and Palestinians. Small terrorist actions by the Arabs against Kibbutzim, which were contested by Zionist organizations, became the daily norm. This turned into a spiral of violence and assassinations, with brutal episodes such as the Buraq and Hebron revolts, which ended with some 200 Jews killed by Arabs, and some 120 Arabs killed by the British army.[4]
Another dark episode of this time was the complicit relations between the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, Haj Almin Al-Husseini, and the Nazi regime, united by a common diary regarding Jews. He had meetings with Adolf Hitler and gave them mutual support, as the extracts of their conversations collect[5]. But it will not be until the adoption of the "United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine" through Resolution 181 (II) of the General Assembly when the war broke out on a large scale. [6] The Jews accepted the plan, but the Arab League announced that, if it became effective, they would not hesitate to invade the territory.
And so, it was. On May 14, 1948, hours after the proclamation of the state of Israel by Ben-Gurion, Israel was invaded by a joint force of Egyptian, Iraqi, Lebanese, Syrian and Jordanian troops. In this way, the 1948 Arab-Israeli War began, beginning a period of war that has not stopped until today, almost 72 years later. Despite the multiple peace agreements reached (with Egypt and Jordan), the dozens of United Nations resolutions, and the Oslo Accords, which established the roadmap for achieving a lasting peace between Israel and Palestine, conflicts continue, and they have seriously affected the development of the societies and peoples of the region.
The Israel Defense Forces
Despite the difficulties suffered since the day of its independence, Israel has managed to establish itself as the only effective democracy in the region, with a strong rule of law and a welfare state. It has a Human Development Index of 0.906, considered very high; is an example in education and development, being the third country in the world with more university graduates over the total population (20%) and is a world leader in R&D in technology. Meanwhile, the countries around it face serious difficulties, and in the case of Palestine, great misery. One of the keys to Israel's success and survival is, without a doubt, its Army. Without it, it would not have been able to lay the foundations of the country that it is today, as it would have been devastated by neighbouring countries from the first day of its independence.
It is not daring to say that Israeli society is one of the most militarized in the world. It is even difficult to distinguish between Israel as a country or Israel as an army. There is no doubt that the structure of the country is based on the Army and on the concept of "one people". The Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) act as the backbone of society and we find an overwhelming part of the country's top officials who have served as active soldiers. The paradigmatic example are the current leaders of the two main Knesset parties: Benny Ganz (former Chief of Staff of the IDF) and Benjamin Netanyahu (a veteran of the special forces in the 1970s, and combat wounded).
This influence exerted by the Tzahal[7] in the country is fundamentally due to three reasons. The first is the reality of war. Although, as we have previously commented, Israel is a prosperous country and practically equal to the rest of the western world, it lives in a reality of permanent conflict, both inside and outside its borders. When it is not carrying out large anti-terrorist operations such as Operation "Protective Edge," carried out in Gaza in 2014, it is in an internal fight against attacks by lone wolves (especially bloody recent episodes of knife attacks on Israeli civilians and military) and against rocket and missile launches from the Gaza Strip. The Israeli population has become accustomed to the sound of missile alarms, and to seeing the "Iron Dome" anti-missile system in operation. It is common for all houses to have small air raid shelters, as well as in public buildings and schools. In them, students learn how to behave in the face of an attack and basic security measures. The vision of the Army on the street is something completely common, whether it be armoured vehicles rolling through the streets, fighters flying over the sky, or platoons of soldiers getting on the public bus with their full equipment. At this point, we must not forget the suffering in which the Palestinian population constantly lives, as well as its harsh living conditions, motivated not only by the Israeli blockade, but also by living under the government of political parties such as Al-Fatah or Hamas. The reality of war is especially present in the territories under dispute with other countries: the Golan Heights in Syria and the so-called Palestinian Territories (the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip). Military operations and clashes with insurgents are practically daily in these areas.
This permanent tension and the reality of war not only affect the population indirectly, but also directly with compulsory military service. Israel is the developed country that spends the most defense budget according to its GDP and its population. [8] Today, Israel invests 4.3% of its GDP in defense (not counting investment in industry and military R&D). [9] In the early 1980s, it came to invest around 22%. Its army has 670,000 soldiers, of whom 170,000 are professionals, and 35.9% of its population (just over 3 million) are ready for combat. It is estimated that the country can carry out a general mobilization around 48-72 hours. Its military strength is based not only on its technological vanguard in terms of weapons systems such as the F-35 (and atomic arsenal), material, armored vehicles (like the Merkava MBT), but also on its compulsory military service system that keeps the majority of the population trained to defend its country. Israel has a unique military service in the western world, being compulsory for all those over 18 years of age, be they men or women. In the case of men, it lasts 32 months, while women remain under military discipline for 21 months, although those that are framed in combat units usually serve the same time as men. Military service has exceptions, such as Arabs who do not want to serve and ultra-Orthodox Jews. However, more and more Israeli Arabs serve in the armed forces, including in mixed units with Druze, Jews and Christians; the same goes for the ultra-orthodox, who are beginning to serve in units adapted to their religious needs. Citizens who complete military service remain in the reserve until they are 40 years old, although it is estimated that only a quarter of them do so actively[10].
Social cohesion
Israeli military service and, by extension, the Israeli Defense Forces are, therefore, the greatest factor of social cohesion in the country, above even religion. This is the second reason why the army influences Israel. The experience of a country protection service carried out by all generations creates great social cohesion. In the Israeli mindset, serving in the military, protecting your family and ensuring the survival of the state is one of the greatest aspirations in life. From the school, within the academic curriculum itself, the idea of patriotism and service to the nation is integrated. And right now, despite huge contrasts between the Jewish majority and minorities, it is also a tool for social integration for Arabs, Druze and Christians. Despite racism and general mistrust towards Arabs, if you serve in the Armed Forces, the reality changes completely: you are respected, you integrate more easily into social life, and your opportunities for work and study after the enlistment period have increased considerably. Mixed units, such as Unit 585 where Bedouins and Christian Arabs serve,[11] allow these minorities to continue to throw down barriers in Israeli society, although on many occasions they find rejection from their own communities.
Israelis residing abroad are also called to service, after which many permanently settle in the country. This enhances the sense of community even for Jews still in the Diaspora.
In short, the IDF creates a sense of duty and belonging to the homeland, whatever the origin, as well as a strong link with the armed forces (which is hardly seen in other western countries) and acceptance of the sacrifices that must be made in order to ensure the survival of the country.
The third and last reason, the most important one, and the one that summarizes the role that the Army has in society and in the country, is the reality that, as said above, the survival of the country depends on the Army. This is how the military occupation of territories beyond the borders established in 1948, the bombings in civilian areas, the elimination of individual objectives are justified by the population and the Government. After 3,000 years, and since 1948 perhaps more than ever, the Israeli people depend on weapons to create a protection zone around them, and after the persecution throughout the centuries culminating in the Holocaust and its return to the "Promised Land," neither the state nor the majority of the population are willing to yield in their security against countries or organizations that directly threaten the existence of Israel as a country. This is why despite the multiple truces and the will (political and real) to end the Arab-Israeli conflict, the country cannot afford to step back in terms of preparing its armed forces and lobbying.
Obviously, during the current Covid-19 pandemic, the Army is having a key role in the success of the country in fighting the virus. The current rate of vaccination (near 70 doses per 100 people) is boosted by the use of reserve medics from the Army, as well as the logistic experience and planning (among obviously many other factors). Also, they have provided thousands of contact tracers, and the construction of hundreds of vaccination posts, and dozens of quarantine facilities. Even could be arguable that the military training could play a role in coping with the harsh restrictions that were imposed in the country.
The State-Army-People trinity exemplifies the reality that Israel lives, where the Army has a fundamental (and difficult) role in society. It is difficult to foresee a change in reality in the near future, but without a doubt, the army will continue to have the leadership role that it has assumed, in different forms, for 3,000 years.
[1] Genesis 15:18 New International Version (NIV). 18: "On that day the Lord made a covenant with Abram and said, 'To your descendants I give this land, from the Wadi [a] of Egypt to the great river, the Euphrates'".
[2] Great Israel matches to previously mentioned Bible passage Gen. 15: 18-21.
[3] Independent, JS (2019, May 16). This is why Palestinians wave keys during the 'Day of Catastrophe'. Retrieved March 23, 2020, from https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/middle-east/nakba-day-catastrophe-palestinians-israel-benjamin-netanyahu-gaza-west-bank-hamas-a8346156.html
[4] Ross Stewart (2004). Causes and Consequences of the Arab-Israeli Conflict. London: Evan Brothers, Ltd., 2004.
[5] Record of the Conversation Between the Führer and the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem on November 28, 1941, in Berlin, Documents on German Foreign Policy, 1918-1945, Series D, Vol. XIII, London , 1964, p. 881ff, in Walter Lacquer and Barry Rubin, The Israel-Arab Reader, (NY: Facts on File, 1984), pp. 79-84. Retrieved from https://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/the-mufti-and-the-f-uuml-hrer#2."Germany stood for uncompromising war against the Jews. That naturally included active opposition to the Jewish national home in Palestine. .... Germany would furnish positive and practical aid to the Arabs involved in the same struggle .... Germany's objective [is] ... solely the destruction of the Jewish element residing in the Arab sphere .... In that hour the Mufti would be the most authoritative spokesman for the Arab world. The Mufti thanked Hitler profusely. "
[6] United Nations General Assembly A / RES / 181 (II) of 29 November 1947.
[7] Tzahal is a Hebrew acronym used to refer to the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF).
[8] Newsroom (8th June 2009). Arming Up: The world's biggest military spenders by population. 03-20-2020, by The Economist Retrieved from: https://www.economist.com/news/2009/06/08/arming-up
[9] Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (nd). SIPRI Military Expenditure Database. Retrieved March 21, 2020, from https://www.sipri.org/databases/milex
[10] Gross, JA (2016, May 30). Just a quarter of all eligible reservists serve in the IDF. Retrieved March 22, 2020, from https://www.timesofisrael.com/just-a-quarter-of-all-eligible-reservists-serve-in-the-idf/
[11] AHRONHEIM, A. (2020, January 12). Arab Christians and Bedouins in the IDF: Meet the members of Unit 585. Retrieved March 19, 2020, from https://www.jpost.com/Israel-News/The-sky-is-the-limit-in-the- IDFs-unique-Unit-585-613948
The wave of diplomatic recognition of Israel by some Arab countries constitutes a shift in regional alliances
![Dubai, the largest city in the United Arab Emirates [Pixabay]. Dubai, the largest city in the United Arab Emirates [Pixabay].](/documents/16800098/0/acuerdos-abraham-blog.jpg/43eef7ab-96b1-fcd7-b19d-4d682361590c?t=1621884303752&imagePreview=1)
▲ Dubai, the largest city in the United Arab Emirates [Pixabay].
ANALYSIS / Ann M. Callahan
With the signing of the Abraham Accords, seven decades of enmity between the states were concluded. With a pronounced shift in regional alliances and a convergence of interests crossing traditional alignments, the agreements can be seen as a product of these regional changes, commencing a new era of Arab-Israeli relations and cooperation. While the historic peace accords seem to present a net positive for the region, it would be a mistake to not take into consideration the losing party in the deal; the Palestinians. It would also be a mistake to dismiss the passion with which many people still view the Palestinian issue and the apparent disconnect between the Arab ruling class and populace.
On the 15th of September, 2020, a joint peace deal was signed between the State of Israel, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and the United States, known also as the Abraham Accords Peace Agreement. The Accords concern a treaty of peace, and a full normalization of the diplomatic relations between the United Emirates and the State of Israel. The United Arab Emirates stands as the first Persian Gulf state to normalize relations with Israel, and the third Arab state, after Egypt in 1979 and Jordan in 1994. The deal was signed in Washington on September 15 by the UAE's Foreign Minister Abdullah bin Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan and the Prime Minister of the State of Israel, Benjamin Netanyahu. It was accepted by the Israeli cabinet on the 12th of October and was ratified by the Knesset (Israel's unicameral parliament) on the 15th of October. The parliament and cabinet of the United Arab Emirates ratified the agreement on the 19th of October. On the same day, Bahrain confirmed its pact with Israel through the Accords, officially called the Abraham Accords: Declaration of Peace, Cooperation, and Constructive Diplomatic and Friendly Relations. Signed by Bahrain's Foreign Minister Abdullatif bin Rashid Al Zayani and Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and the President of the United States Donald Trump as a witness, the ratification indicates an agreement between the signatories to commence an era of alliance and cooperation towards a more stable, prosperous and secure region. The proclamation acknowledges each state's sovereignty and agrees towards a reciprocal opening of embassies and as well as stating intent to seek out consensus regarding further relations including investment, security, tourism and direct flights, technology, healthcare and environmental concerns.
The United States played a significant role in the accords, brokering the newly signed agreements. President of the United States, Donald Trump, pushed for the agreements, encouraging the relations and negotiations and promoting the accords, and hosting the signing at the White House.
As none of the countries involved in the Abraham Accords had ever fought against each other, these new peace deals are not of the same weight or nature as Egypt's peace deal with Israel in 1979. Nevertheless, the accords are much more than a formalizing of what already existed. Now, whether or not the governments collaborated in secret concerning security and intelligence previously, they will now cooperate publicly through the aforementioned areas. For Israel, Bahrain and the UAE, the agreements pave a path for the increase of trade, investment, tourism and technological collaboration. In addition to these gains, a strategic alliance against Iran is a key motivator as the two states and the U.S. regard Iran as the chief threat to the region's stability.
Rationale
What was the rationale for this diplomatic breakthrough and what prompted it to take place this year? It could be considered to be a product of the confluence of several pivotal impetuses.
The accords are seen as a product of a long-term trajectory and a regional reality where over the course of the last decade Arab states, particularly around the Gulf, have begun to shift their priorities. The UAE, Bahrain and Israel had found themselves on the same side of more than one major fissure in the Middle East. These states have also sided with Israel regarding Iran. Saudi Arabia, too, sees Shiite Iran as a major threat, and while, as of now, it has not formalized relations with Israel, it does have ties with the Hebrew state. This opposition to Tehran is shifting alliances in the region and bringing about a strategic realignment of Middle Eastern powers.
Furthermore, opposition to the Sunni Islamic extremist groups presents a major threat to all parties involved. The newly aligned states all object to Turkey's destabilising support of the Muslim Brotherhood and its proxies in the regional conflicts in Gaza, Libya and Syria. Indeed, the signatories' combined fear of transnational jihadi movements, such as Al-Qaeda and ISIS derivatives, has aligned their interests closer to each other.
In addition, there has been a growing frustration and fatigue with the Palestinian Cause, one which could seem endless. A certain amount of patience has been lost and Arab nations that had previously held to the Palestinian cause have begun to follow their own national interests. Looking back to late 2017, when the Trump administration officially recognised Jerusalem as the capital of Israel, had it been a decade earlier there would have been widespread protests and resulting backlash from the regional leaders in response, however it was not the case. Indeed, there was minimal criticism. This may indicate that, at least for the regional leaders, that adherence to the Palestinian cause is lessening in general.
The prospects of closer relations with the economically vibrant state of Israel, and by extension with that of the United States is increasingly attractive to many Arab states. Indeed, expectations of an arms sale of U.S. weapon systems to the UAE, while not written specifically into the accords, is expected to come to pass through a side agreement currently under review by Congress.
From the perspective of Israel, the country has gone through a long political crisis with, in just one year alone, three national elections. In the context of these domestic efforts, prime minister Netanyahu raised propositions of annexing more sections of the contended West Bank. Consequently, the UAE campaigned against it and Washington called for Israel to choose between prospects of annexation or normalization. The normalization was concluded in return for suspending the annexation plans. There is discussion regarding whether or not the suspending of the plans are something temporary or a permanent cessation of the annexation. There is a discrepancy between the English and Arabic versions of the joint treaty. The English version declared that the accord "led to the suspension of Israel's plans to extend its sovereignty". This differs slightly, however significantly, from the Arabic copy in which "[the agreement] has led to Israel's plans to annex Palestinian lands being stopped." This inconsistency did not go unnoticed to the party most affected; the Palestinians. There is a significant disparity between a temporary suspension as opposed to a complete stopping of annexation plans.
For Netanyahu, being a leading figure in a historic peace deal bringing Israel even more out of its isolation without significant concessions would certainly boost his political standing in Israel. After all, since Israel's creation, what it has been longing for is recognition, particularly from its Arab neighbours.
Somewhat similarly to Netanyahu, the Trump Administration had only to gain through the concluding of the Accords. The significant accomplishment of a historic peace deal in the Middle East was certainly a benefit especially leading up to the presidential elections, which took place earlier this November. On analyzing the Administration's approach towards the Middle East, its strategy clearly encouraged the regional realignment and the cultivation of the Gulf states' and Israel's common interests, culminating in the joint accords.
Implications
As a whole, the Abraham Accords seem to have broken the traditional alignment of Arab States in the Middle East. The fact that normalization with Israel has been achieved without a solution to the Palestinian issue is indicative of the shift in trends among Arab nations which were previously staunchly adherent to the Palestinian cause. Already, even Sudan, a state with a violent past with Israel, has officially expressed its consent to work towards such an agreement. Potentially, other Arab states are thought to possibly follow suit in future normalization with Israel.
Unlike Bahrain and the UAE, Sudan has sent troops to fight against Israel in the Arab-Israeli wars. However, following the UAE and Bahrain accords, a Sudan-Israel normalization agreement transpired on October 23rd, 2020. While it is not clear if the agreement solidifies full diplomatic relations, it promotes the normalization of relations between the two countries. Following the announcement of their agreement, the designated foreign minister, Omar Qamar al-Din, clarified that the agreement with Israel was not actually a normalization, rather an agreement to work towards normalization in the future. It is only a preliminary agreement as it requires the approval of an elected parliament before going into force. Regardless, the agreement is a significant step for Sudan as it had previously considered Israel an enemy of the state.
While clandestine relations between Israel and the Gulf states were existent for years, the founding of open relations is a monumental shift. For Israel, putting aside its annexation plans was insignificant in comparison with the many advantages of the Abraham Accords. Contrary to what many expected, no vast concessions were to be made in return for the recognition of sovereignty and establishment of diplomatic ties for which Israel yearns for. In addition, Israel is projected to benefit economically from its new forged relations with the Gulf states between the increased tourism, direct flights, technology and information exchange, commercial relations and investment. Already, following the Accord's commitment, the US, Israel and the UAE have already established the Abraham Fund. Through the program more than $3 billion dollars will be mobilized in the private sector-led development strategies and investment ventures to promote economic cooperation and profitability in the Middle East region through the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation, Israel and the UAE.
The benefits of the accords extend to a variety of areas in the Arab world including, most significantly, possible access to U.S. defence systems. The prospect of the UAE receiving America's prestigious F-35 systems is in fact underway. President Trump, at least, is willing to make the sale. However, it has to pass through Congress which has been consistently dedicated to maintaining Israel's qualitative military edge in the region. According to the Senate leader Mitch McConnell (Rep, KY), "We in congress have an obligation to review any U.S. arm sale package linked to the deal [...] As we help our Arab partners defend against growing threats, we must continue ensuring that Israel's qualitative military edge remains unchallenged". Should the sale be concluded, it will stand as the second largest sale of U.S. arms to one particular nation, and the first transfer of lethal unmanned aerial systems to any Arab ally. The UAE would be the first Arab country to possess the Lockheed Martin 5th generation stealth jet, the most advanced on the market currently.
There is discussion within Israel regarding possible UAE acquisition of the F-35 systems. Prime Minister Netanyahu did the whole deal without including the defense minister and the foreign minister, both political rivals of Netanyahu in the Israeli system. As can be expected, the Israeli defense minister does have a problem regarding the F-35 systems. However, in general, the Accords are extremely popular in Israel.
Due to Bahrain's relative dependence on Saudi Arabia and the kingdom's close ties, it is very likely that it sought out Saudi Arabia's approval before confirming its participation in the Accords. The fact that Saudi Arabia gave permission to Bahrain could be seen as indicative, to a certain extent, of their stance on Arab-Israeli relations. However, the Saudi state has many internal pressures preventing it, at least for the time being, from establishing relations.
For over 250 years, the ruling Saudi family has had a particular relationship with the clerical establishment of the Kingdom. Many, if not the majority of the clerics would be critical of what they would consider an abandonment of Palestine. Although Mohammed bin Salman seems more open to ties with Israel, his influential father, Salman bin Abdulaziz sides with the clerics surrounding the matter.
Differing from the United Arab Emirates, for example, Saudi Arabia gathers a B amount of its legitimacy through its protection of Muslims and promotion of Islam across the world. Since before the establishment of the state of Israel, the Palestinian cause has played a crucial role in Saudi Arabia's regional activities. While it has not prevented Saudi Arabia from engaging in undisclosed relations with Israel, its stance towards Palestine inhibits a broader engagement without a peace deal for Palestine. This issue connected to a critical strain across the region: that between the rulers and the ruled. One manifestation of this discrepancy between classes is that there seems to be a perception among the people of the region that Israel, as opposed to Iran, is the greater threat to regional security. Saudi Arabia has a much larger population than the UAE or Bahrain and with the extensive popular support of the Palestinian cause, the establishment of relations with Israel could elicit considerable unrest.
While Saudi Arabia has engaged in clandestine ties with Israel and been increasingly obliging towards the state (for instance, opening its air space for Israeli direct flights to the UAE and beyond), it seems unlikely that Saudi Arabia will establish open ties with Israel, at least for the near future.
The ongoing coronavirus pandemic has only heightened prevailing social, political and economic tensions all throughout the Middle East. Taking this into account, in fear of provoking unrest, it can be expected that many rulers will be hesitant, or at least cautious, about initiating ties with the state of Israel.
That being said, in today's hard-pressed Middle East, Arab states, while still backing the Palestinian cause, are more and more disposed to work towards various relations with Israel. Saudi Arabia is arguably the most economically and politically influential Arab state in the region. Therefore, if Saudi Arabia were to open relations with Israel, it could invoke the establishment of ties with Israel for other Arab states, possibly invalidating the longstanding idea that such relations could come about solely though the resolution of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Regarding Iran, it cannot but understand the significance and gravity of the Accords and recent regional developments. Just several nautical miles across the Gulf to Iran, Israel has new allies. The economic and strategic advantage that the Accords promote between the countries is undeniable. If Iran felt isolated before, this new development will only emphasize it even more.
In the words of Mike Pompeo, the current U.S. Secretary of State, alongside Bahrain's foreign minister, Abdullatif Al-Zayani, and Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu, the accords "tell malign actors like the Islamic Republic of Iran that their influence in the region is waning and that they are ever more isolated and shall forever be until they change their direction".
Apart from Iran, in the Middle East Turkey and Qatar have been openly board member in their opposition to Israel and the recent Accords. Qatar maintains relations with two of Israel's most critical threats, both Iran and Hamas, the Palestinian militant group. Qatar is a staunch advocate of a two-state solution to the Israel-Palestine conflict. One of Qatar's most steady allies in the region is Turkey. Israel, as well as the UAE, have significant issues with Ankara. Turkey's expansion and building of military instructions in Libya, Sudan and Somalia demonstrate the regional threat that it poses for Israel and the UAE. For Israel in particular, besides Turkey's open support of Hamas, there have been clashes concerning Ankara's interference with Mediterranean maritime economic sovereignty.
With increasing intensity, the President of Turkey, Recep Tayyip Erdogan, has made clear Turkey's revisionist actions. They harshly criticized UAE's normalization with Israel and even said that they would consider revising Ankara's relations with Abu Dhabi. This, however, is somewhat incongruous as Turkey has maintained formal diplomatic relations with Israel since right after its birth in 1949. Turkey's support of the Muslim Brotherhood throughout the region, including in Qatar, is also a source of contention between Erdogan and the UAE and Israel, as well as Saudi Arabia. Turkey is Qatar's largest beneficiary politically, as well as militarily.
In the context of the Abraham Accords, the Palestinians would be the losers undoubtedly. While they had a weak negotiating hand to begin with, with the decreasing Arab solidarity they depend on, they now stand even weaker. The increasing number of Arab countries normalizing relations with Israel has been vehemently condemned by the Palestinians, seeing it as a betrayal of their cause. They feel thoroughly abandoned. It leaves the Palestinians with very limited options making them severely more debilitated. It is uncertain, however, whether this weaker position will steer Palestinians towards peacemaking with Israel or the contrary.
While the regional governments seem more willing to negotiate with Israel, it would be a severe mistake to disregard the fervour with which countless people still view the Palestinian conflict. For many in the Middle East, it is not so much a political stance as a moral obligation. We shall see how this plays out concerning the disparity between the ruling class and the populace of Arab or Muslim majority nations. Iran will likely continue to advance its reputation throughout the region as the only state to openly challenge and oppose Israel. It should amass some amount of popular support, increasing yet even more the rift between the populace and the ruling class in the Middle East.
Future prospects
The agreement recently reached between President Trump's Administration and the kingdom of Morocco by which the U.S. governments recognizes Moroccan sovereignty over the disputed territory of Western Sahara in exchange for the establishment of official diplomatic relations between the kingdom and the state of Israel is but another step in the process Trump would have no doubt continued had he been elected for a second term. Despite this unexpected move, and although the Trump Administration has indicated that other countries are considering establishing relations with Israel soon, further developments seem unlikely before the new U.S. Administration is projected to take office this January of 2021. President-elect Joe Biden will take office on the 20th of January and is expected to instigate his policy and approach towards Iran. This could set the tone for future normalization agreements throughout the region, depending on how Iran is approached by the incoming administration.
In the United States, the signatories of the Abraham Accords have, in a time of intensely polarized politics, enhanced their relations with both Republicans as well as Democrats though the deal. In the future we can expect some countries to join the UAE, Bahrain and Sudan in normalization efforts. However, many will stay back. Saudi Arabia remains central in the region regarding future normalization with Israel. As is the case across the region, while the Arab leaders are increasingly open to ties with Israel, there are internal concerns, between the clerical establishment and the Palestinian cause among the populace - not to mention rising tensions due to the ongoing pandemic.
However, in all, the Accords break the strongly rooted idea that it would take extensive efforts in order for Arab states to associate with Israel, let alone establish full public normalization. It also refutes the traditional Arab-state consensus that there can be no peace with Israel until the Palestinian issue is en route to resolution, if not fully resolved.
Behind the tension between Qatar and its neighbours is the Qatari ambitious foreign policy and its refusal to obey
Recent diplomatic contacts between Qatar and Saudi Arabia have suggested the possibility of a breakthrough in the bitter dispute held by Qatar and its Arab neighbors in the Gulf since 2017. An agreement could be within reach in order to suspend the blockade imposed on Qatar by Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Bahrain (and Egypt), and clarify the relations the Qataris have with Iran. The resolution would help Qatar hosting the 2022 FIFA World Cup free of tensions. This article gives a brief context to understand why things are the way they are.

Ahmad Bin Ali Stadium, one of the premises for the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar
ARTICLE / Isabelle León
The diplomatic crisis in Qatar is mainly a political conflict that has shown how far a country can go to retain leadership in the regional balance of power, as well as how a country can find alternatives to grow regardless of the blockade of neighbors and former trading partners. In 2017, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Bahrain broke diplomatic ties with Qatar and imposed a blockade on land, sea, and air.
When we refer to the Gulf, we are talking about six Arab states: Saudi Arabia, Oman, UAE, Qatar, Bahrain, and Kuwait. As neighbors, these countries founded the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) in 1981 to strengthen their relation economically and politically since all have many similarities in terms of geographical features and resources like oil and gas, culture, and religion. In this alliance, Saudi Arabia always saw itself as the leader since it is the largest and most oil-rich Gulf country, and possesses Mecca and Medina, Islam's holy sites. In this sense, dominance became almost unchallenged until 1995, when Qatar started pursuing a more independent foreign policy.
Tensions grew among neighbors as Iran and Qatar gradually started deepening their trading relations. Moreover, Qatar started supporting Islamist political groups such as the Muslim Brotherhood, considered by the UAE and Saudi Arabia as terrorist organizations. Indeed, Qatar acknowledges the support and assistance provided to these groups but denies helping terrorist cells linked to Al-Qaeda or other terrorist organizations such as the Islamic State or Hamas. Additionally, with the launch of the tv network Al Jazeera, Qatar gave these groups a means to broadcast their voices. Gradually the environment became tense as Saudi Arabia, leader of Sunni Islam, saw the Shia political groups as a threat to its leadership in the region.
Consequently, the Gulf countries, except for Oman and Kuwait, decided to implement a blockade on Qatar. As political conditioning, the countries imposed specific demands that Qatar had to meet to re-establish diplomatic relations. Among them there were the detachment of the diplomatic ties with Iran, the end of support for Islamist political groups, and the cessation of Al Jazeera's operations. Qatar refused to give in and affirmed that the demands were, in some way or another, a violation of the country's sovereignty.
A country that proves resilient
The resounding blockade merited the suspension of economic activities between Qatar and these countries. Most shocking was, however, the expulsion of the Qatari citizens who resided in the other GCC states. A year later, Qatar filed a complaint with the International Court of Justice on grounds of discrimination. The court ordered that the families that had been separated due to the expulsion of their relatives should be reunited; similarly, Qatari students who were studying in these countries should be permitted to continue their studies without any inconvenience. The UAE issued an injunction accusing Qatar of halting the website where citizens could apply for UAE visas as Qatar responded that it was a matter of national security. Between accusations and statements, tensions continued to rise and no real improvement was achieved.
At the beginning of the restrictions, Qatar was economically affected because 40% of the food supply came to the country through Saudi Arabia. The reduction in the oil prices was another factor that participated on the economic disadvantage that situation posed. Indeed, the market value of Qatar decreased by 10% in the first four weeks of the crisis. However, the country began to implement measures and shored up its banks, intensified trade with Turkey and Iran, and increased its domestic production. Furthermore, the costs of the materials necessary to build the new stadiums and infrastructure for the 2022 FIFA World Cup increased; however, Qatar started shipping materials through Oman to avoid restrictions of UAE and successfully coped with the status quo.
This notwithstanding, in 2019, the situation caused almost the rupture of the GCC, an alliance that ultimately has helped the Gulf countries strengthen economic ties with European Countries and China. The gradual collapse of this organisation has caused even more division between the blocking countries and Qatar, a country that hosts the largest military US base in the Middle East, as well as one of Turkey, which gives it an upper hand in the region and many potential strategic alliances.
The new normal or the beginning of the end?
Currently, the situation is slowly opening-up. Although not much progress has been made through traditional or legal diplomatic means to resolve this conflict, sports diplomacy has played a role. The countries have not yet begun to commercialize or have allowed the mobility of citizens, however, the event of November 2019 is an indicator that perhaps it is time to relax the measures. In that month, Qatar was the host of the 24th Arabian Gulf Cup tournament in which the Gulf countries participated with their national soccer teams. Due to the blockade, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Bahrain had boycotted the championship; however, after having received another invitation from the Arabian Gulf Cup Federation, the countries decided to participate and after three years of tensions, sent their teams to compete. The sporting event was emblematic and demonstrated how sport may overcome differences.
Moreover, recently Saudi Arabia has given declarations that the country is willing to engage in the process to lift-up the restrictions. This attitude toward the conflict means, in a way, improvement despite Riyadh still claims the need to address the security concerns that Qatar generates and calls for a commitment to the solution. As negotiations continue, there is a lot of skepticism between the parties that keep hindering the path toward the resolution.
Donald Trump's administration recently reiterated its cooperation and involvement in the process to end Qatar's diplomatic crisis. Indeed, US National Security Adviser Robert O'Brien stated that the US hopes in the next two months there would be an air bridge that will allow the commercial mobilization of citizens. The current scenario might be optimistic, but still, everything has remained in statements as no real actions have been taken. This participation is within the US strategic interest because the end of this rift can signify a victorious situation to the US aggressive foreign policy toward Iran and its desire to isolate the country. This situation remains a priority in Trump's last days in office. Notwithstanding, as the transition for the administration of Joe Biden begins, it is believed that he would take a more critical approach on Saudi Arabia and the UAE, pressuring them to put an end to the restrictions.
This conflict has turned into a political crisis of retention of power or influence over the region. It is all about Saudi Arabia's dominance being threatened by a tiny yet very powerful state, Qatar. Although more approaches to lift-up the rift will likely begin to take place and restrictions will gradually relax, this dynamic has been perceived by the international community and the Gulf countries themselves as the new normal. However, if the crisis is ultimately resolved, mistrust and rivalry will remain and will generate complications in a region that is already prone to insurgencies and instability. All the countries involved indeed have more to lose than to gain, but three years have been enough to show that there are ways to turn situations like these around.
Soft power in the regional race for gaining the upper hand in the cultural and heritage influence among Muslims

A picture taken from the Kingdoms of Fire official trailer
ANALYSIS / Marina García Reina and Pablo Gurbindo
Kingdoms of Fire (in Arabic Mamalik al nar) is the new Emirati and Saudi funded super-production launched in autumn 2019 and born to face the Turkish control in the TV series and shows field for years. The production has counted on a budget of US$ 14 million. The series goes through the story of the last Sultan of Mamluk Egypt, Al-Ashraf Tuman Bay, in his fight against the Ottoman Sultan Selim. The production is the reflection of the regional rivalries in the race for gaining the upper hand in the cultural and heritage influence among Muslims.
Historicity
To understand the controversy this series has arisen we have to comprehend the context where the story takes place and the main characters of the story. The series talks about the Ottoman conquest of the Mamluk Sultanate of 1517. The Ottomans are already known for the general public, but who were the Mamelukes?
A Mameluke is not an ethnic group, it is a military class. The term comes from the Arab mamluk (owned) and it defines a class of slave soldiers. These mamluks had more rights than a common slave as they could carry weapons and hold positions of military responsibility. They were created in the ninth century by the Abbasid Caliphs with the purchase of young slaves and their training on martial and military skills. They became the base of military power in the Middle East. This military elite, similar to the Roman Praetorian Guard, was very powerful and could reach high positions in the military and in the administration. Different groups of Mamluks rebelled against their Caliphs masters, and in Egypt they successfully claimed the Caliphate in 1250, starting the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt and Syria. Their military prowess was demonstrated in 1260 in the battle of Ain Yalut where they famously defeated the Great Mongol Empire and stopped its expansion towards the west.
The Ottoman Empire was formed as one of the independent Turkish principalities that appeared in Anatolia after the fall of the Sultanate of Rum in the thirteenth century. It rapidly expanded across Anatolia and also reached the Balkans confronting the Byzantine Empire, direct heir of the Roman Empire. In 1453, after a long siege, they conquered Constantinople, sealing the fate of the Byzantine Empire.
By the sixteenth century, the Ottomans and the Mamluks were the two main powers of the Middle East, and as a perfect example of the "Thucydides trap", the conflict between these two regional powers became inevitable. In 1515, Ottoman Sultan Selim I launched a campaign to subdue the Mamluks. Incidentally, this is the campaign represented in the Arab series. In October 1516, in the battle of Marj Dabiq, the Mamluk Sultan Al-Ghawri was killed, and Syria fell into Ottoman rule. Tuman Bay II was proclaimed as Sultan and prepared the defence of Egypt. In 1517 the Ottomans entered Egypt and defeated Tuman Bay at the battle of Riadanieh, entering Cairo unopposed. Tuman Bay fled and, supported by the Bedouins, started a guerrilla campaign. But he was betrayed by a Bedouin chief and captured. On April 15, 1517, he was hanged to death on the city gates of Cairo and with him the Mamluk Sultanate ended.
With the end of the Mamluk rule, Egypt became an Ottoman province. The Ottoman control lasted from 1517 until the start of WWI, when the British Empire established a protectorate in the country after the Ottoman Empire entered the war.
A response to Turkish influence
Unlike Saudi Arabia, which until 2012, with the release of Wadjda, had never featured a film shot entirely in the country, other Middle Eastern countries such as Turkey and Iran have taken their first steps in the entertainment industry long before.
Turkey is a clear example of a country with a well-constituted cinema and art industry, hosting several film festivals throughout the year and having an established cinema industry called Yesilcamwhich can be understood as the Turkish version of the US Hollywood or the Indian Bollywood. The first Turkish narrative film was released in 1917. However, it was not till the 1950s when the Turkish entertainment industry truly started to emerge. Yesilcam was born to create a cinema appropriate for the Turkish audience in a period of national identity building and in an attempt to unify multiplicities. Thus, it did not only involve the creation of original Turkish films, but also the adaptation and Turkification of Western cinema.
One of the reasons that promoted the arising of the Turkish cinema was a need to respond to the Egyptian film industry, which was taking the way in the Middle East during the Second World War. It represents a Turkish nationalist feeling through a cinema that would embrace Turkey's Ottoman heritage and modern lifestyle.
Now, Turkish productions are known and watched by audiences worldwide, in more than 140 countries, which has turned Turkey into the world's second largest television shows distributor, generating US$ 350 million a year, only surpassed by the USA.
These Turkish productions embracing the Ottoman period are also a reflection of the current Neo-Ottoman policies carried out by the President Tayyip Erdogan, who many believe is trying to portray himself as a "modern Ottoman ruler and caliph for Muslims worldwide". It is clear that the Turkish President is aware of the impact of its TV shows, as he stated, in a 2016 speech referring to a Turkish show named "The Last Emperor"-narrating important events during the reign of Sultan Abdülhamid-, that the West is treating Turkey in the same way as 130 years ago and, regarding Arabs, he stated that "until the lions start writing their own stories, their hunters will always be the heroes."
A soft power tool
Communication-especially visual communication and, therefore, cinema-plays an important role in either reinforcing the identity status quo or challenging self-views and other-views of the dynamic, multi-faceted self[1]. It is precisely the own and particular Saudi identity that wants to be portrayed by this series.
The massive sums invested in the production of Mamalik al nar, as with other historical TV shows, is an evidence of the importance of the exercise of "soft power" by the cinema and TV show industry in the Middle East. As it has been highlighted above, Turkey has been investing in cinema production to export its image to the world for a long time now. On the other hand, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates have been restrictive when it comes to cinema, not even allowing it within the country in the case of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) for more than 35 years, and they have had few interest on producing and promoting self-made cinema. Now this has dramatically changed. Saudis have an interest in translating their self-conception of matters to the world, and communication is a way of contesting and resisting a dominant culture's encroachment[2] that is being headed by Turkey.
In the words of Yuser Hareb, Genomedia owner(Mamalik al nar's film production company), the series was born from the idea of creating an alternative to the influence that Turkish productions have within Arabs. The producer argues that the Ottoman Empire period is not much of a glorious heritage for Arabs, but more of a "dark time," characterised by repression and criminal actions against Arabs. Turkish historic cinema "adjusts less than 5% to reality," Hareb says, and Mamalik al Nar is intended to break with the Turkish cultural influence in the Middle East by "vindicating Arab history" and stating that Ottomans were neither the protectors of Islam, nor are they the restorers of it.
Dynamics are changing in the region. The Middle East Broadcasting Center (MBC), the large Emirates-based and Saudi-owned average conglomerate that is one of the strongest broadcasting channel in the Arabic speaking world, was in charge of broadcasting in the Arab countries some of the most famous Turkish dramas since 2007, such as the soap opera Gumus, which final episode had 92 million viewers across the region. In March 2018, MBC rejected several Turkish dramas and it even announced an unofficial moratorium on broadcasting any Turkish series. This decision was praised by the Genomedia owner (the producer of Mamalik al nar), Yuser Hareb, pronouncing against those who passively permit the influence of foreigners with their films and series. Furthermore, MBC is also responsible for the broadcasting of Mamalik al nar in the region. The combination of these movements put together can easily portray a deterioration of Turkish-Arab relations.
Egypt also serves as an example of this anti-Turkish trend, when in September 2014, all Turkish series were banned in response to Erdogan's support for the Islamist president Mohammed Morsi (overthrown in July 2013) and his attacks on President Abdelfatah Al-Sisi. This adds to the backing of Turkey of the Muslim Brotherhood and the meddling in Libya to gain regional leadership over the exploration of gas deposits. In short, the backing of Islamist movements constitutes the main argument given when criticising Turkey's "neo-colonialist" aims, which are not completely denied by the Turkish government as it claims the will to be a restorer for the Muslim world.
Double-sided
Ultimately, both the Turkish and the Saudi Arabian sides have the same opinion of what the other is trying to do: influencing the region by their own idiosyncrasy and cultural heritage. It is indeed the crossfire of accusations against one another for influencing and deceiving the audience about the history of the region, especially regarding who should be praised and who condemned.
Turkish and other pro-Erdogan commentators have described Mamalik al nar as an attempt to foment division between Muslims and attacking the Ottoman legacy. Yasin Aktay, an advisor to Erdogan, remarked that there are no Turkish series that attack any Arab country so far, unlike this Saudi series is doing with the former Ottoman Empire by manipulating "historical data for an ideological or political reason". Indeed, it is an attack on "the Ottoman State, but also on contemporary Turkey, which represents it today".
The legacy of the Ottoman Sultanate has been subjected to political and intellectual discussion since medieval times. Specifically, after World War I, when a lot of new Arab nation-states started to consolidate, the leaders of these new-born states called for a nationalist feeling by means of an imperialist discourse, drifting apart Turks and Arabs. It is still today a controversial topic in a region that is blooming and which leadership is being disputed, however -and, perhaps, fortunately-, this ideology does not go beyond the ruling class, and neither the great majority of Arabs see the Ottomans as a nation that invaded and exploited them nor the Turks see Arabs as traitors.
No matter how much Erdogan's Turkey puts the focus on Islam, the big picture of Turkish series is a secular and modern outlook of the region, which has come to be especially interesting to keep up with the region's changing dynamics. That could be overshadowed by salafist movements restricting freedom of speech in what is considered immoral forms of art by some.
All in all, Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates are determined to counterbalance Turkey's effort to increase its regional clout through the use of "soft power" instruments by means of reacting to the abundance of Turkish dramas by launching TV series and shows that offer an "Arab approach" to the matter. In any case, it is still to be seen whether these new Arab productions narrating the ancient history of the Arab territories will have or not a success equivalent to the already consolidated Turkish industry.
[1] Manuel Castells. The rise of network society (New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell, 2009).
[2] Thomas K. Nakayama and Raymond J. Krizek. Nakayama and Raymond J. Krizek (1995). Whitness: A strategic rhetoric (Quarterly Journal of Speech, 1995), 81, 291-319.
![Bahraini and UAE foreign ministers sign Abraham Accords with Israeli premier in September 2020 [White House]. Bahraini and UAE foreign ministers sign Abraham Accords with Israeli premier in September 2020 [White House].](/documents/16800098/0/acuerdos-blog.jpg/ad268976-c84e-2b4c-d2a5-ca36909e72e2?t=1621877040390&imagePreview=1)
Bahraini and UAE foreign ministers sign Abraham Accords with Israeli premier in September 2020 [White House].
essay / Lucas Martín Serrano
It is interesting to incorporate into any geopolitical analysis subject a touch of history. History is a fundamental financial aid for understanding the present. And most conflicts, problems, frictions or obstacles, whether between nations or public or private entities, always have an underlying historical background. Moreover, taken to the field of negotiation, regardless of the level of negotiation, demonstrating a certain historical knowledge of the adversary is useful because, on the one hand, it is not only a sample of interest and respect for him, which will always place us in an advantageous position, but, on the other hand, any stumbling block or difficulty that appears has ample possibilities of having its historical counterpart, and precisely there the path to a solution can be found. The party that has a greater depth of knowledge will significantly increase the chances of a solution that is more favourable to its interests.
In ancient times, the territory now occupied by the United Arab Emirates was inhabited by Arab tribes, nomadic farmers, craftsmen and traders. Plundering the merchant ships of European powers that sailed along its coasts, coming closer than was advisable, was commonplace. And, in a way, a way of life for some of its inhabitants. It was in the 7th century that Islam took root in the local culture. Of the two currents that emerged after the disputes that followed the death of the Prophet, it was the Sunni current that became dominant from the 11th century onwards.
In order to put an end to piracy and secure the maritime trade routes, the United Kingdom signed a peace treaty with the sheikhs in the area in 1820, signature . In 1853, a further step was taken and another agreement was signed, placing the entire territory under the military protectorate of the United Kingdom.
signature The area attracted the attention of powers such as Russia, France and Germany, and in 1892, to protect their interests, the agreement was set up, guaranteeing the British a monopoly on trade and exports.
The area encompassing today's seven United Arab Emirates plus Qatar and Bahrain became known as the "Trucial States".
During World War I, the Gulf's airfields and ports played an important role in the conflict in favour of the UK, development . At the end of World War II in 1945, the League of Arab States (Arab League) was created, made up of those with some colonial independence. The organisation attracted the attention of the Truce states.
In 1960, the Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) was created, with Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait and Venezuela as founding members and headquartered in Vienna, Austria. The seven emirates, which would later form the United Arab Emirates, joined the organisation in 1967.
Since 1968, nine emirates on the eastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula had begun negotiations to form a federal state. Following the withdrawal of British troops final and after Bahrain and Qatar dissociated themselves from the process and gained independence separately, in 1971, six emirates became independent from the British Empire: Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm al Qaywayn and Fujairah, forming the federation of the United Arab Emirates, with a legal system based on the 1971 constitution. Once consolidated, they joined the Arab League on 12 June. The seventh emirate, Ras Al-Khaimah, joined the following year, with the strongest components being the emirates of Dubai and Abu Dhabi, the capital.
It was the beginning of the exploitation of the huge oil wells discovered years earlier that turned the tide at status. After the 1973 oil crisis, the Emirates began to accumulate enormous wealth, as OPEC members decided not to export any more oil to the countries that supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War.
Oil and tourism based on urban growth and technological development are the main sources of prosperity in the country today, and a very important fact from all points of view is that 80-85% of the UAE's population is currently immigrant.
status current
It has been especially during the last decade, and partly as a consequence of events in the region since what became known as the Arab Spring, that the US has emerged as a regional power with the capacity to influence the region.
The main characteristic that can be attributed to this emergence on the international scene is the transformation of a conservative foreign policy, very much geared towards "self-preservation", towards a more open-minded one with a clear vocation not only to play a relevant role in the region, but also to influence it in order to protect its interests.
What can be seen as Abu Dhabi's main ambition is to become a major player capable of influencing the definition and establishment of governance Structures throughout the region according to its own model, securing and expanding trade routes, bringing in its neighbours to create a sufficiently powerful economic node with the capacity to forge closer ties with the entire East African region and Southeast Asia, in what seems another clear example of how the global geopolitical centre is already shifting definitively towards the Asia-Pacific axis.
The Emirati model has been able to evolve to integrate increasing economic openness with a conservative and strong-government model political whose main speech is built on the foundation of a well-entrenched and secure state. And all of this is coupled with a strong capacity as a service provider provider. Interestingly, the social model is relatively secular and liberal based by regional standards.
But a fundamental fact that cannot be forgotten is the outright rejection of any political or religious ideology that poses the slightest threat to the hegemony and supremacy of the state and its leaders.
It is Abu Dhabi, as the largest and most prosperous of the seven emirates, that exerts the most influence in setting the broad lines of both domestic and foreign policy. Indeed, the evolution of the UAE's established model is firmly associated with Abu Dhabi's crown prince and de facto leader of the emirate, Mohamed bin Zayed (MbZ).
What cannot be lost sight of is that, although MbZ and his inner circle of trust share the same vision of the world and politics, their actions and decisions do not necessarily follow a pre-established plan. There is no basic doctrine with set tactical and strategic objectives and the lines of work to follow in order to achieve them.
Their way of carrying out country strategy, if it can be called that, is based on a small group belonging to that inner circle, which puts on the table a number of usually tactical and reactive options to any problems or issues that arise to carry out. Based on these, the top leadership follows an ad hoc decision-making process that can lead to an excessive need for subsequent corrections and adjustments that in turn lead to missed opportunities.
Threats - status security
Emirati authorities have a clear perception of the main geostrategic threats to their development: on the one hand, the Iranian-promoted transnational spread of Islamist political ideology and, on the other, the influence sought by the Muslim Brotherhood and its promoters and supporters, including Qatar and Turkey, is perceived as an existential threat to their vision of a more secular form of government, as well as to the stability of the current regional status quo, given that it can act as a catalyst for radicalism in the area.
However, Abu Dhabi has been much more belligerent in its speech against the Muslim Brotherhood and its supporters, while remaining cautious in its stance against Iran.
The recent agreement with the State of Israel has served to undermine the credibility of many long-held clichés and has also highlighted the emergence of a Sunni-Jewish bloc as civil service examination to the belligerent and growing Shiite current led by Iran and its proxies, active in virtually every country in the region and in all regional conflicts.
This new status should serve to confirm to Western powers that in the Middle East region the view of their own problems has changed and Iran and its particular way of conducting foreign policy and defending its interests are now seen as a far more destabilising factor than the long-running Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The threat posed by Iran has acted as a catalyst in bringing together views, while Israel is nonetheless seen as providing stability both militarily and economically.
The UAE-Israel Treaty
On 15 September, Israel, the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain formalised the normalisation of their relations. This agreement means that four Arab states have now accepted Israel's right to exist, and this is undoubtedly a real diplomatic success.
The fact that it was precisely the UAE and Bahrain is no coincidence. Neither state has engaged in a direct war against Israel. And, if this characteristic is common to both states, Bahrain's relationship with Israel has been much smoother than that of the UAE. This reality is underpinned by the Jewish community based in Al-Qatif and its integration, which has translated into full and active participation in Bahrain's political life. This has helped to ensure that relations between Manama and Jerusalem have been far from conflictual.
Despite being seen as a novelty in the eyes of the general public, the truth is that the recent agreement is the third 'peace treaty' that signature has reached between the Hebrew country and an Arab nation. However, it is the first that seems to have been born with sufficiently solid foundations to augur a new, much more stable and lasting status , in clear contrast to the relations resulting from the previous agreements with Egypt and Jordan, which were very limited to personal relations and in the field of security and conventional diplomacy.
The new agreement with Israel sets out a new path for partnership affecting the Middle East as a whole, including substantially counterbalancing Iran's influence, fostering trade relations, tourism, partnership in subject military intelligence sharing, cooperation in health area and thereby helping to position the UAE to lead Arab diplomacy in the region by offering a solid civil service examination to Islamist groups such as the Muslim Brotherhood and its Palestinian arm in Gaza, Hamas, and thereby opening the door for other countries in the region to move in the same direction.
Israel's decision to fail the announced annexation under its sovereignty of certain areas of the West Bank is test that these moves in the region are much deeper and much more prepared and agreed in advance than might be imagined.
And this is precisely one of the major differences with previous agreements. The great expectation that has been created and the clear indications that other countries, including Saudi Arabia, will follow the UAE's lead.
In fact, one significant step in this direction was taken, and it was as simple as an Israeli "EI-Al" plane flying over Saudi airspace carrying a large issue group of businessmen, staff officials and investors on its way to the Emirates as a gesture of goodwill. And contrary to what might have been expected at other times, this had no repercussions in the Arab world, nor did it provoke any protests or demonstrations against it, subject .
Places such as Amman, Beirut, Tunis and Rabat, where demonstrations against the Israeli "occupation" and similar accusations are traditionally large in terms of participation, remained largely calm on this occasion.
But if this has gone unnoticed by the general population, it has not gone unnoticed by the leaders of the Middle Eastern powers and the violent organisations they use as proxies.
For those aspiring to follow in the UAE's footsteps and establish relations with Israel, this has served as a spur to reaffirm their decision, as the sense of unease or even danger emanating from the streets in the Arab world regarding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict that such a move might provoke has diminished.
For Iran and its proxies , on the other hand, it has been a hard lesson. Not only has the Palestinian cause, which has been raised and put on the table for so long, been significantly diminished in importance, but it has coincided in time with potestas in both Iraq and Lebanon in the opposite direction, i.e. against Iran's interference in the internal affairs of both countries.
In conclusion, it should be noted that, while this absence of protest at the agreement between Israel and the UAE may seem surprising, it is a clear sign of a long process of political maturation and evolution within the Arab world at large.
The people of the Middle East in general no longer aspire to pan-Arabist, pan-Islamic unity, to the establishment of the Great Caliphate or, in the case of Iran or Turkey, to imperialist dreams that are a thing of the past. What the mass of the people and society really want is to improve their well-being, to have more and more attractive economic opportunities, to have a good system educational, to improve the standards of development in all areas, to have the rule of law, and for the rule of law to be equal for all in their respective countries.
The treaty that is the subject of this point fits perfectly within these aspirations and this mental outline . The masses that once took to the streets no longer believe that the Palestinian cause is worthy of more effort and attention than their own struggle for a better future for their nations.
And, importantly, despite the opacity of the ayatollahs' regime, Iran's population is becoming less and less submissive to policies that are leading the country into a series of permanent conflicts with no end in sight, wasting the country's resources to sustain them.
Just two days after advertisement of agreement , the United Arab Emirates lifted the ban on telephone communication with Israel, with Hebrew Foreign Minister Gabi Ashkenazi and his Emirati counterpart Abdullah binZayed symbolising the opening of this new line of communication.
Almost immediately afterwards, a team from the Israeli Foreign Ministry travelled to Abu Dhabi to begin looking for possible sites for the future Israeli embassy.
A significant flow of investment from the UAE is being channelled to Israeli companies seeking new ways to treat COVID19 and to develop new tests to detect the disease. The increase in business deals between Israeli and Emirati companies has been almost immediate, and the "El-Al" company is already working to open a direct corridor between Tel Aviv and Abu Dhabi.
In view of the new status and the new approaches, Morocco, Oman and other Arab countries are now moving to follow in the UAE's footsteps. Israel's attractiveness is only growing, in a significant evolution from being the most hated country in the region to the most desired partner .
One factor to consider, however, is the impact in the US and Europe. In the West, the Palestinian cause is generally gaining support mainly due to the Boycott, Divestment and Sanctions (BDS) movement. As such, changes in relations with Israel are likely not only to fail to undermine that support, but also to spur increased efforts to prevent normalisation through disinformation campaigns spreading hatred towards Israel.
Finally, the civil service examination by Turkey, Qatar and Iran was predictable, but also clarifying. The Iranian president has called agreement a "grave mistake", while his Turkish counterpart has threatened to close the UAE embassy in Turkey. status In both cases, the ultimate reason for this reaction is the same: the use of the Palestinian cause for their own interests and, coincidentally, both are on this occasion coincidental: to distract public opinion from the difficult economic situation that, for different reasons, the two countries are going through.
Regional policy
The most important and enduring element of the UAE's foreign and security policy is its strategic alliances with the US and Saudi Arabia. Although the UAE has pursued a more independent course over the past decade, developments and this new direction would not have been possible without the support of the US, on whose protection the small but wealthy yet sparsely populated state relies, and who can be counted on to export its energy resources in the event of a conflict.
Even during the Obama administration, when relations were strained by US policy towards the events of the 'Arab Spring' and Iran, the strategic alliance between the two nations was maintained.
The clearly defined anti-Iranian policy of Donald Trump's administration, equivalent to that of the UAE, facilitated a rapid improvement in relations once again, and the new US administration saw the UAE as a fundamental pillar on which to base its Middle East policy. Thus, together with Israel and Saudi Arabia, the UAE is now the main US ally in the region.
In contrast to the US, Saudi Arabia became a strategic partner of the UAE's new regional policy under Obama. Indeed, the two nations have maintained close ties since the birth of the Emirates in 1971, but the new, young state unsurprisingly remained in the shadow of the other, more established nation, following the policies of its 'big brother'.
This status changed with the rise to power of Mohammed Bin Zayed who, since 2011, has been committed to spearheading a political line of joint actions in the region that have ultimately been decisive. MbZ found his perfect counterpart in Saudi Prince Mohammed Bin Salman, who gradually, since 2015, took the reins as the visible head of Saudi Arabia's policy. To such an extent that in certain cases, such as Yemen and Qatar, the UAE's leadership and drive seems to have been the unifying force behind joint regional policies.
Alliances
United States
The US role as an ally of the UAE dates back to the early 1980s, just after the 1979 Iranian revolution, which resulted in the loss of its most important ally in the region and the beginning of the Iran-Iraq war.
However, it was the 1990-1991 Gulf War that, with Iraq's invasion of Kuwait on 2 August 1990, showed the UAE how vulnerable the small Gulf states were to military aggression by any of their powerful neighbours.
In order to ensure its protection, and in common with other countries in the region, the UAE favoured an increased US presence on its territory in the years following the war. This concluded with a bilateral security agreement, agreement , signed in July 1994. This gave the US access to the UAE's air and seaports instructions and, in return, it undertook to protect the country from external aggression. Interestingly, and as a measure of how status has evolved, the agreement remained secret at Abu Dhabi's request because of the UAE's fear of criticism and protest both domestically and from Iran.
Initially, the UAE was no more than a US ally in the Persian Gulf. However, its importance as partner grew between 1990 and 2000, in part due to the port of Jebel Ali, which became the US Navy's most used base outside the country, and the Al Dhafra air base, a facility core topic for US activities in the region.
Moreover, since the late 1990s, the UAE has begun a process of presenting itself to its new ally as a reliable and more relevant partner , increasing the quantity and level of its cooperation. framework In line with this, UAE military forces have participated in all major US operations in the Middle East, from the Gulf War in 1991 to Somalia in 1992, Kosovo in 1999, Afghanistan since 2002, Libya since 2011, and Syria (in the fight against Da'esh) between 2014 and 2015. Only the UAE's participation in the invasion of Iraq in 2003 was vehemently avoided. From this involvement, the UAE Armed Forces have gained a great deal of experience on the ground, which has been beneficial to their effectiveness and professionalism.
This involvement in the often controversial US military actions in Arab countries has undoubtedly been a key element for the United States. Not only because of the image and narrative implications of having at least one Muslim country supporting them, but also because Abu Dhabi's contribution has not been limited to the military aspect. Humanitarian organisations have acted in parallel in order to win the support of the population wherever they have intervened by investing huge amounts of money. The most obvious example is Afghanistan, where the UAE has spent millions of dollars on humanitarian projects and development to help stabilise the country, while providing a small contingent of special operations forces in the particularly dangerous southern part of the country since 2003. In addition, between 2012 and 2014 they expanded their deployment with six F16 aircraft to support air operations against the Taliban. Even when the US began its phased withdrawal after 2014, Emirati troops remained in Afghanistan.
Getting the UAE on board in the fight against jihadists was not difficult at all, as its leaders are particularly averse to any form of religious extremism that affects the political system within Islam. This is the main reason for its air force's involvement in the US-led coalition against Daesh in Syria between 2014 and 2015. To such an extent that, after the US aircraft, it was the UAE aircraft that flew the most sorties against jihadist targets.
But partnership was not limited to the US. Both Australia and France had the emirates' air instructions at their disposal to carry out their operations.
Only the open breakdown of hostilities and the UAE's involvement in the 2015 Yemen War reduced its involvement in the fight against Daesh.
But it has not all been easy. The 2003 invasion of Iraq caused deep misgivings in the UAE, which saw it as a grave mistake. Their fear was that such an intervention would end up increasing Iran's influence over Iraq, or lead to civil war, which would destabilise the entire region.
Fears were realised when in 2005 a Shiite coalition close to Iran won the Iraqi elections and war broke out, leaving the UAE with its hands tied to try to influence status. Their main concern at the time was that a premature withdrawal of all US forces would further complicate status.
The renewed relationship with the Trump administration has led to the signature of a new security and cooperation agreement signed in 2017. reference letter In contrast to what happened in 1994, the contents of the agreement have been made public, and mainly relate to the presence of US troops on Emirati soil on a permanent basis. The agreement also covers the training of Emirati armed forces and regular joint exercises.
Thanks to this agreement, the US presence in the UAE is larger than ever. There are currently some 5,000 men deployed between the Al Dhafra airbase, the port of Jebel Ali and a few other small instructions or naval stations. At Al Dhafra air base alone, 3,500 men operate from F-15, F-22 and F-35 fighter jets, reconnaissance aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
For its part, the UAE has continued to develop its own military capabilities by acquiring US-made material, mainly anti-aircraft systems ("Patriot" and THAAD) and combat aircraft (110 F-16s). In addition, for a couple of years now, the UAE has shown great interest in acquiring the new F-35, although negotiations, not without some reluctance, are still ongoing.
In 2018, problems arose in supplying precision-guided munitions to both the UAE and Saudi Arabia, as both countries were using them in the Yemen War. The murder of Saudi journalist Jamal Kashoggi exacerbated resistance from the US congress , forcing President Trump to use his veto power in order to maintain the supply. This gives a measure of how decisive the current administration's attitude towards both countries is.
Despite all the difficulties mentioned above, the current US administration has redoubled its efforts to support the UAE in its regional policies, as they coincide with US objectives.
The first goal has been to build an anti-Iran alliance among Middle Eastern states that includes the UAE as partner core topic along with Saudi Arabia and Egypt. This plan is entirely in line with Abu Dhabi's aspiration to gain some leadership in the region, and is likely to succeed, as the UAE is likely to support the US in a solution to the Palestinian conflict that is quite in line with the Israeli proposal .
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is currently the UAE's most important ally in the region. Both states are financed by oil exports and both are equally wary of the expansionist ambitions of their powerful neighbours, especially Iran.
However, despite this alliance, the UAE has long feared that Saudi Arabia, using its unequal size in terms of population, military strength and oil production capacity, would seek to maintain a hegemonic position in the Persian Gulf.
In 1981, the Persian Gulf countries seized the opportunity to create an alliance that excluded the then major regional powers. Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the UAE created the committee Cooperation for the Arab States of the Gulf (GCC). This committee had a joint military force that never grew to any significant size. The biggest test of the GCC's weakness and ineffectiveness was Iraq's invasion of Kuwait without civil service examination by the supranational body.
As result of the above, the UAE relied on the US for its protection, the only country with both the will and the capacity to carry out the task of defending the small state against potential foreign aggression.
The consequence at the regional level is marked by the convergence of interests of Saudi Arabia and the UAE which, between 2011 and 2019, have pursued common regional political objectives, relying if necessary on their military capabilities.
For example, Bahrain's request for financial aid to the GCC in 2011 when its rulers felt threatened by Shia protest movements. However, its most significant intervention was its support for the coup d'état in Egypt against President Mohamed Morsi and the Muslim Brotherhood in 2013.
India
Socio-political and economic relations between the GCC members and India have always been very close, and have been based on the understanding that a secure and stable political and social environment in the Persian Gulf and Indian subcontinent are critical factors for the respective countries' development and their trans-regional ties.
From India's perspective, the improvement of its technological and economic development goes hand in hand with New Delhi's ability to strengthen its partnerships around the world. In this regard, the Persian Gulf countries, and especially the UAE, are seen as a bridge to knowledge, capabilities, resources and markets to enhance that development.
In 2016, the hitherto bilateral relations between the two countries were formalised in a strategic cooperation agreement called CSP(Comprehensive Strategic Partnership).
For the UAE, India is a modern country, a political phenomenon independent of the West that maintains strong religious and traditional roots without renouncing its diversity. In some ways, and with some reservations, it is a mirror for the UAE.
The agreement cooperation is cross-cutting and covers issues as diverse as counter-terrorism, exchange information and intelligence, anti-money laundering measures, cyber-security, as well as cooperation on subject defence, financial aid humanitarian, etc.
On the more economic side, the initiative includes concrete actions to facilitate trade and investment, with the UAE committing goal $75 billion to support the development of new generation infrastructure in India, especially railways, ports, roads, airports and industrial parks.
With regard to the energy sector, the agreement envisages the UAE's participation in the modernisation of the oil sector in all its branches, taking into account the development of a strategic reservation .
The part dealing with the development of technology for the peaceful use of nuclear energy, as well as cooperation in the aerospace sector including the development and joint launching of satellites, as well as the necessary ground control infrastructure and all necessary applications, is very significant.
Today, India has growing and multifaceted socio-economic ties with both Israel and the Persian Gulf countries, especially the UAE. The diaspora of Indian workers in the Gulf accounts for annual remittances of nearly $50 billion. Trade relations bring in more than $150 billion to India's coffers, and almost two-thirds of India's hydrocarbon needs come from the region. It is therefore evident that the new status is viewed with special interest from this part of the world, assessing opportunities and possible threats.
Clearly, any such agreement that at least a priori brings more stability and a normalisation of relations will always be beneficial, but its weaknesses and the possible evolution of status must also be taken into account.
Thus, from a geopolitical point of view, India has welcomed the re-establishment of relations between the UAE and Israel, as both are strategic partners.
The new landscape that is opening up between Israel and the GCC seems to bring a moderate and consistent solution to the Palestinian problem closer, making it much easier for Indian diplomacy to work .
But one must be cautious, and especially in this part of the world nothing is of one colour. This hopeful agreement could have a perverse effect, further polarising the jihadist sectors of the Arab world and pitting them even more against each other.
The possibility of the Persian Gulf region becoming the new battleground where Iranian and Israeli proxies clash cannot be completely ruled out, especially in Shia-controlled areas. However, this is not a likely option for the time being.
But for India it is even more important to manage the economic implications of the new treaty. With defence and security cooperation as key pillars, both sides are now beginning to contemplate the real economic potential of complementing their economies.
Reactions to the treaty: scenarios
Faced with an event as important as the one described above, it is to be expected that there will be reactions in various directions, and depending on these, the evolution of status may be different.
Actors likely to play a role in the different scenarios include the UAE and the new alliance, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Turkey, Palestine and the Muslim Brotherhood.
It should not be forgotten that the background to this treaty is economic. subject If its development is successful, it will bring stability to a region that has long been punished by all kinds of conflicts and clashes, and will lead to an exponential increase in trade operations, technology transfer and the opening of new routes and cooperation, mainly with Southeast Asia.
The role of the US will be decisive in any of the scenarios that may arise, but in any of them its position will be to minimise physical presence and support the signatories of the treaty with political, economic and defence actions through the supply of military materiel.
The treaty has a strong economic component fixed on the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. This is but one more sign of how the world's geopolitical centre of gravity is shifting to the Asia-Pacific region and this is one of the main reasons for the US's unconditional support.
Members of the UAE government have traditionally viewed more radical Islamist ideologies and policies as an existential threat to the country's core values. Both the Shiite sectarian regime in Iran and the Sunni Muslim Brotherhood, group , are seen as a constant threat to the stability of the region's powers.
For the UAE these transnational movements are a catalyst for radicalism across the region.
In view of the above, the following scenarios are plausible:
Scenario 1
For the moment, the Palestinians are the ones whose interests have been most harmed by the new status . Prominent figures in Palestinian society, as well as senior officials of the Palestinian Authority, have considered the new treaty a betrayal. As mentioned, the Palestinian issue is taking a back seat in the Arab world.
If, as is predicted, more countries join the new treaty in the coming months, the Palestinian Authority may try by all means to bring its demands and struggle back to the forefront. To this end, it would count on the support of Iran and its proxies and Turkey. This status would begin by delegitimising the governments of the countries that have aligned themselves with the UAE and Israel through a strong information campaign at all levels, with massive use of social networks in order to mobilise the most sensitive and pro-Palestinian population. The goal would be promote demonstrations and/or revolts that would create doubts among those who have not yet joined the pact. These doubts could lead to a change of decision or delay in new accessions, or these new treaty candidates could increase the Palestinian-related conditions for joining the treaty. This option is likely to be the most dangerous because of the possibility of internal dissension or disputes that could lead to an implosion of the pact.
It can be considered a likely scenario of intensity average/leave.
Scenario 2
The position that Saudi Arabia takes is core topic. And it will be decisive in gauging Iran's reaction. In the Middle East ecosystem, Iran is the power that has the most to lose from this new alliance. The struggle for hegemony within the Muslim world cannot be forgotten. And this struggle, which is also a religious one, pitting Shiites against Sunnis, has Iran and Saudi Arabia as its main protagonists.
Saudi Arabia is likely to join the treaty, but given the status, and in an attempt not to further strain relations with its main enemy, it may decide not to join the treaty, but to support it from the outside with specific or bilateral agreements. This would always be done with the rest of the Arab member countries, which would act as a bridge for its relations with Israel. It would be a way to wash its face and avoid express recognition of the state of Israel or direct relations with it. It should be borne in mind that there are pockets of Shiite majority in the country that could be spurred on by Iran.
However, in a worst-case scenario, Iran will react through its proxies, stepping up its activity in Yemen, trying to promote protests and revolts inside Saudi Arabia, reinforcing its support for Hamas in Palestine and Hezbollah in Lebanon and even its militias in Iraq.
Support for the protests that have already taken place in Sudan will also be part of this campaign. Sudan is a very unstable country, with a very weak Structures of power that is unlikely to be able to quell high-intensity revolts.
The goal would be to inflame the region under the cover of support for the Palestinian people in order to dissuade further accessions to the treaty, as well as undermine the treaty's effectiveness, giving the image of instability and insecurity in the region. This will discourage potential investors from approaching the UAE, attracted by the enormous economic possibilities it offers, while keeping Saudi Arabia occupied with its southern flank and its internal problems. Some action without a clear or acknowledged perpetrator against vessels transiting the Gulf, as has already happened, or the boarding of one by Iranian forces under any subject accusation or legal ruse, cannot be ruled out. Direct actions involving Iranian forces are unlikely.
Turkey may become involved by providing weapons, technology and even mercenary fighters to any of the factions acting as Iran's proxy.
This scenario can be considered as possible and of intensity average
Scenario 3
Iran needs either the governments or the populations of the various Middle Eastern countries to continue to see Israel as its main enemy and threat. Among other reasons because it is a narrative for domestic consumption that it uses recurrently to divert the attention of its own population from other subject problems. So far, the unifying element of this view of Israel has been the Palestinian conflict. It is therefore likely that actions will be taken that provoke a reaction from Israel. These actions may come from within the state of Israel itself, from Palestinian or Lebanese territory, always at position from Iran's proxies. A provocation that would result in an Israeli attack on Arab territory, most likely against Iran or Syria, cannot be ruled out: result . The final goal would not be the Hebrew state but undermining the instructions of the treaty, creating social unrest among the signatories, preventing Saudi Arabia's accession and being able to use the Palestinian conflict in its own interests.
This is a possible, high-intensity scenario.
Conclusions
The UAE's emergence as an emerging geopolitical power in the Middle East has been as surprising as it has been precipitous, as not so long ago international observers did not give much hope for the life of the new federation of small states that had just come into being.
By contrast, the UAE and Abu Dhabi, its largest and most prosperous emirate, in particular, has been increasing its position over the last decade, playing a decisive role in the region. To such an extent that, to this day, the UAE's actions are seen as having facilitated to some extent the changes we are witnessing.
Western policymakers are generally dazzled by the UAE's perceived liberalism and the ability of its elites to speak both literally and figuratively their own language. It is important that they familiarise themselves with the UAE's model in all its aspects and, importantly core topic, that they understand that Abu Dhabi expects to be treated by all as an equal. Dealing with the UAE in this way and considering it a robust and reliable partner also means sending them the message of a clear intention to support them.
One of the major consequences of this agreement may be to de-escalate the Palestinian conflict, if not end it, then permanently limit it. For generations, this conflict has been used by political and religious leaders across the Arab and Muslim world to distract their attention from other issues. It was an easy and readily available resource . But it is now recognised that it is a territorial dispute between two peoples, and future negotiations have no choice but to go down that road, with the focus on the outdated Palestinian leadership.
There is the not inconsiderable possibility that the agreement agreement could have a domino effect, leading other states in the region to follow in the UAE's footsteps, which in some cases would only mean publicising the de facto relations they already have with the state of Israel. In this sense, talks between Oman's foreign minister and his Israeli counterpart are known to have taken place just after the signature treaty with the UAE was signed.
The Israeli prime minister also held a meeting meeting with Sudanese leader Abdel Fattah Burhan, which could be a sign of upcoming moves on that flank as well.
Although the leak had consequences for a senior Sudanese official, the government did not deny the contacts. And it has all been confirmed when the US, advertisement of Sudan's forthcoming removal from the list of countries sponsoring terrorism, has followed the agreement between Israel and Sudan to normalise diplomatic relations.
For years, US policy has been to demilitarise its position in the Middle East; the cost of its presence has been very high compared to the benefits it brings, as well as generating some animosity. Both the US and other G8 members support the UAE as the region's economic leader. This support provides them with the ideal position to deploy their economic interests in the region(commodities, research and development & investment).
This position of US/UAE support (plus some G8 countries), strengthens the Arab country's role in the region at subject political and by default military, and in a way allows its new allies and supporters to have some influence in organisations such as OPEC, GCC, Arab League) and in neighbouring countries, but from a more Arab and less Western position.
On the issue of the UAE's purchase of the F-35, it is undeniable that this issue makes Israel uncomfortable despite the change in relations. The main reason for this is the fear of an equalisation in military capabilities that could be dangerous. However, this will not be an obstacle to progress on future peace agreements and on development of this one. Such a major operation would take years to materialise and by then, relations between Jerusalem and Abu Dhabi will have been consolidated. Indeed, it might even be welcomed by Israel, as it would strengthen its military capabilities vis-à-vis its main opponents in the region.
It is increasingly apparent in the Arab world that Israel is too small to harbour imperialist aspirations, in contrast to countries such as Turkey and Iran, both of which formed former empires, and which seem intent on trying to restore what they once achieved or were.
Instead, Israel is increasingly seen as a strong, prosperous and dynamic enough country that cooperation with Jerusalem is a smart move that can provide benefits to both sides.
The agreement between Israel and the UAE may have been driven in part by their fear of Iran's advances and the danger it poses. But the benefits to them go far beyond that issue.
These extend to economic investment possibilities, finance, tourism and especially the sharing of know-how. The UAE can benefit from Israel's technological and scientific edge just as Israel can profit from the UAE's position as an international service centre and a key gateway to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. entrance .
In relation to the entrance gateway to the Indian subcontinent, it should be noted that for India the most important part of agreement is to manage the economic side of the synergies caused by it.
The UAE and Bahrain can become intermediaries for Israeli exports of both commodities and services to various parts of the world.
Israel has a strong defence, security and surveillance equipment industry. It is a leader in dryland farming, solar energy, horticulture, high-tech jewellery and pharmaceuticals.
Moreover, Israel has the capacity to provide highly skilled and semi-skilled labour to GCC countries, especially if they come from Sephardic and Mizrahi ethnic groups, many of whom speak Arabic. Even Israeli Arabs can find opportunities to help further build ties and bridges across the cultural divide.
Israel's incursion into the Gulf has the potential to influence the political-economic architecture that India has been building for years, being, for example, one of the largest suppliers of labour, foodstuffs, pharmaceuticals etc.
The largest customers in Dubai's real estate market, as well as the largest issue of tourists visiting the country, come from India. But in this changing scenario there is scope for three-way synergies, making India a major player in this.
The final conclusion that can be drawn by way of evaluation for the future is that this new relationship will undoubtedly be a model for other Sunni states to follow, transforming a region mired in 19th century conflicts into one of the power centres of the 21st century.
* Lieutenant Colonel of Infantry. Geopolitical Analyst
REFERENCES
Acharya, Arabinda, 'COVID-19: A Testing Time for UAE-India Relations? A Perspective from Abu Dhabi", Strategic Analysis, September 2020.
Arab Center for Research and Policy studies, 'The Abraham Agreement: normalization of relations or announcement of an existing Emirati - Israeli alliance? Qatar, August 2020.
Karsh, Ephraim, ed., "The Israel-UAE Peace: A Preliminary Assessment", Ramat Gan: The Begin-Sadat Center for Strategic Studies, cafeteria-Ilan University, September 2020.
Salisbury, Peter, "Risk Perception and Appetite in UAE Foreign and National Security Policy", The Royal Institute of International Affairs, Chatham House Middle East and North Africa Programme, London: July 2020.
Steinber, Guido, "Regional Powers, United Arab Emirates", German Institute for International and Security Affairs, Berlin, July 2020.
The deterioration of the small Mediterranean country's status benefits Hezbollah and its patron saint, Iran.
With four different prime ministers so far this year, it is difficult to escape the vicious circle in which Lebanon finds itself, so that the continuity of the current political system and the severe financial crisis seem inevitable. From this perpetuation emerge some possibilities, almost all of them bleak, for Lebanon's future. Here are some of these scenarios.
![State of the port of Beirut after the explosion of 4 August 2020 [Mehr News Agency/Wikipedia]. State of the port of Beirut after the explosion of 4 August 2020 [Mehr News Agency/Wikipedia].](/documents/16800098/0/libano-futuro-blog.jpg/ed561a7d-5d73-93fa-3cbe-2afacd099fac?t=1621884521341&imagePreview=1)
State of the port of Beirut after the explosion on 4 August 2020 [Mehr News Agency/Wikipedia].
article / Salvador Sánchez Tapia
To say that the Lebanese political system is dysfunctional is nothing new. development Based on a sectarian balance of power established in 1989 after a long civil war, it perpetuates the existence of clientelistic networks, encourages corruption, hampers the country's economic development and hinders the creation of a transversal Lebanese national identity that transcends religious confessions.
For some time now, Lebanon has been immersed in an economic and social crisis of such magnitude that many analysts are wondering whether we are facing a new case of state failure. In October 2019, the country was rocked by a wave of demonstrations that the government itself considered unprecedented, triggered by the executive's advertisement attempt to tackle the serious economic crisis with several unpopular measures, including a tax on the use of the popular Whatsapp application. The protests, initially focused on this issue, soon incorporated complaints against rampant corruption, the uncontrolled increase in the cost of living, and the lack of employment and opportunities in the country.
Popular pressure forced the resignation of the unity government led by Saad Hariri later that month. The government was replaced in January 2020 by a more technical profile government led by former Education minister Hassan Diab. The new government had little room for reform before the coronavirus pandemic was declared, and soon found itself beset by the same street pressure that had toppled the previous government, with demonstrations continuing despite the restrictions imposed by the pandemic.
The devastating explosion in early August 2020 in the port of Beirut only further plunged the country into the downward spiral in which it was already mired. Despite voices that tried to see the hand of Israel or Hezbollah behind the catastrophe that took the lives of 163 people, the Lebanese population soon realised that this was merely the logical consequence of years of corruption, bureaucratic sloppiness and withdrawal of the national infrastructure. Again there was a crescendo of popular outrage; again the government was forced to resign at plenary session of the Executive Council.
With echoes of the explosion still lingering, at the end of August Mustafa Adib, Lebanon's former ambassador to Germany, was tasked by President Aoun to form a government. Unable to complete the arduous task, not least because of Hezbollah's insistence on controlling the Finance Ministry, Adib resigned on 26 September, leaving the country on the brink of the precipice it still finds itself on.
It is difficult to predict Lebanon's future, beyond predicting that it looks bleak, as a complex dynamic of internal and external forces grips the country. Despite the pressure, at least from urbanised and cosmopolitan Beirut, to end it, it is enormously complex to untangle the tangled web of clientelistic networks that have controlled the country since independence, not only because of the benefits it has generated for a small privileged group , but also because many fear the alternatives to a model that, for all its faults, has avoided a repeat of the savage civil war that took place between 1975 and 1990.
Its geographic status makes it difficult for Lebanon to escape the general climate of instability in the Middle East and the influence exerted on the country by regional and international actors such as Israel, Iran, Syria and France, especially considering that the problems of the Levant are so deep and its national leadership so weak that it does not seem to be able to overcome them on its own.
Lebanon's plight is that its own sectarian division makes it difficult for nations to emerge that are willing to donate on a cross-cutting basis to help bridge the divide that divides the country internally, and that the financial aid it may receive from actors such as Iran or Saudi Arabia only reinforces it. The efforts of French President Emmanuel Macron, self-appointed as the driving force behind Lebanese reconstruction, do not seem, for the moment, to be gaining momentum. At the donors' lecture he convened on 9 July with fifteen heads of state, he secured contributions worth $250 million to revitalise Lebanon's moribund Economics . Meanwhile, Beirut's mayor estimates the reconstruction costs of the August explosion in the capital's port at between $3 billion and $5 billion.
As a mirror image of this difficulty, Lebanese communities, comfortably ensconced in the status quo, reject an undoubtedly necessary financial aid if they feel it might be detrimental to their respective power instructions . Hezbollah, for example, does not accept IMF programmes, complicating the achievement of the necessary national consensus that would facilitate IMF support. It is difficult to escape this vicious circle, so that the continuation of the current political system, and with it the continuation of Lebanon's severe financial crisis, seems inevitable. From this perpetuation come some possibilities, almost all of them bleak, for the Lebanese future. The first is that Lebanon will continue to slide down the inclined plane that is turning it into a failed state, and that this condition will eventually lead to a civil war precipitated by events similar to those that occurred during the Arab Spring in other states in the region. Such an eventuality would resurrect the ghosts of the past, produce regional instability that is difficult to measure but which would undoubtedly provoke intervention by regional and international actors, and could ultimately dismember the country, result which would only sow the seeds of further instability throughout the region.
Without going to that extreme, the internal turmoil could break the precarious balance of power on which Lebanese political life is based, to the benefit of one of its sectarian groups. Hezbollah, the undisputed leader of the country's Shia faction, appears here as the most organised and strongest group within the country and, therefore, as the one that stands to gain the most from this breakdown. It should be borne in mind that, in addition to the support of internship all 27 percent of Lebanese Shiites, the militia organisation is viewed favourably by many members of the divided Christian community - some 45 percent of the country's population - who put their desire for an internal Security Service in the country before other considerations. Aware of this, Hezbollah's leader Hasan Nasrallah is sample moderate in his proposals, seeing the Sunni community, supported by Saudi Arabia, as his real rival, and seeking to broaden his power base.
Iran would undoubtedly be the real winner in this scenario, as it seems unrealistic to think of a Hezbollah that, once it has come of age, would have a life of its own outside the ayatollahs' regime. With this new piece, Tehran would complete the Shia arc that connects Iran with Iraq and, through Syria, with the Eastern Mediterranean. The destabilising effects of such a move status, however, cannot be underestimated if one considers that the mere possibility of the Islamic Republic of Iran taking full control of Lebanon constitutes a casus belli for Israel.
In a positive grade , the serious crisis the country is going through and the strong popular pressure, at least in urban areas, may, paradoxically, be a spur to overcome the sectarian system that has contributed so much to generate this status. However, such a transition only stands a chance of progress - however tenuous - with strong external wholesale support.
In this scenario, the role of the international community should not be limited to providing economic resources to prevent the country's collapse. Its involvement must favour the development and sustain civic-political movements with an intersecting base that are capable of replacing those who perpetuate the current system. To this end, in turn, it is imperative that contributing nations lend their financial aid vision, renouncing any attempt to shape a Lebanon to suit their respective national interests, and forcing the elites who control the factions to abdicate the status quo in favour of a true Lebanese identity. The obvious question is: is there any real chance of this happening? The reality, unfortunately, does not allow for much hope.
