Environment. research. Strategy 2025. University of Navarra
PRESENTATION
Environmental sustainability refers to the efficient and rational use of natural resources so that it is possible to improve the well-being of today's society without compromising the quality of life of future generations. This implies taking into account the limits of resource renewal and the cycles of nature, thus achieving a balance between man and the environment.
Through the research multidisciplinary developed in the Biodiversity and Environment Institute (BIOMA) and in other Departments and Schools involved in the environmental area , the goal strategic line Biodiversity and management of ecosystems in the University's Strategy 2025, consists of:

To internship a series of sustainable projects that help reduce our environmental footprint, preserve natural capital and achieve a change of behavior in society, thus demonstrating that it is possible to eliminate the existing conflict between nature conservation and human development .

LABORATORY ENERGY EFFICIENCY OF BUILDINGS
This Living Lab focuses on optimizing energy consumption in the buildings of campus. Through the use of advanced control and monitoring technologies, it seeks to reduce energy expense and carbon emissions, thus improving the sustainability and environmental footprint of campus. In addition, awareness is raised among building occupants to adopt more responsible energy use practices.
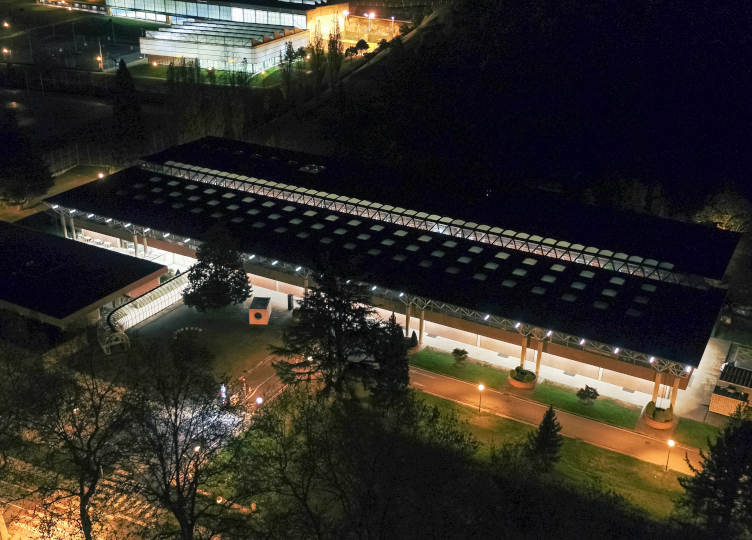

LABORATORY OF RENEWABLE ENERGIES AND ELECTRICAL DISCONNECTION
The main goal of this Living Lab is to develop renewable energy generation and storage systems that allow to electrically disconnect specific buildings of the campus from the conventional network . The implementation of renewable energy together with the use of a hydrogen fuel cell aims not only to reduce the dependence on fossil fuels but also to improve the resilience of campus to external power outages.

LABORATORY OF DIGITIZATION OF CAMPUS THROUGH SIG
Thanks to the development of a Geographic Information System (GIS), this Living Lab has initiated the digitalization of campus, creating a virtual environment that allows for more efficient planning and management of resources. Thanks to this, it is possible to analyze geospatial data to identify opportunities for improvement in the planning of spaces, sustainable mobility routes, location of green areas and services, detection of areas of high biodiversity, etc.

LABORATORY RECYCLING AND ECONOMICS CIRCULAR
This Living Lab promotes the adoption of efficient recycling practices at campus and the implementation of circular Economics principles. It works on waste reduction, proper recycling and reuse of materials, promoting awareness about consumption manager and the positive impact on the environment.

LABORATORY OF BIODIVERSITY AND THE CREATION OF ECOLOGICAL PLOTS
With the goal to increase biodiversity at campus, this Living Lab focuses on creating green spaces and plots that host a wide variety of flora and fauna. In addition to providing habitats for local flora and fauna, these plots help improve air quality and water retention, contributing to the ecological resilience of campus.
LABORATORY FROM MOBILITY SUSTAINABLE
By promoting sustainable transportation alternatives, this Living Lab seeks to reduce the environmental impact caused by the commuting of students, professors and staff from campus. With this goal, options such as the use of bicycles, electric vehicles and the improvement of public transportation are being promoted to reduce dependence on traditional vehicles and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
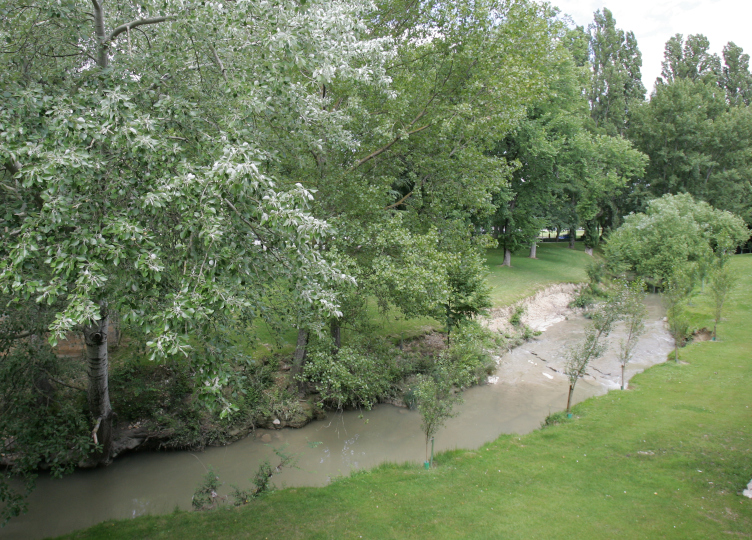

LABORATORY RIVER MONITORING SYSTEM: SADAR RIVER
This Living Lab focuses on the monitoring of the Sadar River as it passes through the university campus , approaching the study through the application of physicochemical, biological and genotoxicity methods. Monthly analyses of parameters such as pH, temperature, nutrients and a wide variety of pollutants will be carried out to assess the health of the river.
In parallel, fish fauna will be investigated using techniques such as electrofishing and environmental DNA. In addition, the toxicity of the water will be examined using the essay SOS/umu, detecting the genotoxic capacity of the samples.
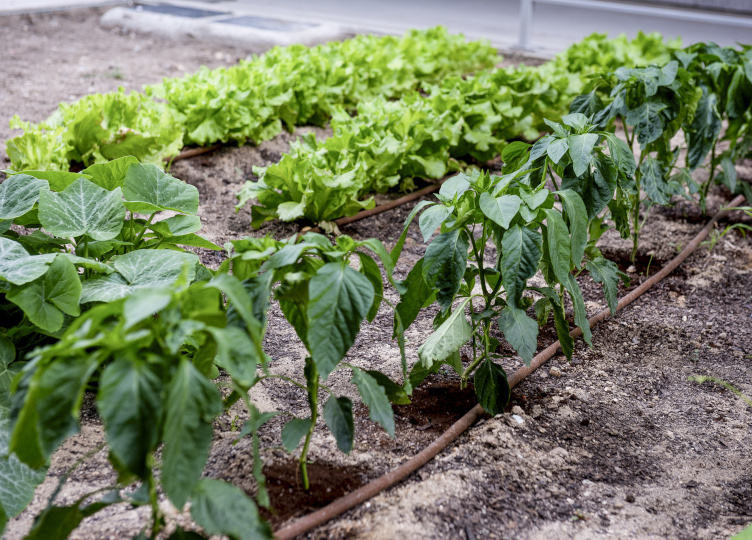

LIVING LAB OF URBAN AGRICULTURE
In the framework of the efforts to promote sustainability and environmental awareness in the Campus University, this initiative aims to transform a specific area of Campus into a space for urban agricultural experimentation. The goal is to create an environment where technology and sustainable agricultural practices converge to generate a positive impact on both the university community and its natural surroundings. To carry out this initiative, the following activities will be developed: selection of the space (5Hc); sensorization; creation of an urban garden; monitoring and assessment.

LIVING LAB AIR QUALITY MONITORING
This project has as goal to establish an extensive network of sensors at Campus to continuously monitor air pollutants, both outdoors and indoors, assessing their impact on human health and ecosystems. Artificial intelligence technologies will be used to develop models that predict pollutant levels, identify their sources, and analyze their distribution and impact. This innovative approach offers a promising alternative for the study of air quality in real time and could be expanded to other areas.

LIVING LAB REFORESTATION WITH IMPROVED PLANT
This Living Lab has as goal to carry out a reforestation in different areas of the Campus University by using advanced forestry techniques. The aim is to achieve a successful integration of plants into the ecosystem and revitalize the natural environment of campus. To achieve this purpose, novel methods will be used in the different phases of the reforestation process.

LIVING LAB FOR PLANT WASTE VALORIZATION
In this Living Lab, the aim is to valorize different plant wastes generated at Campus by analyzing their antibacterial, antifungal and allelopathic properties, looking for innovative ways to reuse these wastes in beneficial applications. In addition, it is intended to test whether the addition of selenated compounds to plant extracts increases their potential as antibacterial, antifungal and antitumor agents. To achieve this, the university community will be actively involved in the selective collection of waste and will work together to identify potential uses that contribute to sustainability and circular Economics .

LIVING LAB SUSTAINABILITY COMMUNICATION
The fundamental purpose of this initiative is to promote a solid environmental awareness and effectively disseminate the results and activities generated in the Living Labs. To this end, a series of communication campaigns designed to share with the university community the significant progress and relevance of each of the actions implemented in these environments are organized. Beyond simply informing, the intention is to deepen awareness of current environmental challenges and highlight the fundamental role played by the University in promoting sustainable development ,
Climate and energy
Carlos Fernández Bandera

Materials and waste
Carmen Jaca

Sustainable building
Ana Sánchez-Ostiz

Communication
Welcome León

Biodiversity and nature
Enrique Baquero
Food system
Carlos Javier González

Water and soils
Paloma Grau

Health and Sustainability
Francisco Guillén

Economy
Ricrdo Mateo

mobility
Juan José Pons
Education
Jordi Puig i Baguer

Air quality
David Elustondo
02 | 06 | 2022
120 secondary school students from all over Spain participate in congress StudIAS
20 | 05 | 2022
The Science Museum of the University of Navarra takes to the streets
03 | 05 | 2022
Ángel Ruiz de Apodaca, Full Professor: "The extensive development of renewable energies requires the training in a legal system that is constantly evolving".
ImagenManuel Castells
27 | 04 | 2022
The Science Museum of the University of Navarra joins the Pamplona Biomarathon with a fish census in the river Arga
Imagen: Ceded
25 | 03 | 2022
"Sustainability and a just energy transition cannot be guaranteed if we do not secure supply and competitiveness".
ImagenManuel Castells
ODS
The SDGs, adopted globally, chart the way forward to end poverty, protect the planet and work towards peace and prosperity for people.
The project 'Environment' aims to contribute in particular to the objectives "Education of quality", "Industry, innovation and infrastructure", "Climate action", "Life under water", "Life of terrestrial ecosystems", "Peace, justice and strong institutions" and "Partnerships to achieve the goals".
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
INDICATORS
- Academic output on the SDGs.
- Revenues from research, collected and settled, from private and public, domestic and international sources.
- Patents originated by the University.
- Sustainably sourced startups.





