Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Analysis .
![Satellite imagery of the Jordan River [NASA]. Satellite imagery of the Jordan River [NASA].](/documents/10174/16849987/jordan-river-blog.jpg)
▲Satellite imagery of the Jordan River [NASA].
ANALYSIS / Marina Díaz Escudero
Water is an essential natural resource, not only for individual survival on Earth, but also for nation-states and their welfare; having an effect on partner-economic development, trade, health and population productivity.
As a natural determinant of power, its accessibility must be considered by states in their policies on national security; "hydropolitics" being the branch of study for this phenomenon. Although it has been, and continues to be, a major source of inter-state conflict, it is an arena in which cooperation and diplomacy between rival countries can set the ground for further political agreements, effectively leading to more stable and peaceful relations.
On the other hand, when water is used as a natural border or must be shared between various countries, concurrent cooperation between all of them is essential to find an effective and non-violent way to approach the resource. Otherwise, an overlapping of different, and potentially contradictory, bilateral agreements may lead to frictions. If one of the concerned countries is not present in negotiations, as some historical events suggest (e.g. 1992 multilateral negotiations in Moscow, where Lebanon and Syria where not present), this will always constitute an obstacle for regional stability.
Moreover, although 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by water, factors such as economic interests, climate change, and explosive population growth are also challenging the sustainable distribution of water sources among countries. The future effects of this scarcity in the region will demand consistent political action in the long-term and current leaders should bear it in mind.
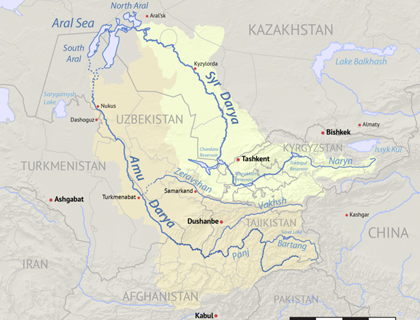
Water availability and conflict in the MENA region
The Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region is known as an arid and semi-arid region, with only 1% of the world's renewable water resources. On average, water availability is only 1,200 cubic meters, around six times less than the worldwide average of 7,000 cubic meters.
As global temperatures rise, more frequent and severe droughts will take place in the region and this will make countries which already have partner-economic rivalries more prone to go to war with each other. According to the World Resources Institute, thirteen of the thirty three states that will suffer from worse water scarcity in the twenty-first century will be Middle Eastern countries.
To quote the findings of the National Intelligence Council (NIC) report, Global Trends: Paradox of Progress, more than thirty countries - nearly half of them in the Middle East - will experience extremely high water stress by 2035, increasing economic, social, and political tensions.
Although claims to the land were and are the main motives for much of the current conflict, water, as part of the contested territories, has always been considered as a primary asset to be won in conflict. In fact, recognition of the importance of water lent the term, the "War over Water", to conflicts in the region, and control over the resource constitutes a significant advantage.
Despite there being several water bodies in the Middle East (Nile, Euphrates, Tigris...), the Jordan River basin is one of the most significant ones today in terms of its influence on current conflicts. The Jordan River Basin is a 223 km long river with an upper course from its sources up to the Galilee Sea, and a lower one, from the latter to the Dead Sea. Territories such as Lebanon, Israel and the West Bank are situated to its West, while Syria and Jordan border it to the East. Water scarcity in the Jordan watershed comes from many different factors, but the existence of cultural, religious and historical differences between the riparian countries (situated on the banks of the river) has led to a centuries-long mismanagement of the source.
Tensions between Zionism and the Arab world on regards to the Jordan River became noticeable in the 1950s, when most Arab countries rejected the Johnston Plan that aimed at dividing the water by constructing a number of dams and canals on the different tributaries of the river. The plan was based on an earlier one commissioned by the United Nations Relief and Works Agency (UNWRA) and was accepted by the water technical committees of the five riparian countries. Nevertheless, the Arab League didn't give the go-ahead and even hardened its position after the Suez Crisis.
In spite of this, Jordan and Israel decided to abide by their allocations and developed two projects, the Israeli National Water Carrier (to transport water from the north to the center and south) and Jordan's East Ghor Main Canal (King Abdullah Canal). In retaliation and with severe consequences, Arab states reunited in an Arab Summit (1964) and decided to divert Jordan's headwaters to the Yarmouk river (for the Syrian Arab Republic and Jordan), depriving Israel of 35% of its Water Carrier capacity.
This provocation led to a series of military clashes and prompted Israel's attack on Arab construction projects; a move that would help precipitate the 1967 Six-Day War, according to some analysts. As a result of the war, Israel gained control of the waters of the West Bank (formely Jordan-annexed in the 1948 war and today still controlled by the Israeli Civil Administration) and the Sea of Galilee (today constituting about 60% of the country's fresh water).
Later, in 1995, by the Article 40 of the Oslo II political agreement, [...] Israel recognized Palestinian water rights in the West Bank and established the Joint Water Committee to manage and develop new supplies and to investigate illegal water withdrawals. Nevertheless, the loss of control over water in the West Bank has never been accepted by neighboring Arab countries as, despite the agreement, much of the water coming from it is still directly given to Israeli consumers (and only a smaller fraction to Palestinians living under their control).
Role of water in Syrian-Israeli hostilities
Hostilities have been covering the diary of Syrian-Israeli relationships ever since the Armistice Agreements signed by Israel with each of the four neighboring Arab countries in 1949. This is compounded by the fact that there is seldom mutual agreement with resolutions proposed by the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
The Golan Heights, a rocky plateau in south-western Syria, was taken away by Israel in the aftermath of the Six-Day War and is still considered an Israeli-occupied territory. In 1974 the Agreement on Disengagement was signed, ending the Yom Kippur War and resulting in the formation of the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF), a buffer zone separating the Israeli portion of the Golan Heights and the rest of Syria. Although Israel kept most of the Golan Heights territory, in 1981 it unilaterally passed the Golan Heights Law to impose its jurisdiction and administration on the occupied territory (refusing to call it "annexation"). These laws did not receive international recognition and were declared void by the UNSC.
The fact that Israel's Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu stated in April 2016 in a weekly cabinet meeting that "the Golan Heights will remain forever in Israeli hands" has once again triggered the rejection of UNSC's members, who have declared that the status of the Heights "remains unchanged."
Rainwater catchment in the Golan Heights feeds into the Jordan River and nowadays provides a third of Israel's water supply. Although "Syria has built several dams in the Yarmouk river sub-basin, which is part of the Jordan River basin", the Golan Heights are likely to remain an important thorn in future Israeli-Syrian relations.
|
Map of the Jordan River Basin [Palestinian Authority]. |
Water as a casus belli between Lebanon and Israel
In March 2002, Lebanon decided to divert part of the Hasbani (a major tributary of the Jordan upper course) to supply the Lebanese Wazzani village. Ariel Sharon, the former Prime Minister of Israel, said that the issue could easily become a "casus belli". According to Israel, Lebanon should have made consultations before pumping any water from the Springs, but both the Lebanese government and Hezbollah (a shi'a militant group) condemned the idea.
The Wazzani project, according to Lebanon, only aimed to redevelop the south by extracting a limited amount of water from the Hasbani; 300 MCM per year (they drew 7 MCM by the time). The actual conflict with Israel began when Lebanon started constructing the pumping station very close to the Israeli border.
The United States (US) decided to establish a State Department water expert in order to assess the situation "and cool tempers" but in 2006, during the Lebanon war, the pumping station and other infrastructures, such as an underground water diversion pipe which run Letani river water to many villages, were destroyed.
Although Israeli-Lebanese tensions have continued due to other issues, such as spying, natural gas control and border incidents, water source domination has been a significant contributor to conflict between the two states.
Inter-Arab conflicts on water allocation
Some inter-Arab conflicts on regards to water distribution have also taken place, but they are small-scale and low level ones. In 1987, an agreement was signed between Jordan and Syria which allowed the latter to build twenty five dams with a limited capacity in the Yarmouk River. Later on it was proved that Syria had been violating the pact by constructing more dams than permitted: in 2014 it had already constructed forty two of them. New bilateral agreements were signed in 2001, 2003 and 2004, but repeated violations of these agreements by Syria in terms of water-allocation became unsustainable for Jordan. Most recently (2012), former Jordan's water minister Hazim El Naser stressed the necessity "to end violations of the water-sharing accords."
Although these are low-level tensions, they could quickly escalate into a regional conflict between Jordan, Syria and Israel, as a decrease of water from the Yarmouk released by Syria to Jordan may prevent Jordan to comply with its commitments towards Israel.
Regional cooperation: from multilateralism to bilateralism
Since the beginning of the last century, attempts to achieve multilateral cooperation and a basin-wide agreement between the five co-riparian countries have been hindered by regional political conflict. Boundary definition, choices about decision-making arrangements, and issues of accountability, together with other political divisions, can help explain the creation of subwatershed communities of interest instead of a major watershed agreement between all neighboring countries.
The Israeli-Palestine peace process began in 1991 with the Conference in Madrid, attended by all riparians: Israel, Jordan, Palestine, Lebanon and Syria. Co-sponsored by the US and the Soviet Union as representatives of the international community, it addressed several regional issues, such as environment, arms control, economic development and, of course, water distribution (in fact, water rights became one of the trickiest areas of discussion).
In 1992, multilateral negotiations about regional cooperation continued in Moscow but this time they were only attended by Israel, the Jordanian-Palestinian delegation and the international community; Syria and Lebanon were not present. "After the failed Johnston plan, external efforts to achieve a multilateral agreement through cooperation on water sources were attempted by the Centre for Environmental Studies and Resource Management (CESAR) [...] As Syria and Lebanon did not want to participate in a process involving Israel, (it) ran parallel processes for Israel, the Palestinian Authority and Jordan on the one hand, and Syria and Lebanon on the other hand."
As a matter of fact, bilateral instruments grew in importance and two treaties, between Israel and Jordan/Palestine respectively, were signed: The Treaty of Peace between The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan and The State of Israel (1994) and The Israeli-Palestinian Interim Agreement on the West Bank and the Gaza Strip (Oslo II, 1995). Discussions about water use and joint water management played an important role and were included in the annexes.
In 1996, the Trilateral Declaration on Principles for Cooperation on Water-Related Matters and New and Additional Water Resources was signed by Israel, Jordan and the Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) and in 2003 the first two initiated a plan called Roadmap for Peace which included the revival of cooperation on regional issues like water.
Although Israel and Syria started some negotiations to solve the Golan Heights' problem in 2008, after the break out of the Syrian civil war distrust between both actors has increased, leaving the most important thorn in multilateral regional negotatiations still unsolved. Nevertheless, "a new government in Syria after the end of the war may provide new opportunities for improved bi- and ultimately multilateral cooperation," says the FAO. The previous year (2007) Jordan and the Syrian Arab Republic also signed some agreements "in regard to shared water in the Yarmouk river basin."
Role of Non-Governmental Organizations
Civil society has also been an important platform for resource-management discussions between riparian countries.
Middle Eastern rhetoric, according to the BBC, "often portrays the issue of water as an existential, zero-sum conflict - casting either Israel as a malevolent sponge sucking up Arab water resources, or the implacably hostile Arabs as threatening Israel's very existence by denying life-giving water."
For this reason, in 2010, Friends of the Earth Middle East (FoEME, also called EcoPeace Middle East) stressed the importance of replacing this win-lose approach for a compromising perspective of mutual gains for all. In this way, their proposals don't "include quantitative water allocations, but the implementation of a joint institutional structure that is continuously tasked with peaceful conflict resolution over water resources; [...] defining water rights not as the access to a certain water quantity, but as a broader bundle of rights and duties to access and use the available water and to uphold quality and quantity standards."
Through "The Good Water Neighbors" project (2001), the NGO tried to raise awareness about the negative consequences of leaving this issue unmanaged and reiterated its willingness to strenghten "institutional capacities for collaboration in the region." According to the staff, Israel, Jordan and Palestine could develop a certain interdependence, focused on water (Israel to Jordan/Palestine) and solar-generated electricity (Jordan to Palestine/Israel), in order to facilitate the powering of desalination plants and produce more cleanwater for sale.
The use of this type of political support for transboundary cooperation, based on water access but focused on solving less cultural and sensitive problems (like environmental sustainability), as a means to opening up avenues for dialogue on other political issues, could be the key for a lasting peace in the region.
According to Gidon Brombert, cofounder and Israeli director of FoEME, adopting "healthy interdependencies is a powerful way to promote regional water and energy stability as a foundation for long-lasting peace between our people."
A testament to the success of these initiatives is the fact that Jordan and Israel scored 56.67 under the Water Cooperation Quotient (WCQ) 2017, which means that there is currently zero risk of a water-related war between both states (50 is the minimum score for this to apply).
Final key points and conclusions
There is no doubt that water issues have been a key discussion point between riparian countries in the Jordan River watershed since the late nineteenth century, and rightly so, as the only way to achieve a long-lasting peace in the region is to accept that water management is an integral part of political discourse and decisions. Not only because it is an essential factor in the conflicts that arise between states, but because agreements on other political matters could be furthered through the establishment of sound agreements in the hydropolitical arena.
In other words, a "baby-step" approach to politics should be applied: peaceful discussions on this and other matters leveraged to talk about other sources of conflict and utilized to improve political relations between two parties. The Korean conflict is a good example: although both Koreas are far from agreeing with regards to their political outlook, they have been able to cooperate in other fields, such as the Winter Olympic games. Communication during the games was used to subtly suggest avenues for a political reapproachment, which now seems to be progressing satisfactorily.
As for multilateral-bilateral conditions of negotiations, it is important to take into account the fact that the Jordan River basin, mainly due to its geological condition as a watershed, has to be shared by several different countries, five to be exact. This may seem obvious but clearly many actors don't see its implications.
Understandably, it is very difficult for a state to manage various bilateral agreements concerning the same asset with countries that are mutually at odds with one another. Their contents can overlap, creating contradictions and making the achievement of a general arrangement not only disorganized, but also challenging. Notwithstanding, a multilaterally agreed distribution of the basin's water - taking into account the necessities of all riparians simultaneously, could more easily pave the way for further cooperation on other, pressing, political issues.
Last but not least, it is important not to forget about policies related to other regional affairs, and their potential effect on water management. Climate change, for instance, will certainly affect water availability in the MENA region and the Jordan River basin, easily disrupting and modifying past and future agreements on the resource's allocation and distribution. Attention should also be paid to interest groups and to the economic situation of the countries involved in the negotiations, as these will be determinant in states' decisions about the implementation of certain future projects.
![Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman and President Donald Trump during a meeting in Washington in 2017 [White House] Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman and President Donald Trump during a meeting in Washington in 2017 [White House]](/documents/10174/16849987/women-arabia-saudi-blog.jpg)
▲Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman and President Donald Trump during a meeting in Washington in 2017 [White House]
ANALYSIS / Naomi Moreno
Saudi Arabia used to be the only country in the world that banned women from driving. This ban was one of the things that the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) was best known for to outsiders not otherwise familiar with the country's domestic politics, and has thus been a casus belli for activists demanding reforms in the kingdom. Last month, Saudi Arabia started issuing the first driver's licenses to women, putting into effect some of the changes promised by the infamous Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman (MBS) in his bid to modernize Saudi Arabian politics. The end of the ban further signals the beginning of a move to expand the rights of women in KSA, and builds on piecemeal developments that took place in the realm of women's rights in the kingdom prior to MBS' entrance to the political scene.
Thus, since 2012, Saudi Arabian women have been able to do sports as well as participate in the Olympic Games; in the 2016 Olympics, four Saudi women were allowed to travel to Rio de Janeiro to compete. Moreover, within the political realm, King Abdullah swore in the first 30 women to the shura council − Saudi Arabia's consultative council − in February 2013, and in the kingdom's 2015 municipal elections, women were able to vote and run for office for the first time. Finally, and highlighting the fact that economic dynamics have similarly played a role in driving progression in the kingdom, the Saudi stock exchange named the first female chairperson in its history − a 39-year-old Saudi woman named Sarah Al Suhaimi − last February.
Further, although KSA may be known to be one of the "worst countries to be a woman", the country has experienced a B breakthrough in the last 5 years and the abovementioned advances in women's rights, to name some, constitute a positive development. However, the most visible reforms have arguably been the work of MBS. The somewhat rash and unprecedented decision to end the ban on driving coincided with MBS' crackdown on ultra-conservative, Wahhabi clerics and the placing of several of the kingdom's richest and most influential men under house arrest, under the pretext of challenging corruption. In addition, under his leadership, the oil-rich kingdom is undergoing economic reforms to reduce the country's dependency on oil, in a bid to modernize the country's economy.
Nonetheless, despite the above mentioned reforms being classified by some as unprecedented, progressive leaps that are putting an end to oppression through challenging underlying ultra-conservatism traditions (as well as those that espouse them), a measure of distrust has arisen among Saudis and outsiders with regards the motivations underlying the as-of-yet seemingly limited reforms that have been introduced. While some perceive the crown prince's actions to be a genuine move towards reforming Saudi society, several indicators point to the possibility that MBS might have more practical reasons that are only tangentially related to progression for progression's sake. As the thinking goes, such decrees may have less to do with genuine reform, and more to do with improving an international image to deflect from some of the kingdom's more controversial practices, both at home and abroad. A number of factors drive this public scepticism.
Reasons for scepticism
The first relates to the fact that KSA is a country where an ultraconservative form of shari'a or Islamic law continues to constitute the primary legal framework. This legal framework is based on the Qur'an and Hadith, within which the public and many private aspects of everyday life are regulated. Unlike in other Muslim majority countries, where only selective elements of the shari'a are adopted, Wahhabism – which is identified by the Court of Strasbourg as a main source of terrorism − has necessitated the strict adherence to a fundamentalist interpretation of shari'a, one that draws from the stricter and more literal Hanbali school of jurisprudence. As such, music and the arts have been strictly controlled and censored. In addition, although the religious police (more commonly known as the Committee for the Promotion of Virtue and the Prevention of Vice) have had their authority curbed to a certain degree, they are still given the authority to enforce Islamic norms of conduct in public by observing suspects and forwarding their findings to the police.
In the past few years, the KSA has been pushing for a more national Wahhabism, one that is more modern in its outlook and suitable for the kingdom's image. Nevertheless, the Wahhabi clergy has been close to the Al Saud dynasty since the mid-18th century, offering it Islamic legitimacy in return for control over parts of the state, and a lavish religious infrastructure of mosques and universities. Therefore, Saudi clerics are pushing back significantly against democratization efforts. As a result, the continuing prevalence of a shari'a system of law raises questions about the ability of the kingdom to seriously democratise and reform to become moderate.
Secondly, and from a domestic point of view, Saudi Arabia is experiencing disharmony. Saudi citizens are not willing to live in a country where any political opposition is quelled by force, and punishments for crimes such as blasphemy, sorcery, and apostasy are gruesome and carried out publicly. This internal issue has thus embodied an identity crisis provoked mainly by the 2003 Iraq war, and reinforced by the events of the Arab Spring. Disillusionment, unemployment, religious and tribal splits, as well as human rights abuses and corruption among an ageing leadership have been among the main grievances of the Saudi people who are no longer as tolerant of oppression.
In an attempt to prevent the spill over of the Arab Spring fervor into the Kingdom, the government spent $130 billion in an attempt to offset domestic unrest. Nonetheless, these grants failed to satisfy the nearly 60 percent of the population under the age of twenty-one, which refused to settle. In fact, in 2016 protests broke out in Qatif, a city in Saudi Arabia's oil-rich, eastern provinces, which prompted Saudis to deploy additional security units to the region. In addition, in September of last year, Saudi authorities, arguing a battle against corruption and a crack down on extremism, arrested dozens of people, including prominent clerics. According to a veteran Saudi journalist, this was an absurd action as "there was nothing that called for such arrests". He argued that several among those arrested were not members of any political organization, but rather individuals with dissenting viewpoints to those held by the ruling family.
Among those arrested was Sheikh Salman al-Awdah, an influential cleric known for agitating for political change and for being a pro-shari'a activist. Awdah's arrest, while potentially disguised as part of the kingdom's attempts to curb the influence of religious hardliners, is perhaps better understood in the context of the Qatar crisis. Thus, when KSA, with the support of a handful of other countries in the region, initiated a blockade of the small Gulf peninsula in June of last year, Awdah welcomed a report on his Twitter account suggesting that the then three-month-old row between Qatar and four Arab countries led by Saudi Arabia may be resolved. The ensuing arrest of the Sheikh seems to confirm a suspicion that it was potentially related to his favouring the renormalization of relations with Qatar, as opposed to it being related to MBS' campaign to moderate Islam in the kingdom.
A third factor that calls into question the sincerity of the modernization campaign is economic. Although Saudi Arabia became a very wealthy country following the discovery of oil in the region, massive inequality between the various classes has grown since, as these resources remain to be controlled by a select few. As a result, nearly one fifth of the population continues to live in poverty, especially in the predominantly Shi'a South where, ironically, much of the oil reservoirs are located. In these areas, sewage runs in the streets, and only crumbs are spent to alleviate the plight of the poor. Further, youth opportunities in Saudi Arabia are few, which leaves much to be desire, and translates into occasional unrest. Thus, the lack of possibilities has led many young men to join various terrorist organizations in search of a new life.
|
Statement by MBS in a conference organized in Riyadh in October 2017 [KSA] |
Vision 2030 and international image
In the context of the Saudi Vision 2030 , the oil rich country is aiming to wean itself of its dependence on the natural resource which, despite its wealth generation capacity, has also been one of the main causes of the country's economic problems. KSA is facing an existential crisis that has led to a re-think of its long-standing practice of selling oil via fixed contracts. This is why Vision 2030 is so important. Seeking to regain better control over its economic and financial destiny, the kingdom has designed an ambitious economic restructuring plan, spearheaded by MBS. Vision 2030 constitutes a reform programme that aims to upgrade the country's financial status by diversifying its economy in a world of low oil prices. Saudi Arabia thus needs overseas firms' investments, most notably in non-oil sectors, in order to develop this state-of-the-art approach. This being said, Vision 2030 inevitably implies reforms on simultaneous fronts that go beyond economic affairs. The action plan has come in at a time when the kingdom is not only dealing with oil earnings and lowering its reserves, but also expanding its regional role. As a result, becoming a more democratic country could attract foreign wealth to a country that has traditionally been viewed in a negative light due to its repressive human rights record.
This being said, Saudi Arabia also has a lot to do regarding its foreign policy in order to improve its international image. Despite this, the Saudi petition to push the US into a war with Iran has not ceased during recent years. Religious confrontation between the Sunni Saudi autocracy and Iran's Shi'a theocracy has characterized the geopolitical tensions that have existed in the region for decades. Riyadh has tried to circumvent criticism of its military intervention in the Yemen through capitalizing on the Trump administration's hostility towards Iran, and involving the US in its campaign; thus granting it a degree of legitimacy as an international alliance against the Houthis. Recently, MBS stated that Trump was the " best person at the right time" to confront Iran. Conveniently enough, Trump and the Republicans are now in charge of US' foreign affairs. Whereas the Obama administration, in its final months, suspended the sale of precision-guided missiles to Saudi Arabia, the Trump administration has moved to reverse this in the context of the Yemeni conflict. In addition, in May of this year, just a month after MBS visited Washington in a meeting which included discussions regarding the Iran accords, the kingdom has heaped praise on president Trump following his decision to withdraw from the Iran nuclear deal.
All things considered, 2018 may go down in history as the irreversible end of the absolute archaic Saudi monarchy. This implosion was necessitated by events, such as those previously mentioned, that Saudi rulers could no longer control or avoid. Hitherto, MBS seems to be fulfilling his father's wishes. He has hand-picked dutiful and like-minded princes and appointed them to powerful positions. As a result, MBS' actions suggest that the kingdom is turning over a new page in which a new generation of princes and technocrats will lead the breakthrough to a more moderate and democratic Saudi Arabia.
New awareness
However, although MBS has declared that the KSA is moving towards changing existing guardianship laws, due to cultural differences among Saudi families, to date, women still need power of attorney from a male relative to acquire a car, and risk imprisonment should they disobey male guardians. In addition, this past month, at least 12 prominent women's rights activists who campaigned for women's driving rights just before the country lifted the ban were arrested. Although the lifting of the ban is now effective, 9 of these activists remain behind bars and are facing serious charges and long jail sentences. As such, women continue to face significant challenges in realizing basic rights, despite the positive average endorsement that MBS' lifting of the driving ban has received.
Although Saudi Arabia is making an effort in order to satisfy the public eye, it is with some degree of scepticism that one should approach the country's motivations. Taking into account Saudi Arabia's current state of affairs, these events suggest that the women's driving decree was an effort in order to improve the country's external image as well as an effort to deflect attention from a host of problematic internal and external affairs, such as the proxy warfare in the region, the arrest of dissidents and clerics this past September, and the Qatari diplomatic crisis, which recently "celebrated" its first anniversary. Allowing women to drive is a relatively trivial sacrifice for the kingdom to make and has triggered sufficient positive reverberations globally. Such baby steps are positive, and should be encouraged, yet overlook the fact that they only represent the tip of the iceberg.
As it stands, the lifting of the driving ban does not translate into a concrete shift in the prevailing legal and cultural mindsets that initially opposed it. Rather, it is an indirect approach to strengthen Saudi's power in economic and political terms. Yet, although women in Saudi Arabia may feel doubtful about the government's intentions, time remains to be their best ally. After decades of an ultraconservative approach to handling their rights, the country has reached awareness that it can no longer sustain its continued oppression of women; and this for economic reasons, but also as a result of global pressures that affect the success of the country's foreign policies which, by extension, also negatively impact on its interests.
The silver lining for Saudi woman is that, even if the issue of women's rights is being leveraged to secure the larger interests of the kingdom, it continues to represent a slow and steady progression to a future in which women may be granted more freedoms. The downside is that, so long as these rights are not grafted into a broader legal framework that secures them beyond the rule of a single individual − like MBS − women's rights (and human rights in general) will continue to be the temporary product of individual whim. Without an overhaul of the shari'a system that perpetuates regressive attitudes towards women, the best that can be hoped for is the continuation of internal and external pressures that coerce the Saudi leadership into exacting further reforms in the meantime. As with all things, time will tell.
![signature of the agreement in Cartagena, in September 2016, before the referendum that rejected it and led to some modifications to the text [Government of Chile] signature of the agreement in Cartagena, in September 2016, before the referendum that rejected it and led to some modifications to the text [Government of Chile]](/documents/10174/16849987/colombia-elecciones-paz-blog.jpg)
▲signature of the agreement in Cartagena, in September 2016, before the referendum that rejected it and led to some modifications to the text [Government of Chile]
ANALYSIS / Camila Oliveros
The agreement The peace agreement signed on November 26, 2016 between the Colombian government and the FARC (Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia) is one of the most decisive issues in the elections of June 17, in its second round, and of the next presidential term.
After lengthy negotiations between the government and the FARC in Havana, and the introduction of modifications to the text initially agreed, following the triumph of the "no" vote in the plebiscite, the agreement The peace agreement was finally signed in November 2016. The long duration of the negotiations and the result of the plebiscite show that the agreement The 52-year conflict has resulted in the deaths of 220,000 people and the forced displacement of nearly 6 million, as well as 25,000 disappeared and nearly 30,000 kidnapped.
Clearly, all Colombians yearn for a lasting peace, but while some believe that what was drafted in Havana is the solution to achieve that peace, others believe that several modifications can still be made to the text. The decision on that and on the speed of the implementation of the agreement it is in the hands of the next president.
Degree Implementation
For now, after more than a year of the signature of the agreement In the end of the Conflict, both negative and positive elements can be highlighted in the implementation of what was agreed in Havana. According to the Observatory for Monitoring the Implementation of the agreement at the beginning of 2018, before the country entered the long electoral process in which it finds itself, only 18.3% of the agreement. That's a relatively small number. leave, which may be partly due to insufficient financial and human resources to implement the agreements quickly and effectively, rather than a lack of commitment on the part of the Government.
However, in the face of this low percentage of what has already been implemented, there are other figures that show that the agreement It's having some positive results. This is the case of the decrease in the homicide rate in Colombia. This became one of the lowest in thirty years, with 24 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants. In addition, the issue The number of displaced persons fell by almost half, from 91,045 displaced persons in 2016 to 48,335 in 2017, according to the Victims Unit. The issue The number of displaced persons had already been declining significantly in previous years, even at a faster rate: in 2002 the figure had been 757,240; in the following 14 years there was a decrease of 47,598 people on an annual average, including the 8 years of the presidency of Álvaro Uribe, who has been the great opponent of the terms of the agreement of peace.
Also the issue The number of victims of landmines has decreased, from 72 in 2016 to 58 in 2017, which has helped to generate a climate of greater trust in rural communities.
It is important to note that in the areas that had been most affected by the armed conflict, agreement with the provisions of the agreement It has been possible to set up new companies that benefit from the mechanisms envisaged for the "areas most affected by the armed conflict" or Zomac. However, these companies find themselves in a complicated environment, because although the FARC has completed the various phases of its demobilization, such as the submission and the return of recruited minors, FARC dissidents and other drug trafficking groups continue to operate in various areas.
Although there has been some progress, most of the implementation of the agreement. How do the two presidential candidates, Iván Duque and Gustavo Petro, deal with it?
Duque or Petro
Iván Duque is a lawyer and politician who has been a senator of the Republic for the Democratic Center, a party headed by former President Uribe, a great opponent of the agreement of peace. That has led many to think that if Duque becomes president, he will leave the agreement of Havana, without complying with it in his four years in office. His proposal is aimed at improving the Economics, reducing taxes on large companies, financing young entrepreneurship and prioritizing investment. In addition, it promotes a major reform of the Colombian justice system.
Gustavo Petro is an economist and politician, but he is also a demobilized member of the M-19 guerrilla group. He is from the center-left Progressive Movement political party. Petro proposes a model that focuses on "changing the model extractivist approach" and to promote agricultural policies. The central axes of its proposal are in the public sphere, fully guaranteed the rights to health, Education "quality, pluralistic, universal and free".
Colombia has never chosen a candidate He is a leftist to be president of the Republic, perhaps because the left is identified with communism and that associates it with the FARC. In any case, Petro has not been against the Havana agreements, and that makes him attractive to many Colombians who want to preserve what was agreed in 2016, in the hope of ending the armed conflict experienced by the country.
The truth is that it is difficult to legally go back on the agreement A constitutional reform established that the next three governments are obliged to comply with the agreement. If Duque wins, the agreement of peace may be subject to further changes, but in no way is Duque synonymous with war and Petro synonymous with peace.
As Duque has said, making certain modifications to the agreements is not ending them. The candidate of the Democratic Center maintains that the agreement It must have certain adjustments that allow for the achievement of a peace that is "credible, sustainable and based on justice". Of agreement With his proposals, the main changes he would promote would be the following two:
Special Jurisdiction and Political Participation
The first has to do with the Special Jurisdiction for Peace (JEP), since Iván Duque in his government plan seeks to simplify the Colombian justice system, going from the current six courts to just one, with the aim of simplifying the Colombian justice system. purpose to achieve greater speed and efficiency in judicial processes. However, with this change, power can be seen as highly concentrated and centralized. A modification of the JEP provided for in the agreement The peace crisis may cause some uncertainty among the former guerrillas, with whom a certain leniency had been agreed.
On the other hand, the big change that Duque could make has to do with political participation. He believes that former FARC members who have been responsible for crimes against humanity cannot be brought to justice. congress without having served a sentence. Duque assures that he does not seek to do away with point 2 of the agreement of peace, which talks about the political participation of former guerrillas in the congress. If a member of the congress A conviction for such a crime is upheld subject, he should leave his seat and be replaced by someone of his own group that he does not have any crimes against humanity.
Although in the event of winning the elections, Gustavo Petro will not propose special modifications to the agreements, whoever the next president is will have serious challenges in relation to the peace process.
|
Party in Tolima in memory of the victims of the conflict [Victims Unit] |
Most Important Challenges in the Next Presidential Term
The presence of FARC dissidents in border areas of the country is one of the challenges that the next president will face; Not only because of security issues, but also because of its link to drug production, which has increased by 52%. The Government is aware that about 10 per cent of the FARC fighting force has remained in the armed struggle, representing a total of at least 700 individuals, although other entities even double that figure. This dissident group is active in fifteen different groups, which have been concentrated in areas of the country such as Nariño, Norte de Santander and Cauca. In addition, another of the armed groups, the ELN (National Liberation Army), has begun to increase its presence in certain border areas, such as Norte de Santander. This not only poses a threat to Colombian security, but could also trigger a war between guerrilla groups and organized crime for control of the illegal coca production and drug trafficking business.
Faced with the continued presence of armed groups in part of Colombian territory, both candidates defend the increase in military personnel in conflict zones. However, in the face of the eradication of illegal crops, Iván Duque advocates the use of glyphosate, a strong herbicide whose employment it is rejected by Gustavo Petro on the grounds of its environmental effects. The use of this chemical, which is controversial in Colombia, could be seen as an effective way to eradicate illicit crops if their contamination is counteracted, for example, by planting new trees in areas where coca production can be eradicated. In any case, some environmentalists have used the negative image of glyphosate to ask for a vote for Petro in the second round of elections.
Another of the great challenges that the next president is going to face is the topic of the Special Jurisdiction for Peace. The JEP is a body that is in charge of judging former guerrillas. It has judicial powers and "represents the backbone of the agreements signed". It is composed of five organs, each responsible for ensuring that essential parts of the agreement: "The conference room of Truth and Responsibility, the conference room of Amnesty and Pardon, the conference room Definition of Legal Situations, the research and indictment, and the tribunal for peace." The JEP is a complex body that depends especially on the progress of the peace process. In fact, one of the reasons for the major delays in the implementation of the agreement It has been slow in the constitution of this institution, which did not begin to function until last January. However, the obstacles suffered by the JEP have not only had to do with lack of activity, but also with issues such as the case of Jesús Santrich.
Santrich, one of the guerrilla leaders, who was a negotiator in Havana on behalf of the FARC and received one of the positions assigned to the new party in the congress, was arrested in April on charges of participating in a scheme to bring 10 tons of cocaine into the United States. Based on a research of the DEA, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, U.S. judicial authorities requested his arrest and are now awaiting his extradition. However, considering that all FARC members must be tried by the JEP, and that this body does not contemplate extradition, Jesús Santrich could not be handed over to the United States. In addition, at the moment there is no evidence of when the alleged drug trafficking crimes were committed, so for now it has not been possible to determine whether they occurred before or after the creation of the JEP. The former guerrilla is imprisoned in a Bogota jail and the FARC insists that he be released. The next president will have to determine how to proceed with the case. This is also a sample that there are gaps in the agreement, which generates a lot of uncertainty and gives room for the next president to take several directions.
Beyond Peace
On June 17, in the second round of the presidential election between Iván Duque and Gustavo Petro, the future of Colombia will be decided. As much as many Colombians believe that the decision is between war or peace, it is wrong to say this. As discussed above, the agreement It is very difficult to go back legally. The substance of the agreement must be respected by the next three governments. Even if it's true that with the candidate of the Democratic Center in power on agreement may undergo more modifications than would be applied by the candidate of the Progressive Movement, the possibility of consolidating peace remains open with either of them. Beyond peace, what is also at stake is the model of Colombian society. Although peace is one of the most important issues, the next president must not leave behind other important elements such as corruption, security, trade and poverty. Economics in the 2018-2022 presidential term of the Republic of Colombia. Candidates' position on these issues should also influence voters.
![ISIS Toyota convoy in Syria [ISIS video footage] ISIS Toyota convoy in Syria [ISIS video footage]](/documents/10174/16849987/toyota-blog.jpg)
▲ISIS Toyota convoy in Syria [ISIS video footage]
ANALYSIS / Ignacio Yárnoz
When you go to a Toyota distributor to buy a Toyota Land Cruiser or a Toyota Hilux, what they proudly tell you is how resistant, fast and reliable the truck is. However, what they do not tell you is how implicated in wars and conflicts the truck has been due to the very same characteristics. We have seen in recent newscasts that in many of today's conflicts, there's a Toyota truck; no matter how remote the country is. This is because, if the AK47 is the favourite weapon for militias in developing countries, the Toyota Hilux and Land Cruiser are the militia's trucks of choice.
This is no surprise when one considers that the Toyota Land Cruiser was initially designed to be a military car inspired by the famous Jeep Willis at the time Japan was occupied by the US after Japan's defeat in World War II. However, its popularity among terrorist groups, militias, as well as developing countries' national armies only gained ground in the 80's when a conflict between Chad and Libya proved the trucks' effectiveness as war machines; simultaneously calling into question the efficacy of traditional war strategies and military logistics.
This little-known story is about how an army comprising 400 Toyota pickups of the Chadian army outmanoeuvred and overwhelmed a vastly superior force equipped with soviet-era tanks and aircrafts of the Libyan army. The historical event demonstrated how a civilian truck was able to shape international borders, tipping the balance in favour of the inferior party to the conflict.
The Toyota War
The Toyota War is the name given to the last phase of the Chad-Libyan War that raged on for almost a decade, yet did not have relevance until its last phase. This last phase began in 1986 and ended a year later with a heavy defeat inflicted on the Libyan army by the Chadians. In total, 7,500 men were killed and 1.5 billion dollars worth of military equipment was destroyed or captured. Conversely, Chad only lost 1,000 men and very little military equipment (because they hardly had any).
The last phase of the conflict developed in the disputed area of the North of Chad, an area that had been occupied by Libyan forces in 1986 due to its natural resources such as uranium (highly interesting for Gadhafi and his nuclear armament project). At the beginning of 1987, the last year of the war, the Libyan expeditionary force comprised 8,000 soldiers, 300 T-55 battle tanks, multiple rocket launchers and regular artillery, as well as Mi-24 helicopters and sixty combat aircrafts. However, the Libyan soldiers were demotivated and disorganized. The Chadians, on the other hand, had nothing but 10,000 brave and motivated soldiers with neither air support nor armoured tanks. However, by 1987, Chad could count on the French Air Force to keep Libyan aircraft grounded but, perhaps more importantly, a 400 Toyota pickups fleet equipped with MILAN (Missile d ́infanterie léger antichar) anti-tank guided missiles sent by the French Government. Additionally, it could also be equipped with .50 calibre machine guns, with archaic flak cannons for anti-air purposes or even rocket clusters to be used as WWII-style artillery.
This logistical combination proved to be superior to that employed by the Libyan army as Toyota pickup trucks could easily outmanoeuvre the heavily armoured Russian tanks. Whereas the latter consumed around 200 L/100 km, the Toyota trucks consumed a fraction, at 10L/100 km. In addition, Toyota Trucks could mobilize groups of 20 people in a single truck, enabling faster transport and deployment of troops to the conflict scene; an advantage the Russian tanks did not have.
Reminiscent of the Maginot line when the Nazi army challenged the old trenches system utilizing a fixed artillery method with the innovative Thunder war strategy, the Chad Army emerged victorious over the Libyans through a simple strategic innovation in military logistics. Something clearly demonstrated in the Battle of Fada. In this instance, a Libyan armoured brigade defending Fada was almost annihilated: 784 Libyans and CDR (Democratic Revolutionary Council) militiamen died, 92 T-55 tanks and 33 BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicles were destroyed, and 13 T-55s and 18 BMP-1s were captured, together with the 81 Libyan soldiers operating them. Chadian losses, on the other hand, were minimal: only 18 soldiers died and three Toyotas were destroyed.
All in all, this situation was one of the first deployments of the Toyota Hilux in a conflict zone, demonstrating the reliability of the truck and its high performance in harsh environments. A testament to the Toyota's endurance was its featuring in the famous TV show "Top Gear" where a 1980's Toyota Hilux was put to a wrecking ball, set on fire, submerged in a sea bay for 5 hours, then left on the top of a building waiting its final demolishment, yet still rolled.
Ever since, Toyota trucks have been sighted in conflicts in Nicaragua, Ethiopia, Rwanda, Liberia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (CDR), Lebanon, Yemen, Sudan, and Pakistan and as the New York Times has reported, the Hilux remains the pirates' 'ride of choice.' The deployment of Daesh of a fleet of hundreds of Toyotas in Mosul in 2014 was a lasting testament of the trucks' durability.
|
Chad's troops during the war against Libya in the 1980s [Wikimedia Commons] |
Adaptability
How could the West deal with this issue? To deploy a massive fleet of Humvees? It would be naïve to attack an enemy with their own means. This hardly appears to constitute an effective solution. Humvees are already being substituted by JLTV (Joint Light Tactical Vehicle) due to their vulnerability to IED's (Improvised Explosive Devices); something insurgents are allowed to use but western countries are not due to international treaties and ethical values (how can a mine be designed such that it can distinguish a civilian truck from a Toyota driven by insurgents?). This proves the challenge that counterinsurgency policies (COIN) entail and the need to move to a next generation as far as COIN strategies are concerned.
The Toyota example is one of many that clearly signals a need for conventional state armies to adapt their logistical capabilities to better match the challenges of non-conventional warfare and insurgencies; the primary forms of conflict in which our nations are today engaged. The first lesson is clearly that the traditional focus on high power and the availability of resources is poorly suited to respond to contemporary insurgencies and military engagement with primarily non-state entities. Rather, there is a growing need for logistical versatility, combining both attack power and high manoeuvrability. The Toyota issue is an interesting example that illustrates how groups like Daesh have been able to mobilize an easily accessible, relatively non-expensive market commodity that has proven to be effective in lending the group precisely the kind of logistical aid required to successfully wage its insurgency. This being said, there are a number of dilemmas posed to nation states engaging in COIN strategies that prevent them from being able to employ the same methodology. Clearly there is a need to constantly engage in the adaptation of COIN strategies to respond to new threats and the surprising innovation of the adversary. However, COIN campaigns have been difficult to manage, and even harder to win, since time immemorial.
Recent research in political science and economics investigates a number of difficulties security forces face during conflicts with insurgent actors (Trebbi et al., 2017). Development and military aid spending have uneven effects, and conventional military strategies, including aerial bombardment, can erode civilian support for the COIN. Although states have historically used mass killings of non-combatants to undermine logistical support for guerrilla actors, evidence from modern insurgencies indicates that these measures may have the opposite effect: in some cases, such measures may encourage recruitment and mobilization (Trebbi et al., 2017). As such, the challenge is to constantly adapt to meet the requirements of contemporary warfare, whilst simultaneously assessing and remaining cognizant of the effects that COIN measures have on the overall campaign.
Adaptation through learning and innovation occurs on a much different time-scale than evolution. Although both involve information exchange with the environment and with elements within the system, evolution occurs over long periods of time through successive generations that have been able to successfully survive to changes (Hayden, 2013). Learning is the process of modifying existing knowledge, behaviours, skills, values, or preferences, and innovation involves the incorporation of a previously unused element into the system, or the recombination of existing elements in new ways.
Airstrikes
In the previous example of the conflict between Chad and Libya, it was mentioned that the Libyan army had its air force inoperative due to the presence of French air support. Another important point to make is that Toyotas may have been effective war machines for the terrain and surrounding environment, yet would nevertheless have been vulnerable to airstrikes had the Libyan army been able to engage air power against the Chadians. Air and space are part of the future of COIN strategies, despite composing only one element of them. They are our eyes (UAV systems), our way to get away or deploy forces (Chinook helicopters for example) and also the sword that can eliminate the threat (e.g. Predator drones). However, maintaining complete dominance over the battle space does not guarantee victory.
Due to the success of the air campaign in Operation Desert Storm, airpower seemed to be the predominating weapon of choice for future warfare. Yet, recent operations in Afghanistan and Iraq have called that assertion into question. Airstrikes in ground operations have proven to be controversial in small wars, especially when it comes to civilian casualties and its impact on civilian morale (an element that could enhance local support to insurgents). This is why, to win popular support, the US air force had to rethink its operations in Afghanistan and Iraq to win popular support (this also a result of Taliban and Pakistani propaganda and political pressure). Most recently, the US, along with France and the UK, have engaged in massive airstrikes on strategic infrastructure devoted to chemical development supposedly for a military use. Although being calibrated, proportional and targeted, those attacks have created a lot of internal discussion in the West and have divided society. As such, the future environment seems certain to further limit the kind of strikes it can make with airpower and missiles.
Consequently, technologically superior air assets nowadays face significant challenges in engaging dispersed and oftentimes unseen opponents. The Air Force must determine how modern airpower can successfully engage an irregular opponent. Air power, the "strategic panacea" of Western policymakers (Maxey, 2018), will no longer maintain the same utility that it does against rural insurgents. Although tactical Predator strikes and aerial reconnaissance may have shifted the street-to-street fighting against Daesh, such operations are severely limited within expansive megacities. The threat of civilian casualties is often too high, even for precision-guided munitions with limited blast radius. Further. buildings and layers of infrastructure often obscure a clear overhead view.
For 2030, the United Nations (UN) suggests that around 60 percent of global population will live in urban areas. There are 512 cities of at least one million inhabitants around the world, and this is expected to grow to 662 cities by 2030. Many of the megacities that will emerge will come from the developing world. That is why it is so urgent to design strategies to adapt to operating within metropolitan environments where small roads prevent large tanks to manoeuvre, where buildings give cover to heavy cannon targets and where one is more exposed to the crosshairs of insurgents taking cover in civilian infrastructure.
As U.S. Army Chief of Staff Gen. Mark Milley remarked in 2016; "In the future, I can say with very high degrees of confidence, the American Army is probably going to be fighting in urban areas. We need to man, organize, train and equip the force for operations in urban areas, highly dense urban areas, and that's a different construct. We're not organized like that right now".
In addition to this, National armies must be able to work through host governments, providing training, equipment and on-the-ground assistance to their local partners. The mere presence of a foreign army in the area often creates a negative perception among the local population and, unfortunately, in other cases, violent opposition. However, if the army patrolling the city wears the national flag, things change. Defeating an insurgency depends upon effective state building.
REFERENCES
Engel, P. (2018). These Toyota trucks are popular with terrorists — here's why. Business Insider. [Accessed 21 Apr. 2018].
S.L.P., I. (2018). The Toyota War in Syria. Instituto de Estrategia S.L.P. [Accessed 21 Apr. 2018].
Wang, A. (2018). How did the Toyota pickup become terrorists' favorite truck?. Quartz.
Maxey, L. (2018). Preparing for the Urban Future of Counterinsurgency.
Smallwarsjournal.com. (2018). Air and Space Power COIN / IW | Small Wars Journal.
Costas, J. (2018). The dark and warlike side of the Toyota Land Cruiser. Motorpasion.com.
Tomes, R. R. (2004). Relearning counterinsurgency warfare. Parameters, 34(1), 16-29.
Hayden, N. K. (2013). Innovation and Learning in Terrorist Organizations: Towards Adaptive Capacity and Resiliency. System Dynamics Society.
Ryan, A., & Dila, M. (2014). Disruptive Innovation Reframed: Insurgent Design for Systemic Transformation.
Trebbi, F., Weese, E., Wright, A. L., & Shaver, A. (2017). Insurgent Learning (No. w23475). National Bureau of Economic Research.
▲Viktor Orban, at a rally near the Romanian border in May 2017 [Károly Árvai/Hungarian government].
ANALYSIS / Elena López-Doriga
On April 8, 2018, parliamentary elections were held in Hungary for the renewal of the 199 members of the National Assembly, the only chamber of the Hungarian Parliament. The high turnout of 68.13% exceeded that of the 2010 elections, when 64.36% of the electoral roll turned out to vote, a record high not seen since 2002. Prime Minister Viktor Orban, in power since 2010, secured a fourth term, the third in a row, as his party, Fidesz, and its ally, the Christian Democratic People's Party, won 134 of the 199 seats. Orban, the longest-serving European leader as head of government after Angela Merkel, has in some respects become as influential a leader as the German chancellor.
These electoral data -the high turnout and the broad support achieved by a leader not well regarded by all in Brussels- raise some questions. Why has there been so much social mobilization at the time of voting? Why is the result of these elections in the spotlight of the European Union?
Historical background
Hungary is a country located in Central Europe bordering Austria, Croatia, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia and Ukraine. The second largest river in Europe, the Danube, crosses the entire country and divides the capital of Budapest into two different territories (Buda and Pest).
Hungary joined the European Union in 2004. This event was longed for by Hungarians as they saw it as an advance in their democracy, a step forward for the country's development and a rapprochement with the admired West. It was the desire to make a change of course in their history, since, after the breakup of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1918, the country lived under two totalitarian regimes since World War II: first under the rule of the Arrow Cross Party (fascist, pro-German and anti-Semitic), during which 80,000 people were deported to Auschwitz, and later by the occupation of the Soviet Union and its post-war policies. In those times individual freedoms and freedom of speech ceased to exist, arbitrary imprisonment became commonplace, and the Hungarian secret police carried out series of purges both within and outside the Party hierarchies. Thus, Hungarian society suffered great repression from the beginning of World War II in 1945, which did not stop until the fall of the Iron Curtain in 1989.
In economic terms, the transition from communism to capitalism was very hard for vast social sectors. From a centralized Economics with highly protected sectors and heavy agricultural subsidies, a particularly severe adjustment plan was adopted by the government elected in March 1990 in the first free elections.
Accession to the European Union symbolized a turning point in Hungary's history, in a process of incorporation to the West that was previously marked by entrance in NATO in 1999. Becoming part of the EU was the step towards the democracy that Hungary desired, and this broad social consensus was evidenced by the majority support that the accession obtained - 83% of the votes - in the referendum of 2003.
Hungary in the European Union
Becoming a new EU member had a positive impact on Hungary's Economics , leading to an obvious development and providing competitive advantages for foreign companies establishing a permanent presence in the country. But despite these appreciable advances and the enthusiasm shown by Hungary upon accession to the EU, the picture has changed a lot since then, so that Euroskepticism has spread markedly among Hungarians. In recent years, a strong disagreement with the Brussels policies adopted during the 2015 refugee crisis has emerged in the domestic public opinion.
That year, Brussels decided to relocate the 120,000 refugees who had arrived in Hungary (from Syria, who were moving along the Balkan route to Germany and Austria) and Italy (mostly from North Africa). To distribute the refugees, quotas were established, setting the issue number of refugees that each country should take in based on its size and GDP. The quota policy was challenged by the group Visegrad countries (Poland, Hungary, Czech Republic and Slovakia) and Romania. Hungary erected a fence several hundred kilometers long on its southern border and refused to accept the reception quotas.
This attitude of closing borders and refusing to take in refugees was criticized by the leaders of the Union, who went so far as to threaten these countries with sanctions. The difficulty of a consensus led to the signing in 2016 of a agreement with Turkey so that this country would retain the flow of Syrian refugees. In 2017 the quotas for the distribution through the EU of the refugees who had previously arrived expired, without fill in thus the relocation initially raised. Although the moment of greatest political confrontation on this issue in the EU has passed, the refugee crisis has created a great divergence between the two targeted blocs, eroding the supposedly common European project .
In light of this status, Hungary's parliamentary elections on April 8, 2018 were particularly important, as the citizens of that country were going to have the opportunity to pronounce themselves on the ongoing pulse between Budapest and Brussels.
The main candidates
Going into the election, the front-runner was the coalition of the conservative Fidesz party and the Christian Democratic People's Party, with 54-year-old Viktor Orbán as candidate. Orbán first came to prominence in 1989 when, at the age of 26, he defied the communist regime and began to champion liberal principles, making him a symbol of Hungarians' aspirations to break free from totalitarianism and embrace Western values. However, his return to power in 2010, after a first term in office between 1998 and 2002, was marked by a shift towards a conservative tendency, characterized by greater control over the Economics, the media and the judiciary. Orban claims to be an advocate of an "illiberal democracy": a system in which, although the Constitution may formally limit the powers of the Government, in internship certain freedoms such as freedom of speech or thought are restricted. Orban often puts to test the red lines of the EU by presenting himself as a defender of a "Christian Europe" and detractor of irregular immigration.
The party that intended to pose the main electoral challenge to Fidesz, taking away a good part of its voters, was surprisingly one located even further to the right: Jobbik (Movement for a Better Hungary), founded in 2003 and considered one of the most powerful extreme right-wing political organizations in the European Union. For years, this party did not hide its xenophobic, anti-Roma, anti-Semitic, nationalist and radically opposed to the prevailing political system in the EU, betting on a Hungary outside it. However, from 2013 onwards he moderated his language. While Orban was adopting an increasingly radical line, the leader of Jobbik, Gábor Vona, was tempering the positions of his party to present it as a conservative option, alternative to Fidesz, capable of attracting votes from the center. Gyöngyösi, one of the party's nationalist leaders, said: "We are the party of the 21st century, while Fidesz is from the last century and represents the old. The division between left and right no longer makes sense, it is part of the past, of the old politics".
On the other side of the political spectrum, a list formed by the Socialist Party(MSZP) and the center-left environmentalist party Parbeszed ("Dialogue"), headed by a leader of the latter, Gargely Karacsony, was running in the elections. The left-wing candidate had broad support from the MSZP, but not from his former colleagues in the environmentalist LMP party, from which he split five years ago, which could lead to a split vote.
|
Completed a second fence at the border with Serbia, in April 2017 [Gergely Botár/Hungarian government]. |
The election campaign
During the campaign there was speculation about a possible loss of votes for Fidesz due to a series of corruption scandals involving government officials accused of embezzling European aid money. Jobbik and other groups of civil service examination took advantage of this status to promote themselves as anti-corruption parties, focusing a good part of their campaign on this issue and advocating for an improvement of public services, especially healthcare.
However, the most prominent topic of the election campaign was not corruption, the malfunctioning of the public health system or low wages, but immigration. The Orbán government had refused to accept the refugee quotas imposed by the EU from Brussels, arguing that taking in migrants is a matter of domestic policy in which foreign organizations should not intervene. He insisted that Hungary has the right to refuse to receive immigrants, especially if they are Muslims, reiterating his rejection of multiculturalism, which he considers a mere illusion. Orbán was of the opinion that the refugees arriving at Hungary's gates were not fighting for their lives, but were economic migrants in search of a better life. Therefore, Orbán's political campaign was a clear message: Illegal immigrants in Hungary: yes or no? Who should decide about Hungary's future, the Hungarians or Brussels?
Reducing the electoral call to one question had the main effect of a broad social mobilization. According to civil service examination, Orbán used the topic of migration to draw popular attention away from widespread corruption.
Another point core topic in Fidesz's political campaign was the constant accusations against George Soros, whom Orbán identified as the main enemy of the State. Soros is an American billionaire, of Jewish-Hungarian origin, who through his Open Society Foundation (OSF) finances various NGOs dedicated to promote liberal, progressive and multicultural values in different parts of the world. In 1989 Soros funded Viktor Orban to study in England, and in 2010 he donated $1 million to his government to help with environmental cleanup after a chemical accident. But Soros' reputation in Hungary took a hit during the 2015 migration crisis. His advocacy of human attention to refugees ran up against Orban's attitude. During the campaign, the latter accused Soros of using OSF to "flood" Europe with a million migrants a year and undermine the continent's "Christian culture."
In addition, prior to the elections, Fidesz passed an amendment to the Hungarian higher Education law, which sets new conditions for foreign universities in Hungary, something that has been seen as a direct attack on the Central European University of Budapest. The Soros-funded institution is highly regarded for promoting critical thinking, liberal values and academic freedom. The new legislation threatens university autonomy, the free hiring of professors and the international character of degrees.
The European Commission showed its differences with the Orbán government on several of the issues that occupied the electoral campaign. Thus, it expressed its dissatisfaction with the new university law, considering that it is not compatible with the fundamental freedoms of the EU internal market, as it "would violate the freedom to provide services and the freedom of establishment". He also criticized that Orbán had not complied with the refugee quota, despite the ruling of the Court of Justice, and that he had campaigned using the disagreement he has with the EU for electoral purposes.
The result of the elections
In the April 8, 2018 elections, the Fidesz party (in its alliance with the Christian Democratic People's Party) won a third consecutive wide victory, even bigger than the previous one, with almost half of the popular vote (48.89%) and its third two-thirds absolute majority (134 out of 199 seats). It was the first time since the fall of communism in 1989 that a party had won three elections in a row.
The Jobbik party managed to become the leading party on civil service examination, coming in second place with 19.33% of the vote and 25 seats. However, its vote growth was minimal and it gained only two extra seats, remaining virtually stagnant at the 2014 figures. Jobbik's second place was rather propitiated by the weakness of the Hungarian Socialist Party (MSZP), whose debacle pushed it into third place, with 12.25% of the vote and 20 seats. It was the first time since 1990 that the MSZP did not come in first or second place, putting an end to the bipartisanship it had maintained with Fidesz since 1998.
On the other hand, since its return to government in 2010, Fidesz has significantly modified the electoral system, reducing the issue number of legislators from 386 to 199 and eliminating the second round, which does not favor the smaller parties, which could form alliances between rounds of voting. By securing two thirds of the chamber, Fidesz will be able to continue governing comfortably and reforming the Constitution to suit itself.
EU reaction
A week after the elections, tens of thousands of opponents took to the streets of Budapest, disagreeing with an electoral system described as "unfair", which has given Prime Minister Viktor Orban a landslide victory at the polls after a campaign based on a refusal to accept refugees.
The congratulatory letter that the president of the European committee , Donald Tusk, addressed to Orban was considered by various media to be cooler than the one issued on other similar occasions. The EU is concerned that Orban continues with his defense of an "illiberal" democracy and that he seems to be leading the country towards authoritarian tendencies. The government's purchase of many media outlets in recent years, in order to isolate civil service examination and make more propaganda, resembles what has happened in countries such as Russia and Turkey.
It is true that with Orban at the head of the government Hungary has grown economically at a good pace and that the middle classes have improved their status, but his latest victory has been due not only to the good economic management , but the defense of values that the Hungarian people consider important (essentialism, Christianity, respect for borders).
European socialists have not been pleased with Orban's new victory, insinuating that it is a setback for democracy in Hungary. The joy that the populist parties have expressed over his victory is test that Orban, whose training Fidesz still belongs to the European People's Party, has become an exponent of modern ultra-nationalism, which threatens democratic ideas of the European Union.
For the time being, Brussels is being cautious with Hungary, even more so than with the British Brexit, since Viktor Orban, seen by many as "the EU rebel", unlike the UK, wants to remain within the bloc, but change part of the ideals he represents.

▲Street art in the city of Medellín
ANALYSIS / María Gabriela Fajardo
Colombia experienced on March 11 the first elections held after signature in 2016 of the Peace agreement between the government and the guerrillas of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC). These elections to the country's bicameral congress - members of the Senate and the House of Representatives were elected - were the first occasion in which the different ideological sectors could measure their forces without the distortion of an armed struggle in significant parts of the territory. Traditionally, social rejection of the guerrilla campaign has been alluded to as an explanation for why the left in Colombia has usually enjoyed little popular support. Has the arrival of peace changed the correlation of political forces and has it led to an improvement in the electoral results of the left?
To answer these questions, we will examine the results obtained by the different political options, grouped into sections of the ideological spectrum (right, center-right, center-left and left), in the elections to congress held since the beginning of this century. An examination of the political composition of congress over the last decade and average will give perspective to the results of the March 11 legislative elections. These elections meant the integration of the FARC into the Colombian political party system, under a different name - Fuerza Alternativa Revolucionaria del Común - but with the same acronym.
In the 2002-2018 period there were also, in addition to the five elections to the congress, as many presidential elections. The latter are mentioned in the analysis because they help to clarify the contexts, but they are not included in the comparative work , given that the presidential elections are governed by more personalistic dynamics and complex vote transfers take place due to the double round process. The March 11 elections, however, provide considerations for the presidential elections of May 27.
Senate
The Parapolitics scandal distorted the reception of the results of the 2002 legislative elections, after paramilitary chief Salvatore Mancuso claimed that 35% of the elected congress were "friends" of his organization. The right wing, represented by the Liberal Party and the Conservative Party, won 41.1% of the Senate seats. This figure does not include the seats won by other minor political groups, among them Colombia Siempre, whose head of list was the current candidate presidential candidate Germán Vargas Lleras. The left, on the other hand, was quite fractioned, in groups such as Vía Alterna and Movimiento Popular Unido, and obtained 14% of the Senate seats. The center-left won 12.9% and the center-right 7%.
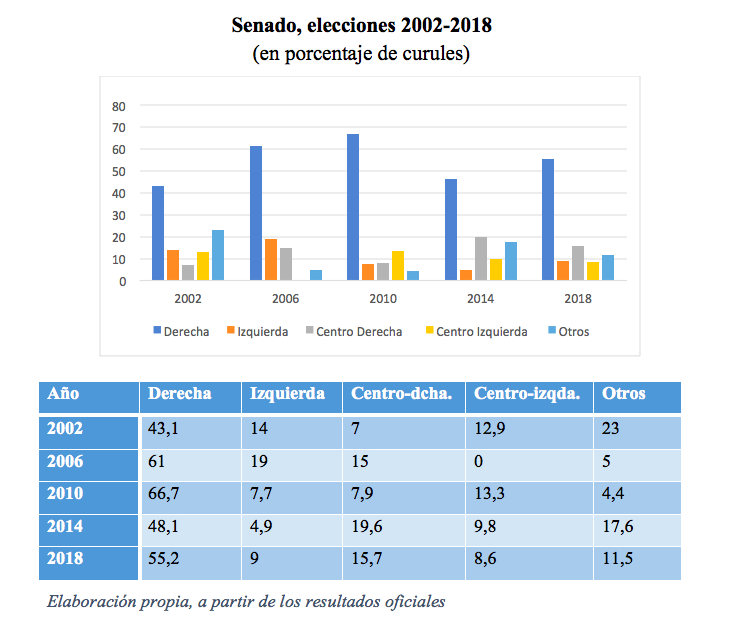 |
In the 2002 presidential elections, held a few months after the legislative elections, Álvaro Uribe became head of state, with the vote of 53.1% of the voters. Uribe ran as an independent candidate , after splitting from the Liberal Party, and had the support of much of the right and center-right, including Cambio Radical, Somos Colombia and the Conservative Party, which then did not participate in the presidential race.
Thus, in the 2006 legislative elections, a new party, the Partido Social de Unidad Nacional (better known as Partido de la U), created by Álvaro Uribe, played a major role. The Partido de la U won the elections, obtaining 20% of the seats: for the first time neither of the two traditional parties (Liberal and Conservative) had won result . The new party was here to stay, so that the right wing was now represented by three parties (de la U, Liberal and Conservative), with 61% of the senators. The left, although it increased to 19% of the Senate seats, was split into several political parties without weight and without the possibility of proposing drastic legislative changes. The center-right, represented by Cambio Radical, was in fourth place, with 15% of seats, while the center-left obtained none.
In 2010 the right wing reached its highest point, with 66.7% of the Senate seats, a figure that includes the three right-wing parties mentioned above and MIRA, a group with a smaller presence. These were moments of political dominance for Uribismo. In the electoral months of 2010, President Uribe was expressing his support to Juan Manuel Santos as candidate presidential. It was thought that he would continue Uribe's policies of confronting the guerrillas and organizing the security forces. However, after coming to power, Santos surprised by disassociating himself from Uribe and opening negotiations with the FARC in 2012, which led to the rupture of the relationship between the two politicians (El periodico, 2017). The strength demonstrated by the right in the 2010 legislative elections was accompanied by a great weakness of the left, which obtained only 7.7% of the Senate seats and would become the perfect ally of President Santos to carry out his diary and his journey towards the political center. The center-left had a representation of 13.3%, thanks to the push of the new Alianza Verde party, and the center-right remained at 7.9%.
 |
The 2014 legislative elections meant the consolidation of a new right-wing party, the Democratic Center, created by Uribe after his separation from the U Party, which had been left in the hands of Santos, who that year would win reelection as Colombian president. The Democratic Center came in second place in the Senate elections, with only one senator less than the U Party (Sanchez, 2018). In 2014, the right went on to control 48.1% of the Senate, from agreement with the ideological realignment of the party system. Thus, several experts came to classify the Partido de la U as center-right, label which they also began to grant to the Partido Liberal, in a political space shared with Cambio Radical; these three parties formed the "Unidad Nacional" (Castillo, 2018). With this, the center-right totaled 19.6% of the seats, while the center-left obtained 9.8%, due to the votes achieved by the Green Party and the Progressives, the latter led by Gustavo Petro, current presidential candidate . The left only reached 4.9%, represented by the minorities of the Polo Democrático, the Unión Patriótica, Marcha Patriótica and the groups that came from the demobilized guerrillas.
In the legislative elections of March 11, there was a reinforcement of right-wing positions, with the return of some parties which in previous elections had slid towards the center-right by defending the negotiation with the FARC and which now wanted to counteract the fear of part of the population of a rise of the radical left, in a very polarized electoral process. Thus, the right rose to 55.2% of the senators, led by those of the Democratic Center, while the center-right fell to 15.9%. The moderate and radical left increased their presence: the center-left rose to 11.5% and the left to 9%. This last percentage does not include the five seats guaranteed to the FARC, which despite not winning any senator electorally, will have those five seats guaranteed by the Peace Accords.
House of Representatives
The results in the 2002-2018 period of the elections for the House of Representatives, held simultaneously with those for the Senate, do not differ much from what was discussed in the previous epigraph; however, they present some variations that should be considered.
The institution was quite affected by parapolitics scandals, a factor that influenced the political polarization of the country, which would be reflected in the elections throughout this period. In 2002, the right won 47% of the seats in the House, with the Liberal Party having the largest representation; the left won 27.1%. From then on, the center-right, which in 2002 obtained 4.2% of the representatives (the center-left took 1.8%) began to take a certain configuration, as the contours of the two traditional parties -Conservative and Liberal- blurred with the division into factions, from which new parties would emerge; this ended the bipartisanship experienced in Colombia throughout the 20th century: the Conservative governed for 48 years and the Liberal for 13.
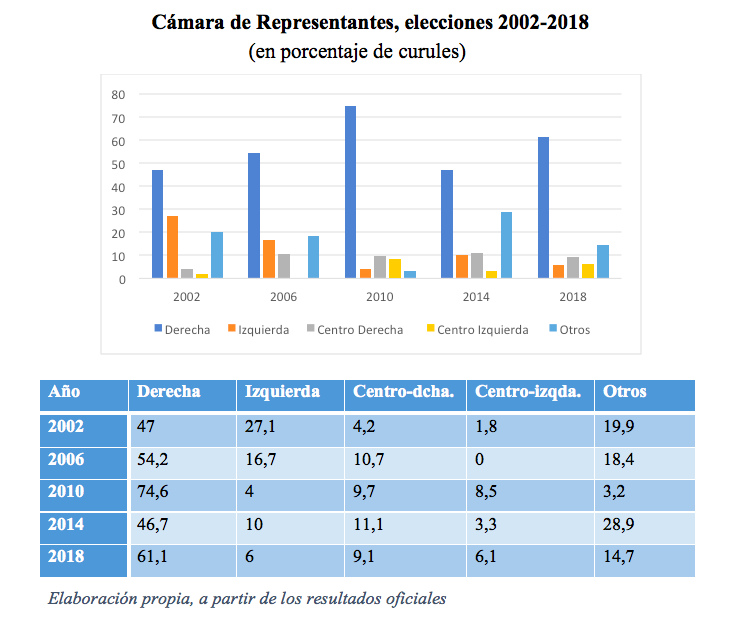 |
The emergence of the Partido de la U, led by Álvaro Uribe and the wide acceptance of his political figure (Uribe became president in 2002 and was reelected in 2006), led for the first time a party other than the two traditional ones to come in second place in the 2006 legislative elections, in which the Partido de la U won 16.7% of the seats in the Chamber, raising the representation of the right to 54.2%. For its part, the left dropped its representation to 16.7% and entered a period of special political weakness (these elections were not good for the center-left either, which did not obtain representation). At a time of President Uribe's successes against the guerrillas, with measures supported by a large part of the population, although not without controversy, the left-wing parties were weighed down by sharing certain ideological assumptions with the guerrillas, as political scientist Andrés Dávila of the Universidad de los Andrés Dávila of the Universidad de los Andres points out.
This dynamic led to an even greater increase of the right wing and a new decline of the left wing in the House of Representatives in 2010, in parallel with what happened in the Senate, in a year in which the candidate promoted by Uribe, Juan Manuel Santos, would also win the presidency. The Partido de la U was ahead of the Liberal Party and the Conservative Party in the House of Representatives, with these three right-wing parties accounting for 74.6% of the seats, the highest percentage of the entire period studied; the center-right party reached 9.7%. For its part, the left, whose largest party was the Polo Democrático, reached only 4%, its worst share in the period, minimally compensated by the maximum representation of the center-right, although this was a modest 8.5%.
The 2014 elections brought with them the presence of a new party headed by Uribe, the Democratic Center, which positioned itself to the right of the previous ones by positioning itself forcefully against the continuation of the peace dialogues with the FARC propitiated by President Santos (El periodico, 2017). The rupture between Santos and Uribe caused their electorate to split, so that in the elections to the House of Representatives the Liberal Party won, followed by the U Party, the Conservative Party and the Democratic Center. Taking into account the shift towards more moderate positions of some of these formations, when grouping them together we have that the right-wing advocates dropped to 46.7% of the seats in the House, while the center-right rose to 11.1%. The left, with the Polo Democrático, improved its representation somewhat to 10%, and the center-left languished at 3.3%.
Four years later, last March 11, the Liberal Party won again the elections to the House of Representatives, followed by the Democratic Center, the Radical Change, the U Party and the Conservative Party. Some of these formations returned during the electoral campaign to clear right-wing positions that they had previously moderated, so that the right wing added 61.1% of the seats (Sánchez, 2018), compared to 6% for the left. For its part, the center-right scored 9.1% and the center-left 6.1%. To these figures must be added the five seats in the House granted by the agreement de Paz to the FARC, which also failed to win any by citizen vote, as in the Senate. With this enlargement, the Colombian bicameral congress goes from 268 to 280 members (the ten members of the FARC party and two that will correspond to the presidential ticket that comes second in the presidential elections).
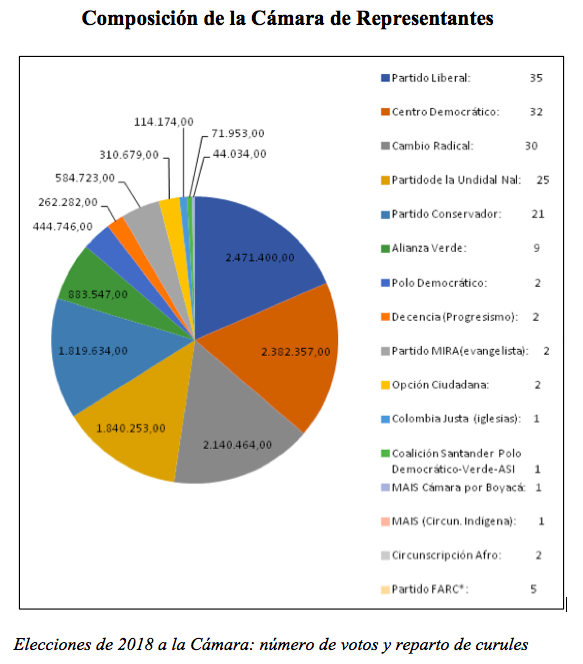 |
The division of the left
The analysis carried out allows us to affirm that right-wing political approaches have remained in the majority in Colombia so far this century, as was the case in previous decades, although no longer in the hegemonic framework of two major parties, but of a wider range of partisan options. In a period in which in many other Latin American countries there were turns to the left -notably, the Bolivarian revolutions- Colombia was a clear exception. In this time, the right in Colombia (not including the center-right) has controlled between 43.3% (2002) and 66.7% (2010) of the Senate seats and between 46.7% (2014) and 74.6% (2010) of those in the House of Representatives. In contrast, the left (not including the equally reduced center-left) has remained a minority: it has moved between 4.9% (2014) and 19% (2006) of the Senate, and between 4% (2010) and 27.1% (2002) of the House.
The 2016 Peace agreement and the integration of the FARC into political life have so far not led to a significant electoral boom of the left. In the legislative elections of March 11, 2018, the right actually recovered positions compared to 2014 in the two institutions of the Contreso, while the left, although it certainly improved its presence in the Senate, but far from the levels of 2002 and 2006, instead lost space in the Chamber.
The fear of broad sectors of the population that the political benefits granted to the FARC, such as guaranteed access to media or campaign financing, would contribute to an electoral advance of the ex-guerrillas did not materialize in these elections. The results of the October 2016 plebiscite, which rejected the agreement de Paz (this came into force in 2017 after some changes, without a new plebiscite), were again reflected in the past legislative elections: Colombians oppose the participation of former members of the belligerent group in politics. FARC candidates obtained only 0.28% of the votes. In addition, this party announced days before the legislative elections that it will not run in the presidential elections, for which the maximum leader of group, Rodrigo Londoño, was running as candidate .
Is Colombia a conservative country? Why has the left in Colombia been so weak electorally? These recurring questions about Colombian politics are not easy to answer. "The left is a sector that has traditionally been very much divided among doctrinal tendencies, for strategic reasons and even by personalities", explains Yeann Basset, director of the Observatory of Electoral Processes of the Universidad del Rosario.
It is worth highlighting what Fabio López, author of the book "Izquierdas y cultura política", said in response to the question of whether there is a left in Colombia:
"One thing is that we come from a defeat, internationally thought, of the left, an enormous setback of the workers' movement, a discrediting of socialist ideas, and another thing is the disappearance of the causes, of the structural reasons that motivate at international and national level some leftist ideas, some roots and some justifications, to appeal to the rescue or better restructuring, a new beginning of some leftist approaches in Colombia".
One of the reasons usually given to explain the difficulty of the left in gaining greater support is the negative weight of the guerrilla subversion. In Colombia, after the constant conflicts, massacres and the pain that the armed conflict has left on Colombians, leftist parties have not achieved the support of the society as in neighboring countries since there is a direct association of leftist party with the guerrillas and what comes with them. The arrival of political leaders such as Uribe to the presidency intensified this association and increased the taboo present today in a large part of the citizens of supporting a leftist party. At the same time, the left has not done much to repair this bad image; the great internal fragmentation and differences among political leaders have not helped the training of a solid left with the capacity to increase its representation in the congress.
Opportunity for the presidential election?
The presidential elections on May 27 are an opportunity for the left to improve its electoral results, which in any case could advance in the future to the extent that peace is consolidated and the past of violence can be forgotten.
The political polarization, which on other occasions has harmed the left, this time is assuming a certain unity of this ideological sector around the candidacy of Gustavo Petro, former mayor of Bogota. The celebration on March 11 of primaries on the right, won by the pro-Uribe Iván Duque, and on the left, won by Petro (Sánchez, 2018), have accentuated the polarization for the presidential elections, increasing citizen mobilization (in the legislative elections there were five more points of participation) and attracting media attention to both candidates. Polarization, at the same time, has reduced support to possible centrist alternatives, as divided as the left was before, so that it cannot be ruled out that Petro may go to a second round, on June 17. A victory against the odds for Petro, for which he should attract the bulk of the moderate electorate, would not mean a radical change in legislative policies, as the congress revalidated last March 11 the dominance of the right.

▲Transfer of migrants from North Africa to the Italian island of Lampedusa [Vito Manzani]
In late 2017, Cable News Network (CNN) published an anonymously recorded video with a hidden camera showing the sale of four men in Libya, for $400 each. It was an example of selling slaves to Libyan citizens for work or in exchange for a ransom, in the case of men, or as sex slaves, in the case of women. The shocking images triggered a global response; several Hollywood celebrities joined the protests calling for an end to the slave trade in Libya. France, Germany, Chad, Nigeria and other countries have urged Libya to address this serious problem through a programme to repatriate migrants and evacuate detention camps, where many of the slave mafias operate. Circumstances, however, do not appear to have improved since the video was posted, mainly due to the continued lack of state coordination to address the problem, along with other factors. How is it possible that a slave trade could have taken place inside Libya?
Libya is a sprawling country located in North Africa, with a long Mediterranean coastline. Until 2011, when the Arab Spring broke out, Libya was one of the most stable countries in the region. It had one of the highest life expectancies in all of Africa, and a educational –From the Education primary school through university – better than most neighbouring countries. However, this status The crisis of stability and relative prosperity came to an end in February 2011, when the uprisings that began in Tunisia, and had spread to countries such as Yemen, Jordan and Egypt, reached Libya.
Unlike other states in the region, which were able to peacefully resolve the protesters' demands, the immediate threat of civil war in Libya forced international intervention to resolve the conflict. The United States (US) and the European Union (EU), with the support of the United Nations (UN), acted against the dictatorial regime of Muammar Gaddafi. With the capture and assassination of Gaddafi by rebel troops, the war seemed to be over. However, in the absence of a viable plan for a political transition, the status it deteriorated further as various political actors attempted to fill the power vacuum left by Gaddafi's demise.
At present, Libya continues to experience severe political instability and is considered to be a failed state. Although there is a government promoted and recognized by the UN, the Government of National Unity (GNA), it does not control the entire country and is challenged by various power groups, many of which are armed militias. Due to this lack of governmental authority, as well as its strategic location on the Mediterranean coast, Libya has become the base of operations for mafias, which take advantage of the willingness of refugees and migrants to reach Europe via the Libyan land route. The open border policy launched by the EU in 2015 has not helped to curb its activities, as it has facilitated the establishment of human smuggling routes. The International Organization for Migration (IOM) estimates that at least 400,000 people are currently in Libyan detention centres, where migrants are a key threat to Libya. goal easy for the slave trade. The GUN has opened a research He has met with European and African leaders to enable the emergency repatriation of refugees and migrants. However, the effectiveness of the Libyan authorities' efforts is limited. A more important issue, however, is the role that the international community can play in alleviating the problem, of which non-governmental organizations (NGOs) have been voices core topic in the discussion.
Testimonials
Since 2015, Oxfam has been widely informing the international community about the migration crisis in Libya, emphasizing the need for European countries to seek and find a solution for the thousands of men, women and children suffering from this crisis status. Documented cases in Libya of the slave trade, carried out by smugglers and militias, have made the search for a solution even more urgent.
In the wake of this alarming status in Libya, on 9 August 2017, Oxfam published a bulletin graduate "You're Not Human Anymore," in which he analyzed the events of the status in Libya and blamed European countries for their "misguided policies aimed at preventing people from reaching Italy." To develop this report, Oxfam spoke "to men and women who have spent months being beaten, tied up like animals and sold as cheap labour in Libya's scandalous slave trade", and drew on the "... anguished testimonies of migrants who spent time in Libya before escaping to Italy."
The testimonies recount shocking scenes of sexual violence, torture and work slave; They also tell of cases of people who have been held captive because they could not pay the price demanded by the smugglers. The latter happened to Peter, an 18-year-old Nigerian: "Once we arrived in Sabah, in Libya, I was taken to the 'Ghetto' (...) They gave us a phone to call our families and ask them for money. If you couldn't pay the 1,500 Libyan dinars [about 100 euros], they held you captive and beat you."
After listening to these testimonies, Oxfam has concluded that European policies need to take into account the experiences of people forced to leave their homes, as the information they provide sample "Libya remains a country marked by systematic human rights abuses and (...) the EU's attempt to ensure that people cannot leave Libya only puts more men, women and children at risk of abuse and exploitation."
Some of the solutions that Oxfam has proposed include promoting search and rescue operations for humanitarian purposes, increasing the issue of immigration applications being accepted to be processed, the creation of safe routes to Europe, and ending the policy that prevents migrants from leaving Libya.
 |
Open, Close Borders
Another international agency that has actively denounced the status The most inhumane issue in Libya is Amnesty International. According to the data The world is facing one of the most serious cases of slavery in the twenty-first century. Refugees and migrants arriving in Libyan territory are detained and tortured in detention centres before being sold into slavery. Those who manage to escape such horrific conditions do not necessarily end up in better circumstances: at least 3,000 people have died trying to cross the Mediterranean.
Being one of the most active organizations with respect to the status in Libya, Amnesty International has order EU Member States to stop closing their borders to refugees and migrants from Libya. He argues that this European policy only encourages and fuels violence and extortion on Libyan territory, making the EU complicit in this crisis.
Amnesty International recalls that, since the end of 2016, the closure of European borders has led to increased control by the department Libya's Anti-Immigration Agency, which now oversees detention centers where refugees and migrants are not only arbitrarily and indefinitely detained, but also frequently sold into slavery. In addition, according to the organization, the inability or unwillingness of Europe to act, mistakenly believing that what happens outside European borders has no consequences for the EU's internal affairs, has allowed the Libyan Coast Guard to intercept people at sea. Instead of reaching the "promised land," migrants are forcibly taken back to Libya, where they are locked up and mistreated again in detention centers. All this is aided by the agreements reached by the EU and the local Libyan authorities, backed by armed groups, regarding the control of migratory flows to Europe.
International coordination
On December 7, 2017, the committee U.N. Security Council held an emergency session to take action on the status of the slave trade in Libya. This status was described as an "abuse of human rights that may also constitute crimes against humanity", in which case the Libyan authorities and all member states of the organization should act accordingly. agreement with the International Public Law bringing those responsible before the International Criminal Court (ICC). In addition, the UN pointed out at that session the Libyan authorities as one of the main actors complicit in the growing phenomenon of the slave trade, due to their ineffectiveness in investigating it and administering justice. The organization has also placed special emphasis on the need for the Government of Libya to secure the borders and for its actions to be supported by various international instruments, so that trafficking in persons can be effectively countered. The UN has also encouraged cooperation with the EU and the African Union (AU) to ensure the protection of refugees and migrants, under the premise that success will only be achieved if all actors involved collaborate.
Meanwhile, the UN is already operating in the territory through the International Organization for Migration (IOM), which has helped 13,000 people leave detention centers in Libya, and another 8,000 from those in Niger. But IOM's efforts do not end in Libya. Once refugees and migrants are safe, the organization stores their information and testimonies and offers them the possibility to return home, ensuring the safety of the people. attendance in the process.
Despite attempts to unify the efforts of all organizations on the ground, the reality is that the UN today does not have an all-inclusive action plan to end slavery in Libya and seek a common solution. According to the organization's reports, slavery in Libya could end by 2030, after 20 years of test and error. However, it is not surprising that most NGOs do not have action plans.
NGO solutions
NGOs play an important role in helping to alleviate the humanitarian problems caused by migration; However, the solutions they suggest often fail to take into account the complex political realities that make reaching those solutions impossible, if not entirely impossible, at least a challenge. How result, many of the proposals offered by human rights agencies such as Oxfam and Amnesty International are too broad to be useful internship. The migration crisis, which reached its peak in the summer of 2015 with the effective invitation of several European nations for refugees to migrate to Europe – along with the relaxation of Dublin regulations and the opening of borders within the EU – paradoxically helped to exacerbate the problem. These measures provided an incentive for mass migration of people who did not fall into the "refugee" category, encouraging risk-taking among immigrants on the premise that the borders would remain open and that all would be welcome.
The result it has not only been the rapid backtracking on this policy by a number of countries that initially supported it, such as Austria, but also a dramatic internal and diplomatic conflict within the EU between countries that are against mass migration to the territory of the Union. The crisis also shed light on the inability of existing laws of both the EU and its member states to find solutions to the migration problem. Thus, the policy of open borders as a solution to the problem may be well-intentioned, but ineffective in providing a balanced solution to the problem.
Similarly, ensure safe passages for migrants back to their homes. home country it is based on the assumption that there is a functioning government in Libya with which such efforts can be coordinated; however, no such entity exists as of yet. While the GUN has a limited amount of control over certain swaths of territory, the problem remains that in other parts of Libya this government exercises no control at all. While assisting (limited) migration and/or repatriation and securing land and sea borders could be a first step in stemming the flow, the fact remains that political instability in Libya – as well as in other nations – is what generates smuggling networks, one of which is the slave trade.
Therefore, the European policy of helping more people by relaxing borders hardly solves the problem. At its height, the migration crisis saw hundreds of thousands of migrants cross open borders in Europe, without any realistic plan to deal with the numbers. In addition, it seems that the international press is reporting less heavily on the various difficulties that immigrants face within their new host states such as result of a utopian politics in which the sky is the limit for immigration. More importantly, the open-door immigration policy – pushed by a number of humanitarian organisations – has also led to the proliferation of smuggling networks within Europe that have necessitated the establishment of new immigration forces. work to confront them, even though the result of this measure could be worse as greater control can lead to the emergence of new routes and access points. Almost 90% of migrants arriving in Europe are facilitated by the multinational smuggling business. The point is that illegal activities thrive as result of failed policies and the inability to find determined policy solutions to the migration crisis: a necessary ingredient for successful practical action.
The Primary Role of States
The lack of government control over territory in Libya, characteristic of a failed state, has made possible the proliferation of illegal and highly humiliating activities against human dignity, such as the slave trade. Images like the one on CNN, which provided evidence of people being sold into slavery in detention centers, have raised international awareness of the problem. Numerous organizations, led by the UN, have intensified their work in recent months to try to put an end to a status so disastrous. These efforts have achieved some results, however, there is no meaningful method to improve them because they are not coordinated at the state level, and the large-scale cooperation required by all parties involved is unlikely to be possible.
Moreover, the effects of the migration crisis are not unique to Libya or Africa, and have manifested themselves in Europe as well. Although human trafficking, both in the slave trade and for other purposes, occurs on a much larger (and rather alarming) scale in the African theatre, the phenomenon has affected Europe in a similar way as it has been in the African theatre. result of its failed – or non-existent – action plan to manage immigration, both internally and externally. The solution is necessarily political, and the reality is that, no matter how intentional and necessary, the independent and rights-based solutions advocated by NGOs will not be decisive in solving the problem. Only states, working together with various NGOs, can put an end to this misery through well-thought-out and coordinated solutions. And the sad reality is that not everyone can necessarily be saved in the process, nor will all immigrants be able to get their "European dream."

▲Lower Nile River, Egypt [Pixabay]
ANALYSIS / Albert Vidal [English version]
Disputes over control of rivers, lakes, and, in particular, final, are particularly alive today and will intensify in the near future, since, according to the World Health Organization, by 2025 half of the world's population will live in water-scarce areas. Currently, the countries with the most water reserves are Brazil, Russia, the United States, Canada, China, Colombia, Indonesia, Peru, India and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Most water available It is found underground, concentrated in aquifers, or surface water (rivers and lakes). The aquifers with the largest reserves are the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System (under the Sahara Desert), the Great Artesian Basin (in Australia), and the Guarani Aquifer (in South America). On the other hand, there are a number of rivers in the world that are of exceptional importance, simply because of the enormous amount of population and economic activity that depend on them. Problems arise when these rivers are not part of a single State, but are contiguous or transboundary rivers, and that leads to disputes between some States.
Flashpoints in Asia
Asia is being particularly affected by this problem. There are currently various tensions revolving around water control. One of the most significant cases concerns the use of water from the Indus River, which supports 300 million people and has caused tensions between Pakistan and India. This river is a resource vital for both countries. With the independence of Pakistan, the Indus became a source of disputes. This was addressed by the Indus Water Treaty (1960), which gave India the three eastern tributaries (the Sutlesh, the Ravi and the Beas) and Pakistan the three western rivers (the Indus, the Jhelum and the Chenab). But due to water scarcity, Pakistan has recently protested against the construction of dams on the Indian side of the river (in Indian-administered Kashmir), which restrict the water supply to Pakistan and reduce the flow of the river. India, for its part, defends itself by saying that such projects are covered by the Treaty; Still, tensions don't seem to be abating. For this reason, Pakistan has order the World Bank to appoint the president of an international arbitration tribunal in order to resolve the dispute. This problem of water reserves is at the heart of the confrontation in Kashmir: without an adequate supply, it would not take long for Pakistan to become a desert.
|
Watersheds in Central Asia [Wikimedia Commons–Shannon I] |
Indus River Basin [Wkiwand] |
In Asia, there is also the dispute over the Mekong River, which runs through Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos and Thailand. This conflict revolves around the construction of dams by various countries, as well as the exploitation of the resources provided by the Mekong River. Eleven dams along the river are planned, which would produce a large amount of electricity and be beneficial to some countries, but in turn could threaten the food security of millions of people. The affected countries (Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos and Thailand) formed the Mekong River Commission (MRC) in 1995. This commission was formed in order to promote dialogue and promote the fair and equitable use of the river's waters. The MRC has mediated between countries several times; in 2010 for the construction of a dam by Laos and Thailand, and the same status It happened in 2013. Talks have not been result and there are fears for the lives of millions of people, who could be affected if the conflict escalates.
The ineffectiveness of this body could be summed up as follows: decisions on the construction of dams are made directly without submitting them to the MRC, and construction companies put such pressure on governments that it is very difficult to carry out environmental impact assessments. Moreover, since it is not a binding treaty, members end up ignoring its guidelines and preferring to "cooperate" in a broad sense. In any case, the talks are continuing although, at the moment, the MRC does not seem able to assume the weight of the negotiations. This gives the conflict an uncertain and dangerous future.
A third source of friction is the ex-Soviet region of Central Asia. During the Cold War, these regions shared resources as follows: the mountainous republics (Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan) had abundant water, and supplied it to the downstream republics (Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan) to generate electricity and irrigate crops. In turn, the downstream republics supplied gas and coal to Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan during the winter. But when the USSR collapsed, all that changed and there began to be water shortages and power cuts, as these independent countries decided to stop sharing water and energy. As the International Crisis Group think-tank proclaims, "the root of the problem lies in the disintegration of the system of sharing sources imposed by the Soviet Union in the region until its collapse in 1991."
Thus, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan have decided to build hydroelectric dams on the Syr Darya and Amu Darya rivers to produce their own energy and thus cope with the constant blackouts (potentially lethal in winter). This, of course, will limit access to water for millions of people living in the other three republics, which has led to small-scale conflicts. Threats have also abounded, such as that of Uzbek President Islom Karimov, who in 2012 said the following: "Water resources could become a future problem that could lead to an escalation of tensions not only in our region, but across the continent"; He added: "I won't name specific countries, but all of this could deteriorate to the point where the result It wouldn't just be a confrontation, it would be wars." Despite the threats, the projects have continued on their way, and therefore an increase in tension in the region can be expected.
|
The Nile Course [Wikimedia Commons–Yale Environment 360] |
Mekong River Basin [Wikimedia Commons–Shannon I] |
Control of the Nile
The Nile River appears as source of tension between various African countries. To understand the existing problem, we must go back more than a century. As early as 1868, Egypt attempted to occupy Ethiopia in order to gain control of the Nile. In 1929 , agreements were signed during the colonial era, in which the waters of the Nile were divided. In these agreements (which were reaffirmed in 1959), Egypt obtained most of the water for its use, while Sudan obtained a small share. The remaining 9 countries in the Nile basin were removed from the treaty. At the same time, Egypt was allowed to build projects on the Nile River while the rest of the riparian countries were forbidden to do the same without Egypt's permission.
In 1999, the Nile Basin Initiative was created: a commission charged with organizing a fair distribution of the Nile's water and resources. But as it did not have the expected effect, in 2010 the agreement of Entebbe (for Ethiopia, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania and Burundi). This agreement, deeply disputed by Egypt and Sudan, allows riparian countries to build dams and other projects, thus breaking the restrictions imposed by colonial treaties. Moreover, this has shifted the balance in the region, as Egypt and Sudan have lost their monopoly on the Nile's resources.
It is vital to understand the status of these actors. The Nile rises in several countries, and ends up passing through Sudan and Egypt to flow into the Mediterranean Sea. Egypt, in particular, is a country totally dependent on the Nile River. It receives more than 90% of its fresh water from this river, and its industry and agriculture need the Nile to survive. Until a few years ago, thanks to colonial treaties, Egypt had exercised a monopoly on the use of water; But recently, the status it's changing.
Therefore, the confrontation has basically arisen between Egypt and Ethiopia (where the Blue Nile is born). The latter is a country with more than 100 million inhabitants, which in 2011 had a project of dam construction: the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD). With an investment of 4,700 million dollars, this dam would solve Ethiopia's energy deficit, and would eventually turn this country into a net exporter of electricity (it would produce 6,000 MW per year). The downside is that the dam will be fed with water from the Blue Nile, a tributary of the Nile River. The danger of evaporation of more than 3 trillion cubic meters per year and the reduction of the flow rate to fill the reservation it could catastrophically affect Egypt. In addition, the dangers arising from the overuse of water are compounded by population growth and the demand for better redistribution of water among riparian countries.
This issue has led to tensions between the two countries: in 2010 an email from a senior Egyptian commander was leaked to Wikileaks stating: "We are discussing military cooperation with Sudan against Ethiopia, with plans to establish a base in Sudan for Egyptian Special Forces with a view to attacking the country."project GERD." Egypt also thought of preparing support for proxy rebel groups in Ethiopia, to destabilize the government. In any case, we must bear in mind that Egypt has always tended to use aggressive rhetoric towards all issues related to the Nile (source of life, the engine of its Economics), but in reality the nation of the pharaohs is not in a position to launch armed actions, since its domestic problems have worn down the country, thus losing its position of clear predominance in the region.
But not all the future is so bleak. In March 2015 , a agreement A preliminary agreement between Egypt, Ethiopia and Sudan on the Renaissance Dam and the sharing of water, accepting Ethiopia's right to build the dam without damaging the water supply of Egypt and Sudan. Although these two countries are alarmed at what will happen once the reservation This is a first step towards an era of cooperation. Abdel Fattah el-Sisi himself (Egypt's president) said at the convention: "We have chosen to cooperate and trust each other, for the sake of the development". Finally, in November of the same year, it was not possible to approve an independent commission of inquiry to look at the consequences of the dam, since after Sudan accused Egypt of using part of the Sudanese quota, a war of declarations began, which jeopardized the fragile cooperation between these countries.
Such cooperation in the field of water resources will have a beneficial impact in many other areas and, although a failure of the negotiations cannot be ruled out, it is likely that thanks to the construction of the GERD and regional cooperation, the ties between these countries will become stronger, which can mark the starting point of a new era of peace and peace. development in this region.
A case of cooperation: the Paraná
The Paraná, a border and cross-border river that rises in Brazil and crosses Paraguay to flow into the Rio de la Plata, is a very different example. Its basin is linked to the Guarani Aquifer (one of the largest water reserves in the world), and that is a guarantee of the large volume of water that this river has throughout the year. For this reason, many hydroelectric power plants have been built, taking advantage of waterfalls and rapids. On the other hand, the importance of this river on a political and economic level is core topic; the Paraná and the La Plata Basin feed the most industrialized and populated area of South America. That is why cooperation has been particularly important.
|
The Paraná, central axis of the La Plata basin [Wikimedia Commons–Kmusser] |
The Itaipu Dam (the second largest in the world and the first in world production) is a binational dam, built by Paraguay and Brazil. It was the result of intense negotiations (not always easy), and now produces an average of 90 million MWh (megawatt-hours) per year. Even so, there was not always concord between Paraguay and Brazil: in 1872 disputes over borders began. After many useless agreements, it was agreed to flood the disputed territories and create a hydroelectric dam. The reluctance that the initiative aroused in Argentina, because the regulation affected the flow that, downstream, would continue to the Río de la Plata, resulted in a three-way pact in 1979. In 1984 the dam became operational. Today it is administered by the Itaipu Binational Entity, a business public-private between Paraguay and Brazil, and supplies more than 16% of the total energy consumed in Brazil, and more than 75% of that consumed in Paraguay. Although the environmental impact was great, Itaipu has promoted campaigns to maintain biological reserves and protect fauna and flora. In addition, it has reforested large areas around the reservoir, and ensures the quality of the water.
This is a clear example of the benefits that can be brought by a reasonable and shared use between countries that decide to cooperate. Thus, countries that are parties to some of the current controversies should look to these examples of behaviour which, although not perfect, can be learned a great deal from them.
Although water can be the source of disputes between peoples and nations (such as the cases cited), it also offers very advantageous opportunities (what happened on the Paraná River or the Nile) for countries that manage to cooperate. This cooperation, initiated to avoid conflicts over water, can lead to new stages of harmony and strengthen trade, political and security relations. Is core topic, then, to show how an attitude of willingness to negotiate and cooperate will always have positive consequences for countries that share river flows.
▲Enrique Peña Nieto and Donald Trump at the July 2017 G20 summit in Hamburg [Presidency of Mexico].
ANALYSIS / Dania Del Carmen Hernández [English version].
Canada, the United States and Mexico are immersed in the renegotiation of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). The trade agreement between these three countries has been somewhat controversial in recent years, especially in the US, where its advisability has been questioned. During the presidential campaign, Donald Trump defended the cancellation of the treaty; later, already in the White House, he accepted that there would be a renegotiation. Trump argued that the pact has reduced US manufacturing jobs and generated a trade deficit of more than $60 billion with Mexico ($18 billion with Canada), so unless new conditions substantially reduced that deficit, the US would withdraw from agreement.
Overall, Americans have positive views of the treaty, with 56% of the population saying NAFTA is beneficial to the country, and 33% saying it is detrimental, from agreement with a November 2017 Pew Researchsurvey . Among those who hold a negative view, the majority are Republicans, with 53% saying Mexico benefits the most, while Democrats overwhelmingly support the pact and only 16% view it negatively.
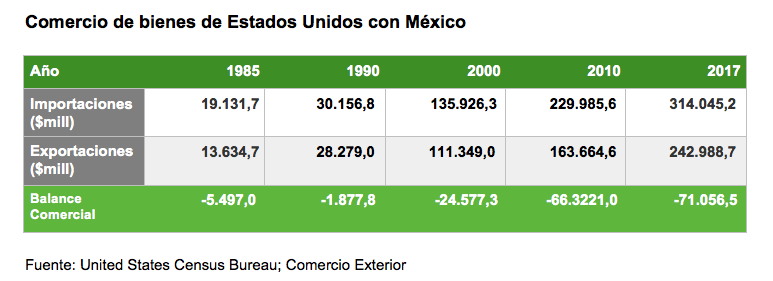 |
Regardless of public acceptance, opinion about the treaty has not always been so dubious. When President Bill Clinton ratified the treaty, it was considered one of the greatest achievements of his presidency. Just as globalization has liberalized trade around the world, NAFTA has also expanded trade very effectively and presented a great issue of opportunities for the U.S., while strengthening the U.S. Economics .
Under NAFTA, trade in U.S. goods and services with Canada and Mexico grew from $337 billion in 1994, when the treaty entered into force, to $1.4 trillion in 2016. The impact has been even greater when taking into account cross-border investments between the three countries, which went from $126.8 billion in 1993 to $731.3 billion in 2016.
Washington's concern is that, despite this increase in trade volume, in relative terms the United States is not achieving sufficiently fruitful results compared to what its neighbors are getting from the treaty. In any case, Canada and Mexico accept that, after almost 25 years in force, the treaty must be revised to adapt it to the new productive and commercial conditions, marked by technological innovations that, as is the case of the Internet development , were not contemplated when the agreement was signed.
Round-by-round examination
The discussion of the three countries touches on numerous aspects, but three blocks can be mentioned, which have to do with certain red lines set by the different parties to the negotiation: the rules of origin; the desire of the United States to end the independent arbitration system, through which Canada and Mexico have the ability to end measures that violate the trade agreement (elimination of Chapter 19), and finally proposals, perhaps less decisive but equally important, aimed at the general update of the treaty.
When negotiations began in August 2017, it was expressed that they could be concluded by January 2018, with six rounds of meetings planned. This issue is already being exceeded, with a seventh round at the end of February, possibly to be followed by others. Now that the initial deadline has been reached, however, it is time to review the status of the discussions. A good way to do this is to follow the evolution of the talks through the rounds of meetings held and thus be able to assess the results that have been recorded so far.
|
Last North American Summit, with Peña Nieto, Trudeau and Obama, held in Canada in June 2016 [Presidency of Mexico]. |
1st Round (Washington, August 16-20, 2017)
The first round of negotiations put on the table the priorities of each of the three countries; it served to set the diary of the main issues to be discussed in the future, without yet addressing concrete measures.
agreement First of all, Donald Trump already made it clear during his election campaign that he considered NAFTA to be unfair to the United States due to the trade deficit that the United States has mainly with Mexico and, to a lesser extent, with Canada.
According to figures from the Office of the US Trade Representative, the US went from a surplus of $1.3 billion in 1994 to a deficit of $64 billion in 2016. Most of this deficit comes from the automotive industry. For the new U.S. Administration, this calls into question whether the agreement will have beneficial effects for the domestic Economics . Mexico, less inclined to introduce major changes, insists that NAFTA has been good for all parties.
Another topic was the wage gap between Mexico and the United States and Canada. Mexico argues that, despite having one of the lowest minimum wages in Latin America, and having had a stagnant average wage for the last two decades, this should not be taken into account in the negotiations, as it believes that Mexican wages will gradually catch up with those of its trading partners. On the contrary, for the US and Canada it is a topic of concern; both countries warn that a wage increase would not harm the growth of the Mexican Economics .
Rules of origin was one of the main topics of discussion. The United States is seeking to increase the percentage of content required to consider a product as originating so that it is not necessary to pay tariffs when moving it between any of the three countries. This was controversial in this first round, as it could negatively affect Mexican and Canadian companies. Specialists warn that the minimum national content requirement does not exist in any free trade agreement in the world.
Finally, the Trump administration hinted at its intentions to eliminate Chapter 19, which guarantees equality in resolving disputes between countries, so that it is not the national laws of each country that resolve the conflict. The United States sees this as a threat to its sovereignty and believes that conflicts should be resolved in such a way that its own democratic processes are not ignored. Canada has conditioned its continued membership in the treaty on the maintenance of this chapter. Mexico also defends guarantees of independence in conflict resolution, although so far in this discussion it was not categorical.
 |
2nd Round (Mexico City, September 1-5, 2017)
Although considered successful by many analysts, the second round of renegotiation continued at a slow pace. Some of the issues that advanced were: wages, market access, investment, rules of origin, trade facilitation, environment, digital trade, SMEs, transparency, anti-corruption, agriculture and textiles.
The president of committee coordinator Mexican Businessmen, Juan Pablo Castañón, insisted that for the moment the wage issue was not subject to negotiation, and denied that any of the parties had any intention of leaving the treaty, despite threats to that effect from the Trump Administration. Castañón said he was in favor of Mexico supporting the maintenance of Chapter 19 or the establishment of a similar instrument for the settlement of trade disputes between the three countries.
Round 3 (Ottawa, September 23-27, 2017)
The delegates made important advances in policies on skill, digital commerce, state-owned enterprises and telecommunications. The main progress was on some aspects related to SMEs.
Canadian Foreign Minister Chrystia Freeland complained that the United States had not made any formal or written proposals in the most complex areas, which in her opinion demonstrates a passive attitude on the part of that country in the context of the negotiations.
U.S. Trade Secretary Robert Lighthizer said that his country is interested in increasing wages in Mexico, under the logic that this is unfair skill , as Mexico has attracted factories and investment with its low wages and weak union rules. However, Mexican business and union leaders are resisting such pressures.
Canada stood firm on its position on Chapter 19, which it considers one of the great achievements of the current agreement. "Our government is absolutely committed to defending it," Freeland said. Washington raised, although without presenting a formal proposal , the modification of the rules of origin to make them stricter and prevent imports from other nations from being considered "made in North America", just because they were assembled in Mexico.
This round took place as the United States slapped a tariff of nearly 220% on C Series aircraft made by Canadian aircraft manufacturer Bombardier, which it considered that business had used a government subsidy to sell its aircraft to the U.S. at artificially low prices.
Round 4 (Virginia, October 11-17, 2017)
The United States presented its formal proposal to raise the rules of origin for the automotive industry and its suggestion to introduce a sunset clause to agreement.
The United States proposed raising from 62.5% to 85% the percentage of components of national origin from one of the three countries in order for the automotive industry to benefit from NAFTA, and that 50% be of U.S. production. association The Mexican Automotive Industry Association (AMIA) rejected proposal.
Washington's interest in weakening the dispute settlement system within the treaty (Chapter 19) was also debated, without a rapprochement of positions.
Finally, there was talk of including a sunset clause, which would cause the treaty to cease to exist after five years, unless the three countries decide to renew it. This proposal was widely criticized, warning that this would go against the essence of agreement and that every five years it would generate uncertainty in the region, as it would affect the investment plans of companies.
These proposals add to the tough negotiating climate, as already in the third round the United States had begun to defend difficult proposals, on issues such as lawsuits for dumping (selling a product below its normal price) in the importation of perishable Mexican products (tomatoes and berries), government purchases and the purchase of textiles.
 |
Round 5 (Mexico City, November 17-21, 2017)
The fifth round took place without much progress. The U.S. maintained its demands and this generated great frustration among the representatives of Mexico and Canada.
The United States received no alternatives to its proposal of wanting to increase the regional composition from 62.5% to 85%, with at least 50% being U.S.-based. On the contrary, its trading partners put on the table data showing the damage that this proposal would cause to the three economies.
Faced with the U.S. desire to limit the issue of concessions that its federal government offers to Mexican and Canadian companies, Mexican negotiators responded with a proposal to limit the country's public contracts to issue of contracts reached by Mexican companies with other governments under NAFTA. Given that the issue of these contracts is quite small, U.S. companies would be restricted in their contracting.
At the end of this fifth round, the most advanced issues are the regulatory improvement of telecommunications and the chapter on sanitary and phytosanitary measures. With the latter, the Americans seek to establish new transparent and non-discriminatory rules, allowing each country to establish the Degree protection it deems appropriate.
Round 6 (Montreal; January 23-29, 2018)
The sixth negotiation showed some progress. The chapter on corruption was finally closed, and there was progress in other areas. Some of the important issues that had been left aside in the previous negotiations were discussed. Progress is slow, but seems to be making headway.
Robert Lightizer rejected the compromise on rules of origin that Canada had previously proposed. The framework was based on the idea that rules of origin should be calculated to include the value of software, engineering and other high-value work, facets that today are not taken into account with a view to goal regional content.
As a form of pressure, Canada threatened to reserve the right to treat its neighboring countries worse than other countries if they enter into agreements. One of them could be China. The proposal was not considered, as the United States and Mexico found it unacceptable.
Beyond the deadline
After more than seven months of meetings, as reflected in this round-by-round review of the talks, the negotiations between the three countries have still not reached the threshold of a pre-agreement that, while awaiting the resolution of more or less important points, would confirm the shared will to continue NAFTA. The hard stances of the United States and the pressure from Canada and Mexico to save the treaty have so far resulted in a "tug of war" that has allowed some partial, but not decisive result . Thus, it is yet to be determined whether the treaty has actually reached its expiration date or whether it can be reissued. For the time being, the three countries are at agreement working towards a renewed treaty.
From what has been seen so far in the negotiations, it is difficult to determine which country will be more willing to yield to the pressure exerted by the others. The most controversial issues have hardly been addressed until recently, so it is not possible to say what each country has achieved in this negotiation process.
The two neighbors of the United States, but especially Canada, continue to warn of the risk of Trump wanting to kill the treaty. An acceleration of the negotiations could help the positive resolution of the process, but the electoral calendar rather threatens postponements. On March 30, campaigning begins for Mexico's presidential election, which will take place on July 1. In September, the U.S. will begin to look more closely at the November congressional elections. A substantial breakthrough before the Mexican presidential elections could put agreement back on track, even if some issues remain to be closed, but if no breakthrough is made in the next meetings, the three countries could be getting used to the idea of the end of NAFTA, which would weigh down the negotiations.
U.S.-China relations do not satisfy either country; They probably never will. They must try to deal with them, peacefully

▲meeting between Xi Jinping and Donald Trump [White House video screebshot]
ANALYSIS / María Granados
The National Security Strategy presented in December by Donald Trump label China and Russia as "rivals" of the United States. It portrays those two countries as actors that "challenge the power, influence, and interests" of Washington and "attempt to erode the security and prosperity" of Americans. Although the document also considers "renegade" states such as Iran and North Korea, and transnational organizations, both jihadist and organized crime, a threat, the arguments of the new US administration are especially focused on China. The Asian nation appears as the great obstacle to the realization of the "America First" promised by Trump, because of its unfair trade and monetary practices.
Thus, the first National Security Strategy document of the Trump era corroborates the speech which he had maintained as candidate. During the election campaign, Trump spoke of China as a "currency manipulator" and accused it of artificially keeping the yuan low. He also threatened Beijing with starting a trade war, complaining about the economic consequences for the U.S. of China's excessive trade surplus in bilateral relations, as well as the reduction of jobs in U.S. manufacturing. Shortly after being elected, before the inauguration of his term, Trump provoked a diplomatic friction with China by talking by phone with the president of Taiwan.
However, since his arrival in the White House, Trump has been concerned with ironing out those rough edges with China. He pledged to uphold the One China Policy, retracted his criticisms, and met in Florida with President Xi Jinping, agreeing to respect each other's sphere of influence and not intervene in each other's internal affairs. This, along with an incipient partnership in the sanctions against North Korea, it seemed to be giving birth to a rapprochement that has not yet materialized. In fact, the U.S. National Security Strategy's official "rival" treatment of China somewhat breaks with a long period of mutual acceptance that began in the 1970s.
Nixon's Opening
The United States and China started from serious antecedents: the Korean War (1950-1953), which pitted China and the USSR in the North against the American-backed South, of which the Vietnam War (1955-1975) was a collateral consequence; and the nuclear danger that began in 1949, the year in which the USSR carried out the first nuclear war. essay effective. For Washington, from an ideological and military point of view, China was an international actor that should be controlled. For Beijing, in alliance with the Soviet Union, it was urgent to spread the speech communism about the "imperialist enemy," which he repeated with intensity throughout the early years of the Cold War.
In 1969, the new U.S. president, Richard Nixon, included in his speech inauguration of mandate one reference letter against isolationism (1). From the other side of the world there were also new messages: the distance that Mao began to establish in relation to the USSR due to its border conflicts. This upset the triangle of international relations that existed in those years of the Cold War (China, USSR, USA), and began to create a bond between Beijing and Washington.
In this way, the first signs of approximation began to appear. In 1971, the U.S. voted to allow Taiwan to join the committee of the United Nations Security Council will be occupied by the People's Republic of China. In 1972 the statement of Shanghai, which established the instructions for the Sino-American rapprochement and which was embodied in five principles:
1. The One China Policy: Establishing diplomatic relations with China meant not being able to establish them with Taiwan, and vice versa, since both claim to be the true and only China.
2. Not supporting Taiwan independence.
3. Do not support the possible invasion of Japan.
4. The peaceful resolution of the conflict with Taiwan, reducing military installations on the island.
5. A commitment to continue to be peaceful allies in the pursuit of lasting cooperation.
Since the rapprochement of the 1970s, relations between the two countries have been heavily influenced by Washington and Beijing's attitude toward Taiwan and the two Koreas, in a sort of indirect Sino-American relations.
|
▲meeting bilateral meeting at Mar-a-Lago, Florida, in April 2017 [White House] |
The Question of Taiwan
The self-styled Republic of China had been the main obstacle to the complete normalization of relations, as seen with the statement of Shanghai. Effective reunification by (mainland) China was prevented by U.S. troops.
After 1973 we find two important documents: the so-called Taiwan Relations Act, by which the United States recognized the island as before, but not that it was a sovereign nation, and the Taiwan Relations Act. statement Set (sometimes referred to as "Second statement of Shanghai"), drastically cutting arms sales to Taiwan. In 1979, Washington and Beijing exchanged ambassadors, and the Americans ceased formal diplomatic relations with Taiwan.
Around 1980, the policy advocated by the mainland Chinese government was "one country, two systems", offering Formosa the exceptionality of a different and economically independent political system, but being part of the one China. However, this formula did not meet the wishes of the twenty-third province for independence. By 1985, the island's government was firmly moving towards democracy (2).
In the late 1990s, Beijing threatened Taiwan with military exercises in surrounding waters, in which missiles were deployed, prompting a forceful response from the United States: sending two aircraft carrier battle groups to the region; In doing so, Washington showed a clear determination to protect the former ally because of its strategic importance.
The status The current situation remains complex. No direct ties have been established between China and its rebel province through messaging or telecommunications; Neither are postal or parcel shipments sent, nor is there a direct connection of flights. Face-to-face meetings between delegates have been infrequent and not very productive.
The North Korea Problem
The Democratic People's Republic of Korea, for its part, is a particularly critical point in Sino-American relations, which also affects South Korea and Japan, which in turn are allies of the United States. Pyongyang has already carried out six underground nuclear tests and continues its missile launches over the Sea of Japan.
China is North Korea's only ally: it is its biggest partner commercial and its main source of food and energy. Beijing has historically opposed tough international sanctions against its neighbor. The will to survive communism is essential when it comes to understanding the close relationship between the sui generis Korean dictatorship and China. It's easy to guess why: if Kim Jong-Un's regime falls, Xi Jinping's could be destabilized. A refugee crisis, with thousands of North Koreans crossing the 1,400-kilometer border bordering the two countries, would have serious effects on the Asian giant. Although they remain strongly linked to Pyongyang, the Chinese have pushed for the resumption of the Six Dialogue and have accepted the application of certain international sanctions.
Trump's blunt assertion that "if China isn't going to solve the North Korea problem, we will" doesn't really dispel doubts about what might happen if Pyongyang crosses the threshold of nuclear capability. Certainly, as the Kim Jong-Un regime has approached that threshold, Beijing has increased its diplomatic, financial and commercial pressures on its neighbor (3). But the possibility that North Korea is already on the verge of reaching its goal The strategic strategy leaves the United States faced with the dilemma of military action, which can hardly be both effective and limited, or having to settle for a policy of containment.
Over the years, Washington has tried to encourage North Korea to irreversibly forget its nuclear program, proposing in return a reward consisting of financial aid, diplomatic advantages and the normalization of relations. At the same time, South Korea hosts 29,000 U.S. military personnel. In March 2017, executive orders from the President and the congress The U.S. government went beyond sanctions: a defense system known as THAAD (Terminal High Altitude Area Defense) (4) was programmed as a preventive measure against a possible attack by the North and with the aim of protecting the environment. goal to ensure the stability of the region.
The THAAD battery is particularly interesting to analyze, because of the double perspective it presents. Their limited range and capability should not worry China, as the interceptors would not be able to hit Chinese intercontinental ballistic missiles at any point in their trajectory, from almost any of the possible launch locations. As such, neither Washington nor Seoul should present the system as a form of retaliation against Beijing for its failed sanctions on North Korea. Unfortunately, U.S. and South Korean officials suggest that the purpose of the installation of the THADD system is to send a warning message to China. This is somewhat counterproductive, since it only offers reasons to justify the nuclearization of the Asian hegemon, in the face of the apparent degradation of its medium-range technology, that of the second Degree nuclear response (second-strike capability).
Mutual dissatisfactions
If the issues of Taiwan and North Korea have occupied a large part of the diary In the bilateral relationship, the issue of China's economic transformation, since its impetus by Deng Xiaoping, has been central to the direct relationship between China and the United States.
Gǎigé kāifàng (reform and opening-up) emphasized modernization and economic and political reform. This led to normalized diplomatic relations and thedevelopment bilateral trade and investment. Cooperation in subject The political, economic and security relations with the former "American imperialists" were based on the prevention of terrorism and the proliferation of nuclear weapons, and the maintenance of peace on the Korean peninsula.
However, there are still unresolved issues. U.S. dissatisfaction stems from China's human rights policy and its financial moves to devalue the currency as a measure to control inflation. These monetary movements call into question the control of the market by the American hegemon, which currently has greater weight and primacy, among other things, because the dollar is the international currency of exchange (it could thus "export its inflation" to Beijing). Washington is also concerned about the U.S.'s dependence on imports from China, which creates a large bilateral trade deficit for Americans. Another potential problem is the sale of missiles and nuclear technology to third States in the Middle East and Asia.
From the Chinese perspective, their dissatisfaction is due to the U.S. arms sales to the rebel province (Taiwan), the defense system established in South Korea (both the THAAD system and the U.S. government). financial aid and a U.S. foreign policy that Beijing dismisses as threatening, imperialist and domineering.
Ways of cooperation
The U.S. consideration of China as a "rival," as stated in the Trump Administration's first National Defense Strategy document, is based on the realization that the Chinese regime is not moving towards democracy as many in the rest of the world had hoped. "For decades, U.S. policy was based on the belief that support for China's rise and its integration into the post-war international order would liberalize China," the document says, noting that Beijing is not sliding toward a regime of political freedoms and respect for human rights, so Washington can no longer be as condescending to Beijing as it once was.
Probably, without China's assumption of the values and principles that give meaning to the United States, a real and confident rapprochement between the two superpowers is impossible. Still, for the survival of both, broad cooperation between them is necessary.
Although a war between the United States and China is not impossible, it is unlikely for a number of reasons, as Steinberg and O'Hanlon argue in Strategic Reassurance and Resolve (2015):
–The common objectives of economic prosperity, the exchange In terms of trade, interdependence, both at the stock market, financial and business levels, make a military confrontation very harmful to both countries. In addition, China has progressively adopted measures against fraud and destabilization by computer manipulation, at the behest of the United States; The issue of cyberespionage, although it continues to provoke mutual disagreements, is regularly addressed by both countries in their bilateral meetings, aware that it is likely to become more important over the years.
The South China Sea is a trade route that has never been closed, although it is a source of dispute to be taken into account, since they remain unresolved even though they have been brought before the Court dealing with the Law of the Sea (following the United Nations Convention on the Sea). The United States has strategic and commercial interests in the region that link it to its allies (Japan and South Korea), so it could be a source of tensions. In any case, it does not currently appear that China wishes to provoke a military escalation in the area, although it has established instructions on artificial islands and moved troops.
The ASEAN code of conduct for the South China Sea, which prevents the use of force, may cause Beijing to rethink increasing its aggressiveness in the region. That push by ASEAN for China to stop claiming maritime sovereignty that has been rejected by the international community are points against the war.
There are a number of joint counter-terrorism (ISIS) and anti-piracy operations involving the two superpowers.
China has increased its financial aid and its work in support of UN peacekeeping missions.
Faced with a scenario of no understanding between Beijing and Washington, but at the same time of no armed confrontation, the following actions should be suggested:
A negotiation that would include fewer arms sales to Taiwan by the US in exchange for greater security on the coasts, and a proportional reduction by China of threats to the island.
–Greater cooperation and transparency in the conduct of arms and troop movements, militarization, restructuring of the armed forces, and military exercises in the Pacific.
–Creation of joint organisations to combat organised crime and cyber-attacks, in particular threats to civilian infrastructure.
- Support and coherence in the prevention of nuclear escalation. Negotiation to reach a firm conclusion on how to weaken the Pyongyang regime. Serious and coherent criticism, knowing the impossibility (as well as harm) of its direct overthrow.
-----------------------------------------
(1) "We seek an open world--open to ideas, open to the exchange of goods and people--a world in which no people, great or small, will live in angry isolation.
We cannot expect to make everyone our friend, but we can try to make no one our enemy". Inaugural Adress (January 20, 1969)
(2) It was the first time that the Democratic Progressive Party succeeded in pressing the elections to the National Assembly and the Legislative Yuan and forming a unified coalition against the Kuomintang. In 1992, the first free legislative elections were held in Taiwan.
(3) "China will be most likely to put diplomatic and financial pressure on North Korea if it believes that failing to do so will lead the United States to destabilize the regime," write Joshua Stanton, Sung- Yoon Lee, and Bruce Klingner in Foreign Affairs.
(4) The system typically has between 48 and 62 interceptor missiles with ranges of up to 200 kilometers, supported by radar with a range of up to about 1,000 kilometers

![Map of the Jordan River Basin [Palestinian Authority]. Map of the Jordan River Basin [Palestinian Authority].](/documents/10174/16849987/jordan-river-mapa.jpg)
![Statement by MBS in a conference organized in Riyadh in October 2017 [KSA] Statement by MBS in a conference organized in Riyadh in October 2017 [KSA]](/documents/10174/16849987/women-arabia-saudi-blog-2.jpg)
![Party in Tolima in memory of the victims of the conflict [Victims Unit] Party in Tolima in memory of the victims of the conflict [Victims Unit]](/documents/10174/16849987/colombia-elecciones-paz-blog-2.jpg)
![Chad's troops during the war against Libya in the 1980s [Wikimedia Commons] Chad's troops during the war against Libya in the 1980s [Wikimedia Commons]](/documents/10174/16849987/toyota-blog-2.jpg)