Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs World order, diplomacy and governance .
[Peter Zeihan, Desunited Nations. The Scramble for Power in an Ungoverned World (New York: Harper Collins, 2020) 453 pgs]
review / Emili J. Blasco
 The world seems to be heading towards what Peter Zeihan calls "the great disorder". His is not a doomsday vision of the international order for the mere pleasure of wallowing in pessimism, but a fully reasoned one. The retreat of the United States is leaving the world without the ubiquitous presence that secured the global structure we have known since the Second World War, forcing other countries into more insecure intercontinental trade and to seek their livelihoods in an environment of "disunited nations".
The world seems to be heading towards what Peter Zeihan calls "the great disorder". His is not a doomsday vision of the international order for the mere pleasure of wallowing in pessimism, but a fully reasoned one. The retreat of the United States is leaving the world without the ubiquitous presence that secured the global structure we have known since the Second World War, forcing other countries into more insecure intercontinental trade and to seek their livelihoods in an environment of "disunited nations".
Zeihan has long been drawing consequences from his seminal idea, set out in his first book, The Accidental Superpower (2014): the success of fracking has given the US energy independence, so it no longer needs Middle Eastern oil and will progressively withdraw from much of the world. In his next book, The Absent Superpower (2016), he detailed how US withdrawal will leave other countries unable to secure important maritime trade routes and reduce the proliferation of developed contacts in this era of globalisation. The latter has now been accelerated by the Covid pandemic, which came as a third volume, Desunited Nations (2020), was about to be published. Zeihan did not have time to include a reference letter to the ravages of the virus, but there was no need because his text went in the same direction in any case.
Zeihan, a geopolitical analyst who worked with George Friedman at Stratfor and now has his own signature, looks this time at how the different powers will adapt to the 'great disorder' and which of them have the best prospects. The book is "about what happens when the global order is not only crumbling, but when many leaders feel that their countries will be better off tearing it down". And it's not just about the Trump administration: "the push for American retreat did not start with Trump, nor will it end with him," says Zeihan.
The author believes that, in the new outline, the United States will remain a superpower, China will not achieve a hegemonic position and Russia will continue its decline. Among other minor powers, France will lead the new Europe (not Germany; while the British are "doomed to a multi-year depression"), Saudi Arabia will give more concern to the world than Iran and Argentina will have a better future than Brazil.
To focus on the US-China rivalry, it would be good to pick up on some of Zeihan's arguments for his scepticism about the consolidation of China's rise.
To be an effective superpower, China needs greater control of the seas. The problem is not to build a large, outward-facing navy, but, since it is already difficult to sustain such a huge effort over time, it must also simultaneously have "a huge defensive navy and a huge air force and a huge internal security force and a huge army and a huge intelligence system and a huge special forces system and a global deployment capability".
For Zeihan, the question is not whether China will be the next hegemon, which "it cannot be", but "whether China can even hold together as a country". The impossibility of feeding its entire population on its own, the lack of sufficient energy sources of its own, strong territorial imbalances and demographic constraints, such as the fact that there are 41 million Chinese men under the age of 40 who will never be able to marry, are all factors that work against China's ability to remain united.
It is not uncommon for American authors to predict a future collapse of China. However, episodes such as the coronavirus, initially seen as a serious stumbling block for Beijing, have never really cut short the forward march of the Asian colossus, even though China's economic growth figures have naturally been moderating over the years. This is why many people's bad omens can sometimes be interpreted more as wishful thinking than realistic analysis. Zeihan certainly writes in a somewhat "loose" manner, with blunt assertions that seek to shake the reader, but his geopolitical axioms seem to be generally endorsed: if you boil down what he says in his three books, you have a clear notice of where the world is supposed to be going; and that is where it is indeed going.

COMMENTARY / Juan Luis López Aranguren
If traditional diplomacy is understood as relations exercised between official representatives of states, in recent years a new concept of diplomacy has gained popularity and has become increasingly important in relations between nations: cultural diplomacy. Assuming that culture is the vehicle through which nations communicate with each other, cultural diplomacy is the exchange of culture, ideas and information that nations around the world engage in to achieve mutual understanding in order to advance the building of a more just and stable world. In this context, the celebration of the Olympic Games is one of the most important cultural diplomacy events that a nation can achieve to project and share its culture and identity with the rest of the world. In this sense, Japan reaffirmed its position as a global benchmark in this diplomacy with its public appearance at the closing ceremony of the Rio 2016 Olympic Games. Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe appeared in the guise of the world-famous character Mario to pick up the baton for the Tokyo 2020 Olympics. In this way, Japan used an icon of Japanese pop culture to project its cultural identity to the entire world.
In this dimension of soft power or cultural diplomacy, the Olympic Games are the greatest exponent of it. Already at their origin, in 776 BC, the Olympic Games proved to be a diplomatic tool of extraordinary strength by forcing a sacred truce between the different city-states participating in them. Therefore, from the very beginning, it was possible to achieve international political objectives by using this cultural tool . This measure was observed to the extent that if any city-state violated this truce, its athletes were expelled from the competition.
This same demonstration has been repeated in more recent times, demonstrating that the Olympics have been a diplomatic battleground throughout history. In 1980 the US and 65 other countries boycotted the Moscow Olympics in protest at the USSR's invasion of Afghanistan. In retaliation, the USSR and 13 other states boycotted the next Olympics in 1984 in Los Angeles.
The upcoming Tokyo 2021 Olympic Games (delayed by one year due to the pandemic) do not carry any controversy from this subject. Instead they have been conceived as a historic opportunity for the country to reinvent itself internally and globally after the Fukushima (or Great East Japan Earthquake) catastrophe. C To this end, an official project graduate Tokyo 2020 Action & Legacy Plan 2016 has been launched, which aims to achieve three objectives: firstly, to maximise the connection of Japanese citizens and communities with the Tokyo Olympics. Secondly, to maximise cultural projection both nationally and globally. Thirdly and lastly, to ensure a valuable bequest for future generations, as was the case with the Tokyo 1964 Olympic Games.
These three objectives set out by the Japanese government will be manifested in five dimensional pillars on which action will be taken. These five pillars are articulated in the manner of Olympic rings, intertwining with each other and strengthening the domestic and international impact of these Olympic Games. These dimensions are, starting with the most immediate to the purely sporting aspect itself, the promotion of sport and health. The second, connecting with culture and Education. The third, also of great importance for its potential to reform Tokyo in particular and Japan in general, is urban planning and sustainability. Not surprisingly, the Japanese government and the Tokyo Metropolitan Government have made great efforts to build ambitious infrastructure to accommodate the Olympics, even to the extent of relocating the famous and iconic Tsukiji fish market that has been a symbol of the city since 1935. Fourthly, the Olympics will be used to revive Economics and technological innovation, in the same way as the 1964 Tokyo Olympics did when it showcased the first Shinkansen or bullet trains that have become one of Japan's technological icons. Finally, fifthly, Japan saw the Olympics as an opportunity to overcome the crisis and trauma caused by the Fukushima disaster (a catastrophe that is referred to in Japan as the Great East Japan Earthquake).
In addition to these five objectives, which range from the more specific to the more general, a sixth goal or unofficial dimension will be added in 2020: to project Japan's recovery from the COVID pandemic both domestically and internationally. In this sense, the Olympic Games will not only be a symbol of overcoming a particular Japanese disaster, but may also enable Japan to position itself as a model in the management against the pandemic and in promoting economic recovery.
![Nicolás Maduro during a broadcasted speech [Gov. of Venezuela]. Nicolás Maduro during a broadcasted speech [Gov. of Venezuela].](/documents/16800098/0/nicolas-maduro.jpg/61303fce-8b6f-0835-73c1-7dc5fe8e6e8f?t=1621887713513&imagePreview=1)
Nicolás Maduro during a broadcasted speech [Gov. of Venezuela] ▲ Nicolás Maduro during a broadcasted speech [Gov. of Venezuela].
ESSAY / Isabelle León Graticola
It is no secret to anyone that Venezuela is going through the most convoluted economic and social crisis in its history, a crisis in which the creators have manipulated the existence of the people, degrading its integrity, and extinguishing everything that once characterized Venezuela.
The country holds a key geopolitical location that serves as a route for North America and the Caribbean to the rest of South America. Likewise, the country is endowed with abundant natural resources like natural gas, iron ore, diamonds, gold, and oil.1 Venezuela has the largest proven oil reserves in the world, with 302 billion barrels in January 2018, emanating an extremely rich country with astonishing potential.2 However, this crisis has not only hindered people's lives but has ironically dissipated the country's resources to consolidate the pillars of the regime to such an extent that today the government of Nicolás Maduro is importing oil from Iran. Inadequate policies that have weakened the society's sense of responsibility and nationalism, decreased foreign investment out of lack of trust, and annihilated the state-led oil production, therefore reinforcing the country's economic downfall and hyperinflation.
The Venezuelan government, headed by Nicolás Maduro, has managed its way to continue holding power despite accusations of corruption, crimes against humanity, and even drugs trafficking involvement. The perplexing partner-economic and political crisis has created an unsustainable and violent context in which poorly informed people are manipulated by the government through speeches that take big significance on how society perceives the actual situation, as well as other countries' statements on the crisis. Up to this point, it has become difficult to understand what keeps bolstering this regime, but if the situation is analysed from the nucleus, the well-orchestrated rhetoric of Chávez and his successor, Maduro, has contributed to support the ends and sustainment of the regime.
Since Maduro reached power, poverty motivated violence has been rampant in Venezuela and insecurity has become a significant part of society's dynamics. Consequently, many protests against the government demanding for freedom and better living standards have taken place. Maduro's regime has been forced to employ tools such as fake news and hateful rhetoric to soften the anger of the people by manipulating them and brainwashing the armed forces to avoid uprisings.
This article aims to analyse how Maduro's rhetoric has maintained a minority in the wrong side of history and a majority in constant battle by making erroneous accusations to third parties to justify the perturbed situation, while the government keeps enriching its wallet at the cost of the people and its smudged operations. Such feverish society gave rise to pure uncertainty, to a place where disinformation takes the form of a lethal weapon for the dangerous context in which it exists.
The background: Chávez's indoctrinated society
First, it is necessary to clarify that the focus of this article is merely on the rhetorical aspect as a pillar of the regime. However, when it comes to the background that has sustained Maduro's administration up to this day, there is a more complex reality, full of crime, death, manipulation, and corruption. Venezuela is an almost abnormal reality because, after more than twenty years, it is still tied to a group of people who have taken absolutely everything from it. From a man that portrayed nothing but hope for the poor, to one who has managed his way sticking to policies damaging to the very people they mean to help, and which, sooner or later, will make the regime collapse.
Hugo Chávez's presidency was characterized by a tremendous and persuasive oratory; he knew how to get to the people. Chávez's measures and campaigns were based on a psychological strategy that won him the admiration of the most impoverished classes of the country. Chávez arrived and gave importance and attention to the big mass of the population that previous governments had systematically neglected. People felt the time had come for them to have what they never had before. Filled with charisma and political mastery, his speeches always contained jokes, dances, and colloquial phrases that were considered indecent by the country's highest class and often misunderstood abroad.
Chávez always built a drastic separation between the ideals of the United States and Venezuela and looked for ways to antagonize the former with his rhetoric. He began to refer to George W. Bush as "Mr. Danger", an imperial literary character of one of the most famous Venezuelan novels, Doña Bárbara.3
Hugo Chávez is one of the most revolutionary characters in Venezuelan history, one who brought the convoluted situation that today perpetuates in the country. Chávez persecuted journalists and political opponents, expropriated lands, nationalized Venezuela's key industries such as telecommunications, electricity, and the refining processes of heavy crudes, and slowly degraded the society as the exercise of power was directed to hold complete control of Venezuela's internal dynamics.4
Chávez extended education and medical assistance to the least favoured classes and improved the living conditions of the needy. This policy did nothing but create among these classes a culture of dependence on the government. Chávez's supporters or Chavistas were the pillars that buttressed the government, while the wealthy were catalogued as "squealing pigs" and "vampires. "5 The Chavistas admired Chavez's charismatic character and his constant gifts; he gave them fridges and TVs, gadgets that they could never afford on their own. He also constructed buildings, under the "mission statement Vivienda" initiative, to give people living in slums a 'proper' home. All of this was possible because the oil prices at the time were skyrocketing; he used the oil income to buy his support. The general standard of life, however, continued to be poor. The government knew what to give and how to manipulate to stay in power, and that is precisely what made Hugo Chávez so powerful and almost impossible to defeat despite strong opposition.
Historically, the United States has opposed left-wing governments in Latin America, so Chávez condemned the US, by referring to them as an imperialist power, or the "Empire". He disgraced US leaders and actions and transferred that anti-imperialistic and anti-capitalist approach to the population, part of which supported him and was blindly loyal to the cause. Chávez's alliance with Cuba under Fidel Castro led to the supply of oil at cut-rate prices, all related to the desire of reducing US economic influence in South America. Chávez's populist initiatives were the tenets of his administration and controversial foreign policy. These, along with his rhetoric and opposition from the Venezuelan wealthy class, deeply polarized the society and gave rise to what Venezuela has today: a divided society that has suffered from the lack of basic necessities, disinformation, and integrity.
Currently, the spokesmen of the Government of Nicolás Maduro address citizens at all hours from public channels and social networks to stir up the disgruntlement of the population toward the external enemy.6 Despite the poorly prepared speeches, the lack of vocabulary, and the improper formulation of sentences, Maduro has kept the colloquial and unformal rhetoric that characterised Chávez, but has failed to draw the connection that the late president enjoyed. The anti-imperialist strategy has been maintained, and, as the justification of the crisis, it has become the epicenter of the regime's speech. Nicolás Maduro's rhetoric revolves around two words: the US and the "Patria", a word frequently used by Chávez.
The base of Maduro's rhetoric: the love for Chávez
Shortly before dying in March 2013, Hugo Chávez appointed Vice President Nicolás Maduro as his successor. Chávez's charisma and legacy are what somehow ensured him that Maduro would provide a smooth transition. After Chávez's passing, Maduro took advantage of the momentum and sentiment that the Chavistas revealed and ensured that if picked, he would follow the steps of his predecessor and would continue to strengthen the 'Bolivarian Revolution'. Along with the continuity with Chávez's legacy, the defence of Venezuelan sovereignty in front of the US, and the social equality became the key messages of his administration.7 Nevertheless, Maduro had little support from the elites and inherited a country that was already economically weak due to the downfall of the oil prices and corruption.
In Chávez's wake, Maduro appealed to the emotion of the audience. He strongly claimed that the people were there for the 'Comandante' and said that "his soul and his spirit was so strong that his body could not stand it anymore, and he was released and now through this universe expanding filling us with blessings and love". He knew what this meant for the people and a crying audience exclaimed "Chávez lives, the fight goes on".
Maduro filled his rhetoric with the love for Chávez. He acknowledged that the Chavistas worshipped him as if he was God and that for ideological reasons, support for Maduro was guaranteed. Nevertheless, others recognised that the situation in the country was not favourable and questioned Maduro's ability to fill the void left by Chávez. When Maduro took power, the country entered a period of reinforced economic decline accompanied by hyperinflation that nowadays exceeds 10 million percent.8 As it was previously stated, the conditions of poverty surpass anything seen before in the country, which is now on the brink of collapse.
Furthermore, Venezuela went through two rounds of mass protests, in 2014 and 2018, that demanded freedom and change. Unfortunately, and as was expected from the government, thousands of violations of human rights were part of the demonstration's dynamics as brutal repression and the unjust imprisonment of demonstrators took place all along. Simultaneously, Maduro managed to call for rallies on the days of the major opposition's marches and retained the populist speech based on ideological arguments and emotional appeals among the minority of supporters to consolidate his power in Venezuela. Last year, in a regime rally on February 23rd, he condemned the elites as he explained that he was certain that from the bottom of his Chavista sentiment of loyalty to this battle, he was never going to be part of one. He stated that Venezuela will continue to be Patria for more many years to come.
The ongoing crisis has forced many to survive rather than to live, but despite all, Maduro remains in control. Maduro has kept Chávez's anti-imperialist policy and has rejected any minimum support from the United States. The government takes advantage of the hunger and the vulnerable situation of its people and makes sure that it remains as the only source of food. It does not take responsibility and instead, blames the crisis on the 'economic war' that the US has imposed on Venezuela.9 When Juan Guaidó sworn himself the legitimate president, Maduro's supporters started raising firms in a campaign called "Hands off Venezuela", while the US was trying to get humanitarian assistance into Venezuela through the Colombian border in the name of Guaidó.
In this sense, he explained in the same concentration speech that they were defending the national territory and the right to live freely and independently. Although it may seem ironic, because the government has killed hundreds of people with its police brutality and torture, this rhetoric is what has kept him the support of the hardcore revolutionary followers. The "Hands off Venezuela", was shouted and accompanied by the worst English pronunciation -that characterizes Maduro-, and followed with insults to Guaidó.
As Maduro yelled "puppet, clown, and beggar of imperialism and Donald Trump. If he is the President, where are the economic and social measures that he has applied for the people? It is a game to deceive and manipulate, it is a game that has failed, the coup d'état has failed" as the network audience shouted, "jail him, jail him!". He drew his speech to a hardcore anti-imperialist audience and firmly stated that the US intended to invade Venezuela and enslave it. Maduro finalized his speech by shouting "wave up the flag, up the Patria, for the people in defense of the Revolution".
Recently, the US State Department released a price for the capture of Maduro and his cabinet, not only for the crimes committed against the Venezuelan population, but also because of their involvement in a huge drug-trafficking network. With this, the regime's position has become more vulnerable and simultaneously pragmatic, but as tough actions were taken against possible threats and opposing figures, Maduro's rhetoric remains to deny its status and manipulating those that still support him. In another public speech, he stated that "Donald Trump's government, in an extravagant and extreme, vulgar, miserable action, launched a set of false accusations and like a racist cowboy of the 21st century, put a price on the heads of revolutionaries that are still willing to fight them". He one more time accused the US of being the main cause of the economic crisis of Venezuela.
Nicolás Maduro's speech has always been directed to the hardcore revolutionaries, those that worship Chávez since the beginning and who firmly believe in the socialist cause. Maduro has maintained his rhetoric despite the changes in the internal situation of the country; he has held an enduring method for antagonizing the opposition, the Venezuelan upper class, and the United States. On the other hand, regarding the strategic foreign allies, the regime openly gives declarations to support them, but again to somehow antagonize the United States. Indeed, this was the case of the US assassination of Qasem Soleimani, the Iranian top commander, in which government representatives attended the Iranian embassy to give the condolences in the name of the regime and swore to avenge Soleimani's death. The administration of Nicolás Maduro has no gray areas, everything is either black or white; the opposition, the upper class, the US, and the US-influenced countries are the enemies, and the rhetoric rarely leans toward a conciliatory message, rather has always revolved around these conflicting parties.
What is left
Twenty years have passed since the Chavismo arrived in the country. Nowadays, a passionate minority of the population keeps supporting Maduro. His regime continues to train armed groups to combat discontent headed by opposition leader Juan Guaidó. The Chavismo keeps being strong, but it has been fragmented by those who believe that the revolution ended at the moment Chávez died, and the ones that are convinced that supporting Maduro means being loyal to Chávez. In the case of Juan Guaidó, he keeps doing his efforts. He still has relative support and keeps being a source of hope. Nevertheless, many criticize the fact that he let again the people cool down. A close change is expected, but no one knows what the movements behind are. Meanwhile, the people will continue suffering and trying to survive.
Upon reflection, it can be noticed that Maduro's entire argumentation revolves around a confrontational rhetoric: the US and capitalism against Venezuela; Guaidó against the Patria; the elites against the Revolution.10 Far from recognising the reality that the country faces and taking actions to improve it, this confrontational approach simply places the blame on those who have tried to bring a change in the internal dynamics of Venezuela. The regime has managed to construct a national united front against a common foreign enemy and to demonize the opposition.
Chávez and Maduro's rhetoric has followed a tangible objective: the Revolution. Maduro's regime up to this point is searching for a way to consolidate its power and sustain itself as the best way to elude a rather somber future in jail. This never-ending nightmare should have long ago collapsed due to the economic catastrophe, hyperinflation, political repression, human rights violations, and the lack of direction for Venezuela. Behind what maintains this structure there is nothing but the exercise of power and the almost absolute control of society. The Patria that they constantly speak of is running out of fuel to keep going. Nonetheless, the rhetorical deceptions of the Bolivarian revolution, which for two decades have appealed to the popular classes, settled in the collective mindset of the Chavismo and brought space for support in the Venezuelan society.
Chávez and Maduro's presidencies have been based on educating and changing the mindset of the population as they wanted; a population that is content with one box of food a month and which, unfortunately, hunts for the easy means to achieve its goals instead of fighting to improve its lot.
Today, the regime is fed on the memory of Hugo Chávez, on his promises, on his battle. As long as it keeps generating an illusion on the supporters, Maduro will appeal to it as a pillar of his administration and of the Revolution.
1. Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries. Venezuela facts and figures. 2019, https://www.opec.org/opec_web/en/about_us/171.htm. Accessed 28 Nov. 2019.
2. US Energy Information Administration - EIA - Independent Statistics and Analysis. Venezuela. Jan. 2019, https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis.php?iso=VEN. Accessed 28 Nov. 2019.
3. Livingstone, G. (2013, March 10). The secret of Hugo Chavez's hold on his people. Retrieved March 17, 2020, from https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/americas/the-secret-of-hugo-chavezs-hold-on-his-people-8527832.html
4. El País. (2007, January 08). Chávez anuncia la nacionalización del servicio eléctrico y las telecomunicaciones. Retrieved July 01, 2020, from https://elpais.com/internacional/2007/01/08/actualidad/1168210811_850215.html
5. The Guardian (2012, October 08). Hugo Chávez: A victory of enduring charisma and political mastery. Retrieved March 17, 2020, from https://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/oct/08/hugo-chavez-victory-political-venezuela
6. Twitter, F., & Miraflores, P. (2017, July 23). Maduro, his ministers and the corruption of language. Retrieved March 15, 2020, from https://elpais.com/elpais/2017/07/22/opinion/1500746848_239358.html
7. Grainger, S. Hugo Chávez and Venezuela Confront his Succession. Dec. 2012. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-20678634. Accessed 29 Nov. 2019.
8. Sánchez, V. Venezuela hyperinflation hits 10 million percent. 'Shock therapy' may be only chance to undo economic damage. Aug. 2019. https://www.cnbc.com/2019/08/02/venezuela-inflation-at-10-million-percent-its-time-for-shock-therapy.html. Accessed 29 Nov. 2019.
9. TVVenezuela. The CLAP boxes no longer have anything to feed Venezuelans. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MelhZDbiFQQ. Sept. 2019. Accessed 30 Nov. 2019.
10. Delgado, A., & Herrero, J. (2019, February 12). Venezuela rhetorics on Twitter: Guaidó vs. Maduro. Retrieved March 18, 2020, from https://beersandpolitics.com/retoricas-de-venezuela-en-twitter-guaido-vs-maduro
Faced with the biggest economic crisis since World War II, the EU itself has decided to borrow to help its member states.

▲ Commission President Von der Layen and the President of the European committee Charles Michel after announcing the agreement in July [committee European]
ANALYSIS / Pablo Gurbindo Palomo
"Deal!". With this "tweet" at 5:30 a.m. on 21 July last, the president of the European committee , Charles Michel, announced the achievement of a agreement after the longest meeting in its history (more than 90 hours of negotiations).
framework After the failed summit in February, European countries were aware of the importance of reaching an agreement on agreement, but some countries saw it as more urgent than others to conclude the Multiannual Financial Framework (MFF) for the next seven years. But as with everything else, the Covid-19 pandemic has overturned this lack of urgency, and has even forced member states to negotiate, in addition to the budget, aid to alleviate the effects of the pandemic on the 27.
The agreement consists of an MFF of 1.074 trillion euros. This is lower than the figure demanded in February by the so-called friends of cohesion (a conglomerate of southern and eastern European countries) and the Commission itself, but also higher than the figure that the frugals (the Netherlands, Austria, Denmark and Sweden) were prepared to accept. But it is not this figure that has been the focus of the discussion, but how much and how the post-pandemic recovery fund to help the countries most affected by the pandemic was to be set up. The Fund was agreed at 750 billion, divided into 390 billion to be given to member states in the form of grants, and the remaining 360 billion to be given in the form of a 70 per cent disbursable loan between 2021 and 2022.
The figures are staggering, and based on the February negotiations, where one part of the membership preferred something more austere, one might ask: How did we arrive at this agreement?
The Hamilton moment
With the arrival of Covid-19 in Europe and a considerable paralysis of all the world's economies, the European capitals quickly realised that the blow was going to be significant and that a strong response was going to be necessary to mitigate the blow. Proposals at the European level were not long in coming. For example, the European Parliament proposed a recovery package on 15 May of 2 trillion euros, and to include this in the MFF 2021-2027.
The most prominentproposal was presented on 18 May by French President Emmanuel Macron and German Chancellor Angela Merkel. And not only because it was promoted by the two main economies of the Union, but also because of its historic content.
There has been talk of Hamilton momentHamilton moment, referring to Alexander Hamilton, one of the founding fathers of the United States and the first Secretary of the Treasury of the newly founded republic. In 1790 the thirteen states that made up the young American nation were heavily indebted due to the war effort of the Revolutionary War, which had ended only seven years earlier. To solve this problem, Hamilton, Secretary of the Treasury, succeeded in convincing the federal government to assume the states' debt by "mutualising" it. This event marked the strengthening of the American federal government and served to create the instructions of the US national identity.
It seems that with the Franco-German proposal the Hamilton moment has arrived. The proposal is based on four pillars:
-
European health strategy, which could include a joint reservation of medical equipment and supplies, coordination in the purchase of vaccines and treatments. In turn, epidemic prevention plans shared among the 27 and common methods for registering the sick.
-
A boost to the modernisation of European industry, supported by an acceleration of the green and digital transition.
-
Strengthening the European industrial sector, supporting production on the Old Continent and the diversification of supply chains to reduce global dependence on the European Economics .
-
500 billion reconstruction fund for the regions most affected by the pandemic on the basis of EU budget programmes.
It is this fourth pillar that we can call "Hamiltonian" and which is historic as it would for the first time in history allow the EU itself to issue debt to finance this fund. This proposal has broken years of a German stance against any collective borrowing subject . "We are experiencing the biggest crisis in our history... Because of the unusual nature of the crisis we are choosing unusual solutions," Merkel said in the joint video conference with Macron.
According to this proposal the funds would not be reimbursed directly by the countries but through the Community funds in the long term deadline, either through its usual resources or through new sources of income. It should also be noted that the proposal spoke of the submission of this fund in the form of subsidies, i.e. without any subject interest for the recipient countries.
Among the reactions to proposal were those of the frugal, who rejected that the funds should be given in the form of grants. "We will continue to show solidarity and support for the countries most affected by the coronavirus crisis, but this must be in the form of loans and not subsidies," said Austrian Chancellor Sebastian Kurz. The frugal proposal is that the financial aid raised on the debt markets should be submit to states at low interest rates, i.e. as a loan, and conditional on a reform programme.
On 27 May the Commission announced its proposalThe EU's new, very similar to the Franco-German one, but enlarged. The proposal is composed of a 1.1 trillion euro MFF and a 750 billion euro recovery plan called Next Generation EU. This recovery plan is based on three pillars financed by new instruments but within pre-existing headings:
The first pillar covers 80% of the recovery plan. It is about supporting Member States in their investments and reforms in line with the Commission's recommendations. To this end, the pillar has these instruments:
-
Recovery and Resilience Mechanism (the most important part of proposal): financial support for investments and reforms by states, especially those related to the green and digital transition and the resilience of national economies, linking them to EU priorities. This mechanism would be made up of 310 billion in grants and 250 billion in loans.
-
React-EU Fund under cohesion policy with 55 billion.
-
Increase in the Just Transition Fund: this fund is intended to support states in undertaking the energy and ecological transition, to move towards a climate-neutral policy. It would be increased to 40 billion.
-
Increase of the European Agricultural Fund development Rural: to support rural areas to comply with the European Green agreement . It would be increased by 15 billion.
The second pillar covers 15% of the plan. It focuses on boosting private investment, and its funds would be managed by the European Investment Bank (EIB):
-
31 billion Solvency Support Instrument
-
EU-Invest programme increased to $15.3 billion
-
New Strategic Investment Fund to promote investment in European strategic sectors
The third pillar covers the remaining 5%. It includes investments in areas that have result been key to the coronavirus crisis:
-
EU4Health programme to strengthen health cooperation. With an budget of 9.4 billion.
-
Reinforcement of the EU Civil Protection Mechanism (EUCPF) by 2 billion.
-
project Horizon Europe for the promotion of research and innovation worth 94.4 billion.
-
Support to the external humanitarian financial aid worth 16.5 billion.
To raise the funding, the Commission would issue its own debt on the market and introduce new taxes of its own, such as a border carbon tax, emission allowances, a digital tax or a tax on large corporations.
It should also be noted that both access to MFF and Next Generation EU aid would be conditional on compliance with the rule of law. This was not to the liking of countries such as Hungary and Poland, which, among others, consider it to be unclear and a form of interference by the EU in their internal affairs.
Negotiation at the European Summit
With this proposal on the table, the heads of state and government of the 27 met on 17 July in Brussels amid great uncertainty. They did not know how long the summit would last and were pessimistic that it would be possible to reach an agreement agreement.
The main sticking points in the negotiations were the amount and form of the reconstruction fund. Countries such as Spain, Italy and Portugal wanted the aid to come in the form of subsidies in full and without any subject conditionality. On the other hand, the frugals, led during the summit by Mark Rutte of the Netherlands, wanted the reconstruction fund to be reduced as much as possible, and in any case to be given in the form of loans to refund and as an "absolute precondition". "Any financial aid from the North means reforms in the South. There is no other option", Rutte said at a press conference in The Hague.
As with all negotiations, the positions were gradually loosening. It was already clear that neither position was going to remain unscathed and that a mixed solution with both subsidies and loans was going to be the solution. But in what percentage? And with reform conditionality?
For Spain, Italy and Portugal the subsidies could not be less than 400 billion, which was already a concession from the initial 500 billion. For the frugal, who were joined by Finland, this figure could not exceed 350 billion, which would reduce the total Fund to 700 billion. This was a major concession by the frugals, who went from talking about zero subsidies to accepting them as 50% of the amount. Michel's final proposal was 390 billion in subsidies and 360 billion in loans to try to convince all sides.
The big stumbling block apart from the percentage was the conditionality of reforms for the submission aid that the frugal advocated. The spectre of the Troika imposed after the 2008 crisis was beginning to appear, to the disgrace of countries such as Spain and Italy. Rutte demanded that the national plans that countries had to present to the Commission in order to receive the Fund should also pass through committee of the 27 and that unanimous approval was necessary. This formula basically allowed any country to veto the national plans. Germany did not go as far as the required unanimity, but did ask for some control by the committee.
Rutte's stance angered many countries that saw proposal as a way of forcing reforms that have nothing to do with economic recovery.
The president of the committee presented a proposal to bring the parties closer together: the "emergency brake". According to Michel's proposal countries will have to send their reform plan to committee and it will have to be C by qualified majority. deadline After its approval, any country is allowed to submit its doubts about the fulfilment of the plans presented by a state to the committee ; in this case, the committee would have a maximum of three months to make a pronouncement. As long as the country does not receive a decision, it would not receive the aid.
For those who may be surprised by the large concessions made by the frugal, it is worth mentioning the figure of the "rebates" or compensatory cheques. These are rebates on a country's contribution to budget and were introduced in 1984 for the United Kingdom. The British were one of the main net contributors to the European budget , but they hardly benefited from its aid, 70% of which went to the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and the Cohesion Fund. It was therefore agreed that the British would have their contribution discounted on a permanent basis. Since then, other net contributor countries have been receiving these cheques. However, in these cases they had to be negotiated with each MFF and were partial on a specific area.
It is a very controversial figure for many countries, and an attempt was already made to remove it in 2005. But what is undeniable is that it is a great bargaining chip. From the outset, the frugal countries have wanted to keep it, and even strengthen it. And given the difficulties in negotiating, the rest of the member states have seen that it is an "affordable" and not very far-fetched way of convincing the "hawks of the north". After some initial posturing, they ended up increasing it: Denmark will receive 377 million (considerably more than the initial 222 million); Austria will double its initial amount to 565 million; Sweden will receive 1.069 billion (up from the initial 823 million); and the Netherlands will receive 1.575 billion. Notably, Germany, as the largest net contributor, will receive 3.671 billion.
The last important negotiation point to be addressed is the conditionality of compliance with the rule of law in order to receive the different funds and aid. Hungary and Poland, for example, have an open transcript for possible violation of article 7 of the Treaty on European Union (TEU), which allows a member state to be sanctioned for violating basic EU values such as respect for human rights or the rule of law. Many countries have pressed the issue, but in the face of difficult negotiations and a possible risk of a veto of agreement depending on the vocabulary used by Hungarian President Viktor Orban, this clause has come to nothing.
To recapitulate, and as stated at the beginning of article, the agreement ended up with an MFF of 1.074 trillion euros; and a post-pandemic reconstruction fund, the Next Generation EU, of 750 billion, divided into 390 billion in the form of subsidies and 360 billion in the form of loans. To this must be added Michel's "emergency brake" for the submission of aid and the significant sum of "rebates".
The cuts
Yes, there have been. Apart from the aforementioned rule of law clause, there have been several cuts in several of the items proposed by the Commission. Firstly, there has been a significant cut in the Just Transition Fund, which has been reduced from the initial 40 billion at proposal to 10 billion, to the anger of Poland in particular. Secondly, the funds for the rural development are reduced from 15 billion to 7 billion. Thirdly, both the 16.5 billion external humanitarian support fund financial aid , the 31 billion solvency support instrument (on its proposal by the Commission) and the 9.4 billion EU4Health programme have come to nothing. And finally, the project Horizon Europe would drop from the 94.4 billion proposed by the Commission to a mere 5 billion.
Winners and losers?
It is difficult to speak of winners and losers in a negotiation where all parties have given quite a lot in order to achieve agreement. Although it remains to be seen whether the countries' positions were truly immovable from the outset or whether they were simply used as an instrument of pressure in the negotiation.
The countries most affected by the pandemic, such as Italy and Spain, can be happy because they will receive a very large sum in the form of subsidies, as they wanted. But this conditionality that they were not going to accept in any way, in a way, is going to come to them softened in the form of Michel's "emergency brake". And the reforms they did not want to be forced to make, they will have to carry out from agreement with the recovery plan they send to committee, which if they are not sufficient may be rejected by the latter.
The frugal have succeeded in getting conditional aid, but more than half of it will be in the form of subsidies. And as a rule, the monetary limits they advocated have been exceeded.
Countries such as Poland or Hungary have succeeded in making the conditionality of the rule of law ineffective in the end, but on the other hand they have received considerable cuts in funds, such as the Just Transition fund, which are important especially in Central Europe for the energy transition.
But, on final, every head of state and government has returned home claiming victory and assuring that he or she has fulfilled his or her goal, which is what a politician must do (or appear to do) at the end of the day.
For both the MFF 2021-2027 and Next Generation EU to go ahead, the European Parliament still needs to ratify it. Although the Parliament has always advocated a more ambitious package than agreed, there is no fear that it will block it.
Conclusion
As I have said, this agreement can be described as historic for several reasons. Apart from the obvious extension of the European committee or the Covid-19 pandemic itself, it is historic because of the Hamilton moment that seems to be about to take place.
Member states seem to have learned that the post-crisis formula of 2008 did not work, that crises affect the whole of the Union and that no one can be left behind. Cases such as Brexit and the rise of Eurosceptic movements across the continent set a dangerous precedent and could even endanger the continuity of project.
The "mutualisation" of debt will allow states that are already heavily indebted, and which due to their high risk premium would have problems financing themselves, to get out of the crisis sooner and better. This decision will obviously cause problems that remain to be seen, but it shows that the 27 have realised that a joint financial aid was necessary and that they cannot go to war on their own. As Merkel said when presenting her post-pandemic plan together with Macron: "This is the worst crisis in European history", adding that to emerge "stronger", it is necessary to cooperate.
This move towards a certain fiscal unity can be seen as a rapprochement to a Federal Europe, at least in the Eurozone, which has been discussed for decades now. Whether this is a path with or without return remains to be seen.
[Richard Haas, The World. A Brief Introduction (New York, NY: Penguin Press, 2020), 378 p].
review / Salvador Sánchez Tapia
 During a fishing workshop on Nantucket with a friend and his son, then a computer engineering student at the prestigious Stanford University, Richard Haass, president of the Council on Foreign Relations, engaged the young man in conversation about his programs of study, and asked him what subjects he had taken, apart from the strictly technical ones. To his surprise, Haass realised how limited issue of these he had taken were. No Economics, no history, no politics.
During a fishing workshop on Nantucket with a friend and his son, then a computer engineering student at the prestigious Stanford University, Richard Haass, president of the Council on Foreign Relations, engaged the young man in conversation about his programs of study, and asked him what subjects he had taken, apart from the strictly technical ones. To his surprise, Haass realised how limited issue of these he had taken were. No Economics, no history, no politics.
Richard Haass uses this anecdote, which he refers to in the introduction to The World. Education A Brief Introduction , to illustrate the general state of higher education in the United States - which is, we might add, not very different from that of other countries - and which can be summed up in this reality: many students in the country that has the best universities in the world, and which is also the most powerful and influential on the planet, which means that its interests are global, can finish their university-level training without a minimal knowledge - let alone understanding - of the world around them, and of its dynamics and workings.
The World. A Brief Introduction is a direct consequence of the author's concern about the seriousness of this important gap for a nation like the United States, and in today's world, where what he calls the "Las Vegas rule" - what happens in the country stays in the country - does not work, given the interconnectedness that results from an omnipresent globalisation that cannot be ignored.
The book is conceived as a basic guide intended to educate readers - hopefully including at least some of the plethora of uneducated students - of different backgrounds and levels of knowledge, on the basic issues and concepts commonly used in the field of International Office.
By the very nature of the work, informed readers should not expect to find in this book any great discoveries, revolutionary theories or novel approaches to contemplate the international order from a new perspective. Instead, what it offers is a systematic presentation of the essential concepts of this field of knowledge that straddles history, political science, sociology, law and geography.
The book avoids any theoretical approach. On the contrary, its goal is eminently practical, and its aim is none other than to present in an orderly and systematic way the information that the average reader needs to know about the world in order to form a criterion of how it works and how it is articulated. It is, in final, to make him or her more "globally educated".
From his vantage point as president of one of the world's leading global think-tanks, and with the experience gained from his years of service as part of the security establishment of the two Bush presidents, Richard Haass has made numerous important contributions to the field of International Office. In the case of the present book, the author's merit lies in the effort he has made to simplify the complexity inherent in International Office. In a simple and attractive prose, accessible to readers of all subject, Richard Haass, demonstrating a great understanding of each of the subjects he deals with, has managed to distil their essence and capture it in the twenty-six chapters of this brief compendium, each of which would justify, on its own, an enormous literary production.
Although each chapter can be read independently, the book is divided into four parts in which the author approaches status the current world and relations between states from different angles. In the first part, Haass introduces the minimum historical framework necessary to understand the configuration of the current international system, focusing in particular on the milestones of the Peace of Westphalia, the two World Wars, the Cold War, and the post-Cold War world.
The second part of the book devotes chapters to different regions of the world, which are briefly analysed from a geopolitical point of view. For each region, the book describes its status, and analyses the main challenges it faces, concluding with a look at its future. The chapter is comprehensive, although the regional division it employs for the analysis is somewhat questionable, and although it inexplicably omits any reference letter to the Arctic as a region with its own geopolitical identity and set to play a growing role in the globalised world to which the book constantly alludes.
The third part of the book is devoted to globalisation as a defining and inescapable phenomenon of the current era with an enormous impact on the stability of the international order. In several chapters, it reviews the multiple manifestations of globalisation - terrorism, nuclear proliferation, climate change, migration, cyberspace, health, international trade, monetary issues, and development- describing in each case its causes and consequences, as well as the options available at all levels to deal with them in a way that is favourable to the stability of the world order.
Finally, the last section deals with world order - the most basic concept in International Office- which it considers indispensable given that its absence translates into loss of life and resources, and threats to freedom and prosperity at the global level. Building on the idea that, at any historical moment, and at any level, forces that promote stable order operate alongside forces that tend towards chaos, the chapter looks at the main sources of stability, analysing their contribution to international order - or disorder - and concluding with what this means for the international era we live in. Aspects such as sovereignty, the balance of power, alliances and war are dealt with in the different chapters that comprise this fourth and final part.
Of particular interest to those who wish to delve deeper into these matters is the coda of the book, entitled Where to Go for More. This final chapter offers the reader a well-balanced and authoritative compendium of journalistic, digital and literary references whose frequent use, highly recommended, will undoubtedly contribute to the educational goal proposed by the author.
It is an informative book, written to improve the training of the American and, beyond that, the global public on issues related to the world order. This didactic nature does not, however, prevent Haass, at times, and despite his promise to provide independent, non-partisan criteria that will make the reader less manipulable, from tinginging these issues with his staff vision of the world order and how it should be, or from criticising - somewhat veiled, it must be said - the current occupant of the White House's international policy, which is not very globalist. Nevertheless, The World. A Brief Introduction offers a simple and complete introduction to the world of International Office, and is almost obligatory reading for anyone who wants to get started in the knowledge of the world order and the mechanisms that regulate it.
[Parag Khanna, The Future is Asian. Simon & Schuster. New York, 2019. 433 p.]
review / Emili J. Blasco
 Parag Khanna's book can be greeted with suspicion from entrance because of the apparent axiomatic character of his degree scroll. However, the blunt assertion on the cover is softened when one begins to read the pages inside. The thesis of the work is that the world is in a process of asianisationnot of chinisationMoreover, this process is presented as another coat of paint on the planet, not as a colour that will be clearly predominant or definitive.
Parag Khanna's book can be greeted with suspicion from entrance because of the apparent axiomatic character of his degree scroll. However, the blunt assertion on the cover is softened when one begins to read the pages inside. The thesis of the work is that the world is in a process of asianisationnot of chinisationMoreover, this process is presented as another coat of paint on the planet, not as a colour that will be clearly predominant or definitive.
It is possible that the discussion over whether the US is in decline and will be replaced by China as the pre-eminent superpower obscures other parallel developments. Those watching Beijing's rise in the world order, writes Khanna, "have often been paralysed by two views: either China will devour the world or it is on the verge of collapse. Neither is correct. "The future is Asian, even for China," he asserts.
Khanna believes that the world is moving towards a multipolar order, which is also the case in Asia, even if China's size often dazzles.
The author's Indian background and also his time living in the United States may have influenced this judgement, but he offers figures to support his words. Of the 5 billion people living in Asia, 3.5 billion are non-Chinese (70%): China thus has only a third of Asia's population; it also accounts for slightly less than half of Asia's GDP. Other data: half of outward investment from the continent is non-Chinese, and more than half of outward investment goes to Asian countries other than China. Asia is therefore "more than China plus".
It is not just a question of size, but of wills. "A China-led Asia is no more acceptable to most Asians than the notion of a US-led West is to Europeans," says Khanna. He rejects the idea that, because of China's power, Asia is heading towards a kind of tributary system like the one ruled in other centuries from Beijing. He points out that such a system did not extend beyond the Far East and was based primarily on trade.
The author reassures those who fear Chinese expansionism: "China has never been an indestructible superpower presiding over all of Asia like a colossus". He warns that while Europe's geographical characteristics have historically led many countries to fear the hegemony of a single power, Asia's geography makes it "inherently multipolar", as natural barriers absorb friction. Indeed, clashes between China and India, China and Vietnam or India and Pakistan have ended in stalemates. "Whereas in Europe wars have occurred when there is a convergence in power between rivals, in Asia wars have occurred when there is a perceived advantage over rivals. So the more powerful China's neighbours like Japan, India or Russia are, the less likely they are to conflict with each other.
For Khanna, Asia will always be a region of distinct and autonomous civilisations, especially now that we are witnessing a revival of old empires. Asia's geopolitical future will not be led by the US or China: "Japan, South Korea, India, Russia, Indonesia, Australia, Iran and Saudi Arabia will never come together under a hegemonic umbrella or unite into a single pole of power".
There will not be, then, a Chineseisation of the world, according to the author, and the Asianisation that is taking place - a shift of the world's weight towards the Indo-Pacific - need not be seen as a threat to those who live elsewhere. Just as there was a Europeanisation of the world in the 19th century, and an Americanisation in the 20th century, we are witnessing an Asianisation in the 21st century. Khanna sees this as "the most recent substratum of sedimentation in the geology of global civilisation", and as a "layer" it does not imply that the world Withdrawal to what came before. "Being more Asian does not necessarily mean being less American or European," he says.
The book analyses the weight and fit of different Asian countries on the continent. Of Russia, he argues that it is strategically closer to China today than at any time since its communist pact in the 1950s. Khanna believes that geography leads to this understanding, as it invites Canada to maintain good relations with the United States; he predicts that climate change will further open up the lands of Siberia, which will integrate them more with the rest of the Asian continent.
As for India and China's relationship, Khanna believes that both countries will have to accept each other as powers more normally. For example, despite India's reluctance towards China's Silk Road and India's own regional connectivity projects, in the end the two countries' preferred corridors will "overlap and even reinforce each other", ensuring that products from inland Asia reach the Indian Ocean. "Geopolitical rivalries will only accelerate the Asianisation of Asia," says Khanna.
In assessing the importance of Asia, the book includes Middle Eastern oil. Technically, the region is part of the continent, but it is such a separate chapter with its own dynamics that it is difficult to see it as Asian territory. The same is true when label is used to refer to Israel or Lebanon. It can give the impression that the author is lumping everything together in order to make the figures more impressive. He argues that the Middle East is becoming less and less dependent on Europe and the United States and is looking more to the East.
Khanna is in a position to reasonably defend himself against most of the objections to his text. Most controversial, however, is his near-defensive justification of technocracy as a system of government. Beyond the descriptive attitude of a model that in some countries has received an important economic and social development , Khanna even seems to endorse its moral superiority.
France and Germany move closer to Poland as the third hard core country, rather than adding Italy or Spain.
Leaving aside criticism of Polish judicial reforms in recent years, Paris and Berlin are seeking a special cooperation Degree with Poland so that it does not act as the European gateway to Washington's influence that the UK used to be. For the French and Germans, Poland seems a more reliable partner than Italy and Spain, whose political instability complicates the elaboration of medium- and long-term security and defence strategies deadline.
![Macron with the Polish President and Prime Minister during his visit visit to Warsaw in February 2020 [Elysée Palace]. Macron with the Polish President and Prime Minister during his visit visit to Warsaw in February 2020 [Elysée Palace].](/documents/10174/16849987/triangulo-weimar-blog.jpg)
Macron with the Polish President and Prime Minister during his visit in Warsaw in February 2020 [Elysée Palace].
article / Jokin de Carlos Sola
The European committee is perhaps the most important body in the EU. It is in charge of setting objectives, it sets the diary to the Parliament and the Commission. It is in this body that the states are represented as such and where issues such as the weight of each country's population and Economics take on particular importance.
France and Germany thus achieve their high profile on the European committee , where their ideological influence over other European governments also translates into unofficial leadership of the Union. Both countries have sought to establish a special cooperation Degree with Poland in order to gain influence over one of the countries with the next largest population and thereby reduce the presence of the United States in Europe. This three-way partnership is embodied in the Weimar Triangle.
On the other hand, Brexit has opened an unofficial degree program to find out who will be the third most influential country in the European Union. All this at a time when politicians such as Emmanuel Macron and Ursula von der Leyen are calling for the strengthening of a common foreign policy. The Netherlands, under Mark Rutte, has sought such a position through alliances with ideologically like-minded countries in the so-called New Hanseatic League. However, Poland also seems to have supporters for the post. Two of the larger countries, Italy and Spain, seem to have fallen out of the degree program .
Recovering a forgotten idea
The Weimar Triangle was born in 1991, with the aim of helping Poland to emerge from communism. goal . In that year a meeting was held between the foreign ministers of the three countries: Roland Dumas, Hans-Dietrich Genscher and Krzysztof Skubiszewski. With this meeting, Poland managed to get France and Germany to give it special consideration among the European countries that had been on the other side of the Iron Curtain and were soon to join NATO and later the EU (Poland joined the Atlantic Alliance in 1999 and the EU in 2004).
Since then, representatives of the three governments have met relatively frequently. By 2016 there had been eight summits of heads of state, as well as 23 meetings of foreign ministers and two meetings of defence ministers. In 2013 the three countries decided to form a battalion under EU command (one of 18), under the name group Combat Weimar or Weimar Battalion, composed of officers and soldiers from the three countries.
Since 2015, however, relations began to cool as Poland's more Atlanticist and less tolerant Law and Justice party came to power. In 2016 Polish Foreign Minister Witold Waszczykowski went so far as to declare that the Weimar Triangle was of no great importance to his country. In the same year there was an attempt to revive tripartite cooperation with a meeting of the three foreign ministers to address issues such as Brexit or the refugee crisis, but without much success.
Over the next three years, cooperation declined and there was French and German criticism of the Polish government. The replacement of Waszczykowski moderated the demonstrations in Warsaw, but relations were not as smooth as they had been at the beginning. Poland's unease towards Berlin was mainly due to the construction of Nord Stream 2 (the doubling of the gas pipeline directly linking Germany and Russia); the distrust of Paris was due to its apparent sympathy with Moscow. For its part, especially after Macron's arrival at the Elysée, France began to distrust Poland because of its close relationship with Washington.
From 2019 onwards, however, a new rapprochement began to emerge. France came to believe that it was better to keep Poland close and thus keep the US at arm's length, while Poland felt that it could actually make its proximity to France and Germany compatible with US military support to defend itself against Russia. In February 2020 Macron visited Warsaw and met with President Duda and Prime Minister Morawiecki to improve relations between the two countries and revive the Triangle idea.
Marginalisation of Spain and Italy
It may come as a surprise that Germany and France look to Poland rather than wanting to rely more on Italy or Spain, countries not only with larger populations but also larger economies. But the reasons are clear. Despite the divergences in foreign policy between France and Poland, it is undeniable that the Slavic country is able to offer something that neither Spain nor Italy can provide: stability. Since 2016, the two Mediterranean countries have been experiencing one domestic political crisis after another, forcing their governments to keep foreign policy issues on the back burner.
In Spain, no government has had an absolute majority in Parliament since 2015, and that is not likely to change. Between 2015 and 2019 there have been four general elections and two prime ministers. This status makes it difficult to pass laws, including the fundamental budget, without which no foreign policy compromise can be expected.
In Italy the beginning of the tornado began with the fall of Matteo Renzi at the end of 2016. Since then the country has seen two prime ministers and three governments. This may not be surprising in the Italian case, but certainly the perceived instability is now greater. Moreover, there is distrust from other European partners over Italy's dealings with China over the New Silk Road, something that is generally more worrying than Poland's flirtations with the US. In geopolitical terms, the possibility of a political crisis making Salvini, who has not been subtle in his admiration for Putin's Russia, prime minister is also a cause for concern.
In contrast, despite a change of prime minister and cabinet in 2018, Poland has shown a clear foreign policy line since Law and Justice came to power, as well as steady economic growth. After the victory in the 2019 elections, everything seems to indicate that Mateusz Morawiecki will remain prime minister until at least 2023. Such policy durability makes Poland a more attractive ally, despite tensions over Poland's controversial judicial reforms.
Moreover, coordination with Poland offers Paris and Berlin a way to further integrate the former Soviet bloc countries into EU decision-making.
Three visions
However, the desire to create a cooperative body within the Weimar Triangle is a real challenge challenge, as each country represents, in one way or another, one of three of the foreign policy agendas that divide Europe.
At one end of the spectrum is French Gaullism, which advocates an independent Europe and is wary of a US presence in Europe, remembering that France already has a strong military. Paris abandoned this perspective for an Atlanticist one in 2007 under Sarkozy, but it has been regained by Macron. This means that Macron's rhetoric could lead to clashes with the Americans, while he also seeks to mark profile himself against Moscow and Beijing.
In the middle is German pragmatism: Germany does not want to increase conflict and prefers to focus on its Economics. On the one hand it is negotiating with the Russians to receive gas for its industrial activity, and on the other it wants US troops to remain on its territory, as their departure would force it to increase its security expense . In Europe's plans for recovery from the Covid-19 pandemic, Germany has clearly been more absent, with Macron taking the lead.
Finally, we find Polish Atlanticism. Poland is perhaps the most Atlanticist country in the EU. Even under the Trump Administration there has been a high level of pro-Americanism among the population and the political class . The government has pushed for the hosting of a US base and Defence Minister Mariusz Błaszczak has enthusiastically praised the role of the US as a defender of the free world. This is nothing new, as the 2003 invasion of Iraq was supported by Poland in the face of French and German rejection. Poland continues to see Russia as its greatest threat and the US and NATO as guarantors of protection.
The Triangle returns
Its geographical status explains Poland's position and it will not stop wanting NATO's instructions on its territory. However, it understands that it needs close allies with greater internal stability - hence its rapprochement with Germany and France - than that offered by the Trump Administration, whose international image is badly damaged, or a United Kingdom more occupied with managing Brexit than security issues.
On the other hand, Macron wants to avoid Poland replacing the UK as the representative of US policy in Europe, so he has changed his strategy to avoid alienating it by criticising its judicial reforms. Macron did not mention them in his visit to Warsaw in February this year and only encouraged 'respect for European values'. Somehow Macron understands that after Brexit he will need Poland to advance his European foreign policy plans, and that is why it is important to bring it to the conference room helm. Macron went so far as to say in Warsaw that Poland, Germany and France should lead the Union post-Brexit. He also announced the dispatch of 600 more men to Poland, which will bring the number of French soldiers in the country to 5,100.
At meeting, both leaders agreed to meet with German Chancellor Angela Merkel, although the limitations imposed by the coronavirus pandemic have slowed down some contacts, while also waiting for Economics to begin to recover. The newly inaugurated German presidency of committee , moreover, discourages Berlin from appearing overly aligned with a certain European vector. The Weimar Triangle may therefore hibernate temporarily; in any case, although this is a risky formula, if coordinated with the Parliament and the Commission, its consolidation could represent a step forward in European cohesion and governance.
[Bruno Maçães, History Has Begun. The Birth of a New America. Hurst and Co. London, 2020. 203 p.]
review / Emili J. Blasco
 What if the United States were not in decline, but quite the opposite? The United States could actually be in its infancy as a great power. This is what Bruno Maçães argues in his new book, whose degree scroll -History Has Begun- In a certain sense, he refutes Fukuyama's end of history, which saw the democratisation of the world at the end of the 20th century as the culmination of the West. Precisely, the hypothesis of the Portuguese-born internationalist is that the US is developing its own original civilisation, separate from what until now has been understood as Western civilisation, in a world in which the very concept of the West is losing strength.
What if the United States were not in decline, but quite the opposite? The United States could actually be in its infancy as a great power. This is what Bruno Maçães argues in his new book, whose degree scroll -History Has Begun- In a certain sense, he refutes Fukuyama's end of history, which saw the democratisation of the world at the end of the 20th century as the culmination of the West. Precisely, the hypothesis of the Portuguese-born internationalist is that the US is developing its own original civilisation, separate from what until now has been understood as Western civilisation, in a world in which the very concept of the West is losing strength.
Maçães' work follows three lines of attention: the progressive separation of the US from Europe, the characteristics that identify the specific American civilisation, and the struggle between the US and China for the new world order. The author had already developed aspects of these themes in his two immediately preceding works, already reviewed here: The Dawn of Eurasia y Belt and RoadThe focus is now on the US. The three titles are basically a sequence: the progressive dissolution of the European peninsula into the Eurasian continent as a whole, the emergence of China as the superpower of this great continental mass, and Washington's remaining role on the planet.
As to whether the US is rising or not leave, Maçães writes in the book's introduction: "Conventional wisdom suggests that the United States has already reached its peak. But what if it is only now beginning to forge its own path forward? The volume is written before the coronavirus crisis and the deep unease in US society today, but even before that some signs of US domestic unrest, such as political polarisation or divergences over the direction of its foreign policy, were already evident. "The present moment in the history of the United States is both a moment of destruction and a moment of creation", says Maçães, who considers that the country is going through "convulsions" characteristic of this process of destructive creation. In his opinion, in any case, they are "the birth pangs of a new culture rather than the death throes of an old civilisation".
One might think that the United States is simply evolving towards a mixed culture as a result of globalisation, so that the influence of some European countries in shaping US society over the last few centuries is now being joined by Asian immigration. Indeed, by mid-century, immigrants from across the Pacific are expected to outnumber those arriving from Mexico and Central America, which, although steeped in indigenous cultures, largely follow the Western paradigm. Between the first European and the new Asian heritage, a 'hybrid Eurasian' culture could develop in the US.
Indeed, at one point in the book, Maçães asserts that the US is 'no longer a European nation', but 'in fundamental respects now seems more similar to countries like India or Russia or even the Republic of Iran'. However, he disagrees with this hybrid Eurasian perspective and argues instead for the development of a new, indigenous American society, separate from modern Western civilisation, rooted in new sentiments and thoughts.
In describing this different way of being, Maçães focuses on a few manifestations, from which he deduces deeper aspects. "Why do Americans speak so loudly?" he asks, referring to one such symptom. His theory is that American life emphasises its own artificiality as a way of reminding its participants that they are, at bottom, experiencing a story. "The American way of life is consciously about language, storytelling, plot and form, and is meant to draw attention to its status as fiction." An entire chapter, for example, is devoted to analysing the importance of television in the US. In the midst of these considerations, the reader might think that the reasoning has been drifting towards a cultural essay and out of the realm of International Office, but in the conclusion of the book the ends are conveniently tied up.
With that loose end out of the way, the book moves on to analyse the tug of war between Washington and Beijing. It recalls that since its rise as a world power around 1900, the US's permanent strategic goal has been to prevent a single power from controlling the whole of Eurasia. Previous threats in this regard were Germany and the USSR, and today it is China. employee Normally, Washington would resort to a balance of power, using Europe, Russia and India against China (using a game historically played by Britain for the goal to prevent a single country from controlling the European continent), but for the moment the US has focused on directly confronting China. Maçães sees the Trump administration's policy as confusing. "If the US wants to adopt a strategy of maximum pressure against Beijing, it needs to be clearer about the end game": is it to constrain Chinese economic power or to convert China to the West's model ?, he asks. He intuits that the ultimate goal is to "decouple" the Western world from China, creating two separate economic spheres.
Maçães believes that China will hardly manage to dominate the supercontinent, since "the unification of the whole of Eurasia under a single power is so far from inevitable that in fact it has never been achieved". In any case, he believes that, because of its interest as a superpower, the US may end up playing not so much the role of "great balancer" (given China's weight, it is difficult for any of its neighbours to exercise a counterweight) as that of "great creator" of the new order. "China must be trimmed down in size and other pieces must be accumulated, if a balance is to be the final product," he asserts.
It is here that the US character as a story and narrative builder finally comes back into the picture, with a somewhat flimsy argument. Maçães can see the US succeeding in this task of "great maker" if it treats its allies with autonomy. As in a novel, his role as narrator "is to bring all the characters together and preserve their own individual spheres"; "the narrator has learned not to impose a single truth on the whole, and at the same time no character will be allowed to replace him". "For the United States," Maçães concludes, "the age of nation-building is over. The age of world building has begun".
High incidence of Covid-19 in the country contrasts with the government's swiftness in implementing measures
Peru has been an example in the Covid-19 crisis for its speed in applying containment measures and for approve one of the largest economic stimulus packages in the world, close to 17% of GDP. However, the high incidence of the pandemic, which has made Peru the second Latin American country in terms of cases of the coronavirus and the third in terms of deaths, has made it necessary to prolong the restrictions on activity longer than expected. This and lower external demand, weaker than initially predicted, have "more than eclipsed" the government's significant economic support, according to the IMF, which forecasts a 13.9% drop in GDP for Peru in 2020, the largest of the region's main economies.
![lecture of the Peruvian president, Martín Vizcarra (r), in the presence of the head of Economics, María Antonieta Alva (l) [Gov. of Peru]. lecture of the Peruvian president, Martín Vizcarra (r), in the presence of the head of Economics, María Antonieta Alva (l) [Gov. of Peru].](/documents/10174/16849987/peru-covid-blog.jpg)
lecture of the Peruvian President, Martín Vizcarra (r), in the presence of the head of Economics, María Antonieta Alva (l) [Gov. of Peru].
ARTICLE / Gabriela Pajuelo
International media such as Bloomberg y The Wall Street Journal have shown admiration for Peru's young minister of Economics , María Antonieta Alva. At 35, with a master's degree from Harvard and some experience in Peru's own administration, Alva designed one of the most ambitious economic stimulus plans in all of South America at the beginning of the crisis.
"From a Latin perspective, Peru is a clear leader in terms of macro response; I could have imagined a very different result if Toni wasn't there," he said. Ricardo HausmannAlva's Harvard professor, who is leading a team of experts advising Peru and ten other countries on how to mitigate the effects of the coronavirus. The minister has also become one of the best-known faces of President Martin Vizcarra's government among the working classes.
Peru was one of the first countries in Latin America to apply a state of emergency, limiting the freedom of meeting and transit in Peruvian territory and restricting economic activity. To prevent mass infection with the virus, the government decreed the closure of borders, restrictions on interprovincial movement, a daily curfew and a mandatory period of national isolation, which has been extended several times and has become one of the longest in the world.
This prolongation, agreed in the face of the high incidence of the pandemic, has damaged the economic outlook more than expected. Moreover, the prolongation of the emergency in countries to which Peru's exports are destined has weakened their demand for raw materials and damaged the resurgence of Peru's Economics . This is the IMF's estimate, which between its April forecast and the one updated in June has added nine more points to the fall in Peru's GDP for 2020. The IMF now considers that Peru's Economics will fall by 13.9% this year, the largest among the region's major countries. Although the ambitious stimulus package will not have prevented this decline, it will boost the recovery, with GDP rising by 6.5% in 2021, the strongest rebound among the largest Latin American economies. With regard to the latter forecast, the IMF specifies that, nevertheless, "there are significant risks to leave , linked to national and global challenges to control the epidemic".
A socio-economic context that does not financial aid to containment
Despite restrictive social distancing measures, the pandemic has had a high incidence in Peru, with 268,602 diagnosed cases (second only to Brazil in Latin America) and 8,761 deaths (behind Brazil and Mexico) as of 25 June. These high figures are partly due to the fact that the country's socio-economic conditions have meant that compliance with containment has not been very strict in certain situations. The social context has made it difficult to respect the mandatory quarantine due to structural problems such as the fragility of health services and infrastructure, the difficulty of efficient public procurement, prison overcrowding and the digital divide.
The high level of labour informalityThe fact that in 2019 it was 72% explains why many people have to continue working to ensure their subsistence, without following certain protocols or having access to certain material; at the same time, this informality prevents greater tax collection that would help to improve budgetary items such as health. Peru is the second Latin American country with the lowest health investment.
On the other hand, inequalitywhich in 2018 was 42.8 in the Gini index, is aggravated by the territorial distribution of expense, linked to the centralisation of employment of the rural population in Lima. During the pandemic, workers from the country's highlands who have migrated to the capital have wanted to return to their places of origin, as many are not on the payroll and have no labour rights, in contravention of the restrictions of mobility.
This social context makes it possible to question some of the economic measures approved, according to some Peruvian academics. The president of high school Peruano de Economics (IPE), Roberto Abusada, warned that Peru's macroeconomic strengths will not help forever. He considered that certain regulations are unenforceableThe "setting parameters such as body mass index (BMI) or an age limit, creates obstacles for this group of people, who could be highly qualified, and could not return to their centre of work".
Economic package
In late April, Minister Alva presented a $26 billion economic stimulus package, representing 12 per cent of GDP. Additional measures a month later raised that percentage to 14.4 per cent of GDP, and even then it would have been closer to 17 per cent. Comparatively speaking, this is one of the largest stimulus packages adopted in the world (in Latin America, the second largest is Brazil, with a stimulus of 11.5 per cent of GDP).
From agreement with the monitoring that the IMF Peru has adopted measures in three different areas: fiscal, monetary and macro-financial, and in terms of the exchange rate and the balance of payments.
First, in terms of fiscal measures, the government approved 1.1 billion soles (0.14% of GDP) to address the health emergency. In addition, various measures have been implemented, among which two stand out: the "Stay at home" voucher and the creation of the Business Support Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises (FAE-MYPE).
The first measure, for which the government approved approximately 3.4 billion soles (0.4% of GDP) in direct transfers, is a 380 soles (US$110) voucher targeted at poor households and vulnerable populations, of which there have been two disbursements. The second measure concerns the creation of a fund of 300 million soles (0.04% of GDP) to support MSEs, in an attempt to guarantee credit for capital for work and to restructure or refinance their debts.
Among other fiscal measures, the government approved a three-month extension of the income tax declaration for SMEs, some flexibility for businesses and households in paying tax obligations and a deferral of household electricity and water payments. The whole package of fiscal support amounts to more than 7% of GDP.
On the other hand, in terms of monetary and macro-financial measures, the Central Bank reservation (BCR) reduced the reserve requirement rate by 200 basis points, bringing it to 4%, and is monitoring the evolution of inflation and its determinants to increase monetary stimulus if necessary. It has also reduced reserves requirements , provided liquidity to the system with a package backed by government guarantees of 60 billion soles (more than 8% of GDP) to support lending and the chain of payments.
In addition, exchange rate and balance of payments measures have been implemented through the BCR's intervention in the foreign exchange market. By 28 May, the BCR had sold approximately USD 2 billion (0.9% of GDP) in foreign exchange swaps. International reserves remain significant, at more than 30% of GDP.
On the other hand, in the field of trade relations, Peru agreed not to impose restrictions on foreign trade operations, while at the same time liberalising the loading of goods, speeding up the issuance of certificates of origin, temporarily eliminating some tariffs and waiving various infractions and penalties contained in the General Customs Law. This was particularly the case for transactions with strategic partners, as the European UnionAccording to Alberto Almendres, the president of Eurochambres (the association of European Chambers in Peru). 50% of foreign investment in Peru comes from Europe.
In terms of Peruvian exports, although the emergence of the coronavirus in China at the beginning of the year slowed down transactions with that country, mining and agricultural exports remained positive. in the first two months of the yearas indicated in the high school research and of the Lima Chamber of Commerce. development (Idexcam). Subsequently, exports of raw materials and tourism have been more affected, especially in the case of exports of raw materials and tourism.
Comparison with Chile and Colombia
The status in Peru can be analysed in comparison with its neighbours Chile and Colombia, which will have a somewhat smaller fall in GDP in 2020, although their recovery will also be somewhat smaller.
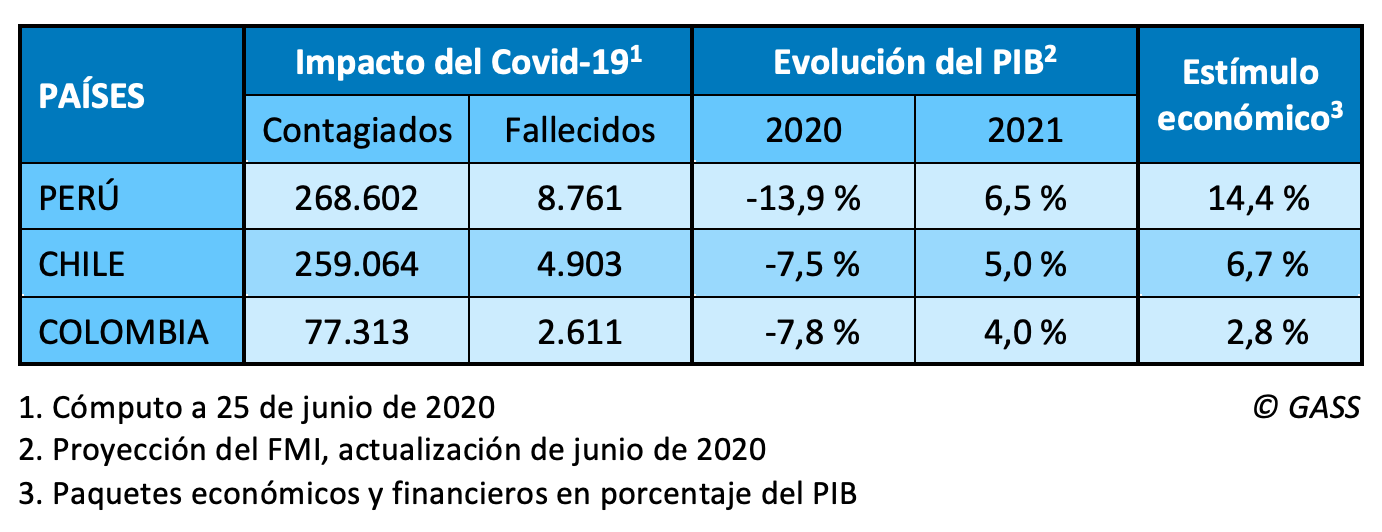
issue As for the issue of confirmed Covid-19 cases as of 25 June, Chile (259,064 cases) is similar in size to Peru (268,602), although the number of deaths is almost half that of Peru (4,903 Chileans and 8,761 Peruvians), which corresponds to the proportion of its total population.
In response to the pandemic, Chilean authorities implemented a series of measures, including the declaration of a state of catastrophe, travel restrictions, school closures, curfews and bans on public gatherings, and a teleworking law. This crisis came just months after the social unrest experienced in the country in the last quarter of 2019.
On the economic front, Chile approved a stimulus of 6.7% of GDP. On 19 March, the authorities presented a fiscal package of up to $11.75 billion focused on supporting employment and corporate liquidity (4.7% of OPIB), and on 8 April an additional $2 billion of financial aid to vulnerable households was announced, as well as a $3 billion (2%) guarantee plan from credit . In its June forecast update , the IMF expects Chile's GDP to fall by 7.5% in 2020 and increase by 5% in 2021.
In Colombia, the level of contagion has been lower (77,313 cases and 2,611 deaths), and its economic package to cope with the crisis has also been smaller: 2.8 per cent of GDP. The government created a National Emergency Mitigation Fund, which will be partially financed by regional and stabilisation funds (around 1.5 per cent of GDP), complemented by the issuance of national bonds and other budgetary resources (1.3 per cent). In its recent update, the IMF forecasts that Colombia's GDP will fall by 7.8% in 2020 and rise by 4% in 2021.
[Tae-Hwan Kwak and Seung-Ho Joo (eds). One Korea: visions of Korean unification. Routledge. New York, 2017. 234 p.]
review / Eduardo Uranga
 Throughout the second half of the 20th century, tensions between superpowers in East Asia made this part of the world a hotspot of the International Office. Tensions remain today, such as the trade war that has pitted the United States against the People's Republic of China since 2018. However, over the past 70 years, one territory in particular has been affected by an ongoing conflict that has repeatedly claimed the world's attention. That region is undoubtedly the Korean peninsula.
Throughout the second half of the 20th century, tensions between superpowers in East Asia made this part of the world a hotspot of the International Office. Tensions remain today, such as the trade war that has pitted the United States against the People's Republic of China since 2018. However, over the past 70 years, one territory in particular has been affected by an ongoing conflict that has repeatedly claimed the world's attention. That region is undoubtedly the Korean peninsula.
This book, co-edited by Tae-Hwan Kwak and Seung-Ho Joo and bringing together various experts on inter-Korean relations, discusses the various possibilities for a future reunification of the two Koreas, as well as the various problems that need to be solved in order to achieve this goal. The perspectives of the various world powers on the conflict are also analysed.
The Korean issue dates back to World War II: after the country was occupied by Japan, its liberation ended up dividing the peninsula in two: North Korea (occupied by the Soviet Union) and South Korea (controlled by the United States). Between 1950 and 1953, the two halves fought a conflict, which eventually consolidated the partition, with a demilitarised zone in between known as the 38th Parallel or KDZ.
One of the formulas for Korean unification described in this book is unification through neutralisation, proposal by both Koreas. However, the constant long-range nuclear missile tests carried out by North Korea in recent years present a major obstacle to this formula. In this atmosphere of mistrust, Korean citizens play an important role in promoting cooperation and friendship on both sides of the border with the goal aim of achieving North Korea's denuclearisation.
Another aspect that plays an important role in forcing a change in North Korea's attitude is its strategic culture. This must be differentiated from the traditional Korean strategic culture. North Korea has adopted various unification strategies over the years, while maintaining the same principles and values. This strategic culture blends elements from the country's strategic position (geopolitically), history and national values. All of this is under the authority of the Juche ideology. This ideology contains some militaristic elements and promotes the unification of Korea through armed conflict and revolutionary actions.
Regarding the perspectives of the various world superpowers on future Korean reunification, China has stated that it favours a long-term approach to unification deadline; a short-term process deadline would collide with Chinese national interests, as Beijing would first have to settle its disputes with Taiwan, or end the trade war against the United States. China has stated that it will not accept Korean unification influenced by a military alliance between the US and South Korea.
On the other hand, the US has not yet opted for a specific Korean unification policy. Since the 1950s, the Korean peninsula has been but one part of the overall US strategic policy for the entire Asia-Pacific region.
The unification of the Korean peninsula will be truncated as long as the US, China and other powers in the region continue to recognise the status quo on the peninsula. It could be argued that armed conflict might be the only way to achieve unification. According to the authors of this book, this would be too costly in terms of resources used and human lives lost. On the other hand, such a war could trigger a conflict on a global scale.
