In the picture
International Maritime Organization's Headquarters, in London [IMO].
Tensions between Greece and Turkey have been escalating in the last years; nevertheless, the two countries have found a possible way of cooperation: mutual support for their respective bids for a seat in international organizations. Turkey aspires to head the International Maritime Organization (IMO), and Greece is campaigning to become a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council. With both candidacies in mind, the two nations try to improve their differences over the past decades. Ankara's attitudes against Cyprus, though, complicate the perspective of a leading role for Turkey at the IMO.
In September 2022, the entire Greek fleet was mobilized in the Aegean Sea to carry out naval exercises with the French Navy. They came as a response to the numerous threats by Ankara about the possible invasion of Greek islands in the Aegean. This episode escalated to a high degree their conflict in the region, with frigates, submarines, missile boats, gunboats, helicopters and fighter aircraft in full formation and ready for deployment. It was yet another episode of military tensions between the Eastern Mediterranean neighbors. Shortly after, at the beginning of 2023, Turkey warned that any Greek naval exercises carried out in the Aegean Sea would trigger Turkish submarine drills in response, indicating that Ankara is not going to tolerate any violation of waters currently disputed between the two Mediterranean neighbors.
Diplomatic relations between the two Eastern Mediterranean nations have been complicated by their rivalry over the sovereignty of many of the islands in the Aegean Sea, as well as by the Cyprus issue and Ankara's reluctance to let any ships bearing the Cypriot flag dock in its national ports. Yet, weeks after their latest incident, it appears that the two countries could have found a new way to cooperate and improve their relations out of their bids for the Secretary Generalship of the International Maritime Organization (Turkey) and a seat as non-permanent member of the UNSC (Greece). With both candidacies in mind, the two have vowed to support each other and try to improve their differences over the past decades.
The two Mediterranean neighbors have recently shown some support for each other on a particular issue: Ankara's bid for the Secretary General position at the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and Athens' bid for a non-permanent seat at the UN Security Council for the 2025-2026 term. The former of them bears a massive symbolical importance for Athens, given its active participation in the organization, and that, if successful, will very likely mark the beginning of a new chapter in Greek-Turkish relations that could affect the overall security scenario of the Eastern Mediterranean.
On March 20th, Turkish Foreign Minister Mevlut Cavusoglu and Greek Foreign Minister Nikos Dendias met in Brussels, where they both expressed mutual support for each other's cause. Greece will support Suat Hayri Aka, the Turkish candidate for the position, who previously served as under-secretary for Maritime Affairs in the Turkish Ministry of Transport. Cavusoglu wrote in social average: "We continue our solidarity after earthquake & train accident. Agreed to mutually support our candidacies." Such position is pivotal for global shipping regulation, dealing with development of regulatory frameworks for global shipping and other aspects of maritime safety and security of transport routes. Among the main issues which will be certainly faced by the upcoming SG of the IMO, which will take office in January 2024, are the commercial consequences of the war in Ukraine, the delicate geopolitical situation across the globe, and the conflicting viewpoints on decarbonization of shipping.
The news of such support came days after former Cyprus shipping deputy minister, Vassilios Demetriades, announced he is considering the option of running as a European candidate for the IMO elections that will take place in June at London. Although he must first discuss the option with the newly elected Cypriot Government, he is considered as a popular figure among EU authorities given his involvement in the drafting of European shipping policy; and could enjoy support from them for his election campaign.
For Cyprus, this Turkish IMO candidacy presents an interesting situation. On one side, it is not able to join Athens in its support for Turkey given Ankara has banned ships bearing the Cypriot flag from docking in any national port, and Demetriades own potential candidacy. "You realize that it will not be possible for our side to support such a candidacy," Cypriot President Nikos Christodoulides stated. On the other side, Cyprus has publicly declared a hypothetical Turkish secretary general at the IMO will not bring any problem for Cyprus nor for its positive relation with Greece. "As far as Cyprus goes, we are not bound in any way by Greece's decision and we certainly cannot support Turkey's candidacy," said Government Spokesperson Konstantinos Letymbiotis.
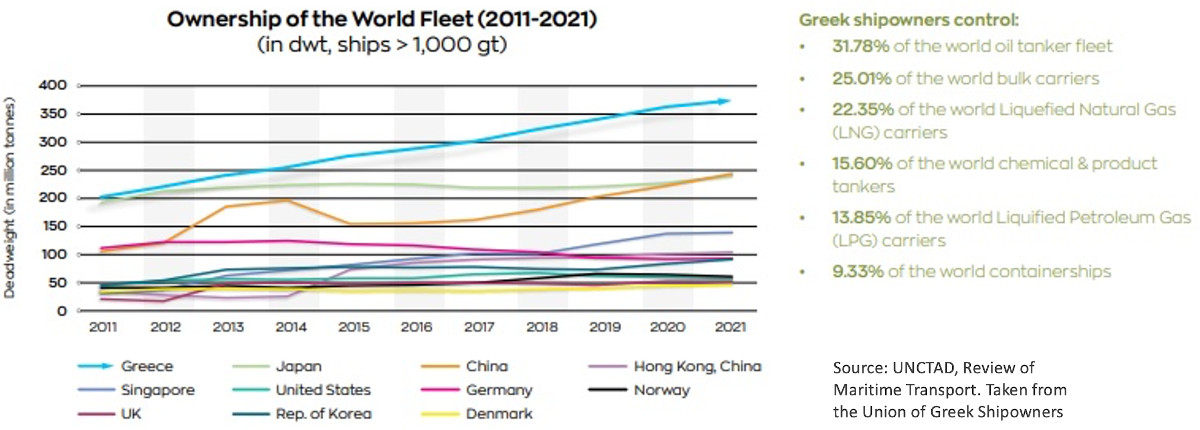
Yet, leaving aside the Cyprus issue, Athens' support for Ankara's bid is much more significant than Turkey's for the UNSC seat. The IMO is of vital importance for Greek interests, as it is the forum where shipping and maritime regulations are made. These interests are not small, considering Greece remains the largest shipping nation in the world, with 5,514 ships which makes up for the 21% of the global merchant fleet and the 59% of the EU's. In the image below, representing the ownership of the world's shipping fleet between 2011 and 2021, Greece is clearly visible as one of the fastest growing fleets. According to the Union of Greek Shipowners, "The total tonnage of the Greek-owned fleet has increased by 45.8% compared to 2014, while even during the COVID-19 pandemic, i.e. since 2019, the tonnage has increased by 7.4%."