DATAI and the University of Salamanca bring advanced statistics closer to data decision making
Experts explore how statistical and machine learning models help predict risks and improve decisions in fields such as medicine, Economics or engineering

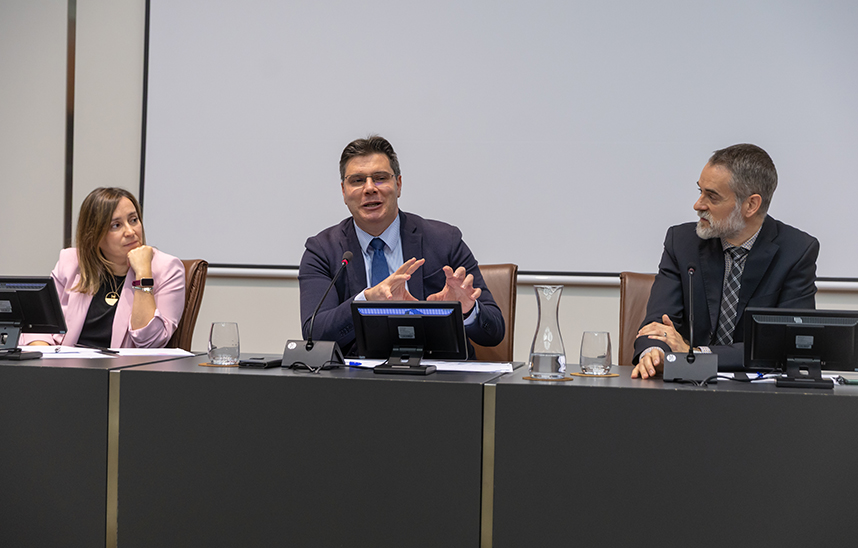
PhotoNaiaraCarrasco/From right to left: José Manuel Sánchez-Santos and Jesús López Fidalgo.
22 | 05 | 2025
The Institute of data Science and Artificial Intelligence (DATAI) of the University of Navarra of the University of Navarra hosted this Thursday a new seminar within its scientific lecture series , in partnership with the University of Salamanca. The session, entitled "Modeling survival and risk: some regression techniques in survival analysis", was given by Professor José Manuel Sánchez-Santos, expert in bioinformatics and member of the research group in Bioinformatics of the University of Salamanca.
Models to understand complex behaviors
During the meeting, Professor Sánchez-Santos presented different statistical and machine learning techniques that allow the construction of models to predict behaviors or results in complex situations, such as when a disease might appear or what factors influence the risk of a future event. "The use of these tools is especially useful in contexts where large volumes of data are involved, as they make it possible to identify which variables are really important without losing precision," explained the expert.
Survival analysis: measuring time to a core topic event
One of the focuses of the seminar was survival analysis, a branch of statistics that makes it possible to predict the time that may elapse before a relevant event occurs, such as a medical recovery, a technical breakdown or a financial default. Professor Sánchez-Santos explained that, for this purpose, tools such as the Kaplan-Meier estimator are used, a method that makes it possible to calculate the probability of an event occurring at different points in time, even when there is not complete information on all the cases. He also highlighted the Cox proportional hazards model , a regression technique that makes it possible to identify which factors significantly influence the risk of that event occurring. Both methods are widely used for their ability to generate robust predictive models applicable in fields such as medicine, Economics and engineering.
From clinical data to personalized treatment
In an approach especially focused on medical research , Sánchez-Santos explained how regression techniques such as Lasso, Ridge and Elastic Net allow robust identification of risk and survival markers. These machine learning tools help to select the most relevant variables from a large set of data, eliminating those that are less significant or redundant. While Lasso tends to select a reduced issue of core topic variables, Ridge adjusts them smoothly without excluding any, and Elastic Net combines both strategies to achieve an effective balance. The expert also stressed the importance of cross-validation, a process that allows to evaluate the stability of the results obtained and to ensure that the identified markers remain consistent across different subsets of data. This robustness is a core topic for advancing the personalization of treatments and improving the clinical prognosis of patients.
The seminar also included real examples of biomedical data sets, especially in cancer cases, where these methodologies not only validate known biomarkers, but also enable the discovery of new ones. According to Jesús López Fidalgo, director of the data Science and Artificial Intelligence Institute (DATAI), "this integration of advanced statistics with bioinformatics opens up new avenues in translational research and significantly improves clinical decision-making in contexts of high uncertainty".
This seminar is part of the series of scientific talks that DATAI organizes with national and international experts, and reinforces its commitment to communicate data science in a rigorous, useful and accessible way for decision makers in complex environments.