Ruta de navegación
Menú de navegación
Blogs
Entries with Categories Global Affairs Analysis .
Temporary Protected Status for Venezuelans and pending TPS termination for Central Americans amid a migration surge at the US-Mexico border

The Venezuelan flag near the US Capitol [Rep. Darren Soto].
ANALYSIS / Alexandria Angela Casarano
On March 8, the Biden administration approved Temporary Protected Status (TPS) for the cohort of 94,000 to 300,000+ Venezuelans already residing in the United States. Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador, and Haiti await the completion of litigation against the TPS terminations of the Trump administration. Meanwhile, the US-Mexico border faces surges in migration and detention facilities for unaccompanied minors battle overcrowding.
TPS and DED. The case of El Salvador
TPS was established by the Immigration Act of 1990 and was first granted to El Salvador that same year due to a then-ongoing civil war. TPS is a temporary immigration benefit that allows migrants to access education and obtain work authorization (EADs). TPS is granted to specific countries in response to humanitarian, environmental, or other crises for 6, 12, or 18-month periods-with the possibility of repeated extension-at the discretion of the Secretary of Homeland Security, taking into account the recommendations of the State Department.
The TPS designation of 1990 for El Salvador expired on June 30,1992. However, following the designation of Deferred Enforced Departure (DED) to El Salvador on June 26, 1992 by George W. Bush, Salvadorans were allowed to remain in the US until December 31, 1994. DED differs from TPS in that it is designated by the US President without the obligation of consultation with the State Department. Additionally, DED is a temporary protection from deportation, not a temporary immigration benefit, which means it does not afford recipients a legal immigration status, although DED also allows for work authorization and access to education.
When DED expired for El Salvador on December 31, 1994, Salvadorans previously protected by the program were granted a 16-month grace period which allowed them to continue working and residing in the US while they applied for other forms of legal immigration status, such as asylum, if they had not already done so.
The federal court system became significantly involved in the status of Salvadoran immigrants in the US beginning in 1985 with the American Baptist Churches v. Thornburgh (ABC) case. The ABC class action lawsuit was filed against the US Government by more than 240,000 immigrants from El Salvador, Guatemala, and former Soviet Bloc countries, on the basis of alleged discriminatory treatment of their asylum claims. The ABC Settlement Agreement of January 31, 1991 created a 240,000-member immigrant group (ABC class members) with special legal status, including protection from deportation. Salvadorans protected under TPS and DED until December 31, 1994 were allowed to apply for ABC benefits up until February 16, 1996.
Venezuela and the 2020 Elections
The 1990's Salvadoran immigration saga bears considerable resemblance to the current migratory tribulations of many Latin American immigrants residing in the US today, as the expiration of TPS for four Latin American countries in 2019 and 2020 has resulted in the filing of three major lawsuits currently working their way through the US federal court system.
Approximately 5 million Venezuelans have left their home country since 2015 following the consolidation of Nicolás Maduro, on economic grounds and in pursuit of political asylum. Heavy sanctions placed on Venezuela by the Trump administration have exacerbated-and continue to exacerbate, as the sanctions have to date been left in place by the Biden administration-the severe economic crisis in Venezuela.
An estimated 238,000 Venezuelans are currently residing in Florida, 67,000 of whom were naturalized US citizens and 55,000 of whom were eligible to vote as of 2018. 70% of Venezuelan voters in Florida chose Trump over Biden in the 2020 presidential elections, and in spite of the Democrats' efforts (including the promise of TPS for Venezuelans) to regain the Latino vote of the crucial swing state, Trump won Florida's 29 electoral votes in the 2020 elections. The weight of the Venezuelan vote in Florida has thus made the humanitarian importance of TPS for Venezuela a political issue as well. The defeat in Florida has probably made President Biden more cautious about relieving the pressure on Venezuela's and Cuba's regimes.
The Venezuelan TPS Act was originally proposed to the US Congress on January 15, 2019, but the act failed. However, just before leaving office, Trump personally granted DED to Venezuela on January 19, 2021. Now, with the TPS designation to Venezuela by the Biden administration on March 8, Venezuelans now enjoy a temporary legal immigration status.
The other TPS. Termination and ongoing litigation
Other Latin American countries have not fared so well. At the beginning of 2019, TPS was designated to a total of four Latin American countries: Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador, and Haiti. Nicaragua and Honduras were first designated TPS on January 5, 1999 in response to Hurricane Mitch. El Salvador was redesignated TPS on March 9, 2001 after two earthquakes hit the country. Haiti was first designated TPS on January 21, 2010 after the Haiti earthquake. Since these designations, TPS was continuously renewed for all four countries. However, under the Trump administration, TPS was allowed to expire without renewal for each country, beginning with Nicaragua on January 5, 2019. Haiti followed on July 22, 2019, then El Salvador on September 9, 2019, and lastly Honduras on January 4, 2020.
As of March 2021, Salvadorans account for the largest share of current TPS holders by far, at a total of 247,697, although the newly eligible Venezuelans could potentially overshadow even this high figure. Honduras and Haiti have 79,415 and 55,338 TPS holders respectively, and Nicaragua has much fewer with only 4,421.
The elimination of TPS for Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador, and Haiti would result in the deportation of many immigrants who for a significant continuous period of time have contributed to the workforce, formed families, and rebuilt their lives in the United States. Birthright citizenship further complicates this reality: an estimated 270,000 US citizen children live in a home with one or more parents with TPS, and the elimination of TPS for these parents could result in the separation of families. Additionally, the conditions of Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador, and Haiti-in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, recent natural disasters (i.e. hurricanes Matthew, Eta, and Iota), and other socioeconomic and political issues-remain far from ideal and certainly unstable.
Three major lawsuits were filed against the US Government in response to the TPS terminations of 2019 and 2020: Saget v. Trump (March 2018), Ramos v. Nielsen (March 2018), and Bhattarai et al. v. Nielsen (February 2019). Kirstjen Nielsen served as Secretary of Homeland Security for two years (2017 - 2019) under Trump. Saget v. Trump concerns Haitian TPS holders. Ramos v. Nielsen concerns 250,000 Salvadoran, Nicaraguan, Haitain and Sudanese TPS holders, and has since been consolidated with Bhattarai et al. v. Nielsen which concerns Nepali and Honduran TPS holders.
All three (now two) lawsuits appeal the TPS eliminations for the countries involved on similar grounds, principally the racial animus (i.e. Trump's statement: "[Haitians] all have AIDS") and unlawful actions (i.e. violations of the Administrative Procedure Act (APA)) of the Trump administration. For Saget v. Trump, the US District Court (E.D. New York) blocked the termination of TPS (affecting Haiti only) on April 11, 2019 through the issuing of preliminary injunctions. For Ramos v. Nielson (consolidated with Bhattarai et al. v. Nielson), the US Court of Appeals of the 9th Circuit has rejected these claims and ruled in favour of the termination of TPS (affecting El Salvador, Nicaragua, Haiti, Honduras, Nepal, and Sudan) on September 14, 2020. This ruling has since been appealed and is currently awaiting revision.
The US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) have honored the orders of the US Courts not to terminate TPS until the litigation for these aforementioned cases is completed. The DHS issued a Federal Register Notice (FRN) on December 9, 2020 which extends TPS for holders from Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador, and Haiti until October 14, 2021. The USCIS has similarly cooperated and has ordered that so long as the litigation remains effective, no one will lose TPS. The USCIS has also ordered that in case of TPS elimination once the litigation is completed, Nicaragua and Haiti will have 120 grace days to orderly transition out of TPS, Honduras will have 180, and El Salvador will have 365 (time frames which are proportional to the number of TPS holders from each country, though less so for Haiti).
The Biden Administration's Migration Policy
On the campaign trail, Biden repeatedly emphasized his intentions to reverse the controversial immigration policies of the Trump administration, promising immediate cessation of the construction of the border wall, immediate designation of TPS to Venezuela, and the immediate sending of a bill to create a "clear [legal] roadmap to citizenship" for 11 million+ individuals currently residing in the US without legal immigration status. Biden assumed office on January 20, 2021, and issued an executive order that same day to end the government funding for the construction of the border wall. On February 18, 2021, Biden introduced the US Citizenship Act of 2021 to Congress to provide a legal path to citizenship for immigrants residing in the US illegally, and issued new executive guidelines to limit arrests and deportations by ICE strictly to non-citizen immigrants who have recently crossed the border illegally. Non-citizen immigrants already residing in the US for some time are now only to be arrested/deported by ICE if they pose a threat to public safety (defined by conviction of an aggravated felony (i.e. murder or rape) or of active criminal street gang participation).
Following the TPS designation to Venezuela on March 8, 2021, there has been additional talk of a TPS designation for Guatemala on the grounds of the recent hurricanes which have hit the country.
On March 18, 2021, the Dream and Promise Act passed in the House. With the new 2021 Democrat majority in the Senate, it seems likely that this legislation which has been in the making since 2001 will become a reality before the end of the year. The Dream and Promise Act will make permanent legal immigration status accessible (with certain requirements and restrictions) to individuals who arrived in the US before reaching the age of majority, which is expected to apply to millions of current holders of DACA and TPS.
If the US Citizenship Act of 2021 is passed by Congress as well, together these two acts would make the Biden administration's lofty promises to create a path to citizenship for immigrants residing illegally in the US a reality. Since March 18, 2021, the National TPS Alliance has been hosting an ongoing hunger strike in Washington, DC in order to press for the speedy passage of the acts.
The current migratory surge at the US-Mexico border
While the long-term immigration forecast appears increasingly more positive as Biden's presidency progresses, the immediate immigration situation at the US-Mexico border is quite dire. Between December 2020 and February 2021, the US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) reported a 337% increase in the arrival of families, and an 89% increase in the arrival of unaccompanied minors. CBP apprehensions of migrants crossing the border illegally in March 2021 have reached 171,00, which is the highest monthly total since 2006.
Currently, there are an estimated 4,000 unaccompanied minors in CBP custody, and an additional 15,000 unaccompanied minors in the custody of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
The migratory CBP facility in Donna, TX designated specifically to unaccompanied minors has been filled at 440% to 900% of its COVID-19 capacity of just 500 minors since March 9, 2021. Intended to house children for no more than a 72-hour legal limit, due to the current overwhelmed system, some children have remained in the facility for more than weeks at a time before being transferred on to HHS.
In order to address the overcrowding, the Biden administration announced the opening of the Delphia Emergency Intake Site (next to the Donna facility) on April 6, 2021, which will be used to house up to 1,500 unaccompanied minors. Other new sites have been opened by HHS in Texas and California, and HHS has requested the Pentagon to allow it to temporarily utilize three military facilities in these same two states.
Political polarization has contributed to a great disparity in the interpretation of the recent surge in migration to the US border since Biden took office. Termed a "challenge" by Democrats and a "crisis" by Republicans, both parties offer very different explanations for the cause of the situation, each placing the blame on the other.
The country left the cartel in order to expand pumping, but the Covid-19 crisis has cut extraction volumes by 10.8%.

Construction of a variant of the oil pipeline that crosses the Andes, from the Ecuadorian Amazon to the Pacific [Petroecuador].
ANALYSIS / Jack Acrich and Alejandro Haro
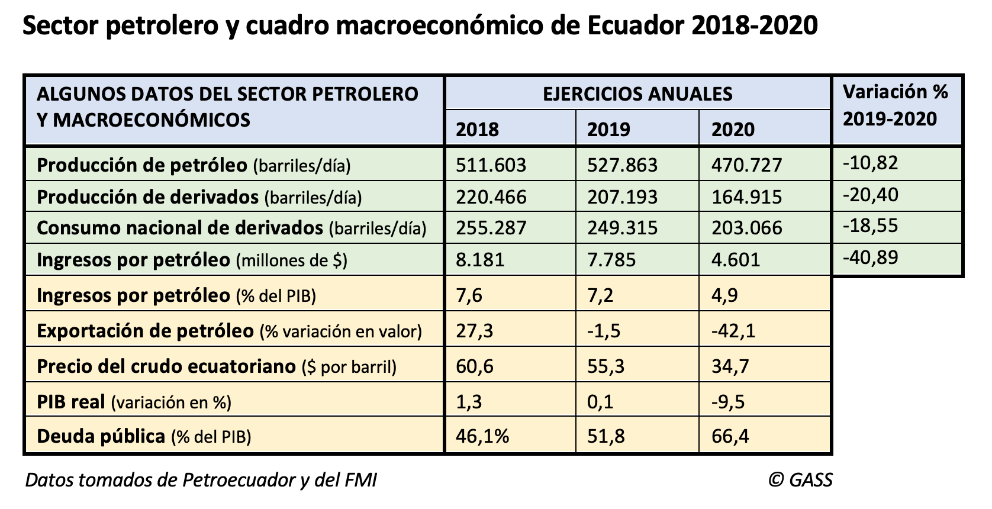
Ecuador left the Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) on 1 January 2020 to avoid having to continue to join the production cuts imposed by group , which it agrees to in order to push up the world price of crude oil. Ecuador preferred to sell more barrels, albeit at a lower price, because by exporting more at the end of the day written request it could increase its income and thus get out of its serious financial situation status , which the coronavirus emergency has only accentuated, with a fall in GDP in 2020 currently estimated at 9.5 per cent.
However, domestic economic difficulties and the difficult international situation have not only prevented Ecuador from expanding pumping, but oil production has fallen by 10.8% in the last year. average In 2020, Ecuador extracted 472,000 barrels of oil per day, especially affected by the sharp reduction in activity in April with the beginning of the confinement, which was not compensated for the rest of the year. agreement This is a volume that is below the 500,000 line that has always been exceeded in recent years (in 2019 production was 528,000), according to figures from Petroecuador, the state hydrocarbons company. The reduction in global consumption during the Covid-19 year also correlated with a drop in the consumption of derivatives in Ecuador, especially gasoline and diesel, which fell by 18.5%.
International investment constrained by the pandemic context and reduced consumption marked a status that could hardly lead to an increase in production. In 2020, Ecuador saw a drop in the value of oil exports of 42.1% (twice as much as total exports), which, combined with a deterioration in the price of a barrel of oil, meant a 40.9% reduction in public revenue from the oil sector, according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) data .
The figures for the first two months of 2021 indicate an accentuation of the fall in crude oil production (-4.73% compared to January and February 2020) and derivatives (-7.47%), as well as their export (-22.8%).
Cutting expense and seeking oil revenues
Exiting OPEC did not pose any particular risk for Ecuador, which had already left the organisation in a previous period. Its limited weight in OPEC and the progressive decline in the cartel's own strength meant that Ecuador's attempt to go it alone was not particularly costly. The absolute priority of Lenín Moreno's government was to rebalance the country's macroeconomic picture - battered by the high public expense of his predecessor, Rafael Correa - and for this it urgently needed to increase state revenue, a significant part of which in Ecuador normally comes from the hydrocarbons sector.
When he became president in 2017, Moreno set out to steer the country towards more market-friendly energy policies. The president was determined to break with the nationalist approach of his predecessor, whose policies discouraged foreign investment in the oil industry while significantly increasing public debt. Among the most costly programmes undertaken by Correa was to maintain high subsidies for energy consumption, with especially low fuel prices.
In order to overcome the financial status that Ecuador found itself in when he took office, Moreno approached the IMF to apply for financial aid financial, and committed to structural reforms, including the gradual dismantling of subsidies. These reforms, however, were not well received and the social unrest that spread throughout the country put further pressure on the oil industry.
In February 2019, Moreno negotiated an IMF loan to help reduce the country's large fiscal deficit and huge external debt, which by the end of 2018 had reached 46.1 per cent of GDP and twelve months later would reach 51.8 per cent. The committed 'bailout' was for $10.2 billion, of which $6.5 billion came from the IMF and the rest from other international agencies.
As part of austerity measures agreed with the IMF, Moreno was forced to end government subsidies that had kept petrol prices low for decades. In early October 2019 he announced a plan of cuts to save $2.27 billion a year, essentially withdrawing the fuel subsidy. The advertisement decree, which would later be annulled, immediately provoked massive protests, both from transporters and low-income sectors, as well as most notably from indigenous communities. The street violence forced the president to leave Quito for a few days and move to Guayaquil.
To address the need for revenue, Moreno sought to rely on the oil industry, which accounts for roughly a third of the country's total exports. He initially expressed the intention to seek a rise from the 545,000 barrels of crude oil produced at the time to almost 700,000 barrels a day.
goal One of the measures taken in this direction was to promote the development and the exploitation of the Ishpingo-Tiputini-Tambococha field, with the aim of increasing oil production by 90,000 barrels a day. This decision met with social rejection due to the environmental damage it could cause, as the Yasuní National Park, in the Ecuadorian Amazon, has been declared a protected area. The government then decided to postpone the expansion of production, first to 2021 and then to 2022. The civil service examination was especially led by indigenous communities, in a mobilisation that partly explains the success in the 2021 presidential elections of Yaku Pérez's indigenist Pachakutik movement, which almost made it to the second round.
Another measure was to reverse some of his predecessor's emblematic policies. For example, he eliminated the service contracts introduced under President Correa, thus restoring the model production-sharing contract. This reform was more favourable to international oil companies, as it allowed them to retain a share of oil reserves; it also offered them financial incentives to invest in the country. The new model was first applied in the tenders awarded during the twelfth Intracampos oil round, in the Oriente region, which is rich in oil reserves. Under this contract modality , the Moreno administration awarded seven of the eight exploration blocks on offer with a total investment of more than $1.17 billion.
Fall in production
Due to the urgency of increasing revenues, Ecuador resisted the plan of production cuts that OPEC has been imposing on its members at various times since the abrupt fall in oil prices in 2014. Initially, the organisation accepted that some of its members, with moderate or very low production volumes compared to previous figures, as was the case of Venezuela, would maintain their extraction rates. But since it could no longer be an exception, Ecuador preferred to announce at the end of 2019 that it would leave OPEC and not have to reduce its production to 508,000 barrels per day in 2020, which was the quota set for it.
What is striking is that last year production finally fell from 528,000 barrels per day in 2019 to 472,000 (a drop of 10.8%), and not because of decisions taken at OPEC headquarters in Vienna but because of the various difficulties subject caused by the Covid-19 crisis. Petroecuador's oil exports fell from 331,321 barrels per day in 2019 to 316,000, a drop of 4.6%, which in monetary terms was greater, as the price of a barrel of Ecuadorian mixed oil fell from 55.3 dollars in 2019 to 34.7 in 2020.
One element that makes it difficult for Ecuador to take better advantage of its hydrocarbon potential is that it has insufficient infrastructure for refining crude oil. The country has three refineries, but their capacity does not reach the volume of domestic consumption of oil derivatives, which means that it must import diesel, naphtha and other products. This means that in times of high oil prices, Ecuador benefits from exports, but also has to pay a higher invoice price for imports of derivatives. In 2020, Petroecuador had to import 137,300 barrels per day.
The complicated situation caused by the pandemic has continued to put pressure on Ecuador's public debt, which reached 66.4% at the end of 2020, despite all the attempts made by the Moreno government to reduce it.
The next president, due to take office at the end of May 2021, will also have little room for manoeuvre due to these debt volumes and will have to continue to rely on higher oil revenues to balance public finances. The expansionary policies of expense during Correa's presidency took place in the context of the commodity super-cycle, which benefited South America so much, but this is unlikely to be repeated in the short term deadline.
OPEC's loss of weight
With its departure from OPEC, Ecuador left an international organisation that was created in 1960 with the aim of regulating the world oil market and controlling oil prices to a certain extent. goal . The founding members were Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela. Over time, other countries joined OPEC and today it is made up of thirteen members: Algeria, Angola, Republic of Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, United Arab Emirates and the five founding countries. When it was created, the organisation sought to establish, acting as a cartel, a kind of counterweight to a series of Western energy transnationals, mainly from the United States and the United Kingdom. OPEC members account for about 40 per cent of world oil production and contain about 80 per cent of the world's proven oil reserves. To be admitted as a member of the organisation it is necessary to have substantial oil exports and to share those of the member countries.
Ecuador joined OPEC in 1973, but suspended its membership in 1992. Subsequently, in 2007 it resumed active participation until its leave in January 2020. Considering that Ecuador was one of OPEC's smaller members, it did not really have much influence in the organisation and its exit does not represent a substantial loss for the organisation. However, it is a second departure in just one year, as Qatar, which had more weight in the cartel, left on 1 January 2019. In its case, its divorce from OPEC was due to other reasons, such as its tensions with Saudi Arabia and its desire to focus on the gas sector, of which it is one of the world's largest producers.
These moves are an example of OPEC's loss of influence. This has led it to establish alliances with producers that are not part of the organisation, such as Russia and some other countries forming OPEC+. With the decline of oil production in Venezuela and the decreasing ability of other members to control their production and exports, Saudi Arabia has been increasingly consolidating its position as the cartel's leader, accounting for around a third of the total production, with approximately 9.4 million barrels per day. In a way, Saudi Arabia and Russia remain, in a head to head battle, as the main countries seeking to cut production in an attempt to increase prices. Additionally, thanks to fracking, the United States has become the largest oil producer, representing a major influence on the international crude oil market, affecting the power that OPEC may have.
 Detainee in a Xinjiang re-education camp located in Lop County listening to "de-radicalization" talks [Baidu baijiahao].
Detainee in a Xinjiang re-education camp located in Lop County listening to "de-radicalization" talks [Baidu baijiahao].
ESSAY / Rut Noboa
Over the last few years, reports of human rights violations against Uyghur Muslims, such as extrajudicial detentions, torture, and forced labor, have been increasingly reported in the Xinjiang province's so-called "re-education" camps. However, the implications of the Chinese undertakings on the province's ethnic minority are not only humanitarian, having direct links to China's ongoing economic projects, such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and natural resource extraction in the region. Asides from China's economic diary, ongoing projects in Xinjiang appear to prototype future Chinese initiatives in terms of expanding the surveillance state, particularly within the scope of technology. When it comes to other international actors, the Xinjiang dispute has evidenced a growing diplomatic split between countries against it, mostly western liberal democracies, and countries willing to at least defend it, mostly countries with important ties to China and dubious human rights records. The issue also has important repercussions for multinational companies, with supply chains of well-known international companies such as Nike and Apple benefitting from forced Uyghur labour. The situation in Xinjiang is critically worrisome when it comes to the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly considering recent outbreaks in Kashgar, how highly congested these "reeducation" camps, and potential censorship from the government. Finally, Uyghur communities continue to be an important factor within this conversation, not only as victims of China's policies but also as dissidents shaping international opinion around the matter.
The Belt and Road Initiative
Firstly, understanding Xinjiang's role in China's ongoing projects requires a strong geographical perspective. The northwestern province borders Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India, giving it important contact with other regional players.
This also places it at the very heart of the BRI. With it setting up the twenty-first century "Silk Road" and connecting all of Eurasia, both politically and economically, with China, it is no surprise that it has managed to establish itself as China's biggest infrastructural project and quite possibly the most important undertaking in Chinese policy today. Through more and more ambitious efforts, China has established novel and expansive connections throughout its newfound spheres of influence. From negotiations with Pakistan and the establishment of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) securing one of the most important routes in the initiative to Sri Lanka defaulting on its loan and giving China control over the Hambantota Port, the Chinese government has managed to establish consistent access to major trade routes.
However, one important issue remains: controlling its access to Central Asia. One of the BRI's initiative's key logistical hubs is Xinjiang, where the Uyghurs pose an important challenge to the Chinese government. The Uyghur community's attachment to its traditional lands and culture is an important risk to the effective implementation of the BRI in Xinjiang. This perception is exacerbated by existing insurrectionist groups such as the East Turkestan independence movement and previous events in Chinese history, including the existence of an independent Uyghur state in the early 20th century[1]. Chinese infrastructure projects that cross through the Xinjiang province, such as the Central Asian High-speed Rail are a priority that cannot be threatened by instability in the region, inspiring the recent "reeducation" and "de-extremification" policies.
Natural resource exploitation
Another factor for China's growing control over the region is the fact that Xinjiang is its most important energy-producing region, even reaching the point where key pipeline projects connect the northwestern province with China's key coastal cities and approximately 60% of the province's gross regional production comes from oil and natural gas extraction and related industries[2]. With China's energy consumption being on a constant rise[3] as a result of its growing economy, control over Xinjiang is key to Chinese.
Additionally, even though oil and natural gas are the region's main industries, the Chinese government has also heavily promoted the industrial-scale production of cotton, serving as an important connection with multinational textile-based corporations seeking cheap labour for their products.
This issue not only serves as an important reason for China to control the Uyghurs but also promotes instability in the region. The increased immigration from a largely Han Chinese workforce, perceived unequal distribution of revenue to Han-dominated firms, and increased environmental costs of resource exploitation have exacerbated the pre-existing ethnic conflict.
A growing diplomatic split
The situation in Xinjiang also has important implications for international perceptions of Chinese propaganda. China's actions have received noticeable backlash from several states, with 22 states issuing a joint statement to the Human Rights Council on the treatment of Uyghurs and other ethnic minorities in Xinjiang on July 8, 2019. These states called upon China "to uphold its national laws and international obligations and to respect human rights and fundamental freedoms".
Meanwhile, on July 12, 2019, 50 (originally 37) other states issued a competing letter to the same institution, commending "China's remarkable achievements in the field of human rights", stating that people in Xinjiang "enjoy a stronger sense of happiness, fulfillment and security".
This diplomatic split represents an important and growing division in world politics. When we look at the signatories of the initial letter, it is clear to see that all are developed democracies and most (except for Japan) are Western. Meanwhile, those countries that chose to align themselves with China represent a much more heterogeneous group with states from the Middle East, Asia, and Africa[4]. Many of these have questionable human rights records and/or receive important funding and investment from the Chinese government, reflecting both the creation of an alternative bloc distanced from Western political influence as well as an erosion of preexisting human rights standards.
China's Muslim-majority allies: A Pakistani case study
The diplomatic consequences of the Xinjiang controversy are not only limited to this growing split, also affecting the political rhetoric of individual countries. In the last years, Pakistan has grown to become one of China's most important allies, particularly within the context of CPEC being quite possibly one of the most important components of the BRI.
As a Muslim-majority country, Pakistan has traditionally placed pan-Islamic causes, such as the situations in Palestine and Kashmir, at the centre of its foreign policy. However, Pakistan's position on Xinjiang appears not just subdued but even complicit, never openly criticising the situation and even being part of the mentioned letter in support of the Chinese government (alongside other Muslim-majority states such as Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE). With Pakistani Prime Minister Imran Khan addressing the General Assembly in September 2019 on Islamophobia in post-9/11 Western countries as well as in Kashmir but conveniently omitting Uyghurs in Xinjiang[5], Pakistani international rhetoric weakens itself constantly. Due to relying on China for political and economic support, it appears that Pakistan will have to censor itself on these issues, something that also rings true for many other Muslim-majority countries.
Central Asia: complacent and supportive
Another interesting case study within this diplomatic split is the position of different countries in the Central Asian region. These states - Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan - have the closest cultural ties to the Uyghur population. However, their foreign policy hasn't been particularly supportive of this ethnic group with Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan avoiding the spotlight and not participating in the UNHRC dispute and Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan being signatories of the second letter, explicitly supporting China. These two postures can be analyzed through the examples of Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan.
Kazakhstan has taken a mostly ambiguous position to the situation. Having the largest Uyghur population outside China and considering Kazakhs also face important persecution from Chinese policies that discriminate against minority ethnic groups in favour of Han Chinese citizens, Kazakhstan is quite possibly one of the states most affected by the situation in Xinjiang. However, in the last decades, Kazakhstan has become increasingly economically and, thus, politically dependent on China. After the fall of the Soviet Union, Kazakhstan implemented what some would refer to as a "multi-vector" approach, seeking to balance its economic engagements with different actors such as Russia, the United States, European countries, and China. However, with American and European interests in Kazakhstan decreasing over time and China developing more and more ambitious foreign policy within the framework of strategies such as the Belt and Road Initiative, the Central Asian state has become intimately tied to China, leading to its deafening silence on Uyghurs in Xinjiang.
A different argument could be made for Uzbekistan. Even though there is no official statistical data on the Uyghur population living in Uzbekistan and former president Islam Karimov openly stated that no Uyghurs were living there, this is highly questionable due to the existing government censorship in the country. Also, the role of Uyghurs in Uzbekistan is difficult to determine due to a strong process of cultural and political assimilation, particularly in the post-Soviet Uzbekistan. By signing the letter to the UNHCR in favour of China's practices, the country has chosen a more robust support of its policies.
All in all, the countries in Central Asia appear to have chosen to tolerate and even support Chinese policies, sacrificing cultural values for political and economic stability.
Forced labour, the role of companies, and growing backlash
In what appears to be a second stage in China's "de-extremification" policies, government officials have claimed that the "trainees "in its facilities have "graduated", being transferred to factories outside of the province. China claims these labor transfers (which it refers to as vocational training) to be part of its "Xinjiang Aid" central policy[6]. Nevertheless, human rights groups and researchers have become growingly concerned over their labor standards, particularly considering statements from Uyghur workers who have left China describing the close surveillance from personnel and constant fear of being sent back to detention camps.
Within this context, numerous companies (both Chinese and foreign) with supply chain connections with factories linked to forced Uyghur labour have become entangled in growing international controversies, ranging from sportswear producers like Nike, Adidas, Puma, and Fila to fashion brands like H&M, Zara, and Tommy Hilfiger to even tech players such as Apple, Sony, Samsung, and Xiaomi[7]. Choosing whether to terminate relationships with these factories is a complex choice for these companies, having to either lose important components of their intricate supply chains or face growing backlash on an increasingly controversial issue.
The allegations have been taken seriously by these groups with organizations such as the Human Rights Watch calling upon concerned governments to take action within the international stage, specifically through the United Nations Human Rights Council and by imposing targeted sanctions at responsible senior officials. Another important voice is the Coalition to End Forced Labour in the Uyghur Region, a coalition of civil society organizations and trade unions such as the Human Rights Watch, the Investor Alliance for Human Rights, the World Uyghur Congress, and the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation, pressuring the brands and retailers involved to exclude Xinjiang from all components of the supply chain, especially when it comes to textiles, yarn or cotton as well as calling upon governments to adopt legislation that requires human rights due diligence in supply chains. Additionally, the Australian Strategic Policy Institute, the same organisation that carried out the initial report on forced Uyghur labor and surveillance beyond Xinjiang and within the context of these labor transfers, recently created the Xinjiang Data Project. This initiative documents ongoing Chinese policies on the Uyghur community with open-source data such as satellite imaging and official statistics and could be decidedly useful for human rights defenders and researchers focused on the topic.
One important issue when it comes to the labour conditions faced by Uyghurs in China comes from the failures of the auditing and certification industry. To respond to the concerns faced by having Xinjiang-based suppliers, many companies have turned to auditors. However, with at least five international auditors publicly stating that they would not carry out labor-audit or inspection services in the province due to the difficulty of working with the high levels of government censorship and monitoring, multinational companies have found it difficult to address these issues[8]. Additionally, we must consider that auditing firms could be inspecting factories that in other contexts are their clients, adding to the industry's criticism. These complaints have led human rights groups to argue that overarching reform will be crucial for the social auditing industry to effectively address issues such as excessive working hours, unsafe labor conditions, physical abuse, and more[9].
Xinjiang: a prototype for the surveillance state
From QR codes to the collection of biometric data, Xinjiang has rapidly become the lab rat for China's surveillance state, especially when it comes to technology's role in the issue.
One interesting area being massively affected by this is travel. As of September 2016, passport applicants in Xinjiang are required to submit a DNA sample, a voice recording, a 3D image of themselves, and their fingerprints, much harsher requirements than citizens in other regions. Later in 2016, Public Security Bureaus across Xinjiang issued a massive recall of passports for an "annual review" followed by police "safekeeping"[10].
Another example of how a technologically aided surveillance state is developing in Xinjiang is the Integrated Joint Operations Platform (IJOP), a big data program for policing that selects individuals for possible detention based on specific criteria. According to the Human Rights Watch, which analyzed two leaked lists of detainees and first reported on the policing program in early 2018, the majority of people identified by the program are being persecuted because of lawful activities, such as reciting the Quran and travelling to "sensitive" countries such as Saudi Arabia and Turkey. Additionally, some criteria for detention appear to be intentionally vague, including "being generally untrustworthy" and "having complex social ties"[11].
Xinjiang's case is particularly relevant when it comes to other Chinese initiatives, such as the Social Credit System, with initial measures in Xinjiang potentially aiding to finetune the details of an evolving surveillance state in the rest of China.
Uyghur internment camps and COVID-19
The implications of the COVID-19 pandemic for Uyghurs in Xinjiang are pressing issues, particularly due to the virus's rapid spread in highly congested areas such as these "reeducation" camps.
Currently, Kashgar, one of Xinjiang's prefectures is facing China's most recent coronavirus outbreak[12]. Information from the Chinese government points towards a limited outbreak that is being efficiently controlled by state authorities. However, the authenticity of this data is highly controversial within the context of China's early handling of the pandemic and reliance on government censorship.
Additionally, the pandemic has more consequences for Uyghurs than the virus itself. As the pandemic gives governments further leeway to limit rights such as the right to assembly, right to protest, and freedom of movement, the Chinese government gains increased lines of action in Xinjiang.
Uyghur communities abroad
The situation for Uyghurs living abroad is far from simple. Police harassment of Uyghur immigrants is quite common, particularly through the manipulation and coercion of their family members still living in China. These threatening messages requesting staff information or pressuring dissidents abroad to remain silent. The officials rarely identify themselves and in some cases these calls or messages don't necessarily even come from government authorities, instead coming from coerced family members and friends[13]. One interesting case was reported in August 2018 by US news publication The Daily Beast in which an unidentified Uyghur American woman was asked by her mother to send over pictures of her US license plate number, her phone number, her bank account number, and her ID card under the excuse that China was creating a new ID system for all Chinese citizens, even those living abroad[14]. A similar situation was reported by Foreign Policy when it came to Uyghurs in France who have been asked to send over home, school, and work addresses, French or Chinese IDs, and marriage certificates if they were married in France[15].
Regardless of Chinese efforts to censor Uyghur dissidents abroad, their nonconformity has only grown with the strengthening of Uyghur repression in mainland China. Important international human rights groups such as Amnesty International and the Human Rights Watch have been constantly addressing the crisis while autonomous Uyghur human rights groups, such as the Uyghur Human Rights Project, the Uyghur American Association, and the Uyghur World Congress, have developed from communities overseas. Asides from heavily protesting policies such as the internment camps and increasing surveillance in Xinjiang, these groups have had an important role when it comes to documenting the experiences of Uyghur immigrants. However, reports from both human rights group and average agencies when it comes to the crisis have been met with staunch rejection from China. One such case is the BBC being banned in China after recently reporting on Xinjiang internment camps, leading it to be accused of not being "factual and fair" by the China National Radio and Television Administration. The UK's Foreign Secretary Dominic Raab referred to the actions taken by the state authorities as "an unacceptable curtailing of average freedom" and stated that they would only continue to damage China's international reputation[16].
One should also think prospectively when it comes to Uyghur communities abroad. As seen in the diplomatic split between countries against China's policies in Xinjiang and those who support them (or, at the very least, are willing to tolerate them for their political interest), a growing number of countries can excuse China's treatment of Uyghur communities. This could eventually lead to countries permitting or perhaps even facilitating China's attempts at coercing Uyghur immigrants, an important prospect when it comes to countries within the BRI and especially those with an important Uyghur population, such as the previously mentioned example of Kazakhstan.
REFERENCES
[1] Qian, Jingyuan. 2019. "Ethnic Conflicts and the Rise of Anti-Muslim Sentiment in Modern China." Department of Political Science, University of Wisconsin-Madison. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3450176.
[2] Cao, Xun, Haiyan Duan, Chuyu Liu, James A. Piazza, and Yingjie Wei. 2018. "Digging the "Ethnic Violence in China" Database: The Effects of Inter-Ethnic Inequality and Natural Resources Exploitation in Xinjiang." The China Review (The Chinese University of Hong Kong) 18 (No. 2 SPECIAL THEMED SECTION: Frontiers and Ethnic Groups in China): 121-154. Accessed November 15, 2020. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26435650
[3] International Energy Agency. 2020. Data & Statistics - IEA. Accessed November 14, 2020. https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics?country=CHINA&fuel=Energy%20consumption&indicator=TotElecCons.
[4] Yellinek, Roie, and Elizabeth Chen. 2019. "The "22 vs. 50" Diplomatic Split Between the West and China." China Brief (The Jamestown Foundation) 19 (No. 22): 20-25. Accessed November 14, 2020. https://jamestown.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/Read-the-12-31-2019-CB-Issue-in-PDF.pdf?x91188.
[5] United Nations General Assembly. 2019. "General Assembly official records, 74th session : 9th plenary meeting." New York. Accessed October 18, 2020.
[6] Xu, Vicky Xiuzhong, Danielle Cave, James Leibold, Kelsey Munro, and Nathan Ruser. 2020. "Uyghurs for sale: 'Re-education', forced labour and surveillance beyond Xinjiang." Policy Brief, International Cyber Policy Centre, Australian Strategic Policy Paper. Accessed November 14, 2020. https://www.aspi.org.au/report/uyghurs-sale
[7] Ibid.
[8] Xiao, Eva. 2020. Auditors to Stop Inspecting Factories in China's Xinjiang Despite Forced-Labor Concerns. 21 September. Accessed December 2020, 16. https://www.wsj.com/articles/auditors-say-they-no-longer-will-inspect-labor-conditions-at-xinjiang-factories-11600697706.
[9] Kashyap, Aruna. 2020. Social Audit Reforms and the Labor Rights Ruse. 7 October. Accessed December 16, 2020. https://www.hrw.org/news/2020/10/07/social-audit-reforms-and-labor-rights-ruse.
[10] Human Rights Watch. 2016. China: Passports Arbitrarily Recalled in Xinjiang. 21 November. Accessed November 15, 2020. https://www.hrw.org/news/2016/11/22/china-passports-arbitrarily-recalled-xinjiang
[11] Human Rights Watch. 2020. China: Big Data Program Targets Xinjiang's Muslims. 9 December. Accessed December 17, 2020. https://www.hrw.org/news/2020/12/09/china-big-data-program-targets-xinjiangs-muslims.
[12] National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. 2020. How China's Xinjiang is tackling new COVID-19 outbreak. 29 October. Accessed November 14, 2020. http://en.nhc.gov.cn/2020-10/29/c_81994.htm.
[13] Uyghur Human Rights Project. 2019. "Repression Across Borders: The CCP's Illegal Harassment and Coercion of Uyghur Americans."
[14] Allen-Ebrahimian, Bethany. 2018. Chinese Cops Now Spying on American Soil. 14 August. Accessed December 7, 2020. https://www.thedailybeast.com/chinese-police-are-spying-on-uighurson-american-soil.
[15] Allen-Ebrahimian. 2018. Chinese Police Are Demanding staff Information From Uighurs in France. 2 March. Accessed December 7, 2020. https://foreignpolicy.com/2018/03/02/chinese-police-are-secretly-demanding-staff-information-from-french-citizens-uighurs-xinjiang/.
[16] Reuters Staff. 2021. BBC World News barred in mainland China, radio dropped by HK public broadcaster. 11 February. Accessed February 16, 2021. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-britain-bbc/bbc-world-news-barred-from-airing-in-china-idUSKBN2AB214.
The hydrocarbon field is the centrepiece of President Alberto Fernández's 2020-2023 Gas Plan, which subsidises part of the investment.

Activity of YPF, Argentina's state-owned hydrocarbon company [YPF].
ANALYSIS / Ignacio Urbasos Arbeloa
Argentina is facing a deep economic crisis that is having a severe impact on the standard of living of its citizens. The country, which had managed to emerge with enormous sacrifices from the corralito of 2001, sees its leaders committing the same macroeconomic recklessness that led the national Economics to collapse. After a hugely disappointing mandate by Mauricio Macri and his economic "gradualism", the new administration of Alberto Fernández has inherited a very delicate status , now aggravated by the global and national crisis generated by Covid-19. Public debt is now almost 100% of GDP, the Argentine peso is worth less than 90 units to the US dollar, while the public deficit persists. The Economics is still in recession, accumulating four years of decline. The IMF, which lent nearly $44 billion to Argentina in 2018 in the largest loan in the institution's history, has begun to lose patience with the lack of structural reforms and hints of debt restructuring by the government. In this critical status , Argentines are looking to the development unconventional oil industry as a possible way out of the economic crisis. In particular, the Vaca Muerta super field has been the focus of attention of international investors, government and citizens for the last decade, being a very promising project not Exempt of environmental and technical challenges.
The energy sector in Argentina: a history of fluctuations
The oil sector in Argentina has more than 100 years of history since oil was discovered in the Patagonian desert in 1907. The geographical difficulties of area - lack of water, distance from Buenos Aires and salty winds of more than 100 km/h - meant that project advanced very slowly until the outbreak of the First World War. The European conflict interrupted coal imports from England, which until then had accounted for 95% of Argentina's energy consumption. business The emergence of oil in the inter-war period as a strategic raw subject commodity revalued the sector, which began to receive huge foreign and domestic investment in the 1920s. By 1921, YPF, the first state-owned oil company in Latin America, was created, with energy self-sufficiency as its main goal goal. The country's political upheaval during the so-called Década Infame (1930-43) and the effects of the Great Depression damaged the incipient oil sector. The years of Perón's government saw a timid take-off of the oil industry with the opening of the sector to foreign companies and the construction of the first oil pipelines. In 1958, Arturo Frondizi became President of Argentina and sanctioned the Hydrocarbons Law of 1958, achieving an impressive development of the sector in only 4 years with an immense policy of public and private investment that multiplied oil production threefold, extended the network of gas pipelines and generalised access to natural gas for industry and households. The oil regime in Argentina kept the ownership of resource in the hands of the state, but allowed the participation of private and foreign companies in the production process.
Since the successful 1960s in subject oil, the sector entered a period of relative stagnation in parallel with Argentina's chaotic politics and Economics at the time. The 1970s was a complex journey in the desert for YPF, mired in huge debt and unable to increase production and secure the longed-for self-sufficiency.
The so-called Washington Consensus and the arrival of Carlos Menem to the presidency in 1990 saw the privatisation of YPF and the fragmentation of the state monopoly over the sector. By 1998, YPF was fully privatised under the ownership of Repsol, which controlled 97.5% of its capital. It was in the period 1996-2003 that peak oil production was reached, exporting natural gas to Chile, Brazil and Uruguay, and exceeding 300,000 barrels of crude oil per day in net exports.
However, a turnaround soon began in the face of state intervention in the market. Domestic consumption with fixed sales prices for oil producers was less attractive than the export market, encouraging private companies to overproduce in order to export oil and increase revenues exponentially. With the rise in oil prices of the so-called "commodity super-cycle" during the first decade of this century, the price differential between exports and domestic sales widened, creating a real incentive to focus on production. Exploration was thus left in the background, as domestic consumption grew rapidly due to tax incentives and a near horizon was foreseen without the possibility of exports and, therefore, lower income from the increase in reserves.
The exit from the 2001 crisis took place in a context of fiscal and trade surpluses, which allowed the country to regain the confidence of international creditors and reduce the volume of public debt. It was precisely the energy sector that was the main driver of this recovery, accounting for more than half of the trade surplus in the period 2004-2006 and one of Argentina's main sources of fiscal revenue. However, as mentioned above, this production was not sustainable due to the existence of a fiscal framework that distorted oil companies' incentives in favour of immediate consumption without investing in exploration. By 2004, a new tariff was applied to crude oil exports that floated on the basis of the international price of crude, reaching 45% if the price was above 45 dollars. The excessively rentier approach of Néstor Kirchner's presidency ended up dilapidating the sector's investment incentives, although it is true that they allowed for a spectacular increase in derived fiscal revenues, boosting Argentina's generous social and debt repayment plans. sample As a good illustration of this decline in exploration, in the 1980s more than 100 exploratory wells were drilled annually, in 1990 the figure exceeded 90, and by 2010 the figure was 26 wells per year. This figure is particularly dramatic if one takes into account the dynamics that the oil and gas sector tends to follow, with large investments in exploration and infrastructure in times of high prices, as was the case between 2001-2014.
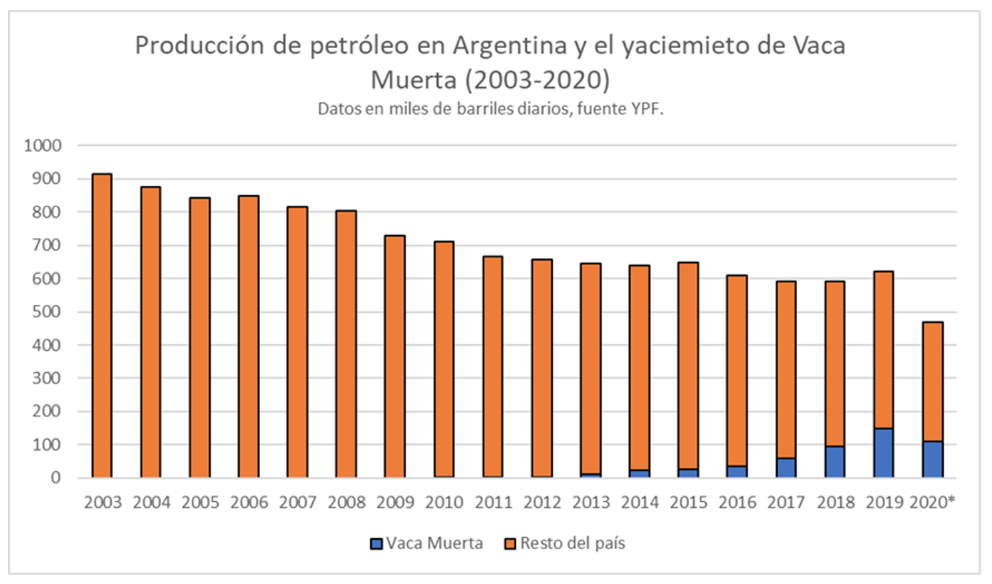
In 2011, after a decade of debate on the oil sector in Argentina, President Cristina Fernández decided to expropriate 51 per cent of the shares of YPF held by Repsol, citing reasons of energy sovereignty and the decline of the sector. This decision followed the line taken by Hugo Chávez and Evo Morales in 2006 to increase the state's weight in the hydrocarbons sector at a time of electoral success for the Latin American left. The expropriation took place in the same year that Argentina became a net energy importer and coincided with the finding of the large shale reserves in Neuquén precisely by YPF, now known as Vaca Muerta. YPF at the time was the direct producer of approximately one third of Argentina's total volume. The expropriation took place at the same time as the imposition of the "cepo cambiario", a system of capital controls that made private foreign investment in the sector even less attractive. Not only was the country unable to recover its energy self-sufficiency, but it also entered a period of intense imports that hampered access to dollars and produced a large part of the macroeconomic imbalance of the current economic crisis.
The arrival of Mauricio Macri in 2015 heralded a new phase for the sector with policies more favourable to private initiative. One of the first measures was to establish a fixed price at the "wellhead" of the Vaca Muerta oil fields with the idea of encouraging the start-up of projects. As the economic crisis worsened, the unpopular measure of increasing electricity and fuel prices by more than 30 per cent was chosen, generating enormous discontent in the context of a constant devaluation of the Argentine peso and the rising cost of living. The energy portfolio was marked by enormous instability, with three different ministers who generated enormous legal insecurity by constantly changing the hydrocarbons regulatory framework . Renewable solar and wind energy, boosted by a new energy plan and greater liberalisation of investment, managed to double their energy contribution during Mauricio Macri's time in the Casa Rosada.
Alberto Fernández's first years have been marked by unconditional support for the hydrocarbons sector, with Vaca Muerta being the central axis of his energy policy, announcing the 2020-2023 Gas Plan that will subsidise part of the investment in the sector. On the other hand, despite the context of the health emergency, 39 renewable energy projects were installed in 2020, with an installed capacity of around 1.5 GW, an increase of almost 60% over the previous year. In any case, the continuity of this growth will depend on access to foreign currency in the country, which is essential to be able to buy panels and windmills from abroad. The boom in renewable energy in Argentina led the Danish company Vestas to install the first windmill assembly plant in the country in 2018, which already has several plants producing solar panels to supply domestic demand.
Characteristics of Vaca Muerta
Vaca Muerta is not a field from a technical point of view, it is a sedimentary training of enormous magnitude with dispersed deposits of natural gas and oil that can only be exploited with unconventional techniques: hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling. These characteristics make Vaca Muerta a complex activity, which requires attracting as much talent as possible, especially from international players with experience in the exploitation of unconventional hydrocarbons. Likewise, conditions in the province of Neuquén are complex given the scarcity of rainfall and the importance of the fruit and vegetable industry, in direct competition with the water resources required for the exploitation of unconventional oil.
Since finding, the potential of Vaca Muerta has been compared to that of the Eagle Ford basin in the United States, which produces more than one million barrels per day. Evidently, the Neuquén region has neither Texas' oil business ecosystem nor its fiscal facilities, making what might be geologically similar in reality two totally different stories. In December 2020, Vaca Muerte produced 124,000 barrels of oil per day, a figure that is expected to gradually increase over the course of this year to 150,000 barrels per day, about 30% of the 470,000 barrels per day Argentina produced in 2020. Natural gas follows a slower process, pending the development of infrastructure that will allow the transport of large volumes of gas to consumption and export centres. In this regard, Fernández announced in November 2020 the Plan for the Promotion of Argentine Gas Production 2020-2023, with which the Casa Rosada seeks to save dollars by substituting imports. The plan facilitates the acquisition of dollars for investors and improves the maximum selling price of natural gas by almost 50%, to 3.70 dollars per mbtu, in the hope of receiving the necessary investment, estimated at 6.5 billion dollars, to achieve gas self-sufficiency. Argentina already has the capacity to export natural gas to Chile, Uruguay and Brazil through pipelines. Unfortunately, the floating vessel exporting natural gas from Vaca Muerte left Argentina at the end of 2020 after YPF unilaterally broke the ten-year contract with the vessel's owner, Exmar, citing economic difficulties, limiting the capacity to sell natural gas outside the continent.
One of the great advantages of Vaca Muerta is the presence of international companies with experience in the aforementioned US unconventional oil basins. The post-2014 learning curve of the US fracking sector is being applied in Vaca Muerta, which has seen drilling costs fall by 50% since 2014 while gaining in productivity. The influx of US capital may accelerate if Joe Biden's administration fiscally and environmentally restricts oil activities in the country, from agreement with its environmentalist diary . Currently the main operator in Vaca Muerta after YPF is Chevron, followed by Tecpetrol, Wintershell, Shell, Total and Pluspetrol, in an ecosystem with 18 oil companies working in different blocks.
Vaca Muerta as a national strategy
It is clear that achieving energy self-sufficiency will help Argentina's macroeconomic problems, the main headache for its citizens in recent years. No Exempt of environmental risk, Vaca Muerta could be a lifeline for a country whose international credibility is at an all-time low. Alberto Fernández's pro-hydrocarbon narrative follows the line of his Mexican counterpart Andrés guide López Obrador, with whom he intends to lead a new moderate left-wing axis in Latin America. The spectre of the nationalisation of YPF by the now vice-president Cristina Fernández, as well as the recent breach of contract with Exmar, continue to generate uncertainty among international investors. status Moreover, the poor financial performance of YPF, the main player in Vaca Muerta, with a debt of more than 8 billion dollars, is a major drag on the country's oil prospects. Similarly, Vaca Muerta is far from realising its potential, with significant but insufficient production to guarantee revenues that would bring about a radical change in Argentina's economic and social status . In order to guarantee its success, a context of favourable oil prices and the fluid arrival of foreign investors are needed. Two variables that cannot be taken for granted given Argentina's political context and the increasingly strong decarbonisation policy of traditional oil companies.
The big question now is how to reconcile the large-scale fossil fuel development with Argentina's latest commitments on climate change subject : to reduce CO2 emissions by 19% by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. Similarly, the promising trajectory of renewable energy development during Mauricio Macri's presidency may lose momentum if the oil and gas sector attracts public and private investment, crowding out solar and wind.
Vaca Muerta is likely to advance slowly but surely as international oil prices stabilise upwards. The possibility of generating foreign currency and boosting a Economics on the verge of collapse should not be underestimated, but expecting Vaca Muerta to solve Argentina's problems on its own can only end in a new episode of frustration in the southern country.
A last-minute minimum agreement avoids the chaos of a no-deal Brexit agreement, but further negotiations will have to take place over the next few years.

Fragment of Brexit mural [Pixabay].
ANALYSIS / Pablo Gurbindo
After the United Kingdom officially left the European Union on 31 January 2020 at midnight, with the agreement Withdrawal entrance in force, it seemed that the issue that has practically monopolised the discussion in Brussels in recent years had been settled. But nothing could be further from the truth. The "political Brexit" had been resolved, but the "economic Brexit" still had to be resolved.
To avoid chaos, agreement provided for a transition period of 11 months, until 31 December 2020. During this period the UK, despite being outside the EU, was to continue to be subject to European legislation and the Court of Justice of the EU as before, but without having a voice and a vote in the EU. The goal of this transition was to give both sides time to reach a agreement to define the future relationship. All parties knew that 11 months would not be enough time. Only a new trade agreement takes years to negotiate, the agreement with Canada took 7 years, for example. For this, the transition period included a possible extension before 30 June, but Johnson did not want to ask for it, and promised his citizens to have a trade agreement by 1 January 2021.
With the fear of a possible no-deal Brexit agreement, and the serious consequences it would have for the economies and citizens on both sides, agreement was finally reached on 24 December, just one week before the end of the transition period.
This agreement entered into force on 1 January 2021 provisional, as there was not enough time for it to enter into force within a week C. The question now is: what does this agreement consist of, what have been the sticking points, and what have been the first tangible consequences during these first months?
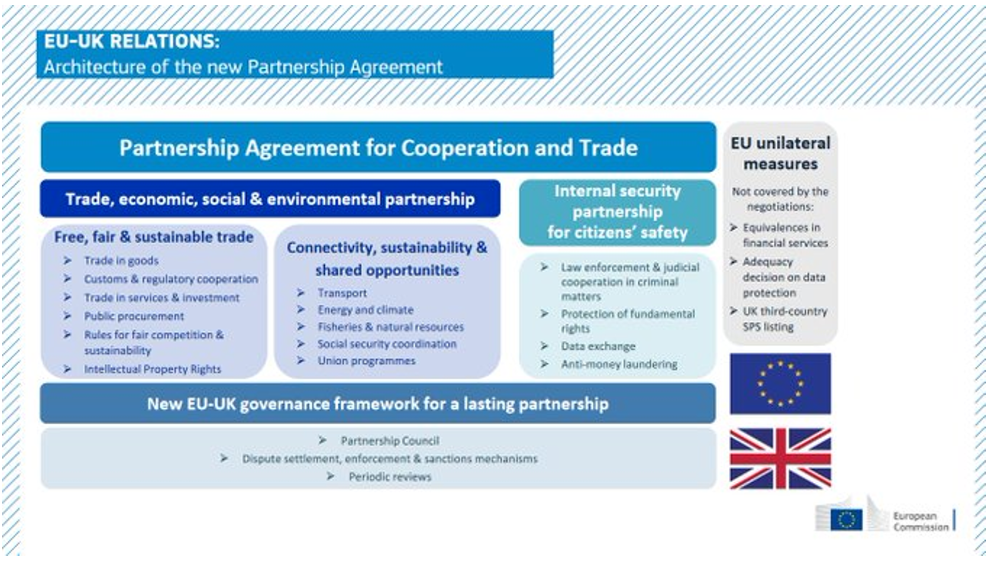
The agreement for Trade and Cooperation (TCC)
What needs to be made clear from the outset is that this is a minimum agreement . It is a hard Brexit. Brexit has been avoided without agreement which would have been catastrophic, but it is still a hard Brexit.
The PCA between the UK and the EU comprises a free trade agreement , a close association on subject on citizen security and a general framework on governance.
The most important points of agreement are the following:
Trade in goods
The PCA is very ambitious in this respect, as it establishes free trade between the two parties without any subject tariffs or quotas on any product. If there had been no agreement in this sense, their trade relationship would have been governed by World Trade Organisation (WTO) rules, with their corresponding quotas and tariffs. However, there is a catch to this free trade. This absence of any subject tariff or quota is only for "British originating" products, and this is where the complexity lies.
The rules of origin are detailed in the PCA, and although as a general rule the agreement is generous in qualifying a product as "British", there are certain sectors where this certification will be more demanding. For example, for an electric vehicle produced in the UK and exported to the EU to avoid tariffs, at least 45% of its added value must be British or European and its battery must be entirely British or European. From now on, proving the origin of each shipment in certain sectors is going to become a bureaucratic hell that did not exist before 31 December. And the re-export of unprocessed foreign goods from British soil to Europe will now be subject to a double tariff: one from entrance to the UK and another from entrance to the EU.
However, even if there is no subject tariff or quota on products, the usual trade flow will not be maintained. For example, in the area of trade in agri-food products, the absence of agreement in the UK's sanitary and phytosanitary regime means that from now on, trade in these products will require sanitary certificates that were not previously required. This increase in "red tape" may have important consequences for products that are more easily substitutable, as importers of these products will prefer to avoid this extra bureaucracy by switching from British to European suppliers.
Financial services
On subject services agreement is rather poor, but the lack of agreement for financial services, a very important sector for the UK, which alone generates 21% of UK services exports, is notable.
While the UK was part of the Union, its financial institutions could operate freely throughout the EU thanks to the "financial passport", as all Member States have agreed similar market regulation and supervision rules. But this no longer applies to the UK.
The UK government unilaterally decided to maintain easy access to its markets for EU entities, but the EU has not reciprocated.
In the absence of agreements at subject financial, the European rules and regulations referring to third country entities, as a general rule, simply makes it easier for these entities to establish themselves in the Union in order to be able to operate in its markets.
One of the EU's objectives with this lack of reciprocity may have been the desire to wrest part of its capital from the City of London, Europe's leading financial place .
Citizens
Most of this section was resolved with the agreement Withdrawal, which guaranteed for life the maintenance of acquired rights (residency program, work...) for European citizens who were already on British soil, or British citizens who were on European soil.
In the PCA it has been agreed to abolish the need for apply for visa bilaterally for tourist stays not exceeding 3 months. For these cases it will now be necessary to carry a passport, a national identity card will not suffice. For longer stays, however, visas will be required from residency program or work.
As for the recognition of professional and university degrees and qualifications, despite the UK's interest in maintaining them automatically as they have been until now, the EU has not allowed this. This could mean, for example, that qualified professionals such as lawyers or nurses would find it more difficult to have their degree scroll recognised and be able to work.
data protection and security cooperation
The agreement will allow police and legal cooperation to continue, but not with the same intensity as before. The UK will no longer be part of the instructions of data on these matters. Exchanges of information will only be made at written request either by requesting information or by sending information on its own initiative.
British relations with Europol (European Police Office) or Eurojust (European Agency for Judicial Cooperation) will be maintained, but as an external partnership .
Participation in Union programmes
The UK will continue to be part of a number of Community programmes such as: Horizon, the main European scientific cooperation programme; Euratom, through a cooperationagreement external to the PCA; ITER, an international programme for the study of fusion energy; Copernicus, a programme led by the European Space Agency for the development autonomous and continuous Earth observation capability; and SST (Space Surveillance and Tracking) a European programme for tracking space objects for collision avoidance.
But on the other hand the UK will not continue in other programmes, notably the important Erasmus student exchange programme. Johnson has already announced the creation of a national student exchange programme named after the British mathematician Alan Turing, who cracked the Enigma code during World War II.
Negotiation sticking points
There have been certain points that, due to their complexity or symbolism, have been the main points of friction between the Union and the United Kingdom. They have even jeopardised the success of the negotiations. The three main sticking points for the negotiations have been: fisheries, the level-playing field and governance.
The disproportionate importance of fisheries in the negotiations is surprising, given that it represents only 0.1% of British GDP, and is not an essential sector for the EU either. Its importance lies in its symbolic value, and the importance given to it by Brexit supporters as an example of regaining lost sovereignty. It should also be borne in mind that it is one of the points on which the UK had the upper hand in the negotiations. British waters are home to some of Europe's main fishing grounds, which have accounted for 15% of total European fishing. Of these fisheries, 57% were taken by the EU-27, with the remaining 43% taken by British fishermen. This percentage greatly infuriated the British fishing sector, which was one of the main sectors that supported Brexit.
The UK's intention was to negotiate annual access quotas to its waters, following Norway's example with the EU. But in the end a 25% cut in catches has been agreed on a progressive basis, but maintaining access to British waters. This agreement will be in force for the next five and a half years, after which new negotiations will be necessary and then on an annual basis. In return, the EU has retained the possibility of trade retaliation in the event that European fishermen are denied access to British waters.
"Level-playing field
The topic of the unfair skill was one of the issues of greatest concern in Brussels. Given that from now on the British do not have to follow European legislation, there was concern that, just a few miles from the Union, a country of the size and weight of the United Kingdom would considerably reduce its labour, environmental, tax and public aid standards. This could result in many European companies deciding to relocate to the UK because of these lower standards.
The agreement establishes a monitoring and retaliation mechanism in cases of discrepancies if one of the parties feels aggrieved. If there is a dispute, depending on the case, it will be submitted to a panel of experts, or it will be submitted to arbitration. For the EU, a system where tariff compensation would have been automatic and if not interpreted by the CJEU would have been preferable. But for the UK one of its main negotiating objectives was not to be under the jurisdiction of the CJEU in any way.
Governance
The design governance of agreement is complex. It is chaired by the committee of association Joint which will ensure that the PCA is correctly implemented and interpreted, and where all issues that may arise will be discussed. This committee will be assisted by more than thirty specialised committees and technical groups.
If a dispute arises, it will be referred to this committee of association Joint. If a solution is not reached by mutual agreement agreement , then an external arbitration will be used, the decision of which is binding. In case of non-compliance, the aggrieved party is entitled to retaliate.
This instrument allows the EU to cover its back against the risk of the UK breaching part of the agreement. This risk gained momentum during the negotiations, when Johnson presented the Internal Market Act to the UK Parliament, which aimed to prevent any internal UK customs subject . This Act would go against the "Irish safeguard" agreed by Johnson himself and the EU. This bill would go against the "Irish safeguard" agreed by Johnson himself and the EU in the agreement Withdrawal, and would go against international law as a clear contravention of the "pacta sunt servanda" principle. In the end this law was not passed, but it created great tension between the EU and the UK, in the UK's civil service examination to Johnson and even within its own ranks by calling the country's international credibility into question.
Consequences
During the first few months of the PCA's entry into force, entrance , several important consequences have already become apparent.
The UK's controversial withdrawal from the Erasmus programme has already been felt. According to UK universities, applications for programs of study from EU citizens have fallen by 40%. The pandemic has played a role in this significant reduction, but it should also be noted that fees university applications in the UK after the exit of the programme have increased by a factor of four.
In terms of financial services, the City of London has already lost degree scroll as Europe's leading financial centre to Amsterdam in the first few months of the year. Daily equity trading in Amsterdam in January amounted to 9.2 billion euros, higher than the 8.6 billion euros managed by the City. London's average last year was 17.5 billion euros, well ahead of Europe's second largest place , Frankfurt, with average of 5.9 billion euros. Last year, Amsterdam's trading figure average was €2.6 billion, making it the sixth largest European financial place . The EU's lack of reciprocity in financial services has been able to fulfil its goal for the time being.
One of the most curious anecdotes demonstrating the changes that Brexit has brought about during these first months was the viral video of Dutch customs authorities confiscating ham sandwiches from transporters arriving by ferry from the UK to the Netherlands. With the PCA in force, entrance , animal products are not allowed to be exported without the corresponding health certificates.
Despite the absence of tariffs and quotas, the increased bureaucracy was expected to affect the trade exchange and it has. According to data from the UK Road Transport association , UK exports to the EU via the ports fell by 68% in January compared to the same month last year.
It seemed that the British fishing sectors could be among the main beneficiaries of agreement, but after these first few months British fishermen are not satisfied. New bureaucratic requirements are slowing down deliveries and some fishermen are complaining that their catches are going to waste because they cannot be delivered on time to certain European markets. According to Scottish fishermen's representatives, delays due to red tape are causing the industry to lose £1 million a day. It should be borne in mind that UK fish exports to the EU accounted for 67% of the total in 2019. In response to complaints from the sector, the British government has already announced a £23 million financial aid .
Conclusion
The agreement reached is undoubtedly a better result than no agreement, but it is an incomplete agreement , and further negotiations will be necessary. The future of the PCA will depend on the change of position of the UK, which during the negotiation has prioritised regulatory autonomy and regaining its "lost sovereignty". The agreement is also fragile as it allows either side to terminate the negotiated relationship if 12 months' notice is given.
The European Union and the United Kingdom are doomed to understand each other. The EU will have to learn to live with a neighbour with a lot of power and influence, and the UK will have to learn to live in the sphere of influence of the 27.
But, when the time comes, the UK will always have the option of the article 49 of the EU Treaty, which regulates the accession of new countries to the Union.
The low voter turnout did not lead to questioning the re-election of Rebelo de Sousa, but it helped the far-right candidate to get a distant third place.

President Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa during a statement to the nation, in January 2021 [Portuguese Presidency].
ANALYSIS / Elena López-Dóriga
Last Sunday 24th of January of 2021 Portugal held presidential elections despite of the country being in lockdown due to the advance of the Covid-19 pandemic. The President of the Republic Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa was re-elected, winning another five-year term after a campaign fought amid one of the world's worst outbreaks of coronavirus. The re-elected president won with a majority of 60.7% of the votes, therefore, with no need to go for a second round. It was already certain that he was going to win this election as he was already known as the favorite candidate in the polls. Nevertheless, the triggering questions for this election relied in how much the turnout could be affected due to the critical situation of coronavirus that Portugal was facing in the middle of a lockdown, and how much relevance was the new far-right wing party Chega was going to achieve, as it had been attaining a lot of popularity since its creation in the last April 2019. The elections were marked indeed by the historic absence of almost 61% (the electoral turnout was 39.24% of the registered voters), and the third position in the ranking of André Ventura, the leader of Chega.
Historical background of the political system
Portugal had the longest lasting authoritarian regime in Western Europe in the 20th century, between 1926 until 1974; it was led by Antonio de Oliveira Salazar in a historical period known as "Estado Novo". Autarchy and tradition had limits, as Portugal managed to join the NATO in 1949 and the EFTA in 1960, allowing economic growth for the country and the development of social policies that benefited the citizens. However, after the nearly fifty years of authoritarian rule and compared to other European countries, Portugal was still much more rural and its population much more likely to be illiterate or to have only a few years of schooling. After the Revolution of April 25th also known as the "Carnation Revolution", which overthrew the regime leded by Salazar's successor Marcelo Caetano, there was a transition towards a parliamentary democracy based on a new constitution.
The political and economic instability in the first years following the revolution was high since the democratic transition was done through a revolutionary rupture made led by the Movement of the Armed Forces (MFA). However, the MFA kept the promise to leave the government after one year, and the first Constituent Assembly elections were held on 25 of April of 1975, exactly one year after the Revolution. The Portuguese semi-presidential regime was defined as a system of government in which the president of the Republic, appointed by means of direct popular vote in a competitive election. The impacted choice of electoral system was the proportional representation system, which aimed to reflect the full distribution of voter's preferences as closely as possible. Voters were grouped in "districts" and the number of votes is fairly proportional to the population in each district. The National Assembly was composed by 250 members initially, but it was reduced to 230 seats in 1989.
An economic background
In 1960 Portugal joined the EFTA as a liberal state with a social model, and finally entered the European Union in the year 1986 as well as Spain. It thought that the Economic and Monetary Union would ensure peace among the Europeans, acceleration of the economic development and improve the levels of social justice. Portugal's policy makers eagerly endorsed the European integration process, and it became an economic policy priority to be in the group of early euro adopters.
While Portugal experienced rapid economic growth in the years that preceded the launch of the euro (between 1995 and 2000), the country's macroeconomic performance since the introduction of the euro was not as high as expected. Nonetheless, the country registered strong progress in a number of social-economic indicators. Between 2009 and 2016 Portugal experienced a severe economic crisis characterized by falling GDP, high unemployment, rising government debt and high bond yields. This was caused by a combination of the global recession, lack of competitiveness and limitations of being in the Euro. In May 2011, due to increasingly untenable interest rates on its bonds, Portugal necessitated a bailout, and accepted a package of 78 billion euros from the European Commission, the European Central Bank and the International Monetary Fund, known colloquially as the Troika, in return of addressing its financial unsustainability. Between 2010 and 2020 Portugal experienced a boom in tourism that made the industry one of the biggest contributors to the national economy and the largest employer, with almost 1 million direct and indirect jobs according to the World Travel & Tourism Council.
The result of the elections
In order to understand the Portuguese political scene, we need to make a distinction between the right-wing parties and the left-wing parties. On the one hand, there are the right-wing parties Chega and CDS-PP (People's Party), in the center-right there is the Social Democratic Party (PPD/PSD), in the center-left the Socialist Party (PS), and the Left Bloc (BE) and the PCP (Portuguese Communist Party) on the left.
The 2021 presidential elections were won by Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa, former leader of the Social Democratic Party (PPD/PSD), with a majority of 60.7% of the votes. The PSD was founded on the year 1974 and has remained one of the main political parties of the country, either staying in government or in the opposition. Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa joined the party the same year of its creation and became a member of the National Assembly. In 2016 he won the presidential elections in the first round with 52% of the votes, succeeding Anival Cavaco Silva, member of the Social Democratic Party as well. This time, in his victory speech, the president renewed his commitment to the Portuguese, saying he was going to be a president that "respects pluralism and difference, a President who never gives up on social justice". Nevertheless, the question for these elections was not who was going to be in first place, as the polls were already announcing that Marcelo would be re-elected by majority according to CESOP (Centro de Estudos e Sondagens da Universidade Católica Portuguesa), the question was actually who was going to win the second and the third position, the Socialist Party or the new far right-wing party of Chega.
The second position was finally won by Ana Gomes from the Socialist Party (PS), with 12,97% of the votes. The main difference between PSD and PS lies in the fact that PSD seeks to preserve costumes and liberalize the economy, whereas the PS would like to liberalize the costumes and be more conservative with the economy. The PS was created in 1973 and managed to take two of its leaders to the country's presidency, between 1986 until 2006. The Socialist Party started to make a difference when they chose to act on topics classified as "fracturing" such as de facto unions, abortion, same-sex marriage (which was approved in the year 2009), gender quota systems and euthanasia.
When it comes to how the healthcare system should be managed, the PSD explains in its program that it defends a health sector with more private initiative, referring to this model as a "freedom of choice" one. The PS, instead, defends that it is essential to focus on the centrality of the National Healthcare Services to "look at the careers of health professionals, so they don't continue to be pushed to the private sector or to emigration".
The pandemic of the coronavirus has been an important issue discussed during the campaign. Even though in the United States postal voting gained a relevant dimension this year because of the pandemic, in Portugal none of this was possible, because according to paragraph 3, article 121 of the Constitution of the Republic, in the election for the president of the Republic the right to vote must be exercised in person in the national territory. Ana Gomes criticized the impossibility of postal voting for many Portuguese emigrants: "It is unworthy that our emigrants, most of them, could not vote because postal voting or electronic voting had not been regulated. This is an indignity, and the responsibility rests with President Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa", she said. She also claimed that it was a mistake for the elections to be scheduled so late taking into account the advance of the pandemic and not allowing all the measures to be ensured in order to guarantee an opportunity for all people to vote and avoid a high abstention: in fact, these elections were the ones with the highest abstention in Portugal's history, with almost 61%.
The rise of the far right-wing party Chega
Many European countries have witnessed the rise of extreme right-wing parties over the last few years, which have gained significant votes and sometimes threatened the position of traditional parties. In Portugal, however, far right-wing parties had failed to gain electoral support until recently, when the political party of Chega was created in 2009. Chega literally means in Portuguese "Enough!" and the leader running the party is André Ventura, an ex-TV commentator on football and true crime legal shows. Polls were certain about the fact that he was going to be in close competition for second place in the election, and indeed he was very close as he attained 11.9% of the votes.
Ventura took advantage of the intense torrent of average attention surrounding him and his party which helped the party grow exponentially in popularity. Ventura's tactics and topics of interest were prototypical right-wing; they have even been considered populist by many because of the charismatic leader giving empowered speeches about the Portuguese identity referring to his party as "the voice of the people" and confronting this group against "the system". Among his most controversial claims during the campaign was his repeated quote "I will not be the president of all Portuguese", but only of the good or decent Portuguese ("Portugueseses de bem"). Amid those he excludes from that definition are, most preeminently, criminals and people who live on state subsidies. He claimed that there are two groups of people in Portugal, the ones that work and the ones that barely work but live at the expense of those that do work and pay taxes. That is why he referred to himself as "a president without fear of the system" that aims to change radically. His diary was heavily focused on criminality (and support to the police) and the alleged misuse of public money and corruption.
Like Donald Trump in the US or the political party Vox in Spain, the Chega leader has used the social network of Twitter to explain or reinforce some of his most controversial political positions. As a characteristic of many extreme right-wing parties, Chega is anti-immigration and often explicitly targets the 'gypsies', known in Portugal as 'ciganos', as an ethnic minority that lives at the expense of the state subsidies. In the speech André Ventura gave just when the results of the elections were known, he admitted that the objective of reaching the second position was not achieved but he said that it was a historic night in which a party declared anti-system broke with the spectrum of the traditional right with around half a million votes; he warned the winner party of PSD that Chega was going to be a "fundamental part" of the Portuguese politics.
Elections in the worst moment of the pandemic
In the week before the election, Portugal reported the highest daily averages in the world for new coronavirus cases and deaths per 100,000 inhabitants, according to data collected by the John Hopkins University. Despite of the country being in lockdown due to the high incidence of Covid-19 and the critical situation of the hospitals, in the last week, the country registered more than 80,000 new cases of coronavirus, which turned Portugal into the country with more cases at an international level (10,3 million people). This numbers were very striking for Portugal, as this third wave of coronavirus was hitting harder than the first one in March 2020, where the country managed to control the pandemic and never witnessed the collapse of hospitals that happened in Spain or Italy. In his victory speech, the re-elected president vowed to make the fight against Covid-19 his top priority. The situation got so critical to the point that Germany's military agreed to send medical staff and equipment to Portugal, where space in hospital intensive care units was running out after the surge in coronavirus infections.
Coronavirus marked this 2021 presidential elections and the pandemic was probably the reason why Portugal had the lowest level of electoral turnout ever, as people from risk groups did not want to risk leaving home and others were required to stay at home in quarantine. Other reasons for the 60.76% abstention was a possible lack of interest in politics and a lower voting by the Portuguese living abroad.
The presidency of Portugal in the Council of the EU
The Council of the European Union is the institution that represents the governments of the EU; its presidency rotates among the EU member states every six months. This year, from January to June, it is Portugal national government's turn to preside the Council, succeeding Germany and preceding Slovenia. Therefore, Portugal's current prime minister and head of government Antonio Costa took over the baton, the symbol of the EU Council Presidency. He belongs to the Socialist Party, but the recent re-election of the Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa as a head of state will not affect the main priorities for the Portuguese presidency: the economic and social recovery based on the engines of the climate and digital transitions, drivers for growth and more and better jobs, the development of the European Union Social Pillar and the reinforcement of the strategic autonomy. Besides, Antonio Costa was elected in the year 2015 and has already been working with Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa as a president since its first election in 2016. Costa congratulated him on the victory "with the best wishes for the continuity of the presidential term... in fruitful institutional cooperation".
In the previous six months of German Presidency, the Covid-19 pandemic was the central challenge, and Angela Merkel concluded in her final speech that Europe was committed to the fight against the virus by promoting, procuring and distributing vaccines. She gave the word to Antonio Costa, who remarked what will be the motto of the Portuguese presidency: "Time to deliver: a fair, green and digital recovery".
The wave of diplomatic recognition of Israel by some Arab countries constitutes a shift in regional alliances
![Dubai, the largest city in the United Arab Emirates [Pixabay]. Dubai, the largest city in the United Arab Emirates [Pixabay].](/documents/16800098/0/acuerdos-abraham-blog.jpg/43eef7ab-96b1-fcd7-b19d-4d682361590c?t=1621884303752&imagePreview=1)
▲ Dubai, the largest city in the United Arab Emirates [Pixabay].
ANALYSIS / Ann M. Callahan
With the signing of the Abraham Accords, seven decades of enmity between the states were concluded. With a pronounced shift in regional alliances and a convergence of interests crossing traditional alignments, the agreements can be seen as a product of these regional changes, commencing a new era of Arab-Israeli relations and cooperation. While the historic peace accords seem to present a net positive for the region, it would be a mistake to not take into consideration the losing party in the deal; the Palestinians. It would also be a mistake to dismiss the passion with which many people still view the Palestinian issue and the apparent disconnect between the Arab ruling class and populace.
On the 15th of September, 2020, a joint peace deal was signed between the State of Israel, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and the United States, known also as the Abraham Accords Peace Agreement. The Accords concern a treaty of peace, and a full normalization of the diplomatic relations between the United Emirates and the State of Israel. The United Arab Emirates stands as the first Persian Gulf state to normalize relations with Israel, and the third Arab state, after Egypt in 1979 and Jordan in 1994. The deal was signed in Washington on September 15 by the UAE's Foreign Minister Abdullah bin Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan and the Prime Minister of the State of Israel, Benjamin Netanyahu. It was accepted by the Israeli cabinet on the 12th of October and was ratified by the Knesset (Israel's unicameral parliament) on the 15th of October. The parliament and cabinet of the United Arab Emirates ratified the agreement on the 19th of October. On the same day, Bahrain confirmed its pact with Israel through the Accords, officially called the Abraham Accords: Declaration of Peace, Cooperation, and Constructive Diplomatic and Friendly Relations. Signed by Bahrain's Foreign Minister Abdullatif bin Rashid Al Zayani and Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and the President of the United States Donald Trump as a witness, the ratification indicates an agreement between the signatories to commence an era of alliance and cooperation towards a more stable, prosperous and secure region. The proclamation acknowledges each state's sovereignty and agrees towards a reciprocal opening of embassies and as well as stating intent to seek out consensus regarding further relations including investment, security, tourism and direct flights, technology, healthcare and environmental concerns.
The United States played a significant role in the accords, brokering the newly signed agreements. President of the United States, Donald Trump, pushed for the agreements, encouraging the relations and negotiations and promoting the accords, and hosting the signing at the White House.
As none of the countries involved in the Abraham Accords had ever fought against each other, these new peace deals are not of the same weight or nature as Egypt's peace deal with Israel in 1979. Nevertheless, the accords are much more than a formalizing of what already existed. Now, whether or not the governments collaborated in secret concerning security and intelligence previously, they will now cooperate publicly through the aforementioned areas. For Israel, Bahrain and the UAE, the agreements pave a path for the increase of trade, investment, tourism and technological collaboration. In addition to these gains, a strategic alliance against Iran is a key motivator as the two states and the U.S. regard Iran as the chief threat to the region's stability.
Rationale
What was the rationale for this diplomatic breakthrough and what prompted it to take place this year? It could be considered to be a product of the confluence of several pivotal impetuses.
The accords are seen as a product of a long-term trajectory and a regional reality where over the course of the last decade Arab states, particularly around the Gulf, have begun to shift their priorities. The UAE, Bahrain and Israel had found themselves on the same side of more than one major fissure in the Middle East. These states have also sided with Israel regarding Iran. Saudi Arabia, too, sees Shiite Iran as a major threat, and while, as of now, it has not formalized relations with Israel, it does have ties with the Hebrew state. This opposition to Tehran is shifting alliances in the region and bringing about a strategic realignment of Middle Eastern powers.
Furthermore, opposition to the Sunni Islamic extremist groups presents a major threat to all parties involved. The newly aligned states all object to Turkey's destabilising support of the Muslim Brotherhood and its proxies in the regional conflicts in Gaza, Libya and Syria. Indeed, the signatories' combined fear of transnational jihadi movements, such as Al-Qaeda and ISIS derivatives, has aligned their interests closer to each other.
In addition, there has been a growing frustration and fatigue with the Palestinian Cause, one which could seem endless. A certain amount of patience has been lost and Arab nations that had previously held to the Palestinian cause have begun to follow their own national interests. Looking back to late 2017, when the Trump administration officially recognised Jerusalem as the capital of Israel, had it been a decade earlier there would have been widespread protests and resulting backlash from the regional leaders in response, however it was not the case. Indeed, there was minimal criticism. This may indicate that, at least for the regional leaders, that adherence to the Palestinian cause is lessening in general.
The prospects of closer relations with the economically vibrant state of Israel, and by extension with that of the United States is increasingly attractive to many Arab states. Indeed, expectations of an arms sale of U.S. weapon systems to the UAE, while not written specifically into the accords, is expected to come to pass through a side agreement currently under review by Congress.
From the perspective of Israel, the country has gone through a long political crisis with, in just one year alone, three national elections. In the context of these domestic efforts, prime minister Netanyahu raised propositions of annexing more sections of the contended West Bank. Consequently, the UAE campaigned against it and Washington called for Israel to choose between prospects of annexation or normalization. The normalization was concluded in return for suspending the annexation plans. There is discussion regarding whether or not the suspending of the plans are something temporary or a permanent cessation of the annexation. There is a discrepancy between the English and Arabic versions of the joint treaty. The English version declared that the accord "led to the suspension of Israel's plans to extend its sovereignty". This differs slightly, however significantly, from the Arabic copy in which "[the agreement] has led to Israel's plans to annex Palestinian lands being stopped." This inconsistency did not go unnoticed to the party most affected; the Palestinians. There is a significant disparity between a temporary suspension as opposed to a complete stopping of annexation plans.
For Netanyahu, being a leading figure in a historic peace deal bringing Israel even more out of its isolation without significant concessions would certainly boost his political standing in Israel. After all, since Israel's creation, what it has been longing for is recognition, particularly from its Arab neighbours.
Somewhat similarly to Netanyahu, the Trump Administration had only to gain through the concluding of the Accords. The significant accomplishment of a historic peace deal in the Middle East was certainly a benefit especially leading up to the presidential elections, which took place earlier this November. On analyzing the Administration's approach towards the Middle East, its strategy clearly encouraged the regional realignment and the cultivation of the Gulf states' and Israel's common interests, culminating in the joint accords.
Implications
As a whole, the Abraham Accords seem to have broken the traditional alignment of Arab States in the Middle East. The fact that normalization with Israel has been achieved without a solution to the Palestinian issue is indicative of the shift in trends among Arab nations which were previously staunchly adherent to the Palestinian cause. Already, even Sudan, a state with a violent past with Israel, has officially expressed its consent to work towards such an agreement. Potentially, other Arab states are thought to possibly follow suit in future normalization with Israel.
Unlike Bahrain and the UAE, Sudan has sent troops to fight against Israel in the Arab-Israeli wars. However, following the UAE and Bahrain accords, a Sudan-Israel normalization agreement transpired on October 23rd, 2020. While it is not clear if the agreement solidifies full diplomatic relations, it promotes the normalization of relations between the two countries. Following the announcement of their agreement, the designated foreign minister, Omar Qamar al-Din, clarified that the agreement with Israel was not actually a normalization, rather an agreement to work towards normalization in the future. It is only a preliminary agreement as it requires the approval of an elected parliament before going into force. Regardless, the agreement is a significant step for Sudan as it had previously considered Israel an enemy of the state.
While clandestine relations between Israel and the Gulf states were existent for years, the founding of open relations is a monumental shift. For Israel, putting aside its annexation plans was insignificant in comparison with the many advantages of the Abraham Accords. Contrary to what many expected, no vast concessions were to be made in return for the recognition of sovereignty and establishment of diplomatic ties for which Israel yearns for. In addition, Israel is projected to benefit economically from its new forged relations with the Gulf states between the increased tourism, direct flights, technology and information exchange, commercial relations and investment. Already, following the Accord's commitment, the US, Israel and the UAE have already established the Abraham Fund. Through the program more than $3 billion dollars will be mobilized in the private sector-led development strategies and investment ventures to promote economic cooperation and profitability in the Middle East region through the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation, Israel and the UAE.
The benefits of the accords extend to a variety of areas in the Arab world including, most significantly, possible access to U.S. defence systems. The prospect of the UAE receiving America's prestigious F-35 systems is in fact underway. President Trump, at least, is willing to make the sale. However, it has to pass through Congress which has been consistently dedicated to maintaining Israel's qualitative military edge in the region. According to the Senate leader Mitch McConnell (Rep, KY), "We in congress have an obligation to review any U.S. arm sale package linked to the deal [...] As we help our Arab partners defend against growing threats, we must continue ensuring that Israel's qualitative military edge remains unchallenged". Should the sale be concluded, it will stand as the second largest sale of U.S. arms to one particular nation, and the first transfer of lethal unmanned aerial systems to any Arab ally. The UAE would be the first Arab country to possess the Lockheed Martin 5th generation stealth jet, the most advanced on the market currently.
There is discussion within Israel regarding possible UAE acquisition of the F-35 systems. Prime Minister Netanyahu did the whole deal without including the defense minister and the foreign minister, both political rivals of Netanyahu in the Israeli system. As can be expected, the Israeli defense minister does have a problem regarding the F-35 systems. However, in general, the Accords are extremely popular in Israel.
Due to Bahrain's relative dependence on Saudi Arabia and the kingdom's close ties, it is very likely that it sought out Saudi Arabia's approval before confirming its participation in the Accords. The fact that Saudi Arabia gave permission to Bahrain could be seen as indicative, to a certain extent, of their stance on Arab-Israeli relations. However, the Saudi state has many internal pressures preventing it, at least for the time being, from establishing relations.
For over 250 years, the ruling Saudi family has had a particular relationship with the clerical establishment of the Kingdom. Many, if not the majority of the clerics would be critical of what they would consider an abandonment of Palestine. Although Mohammed bin Salman seems more open to ties with Israel, his influential father, Salman bin Abdulaziz sides with the clerics surrounding the matter.
Differing from the United Arab Emirates, for example, Saudi Arabia gathers a B amount of its legitimacy through its protection of Muslims and promotion of Islam across the world. Since before the establishment of the state of Israel, the Palestinian cause has played a crucial role in Saudi Arabia's regional activities. While it has not prevented Saudi Arabia from engaging in undisclosed relations with Israel, its stance towards Palestine inhibits a broader engagement without a peace deal for Palestine. This issue connected to a critical strain across the region: that between the rulers and the ruled. One manifestation of this discrepancy between classes is that there seems to be a perception among the people of the region that Israel, as opposed to Iran, is the greater threat to regional security. Saudi Arabia has a much larger population than the UAE or Bahrain and with the extensive popular support of the Palestinian cause, the establishment of relations with Israel could elicit considerable unrest.
While Saudi Arabia has engaged in clandestine ties with Israel and been increasingly obliging towards the state (for instance, opening its air space for Israeli direct flights to the UAE and beyond), it seems unlikely that Saudi Arabia will establish open ties with Israel, at least for the near future.
The ongoing coronavirus pandemic has only heightened prevailing social, political and economic tensions all throughout the Middle East. Taking this into account, in fear of provoking unrest, it can be expected that many rulers will be hesitant, or at least cautious, about initiating ties with the state of Israel.
That being said, in today's hard-pressed Middle East, Arab states, while still backing the Palestinian cause, are more and more disposed to work towards various relations with Israel. Saudi Arabia is arguably the most economically and politically influential Arab state in the region. Therefore, if Saudi Arabia were to open relations with Israel, it could invoke the establishment of ties with Israel for other Arab states, possibly invalidating the longstanding idea that such relations could come about solely though the resolution of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Regarding Iran, it cannot but understand the significance and gravity of the Accords and recent regional developments. Just several nautical miles across the Gulf to Iran, Israel has new allies. The economic and strategic advantage that the Accords promote between the countries is undeniable. If Iran felt isolated before, this new development will only emphasize it even more.
In the words of Mike Pompeo, the current U.S. Secretary of State, alongside Bahrain's foreign minister, Abdullatif Al-Zayani, and Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu, the accords "tell malign actors like the Islamic Republic of Iran that their influence in the region is waning and that they are ever more isolated and shall forever be until they change their direction".
Apart from Iran, in the Middle East Turkey and Qatar have been openly board member in their opposition to Israel and the recent Accords. Qatar maintains relations with two of Israel's most critical threats, both Iran and Hamas, the Palestinian militant group. Qatar is a staunch advocate of a two-state solution to the Israel-Palestine conflict. One of Qatar's most steady allies in the region is Turkey. Israel, as well as the UAE, have significant issues with Ankara. Turkey's expansion and building of military instructions in Libya, Sudan and Somalia demonstrate the regional threat that it poses for Israel and the UAE. For Israel in particular, besides Turkey's open support of Hamas, there have been clashes concerning Ankara's interference with Mediterranean maritime economic sovereignty.
With increasing intensity, the President of Turkey, Recep Tayyip Erdogan, has made clear Turkey's revisionist actions. They harshly criticized UAE's normalization with Israel and even said that they would consider revising Ankara's relations with Abu Dhabi. This, however, is somewhat incongruous as Turkey has maintained formal diplomatic relations with Israel since right after its birth in 1949. Turkey's support of the Muslim Brotherhood throughout the region, including in Qatar, is also a source of contention between Erdogan and the UAE and Israel, as well as Saudi Arabia. Turkey is Qatar's largest beneficiary politically, as well as militarily.
In the context of the Abraham Accords, the Palestinians would be the losers undoubtedly. While they had a weak negotiating hand to begin with, with the decreasing Arab solidarity they depend on, they now stand even weaker. The increasing number of Arab countries normalizing relations with Israel has been vehemently condemned by the Palestinians, seeing it as a betrayal of their cause. They feel thoroughly abandoned. It leaves the Palestinians with very limited options making them severely more debilitated. It is uncertain, however, whether this weaker position will steer Palestinians towards peacemaking with Israel or the contrary.
While the regional governments seem more willing to negotiate with Israel, it would be a severe mistake to disregard the fervour with which countless people still view the Palestinian conflict. For many in the Middle East, it is not so much a political stance as a moral obligation. We shall see how this plays out concerning the disparity between the ruling class and the populace of Arab or Muslim majority nations. Iran will likely continue to advance its reputation throughout the region as the only state to openly challenge and oppose Israel. It should amass some amount of popular support, increasing yet even more the rift between the populace and the ruling class in the Middle East.
Future prospects
The agreement recently reached between President Trump's Administration and the kingdom of Morocco by which the U.S. governments recognizes Moroccan sovereignty over the disputed territory of Western Sahara in exchange for the establishment of official diplomatic relations between the kingdom and the state of Israel is but another step in the process Trump would have no doubt continued had he been elected for a second term. Despite this unexpected move, and although the Trump Administration has indicated that other countries are considering establishing relations with Israel soon, further developments seem unlikely before the new U.S. Administration is projected to take office this January of 2021. President-elect Joe Biden will take office on the 20th of January and is expected to instigate his policy and approach towards Iran. This could set the tone for future normalization agreements throughout the region, depending on how Iran is approached by the incoming administration.
In the United States, the signatories of the Abraham Accords have, in a time of intensely polarized politics, enhanced their relations with both Republicans as well as Democrats though the deal. In the future we can expect some countries to join the UAE, Bahrain and Sudan in normalization efforts. However, many will stay back. Saudi Arabia remains central in the region regarding future normalization with Israel. As is the case across the region, while the Arab leaders are increasingly open to ties with Israel, there are internal concerns, between the clerical establishment and the Palestinian cause among the populace - not to mention rising tensions due to the ongoing pandemic.
However, in all, the Accords break the strongly rooted idea that it would take extensive efforts in order for Arab states to associate with Israel, let alone establish full public normalization. It also refutes the traditional Arab-state consensus that there can be no peace with Israel until the Palestinian issue is en route to resolution, if not fully resolved.
Soft power in the regional race for gaining the upper hand in the cultural and heritage influence among Muslims

A picture taken from the Kingdoms of Fire official trailer
ANALYSIS / Marina García Reina and Pablo Gurbindo
Kingdoms of Fire (in Arabic Mamalik al nar) is the new Emirati and Saudi funded super-production launched in autumn 2019 and born to face the Turkish control in the TV series and shows field for years. The production has counted on a budget of US$ 14 million. The series goes through the story of the last Sultan of Mamluk Egypt, Al-Ashraf Tuman Bay, in his fight against the Ottoman Sultan Selim. The production is the reflection of the regional rivalries in the race for gaining the upper hand in the cultural and heritage influence among Muslims.
Historicity
To understand the controversy this series has arisen we have to comprehend the context where the story takes place and the main characters of the story. The series talks about the Ottoman conquest of the Mamluk Sultanate of 1517. The Ottomans are already known for the general public, but who were the Mamelukes?
A Mameluke is not an ethnic group, it is a military class. The term comes from the Arab mamluk (owned) and it defines a class of slave soldiers. These mamluks had more rights than a common slave as they could carry weapons and hold positions of military responsibility. They were created in the ninth century by the Abbasid Caliphs with the purchase of young slaves and their training on martial and military skills. They became the base of military power in the Middle East. This military elite, similar to the Roman Praetorian Guard, was very powerful and could reach high positions in the military and in the administration. Different groups of Mamluks rebelled against their Caliphs masters, and in Egypt they successfully claimed the Caliphate in 1250, starting the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt and Syria. Their military prowess was demonstrated in 1260 in the battle of Ain Yalut where they famously defeated the Great Mongol Empire and stopped its expansion towards the west.
The Ottoman Empire was formed as one of the independent Turkish principalities that appeared in Anatolia after the fall of the Sultanate of Rum in the thirteenth century. It rapidly expanded across Anatolia and also reached the Balkans confronting the Byzantine Empire, direct heir of the Roman Empire. In 1453, after a long siege, they conquered Constantinople, sealing the fate of the Byzantine Empire.
By the sixteenth century, the Ottomans and the Mamluks were the two main powers of the Middle East, and as a perfect example of the "Thucydides trap", the conflict between these two regional powers became inevitable. In 1515, Ottoman Sultan Selim I launched a campaign to subdue the Mamluks. Incidentally, this is the campaign represented in the Arab series. In October 1516, in the battle of Marj Dabiq, the Mamluk Sultan Al-Ghawri was killed, and Syria fell into Ottoman rule. Tuman Bay II was proclaimed as Sultan and prepared the defence of Egypt. In 1517 the Ottomans entered Egypt and defeated Tuman Bay at the battle of Riadanieh, entering Cairo unopposed. Tuman Bay fled and, supported by the Bedouins, started a guerrilla campaign. But he was betrayed by a Bedouin chief and captured. On April 15, 1517, he was hanged to death on the city gates of Cairo and with him the Mamluk Sultanate ended.
With the end of the Mamluk rule, Egypt became an Ottoman province. The Ottoman control lasted from 1517 until the start of WWI, when the British Empire established a protectorate in the country after the Ottoman Empire entered the war.
A response to Turkish influence
Unlike Saudi Arabia, which until 2012, with the release of Wadjda, had never featured a film shot entirely in the country, other Middle Eastern countries such as Turkey and Iran have taken their first steps in the entertainment industry long before.
Turkey is a clear example of a country with a well-constituted cinema and art industry, hosting several film festivals throughout the year and having an established cinema industry called Yesilcamwhich can be understood as the Turkish version of the US Hollywood or the Indian Bollywood. The first Turkish narrative film was released in 1917. However, it was not till the 1950s when the Turkish entertainment industry truly started to emerge. Yesilcam was born to create a cinema appropriate for the Turkish audience in a period of national identity building and in an attempt to unify multiplicities. Thus, it did not only involve the creation of original Turkish films, but also the adaptation and Turkification of Western cinema.
One of the reasons that promoted the arising of the Turkish cinema was a need to respond to the Egyptian film industry, which was taking the way in the Middle East during the Second World War. It represents a Turkish nationalist feeling through a cinema that would embrace Turkey's Ottoman heritage and modern lifestyle.
Now, Turkish productions are known and watched by audiences worldwide, in more than 140 countries, which has turned Turkey into the world's second largest television shows distributor, generating US$ 350 million a year, only surpassed by the USA.
These Turkish productions embracing the Ottoman period are also a reflection of the current Neo-Ottoman policies carried out by the President Tayyip Erdogan, who many believe is trying to portray himself as a "modern Ottoman ruler and caliph for Muslims worldwide". It is clear that the Turkish President is aware of the impact of its TV shows, as he stated, in a 2016 speech referring to a Turkish show named "The Last Emperor"-narrating important events during the reign of Sultan Abdülhamid-, that the West is treating Turkey in the same way as 130 years ago and, regarding Arabs, he stated that "until the lions start writing their own stories, their hunters will always be the heroes."
A soft power tool
Communication-especially visual communication and, therefore, cinema-plays an important role in either reinforcing the identity status quo or challenging self-views and other-views of the dynamic, multi-faceted self[1]. It is precisely the own and particular Saudi identity that wants to be portrayed by this series.
The massive sums invested in the production of Mamalik al nar, as with other historical TV shows, is an evidence of the importance of the exercise of "soft power" by the cinema and TV show industry in the Middle East. As it has been highlighted above, Turkey has been investing in cinema production to export its image to the world for a long time now. On the other hand, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates have been restrictive when it comes to cinema, not even allowing it within the country in the case of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) for more than 35 years, and they have had few interest on producing and promoting self-made cinema. Now this has dramatically changed. Saudis have an interest in translating their self-conception of matters to the world, and communication is a way of contesting and resisting a dominant culture's encroachment[2] that is being headed by Turkey.
In the words of Yuser Hareb, Genomedia owner(Mamalik al nar's film production company), the series was born from the idea of creating an alternative to the influence that Turkish productions have within Arabs. The producer argues that the Ottoman Empire period is not much of a glorious heritage for Arabs, but more of a "dark time," characterised by repression and criminal actions against Arabs. Turkish historic cinema "adjusts less than 5% to reality," Hareb says, and Mamalik al Nar is intended to break with the Turkish cultural influence in the Middle East by "vindicating Arab history" and stating that Ottomans were neither the protectors of Islam, nor are they the restorers of it.
Dynamics are changing in the region. The Middle East Broadcasting Center (MBC), the large Emirates-based and Saudi-owned average conglomerate that is one of the strongest broadcasting channel in the Arabic speaking world, was in charge of broadcasting in the Arab countries some of the most famous Turkish dramas since 2007, such as the soap opera Gumus, which final episode had 92 million viewers across the region. In March 2018, MBC rejected several Turkish dramas and it even announced an unofficial moratorium on broadcasting any Turkish series. This decision was praised by the Genomedia owner (the producer of Mamalik al nar), Yuser Hareb, pronouncing against those who passively permit the influence of foreigners with their films and series. Furthermore, MBC is also responsible for the broadcasting of Mamalik al nar in the region. The combination of these movements put together can easily portray a deterioration of Turkish-Arab relations.
Egypt also serves as an example of this anti-Turkish trend, when in September 2014, all Turkish series were banned in response to Erdogan's support for the Islamist president Mohammed Morsi (overthrown in July 2013) and his attacks on President Abdelfatah Al-Sisi. This adds to the backing of Turkey of the Muslim Brotherhood and the meddling in Libya to gain regional leadership over the exploration of gas deposits. In short, the backing of Islamist movements constitutes the main argument given when criticising Turkey's "neo-colonialist" aims, which are not completely denied by the Turkish government as it claims the will to be a restorer for the Muslim world.
Double-sided
Ultimately, both the Turkish and the Saudi Arabian sides have the same opinion of what the other is trying to do: influencing the region by their own idiosyncrasy and cultural heritage. It is indeed the crossfire of accusations against one another for influencing and deceiving the audience about the history of the region, especially regarding who should be praised and who condemned.
Turkish and other pro-Erdogan commentators have described Mamalik al nar as an attempt to foment division between Muslims and attacking the Ottoman legacy. Yasin Aktay, an advisor to Erdogan, remarked that there are no Turkish series that attack any Arab country so far, unlike this Saudi series is doing with the former Ottoman Empire by manipulating "historical data for an ideological or political reason". Indeed, it is an attack on "the Ottoman State, but also on contemporary Turkey, which represents it today".
The legacy of the Ottoman Sultanate has been subjected to political and intellectual discussion since medieval times. Specifically, after World War I, when a lot of new Arab nation-states started to consolidate, the leaders of these new-born states called for a nationalist feeling by means of an imperialist discourse, drifting apart Turks and Arabs. It is still today a controversial topic in a region that is blooming and which leadership is being disputed, however -and, perhaps, fortunately-, this ideology does not go beyond the ruling class, and neither the great majority of Arabs see the Ottomans as a nation that invaded and exploited them nor the Turks see Arabs as traitors.
No matter how much Erdogan's Turkey puts the focus on Islam, the big picture of Turkish series is a secular and modern outlook of the region, which has come to be especially interesting to keep up with the region's changing dynamics. That could be overshadowed by salafist movements restricting freedom of speech in what is considered immoral forms of art by some.
All in all, Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates are determined to counterbalance Turkey's effort to increase its regional clout through the use of "soft power" instruments by means of reacting to the abundance of Turkish dramas by launching TV series and shows that offer an "Arab approach" to the matter. In any case, it is still to be seen whether these new Arab productions narrating the ancient history of the Arab territories will have or not a success equivalent to the already consolidated Turkish industry.
[1] Manuel Castells. The rise of network society (New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell, 2009).
[2] Thomas K. Nakayama and Raymond J. Krizek. Nakayama and Raymond J. Krizek (1995). Whitness: A strategic rhetoric (Quarterly Journal of Speech, 1995), 81, 291-319.
Ankara is implementing a strategic plan for the control of the three maritime zones surrounding the country.
![Parade of members of the Turkish Naval Force [Nérostrateur]. Parade of members of the Turkish Naval Force [Nérostrateur].](/documents/16800098/0/patria-azul-blog.jpg/5937153d-b304-227a-960f-0e5d972800a4?t=1621884766294&imagePreview=1)
▲ Parade of members of the Turkish Naval Force [Nérostrateur].
ANALYSIS / Lucas Martín*.
Several recent Turkish actions indicate the implementation of the so-called "Blue Homeland" doctrine.
Among the various facts to be taken into account we can take as an initial element the agreement signed with one of the two contenders for power in Libya, the GNA to be more precise.
Through it, the GNA de facto handed over control of Libyan territorial waters to Turkey while establishing a maritime corridor for Ankara in the eastern Mediterranean Sea.
The importance of having de facto control of these waters is not only the enormous volume of maritime traffic that passes through them, but also the fact that they contain strategic natural gas reserves and are also a transit area for several gas pipelines supplying Europe.
If we add this treaty to Turkey's movements in the Mediterranean, the Aegean, as well as its involvement in the conflicts in Syria and Libya, we see that they are but different but complementary parts of an ambitious plan that Ankara has been carefully plotting for several years to gain maritime control of the Eastern Mediterranean and adjacent areas. The ultimate goal of this plan is to give Turkey economic and energy independence that will ensure the country's growth in all areas.
"Mavi Vatam" - Blue Homeland
The so-called "Gerasimov Doctrine", which theorises the evolution of military conflicts and provides guidelines for action in today's framework , is well known. But it is much less well known that a country like Turkey developed its own doctrine almost two decades ago in an attempt to outline the geostrategic moves needed to achieve basic objectives for the Turkish nation's development and achieve its leading role in the international concert.
The father of this plan is Admiral Cem Gurdeniz, and it was first presented in 2006 under the name "Blue Homeland Doctrine".
The Admiral bases his theory on three pillars, which would take too long to discuss in detail. However, it is interesting to dwell at least briefly on the second pillar. Under this, Gurdeniz defines what he considers to be the areas of maritime jurisdiction that belong to Turkey and that he values as vital for its survival and development. These encompass areas of the Black Sea, the Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. By defining these he establishes territorial waters, the continental shelf and the exclusive economic zone (EEZ).
agreement The admiral himself acknowledges that the problem is far from being in the Black Sea, where an agreement was reached with the former Soviet Union to establish the limits of the continental shelf in 1978 and later, in 1987, the EEZ. Moreover, after the demise of the USSR, agreements were reached with Georgia, Bulgaria and Ukraine.
The issue is centred on the Mediterranean and the Aegean. Precisely the current epicentre of events.
The current established limits, EEZ agreements, etc., have been imposed on Turkey by the EU, according to our protagonist, who considers them particularly burdensome with regard to the Greek zone and Cyprus. Turkey places the onus on the EU to prevent Turkey's development to some extent, which is interesting when Turkey itself has tried to join the Union.
The pivot on which Turkey's recent actions have hinged is defiance. And this is found again in the admiral's own words, which state that the "Blue Homeland" is "challenging and notoriously challenging the current map".
But despite what it may seem, this is not the final goal of the "Mavi Vatam" doctrine. This challenge is the way to achieve its real goal, which is none other than to achieve control and consolidation of the three maritime areas surrounding the country in order to exert its influence at both the regional and international level and to gain the energy resources necessary to sustain Turkey's economic and demographic growth without having to rely on third countries.
But as is rule in these matters, history always plays a key role, and this time is no different.
The Turks continue to view as an affront the Treaty of Lausanne, signed in 1923, which confines the country to its current borders and boundaries. This invalidated the far more beneficial Treaty of Sèvres, signed by the Ottoman Empire after the First World War.
At Lausanne, the fragmentation of the empire was de facto dictated, defining not only Turkey's borders, but also those of Greece and Bulgaria, concluding Turkish sovereignty over the Dodecanese islands, Cyprus, Egypt, Sudan, Syria and Iraq. Kurdistan ceased to be a unit, split between several countries, and Armenia was divided between Turkey and the USSR. The conditions limited the Turks' ability to act, placing the country under the umbrella of Western powers, status which has been maintained for almost 100 years since signature.
In order to understand the current status , a number of factors and circumstances must be taken into account that form the basis of the current situation.
During the Cold War period and with the existence of the communist bloc and its military alliance, the Warsaw Pact, the West's protective umbrella over Turkey became more of a necessity forced by circumstances than an imposition. The Ottoman country's geostrategic status made it of vital importance to both blocs, and in the event of hostilities it would be one of the first territories to suffer the consequences. As a vivid example of this geostrategic core topic , it is worth recalling the role played by the American instructions equipped with nuclear ballistic missiles located on Turkish soil in the negotiations to de-escalate what later became known as the "Cuban missile crisis".
But from the distant 1960s to the present day, the world has changed completely. The balances of power have shifted, and events since the beginning of the 21st century, and especially during the last decade, have led today's leaders to believe that their time has come.
At the time, the fall of the communist bloc and Russia's period of weakness began to lay the groundwork instructions for an idea deeply rooted in Turkey today, the main thrust of which is that the protective umbrella of the West is no longer so necessary (it should not be forgotten that this umbrella was also seen in some ways as a corset).
The consolidation of this idea has coincided with a period of great economic and demographic growth in the Ottoman country, with forecasts of reaching 90 million inhabitants by 2030. Both parameters have major economic implications, as they imply an increase B in the country's energy needs. If these needs are not met, it will not be possible to sustain this population growth or to match it with an adequate industrial development .
The basis of the essential industrial development is energy independence. This is one of the factors core topic that can enable the various projects to go ahead. At present, energy needs are covered by supplies from third countries. The main exporters of energy resources to Turkey are Russia, Iran, Iraq and Libya. This external dependence is one of the reasons for the spectacular development of Turkey's military capabilities in recent years and its direct involvement in various unstable scenarios: maintaining an uninterrupted supply of energy. This is one of the main reasons for the interventions in northern Syria, northern Iraq and Libya.
However, this is not the only reason for such interventions; there are other political motivations, commitments that compel Turkey to take sides in one way or another. The Kurdish problem, worthy in itself of a monograph, is one of them.
But despite possible political motivations, the main focus of the "Blue Fatherland Doctrine" is the need to achieve energy independence. This requires taking control of the necessary energy resources and achieving freedom of action in this field.
There are two spheres that he defines to achieve this goal. The first would consist of the establishment of a security and immediate control of the seas surrounding the country: the Mediterranean, the Aegean and the Black Sea, area . The second, of a strategic nature, extends to the Red Sea, the Caspian Sea and the Arabian Sea, including the Persian Gulf.
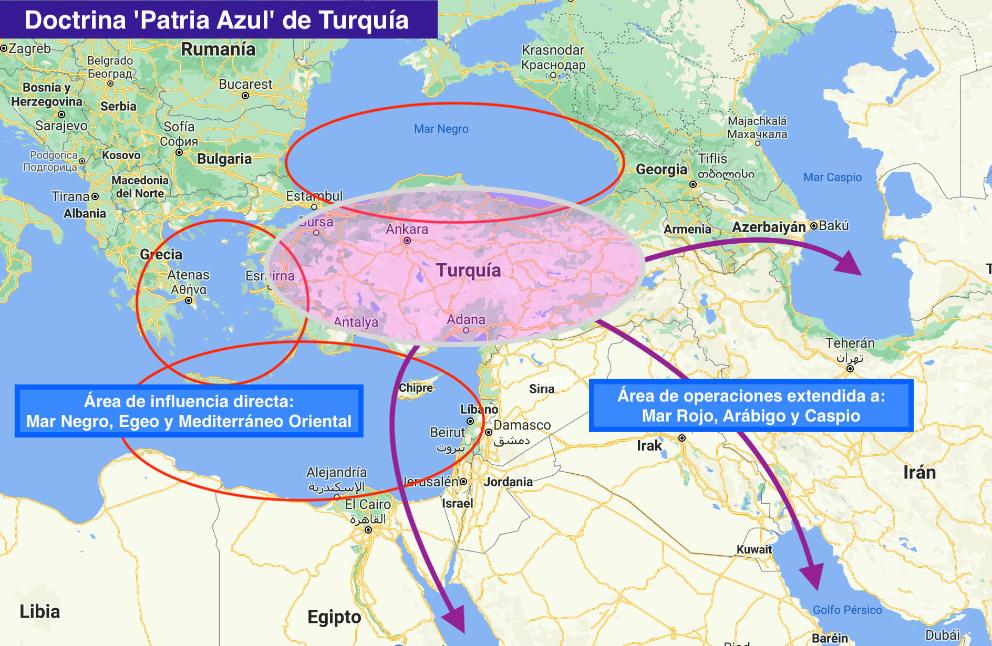
Turkey's dominance of the maritime space includes control over the oil and gas reserves in these waters. This position of maritime dominance is reinforced by establishing alliances with the countries in the area, providing them with support, setting up military instructions on their territory and providing military equipment and training to their armies, thus securing their support. This is a fact, and Turkey already has instructions in Somalia, Sudan, Libya and Qatar, to which it supplies its own weapons systems and with which it has various military agreements.
An aside is in order here. These moves are not welcomed by all countries in the region, some of which see their current position and their own aspirations to grow in power and influence in the region as threatened. The existence of a dominant regional power does not usually leave much room for manoeuvre. It is also important to quote here the words of the father of the "Blue Homeland" doctrine: "Turkey does not need an ally to protect the homeland. The homeland is the homeland. Our continental shelf is our homeland and we have to protect it.
However, he claims that in the future relations between Italy, Tunisia, Libya and Turkey will be the main axis of the Mediterranean. He deliberately leaves out countries such as France, Greece and Spain.
area Traditionally, the Turkish Naval Force's usual area of operations was the Mediterranean, the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea. Recently, however, it has expanded its area of operations to the Red Sea, the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf, and even operates closely with Pakistan. partnership .
This strategic vision, centred on the dominance of the sea, apart from the reasons given above regarding the control of energy resources, can be explained by Turkey's conviction that its special rugged terrain already offers a natural defence and deterrent against any land-based aggression.
Moreover, the "Blue Homeland" doctrine is based on the assumption that Turkey must be an eminently maritime power. It is therefore a realistic doctrine of self-defence of the maritime areas that are rightfully Turkey's, to protect them with an eye to future generations.
Thus, the maritime borders, which stretch across three different seas, are so far perceived as the nation's weak point. And this is precisely what is in the process of being transformed.
reference letter This view has its historical roots in the former Ottoman Empire, which Admiral Cem Gürdeniz refers to on numerous occasions in his writings. It was this view that led Erdogan, shortly after coming to power, to initiate a comprehensive programme of development and modernisation of his naval force known as "Milgem". In this project , heavy investments have been made all over subject, and no effort has been spared, because in order to achieve the development of an armed forces, especially in its maritime aspect, that will sustain the goal of establishing itself as a regional and international power, it is core topic an independent technological development of Turkish industry.
In recent years, the Turkish defence industry has undergone a dramatic evolution, demonstrating the effectiveness of its developments in the Libyan, Syrian and, more currently, Armenia-Azerbaijan conflict. Great emphasis has been placed on the development of warships, unmanned aerial systems (UAVs) and advanced weapons systems of high quality. The chapter on UAVs is particularly significant, and should be the subject of an in-depth study, including from a national point of view in Spain.
Once again, there are two clearly defined intentions here. On the one hand, to achieve a state-of-the-art technological level in its armed forces that will support the achievement of the objectives outlined above, and on the other, to position itself as reference letter in the field of arms exports, to earn revenue and to be able to influence the countries of its interest and their policies in the same way as the United States, China and Russia do.
More specifically, theMilgemprogramme framework has built four anti-submarine corvettes, an intelligence gathering vessel, four surface warfare frigates and four anti-aircraft frigates. The programme also includes four state-of-the-art corvettes for the Pakistan Navy as a way of exporting its advances, enhancing the already close partnership relationship between the two countries and, of course, providing economic benefits for the arms industry.
Similarly, 33 new landing craft capable of transporting both troops and armoured vehicles have been delivered to the Turkish Naval Force. Turkey's amphibious assault capabilities, development and further development, are a factor in a possible increase in tension with Greece, especially with regard to claims over the islands to the east of the country and its waters.
The development of naval warfare capabilities is completed with the production of six new submarines from invoice German-built under licence of HDW in Turkey itself, namely the model U-214. These new submersibles are equipped with an AIP system that allows them to remain for long periods without surfacing, and join the ten that the Ottoman country has operated so far.
This is one of the most significant in terms of its destabilising capacity. Until now it has been Greece that has maintained a certain technological superiority in this field. But the entry into service of the new Turkish units, entrance , significantly changes the balance of power. In addition to serving as perfect intelligence gathering platforms, especially in the SIGINT (Signals Intelligence) and COMINT (Communications Intelligence) disciplines, submarines are excellent deterrent weapons, capable of denying an entire fleet access to an extensive area.
The most significant element of Turkey's pretentious programme is an amphibious assault ship (LHD) called the "Anadolu". This ship, with very similar characteristics to the "Juan Carlos I" operated by the Spanish Navy, is a qualitative leap in terms of the capabilities it provides, as it can not only transport landing barges, but also operate different types of helicopters, UAVs and, where appropriate, vertical take-off fighter aircraft from its deck.
Currently, the only such aircraft compatible with the ship is the American F-35 B, which is the vertical take-off and landing (VSTOL) variant. Turkey was one of the nations that had decided to acquire this fighter aircraft, albeit in its A version, which is the standard version for the air force, the first units of which were already scheduled to be delivered to submission .
But the Ankara government's decision to acquire state-of-the-art Russian anti-aircraft equipment, such as the S-400 system, has led the US to veto its continuation of the F-35 B procurement programme. In fact, the first aircraft destined for the Ottoman country have been sold to the USAF. In any case, Turkey's intention was not to acquire the VSTOL version, which leaves Turkey's real intention as to which aircraft will equip the ship open to question.
The project will be completed with the construction of a second amphibious assault ship, the "Trakya". The possession of two units of this subject provides the Turkish naval force with capabilities far superior to those of its neighbours in the region, giving it the ability to project its amphibious force in strategic operations and in two theatres simultaneously.
The real value of these capabilities is not the operational capability itself, but the deterrent capability it represents.
Turkey's involvement in the conflicts in Syria and Libya has provided the Turkish Armed Forces, and within these its naval units, with enormous and valuable combat experience that has been very useful for update and improving its doctrine and operational capabilities. This, together with the high quality of the training quality of its units, the quality of its equipment and the technological and weapons development described above, are the three pillars necessary for the implementation of the "Blue Homeland" doctrine. The great unknown is how the other regional powers, which are directly affected by the advance of this strategic plan, will react.
In conclusion, it can be said that interests are multiple and often intersecting, affecting not only the countries bordering this area of the Mediterranean, but also powers such as Russia and France and international organisations such as NATO.
Incidents between supposedly allied nations have already occurred, even leading to France's withdrawal from NATO's Mediterranean operation due to a problem between a French and a Turkish frigate, and resulting in an attack on Turkish positions by "Rafale" aircraft from instructions in the United Arab Emirates, but whose nationality remains unclear.
status There is no doubt that Turkey's attitude, and the implementation of its plan, puts the Atlantic Alliance in a weak position, as one of the reasons behind the plan is Turkey's perception that it no longer needs the protection of the Western umbrella for the defence of its interests.
On the other hand, Turkey is playing with the trump card of holding the key to the door of entrance to the torrent of migrants from Syria, Libya, Somalia and Eritrea to the EU. And it will use it as a pressure measure in the face of any European reaction or stance against its interests.
The Eastern Mediterranean has regained the leading role in world geopolitics that it had in the 16th century, only this time we have new powers such as Russia that also claim their space and their need for a permanent and strong presence in the area. We cannot ignore the relationship between this Russian need and the Crimean conflict and the strategic need to be able to control to some extent both sides of the Bosporus and ensure the Black Sea fleet's access to the Mediterranean.
All these economic, energy and political interests are creating a very complicated status where the "internal" conflicts in Syria and Libya also come together, creating an over-presence of military units, combatants, private military companies, weapons systems, aircraft, UAVs, etc. that at any moment, and due to any unexpected error, could lead to an incident that, however slight, could have unforeseeable and irreparable consequences.
* The author is an infantry lieutenant colonel and geopolitical analyst.
REFERENCES
Kasapoglu, 'The Blue Homeland': Turkey's largest naval drill. Anadolu Agency 27 February.
SETA Security Sadar Turkey's geopolitical landscape in 2020
Kara Harp Okulu Bilim Dergisi, "An assesment of eastern mediterranean maritime boundary delimitation agreement between Turkey and Libya" Science Journal of Turkish Military Academy Haziran /June 2020
Eyal Pinko, "Turkey's Maritime Strategy Ambitions: The Blue Homeland Doctrine (Mavi Vatan)" Research Institute for European and American Studies(www.rieas.gr) April 2020
Faced with the biggest economic crisis since World War II, the EU itself has decided to borrow to help its member states.

▲ Commission President Von der Layen and the President of the European committee Charles Michel after announcing the agreement in July [committee European]
ANALYSIS / Pablo Gurbindo Palomo
"Deal!". With this "tweet" at 5:30 a.m. on 21 July last, the president of the European committee , Charles Michel, announced the achievement of a agreement after the longest meeting in its history (more than 90 hours of negotiations).
framework After the failed summit in February, European countries were aware of the importance of reaching an agreement on agreement, but some countries saw it as more urgent than others to conclude the Multiannual Financial Framework (MFF) for the next seven years. But as with everything else, the Covid-19 pandemic has overturned this lack of urgency, and has even forced member states to negotiate, in addition to the budget, aid to alleviate the effects of the pandemic on the 27.
The agreement consists of an MFF of 1.074 trillion euros. This is lower than the figure demanded in February by the so-called friends of cohesion (a conglomerate of southern and eastern European countries) and the Commission itself, but also higher than the figure that the frugals (the Netherlands, Austria, Denmark and Sweden) were prepared to accept. But it is not this figure that has been the focus of the discussion, but how much and how the post-pandemic recovery fund to help the countries most affected by the pandemic was to be set up. The Fund was agreed at 750 billion, divided into 390 billion to be given to member states in the form of grants, and the remaining 360 billion to be given in the form of a 70 per cent disbursable loan between 2021 and 2022.
The figures are staggering, and based on the February negotiations, where one part of the membership preferred something more austere, one might ask: How did we arrive at this agreement?
The Hamilton moment
With the arrival of Covid-19 in Europe and a considerable paralysis of all the world's economies, the European capitals quickly realised that the blow was going to be significant and that a strong response was going to be necessary to mitigate the blow. Proposals at the European level were not long in coming. For example, the European Parliament proposed a recovery package on 15 May of 2 trillion euros, and to include this in the MFF 2021-2027.
The most prominentproposal was presented on 18 May by French President Emmanuel Macron and German Chancellor Angela Merkel. And not only because it was promoted by the two main economies of the Union, but also because of its historic content.
There has been talk of Hamilton momentHamilton moment, referring to Alexander Hamilton, one of the founding fathers of the United States and the first Secretary of the Treasury of the newly founded republic. In 1790 the thirteen states that made up the young American nation were heavily indebted due to the war effort of the Revolutionary War, which had ended only seven years earlier. To solve this problem, Hamilton, Secretary of the Treasury, succeeded in convincing the federal government to assume the states' debt by "mutualising" it. This event marked the strengthening of the American federal government and served to create the instructions of the US national identity.
It seems that with the Franco-German proposal the Hamilton moment has arrived. The proposal is based on four pillars:
-
European health strategy, which could include a joint reservation of medical equipment and supplies, coordination in the purchase of vaccines and treatments. In turn, epidemic prevention plans shared among the 27 and common methods for registering the sick.
-
A boost to the modernisation of European industry, supported by an acceleration of the green and digital transition.
-
Strengthening the European industrial sector, supporting production on the Old Continent and the diversification of supply chains to reduce global dependence on the European Economics .
-
500 billion reconstruction fund for the regions most affected by the pandemic on the basis of EU budget programmes.
It is this fourth pillar that we can call "Hamiltonian" and which is historic as it would for the first time in history allow the EU itself to issue debt to finance this fund. This proposal has broken years of a German stance against any collective borrowing subject . "We are experiencing the biggest crisis in our history... Because of the unusual nature of the crisis we are choosing unusual solutions," Merkel said in the joint video conference with Macron.
According to this proposal the funds would not be reimbursed directly by the countries but through the Community funds in the long term deadline, either through its usual resources or through new sources of income. It should also be noted that the proposal spoke of the submission of this fund in the form of subsidies, i.e. without any subject interest for the recipient countries.
Among the reactions to proposal were those of the frugal, who rejected that the funds should be given in the form of grants. "We will continue to show solidarity and support for the countries most affected by the coronavirus crisis, but this must be in the form of loans and not subsidies," said Austrian Chancellor Sebastian Kurz. The frugal proposal is that the financial aid raised on the debt markets should be submit to states at low interest rates, i.e. as a loan, and conditional on a reform programme.
On 27 May the Commission announced its proposalThe EU's new, very similar to the Franco-German one, but enlarged. The proposal is composed of a 1.1 trillion euro MFF and a 750 billion euro recovery plan called Next Generation EU. This recovery plan is based on three pillars financed by new instruments but within pre-existing headings:
The first pillar covers 80% of the recovery plan. It is about supporting Member States in their investments and reforms in line with the Commission's recommendations. To this end, the pillar has these instruments:
-
Recovery and Resilience Mechanism (the most important part of proposal): financial support for investments and reforms by states, especially those related to the green and digital transition and the resilience of national economies, linking them to EU priorities. This mechanism would be made up of 310 billion in grants and 250 billion in loans.
-
React-EU Fund under cohesion policy with 55 billion.
-
Increase in the Just Transition Fund: this fund is intended to support states in undertaking the energy and ecological transition, to move towards a climate-neutral policy. It would be increased to 40 billion.
-
Increase of the European Agricultural Fund development Rural: to support rural areas to comply with the European Green agreement . It would be increased by 15 billion.
The second pillar covers 15% of the plan. It focuses on boosting private investment, and its funds would be managed by the European Investment Bank (EIB):
-
31 billion Solvency Support Instrument
-
EU-Invest programme increased to $15.3 billion
-
New Strategic Investment Fund to promote investment in European strategic sectors
The third pillar covers the remaining 5%. It includes investments in areas that have result been key to the coronavirus crisis:
-
EU4Health programme to strengthen health cooperation. With an budget of 9.4 billion.
-
Reinforcement of the EU Civil Protection Mechanism (EUCPF) by 2 billion.
-
project Horizon Europe for the promotion of research and innovation worth 94.4 billion.
-
Support to the external humanitarian financial aid worth 16.5 billion.
To raise the funding, the Commission would issue its own debt on the market and introduce new taxes of its own, such as a border carbon tax, emission allowances, a digital tax or a tax on large corporations.
It should also be noted that both access to MFF and Next Generation EU aid would be conditional on compliance with the rule of law. This was not to the liking of countries such as Hungary and Poland, which, among others, consider it to be unclear and a form of interference by the EU in their internal affairs.
Negotiation at the European Summit
With this proposal on the table, the heads of state and government of the 27 met on 17 July in Brussels amid great uncertainty. They did not know how long the summit would last and were pessimistic that it would be possible to reach an agreement agreement.
The main sticking points in the negotiations were the amount and form of the reconstruction fund. Countries such as Spain, Italy and Portugal wanted the aid to come in the form of subsidies in full and without any subject conditionality. On the other hand, the frugals, led during the summit by Mark Rutte of the Netherlands, wanted the reconstruction fund to be reduced as much as possible, and in any case to be given in the form of loans to refund and as an "absolute precondition". "Any financial aid from the North means reforms in the South. There is no other option", Rutte said at a press conference in The Hague.
As with all negotiations, the positions were gradually loosening. It was already clear that neither position was going to remain unscathed and that a mixed solution with both subsidies and loans was going to be the solution. But in what percentage? And with reform conditionality?
For Spain, Italy and Portugal the subsidies could not be less than 400 billion, which was already a concession from the initial 500 billion. For the frugal, who were joined by Finland, this figure could not exceed 350 billion, which would reduce the total Fund to 700 billion. This was a major concession by the frugals, who went from talking about zero subsidies to accepting them as 50% of the amount. Michel's final proposal was 390 billion in subsidies and 360 billion in loans to try to convince all sides.
The big stumbling block apart from the percentage was the conditionality of reforms for the submission aid that the frugal advocated. The spectre of the Troika imposed after the 2008 crisis was beginning to appear, to the disgrace of countries such as Spain and Italy. Rutte demanded that the national plans that countries had to present to the Commission in order to receive the Fund should also pass through committee of the 27 and that unanimous approval was necessary. This formula basically allowed any country to veto the national plans. Germany did not go as far as the required unanimity, but did ask for some control by the committee.
Rutte's stance angered many countries that saw proposal as a way of forcing reforms that have nothing to do with economic recovery.
The president of the committee presented a proposal to bring the parties closer together: the "emergency brake". According to Michel's proposal countries will have to send their reform plan to committee and it will have to be C by qualified majority. deadline After its approval, any country is allowed to submit its doubts about the fulfilment of the plans presented by a state to the committee ; in this case, the committee would have a maximum of three months to make a pronouncement. As long as the country does not receive a decision, it would not receive the aid.
For those who may be surprised by the large concessions made by the frugal, it is worth mentioning the figure of the "rebates" or compensatory cheques. These are rebates on a country's contribution to budget and were introduced in 1984 for the United Kingdom. The British were one of the main net contributors to the European budget , but they hardly benefited from its aid, 70% of which went to the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and the Cohesion Fund. It was therefore agreed that the British would have their contribution discounted on a permanent basis. Since then, other net contributor countries have been receiving these cheques. However, in these cases they had to be negotiated with each MFF and were partial on a specific area.
It is a very controversial figure for many countries, and an attempt was already made to remove it in 2005. But what is undeniable is that it is a great bargaining chip. From the outset, the frugal countries have wanted to keep it, and even strengthen it. And given the difficulties in negotiating, the rest of the member states have seen that it is an "affordable" and not very far-fetched way of convincing the "hawks of the north". After some initial posturing, they ended up increasing it: Denmark will receive 377 million (considerably more than the initial 222 million); Austria will double its initial amount to 565 million; Sweden will receive 1.069 billion (up from the initial 823 million); and the Netherlands will receive 1.575 billion. Notably, Germany, as the largest net contributor, will receive 3.671 billion.
The last important negotiation point to be addressed is the conditionality of compliance with the rule of law in order to receive the different funds and aid. Hungary and Poland, for example, have an open transcript for possible violation of article 7 of the Treaty on European Union (TEU), which allows a member state to be sanctioned for violating basic EU values such as respect for human rights or the rule of law. Many countries have pressed the issue, but in the face of difficult negotiations and a possible risk of a veto of agreement depending on the vocabulary used by Hungarian President Viktor Orban, this clause has come to nothing.
To recapitulate, and as stated at the beginning of article, the agreement ended up with an MFF of 1.074 trillion euros; and a post-pandemic reconstruction fund, the Next Generation EU, of 750 billion, divided into 390 billion in the form of subsidies and 360 billion in the form of loans. To this must be added Michel's "emergency brake" for the submission of aid and the significant sum of "rebates".
The cuts
Yes, there have been. Apart from the aforementioned rule of law clause, there have been several cuts in several of the items proposed by the Commission. Firstly, there has been a significant cut in the Just Transition Fund, which has been reduced from the initial 40 billion at proposal to 10 billion, to the anger of Poland in particular. Secondly, the funds for the rural development are reduced from 15 billion to 7 billion. Thirdly, both the 16.5 billion external humanitarian support fund financial aid , the 31 billion solvency support instrument (on its proposal by the Commission) and the 9.4 billion EU4Health programme have come to nothing. And finally, the project Horizon Europe would drop from the 94.4 billion proposed by the Commission to a mere 5 billion.
Winners and losers?
It is difficult to speak of winners and losers in a negotiation where all parties have given quite a lot in order to achieve agreement. Although it remains to be seen whether the countries' positions were truly immovable from the outset or whether they were simply used as an instrument of pressure in the negotiation.
The countries most affected by the pandemic, such as Italy and Spain, can be happy because they will receive a very large sum in the form of subsidies, as they wanted. But this conditionality that they were not going to accept in any way, in a way, is going to come to them softened in the form of Michel's "emergency brake". And the reforms they did not want to be forced to make, they will have to carry out from agreement with the recovery plan they send to committee, which if they are not sufficient may be rejected by the latter.
The frugal have succeeded in getting conditional aid, but more than half of it will be in the form of subsidies. And as a rule, the monetary limits they advocated have been exceeded.
Countries such as Poland or Hungary have succeeded in making the conditionality of the rule of law ineffective in the end, but on the other hand they have received considerable cuts in funds, such as the Just Transition fund, which are important especially in Central Europe for the energy transition.
But, on final, every head of state and government has returned home claiming victory and assuring that he or she has fulfilled his or her goal, which is what a politician must do (or appear to do) at the end of the day.
For both the MFF 2021-2027 and Next Generation EU to go ahead, the European Parliament still needs to ratify it. Although the Parliament has always advocated a more ambitious package than agreed, there is no fear that it will block it.
Conclusion
As I have said, this agreement can be described as historic for several reasons. Apart from the obvious extension of the European committee or the Covid-19 pandemic itself, it is historic because of the Hamilton moment that seems to be about to take place.
Member states seem to have learned that the post-crisis formula of 2008 did not work, that crises affect the whole of the Union and that no one can be left behind. Cases such as Brexit and the rise of Eurosceptic movements across the continent set a dangerous precedent and could even endanger the continuity of project.
The "mutualisation" of debt will allow states that are already heavily indebted, and which due to their high risk premium would have problems financing themselves, to get out of the crisis sooner and better. This decision will obviously cause problems that remain to be seen, but it shows that the 27 have realised that a joint financial aid was necessary and that they cannot go to war on their own. As Merkel said when presenting her post-pandemic plan together with Macron: "This is the worst crisis in European history", adding that to emerge "stronger", it is necessary to cooperate.
This move towards a certain fiscal unity can be seen as a rapprochement to a Federal Europe, at least in the Eurozone, which has been discussed for decades now. Whether this is a path with or without return remains to be seen.
